
使用MQL5经济日历进行交易(第七部分):基于资源型新闻事件分析的策略测试准备
概述
在本文中,我们通过为非实盘模式下的策略测试做准备,进一步推进了MQL5经济日历系列的研究,利用嵌入的经济事件数据实现可靠的回测。在第六部分基于新闻分析和倒计时定时器实现交易信号自动化的基础上,我们现聚焦于从资源文件加载新闻事件,并应用用户自定义的筛选条件,从而在策略测试器中模拟实盘环境。本文将围绕以下主题展开:
让我们开始深入实践!
静态数据集成的重要性
对于那些致力于开发和测试稳健策略的人来说,静态数据集成至关重要,尤其是在MQL5这类环境中——其历史经济事件数据不会长期保留。与实盘交易不同(实盘时平台可获取实时新闻资讯),策略测试器无法访问此类动态更新。其不会存储大量历史事件档案,导致我们缺乏原生方案来对新闻驱动型策略进行回测。通过从外部来源下载这些数据并自行整理(无论是存储为文件、数据库还是嵌入资源),我们就能掌控一套可跨多次测试重复使用的统一数据集,确保策略每次测试时都面对相同的市场条件。
除了克服平台限制外,静态数据集成还能提供实盘资讯所无法企及的灵活性。正如我们在先前版本中所见,经济日历虽然包含事件日期、时间、货币和影响级别等关键细节,但是这些数据未必以适合长期算法分析的格式保存。通过手动整理这些信息,我们可以根据需求定制数据——例如筛选特定货币或高影响力事件——从而更深入地洞察新闻如何影响市场行为,而无需依赖实时数据可用性。
此外,这种方法还能提升效率与独立性。提前收集并存储静态数据意味着测试过程中无需依赖互联网连接或第三方服务,减少了可能影响结果准确性的变量。还使我们能够模拟罕见或特定场景(如重大经济公告),通过精心策划涵盖多年或聚焦关键时刻的数据集——这是实盘系统或平台有限存储难以轻松实现的。最终,静态数据集成填补了实盘交易洞察与回测精度之间的鸿沟,为策略开发奠定了坚实的基础。
数据存储将是关键考量因素,而MQL5提供了多种存储格式选择,涵盖文本(txt)格式、逗号分隔值(CSV)、美国国家标准协会(ANSI)编码、二进制(bin)格式、Unicode编码,以及如下所述的数据库组织形式。
我们不会选用最简单,而是最便捷的格式,即CSV格式。如此一来,我们就能随时掌握数据,无需耗费数小时等待策略回测,从而节省大量时间和精力。让我们开始吧!
在MQL5中的实现
首先,我们需要以与之前类似的方式构建数据收集与整理框架。因此,我们需要一些可供用户自定义的输入参数,就像之前那样,具体如下:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| MQL5 NEWS CALENDAR PART 7.mq5 | //| Copyright 2025, Allan Munene Mutiiria. | //| https://t.me/Forex_Algo_Trader | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2025, Allan Munene Mutiiria." #property link "https://youtube.com/@ForexAlgo-Trader?" #property version "1.00" #property strict //---- Input parameter for start date of event filtering input datetime StartDate = D'2025.03.01'; // Download Start Date //---- Input parameter for end date of event filtering input datetime EndDate = D'2025.03.21'; // Download End Date //---- Input parameter to enable/disable time filtering input bool ApplyTimeFilter = true; //---- Input parameter for hours before event to consider input int HoursBefore = 4; //---- Input parameter for minutes before event to consider input int MinutesBefore = 10; //---- Input parameter for hours after event to consider input int HoursAfter = 1; //---- Input parameter for minutes after event to consider input int MinutesAfter = 5; //---- Input parameter to enable/disable currency filtering input bool ApplyCurrencyFilter = true; //---- Input parameter defining currencies to filter (comma-separated) input string CurrencyFilter = "USD,EUR,GBP,JPY,AUD,NZD,CAD,CHF"; // All 8 major currencies //---- Input parameter to enable/disable impact filtering input bool ApplyImpactFilter = true; //---- Enumeration for event importance filtering options enum ENUM_IMPORTANCE { IMP_NONE = 0, // None IMP_LOW, // Low IMP_MEDIUM, // Medium IMP_HIGH, // High IMP_NONE_LOW, // None,Low IMP_NONE_MEDIUM, // None,Medium IMP_NONE_HIGH, // None,High IMP_LOW_MEDIUM, // Low,Medium IMP_LOW_HIGH, // Low,High IMP_MEDIUM_HIGH, // Medium,High IMP_NONE_LOW_MEDIUM, // None,Low,Medium IMP_NONE_LOW_HIGH, // None,Low,High IMP_NONE_MEDIUM_HIGH, // None,Medium,High IMP_LOW_MEDIUM_HIGH, // Low,Medium,High IMP_ALL // None,Low,Medium,High (default) }; //---- Input parameter for selecting importance filter input ENUM_IMPORTANCE ImportanceFilter = IMP_ALL; // Impact Levels (Default to all)
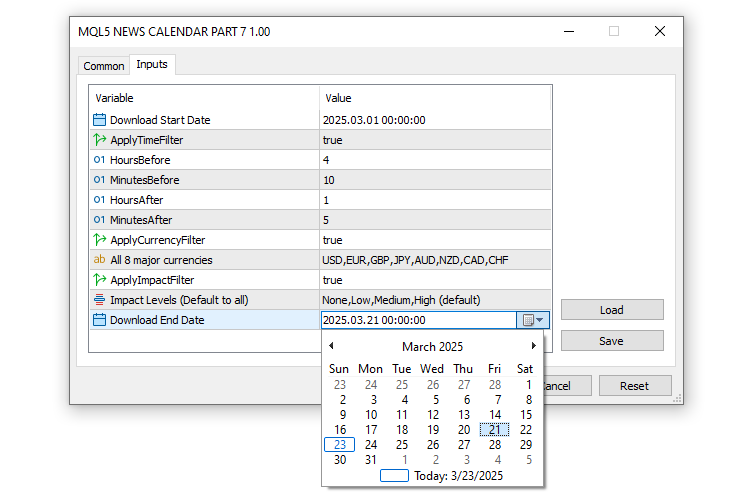
这部分中,我们设置了基础输入参数和一个枚举类型,以便自定义交易系统如何处理经济事件以进行策略测试。我们将“StartDate”和“EndDate”定义为日期时间型变量,分别设置为2025年3月1日和2025年3月21日,以指定下载和分析事件数据的时间范围。为了控制围绕这些事件的时间筛选,我们引入了“ApplyTimeFilter”(应用时间筛选)作为布尔型参数,默认值为 true,同时设置了“HoursBefore”(事前小时数,4小时)、“MinutesBefore”(事前分钟数,10分钟)、“HoursAfter”(事后小时数,1小时)和“MinutesAfter”(事后分钟数,5分钟),这些参数用于确定相对于给定K线的事件考虑时间窗口。
对于针对特定货币的分析,我们引入了“ApplyCurrencyFilter”(应用货币筛选,默认值为 true)和“CurrencyFilter”(货币筛选),后者是一个 string 类型参数,列出了所有八大主要货币——“USD(美元)、EUR(欧元)、GBP(英镑)、JPY(日元)、AUD(澳元)、NZD(新西兰元)、CAD(加元)、CHF(瑞士法郎)”——以便专注于相关市场。我们还启用了基于影响程度的筛选功能,将“ApplyImpactFilter”(应用影响程度筛选)设置为true,并借助“ENUM_IMPORTANCE”枚举类型提供灵活的选项,如“IMP_NONE”(无影响)、“IMP_LOW”(低影响)、“IMP_MEDIUM”(中等影响)、“IMP_HIGH”(高影响)以及直至“IMP_ALL”(所有影响程度)的组合选项,其中“ImportanceFilter”(影响程度筛选)默认设置为“IMP_ALL”,以包含所有影响程度的事件。效果如下:
有了这些输入参数后,接下来我们需要声明一个包含8个输入字段的结构体,以模拟MQL5经济日历的常规及默认结构,如下所示:
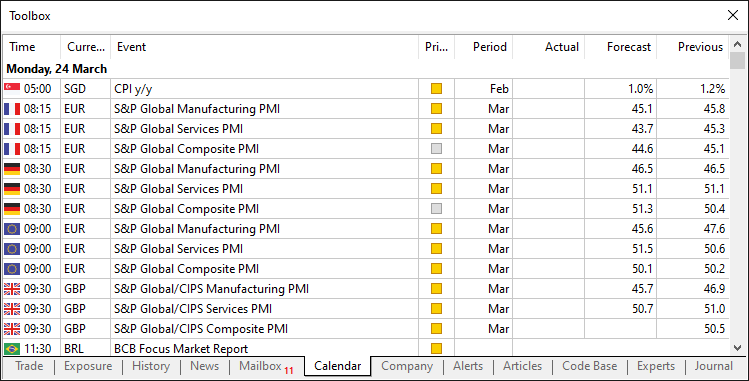
我们通过以下逻辑实现该格式:
//---- Structure to hold economic event data struct EconomicEvent { string eventDate; //---- Date of the event string eventTime; //---- Time of the event string currency; //---- Currency affected by the event string event; //---- Event description string importance; //---- Importance level of the event double actual; //---- Actual value of the event double forecast; //---- Forecasted value of the event double previous; //---- Previous value of the event }; //---- Array to store all economic events EconomicEvent allEvents[]; //---- Array for currency filter values string curr_filter[]; //---- Array for importance filter values string imp_filter[];
首先,我们定义一个名为“EconomicEvent”的结构体(struct),用于封装经济事件的关键细节,包括用字符串表示事件时间点的“eventDate”和“eventTime”、用于识别受影响市场的“currency”、用于描述事件的“event”、用于表明事件影响程度的“importance”,以及用双精度型表示事件数值结果的“actual”、“forecast”和“previous”。
为了存储和处理这些事件,我们创建三个数组:“allEvents”是一个“EconomicEvent”结构体数组,用于存储所有加载的事件;“curr_filter”是一个字符串数组,用于存储“CurrencyFilter”(货币筛选)输入中指定的货币;“imp_filter”是另一个字符串数组,用于管理通过“ImportanceFilter”(重要性筛选)选择的重要性级别。这种设计模仿了默认结构,只不过我们将“Period”(时间段)部分调整为在结构体开头包含事件日期。接下来,我们需要从用户输入中获取筛选条件,将其转换为计算机能够理解的形式并初始化。为了保持代码的模块化,我们将使用函数来实现这些功能。
//---- Function to initialize currency and impact filters void InitializeFilters() { //---- Currency Filter Section //---- Check if currency filter is enabled and has content if (ApplyCurrencyFilter && StringLen(CurrencyFilter) > 0) { //---- Split the currency filter string into array int count = StringSplit(CurrencyFilter, ',', curr_filter); //---- Loop through each currency filter entry for (int i = 0; i < ArraySize(curr_filter); i++) { //---- Temporary variable for trimming string temp = curr_filter[i]; //---- Remove leading whitespace StringTrimLeft(temp); //---- Remove trailing whitespace StringTrimRight(temp); //---- Assign trimmed value back to array curr_filter[i] = temp; //---- Print currency filter for debugging Print("Currency filter [", i, "]: '", curr_filter[i], "'"); } } else if (ApplyCurrencyFilter) { //---- Warn if currency filter is enabled but empty Print("Warning: CurrencyFilter is empty, no currency filtering applied"); //---- Resize array to zero if no filter applied ArrayResize(curr_filter, 0); } }
这部分中,我们在系统的“InitializeFilters”函数中设置货币筛选部分,以便在策略测试期间为有效的事件分析做好准备。我们首先使用StringLen函数检查“ApplyCurrencyFilter”变量是否为true,以及“CurrencyFilter”字符串是否有内容;如果满足条件,我们便使用StringSplit函数将逗号分隔的“CurrencyFilter”(如“USD, EUR, GBP”)拆分到“curr_filter”数组中,同时将拆分到的元素数量保存至“count”中。
接下来,我们使用for循环遍历“curr_filter”数组中的每个元素,将其赋值给临时字符串“temp”,通过StringTrimLeft和StringTrimRight函数去除首尾空白字符进行清理,然后用清理后的值更新“curr_filter”数组,并通过Print函数输出调试信息(例如“Currency filter [0]: 'USD'”)。然而,如果启用了"ApplyCurrencyFilter"但"CurrencyFilter" 为空,我们会使用"Print"函数发出警告——“警告:货币筛选器为空,未应用货币筛选”,并使用ArrayResize函数将数组大小调整为0,以禁用筛选功能。这种严谨的初始化过程将确保货币筛选器能够可靠地根据用户输入生成,从而在策略测试器中支持准确的事件处理。对于影响程度筛选器,我们采用类似的精细化逻辑。
//---- Impact Filter Section (using enum) //---- Check if impact filter is enabled if (ApplyImpactFilter) { //---- Switch based on selected importance filter switch (ImportanceFilter) { case IMP_NONE: //---- Resize array for single importance level ArrayResize(imp_filter, 1); //---- Set importance to "None" imp_filter[0] = "None"; break; case IMP_LOW: //---- Resize array for single importance level ArrayResize(imp_filter, 1); //---- Set importance to "Low" imp_filter[0] = "Low"; break; case IMP_MEDIUM: //---- Resize array for single importance level ArrayResize(imp_filter, 1); //---- Set importance to "Medium" imp_filter[0] = "Medium"; break; case IMP_HIGH: //---- Resize array for single importance level ArrayResize(imp_filter, 1); //---- Set importance to "High" imp_filter[0] = "High"; break; case IMP_NONE_LOW: //---- Resize array for two importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 2); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "None"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "Low"; break; case IMP_NONE_MEDIUM: //---- Resize array for two importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 2); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "None"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "Medium"; break; case IMP_NONE_HIGH: //---- Resize array for two importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 2); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "None"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "High"; break; case IMP_LOW_MEDIUM: //---- Resize array for two importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 2); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "Low"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "Medium"; break; case IMP_LOW_HIGH: //---- Resize array for two importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 2); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "Low"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "High"; break; case IMP_MEDIUM_HIGH: //---- Resize array for two importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 2); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "Medium"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "High"; break; case IMP_NONE_LOW_MEDIUM: //---- Resize array for three importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 3); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "None"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "Low"; //---- Set third importance level imp_filter[2] = "Medium"; break; case IMP_NONE_LOW_HIGH: //---- Resize array for three importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 3); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "None"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "Low"; //---- Set third importance level imp_filter[2] = "High"; break; case IMP_NONE_MEDIUM_HIGH: //---- Resize array for three importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 3); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "None"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "Medium"; //---- Set third importance level imp_filter[2] = "High"; break; case IMP_LOW_MEDIUM_HIGH: //---- Resize array for three importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 3); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "Low"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "Medium"; //---- Set third importance level imp_filter[2] = "High"; break; case IMP_ALL: //---- Resize array for all importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 4); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "None"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "Low"; //---- Set third importance level imp_filter[2] = "Medium"; //---- Set fourth importance level imp_filter[3] = "High"; break; } //---- Loop through impact filter array to print values for (int i = 0; i < ArraySize(imp_filter); i++) { //---- Print each impact filter value Print("Impact filter [", i, "]: '", imp_filter[i], "'"); } } else { //---- Notify if impact filter is disabled Print("Impact filter disabled"); //---- Resize impact filter array to zero ArrayResize(imp_filter, 0); }
对于影响程度筛选流程,我们首先检查“ApplyImpactFilter”变量是否为true;如果是,则根据“ImportanceFilter”枚举值使用switch语句确定需纳入“imp_filter”数组的影响级别。对于单级别选项(如“IMP_NONE”、“IMP_LOW”、“IMP_MEDIUM”或“IMP_HIGH”),我们使用ArrayResize函数将“imp_filter”数组大小调整为1,并赋值对应的字符串(例如“imp_filter[0] = 'None'”);对于双级别选项(如“IMP_NONE_LOW”或“IMP_MEDIUM_HIGH”),则将数组大小调整为2并设置两个值(例如“imp_filter[0] = 'None', imp_filter[1] = 'Low'”);对于三级别选项(如“IMP_LOW_MEDIUM_HIGH”),数组大小调整为3;而对于“IMP_ALL”选项,数组大小调整为4,涵盖“None”、“Low”、“Medium”和“High”全部四个级别。
设置好数组后,我们使用ArraySize函数获取“imp_filter”数组的大小,并通过循环遍历该数组,同时利用Print函数输出每个值以供调试(例如“Impact filter [0]: 'None'”)。如果“ApplyImpactFilter”为 false,则通过"Print"函数向用户发出通知——“影响程度筛选已禁用”,并将“imp_filter”数组大小调整为0。
至此,现在我们需要在OnInit事件处理器中调用该函数。
int OnInit() { //---- Initialize filters InitializeFilters(); //---- Return successful initialization return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } void OnDeinit(const int reason) { //---- Print termination reason Print("EA terminated, reason: ", reason); }
我们在OnInit事件处理器中调用该函数,并在OnDeinit事件处理器中打印程序终止的原因。以下是输出结果。
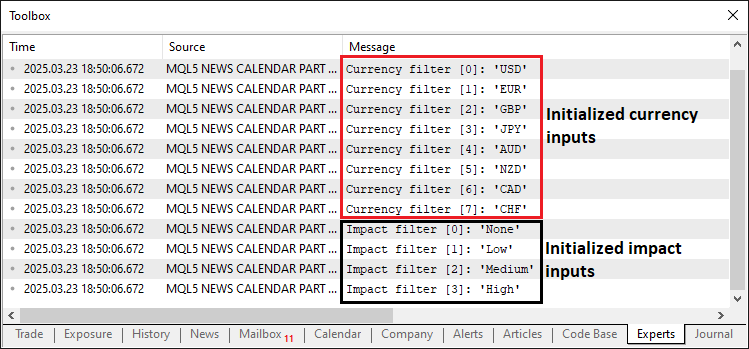
由图可见,我们已正确初始化并解析了筛选器输入,并将其存储了起来。现在,我们只需从实时数据流中获取数据并存储即可。这里的逻辑是:首先需要在实时模式下运行一次程序,以便从MQL5经济日历数据库下载数据,然后在测试模式下加载并使用这些数据。以下是初始化逻辑。
//---- Check if not running in tester mode if (!MQLInfoInteger(MQL_TESTER)) { //---- Validate date range if (StartDate >= EndDate) { //---- Print error for invalid date range Print("Error: StartDate (", TimeToString(StartDate), ") must be earlier than EndDate (", TimeToString(EndDate), ")"); //---- Return initialization failure return(INIT_PARAMETERS_INCORRECT); } //---- Array to hold calendar values MqlCalendarValue values[]; //---- Fetch calendar data for date range if (!CalendarValueHistory(values, StartDate, EndDate)) { //---- Print error if calendar data fetch fails Print("Error fetching calendar data: ", GetLastError()); //---- Return initialization failure return(INIT_FAILED); } //---- Array to hold economic events EconomicEvent events[]; //---- Counter for events int eventCount = 0; //---- Loop through calendar values for (int i = 0; i < ArraySize(values); i++) { //---- Structure for event details MqlCalendarEvent eventDetails; //---- Fetch event details by ID if (!CalendarEventById(values[i].event_id, eventDetails)) continue; //---- Structure for country details MqlCalendarCountry countryDetails; //---- Fetch country details by ID if (!CalendarCountryById(eventDetails.country_id, countryDetails)) continue; //---- Structure for value details MqlCalendarValue value; //---- Fetch value details by ID if (!CalendarValueById(values[i].id, value)) continue; //---- Resize events array for new event ArrayResize(events, eventCount + 1); //---- Convert event time to string string dateTimeStr = TimeToString(values[i].time, TIME_DATE | TIME_MINUTES); //---- Extract date from datetime string events[eventCount].eventDate = StringSubstr(dateTimeStr, 0, 10); //---- Extract time from datetime string events[eventCount].eventTime = StringSubstr(dateTimeStr, 11, 5); //---- Assign currency from country details events[eventCount].currency = countryDetails.currency; //---- Assign event name events[eventCount].event = eventDetails.name; //---- Map importance level from enum to string events[eventCount].importance = (eventDetails.importance == 0) ? "None" : // CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_NONE (eventDetails.importance == 1) ? "Low" : // CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_LOW (eventDetails.importance == 2) ? "Medium" : // CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_MODERATE "High"; // CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_HIGH //---- Assign actual value events[eventCount].actual = value.GetActualValue(); //---- Assign forecast value events[eventCount].forecast = value.GetForecastValue(); //---- Assign previous value events[eventCount].previous = value.GetPreviousValue(); //---- Increment event count eventCount++; } }
这部分中,我们在OnInit函数内处理实时模式下的数据获取,确保经济事件数据被收集以供后续在策略测试中使用。首先,我们使用MQLInfoInteger函数结合MQL_TESTER参数检查系统是否未处于测试模式;如果为true,则验证“StartDate”是否早于“EndDate”,如果日期无效,则打印错误信息并返回 INIT_PARAMETERS_INCORRECT(初始化参数错误)。接下来,我们声明一个名为“values”的MqlCalendarValue数组,并使用CalendarValueHistory函数获取“StartDate”至“EndDate”期间的经济日历数据;如果数据获取失败,则通过GetLastError打印错误信息并返回“INIT_FAILED”。
随后,我们初始化一个名为"events"的"EconomicEvent"数组和一个用于跟踪事件数量的整数"eventCount",并使用ArraySize函数遍历"values"数组。在每次迭代中,我们使用CalendarEventById函数将事件详情获取到MqlCalendarEvent结构体“eventDetails”中,使用CalendarCountryById函数将国家详情获取到MqlCalendarCountry结构体“countryDetails”中,并通过“CalendarValueById”将数值详情获取到 MqlCalendarValue 结构体“value”中;如果任何一次获取操作失败,则跳过当前事件。我们使用ArrayResize函数调整“events”数组的大小,利用TimeToString函数将事件时间转换为字符串“dateTimeStr”,并使用StringSubstr函数提取“eventDate”和“eventTime”。接着,我们从“countryDetails”中获取“currency”,从“eventDetails.name”中获取“event”,并将数值形式的“importance”映射为字符串(“None”、“Low”、“Medium”、“High”)。最后,我们使用“value”结构体的方法设置“actual”、“forecast”和“previous”,并递增“eventCount”,从而构建一个用于实时模式处理的全面事件数据集。现在,我们需要一个函数来将这些信息存储到数据文件中。
//---- Function to write events to a CSV file void WriteToCSV(string fileName, EconomicEvent &events[]) { //---- Open file for writing in CSV format int handle = FileOpen(fileName, FILE_WRITE | FILE_CSV, ','); //---- Check if file opening failed if (handle == INVALID_HANDLE) { //---- Print error message with last error code Print("Error creating file: ", GetLastError()); //---- Exit function on failure return; } //---- Write CSV header row FileWrite(handle, "Date", "Time", "Currency", "Event", "Importance", "Actual", "Forecast", "Previous"); //---- Loop through all events to write to file for (int i = 0; i < ArraySize(events); i++) { //---- Write event data to CSV file FileWrite(handle, events[i].eventDate, events[i].eventTime, events[i].currency, events[i].event, events[i].importance, DoubleToString(events[i].actual, 2), DoubleToString(events[i].forecast, 2), DoubleToString(events[i].previous, 2)); //---- Print event details for debugging Print("Writing event ", i, ": ", events[i].eventDate, ", ", events[i].eventTime, ", ", events[i].currency, ", ", events[i].event, ", ", events[i].importance, ", ", DoubleToString(events[i].actual, 2), ", ", DoubleToString(events[i].forecast, 2), ", ", DoubleToString(events[i].previous, 2)); } //---- Flush data to file FileFlush(handle); //---- Close the file handle FileClose(handle); //---- Print confirmation of data written Print("Data written to ", fileName, " with ", ArraySize(events), " events."); //---- Verify written file by reading it back int verifyHandle = FileOpen(fileName, FILE_READ | FILE_TXT); //---- Check if verification file opening succeeded if (verifyHandle != INVALID_HANDLE) { //---- Read entire file content string content = FileReadString(verifyHandle, (int)FileSize(verifyHandle)); //---- Print file content for verification Print("File content after writing (size: ", FileSize(verifyHandle), " bytes):\n", content); //---- Close verification file handle FileClose(verifyHandle); } }
这部分中,我们编写“WriteToCSV”函数,以系统化的方式将经济事件数据导出至CSV文件。首先,我们使用FileOpen函数以"FILE_WRITE | FILE_CSV"模式(逗号分隔符)打开由"fileName"指定的文件,并将返回的文件句柄存储在"handle"变量中;如果操作失败且“handle”等于"INVALID_HANDLE",则使用"Print"函数显示包含GetLastError错误代码的错误信息,并通过"return"退出函数。成功打开文件后,我们使用 FileWrite函数写入表头行,定义数据列的标题为“Date”、“Time”、“Currency”、“Event”、“Importance”、“Actual”、“Forecast”和“Previous”,以此组织数据结构。
随后,我们使用ArraySize函数确定“events”数组的大小,并遍历该数组。对于每个事件,我们调用"FileWrite"记录其属性——包括“eventDate”、“eventTime”、“currency”、“event”、“importance”,以及使用DoubleToString函数将数值类型的“actual”、“forecast”(预测值)和“previous”(前值)转换为字符串(格式化为保留两位小数),同时通过“Print”函数输出这些详细信息以供调试。
完成循环后,我们通过调用FileFlush函数(针对“handle”句柄)确保所有数据均已写入文件,随后使用FileClose函数关闭文件,并通过消息确认操作成功。
为验证输出结果,我们使用“FILE_READ | FILE_TXT”模式重新以只读方式打开文件,并将该文件句柄存储在“verifyHandle”中;如果操作成功,则通过FileSize函数获取文件字节大小,并使用FileReadString函数将完整内容读取到“content”变量中,随后打印内容以供检查(例如:“写入后的文件内容(大小:X字节):\n”content“”),最后关闭文件。这一完整流程确保事件数据被准确保存并可供核查,使其成为策略测试器中回测的可靠数据来源。现在,我们可以使用该函数完成数据保存操作。
//---- Define file path for CSV string fileName = "Database\\EconomicCalendar.csv"; //---- Check if file exists and print appropriate message if (!FileExists(fileName)) Print("Creating new file: ", fileName); else Print("Overwriting existing file: ", fileName); //---- Write events to CSV file WriteToCSV(fileName, events); //---- Print instructions for tester mode Print("Live mode: Data written. To use in tester, manually add ", fileName, " as a resource and recompile.");
为完成实时模式下的数据处理流程,我们将“fileName”设置为“Database\EconomicCalendar.csv”,并使用"FileExists"自定义函数检查文件是否存在。随后,我们调用“WriteToCSV”函数,传入“fileName”和“events”作为参数以保存数据,并通过“Print”函数输出使用说明——“实时模式:数据已写入。如需在测试器中使用,请将‘fileName’添加为资源并重新编译。”——供测试器场景。以下是用于检查文件是否存在的自定义函数代码段:
//---- Function to check if a file exists bool FileExists(string fileName) { //---- Open file in read mode to check existence int handle = FileOpen(fileName, FILE_READ | FILE_CSV); //---- Check if file opened successfully if (handle != INVALID_HANDLE) { //---- Close the file handle FileClose(handle); //---- Return true if file exists return true; } //---- Return false if file doesn't exist return false; }
在用于策略测试中检查文件是否存在的“FileExists”函数中,我们以“FILE_READ | FILE_CSV”模式使用FileOpen函数打开“fileName”指定的文件,如果返回的句柄“handle”不是“INVALID_HANDLE”,则通过 FileClose函数关闭文件并返回true(表示文件存在);否则返回false(表示文件不存在)。该函数可确认文件状态,为数据处理提供依据。以下是在实时模式下运行后的输出结果。
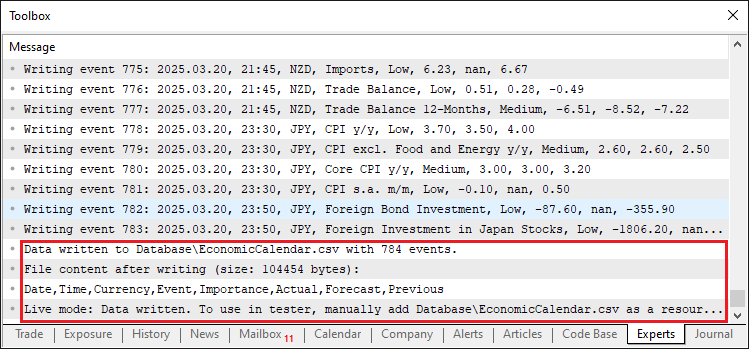
由图可见,数据已成功保存并且可供访问。
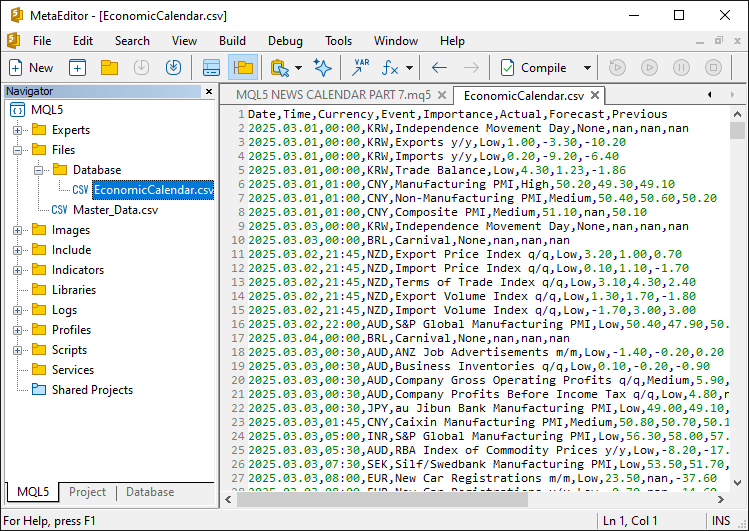
要在测试器模式下使用这些数据,我们需要将其嵌入到可执行文件中。为此,需要将数据作为资源添加。
//---- Define resource file for economic calendar data #resource "\\Files\\Database\\EconomicCalendar.csv" as string EconomicCalendarData
这部分中,我们将静态数据资源集成到程序中,以支持策略测试。通过使 #resource指令,我们将位于“\Files\Database\EconomicCalendar.csv”的文件嵌入程序,并将其赋值给字符串变量“EconomicCalendarData”。这样一来,该文件会被打包进可执行文件中,即使外部文件被删除,也不会影响程序运行。现在,我们可以编写一个函数来加载该文件的内容。
//---- Function to load events from resource file bool LoadEventsFromResource() { //---- Get data from resource string fileData = EconomicCalendarData; //---- Print raw resource content for debugging Print("Raw resource content (size: ", StringLen(fileData), " bytes):\n", fileData); //---- Array to hold lines from resource string lines[]; //---- Split resource data into lines int lineCount = StringSplit(fileData, '\n', lines); //---- Check if resource has valid data if (lineCount <= 1) { //---- Print error if no data lines found Print("Error: No data lines found in resource! Raw data: ", fileData); //---- Return false on failure return false; } //---- Reset events array ArrayResize(allEvents, 0); //---- Index for event array int eventIndex = 0; //---- Loop through each line (skip header at i=0) for (int i = 1; i < lineCount; i++) { //---- Check for empty lines if (StringLen(lines[i]) == 0) { //---- Print message for skipped empty line Print("Skipping empty line ", i); //---- Skip to next iteration continue; } //---- Array to hold fields from each line string fields[]; //---- Split line into fields int fieldCount = StringSplit(lines[i], ',', fields); //---- Print line details for debugging Print("Line ", i, ": ", lines[i], " (field count: ", fieldCount, ")"); //---- Check if line has minimum required fields if (fieldCount < 8) { //---- Print error for malformed line Print("Malformed line ", i, ": ", lines[i], " (field count: ", fieldCount, ")"); //---- Skip to next iteration continue; } //---- Extract date from field string dateStr = fields[0]; //---- Extract time from field string timeStr = fields[1]; //---- Extract currency from field string currency = fields[2]; //---- Extract event description (handle commas in event name) string event = fields[3]; //---- Combine multiple fields if event name contains commas for (int j = 4; j < fieldCount - 4; j++) { event += "," + fields[j]; } //---- Extract importance from field string importance = fields[fieldCount - 4]; //---- Extract actual value from field string actualStr = fields[fieldCount - 3]; //---- Extract forecast value from field string forecastStr = fields[fieldCount - 2]; //---- Extract previous value from field string previousStr = fields[fieldCount - 1]; //---- Convert date and time to datetime format datetime eventDateTime = StringToTime(dateStr + " " + timeStr); //---- Check if datetime conversion failed if (eventDateTime == 0) { //---- Print error for invalid datetime Print("Error: Invalid datetime conversion for line ", i, ": ", dateStr, " ", timeStr); //---- Skip to next iteration continue; } //---- Resize events array for new event ArrayResize(allEvents, eventIndex + 1); //---- Assign event date allEvents[eventIndex].eventDate = dateStr; //---- Assign event time allEvents[eventIndex].eventTime = timeStr; //---- Assign event currency allEvents[eventIndex].currency = currency; //---- Assign event description allEvents[eventIndex].event = event; //---- Assign event importance allEvents[eventIndex].importance = importance; //---- Convert and assign actual value allEvents[eventIndex].actual = StringToDouble(actualStr); //---- Convert and assign forecast value allEvents[eventIndex].forecast = StringToDouble(forecastStr); //---- Convert and assign previous value allEvents[eventIndex].previous = StringToDouble(previousStr); //---- Print loaded event details Print("Loaded event ", eventIndex, ": ", dateStr, " ", timeStr, ", ", currency, ", ", event); //---- Increment event index eventIndex++; } //---- Print total events loaded Print("Loaded ", eventIndex, " events from resource into array."); //---- Return success if events were loaded return eventIndex > 0; }
我们定义“LoadEventsFromResource”函数,用于从嵌入的资源中加载经济事件数据,以支持策略测试。首先,将“EconomicCalendarData”资源赋值给“fileData”变量,并通过“Print”函数打印其原始内容(包括使用StringLen函数获取文件大小),以便调试。接下来,我们使用StringSplit函数以换行符为分隔符将“fileData”拆分为“lines”数组,并将行数存储在“lineCount”中。如果“lineCount”小于等于1(即无有效数据行),则打印错误信息并返回false。然后,我们使用ArrayResize函数将“allEvents”数组重置为空,并初始化“eventIndex”为0。随后从索引1开始遍历“lines”数组(跳过表头行)。对于每一行数据,我们先通过StringLen检查是否为空行,如果为空则打印跳过信息并继续处理下一行;否则,以逗号为分隔符将该行拆分为“fields”数组。
如果字段数量“fieldCount”小于8,则打印错误信息并跳过该行;否则,提取“dateStr”、“timeStr”和“currency”,并通过循环拼接字段(处理逗号分隔符)构建完整的“event”,随后提取“importance”、“actualStr”、“forecastStr”和“previousStr”。接下来,使用StringToTime函数将“dateStr”和“timeStr”合并转换为“eventDateTime”,如果转换失败则打印错误并跳过;然后通过"ArrayResize"调整“allEvents”数组大小,将所有值(数值类型使用StringToDouble转换)存入数组,打印事件详情,并递增“eventIndex”。最后,打印已加载的事件总数“eventIndex”,如果成功加载事件,则返回true,确保数据已准备好供策略测试器使用。现在,我们可以在测试器模式的初始化阶段调用此函数。
else { //---- Check if resource data is empty in tester mode if (StringLen(EconomicCalendarData) == 0) { //---- Print error for empty resource Print("Error: Resource EconomicCalendarData is empty. Please run in live mode, add the file as a resource, and recompile."); //---- Return initialization failure return(INIT_FAILED); } //---- Print message for tester mode Print("Running in Strategy Tester, using embedded resource: Database\\EconomicCalendar.csv"); //---- Load events from resource if (!LoadEventsFromResource()) { //---- Print error if loading fails Print("Failed to load events from resource."); //---- Return initialization failure return(INIT_FAILED); } }
这部分中,如果通过 StringLen检测到“EconomicCalendarData”为空,则打印错误信息并返回"INIT_FAILED";否则,使用"Print"函数输出测试器模式启动消息,并调用"LoadEventsFromResource"函数加载事件数据,如果加载失败,同样打印错误信息并返回"INIT_FAILED"。此流程可确保在回测(测试器模式)中正确加载事件数据。以下是输出结果。
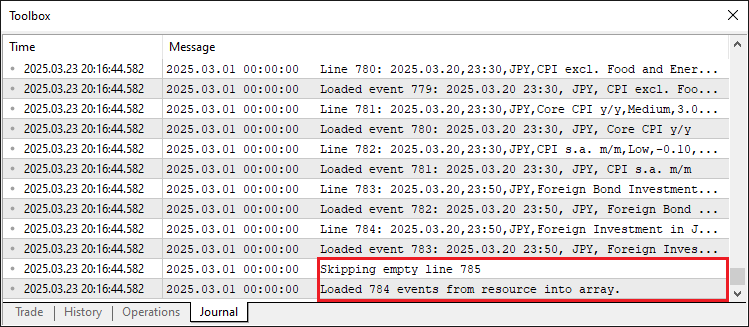
由图可见,数据已成功加载。数据格式异常处理及空行跳过逻辑也均正常生效。现在,我们可以进入OnTick事件处理器,模拟实时模式下的数据处理流程。因此,我们需按K线周期(而非每个tick)处理数据。
//---- Variable to track last bar time datetime lastBarTime = 0; //---- Tick event handler void OnTick() { //---- Get current bar time datetime currentBarTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, 0); //---- Check if bar time has changed if (currentBarTime != lastBarTime) { //---- Update last bar time lastBarTime = currentBarTime; //---- } }
我们定义一个名为“lastBarTime”的日期时间型变量,并初始化为0,用于记录上一根K线的生成时间。在OnTick函数中,通过iTime函数(传入_Symbol、_Period和K线索引0)获取当前K线的生成时间,存储到“currentBarTime”变量中;如果“currentBarTime”与“lastBarTime”不同,则更新“lastBarTime”为当前时间,确保系统仅在新K线生成时触发事件处理逻辑。接下来,我们可以按照此前版本的方式,定义一个函数来模拟实时模式下的数据处理流程,具体实现如下:
//---- Function to filter and print economic events void FilterAndPrintEvents(datetime barTime) { //---- Get total number of events int totalEvents = ArraySize(allEvents); //---- Print total events considered Print("Total considered data size: ", totalEvents, " events"); //---- Check if there are events to filter if (totalEvents == 0) { //---- Print message if no events loaded Print("No events loaded to filter."); //---- Exit function return; } //---- Array to store filtered events EconomicEvent filteredEvents[]; //---- Counter for filtered events int filteredCount = 0; //---- Variables for time range datetime timeBefore, timeAfter; //---- Apply time filter if enabled if (ApplyTimeFilter) { //---- Structure for bar time MqlDateTime barStruct; //---- Convert bar time to structure TimeToStruct(barTime, barStruct); //---- Calculate time before event MqlDateTime timeBeforeStruct = barStruct; //---- Subtract hours before timeBeforeStruct.hour -= HoursBefore; //---- Subtract minutes before timeBeforeStruct.min -= MinutesBefore; //---- Adjust for negative minutes if (timeBeforeStruct.min < 0) { timeBeforeStruct.min += 60; timeBeforeStruct.hour -= 1; } //---- Adjust for negative hours if (timeBeforeStruct.hour < 0) { timeBeforeStruct.hour += 24; timeBeforeStruct.day -= 1; } //---- Convert structure to datetime timeBefore = StructToTime(timeBeforeStruct); //---- Calculate time after event MqlDateTime timeAfterStruct = barStruct; //---- Add hours after timeAfterStruct.hour += HoursAfter; //---- Add minutes after timeAfterStruct.min += MinutesAfter; //---- Adjust for minutes overflow if (timeAfterStruct.min >= 60) { timeAfterStruct.min -= 60; timeAfterStruct.hour += 1; } //---- Adjust for hours overflow if (timeAfterStruct.hour >= 24) { timeAfterStruct.hour -= 24; timeAfterStruct.day += 1; } //---- Convert structure to datetime timeAfter = StructToTime(timeAfterStruct); //---- Print time range for debugging Print("Bar time: ", TimeToString(barTime), ", Time range: ", TimeToString(timeBefore), " to ", TimeToString(timeAfter)); } else { //---- Print message if no time filter applied Print("Bar time: ", TimeToString(barTime), ", No time filter applied, using StartDate to EndDate only."); //---- Set time range to date inputs timeBefore = StartDate; timeAfter = EndDate; } //---- Loop through all events for filtering for (int i = 0; i < totalEvents; i++) { //---- Convert event date and time to datetime datetime eventDateTime = StringToTime(allEvents[i].eventDate + " " + allEvents[i].eventTime); //---- Check if event is within date range bool inDateRange = (eventDateTime >= StartDate && eventDateTime <= EndDate); //---- Skip if not in date range if (!inDateRange) continue; //---- Time Filter Check //---- Check if event is within time range if filter applied bool timeMatch = !ApplyTimeFilter || (eventDateTime >= timeBefore && eventDateTime <= timeAfter); //---- Skip if time doesn't match if (!timeMatch) continue; //---- Print event details if time passes Print("Event ", i, ": Time passes (", allEvents[i].eventDate, " ", allEvents[i].eventTime, ") - ", "Currency: ", allEvents[i].currency, ", Event: ", allEvents[i].event, ", Importance: ", allEvents[i].importance, ", Actual: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].actual, 2), ", Forecast: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].forecast, 2), ", Previous: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].previous, 2)); //---- Currency Filter Check //---- Default to match if filter disabled bool currencyMatch = !ApplyCurrencyFilter; //---- Apply currency filter if enabled if (ApplyCurrencyFilter && ArraySize(curr_filter) > 0) { //---- Initially set to no match currencyMatch = false; //---- Check each currency in filter for (int j = 0; j < ArraySize(curr_filter); j++) { //---- Check if event currency matches filter if (allEvents[i].currency == curr_filter[j]) { //---- Set match to true if found currencyMatch = true; //---- Exit loop on match break; } } //---- Skip if currency doesn't match if (!currencyMatch) continue; } //---- Print event details if currency passes Print("Event ", i, ": Currency passes (", allEvents[i].currency, ") - ", "Date: ", allEvents[i].eventDate, " ", allEvents[i].eventTime, ", Event: ", allEvents[i].event, ", Importance: ", allEvents[i].importance, ", Actual: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].actual, 2), ", Forecast: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].forecast, 2), ", Previous: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].previous, 2)); //---- Impact Filter Check //---- Default to match if filter disabled bool impactMatch = !ApplyImpactFilter; //---- Apply impact filter if enabled if (ApplyImpactFilter && ArraySize(imp_filter) > 0) { //---- Initially set to no match impactMatch = false; //---- Check each importance in filter for (int k = 0; k < ArraySize(imp_filter); k++) { //---- Check if event importance matches filter if (allEvents[i].importance == imp_filter[k]) { //---- Set match to true if found impactMatch = true; //---- Exit loop on match break; } } //---- Skip if importance doesn't match if (!impactMatch) continue; } //---- Print event details if impact passes Print("Event ", i, ": Impact passes (", allEvents[i].importance, ") - ", "Date: ", allEvents[i].eventDate, " ", allEvents[i].eventTime, ", Currency: ", allEvents[i].currency, ", Event: ", allEvents[i].event, ", Actual: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].actual, 2), ", Forecast: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].forecast, 2), ", Previous: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].previous, 2)); //---- Add event to filtered array ArrayResize(filteredEvents, filteredCount + 1); //---- Assign event to filtered array filteredEvents[filteredCount] = allEvents[i]; //---- Increment filtered count filteredCount++; } //---- Print summary of filtered events Print("After ", (ApplyTimeFilter ? "time filter" : "date range filter"), ApplyCurrencyFilter ? " and currency filter" : "", ApplyImpactFilter ? " and impact filter" : "", ": ", filteredCount, " events remaining."); //---- Check if there are filtered events to print if (filteredCount > 0) { //---- Print header for filtered events Print("Filtered Events at Bar Time: ", TimeToString(barTime)); //---- Print filtered events array ArrayPrint(filteredEvents, 2, " | "); } else { //---- Print message if no events found Print("No events found within the specified range."); } }
这部分中,我们构建“FilterAndPrintEvents”函数的实现逻辑,用于筛选并显示与指定K线相关的经济事件。首先,通过ArraySize函数获取“allEvents”数组中的事件总数“totalEvents”并打印,如果总数为0,则直接退出。接下来,我们初始化一个“EconomicEvent”数组“filteredEvents”,用于存储筛选结果,并设置计数器“filteredCount”为0。同时定义时间筛选的边界变量“timeBefore”和“timeAfter”。如果"ApplyTimeFilter"为true,我们先用TimeToStruct函数将"barTime"转换为时间结构体"barStruct",再分别减去“HoursBefore”和“MinutesBefore”(均修正负值),得到"timeBeforeStruct",再加上“HoursAfter”和“MinutesAfter”(均修正溢出),得到"timeAfterStruct",再使用StructToTime函数将"timeBeforeStruct"和"timeAfterStruct"转换回日期时间型,并打印筛选时间范围;否则,将"timeBeforeStruct"和"timeAfterStruct"设置为 "StartDate"与"EndDate",并打印无过滤提示。
我们遍历"allEvents",以"totalEvents"为总数,使用StringToTime 将每个"eventDate"和"eventTime"转成"eventDateTime",并检查是否落在"StartDate"与"EndDate"之间,得到"inDateRange";如果不在范围内则跳过。 对于时间过滤,使用"ApplyTimeFilter"与区间测试"timeMatch",通过则打印详情;对于货币过滤,使用"ApplyCurrencyFilter"与"curr_filter" ,通过ArraySize函数与循环设置"currencyMatch",匹配则打印;对于影响过滤,用 "ApplyImpactFilter"与"imp_filter"设置"impactMatch",匹配则打印。符合筛选条件的事件会通过ArrayResize函数扩展“filteredEvents”数组,同时递增“filteredCount”计数器以记录匹配事件的总数。
最后,我们打印摘要信息;如果"filteredCount"为正,则使用ArrayPrint输出过滤后的事件列表;否则,打印“无事件”提示,确保测试阶段的事件分析完整详尽。随后,我们在tick事件处理器中调用该函数。
void OnTick() { //---- Get current bar time datetime currentBarTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, 0); //---- Check if bar time has changed if (currentBarTime != lastBarTime) { //---- Update last bar time lastBarTime = currentBarTime; //---- Filter and print events for current bar FilterAndPrintEvents(currentBarTime); } }
运行程序后,我们得到以下结果:
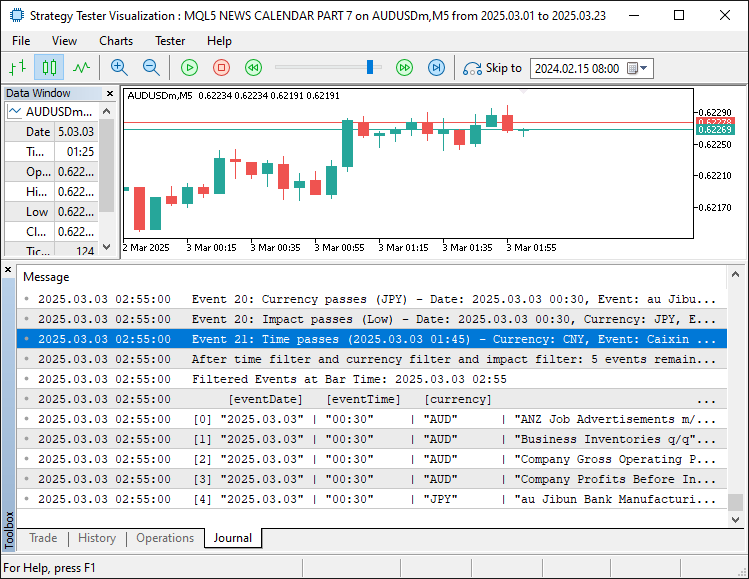
从图像中可以确认,筛选功能已启用且运行符合预期。目前仅需完成逻辑测试,相关内容将在下一部分展开。
测试
为进行全面测试,我们将所有流程录制为演示视频,您可通过下方附件查看完整操作细节。
结论
总之,我们通过为MQL5经济日历系列构建策略测试支持体系,利用预存文件的静态数据实现了高可信度的历史回测,显著提升了系统的性能。这一改进将实时事件分析与策略测试器连接起来,并通过灵活的过滤机制克服数据限制,实现精确的策略验证。接下来,我们将探讨如何根据这些结果优化交易执行,并将其集成到仪表板中。请您持续关注。
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/17603
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 重构经典策略(第十四部分):高胜率交易形态
重构经典策略(第十四部分):高胜率交易形态
 从新手到专家:对K线进行编程
从新手到专家:对K线进行编程
 交易中的神经网络:层次化双塔变换器(Hidformer)
交易中的神经网络:层次化双塔变换器(Hidformer)
 MQL5中表格模型的实现:应用MVC概念
MQL5中表格模型的实现:应用MVC概念