
MQL5経済指標カレンダーを使った取引(第7回):リソースベースのニュースイベント分析による戦略テストの準備
はじめに
この記事では、MQL5経済指標カレンダーシリーズの続編として、非リアルタイムモードでの戦略テストに向けて取引システムを準備する方法を紹介します。経済イベントのデータをリソースファイルから読み込み、信頼性の高いバックテストを実施することを目的としています。第6回では、ニュース分析とカウントダウンタイマーによる自動エントリーの仕組みを構築しましたが、今回は、ユーザーが指定した条件でニュースイベントをフィルタリングし、ストラテジーテスターで、ライブ環境を模擬したテストを実現します。この記事は次のトピックで構成されています。
さあ、始めましょう。
静的データ統合の重要性
静的データの統合は、堅牢な戦略を開発・検証したいと考えるトレーダーにとって不可欠です。特にMQL5のような環境では、過去の経済イベントデータが長期間保存されないため、その重要性が際立ちます。ライブ取引ではプラットフォームがリアルタイムのニュースフィードを取得できますが、ストラテジーテスターではこのような動的更新に対応していません。過去のイベントを網羅的に保持しておらず、ニュース主導型の戦略をバックテストするためのネイティブな解決策が存在しないのです。このような制約を補うために、外部ソースから経済データをダウンロードし、ファイル、データベース、あるいはリソースとして埋め込むことで、自分自身で管理できる一貫性のあるデータセットを構築することができます。この方法により、複数のテストにわたって同じ条件で戦略を検証でき、テスト環境の再現性が確保されます。
また、静的データの統合は、ライブフィードでは得られない柔軟性ももたらします。これまでのシリーズでも確認したように、経済指標カレンダーにはイベントの日時、通貨、影響度などの重要な情報が含まれますが、長期にわたるアルゴリズム分析に適した形式で保存されることはほとんどありません。これらの情報を手動で構造化することで、たとえば特定の通貨や高インパクトイベントだけを抽出するなど、自分のニーズに合わせたデータ処理が可能になり、リアルタイム依存から解放された、より深い市場分析がおこなえるようになります。
さらに、このアプローチは効率性と独立性も高めます。事前に静的データを収集・保存しておけば、インターネット接続や外部サービスに依存することなくテストが実施でき、検証結果を左右する不要な変数を排除できます。また、過去の大規模な経済発表など、稀なシナリオを再現することも可能になり、リアルタイムのシステムや限定的なプラットフォームのストレージでは実現困難な状況を自在にシミュレーションできます。結局のところ、静的データの統合は、ライブ取引で得られる知見と、バックテストの精度との間のギャップを埋めるものであり、戦略開発における確かな土台を築く手段なのです。
なお、データの保存形式も重要な検討ポイントです。MQL5では、テキスト(txt)形式、Comma Separated Values(CSV)、ANSI(アメリカ国家規格協会準拠)、バイナリ(bin)、Unicodeなど、そして以下のようなデータベース構造にも対応しています。
この記事では、最も簡単な形式ではなく、最も便利な形式であるCSV形式を使用します。こうすることで、データを手元に保持することで、戦略のバックテストを長時間待つ必要がなくなり、大幅な時間と労力の節約になります。それでは始めましょう。
MQL5での実装
はじめに、これまでの構成を反映させる形で、データの収集と整理の仕組みを構築する必要があります。そのため、以前と同様に、ユーザーがカスタマイズできるいくつかの入力項目が必要になります。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| MQL5 NEWS CALENDAR PART 7.mq5 | //| Copyright 2025, Allan Munene Mutiiria. | //| https://t.me/Forex_Algo_Trader | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2025, Allan Munene Mutiiria." #property link "https://youtube.com/@ForexAlgo-Trader?" #property version "1.00" #property strict //---- Input parameter for start date of event filtering input datetime StartDate = D'2025.03.01'; // Download Start Date //---- Input parameter for end date of event filtering input datetime EndDate = D'2025.03.21'; // Download End Date //---- Input parameter to enable/disable time filtering input bool ApplyTimeFilter = true; //---- Input parameter for hours before event to consider input int HoursBefore = 4; //---- Input parameter for minutes before event to consider input int MinutesBefore = 10; //---- Input parameter for hours after event to consider input int HoursAfter = 1; //---- Input parameter for minutes after event to consider input int MinutesAfter = 5; //---- Input parameter to enable/disable currency filtering input bool ApplyCurrencyFilter = true; //---- Input parameter defining currencies to filter (comma-separated) input string CurrencyFilter = "USD,EUR,GBP,JPY,AUD,NZD,CAD,CHF"; // All 8 major currencies //---- Input parameter to enable/disable impact filtering input bool ApplyImpactFilter = true; //---- Enumeration for event importance filtering options enum ENUM_IMPORTANCE { IMP_NONE = 0, // None IMP_LOW, // Low IMP_MEDIUM, // Medium IMP_HIGH, // High IMP_NONE_LOW, // None,Low IMP_NONE_MEDIUM, // None,Medium IMP_NONE_HIGH, // None,High IMP_LOW_MEDIUM, // Low,Medium IMP_LOW_HIGH, // Low,High IMP_MEDIUM_HIGH, // Medium,High IMP_NONE_LOW_MEDIUM, // None,Low,Medium IMP_NONE_LOW_HIGH, // None,Low,High IMP_NONE_MEDIUM_HIGH, // None,Medium,High IMP_LOW_MEDIUM_HIGH, // Low,Medium,High IMP_ALL // None,Low,Medium,High (default) }; //---- Input parameter for selecting importance filter input ENUM_IMPORTANCE ImportanceFilter = IMP_ALL; // Impact Levels (Default to all)
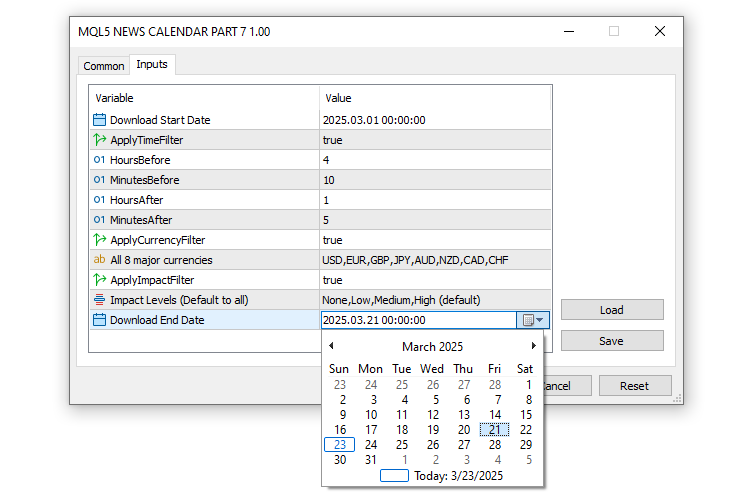
ここでは、戦略テストにおける経済イベントの処理をカスタマイズするために、取引システムの基本的な入力パラメータと列挙型を設定します。まず、StartDateとEndDateというdatetime型の変数を定義し、2025年3月1日から2025年3月21日までの期間を指定します。これは、イベントデータのダウンロードおよび分析の対象期間を明示するためです。イベントの前後における時間ベースのフィルタリングを制御するために、ブール型変数ApplyTimeFilter(デフォルトはtrue)を用意し、それに加えてHoursBefore(4時間)、MinutesBefore(10分)、HoursAfter(1時間)、MinutesAfter(5分)を設定します。これにより、特定のローソク足(バー)に対して、どの時間範囲のイベントを対象とするかを決めることができます。
通貨別の分析に対応するため、ApplyCurrencyFilter(デフォルトはtrue)とstring型変数CurrencyFilterも導入します。CurrencyFilterには、主要8通貨「USD, EUR, GBP, JPY, AUD, NZD, CAD, CHF」を指定し、関連する市場だけに絞って分析できるようにします。さらに、イベントの重要度によるフィルタリングも可能にするため、ApplyImpactFilterをtrueに設定し、それをサポートする列挙型ENUM_IMPORTANCEを定義します。ENUM_IMPORTANCEには、IMP_NONE、IMP_LOW、IMP_MEDIUM、IMP_HIGHなどの選択肢が用意されており、これらを組み合わせたIMP_ALLまで柔軟に選択できます。初期値のImportanceFilterにはIMP_ALLが指定され、すべての重要度レベルのイベントが対象となります。以下がその結果です。
これらの入力パラメータを設定したら、次におこなうべきことは、以下にあるMQL5の経済指標カレンダーにおける通常の標準構造を模倣した、8つのフィールドを持つ構造体を宣言することです。
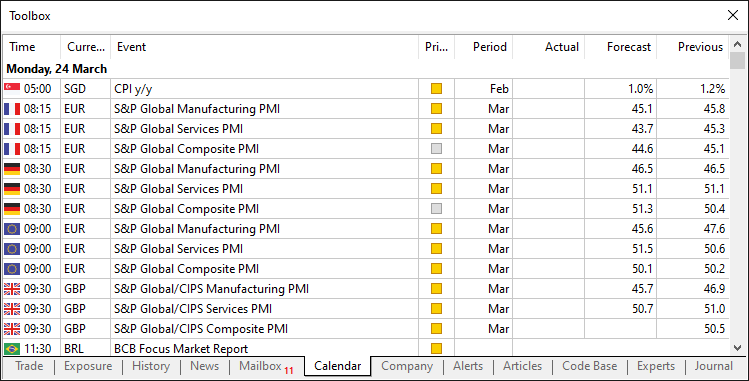
このフォーマットは、次のロジックによって実現されます。
//---- Structure to hold economic event data struct EconomicEvent { string eventDate; //---- Date of the event string eventTime; //---- Time of the event string currency; //---- Currency affected by the event string event; //---- Event description string importance; //---- Importance level of the event double actual; //---- Actual value of the event double forecast; //---- Forecasted value of the event double previous; //---- Previous value of the event }; //---- Array to store all economic events EconomicEvent allEvents[]; //---- Array for currency filter values string curr_filter[]; //---- Array for importance filter values string imp_filter[];
まずはじめに、EconomicEventという構造体(struct)を定義し、イベントの主要な情報をまとめます。eventDateとeventTimeはイベントの発生時刻を表す文字列として扱い、currencyは影響を受ける通貨、eventはイベントの説明文、importanceはそのイベントの影響度を示します。さらに、actual、forecast、previousは、それぞれの数値的な結果を格納するためのdouble型の変数として定義します。
次に、これらのイベントを保存・処理するために、3つの配列を作成します。allEventsは、読み込まれたすべてのEconomicEvent構造体を格納する配列です。curr_filterは、ユーザーがCurrencyFilterで指定した通貨を保持する文字列配列、imp_filterはImportanceFilterで選択された重要度を管理する文字列配列です。この構造体は、MQL5の経済カレンダーにおける標準的な構成を模倣していますが、Periodの情報を構造体の先頭にあるeventDateで代用している点が異なります。このあとに必要な処理は、ユーザーの入力からフィルター条件を取得し、それをプログラムが理解できる形に変換して初期化することです。コードをモジュール化してわかりやすく保つために、これらの処理は関数を使って実装していきます。
//---- Function to initialize currency and impact filters void InitializeFilters() { //---- Currency Filter Section //---- Check if currency filter is enabled and has content if (ApplyCurrencyFilter && StringLen(CurrencyFilter) > 0) { //---- Split the currency filter string into array int count = StringSplit(CurrencyFilter, ',', curr_filter); //---- Loop through each currency filter entry for (int i = 0; i < ArraySize(curr_filter); i++) { //---- Temporary variable for trimming string temp = curr_filter[i]; //---- Remove leading whitespace StringTrimLeft(temp); //---- Remove trailing whitespace StringTrimRight(temp); //---- Assign trimmed value back to array curr_filter[i] = temp; //---- Print currency filter for debugging Print("Currency filter [", i, "]: '", curr_filter[i], "'"); } } else if (ApplyCurrencyFilter) { //---- Warn if currency filter is enabled but empty Print("Warning: CurrencyFilter is empty, no currency filtering applied"); //---- Resize array to zero if no filter applied ArrayResize(curr_filter, 0); } }
ここでは、戦略テスト時のイベント解析を正確におこなうために、InitializeFilters関数内で通貨フィルタリングの初期化処理を実装します。まず、ApplyCurrencyFilter変数がtrueであり、StringLen関数でCurrencyFilter文字列に長さがあるかを確認します。条件を満たす場合、カンマ区切りのCurrencyFilter(例:"USD, EUR, GBP")をStringSplit関数でcurr_filter配列に分割し、その要素数をcount変数に格納します。
次に、forループでcurr_filterの各要素を順に処理します。まず一時的にstring型のtemp変数に格納し、StringTrimLeftとStringTrimRight関数で前後の空白を除去します。トリミング後の値でcurr_filterを更新し、Print関数で「Currency filter [0]: 'USD'」のようにデバッグ表示をおこないます。もしApplyCurrencyFilterが有効にもかかわらずCurrencyFilterが空文字だった場合は、Print関数で「Warning: CurrencyFilter is empty, no currency filtering applied」という警告を出し、ArrayResize関数で配列サイズを0に設定してフィルタリングを無効化します。このようにユーザー入力から確実に通貨フィルタを初期化することで、ストラテジーテスター内でのイベント処理が正確におこなわれるようになります。影響フィルタについても同様のロジックを適用します。
//---- Impact Filter Section (using enum) //---- Check if impact filter is enabled if (ApplyImpactFilter) { //---- Switch based on selected importance filter switch (ImportanceFilter) { case IMP_NONE: //---- Resize array for single importance level ArrayResize(imp_filter, 1); //---- Set importance to "None" imp_filter[0] = "None"; break; case IMP_LOW: //---- Resize array for single importance level ArrayResize(imp_filter, 1); //---- Set importance to "Low" imp_filter[0] = "Low"; break; case IMP_MEDIUM: //---- Resize array for single importance level ArrayResize(imp_filter, 1); //---- Set importance to "Medium" imp_filter[0] = "Medium"; break; case IMP_HIGH: //---- Resize array for single importance level ArrayResize(imp_filter, 1); //---- Set importance to "High" imp_filter[0] = "High"; break; case IMP_NONE_LOW: //---- Resize array for two importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 2); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "None"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "Low"; break; case IMP_NONE_MEDIUM: //---- Resize array for two importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 2); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "None"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "Medium"; break; case IMP_NONE_HIGH: //---- Resize array for two importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 2); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "None"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "High"; break; case IMP_LOW_MEDIUM: //---- Resize array for two importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 2); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "Low"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "Medium"; break; case IMP_LOW_HIGH: //---- Resize array for two importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 2); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "Low"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "High"; break; case IMP_MEDIUM_HIGH: //---- Resize array for two importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 2); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "Medium"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "High"; break; case IMP_NONE_LOW_MEDIUM: //---- Resize array for three importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 3); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "None"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "Low"; //---- Set third importance level imp_filter[2] = "Medium"; break; case IMP_NONE_LOW_HIGH: //---- Resize array for three importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 3); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "None"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "Low"; //---- Set third importance level imp_filter[2] = "High"; break; case IMP_NONE_MEDIUM_HIGH: //---- Resize array for three importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 3); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "None"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "Medium"; //---- Set third importance level imp_filter[2] = "High"; break; case IMP_LOW_MEDIUM_HIGH: //---- Resize array for three importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 3); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "Low"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "Medium"; //---- Set third importance level imp_filter[2] = "High"; break; case IMP_ALL: //---- Resize array for all importance levels ArrayResize(imp_filter, 4); //---- Set first importance level imp_filter[0] = "None"; //---- Set second importance level imp_filter[1] = "Low"; //---- Set third importance level imp_filter[2] = "Medium"; //---- Set fourth importance level imp_filter[3] = "High"; break; } //---- Loop through impact filter array to print values for (int i = 0; i < ArraySize(imp_filter); i++) { //---- Print each impact filter value Print("Impact filter [", i, "]: '", imp_filter[i], "'"); } } else { //---- Notify if impact filter is disabled Print("Impact filter disabled"); //---- Resize impact filter array to zero ArrayResize(imp_filter, 0); }
影響フィルタリング処理ではまず変数ApplyImpactFilterがtrueかどうかを確認します。trueならImportanceFilter列挙型の値に応じてswitch文を使いimp_filter配列に含める影響度を決定します。単一レベルのIMP_NONEやIMP_LOW、IMP_MEDIUM、IMP_HIGHの場合はArrayResize関数でimp_filterのサイズを1にして対応する文字列を代入します(例:imp_filter[0] = 'None')。二段階のIMP_NONE_LOWやIMP_MEDIUM_HIGHの場合はサイズを2にして二つの値を設定します(例:imp_filter[0] = 'None'、imp_filter[1] = 'Low')。三段階のIMP_LOW_MEDIUM_HIGHではサイズを3に、IMP_ALLではサイズを4にしてNone、Low、Medium、Highのすべてを含めます。
配列設定後はArraySize関数で要素数を取得しforループで各要素をPrint関数で出力してデバッグします(例:Impact filter[0]='None')。ApplyImpactFilterがfalseの場合はPrint関数で「Impact filter disabled」と通知しArrayResize関数でimp_filterのサイズを0にしてフィルタを無効化します
これで、OnInitイベントハンドラで関数を呼び出す必要があります。
int OnInit() { //---- Initialize filters InitializeFilters(); //---- Return successful initialization return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } void OnDeinit(const int reason) { //---- Print termination reason Print("EA terminated, reason: ", reason); }
OnInitイベントハンドラで関数を呼び出し、OnDeinitイベントハンドラでプログラム終了の理由も出力します。以下はその結果です。
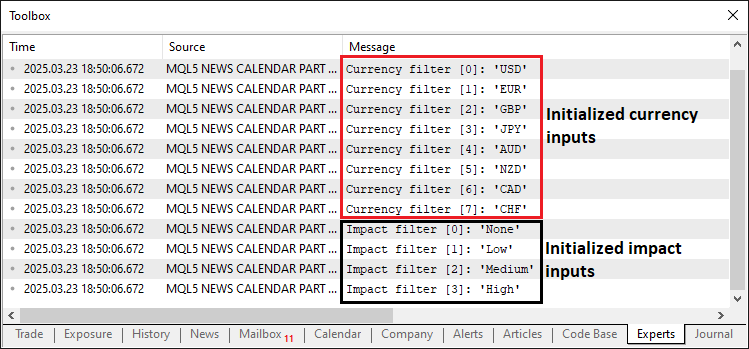
画像から初期化とフィルタ入力のデコードが正しくおこなわれて格納されていることがわかります。次に必要なのはライブストリームからデータを取得して保存することです。ロジックとしてはまずライブモードで一度プログラムを実行し、MQL5経済指標カレンダーのデータベースからデータをダウンロードします。その後テストモードでそのデータを読み込んで使用します。以下が初期化のロジックです。
//---- Check if not running in tester mode if (!MQLInfoInteger(MQL_TESTER)) { //---- Validate date range if (StartDate >= EndDate) { //---- Print error for invalid date range Print("Error: StartDate (", TimeToString(StartDate), ") must be earlier than EndDate (", TimeToString(EndDate), ")"); //---- Return initialization failure return(INIT_PARAMETERS_INCORRECT); } //---- Array to hold calendar values MqlCalendarValue values[]; //---- Fetch calendar data for date range if (!CalendarValueHistory(values, StartDate, EndDate)) { //---- Print error if calendar data fetch fails Print("Error fetching calendar data: ", GetLastError()); //---- Return initialization failure return(INIT_FAILED); } //---- Array to hold economic events EconomicEvent events[]; //---- Counter for events int eventCount = 0; //---- Loop through calendar values for (int i = 0; i < ArraySize(values); i++) { //---- Structure for event details MqlCalendarEvent eventDetails; //---- Fetch event details by ID if (!CalendarEventById(values[i].event_id, eventDetails)) continue; //---- Structure for country details MqlCalendarCountry countryDetails; //---- Fetch country details by ID if (!CalendarCountryById(eventDetails.country_id, countryDetails)) continue; //---- Structure for value details MqlCalendarValue value; //---- Fetch value details by ID if (!CalendarValueById(values[i].id, value)) continue; //---- Resize events array for new event ArrayResize(events, eventCount + 1); //---- Convert event time to string string dateTimeStr = TimeToString(values[i].time, TIME_DATE | TIME_MINUTES); //---- Extract date from datetime string events[eventCount].eventDate = StringSubstr(dateTimeStr, 0, 10); //---- Extract time from datetime string events[eventCount].eventTime = StringSubstr(dateTimeStr, 11, 5); //---- Assign currency from country details events[eventCount].currency = countryDetails.currency; //---- Assign event name events[eventCount].event = eventDetails.name; //---- Map importance level from enum to string events[eventCount].importance = (eventDetails.importance == 0) ? "None" : // CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_NONE (eventDetails.importance == 1) ? "Low" : // CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_LOW (eventDetails.importance == 2) ? "Medium" : // CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_MODERATE "High"; // CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_HIGH //---- Assign actual value events[eventCount].actual = value.GetActualValue(); //---- Assign forecast value events[eventCount].forecast = value.GetForecastValue(); //---- Assign previous value events[eventCount].previous = value.GetPreviousValue(); //---- Increment event count eventCount++; } }
ここではOnInit関数内でライブモード時のデータ取得を行い、その後の戦略テスト用に経済イベントデータを収集します。まずMQLInfoInteger関数にMQL_TESTERを指定してシステムがテスターモードでないかを確認します。テスターでない場合はStartDateがEndDateより前になっているかをチェックし、条件を満たさないときはエラーをPrintしINIT_PARAMETERS_INCORRECTを返します。次にMqlCalendarValue型の配列valuesを宣言し、CalendarValueHistory関数でStartDate~EndDateの期間のデータを取得します。取得に失敗した場合はGetLastError関数でエラー内容をPrintしINIT_FAILEDを返します。
取得が成功したらEconomicEvent型の配列eventsと整数eventCountを初期化し、ArraySize関数でvaluesの要素数をループします。各ループ内でCalendarEventById関数を使いMqlCalendarEvent型のeventDetailsにイベント詳細を、CalendarEventById関数でMqlCalendarCountry型のcountryDetailsに通貨詳細を、CalendarCountryById関数でMqlCalendarValue型のvalueに数値データを取得します。いずれかの取得に失敗した場合はスキップします。成功したらArrayResize関数でeventsのサイズを拡張し、TimeToString関数で時間情報を文字列dateTimeStrに変換、StringSubstr関数でeventDateとeventTimeに分割します。currencyにはcountryDetailsの通貨コードを、eventにはeventDetails.nameを設定し、importanceは数値から文字列(「None」、「Low」、「Medium」、「High」)へマッピングします。actual、forecast、previousはvalue.actual value.forecast value.previousで設定し、eventCountをインクリメントします。こうしてライブモード用の包括的なイベントデータセットが構築されます。次のステップはこのデータをCSVファイルなどに書き出す関数を実装することです。
//---- Function to write events to a CSV file void WriteToCSV(string fileName, EconomicEvent &events[]) { //---- Open file for writing in CSV format int handle = FileOpen(fileName, FILE_WRITE | FILE_CSV, ','); //---- Check if file opening failed if (handle == INVALID_HANDLE) { //---- Print error message with last error code Print("Error creating file: ", GetLastError()); //---- Exit function on failure return; } //---- Write CSV header row FileWrite(handle, "Date", "Time", "Currency", "Event", "Importance", "Actual", "Forecast", "Previous"); //---- Loop through all events to write to file for (int i = 0; i < ArraySize(events); i++) { //---- Write event data to CSV file FileWrite(handle, events[i].eventDate, events[i].eventTime, events[i].currency, events[i].event, events[i].importance, DoubleToString(events[i].actual, 2), DoubleToString(events[i].forecast, 2), DoubleToString(events[i].previous, 2)); //---- Print event details for debugging Print("Writing event ", i, ": ", events[i].eventDate, ", ", events[i].eventTime, ", ", events[i].currency, ", ", events[i].event, ", ", events[i].importance, ", ", DoubleToString(events[i].actual, 2), ", ", DoubleToString(events[i].forecast, 2), ", ", DoubleToString(events[i].previous, 2)); } //---- Flush data to file FileFlush(handle); //---- Close the file handle FileClose(handle); //---- Print confirmation of data written Print("Data written to ", fileName, " with ", ArraySize(events), " events."); //---- Verify written file by reading it back int verifyHandle = FileOpen(fileName, FILE_READ | FILE_TXT); //---- Check if verification file opening succeeded if (verifyHandle != INVALID_HANDLE) { //---- Read entire file content string content = FileReadString(verifyHandle, (int)FileSize(verifyHandle)); //---- Print file content for verification Print("File content after writing (size: ", FileSize(verifyHandle), " bytes):\n", content); //---- Close verification file handle FileClose(verifyHandle); } }
ここではWriteToCSV関数を作成し、経済イベントデータをCSVファイルに体系的に書き出します。まずFileOpen関数を使いFILE_WRITE | FILE_CSVモードでカンマ区切りのファイルをfileNameで開き、その戻り値をhandleに格納します。もしhandleがINVALID_HANDLEであればGetLastErrorのコードを含むエラーメッセージをPrint関数で表示し、関数をreturnで抜けます。ファイルが開けたらFileWrite関数でヘッダー行を書き込みます。列はDate、Time、Currency、Event、Importance、Actual、Forecast、Previousとし、データの項目を整理します。
次にevents配列をArraySize関数でループ回数を取得し、各イベントについてFileWriteを呼び出してeventDate、eventTime、currency、event、importance、actual、forecast、previousの各フィールドを書き込みます。actual、forecast、previousはDoubleToString関数で少数第2位までの文字列に変換します。また同時にPrint関数でデバッグ用に各行の内容をログ出力します。
ループ終了後はFileFlush関数でバッファの内容を確実にファイルに書き込み、FileClose関数でファイルを閉じます。正常に完了した旨をPrintで報告します。
出力確認のために「FILE_READ|FILE_TXT」モードでファイルを再度FileOpenし、そのハンドルをverifyHandleに格納します。開けたらFileSize関数でバイト数を取得し、FileReadString関数でcontentに全文を読み込みます。Print関数で「File content after writing (size: X bytes):\n"content"」の形式で中身を表示し、最後にFileClose関数で閉じます。この徹底したプロセスにより、イベントデータが正確に保存され、確認・検証できるため、ストラテジーテスターでのバックテスト用リソースとして信頼性が高まります。これで、データ保存プロセスに関数を使用できるようになります。
//---- Define file path for CSV string fileName = "Database\\EconomicCalendar.csv"; //---- Check if file exists and print appropriate message if (!FileExists(fileName)) Print("Creating new file: ", fileName); else Print("Overwriting existing file: ", fileName); //---- Write events to CSV file WriteToCSV(fileName, events); //---- Print instructions for tester mode Print("Live mode: Data written. To use in tester, manually add ", fileName, " as a resource and recompile.");
ライブモードのデータ処理を締めくくるために、まずfileNameを「Database\EconomicCalendar.csv」に設定し、カスタム関数FileExistsでファイルの存在を確認します。続いて、WriteToCSV関数をfileNameとeventsを引数に呼び出してデータを書き込み、Print関数でメッセージ「"Live mode:Data written」を表示します。テスターで使用するには、fileNameをリソースに追加した上で再コンパイルしてください。ファイルの存在をチェックするカスタム関数のコードスニペットは以下の通りです。
//---- Function to check if a file exists bool FileExists(string fileName) { //---- Open file in read mode to check existence int handle = FileOpen(fileName, FILE_READ | FILE_CSV); //---- Check if file opened successfully if (handle != INVALID_HANDLE) { //---- Close the file handle FileClose(handle); //---- Return true if file exists return true; } //---- Return false if file doesn't exist return false; }
FileExists関数では、戦略テスト用にファイルの存在を確認するために、FileOpen関数でFILE_READ|FILE_CSVモードでfileNameを開きます。handleがINVALID_HANDLEでない場合はFileCloseで閉じてtrueを返し、そうでない場合はfalseを返します。これによりデータ処理に必要なファイルの有無を確実に確認できます。ライブモードで実行した結果は以下のとおりです。
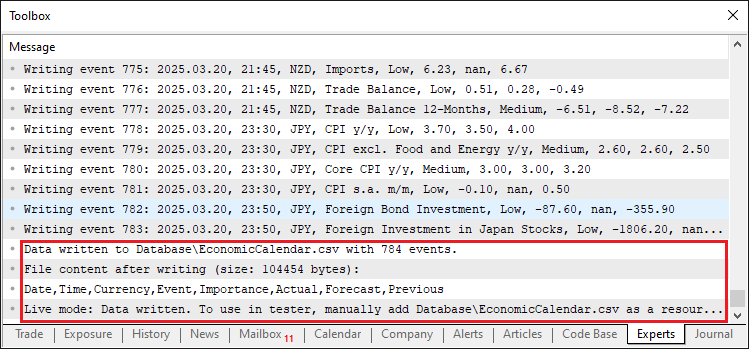
画像から、データが保存され、アクセスできることがわかります。
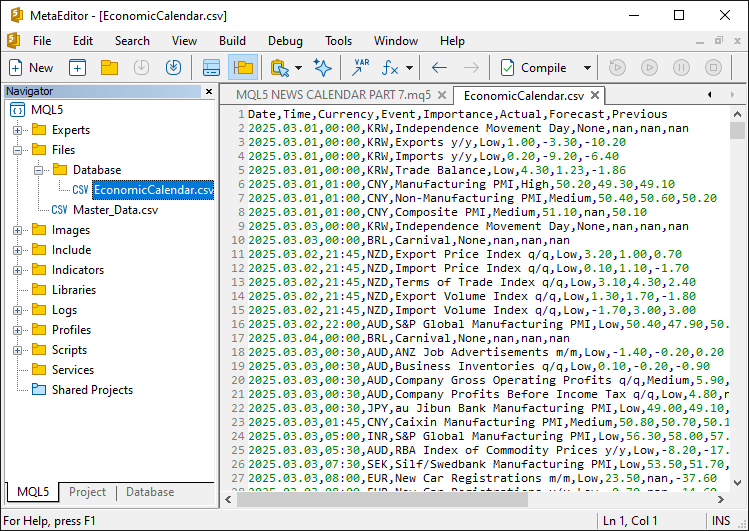
テスターモードでデータを使用するには実行ファイルに保存する必要があります。そのためリソースとして追加します。
//---- Define resource file for economic calendar data #resource "\\Files\\Database\\EconomicCalendar.csv" as string EconomicCalendarData
ここでは静的データリソースをプログラムに統合し、戦略テストをサポートします。#resourceディレクティブを使って\Files\Database\EconomicCalendar.csvのファイルを埋め込み、EconomicCalendarDataという文字列変数に割り当てます。こうすることで実行ファイル内にデータが含まれ、外部ファイルが削除されても問題なく利用できます。次にこのリソースから内容を読み込む関数を用意します。
//---- Function to load events from resource file bool LoadEventsFromResource() { //---- Get data from resource string fileData = EconomicCalendarData; //---- Print raw resource content for debugging Print("Raw resource content (size: ", StringLen(fileData), " bytes):\n", fileData); //---- Array to hold lines from resource string lines[]; //---- Split resource data into lines int lineCount = StringSplit(fileData, '\n', lines); //---- Check if resource has valid data if (lineCount <= 1) { //---- Print error if no data lines found Print("Error: No data lines found in resource! Raw data: ", fileData); //---- Return false on failure return false; } //---- Reset events array ArrayResize(allEvents, 0); //---- Index for event array int eventIndex = 0; //---- Loop through each line (skip header at i=0) for (int i = 1; i < lineCount; i++) { //---- Check for empty lines if (StringLen(lines[i]) == 0) { //---- Print message for skipped empty line Print("Skipping empty line ", i); //---- Skip to next iteration continue; } //---- Array to hold fields from each line string fields[]; //---- Split line into fields int fieldCount = StringSplit(lines[i], ',', fields); //---- Print line details for debugging Print("Line ", i, ": ", lines[i], " (field count: ", fieldCount, ")"); //---- Check if line has minimum required fields if (fieldCount < 8) { //---- Print error for malformed line Print("Malformed line ", i, ": ", lines[i], " (field count: ", fieldCount, ")"); //---- Skip to next iteration continue; } //---- Extract date from field string dateStr = fields[0]; //---- Extract time from field string timeStr = fields[1]; //---- Extract currency from field string currency = fields[2]; //---- Extract event description (handle commas in event name) string event = fields[3]; //---- Combine multiple fields if event name contains commas for (int j = 4; j < fieldCount - 4; j++) { event += "," + fields[j]; } //---- Extract importance from field string importance = fields[fieldCount - 4]; //---- Extract actual value from field string actualStr = fields[fieldCount - 3]; //---- Extract forecast value from field string forecastStr = fields[fieldCount - 2]; //---- Extract previous value from field string previousStr = fields[fieldCount - 1]; //---- Convert date and time to datetime format datetime eventDateTime = StringToTime(dateStr + " " + timeStr); //---- Check if datetime conversion failed if (eventDateTime == 0) { //---- Print error for invalid datetime Print("Error: Invalid datetime conversion for line ", i, ": ", dateStr, " ", timeStr); //---- Skip to next iteration continue; } //---- Resize events array for new event ArrayResize(allEvents, eventIndex + 1); //---- Assign event date allEvents[eventIndex].eventDate = dateStr; //---- Assign event time allEvents[eventIndex].eventTime = timeStr; //---- Assign event currency allEvents[eventIndex].currency = currency; //---- Assign event description allEvents[eventIndex].event = event; //---- Assign event importance allEvents[eventIndex].importance = importance; //---- Convert and assign actual value allEvents[eventIndex].actual = StringToDouble(actualStr); //---- Convert and assign forecast value allEvents[eventIndex].forecast = StringToDouble(forecastStr); //---- Convert and assign previous value allEvents[eventIndex].previous = StringToDouble(previousStr); //---- Print loaded event details Print("Loaded event ", eventIndex, ": ", dateStr, " ", timeStr, ", ", currency, ", ", event); //---- Increment event index eventIndex++; } //---- Print total events loaded Print("Loaded ", eventIndex, " events from resource into array."); //---- Return success if events were loaded return eventIndex > 0; }
LoadEventsFromResource関数では、埋め込まれたリソースから経済イベントデータを読み込んでallEvents配列を構築します。まずEconomicCalendarDataリソースをfileDataに割り当て、Print関数で生の内容とStringLen関数で取得したサイズをデバッグ表示します。次にStringSplit関数を改行区切りで呼び出してfileDataをlines配列に分割し、要素数をlineCountに格納します。lineCountが1以下の場合はエラーをPrintしてfalseを返します。続いてArrayResize関数でallEventsを長さ0にリセットし、eventIndexを0で初期化します。forループでlinesを1から開始しヘッダーをスキップします。各行についてStringLenで空行をチェックし、空文字ならPrintで「skip」メッセージを出して次へ進みます。空でなければStringSplitで行をカンマ区切りのfields配列に分割しfieldCountを取得します。
fieldCountが8未満ならエラーをPrintしてスキップし、そうでなければdateStr、timeStr、currencyをfields[0]からfields[2]までで取得し、fields[3]以降をループで連結してeventを構築します。続いてfieldsからimportance、actualStr、forecastStr、previousStrを取り出します。StringToTime関数でdateStrとtimeStrをeventDateTimeに変換し、失敗した場合はエラーを表示して処理をスキップします。その後ArrayResize関数でallEventsのサイズを調整し、StringToDouble関数で数値を変換しながら構造体の各フィールドを設定します。最後にPrint関数でイベントを出力し、eventIndexをインクリメントします。最後に、eventIndexの合計をPrint関数で出力し、イベントが読み込まれていればtrueを返します。これにより、ストラテジーテスターで使用するためのデータが確実に準備されていることが保証されます。これで、テスターモードの初期化時にこの関数を呼び出せるようになります。
else { //---- Check if resource data is empty in tester mode if (StringLen(EconomicCalendarData) == 0) { //---- Print error for empty resource Print("Error: Resource EconomicCalendarData is empty. Please run in live mode, add the file as a resource, and recompile."); //---- Return initialization failure return(INIT_FAILED); } //---- Print message for tester mode Print("Running in Strategy Tester, using embedded resource: Database\\EconomicCalendar.csv"); //---- Load events from resource if (!LoadEventsFromResource()) { //---- Print error if loading fails Print("Failed to load events from resource."); //---- Return initialization failure return(INIT_FAILED); } }
ここでは、EconomicCalendarDataが空であるかどうかをStringLen関数で確認し、空であればエラーメッセージをPrint関数で表示してINIT_FAILEDを返します。そうでない場合は、Print関数でテスターモードのメッセージを出力し、LoadEventsFromResource関数を呼び出します。もしこの関数が失敗した場合は、エラーメッセージとともにINIT_FAILEDを返します。これにより、イベントデータが正しく読み込まれ、バックテストに必要な準備が整っていることが保証されます。以下はその結果です。
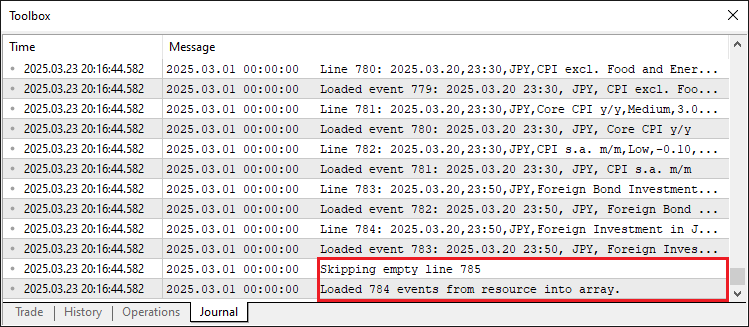
画像から、データが正常に読み込まれていることが確認できます。また、データの不整形や空行のスキップも正しく処理されています。これで、次はOnTickイベントハンドラに進み、あたかもライブモードであるかのようにデータ処理をシミュレートすることができます。この目的のために、すべてのティックごとではなく、バー(ローソク足)単位でデータを処理するようにします。
//---- Variable to track last bar time datetime lastBarTime = 0; //---- Tick event handler void OnTick() { //---- Get current bar time datetime currentBarTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, 0); //---- Check if bar time has changed if (currentBarTime != lastBarTime) { //---- Update last bar time lastBarTime = currentBarTime; //---- } }
datetime型の変数lastBarTimeを0で初期化し、直前のバーの時間を記録できるようにします。OnTick関数内では、iTime関数を使用して現在のバーの時間を取得します。_Symbol、_Period、バーインデックス0を使ってcurrentBarTimeに格納します。このcurrentBarTimeがlastBarTimeと異なっていれば、新しいバーが形成されたことになるため、lastBarTimeをcurrentBarTimeで更新します。これにより、システムは新しいバーの出現時にのみイベント処理をおこなうようになります。この準備が整ったら、以前のバージョンと同様の形式で、ライブシミュレーションのデータ処理をおこなう関数を定義できます。
//---- Function to filter and print economic events void FilterAndPrintEvents(datetime barTime) { //---- Get total number of events int totalEvents = ArraySize(allEvents); //---- Print total events considered Print("Total considered data size: ", totalEvents, " events"); //---- Check if there are events to filter if (totalEvents == 0) { //---- Print message if no events loaded Print("No events loaded to filter."); //---- Exit function return; } //---- Array to store filtered events EconomicEvent filteredEvents[]; //---- Counter for filtered events int filteredCount = 0; //---- Variables for time range datetime timeBefore, timeAfter; //---- Apply time filter if enabled if (ApplyTimeFilter) { //---- Structure for bar time MqlDateTime barStruct; //---- Convert bar time to structure TimeToStruct(barTime, barStruct); //---- Calculate time before event MqlDateTime timeBeforeStruct = barStruct; //---- Subtract hours before timeBeforeStruct.hour -= HoursBefore; //---- Subtract minutes before timeBeforeStruct.min -= MinutesBefore; //---- Adjust for negative minutes if (timeBeforeStruct.min < 0) { timeBeforeStruct.min += 60; timeBeforeStruct.hour -= 1; } //---- Adjust for negative hours if (timeBeforeStruct.hour < 0) { timeBeforeStruct.hour += 24; timeBeforeStruct.day -= 1; } //---- Convert structure to datetime timeBefore = StructToTime(timeBeforeStruct); //---- Calculate time after event MqlDateTime timeAfterStruct = barStruct; //---- Add hours after timeAfterStruct.hour += HoursAfter; //---- Add minutes after timeAfterStruct.min += MinutesAfter; //---- Adjust for minutes overflow if (timeAfterStruct.min >= 60) { timeAfterStruct.min -= 60; timeAfterStruct.hour += 1; } //---- Adjust for hours overflow if (timeAfterStruct.hour >= 24) { timeAfterStruct.hour -= 24; timeAfterStruct.day += 1; } //---- Convert structure to datetime timeAfter = StructToTime(timeAfterStruct); //---- Print time range for debugging Print("Bar time: ", TimeToString(barTime), ", Time range: ", TimeToString(timeBefore), " to ", TimeToString(timeAfter)); } else { //---- Print message if no time filter applied Print("Bar time: ", TimeToString(barTime), ", No time filter applied, using StartDate to EndDate only."); //---- Set time range to date inputs timeBefore = StartDate; timeAfter = EndDate; } //---- Loop through all events for filtering for (int i = 0; i < totalEvents; i++) { //---- Convert event date and time to datetime datetime eventDateTime = StringToTime(allEvents[i].eventDate + " " + allEvents[i].eventTime); //---- Check if event is within date range bool inDateRange = (eventDateTime >= StartDate && eventDateTime <= EndDate); //---- Skip if not in date range if (!inDateRange) continue; //---- Time Filter Check //---- Check if event is within time range if filter applied bool timeMatch = !ApplyTimeFilter || (eventDateTime >= timeBefore && eventDateTime <= timeAfter); //---- Skip if time doesn't match if (!timeMatch) continue; //---- Print event details if time passes Print("Event ", i, ": Time passes (", allEvents[i].eventDate, " ", allEvents[i].eventTime, ") - ", "Currency: ", allEvents[i].currency, ", Event: ", allEvents[i].event, ", Importance: ", allEvents[i].importance, ", Actual: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].actual, 2), ", Forecast: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].forecast, 2), ", Previous: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].previous, 2)); //---- Currency Filter Check //---- Default to match if filter disabled bool currencyMatch = !ApplyCurrencyFilter; //---- Apply currency filter if enabled if (ApplyCurrencyFilter && ArraySize(curr_filter) > 0) { //---- Initially set to no match currencyMatch = false; //---- Check each currency in filter for (int j = 0; j < ArraySize(curr_filter); j++) { //---- Check if event currency matches filter if (allEvents[i].currency == curr_filter[j]) { //---- Set match to true if found currencyMatch = true; //---- Exit loop on match break; } } //---- Skip if currency doesn't match if (!currencyMatch) continue; } //---- Print event details if currency passes Print("Event ", i, ": Currency passes (", allEvents[i].currency, ") - ", "Date: ", allEvents[i].eventDate, " ", allEvents[i].eventTime, ", Event: ", allEvents[i].event, ", Importance: ", allEvents[i].importance, ", Actual: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].actual, 2), ", Forecast: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].forecast, 2), ", Previous: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].previous, 2)); //---- Impact Filter Check //---- Default to match if filter disabled bool impactMatch = !ApplyImpactFilter; //---- Apply impact filter if enabled if (ApplyImpactFilter && ArraySize(imp_filter) > 0) { //---- Initially set to no match impactMatch = false; //---- Check each importance in filter for (int k = 0; k < ArraySize(imp_filter); k++) { //---- Check if event importance matches filter if (allEvents[i].importance == imp_filter[k]) { //---- Set match to true if found impactMatch = true; //---- Exit loop on match break; } } //---- Skip if importance doesn't match if (!impactMatch) continue; } //---- Print event details if impact passes Print("Event ", i, ": Impact passes (", allEvents[i].importance, ") - ", "Date: ", allEvents[i].eventDate, " ", allEvents[i].eventTime, ", Currency: ", allEvents[i].currency, ", Event: ", allEvents[i].event, ", Actual: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].actual, 2), ", Forecast: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].forecast, 2), ", Previous: ", DoubleToString(allEvents[i].previous, 2)); //---- Add event to filtered array ArrayResize(filteredEvents, filteredCount + 1); //---- Assign event to filtered array filteredEvents[filteredCount] = allEvents[i]; //---- Increment filtered count filteredCount++; } //---- Print summary of filtered events Print("After ", (ApplyTimeFilter ? "time filter" : "date range filter"), ApplyCurrencyFilter ? " and currency filter" : "", ApplyImpactFilter ? " and impact filter" : "", ": ", filteredCount, " events remaining."); //---- Check if there are filtered events to print if (filteredCount > 0) { //---- Print header for filtered events Print("Filtered Events at Bar Time: ", TimeToString(barTime)); //---- Print filtered events array ArrayPrint(filteredEvents, 2, " | "); } else { //---- Print message if no events found Print("No events found within the specified range."); } }
ここでは、指定したバーに関連する経済イベントをフィルタして表示するために、FilterAndPrintEvents関数を構築します。まず、ArraySize関数でallEventsのサイズを取得し、それをtotalEventsとしてPrint関数で出力します。もしtotalEventsが0であれば、何も処理せずにreturnします。次に、EconomicEvent型の配列filteredEventsを初期化し、filteredCountを0に設定します。その後、時間フィルタ用にtimeBeforeとtimeAfterを定義します。ApplyTimeFilterがtrueであれば、TimeToStruct関数でbarTimeをbarStructに変換し、HoursBeforeとMinutesBeforeを減算してtimeBeforeStructを調整(マイナス補正)、HoursAfterとMinutesAfterを加算してtimeAfterStructを調整(オーバーフロー補正)し、それぞれStructToTime関数でdatetime型に変換して範囲をPrintで表示します。ApplyTimeFilterがfalseの場合は、StartDateとEndDateをそのままtimeBeforeとtimeAfterに設定し、「フィルタなし」メッセージを出力します。
次に、totalEvents分ループし、各イベントのeventDateとeventTimeをStringToTime関数でeventDateTimeに変換します。そして、eventDateTimeがStartDate~EndDateの範囲にあるかどうかをinDateRangeとして判定し、範囲外であればスキップします。ApplyTimeFilterが有効な場合、eventDateTimeがtimeBefore~timeAfterの範囲内であればtimeMatchをtrueとし、範囲内である旨をPrintで出力します。通貨についてはApplyCurrencyFilterがtrueなら、curr_filterのArraySizeでループして、eventのcurrencyと一致するかをcurrencyMatchでチェックし、一致すればPrintで出力します。インパクトレベルについてもApplyImpactFilterがtrueの場合、imp_filterと一致するかimpactMatchを確認し、マッチすれば出力します。すべての条件を満たすイベントはfilteredEventsにArrayResize関すで格納し、filteredCountをインクリメントします。
最後に、フィルタ結果のサマリーをPrintで出力し、filteredCountが1以上であればArrayPrintでfilteredEventsの内容を一覧表示し、そうでなければ「該当イベントなし」メッセージを出力します。これにより、テスト環境での経済イベント分析を詳細におこなうことができます。次に、ティックイベントハンドラで関数を呼び出します。
void OnTick() { //---- Get current bar time datetime currentBarTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, 0); //---- Check if bar time has changed if (currentBarTime != lastBarTime) { //---- Update last bar time lastBarTime = currentBarTime; //---- Filter and print events for current bar FilterAndPrintEvents(currentBarTime); } }
プログラムを実行すると、次の結果が得られます。
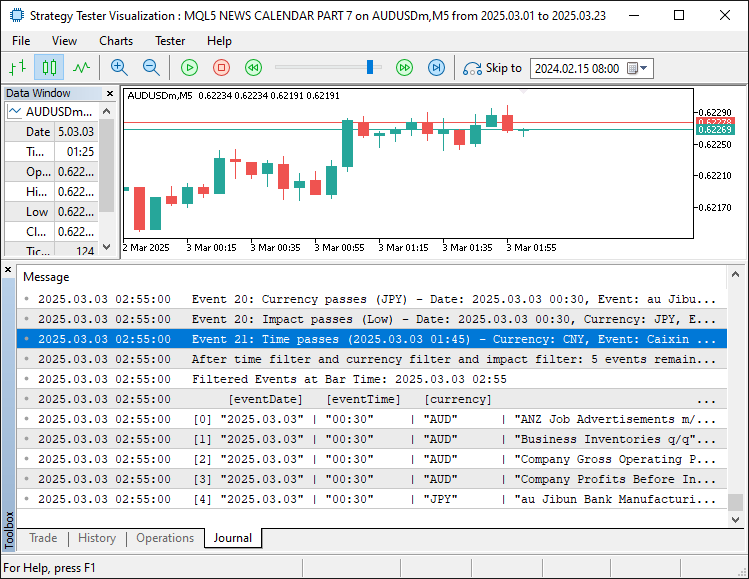
画像から、フィルタリングが有効になっていて、期待どおりに機能していることがわかります。 あとはロジックのテストをおこなうだけであり、その内容は次のセクションで扱います。
テスト
詳細なテストについては、すべてをビデオで視覚化しました。以下に添付されているビデオでご覧いただけます。
<// ビデオはこちら //>
結論
結論として、今回はMQL5経済指標カレンダーシリーズを強化し、静的データを保存ファイルとして利用することで、ストラテジーテスターに対応した信頼性の高いバックテスト環境を整備しました。これにより、ライブイベント分析とテスターモードの橋渡しが可能となり、柔軟なフィルタ処理を通じて、データ制限を克服しながら精度の高い戦略検証が実現します。次回は、この検証結果をもとにしたエントリー戦略の最適化や、ダッシュボードへの統合について解説していきますので、どうぞお楽しみに。
MetaQuotes Ltdにより英語から翻訳されました。
元の記事: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/17603
警告: これらの資料についてのすべての権利はMetaQuotes Ltd.が保有しています。これらの資料の全部または一部の複製や再プリントは禁じられています。
この記事はサイトのユーザーによって執筆されたものであり、著者の個人的な見解を反映しています。MetaQuotes Ltdは、提示された情報の正確性や、記載されているソリューション、戦略、または推奨事項の使用によって生じたいかなる結果についても責任を負いません。
 古典的な戦略を再構築する(第14回):高確率セットアップ
古典的な戦略を再構築する(第14回):高確率セットアップ
 初心者からエキスパートへ:ローソク足のプログラミング
初心者からエキスパートへ:ローソク足のプログラミング
 MQL5で取引管理者パネルを作成する(第10回):外部リソースベースのインターフェイス
MQL5で取引管理者パネルを作成する(第10回):外部リソースベースのインターフェイス
 既存のMQL5取引戦略へのAIモデルの統合
既存のMQL5取引戦略へのAIモデルの統合
- 無料取引アプリ
- 8千を超えるシグナルをコピー
- 金融ニュースで金融マーケットを探索