Automatização de estratégias de trading com MQL5 (Parte 13): Criação de um algoritmo de negociação para o padrão "Cabeça e Ombros"
Introdução
No artigo anterior (Parte 12), implementamos a estratégia de mitigação de blocos de ordem (Mitigation Order Blocks, MOB) na linguagem MetaQuotes Language 5 (MQL5), para aproveitar zonas institucionais de preço na negociação. Agora, na Parte 13, focaremos na construção de um algoritmo de negociação "Cabeça e Ombros", automatizando esse padrão clássico de reversão para identificar pontos de virada de mercado com precisão. O artigo abordará os seguintes tópicos:
- Estudo da arquitetura do padrão Cabeça e Ombros
- Implementação em MQL5
- Testes em histórico
- Considerações finais
Ao final deste artigo, você terá um EA totalmente funcional, pronto para operar com base no padrão "Cabeça e Ombros", então vamos direto ao trabalho!
Estudo da arquitetura do padrão Cabeça e Ombros
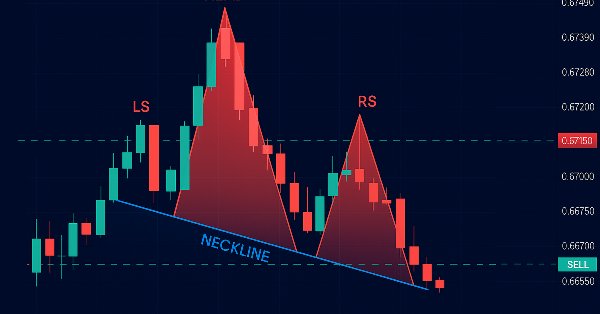
O padrão Cabeça e Ombros é uma formação clássica de gráfico amplamente reconhecida na análise técnica para prever reversões de tendência, ocorrendo tanto em versões padrão (de baixa) quanto invertidas (de alta), cada uma caracterizada por uma sequência distinta de picos ou vales de preço. No padrão clássico (de baixa), em nosso programa, uma tendência de alta é seguida por três picos: o ombro esquerdo atinge um máximo, a cabeça se eleva significativamente mais alto no ponto culminante da tendência (superando visivelmente ambos os ombros), e o ombro direito cai abaixo da cabeça, mas permanece próximo em altura ao ombro esquerdo. Todos são conectados por uma linha de pescoço, que une dois vales; assim que o preço rompe essa linha, abriremos uma operação de venda no rompimento, definindo um stop loss acima do ombro direito e um take profit projetando a altura da cabeça até a linha de pescoço para baixo, como mostrado na figura abaixo.
Para o padrão invertido, uma tendência de baixa leva à formação de três vales: o ombro esquerdo marca um mínimo, a cabeça se aprofunda visivelmente (abaixo de ambos os ombros), e o ombro direito para próximo do nível do ombro esquerdo. A linha de pescoço passa pelos topos; o rompimento do preço acima desse nível acionará uma entrada de compra com stop loss abaixo do ombro direito e take profit projetado para cima pela distância da linha de pescoço até a cabeça. Tudo é construído com base na altura destacada da cabeça e na quase simetria dos ombros, que são nossas diretrizes principais. Abaixo está a ilustração correspondente.
Quanto ao gerenciamento de risco, implementaremos uma função adicional de trailing stop para maximizar a captura de lucro. Vamos lá!
Implementação em MQL5
Para criar o programa em MQL5, abra o MetaEditor, vá até o Navegador, localize a pasta "Indicators", clique na aba "Criar" (New) e siga as instruções para gerar o arquivo. Assim que isso for feito, dentro do ambiente de programação precisaremos declarar algumas variáveis globais, que serão utilizadas em toda a aplicação.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Head & Shoulders Pattern EA.mq5 | //| Copyright 2025, Allan Munene Mutiiria. | //| https://t.me/Forex_Algo_Trader | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2025, Allan Munene Mutiiria." #property link "https://youtube.com/@ForexAlgo-Trader?" #property version "1.00" #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> //--- Include the Trade.mqh library for trading functions CTrade obj_Trade; //--- Trade object for executing and managing trades // Input Parameters input int LookbackBars = 50; // Number of historical bars to analyze for pattern detection input double ThresholdPoints = 70.0; // Minimum price movement in points to identify a reversal input double ShoulderTolerancePoints = 15.0; // Maximum allowable price difference between left and right shoulders input double TroughTolerancePoints = 30.0; // Maximum allowable price difference between neckline troughs or peaks input double BufferPoints = 10.0; // Additional points added to stop-loss for safety buffer input double LotSize = 0.1; // Volume of each trade in lots input ulong MagicNumber = 123456; // Unique identifier for trades opened by this EA input int MaxBarRange = 30; // Maximum number of bars allowed between key pattern points input int MinBarRange = 5; // Minimum number of bars required between key pattern points input double BarRangeMultiplier = 2.0; // Maximum multiple of the smallest bar range for pattern uniformity input int ValidationBars = 3; // Number of bars after right shoulder to validate breakout input double PriceTolerance = 5.0; // Price tolerance in points for matching traded patterns input double RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier = 1.5; // Maximum multiple of pattern range for right shoulder to breakout distance input int MaxTradedPatterns = 20; // Maximum number of patterns stored in traded history input bool UseTrailingStop = false; // Toggle to enable or disable trailing stop functionality input int MinTrailPoints = 50; // Minimum profit in points before trailing stop activates input int TrailingPoints = 30; // Distance in points to maintain behind current price when trailing
Começamos com #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> e o objeto CTrade obj_Trade, que servem para incluir os arquivos de negociação adicionais responsáveis pelo gerenciamento das operações. Definimos parâmetros de entrada como 'LookbackBars' (por padrão 50) para análise histórica, 'ThresholdPoints' (por padrão 70.0) para confirmação de reversão e 'ShoulderTolerancePoints' (por padrão 15.0), além de 'TroughTolerancePoints' (por padrão 30.0) para manter a simetria. Os demais parâmetros de entrada não necessitam de explicação adicional. Comentários detalhados foram adicionados no código para facilitar a compreensão. Em seguida, é necessário definir algumas estruturas que utilizaremos tanto na detecção dos padrões quanto no controle das operações em andamento.
// Structure to store peaks and troughs struct Extremum { int bar; //--- Bar index where extremum occurs datetime time; //--- Timestamp of the bar double price; //--- Price at extremum (high for peak, low for trough) bool isPeak; //--- True if peak (high), false if trough (low) }; // Structure to store traded patterns struct TradedPattern { datetime leftShoulderTime; //--- Timestamp of the left shoulder double leftShoulderPrice; //--- Price of the left shoulder };
Criamos duas estruturas principais usando a palavra-chave struct para gerenciar nosso algoritmo de negociação "Cabeça e Ombros": a primeira, chamada 'Extremum', armazena picos e vales através dos campos bar (índice), time (carimbo de tempo), price (valor) e isPeak (true para picos, false para vales), permitindo identificar com precisão os componentes do padrão; a segunda, 'TradedPattern', é responsável por monitorar as negociações executadas, utilizando 'leftShoulderTime' e 'leftShoulderPrice' para evitar duplicidade de operações. Para garantir que o EA opere apenas uma vez por barra e mantenha o controle das operações atuais, declaramos uma variável e um array da seguinte forma.
// Global Variables static datetime lastBarTime = 0; //--- Tracks the timestamp of the last processed bar to avoid reprocessing TradedPattern tradedPatterns[]; //--- Array to store details of previously traded patterns
Após essas etapas, todas as configurações básicas estão concluídas. No entanto, como precisaremos exibir o padrão diretamente no gráfico, é necessário criar a arquitetura gráfica e os componentes de barra, de modo a assegurar que o padrão desenhado atenda aos critérios exigidos.
int chart_width = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_WIDTH_IN_PIXELS); //--- Width of the chart in pixels for visualization int chart_height = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_HEIGHT_IN_PIXELS); //--- Height of the chart in pixels for visualization int chart_scale = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_SCALE); //--- Zoom level of the chart (0-5) int chart_first_vis_bar = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_FIRST_VISIBLE_BAR); //--- Index of the first visible bar on the chart int chart_vis_bars = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_VISIBLE_BARS); //--- Number of visible bars on the chart double chart_prcmin = ChartGetDouble(0, CHART_PRICE_MIN, 0); //--- Minimum price visible on the chart double chart_prcmax = ChartGetDouble(0, CHART_PRICE_MAX, 0); //--- Maximum price visible on the chart //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Converts the chart scale property to bar width/spacing | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int BarWidth(int scale) { return (int)pow(2, scale); } //--- Calculates bar width in pixels based on chart scale (zoom level) //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Converts the bar index (as series) to x in pixels | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int ShiftToX(int shift) { return (chart_first_vis_bar - shift) * BarWidth(chart_scale) - 1; } //--- Converts bar index to x-coordinate in pixels on the chart //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Converts the price to y in pixels | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int PriceToY(double price) { //--- Function to convert price to y-coordinate in pixels if (chart_prcmax - chart_prcmin == 0.0) return 0; //--- Return 0 if price range is zero to avoid division by zero return (int)round(chart_height * (chart_prcmax - price) / (chart_prcmax - chart_prcmin) - 1); //--- Calculate y-pixel position based on price and chart dimensions }
Preparamos e equipamos o programa com recursos de visualização, definindo variáveis como 'chart_width' e 'chart_height', usando a função ChartGetInteger para obter as dimensões do gráfico; 'chart_scale' para o nível de zoom; 'chart_first_vis_bar' e 'chart_vis_bars' para informações sobre as barras visíveis; além de 'chart_prcmin' e 'chart_prcmax', obtidas com ChartGetDouble, para determinar o intervalo de preços. Utilizamos a função 'BarWidth', com o parâmetro pow, para calcular a distância entre as barras com base em 'chart_scale', a função 'ShiftToX' para converter índices de barras em coordenadas x a partir de 'chart_first_vis_bar' e 'chart_scale', e a função 'PriceToY', com o parâmetro round, para mapear preços em coordenadas y, considerando 'chart_height', 'chart_prcmax' e 'chart_prcmin'. Esse conjunto de cálculos garante uma representação visual precisa do padrão. Com isso, as configurações estão concluídas. Podemos prosseguir para a inicialização do programa no manipulador de eventos OnInit.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- Expert Advisor initialization function obj_Trade.SetExpertMagicNumber(MagicNumber); //--- Set the magic number for trades opened by this EA ArrayResize(tradedPatterns, 0); //--- Initialize tradedPatterns array with zero size return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); //--- Return success code to indicate successful initialization }
Em OnInit, utilizamos o método 'SetExpertMagicNumber' do objeto 'obj_Trade' para atribuir um 'MagicNumber', que atua como identificador único de todas as operações, garantindo que as posições do nosso programa sejam distintas, e chamamos a função ArrayResize para ajustar o tamanho do array 'tradedPatterns' para zero, limpando qualquer dado anterior e preparando-o para uma nova execução. Concluímos o processo retornando INIT_SUCCEEDED, confirmando a configuração bem-sucedida e deixando o EA pronto para detectar e negociar o padrão de forma eficiente. Agora podemos seguir para o manipulador de eventos OnTick, garantindo que a análise seja executada uma vez por barra.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { //--- Main tick function executed on each price update datetime currentBarTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, 0); //--- Get the timestamp of the current bar if (currentBarTime == lastBarTime) return; //--- Exit if the current bar has already been processed lastBarTime = currentBarTime; //--- Update the last processed bar time // Update chart properties chart_width = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_WIDTH_IN_PIXELS); //--- Update chart width in pixels chart_height = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_HEIGHT_IN_PIXELS); //--- Update chart height in pixels chart_scale = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_SCALE); //--- Update chart zoom level chart_first_vis_bar = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_FIRST_VISIBLE_BAR); //--- Update index of the first visible bar chart_vis_bars = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_VISIBLE_BARS); //--- Update number of visible bars chart_prcmin = ChartGetDouble(0, CHART_PRICE_MIN, 0); //--- Update minimum visible price on chart chart_prcmax = ChartGetDouble(0, CHART_PRICE_MAX, 0); //--- Update maximum visible price on chart // Skip pattern detection if a position is already open if (PositionsTotal() > 0) return; //--- Exit function if there are open positions to avoid multiple trades }
No manipulador de eventos OnTick, que é acionado a cada atualização de preço para monitorar as mudanças do mercado e reagir em tempo real, usamos a função iTime para obter o 'currentBarTime' da última barra e o comparamos com 'lastBarTime' para evitar processamento repetido, atualizando 'lastBarTime' apenas quando novas barras são formadas. Em seguida, atualizamos os elementos visuais do gráfico chamando novamente ChartGetInteger para atualizar 'chart_width', 'chart_height', 'chart_scale', 'chart_first_vis_bar' e 'chart_vis_bars', além de ChartGetDouble para 'chart_prcmin' e 'chart_prcmax'. Também utilizamos a função PositionsTotal para verificar se há operações abertas e encerrá-las antecipadamente, caso existam, a fim de evitar sobreposição de posições. Depois disso, podemos definir a função responsável por identificar os pontos de extremidade ou pontos-chave do padrão.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Find extrema in the last N bars | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void FindExtrema(Extremum &extrema[], int lookback) { //--- Function to identify peaks and troughs in price history ArrayFree(extrema); //--- Clear the extrema array to start fresh int bars = Bars(_Symbol, _Period); //--- Get total number of bars available if (lookback >= bars) lookback = bars - 1; //--- Adjust lookback if it exceeds available bars double highs[], lows[]; //--- Arrays to store high and low prices ArraySetAsSeries(highs, true); //--- Set highs array as time series (newest first) ArraySetAsSeries(lows, true); //--- Set lows array as time series (newest first) CopyHigh(_Symbol, _Period, 0, lookback + 1, highs); //--- Copy high prices for lookback period CopyLow(_Symbol, _Period, 0, lookback + 1, lows); //--- Copy low prices for lookback period bool isUpTrend = highs[lookback] < highs[lookback - 1]; //--- Determine initial trend based on first two bars double lastHigh = highs[lookback]; //--- Initialize last high price double lastLow = lows[lookback]; //--- Initialize last low price int lastExtremumBar = lookback; //--- Initialize last extremum bar index for (int i = lookback - 1; i >= 0; i--) { //--- Loop through bars from oldest to newest if (isUpTrend) { //--- If currently in an uptrend if (highs[i] > lastHigh) { //--- Check if current high exceeds last high lastHigh = highs[i]; //--- Update last high price lastExtremumBar = i; //--- Update last extremum bar index } else if (lows[i] < lastHigh - ThresholdPoints * _Point) { //--- Check if current low indicates a reversal (trough) int size = ArraySize(extrema); //--- Get current size of extrema array ArrayResize(extrema, size + 1); //--- Resize array to add new extremum extrema[size].bar = lastExtremumBar; //--- Store bar index of the peak extrema[size].time = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, lastExtremumBar); //--- Store timestamp of the peak extrema[size].price = lastHigh; //--- Store price of the peak extrema[size].isPeak = true; //--- Mark as a peak //Print("Extrema added: Bar ", lastExtremumBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(extrema[size].time), ", Price ", DoubleToString(lastHigh, _Digits), ", IsPeak true"); //--- Log new peak isUpTrend = false; //--- Switch trend to downtrend lastLow = lows[i]; //--- Update last low price lastExtremumBar = i; //--- Update last extremum bar index } } else { //--- If currently in a downtrend if (lows[i] < lastLow) { //--- Check if current low is below last low lastLow = lows[i]; //--- Update last low price lastExtremumBar = i; //--- Update last extremum bar index } else if (highs[i] > lastLow + ThresholdPoints * _Point) { //--- Check if current high indicates a reversal (peak) int size = ArraySize(extrema); //--- Get current size of extrema array ArrayResize(extrema, size + 1); //--- Resize array to add new extremum extrema[size].bar = lastExtremumBar; //--- Store bar index of the trough extrema[size].time = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, lastExtremumBar); //--- Store timestamp of the trough extrema[size].price = lastLow; //--- Store price of the trough extrema[size].isPeak = false; //--- Mark as a trough //Print("Extrema added: Bar ", lastExtremumBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(extrema[size].time), ", Price ", DoubleToString(lastLow, _Digits), ", IsPeak false"); //--- Log new trough isUpTrend = true; //--- Switch trend to uptrend lastHigh = highs[i]; //--- Update last high price lastExtremumBar = i; //--- Update last extremum bar index } } } }
Aqui definimos precisamente os picos e vales que compõem o nosso padrão "Cabeça e Ombros", implementando a função 'FindExtrema', que analisa as últimas 'lookback' barras para construir o array 'extrema' com os pontos críticos de preço. Iniciamos limpando o array 'extrema' com a função ArrayFree para garantir um “estado limpo”, em seguida usamos a função 'Bars' para obter o número total de barras disponíveis e ajustamos o valor de 'lookback' caso ele exceda esse limite, assegurando que permanecemos dentro do intervalo de dados visível do gráfico. Depois, preparamos os arrays 'highs' e 'lows' para armazenar os dados de preços máximos e mínimos, configurando-os como séries temporais com a função ArraySetAsSeries (onde os valores mais recentes vêm primeiro), e preenchemos ambos usando CopyHigh e CopyLow, para extrair os valores máximos e mínimos de preço das últimas 'lookback + 1' barras.
No laço, que percorre das barras mais antigas até as mais recentes, determinamos a direção da tendência utilizando a variável 'isUpTrend', com base no movimento inicial do preço, em seguida acompanhamos 'lastHigh' ou 'lastLow' e seus respectivos 'lastExtremumBar'. Quando ocorre uma reversão que excede o valor definido em ThresholdPoints, expandimos o array 'extrema' com a função ArrayResize, armazenando elementos como bar, time (obtido via iTime), price e isPeak (true para picos e false para vales), além de incluir a direção da tendência, o que permite identificar o padrão com precisão. Agora podemos capturar os níveis de preço relevantes e armazená-los para uso posterior.
Extremum extrema[]; //--- Array to store identified peaks and troughs FindExtrema(extrema, LookbackBars); //--- Find extrema in the last LookbackBars bars
Aqui declaramos o array 'extrema' do tipo Extremum, destinado a armazenar os picos e vales identificados, que representarão os ombros e a cabeça do padrão. Em seguida, chamamos a função FindExtrema, passando 'extrema' e 'LookbackBars' como argumentos, para analisar as últimas barras definidas por 'LookbackBars' e preencher o array com os pontos críticos, estabelecendo a base para o reconhecimento de padrões e para as decisões de negociação subsequentes. Quando exibimos os valores do array usando a função ArrayPrint, obtemos uma estrutura semelhante à mostrada abaixo.
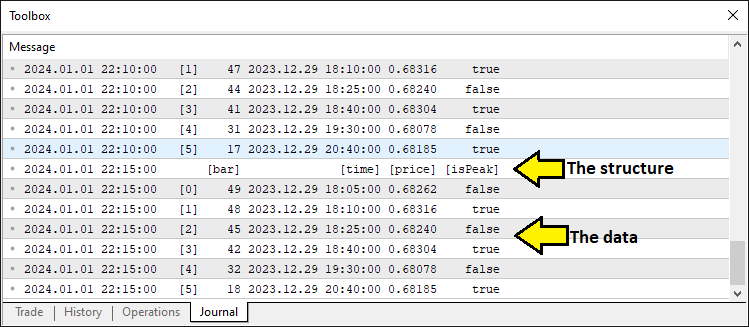
Isso confirma que já possuímos os pontos de dados necessários. Assim, podemos avançar para a definição dos componentes do padrão. Para tornar o código mais modular, fazemos isso mediante funções.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Detect standard Head and Shoulders pattern | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool DetectHeadAndShoulders(Extremum &extrema[], int &leftShoulderIdx, int &headIdx, int &rightShoulderIdx, int &necklineStartIdx, int &necklineEndIdx) { //--- Function to detect standard H&S pattern int size = ArraySize(extrema); //--- Get the size of the extrema array if (size < 6) return false; //--- Return false if insufficient extrema for pattern (need at least 6 points) for (int i = size - 6; i >= 0; i--) { //--- Loop through extrema to find H&S pattern (start at size-6 to ensure enough points) if (!extrema[i].isPeak && extrema[i+1].isPeak && !extrema[i+2].isPeak && //--- Check sequence: trough, peak (LS), trough extrema[i+3].isPeak && !extrema[i+4].isPeak && extrema[i+5].isPeak) { //--- Check sequence: peak (head), trough, peak (RS) double leftShoulder = extrema[i+1].price; //--- Get price of left shoulder double head = extrema[i+3].price; //--- Get price of head double rightShoulder = extrema[i+5].price; //--- Get price of right shoulder double trough1 = extrema[i+2].price; //--- Get price of first trough (neckline start) double trough2 = extrema[i+4].price; //--- Get price of second trough (neckline end) bool isHeadHighest = true; //--- Flag to verify head is the highest peak in range for (int j = MathMax(0, i - 5); j < MathMin(size, i + 10); j++) { //--- Check surrounding bars (5 before, 10 after) for higher peaks if (extrema[j].isPeak && extrema[j].price > head && j != i + 3) { //--- If another peak is higher than head isHeadHighest = false; //--- Set flag to false break; //--- Exit loop as head is not highest } } int lsBar = extrema[i+1].bar; //--- Get bar index of left shoulder int headBar = extrema[i+3].bar; //--- Get bar index of head int rsBar = extrema[i+5].bar; //--- Get bar index of right shoulder int lsToHead = lsBar - headBar; //--- Calculate bars from left shoulder to head int headToRs = headBar - rsBar; //--- Calculate bars from head to right shoulder if (lsToHead < MinBarRange || lsToHead > MaxBarRange || headToRs < MinBarRange || headToRs > MaxBarRange) continue; //--- Skip if bar ranges are out of bounds int minRange = MathMin(lsToHead, headToRs); //--- Get the smaller of the two ranges for uniformity check if (lsToHead > minRange * BarRangeMultiplier || headToRs > minRange * BarRangeMultiplier) continue; //--- Skip if ranges exceed uniformity multiplier bool rsValid = false; //--- Flag to validate right shoulder breakout int rsBarIndex = extrema[i+5].bar; //--- Get bar index of right shoulder for validation for (int j = rsBarIndex - 1; j >= MathMax(0, rsBarIndex - ValidationBars); j--) { //--- Check bars after right shoulder for breakout if (iLow(_Symbol, _Period, j) < rightShoulder - ThresholdPoints * _Point) { //--- Check if price drops below RS by threshold rsValid = true; //--- Set flag to true if breakout confirmed break; //--- Exit loop once breakout is validated } } if (!rsValid) continue; //--- Skip if right shoulder breakout not validated if (isHeadHighest && head > leftShoulder && head > rightShoulder && //--- Verify head is highest and above shoulders MathAbs(leftShoulder - rightShoulder) < ShoulderTolerancePoints * _Point && //--- Check shoulder price difference within tolerance MathAbs(trough1 - trough2) < TroughTolerancePoints * _Point) { //--- Check trough price difference within tolerance leftShoulderIdx = i + 1; //--- Set index for left shoulder headIdx = i + 3; //--- Set index for head rightShoulderIdx = i + 5; //--- Set index for right shoulder necklineStartIdx = i + 2; //--- Set index for neckline start (first trough) necklineEndIdx = i + 4; //--- Set index for neckline end (second trough) Print("Bar Ranges: LS to Head = ", lsToHead, ", Head to RS = ", headToRs); //--- Log bar ranges for debugging return true; //--- Return true to indicate pattern found } } } return false; //--- Return false if no pattern detected }
Aqui definimos o padrão clássico utilizando a função 'DetectHeadAndShoulders', que examina o array 'extrema' em busca de uma sequência válida composta por seis pontos: vale, pico (ombro esquerdo), vale, pico (cabeça), vale e pico (ombro direito). São exigidas, no mínimo, seis entradas, verificadas pela função ArraySize. Iteramos sobre 'extrema', começando de tamanho - 6, analisando a estrutura do padrão com picos e vales alternados. Em seguida, extraímos os preços correspondentes aos vales (leftShoulder, head, rightShoulder) e à linha de pescoço (trough1, trough2). Um laço interno assegura que a cabeça seja o pico mais alto dentro do intervalo considerado, o que é determinado através das funções MathMax e MathMin. As distâncias entre os pontos são avaliadas com base nos parâmetros MinBarRange e MaxBarRange, enquanto a uniformidade é garantida com o uso do parâmetro BarRangeMultiplier.
Confirmamos o rompimento do ombro direito verificando a função iLow em relação ao valor de 'ThresholdPoints', dentro do intervalo definido por 'ValidationBars'. Se a cabeça estiver acima de ambos os ombros e as tolerâncias ('ShoulderTolerancePoints', 'TroughTolerancePoints') forem atendidas, atribuímos os índices correspondentes, como 'leftShoulderIdx', 'headIdx' e 'necklineStartIdx', registramos os intervalos de barras com a função Print para fins de depuração e retornamos o valor true, sinalizando que o padrão foi detectado. Caso contrário, retornamos false. A mesma lógica é aplicada para identificar o padrão inverso.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Detect inverse Head and Shoulders pattern | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool DetectInverseHeadAndShoulders(Extremum &extrema[], int &leftShoulderIdx, int &headIdx, int &rightShoulderIdx, int &necklineStartIdx, int &necklineEndIdx) { //--- Function to detect inverse H&S pattern int size = ArraySize(extrema); //--- Get the size of the extrema array if (size < 6) return false; //--- Return false if insufficient extrema for pattern (need at least 6 points) for (int i = size - 6; i >= 0; i--) { //--- Loop through extrema to find inverse H&S pattern if (extrema[i].isPeak && !extrema[i+1].isPeak && extrema[i+2].isPeak && //--- Check sequence: peak, trough (LS), peak !extrema[i+3].isPeak && extrema[i+4].isPeak && !extrema[i+5].isPeak) { //--- Check sequence: trough (head), peak, trough (RS) double leftShoulder = extrema[i+1].price; //--- Get price of left shoulder double head = extrema[i+3].price; //--- Get price of head double rightShoulder = extrema[i+5].price; //--- Get price of right shoulder double peak1 = extrema[i+2].price; //--- Get price of first peak (neckline start) double peak2 = extrema[i+4].price; //--- Get price of second peak (neckline end) bool isHeadLowest = true; //--- Flag to verify head is the lowest trough in range int headBar = extrema[i+3].bar; //--- Get bar index of head for range check for (int j = MathMax(0, headBar - 5); j <= MathMin(Bars(_Symbol, _Period) - 1, headBar + 5); j++) { //--- Check 5 bars before and after head if (iLow(_Symbol, _Period, j) < head) { //--- If any low is below head isHeadLowest = false; //--- Set flag to false break; //--- Exit loop as head is not lowest } } int lsBar = extrema[i+1].bar; //--- Get bar index of left shoulder int rsBar = extrema[i+5].bar; //--- Get bar index of right shoulder int lsToHead = lsBar - headBar; //--- Calculate bars from left shoulder to head int headToRs = headBar - rsBar; //--- Calculate bars from head to right shoulder if (lsToHead < MinBarRange || lsToHead > MaxBarRange || headToRs < MinBarRange || headToRs > MaxBarRange) continue; //--- Skip if bar ranges are out of bounds int minRange = MathMin(lsToHead, headToRs); //--- Get the smaller of the two ranges for uniformity check if (lsToHead > minRange * BarRangeMultiplier || headToRs > minRange * BarRangeMultiplier) continue; //--- Skip if ranges exceed uniformity multiplier bool rsValid = false; //--- Flag to validate right shoulder breakout int rsBarIndex = extrema[i+5].bar; //--- Get bar index of right shoulder for validation for (int j = rsBarIndex - 1; j >= MathMax(0, rsBarIndex - ValidationBars); j--) { //--- Check bars after right shoulder for breakout if (iHigh(_Symbol, _Period, j) > rightShoulder + ThresholdPoints * _Point) { //--- Check if price rises above RS by threshold rsValid = true; //--- Set flag to true if breakout confirmed break; //--- Exit loop once breakout is validated } } if (!rsValid) continue; //--- Skip if right shoulder breakout not validated if (isHeadLowest && head < leftShoulder && head < rightShoulder && //--- Verify head is lowest and below shoulders MathAbs(leftShoulder - rightShoulder) < ShoulderTolerancePoints * _Point && //--- Check shoulder price difference within tolerance MathAbs(peak1 - peak2) < TroughTolerancePoints * _Point) { //--- Check peak price difference within tolerance leftShoulderIdx = i + 1; //--- Set index for left shoulder headIdx = i + 3; //--- Set index for head rightShoulderIdx = i + 5; //--- Set index for right shoulder necklineStartIdx = i + 2; //--- Set index for neckline start (first peak) necklineEndIdx = i + 4; //--- Set index for neckline end (second peak) Print("Bar Ranges: LS to Head = ", lsToHead, ", Head to RS = ", headToRs); //--- Log bar ranges for debugging return true; //--- Return true to indicate pattern found } } } return false; //--- Return false if no pattern detected }
Definimos a função 'DetectInverseHeadAndShoulders' para detectar o padrão invertido. Ela percorre o array extrema em busca de uma sequência de seis pontos — pico, vale (ombro esquerdo), pico, vale (cabeça), pico e vale (ombro direito) — exigindo no mínimo seis registros, validados pela função ArraySize. O laço é executado de 'size - 6' em diante, confirmando a alternância pico-vale. Em seguida, extraímos os preços correspondentes a 'leftShoulder', 'head', 'rightShoulder' e aos picos da linha de pescoço ('peak1', 'peak2'). O laço interno verifica se a cabeça é o ponto mais baixo dentro de um intervalo de cinco barras ao redor de headBar, utilizando as funções MathMax, MathMin e iLow, enquanto a função 'Bars' garante que permanecemos dentro dos limites do gráfico.
Definimos a distância entre as barras usando 'MinBarRange' e 'MaxBarRange', calculamos a uniformidade com a função 'MathMin' e o parâmetro 'BarRangeMultiplier', e confirmamos o rompimento do ombro direito com a função iHigh, comparando com 'ThresholdPoints' e 'ValidationBars'. Se a cabeça estiver abaixo de ambos os ombros e as tolerâncias ('ShoulderTolerancePoints', 'TroughTolerancePoints') forem respeitadas, definimos os índices como 'leftShoulderIdx' e 'necklineStartIdx', registramos os intervalos e retornamos true; caso contrário, retornamos false. Com essas duas funções implementadas, podemos prosseguir para a identificação efetiva dos padrões, conforme descrito a seguir.
int leftShoulderIdx, headIdx, rightShoulderIdx, necklineStartIdx, necklineEndIdx; //--- Indices for pattern components // Standard Head and Shoulders (Sell) if (DetectHeadAndShoulders(extrema, leftShoulderIdx, headIdx, rightShoulderIdx, necklineStartIdx, necklineEndIdx)) { //--- Check for standard H&S pattern double closePrice = iClose(_Symbol, _Period, 1); //--- Get the closing price of the previous bar double necklinePrice = extrema[necklineEndIdx].price; //--- Get the price of the neckline end point if (closePrice < necklinePrice) { //--- Check if price has broken below the neckline (sell signal) datetime lsTime = extrema[leftShoulderIdx].time; //--- Get the timestamp of the left shoulder double lsPrice = extrema[leftShoulderIdx].price; //--- Get the price of the left shoulder //--- } }
Aqui avançamos declarando as variáveis 'leftShoulderIdx', 'headIdx', 'rightShoulderIdx', 'necklineStartIdx' e 'necklineEndIdx', destinadas a armazenar os índices dos componentes do padrão. Em seguida, utilizamos a função DetectHeadAndShoulders para verificar o array extrema em busca do padrão clássico, passando esses índices como parâmetros de referência. Quando o padrão é detectado, obtemos o 'closePrice' através da função iClose para a barra anterior e o 'necklinePrice' de 'extrema[necklineEndIdx].price', gerando um sinal de venda quando 'closePrice' fica abaixo de 'necklinePrice'. Depois extraímos 'lsTime' e 'lsPrice' de extrema[leftShoulderIdx], preparando a execução da negociação com base na posição do ombro esquerdo. Nesse ponto, é essencial garantir que o padrão ainda não tenha sido negociado. Para isso, definimos uma função de verificação.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Check if pattern has already been traded | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool IsPatternTraded(datetime lsTime, double lsPrice) { //--- Function to check if a pattern has already been traded int size = ArraySize(tradedPatterns); //--- Get the current size of the tradedPatterns array for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { //--- Loop through all stored traded patterns if (tradedPatterns[i].leftShoulderTime == lsTime && //--- Check if left shoulder time matches MathAbs(tradedPatterns[i].leftShoulderPrice - lsPrice) < PriceTolerance * _Point) { //--- Check if left shoulder price is within tolerance Print("Pattern already traded: Left Shoulder Time ", TimeToString(lsTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(lsPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log that pattern was previously traded return true; //--- Return true to indicate pattern has been traded } } return false; //--- Return false if no match found }
Aqui garantimos que o programa evite duplicação de operações implementando a função 'IsPatternTraded', responsável por verificar se o padrão identificado por 'lsTime' e 'lsPrice' já existe no array 'tradedPatterns'. Utilizamos a função ArraySize para obter o tamanho ('size') do array e, em seguida, percorremos seus elementos em um laço, comparando cada registro com os valores de 'leftShoulderTime' e 'leftShoulderPrice', verificando se há correspondência com 'lsTime' e 'lsPrice' dentro do limite definido por 'PriceTolerance', utilizando a função MathAbs. Caso uma correspondência seja encontrada, registramos essa ocorrência no log por meio da função Print, incluindo TimeToString e DoubleToString para facilitar a leitura, e retornamos o valor true; caso contrário, retornamos false, permitindo que uma nova operação seja executada. Em seguida, chamamos essa função de verificação e prosseguimos apenas se não houver correspondência encontrada.
if (IsPatternTraded(lsTime, lsPrice)) return; //--- Exit if this pattern has already been traded datetime breakoutTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, 1); //--- Get the timestamp of the breakout bar (previous bar) int lsBar = extrema[leftShoulderIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the left shoulder int headBar = extrema[headIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the head int rsBar = extrema[rightShoulderIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the right shoulder int necklineStartBar = extrema[necklineStartIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the neckline start int necklineEndBar = extrema[necklineEndIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the neckline end int breakoutBar = 1; //--- Set breakout bar index (previous bar) int lsToHead = lsBar - headBar; //--- Calculate number of bars from left shoulder to head int headToRs = headBar - rsBar; //--- Calculate number of bars from head to right shoulder int rsToBreakout = rsBar - breakoutBar; //--- Calculate number of bars from right shoulder to breakout int lsToNeckStart = lsBar - necklineStartBar; //--- Calculate number of bars from left shoulder to neckline start double avgPatternRange = (lsToHead + headToRs) / 2.0; //--- Calculate average bar range of the pattern for uniformity check if (rsToBreakout > avgPatternRange * RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier) { //--- Check if breakout distance exceeds allowed range Print("Pattern rejected: Right Shoulder to Breakout (", rsToBreakout, ") exceeds ", RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier, "x average range (", avgPatternRange, ")"); //--- Log rejection due to excessive breakout range return; //--- Exit function if pattern is invalid } double necklineStartPrice = extrema[necklineStartIdx].price; //--- Get the price of the neckline start point double necklineEndPrice = extrema[necklineEndIdx].price; //--- Get the price of the neckline end point datetime necklineStartTime = extrema[necklineStartIdx].time; //--- Get the timestamp of the neckline start point datetime necklineEndTime = extrema[necklineEndIdx].time; //--- Get the timestamp of the neckline end point int barDiff = necklineStartBar - necklineEndBar; //--- Calculate bar difference between neckline points for slope double slope = (necklineEndPrice - necklineStartPrice) / barDiff; //--- Calculate the slope of the neckline (price change per bar) double breakoutNecklinePrice = necklineStartPrice + slope * (necklineStartBar - breakoutBar); //--- Calculate neckline price at breakout point // Extend neckline backwards int extendedBar = necklineStartBar; //--- Initialize extended bar index with neckline start datetime extendedNecklineStartTime = necklineStartTime; //--- Initialize extended neckline start time double extendedNecklineStartPrice = necklineStartPrice; //--- Initialize extended neckline start price bool foundCrossing = false; //--- Flag to track if neckline crosses a bar within range for (int i = necklineStartBar + 1; i < Bars(_Symbol, _Period); i++) { //--- Loop through bars to extend neckline backwards double checkPrice = necklineStartPrice - slope * (i - necklineStartBar); //--- Calculate projected neckline price at bar i if (NecklineCrossesBar(checkPrice, i)) { //--- Check if neckline intersects the bar's high-low range int distance = i - necklineStartBar; //--- Calculate distance from neckline start to crossing bar if (distance <= avgPatternRange * RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier) { //--- Check if crossing is within uniformity range extendedBar = i; //--- Update extended bar index extendedNecklineStartTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, i); //--- Update extended neckline start time extendedNecklineStartPrice = checkPrice; //--- Update extended neckline start price foundCrossing = true; //--- Set flag to indicate crossing found Print("Neckline extended to first crossing bar within uniformity: Bar ", extendedBar); //--- Log successful extension break; //--- Exit loop after finding valid crossing } else { //--- If crossing exceeds uniformity range Print("Crossing bar ", i, " exceeds uniformity (", distance, " > ", avgPatternRange * RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier, ")"); //--- Log rejection of crossing break; //--- Exit loop as crossing is too far } } } if (!foundCrossing) { //--- If no valid crossing found within range int barsToExtend = 2 * lsToNeckStart; //--- Set fallback extension distance as twice LS to neckline start extendedBar = necklineStartBar + barsToExtend; //--- Calculate extended bar index if (extendedBar >= Bars(_Symbol, _Period)) extendedBar = Bars(_Symbol, _Period) - 1; //--- Cap extended bar at total bars if exceeded extendedNecklineStartTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, extendedBar); //--- Update extended neckline start time extendedNecklineStartPrice = necklineStartPrice - slope * (extendedBar - necklineStartBar); //--- Update extended neckline start price Print("Neckline extended to fallback (2x LS to Neckline Start): Bar ", extendedBar, " (no crossing within uniformity)"); //--- Log fallback extension } Print("Standard Head and Shoulders Detected:"); //--- Log detection of standard H&S pattern Print("Left Shoulder: Bar ", lsBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(lsTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(lsPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log left shoulder details Print("Head: Bar ", headBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(extrema[headIdx].time), ", Price ", DoubleToString(extrema[headIdx].price, _Digits)); //--- Log head details Print("Right Shoulder: Bar ", rsBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time), ", Price ", DoubleToString(extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, _Digits)); //--- Log right shoulder details Print("Neckline Start: Bar ", necklineStartBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(necklineStartTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(necklineStartPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log neckline start details Print("Neckline End: Bar ", necklineEndBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(necklineEndTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(necklineEndPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log neckline end details Print("Close Price: ", DoubleToString(closePrice, _Digits)); //--- Log closing price at breakout Print("Breakout Time: ", TimeToString(breakoutTime)); //--- Log breakout timestamp Print("Neckline Price at Breakout: ", DoubleToString(breakoutNecklinePrice, _Digits)); //--- Log neckline price at breakout Print("Extended Neckline Start: Bar ", extendedBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(extendedNecklineStartTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(extendedNecklineStartPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log extended neckline start details Print("Bar Ranges: LS to Head = ", lsToHead, ", Head to RS = ", headToRs, ", RS to Breakout = ", rsToBreakout, ", LS to Neckline Start = ", lsToNeckStart); //--- Log bar ranges for pattern analysis
Aqui aprimoramos o reconhecimento de padrões verificando o padrão detectado e configurando a negociação de venda. Iniciamos com a função 'IsPatternTraded', que verifica se os valores 'lsTime' e 'lsPrice' correspondem a uma operação anterior no array 'tradedPatterns'; se o retorno for true, encerramos a execução para evitar duplicidade. Em seguida, usamos a função iTime para atribuir a variável breakoutTime como a marca de tempo da barra anterior e obtemos os índices das barras — 'lsBar', 'headBar', 'rsBar', 'necklineStartBar' e 'necklineEndBar' — a partir de 'extrema', calculando intervalos como 'lsToHead', 'headToRs' e 'rsToBreakout'. Caso 'rsToBreakout' ultrapasse o valor de 'avgPatternRange' multiplicado por RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier, o padrão é descartado e registrado com a função Print.
Depois disso, definimos a inclinação (slope) da linha de pescoço com base nos valores 'necklineStartPrice' e 'necklineEndPrice' em relação a 'barDiff', calculamos o 'breakoutNecklinePrice' e estendemos a linha de pescoço para trás por meio de um laço, utilizando a função NecklineCrossesBar para identificar o ponto de interseção dentro do intervalo 'avgPatternRange * RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier'. Durante esse processo, atualizamos 'extendedBar', 'extendedNecklineStartTime' (obtido via iTime) e 'extendedNecklineStartPrice'. Caso a interseção não seja válida, retornamos a '2 * lsToNeckStart', limitando o processo ao número total de 'Bars', e registramos todos os detalhes — índices de barras, preços e intervalos — com as funções Print, TimeToString e DoubleToString, garantindo documentação completa e rastreável do processo. O trecho de código da função personalizada apresenta a seguinte estrutura.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Check if neckline crosses a bar's high-low range | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool NecklineCrossesBar(double necklinePrice, int barIndex) { //--- Function to check if neckline price intersects a bar's range double high = iHigh(_Symbol, _Period, barIndex); //--- Get the high price of the specified bar double low = iLow(_Symbol, _Period, barIndex); //--- Get the low price of the specified bar return (necklinePrice >= low && necklinePrice <= high); //--- Return true if neckline price is within bar's high-low range }
A função verifica se o valor de 'necklinePrice' cruza o intervalo de preços da barra em 'barIndex', garantindo a extensão precisa da linha de pescoço. Utilizamos a função iHigh para obter o preço máximo (high) da barra e a função iLow para obter o preço mínimo (low). Em seguida, retornamos true se 'necklinePrice' estiver entre os valores de 'low' e 'high', confirmando que a linha de pescoço cruza o intervalo da barra e validando o padrão. Caso o padrão seja confirmado, passamos à sua visualização no gráfico. Para isso, são necessárias funções que permitam desenhá-lo e marcá-lo.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Draw a trend line for visualization | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void DrawTrendLine(string name, datetime timeStart, double priceStart, datetime timeEnd, double priceEnd, color lineColor, int width, int style) { //--- Function to draw a trend line on the chart if (ObjectCreate(0, name, OBJ_TREND, 0, timeStart, priceStart, timeEnd, priceEnd)) { //--- Create a trend line object if possible ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_COLOR, lineColor); //--- Set the color of the trend line ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_STYLE, style); //--- Set the style (e.g., solid, dashed) of the trend line ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_WIDTH, width); //--- Set the width of the trend line ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_BACK, true); //--- Set the line to draw behind chart elements ChartRedraw(); //--- Redraw the chart to display the new line } else { //--- If line creation fails Print("Failed to create line: ", name, ". Error: ", GetLastError()); //--- Log the error with the object name and error code } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Draw a filled triangle for visualization | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void DrawTriangle(string name, datetime time1, double price1, datetime time2, double price2, datetime time3, double price3, color fillColor) { //--- Function to draw a filled triangle on the chart if (ObjectCreate(0, name, OBJ_TRIANGLE, 0, time1, price1, time2, price2, time3, price3)) { //--- Create a triangle object if possible ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_COLOR, fillColor); //--- Set the fill color of the triangle ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_STYLE, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Set the border style to solid ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_WIDTH, 1); //--- Set the border width to 1 pixel ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_FILL, true); //--- Enable filling of the triangle ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_BACK, true); //--- Set the triangle to draw behind chart elements ChartRedraw(); //--- Redraw the chart to display the new triangle } else { //--- If triangle creation fails Print("Failed to create triangle: ", name, ". Error: ", GetLastError()); //--- Log the error with the object name and error code } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Draw text label for visualization | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void DrawText(string name, datetime time, double price, string text, color textColor, bool above, double angle = 0) { //--- Function to draw a text label on the chart int chartscale = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_SCALE); //--- Get the current chart zoom level int dynamicFontSize = 5 + int(chartscale * 1.5); //--- Calculate font size based on zoom level for visibility double priceOffset = (above ? 10 : -10) * _Point; //--- Set price offset above or below the point for readability if (ObjectCreate(0, name, OBJ_TEXT, 0, time, price + priceOffset)) { //--- Create a text object if possible ObjectSetString(0, name, OBJPROP_TEXT, text); //--- Set the text content of the label ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_COLOR, textColor); //--- Set the color of the text ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_FONTSIZE, dynamicFontSize); //--- Set the font size based on chart scale ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_ANCHOR, ANCHOR_CENTER); //--- Center the text at the specified point ObjectSetDouble(0, name, OBJPROP_ANGLE, angle); //--- Set the rotation angle of the text in degrees ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_BACK, false); //--- Set the text to draw in front of chart elements ChartRedraw(); //--- Redraw the chart to display the new text Print("Text created: ", name, ", Angle: ", DoubleToString(angle, 2)); //--- Log successful creation of the text with its angle } else { //--- If text creation fails Print("Failed to create text: ", name, ". Error: ", GetLastError()); //--- Log the error with the object name and error code } }
Aqui enriquecemos o programa com recursos visuais para destacar o padrão diretamente no gráfico, começando com a função 'DrawTrendLine', que utiliza ObjectCreate para desenhar uma linha entre 'timeStart' e 'priceStart' até 'timeEnd' e 'priceEnd', configurando propriedades como lineColor, style e width por meio de ObjectSetInteger, renderizando a linha atrás das barras com OBJPROP_BACK e atualizando a exibição com ChartRedraw, registrando erros no log com 'Print' e GetLastError, caso ocorram falhas.
Em seguida, implementamos a função 'DrawTriangle' para sombrear a estrutura do padrão, chamando 'ObjectCreate' com três pontos (time1, price1, etc.), aplicando 'fillColor' e uma borda sólida por meio de ObjectSetInteger, ativando o preenchimento com OBJPROP_FILL, posicionando o triângulo atrás do gráfico e atualizando a visualização com ChartRedraw, registrando erros com 'Print' caso ocorram.
Por fim, adicionamos a função 'DrawText' para marcar os pontos-chave do padrão, utilizando ChartGetInteger para ajustar dinamicamente o tamanho da fonte ('dynamicFontSize') com base em 'chartscale', posicionando o texto conforme 'time' e 'price' com deslocamento via 'ObjectCreate', configurando-o com 'ObjectSetString' ('text'), 'ObjectSetInteger' ('textColor' e 'FONTSIZE') e 'ObjectSetDouble' ('angle'), desenhando-o em primeiro plano com ChartRedraw e confirmando a criação com 'Print' e 'DoubleToString' ou relatando erros. Agora, podemos chamar essas funções para adicionar os elementos visuais necessários, e o primeiro passo é inserir as linhas conforme descrito a seguir.
string prefix = "HS_" + TimeToString(extrema[headIdx].time, TIME_MINUTES); //--- Create unique prefix for chart objects based on head time // Lines DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_LeftToNeckStart", lsTime, lsPrice, necklineStartTime, necklineStartPrice, clrRed, 3, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from left shoulder to neckline start DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_NeckStartToHead", necklineStartTime, necklineStartPrice, extrema[headIdx].time, extrema[headIdx].price, clrRed, 3, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from neckline start to head DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_HeadToNeckEnd", extrema[headIdx].time, extrema[headIdx].price, necklineEndTime, necklineEndPrice, clrRed, 3, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from head to neckline end DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_NeckEndToRight", necklineEndTime, necklineEndPrice, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, clrRed, 3, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from neckline end to right shoulder DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_Neckline", extendedNecklineStartTime, extendedNecklineStartPrice, breakoutTime, breakoutNecklinePrice, clrBlue, 2, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw neckline from extended start to breakout DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_RightToBreakout", extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, breakoutTime, breakoutNecklinePrice, clrRed, 3, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from right shoulder to breakout DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_ExtendedToLeftShoulder", extendedNecklineStartTime, extendedNecklineStartPrice, lsTime, lsPrice, clrRed, 3, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from extended neckline to left shoulder
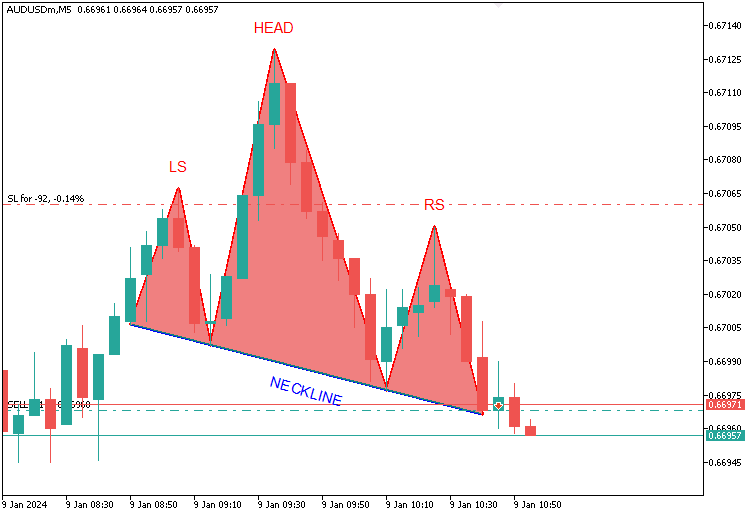
Aqui representamos visualmente o padrão clássico, criando um prefixo exclusivo com base na marca de tempo da cabeça usando TimeToString e desenhando as linhas de tendência com a função 'DrawTrendLine', conectando o ombro esquerdo ao início da linha de pescoço, o início da linha de pescoço à cabeça, a cabeça ao final da linha de pescoço e o final da linha de pescoço ao ombro direito, todas em vermelho e com espessura 3. Ao mesmo tempo, a linha de pescoço, do ponto inicial estendido até o ponto de rompimento, é destacada em azul com espessura 2, e linhas adicionais conectam o ombro direito ao ponto de rompimento e a linha de pescoço estendida de volta ao ombro esquerdo, também em vermelho. Tudo o conjunto é desenhado em um estilo uniforme, de modo a representar o padrão de forma clara no gráfico. Após a compilação, obtemos o seguinte resultado.
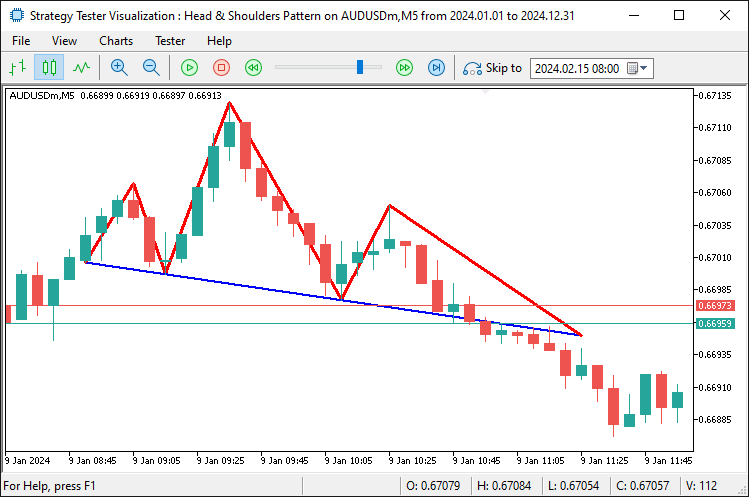
Para adicionar triângulos, utilizamos a função 'DrawTriangle'. Tecnicamente, criamos esses triângulos nas regiões dos ombros e da cabeça.
// Triangles DrawTriangle(prefix + "_LeftShoulderTriangle", lsTime, lsPrice, necklineStartTime, necklineStartPrice, extendedNecklineStartTime, extendedNecklineStartPrice, clrLightCoral); //--- Draw triangle for left shoulder area DrawTriangle(prefix + "_HeadTriangle", extrema[headIdx].time, extrema[headIdx].price, necklineStartTime, necklineStartPrice, necklineEndTime, necklineEndPrice, clrLightCoral); //--- Draw triangle for head area DrawTriangle(prefix + "_RightShoulderTriangle", extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, necklineEndTime, necklineEndPrice, breakoutTime, breakoutNecklinePrice, clrLightCoral); //--- Draw triangle for right shoulder area
Aqui aprimoramos a visualização usando a função 'DrawTriangle' para sombrear as áreas principais com uma coloração coral clara, formando um triângulo na região do ombro esquerdo que conecta o ponto do ombro esquerdo ao início da linha de pescoço e ao início da linha de pescoço estendida. O segundo triângulo representa a cabeça, indo do ponto da cabeça até o início e o fim da linha de pescoço, enquanto o terceiro corresponde ao ombro direito, ligando o ponto do ombro direito ao fim da linha de pescoço e ao ponto de rompimento, realçando toda a estrutura do padrão no gráfico. Após a compilação, obtemos o seguinte resultado.
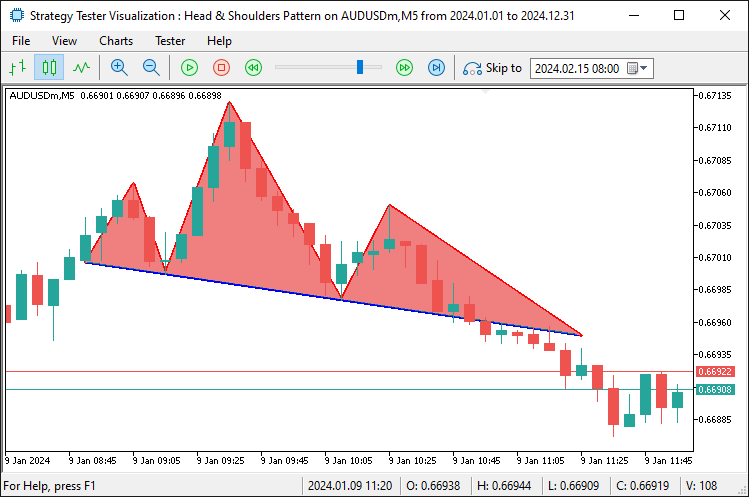
Por fim, precisamos adicionar rótulos ao padrão para torná-lo completamente visual e mais fácil de interpretar.
// Text Labels DrawText(prefix + "_LS_Label", lsTime, lsPrice, "LS", clrRed, true); //--- Draw "LS" label above left shoulder DrawText(prefix + "_Head_Label", extrema[headIdx].time, extrema[headIdx].price, "HEAD", clrRed, true); //--- Draw "HEAD" label above head DrawText(prefix + "_RS_Label", extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, "RS", clrRed, true); //--- Draw "RS" label above right shoulder datetime necklineMidTime = extendedNecklineStartTime + (breakoutTime - extendedNecklineStartTime) / 2; //--- Calculate midpoint time of the neckline double necklineMidPrice = extendedNecklineStartPrice + slope * (iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, extendedNecklineStartTime) - iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, necklineMidTime)); //--- Calculate midpoint price of the neckline // Calculate angle in pixel space int x1 = ShiftToX(iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, extendedNecklineStartTime)); //--- Convert extended neckline start to x-pixel coordinate int y1 = PriceToY(extendedNecklineStartPrice); //--- Convert extended neckline start price to y-pixel coordinate int x2 = ShiftToX(iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, breakoutTime)); //--- Convert breakout time to x-pixel coordinate int y2 = PriceToY(breakoutNecklinePrice); //--- Convert breakout price to y-pixel coordinate double pixelSlope = (y2 - y1) / (double)(x2 - x1); //--- Calculate slope in pixel space (rise over run) double necklineAngle = -atan(pixelSlope) * 180 / M_PI; //--- Calculate neckline angle in degrees, negated for visual alignment Print("Pixel X1: ", x1, ", Y1: ", y1, ", X2: ", x2, ", Y2: ", y2, ", Pixel Slope: ", DoubleToString(pixelSlope, 4), ", Neckline Angle: ", DoubleToString(necklineAngle, 2)); //--- Log pixel coordinates and angle DrawText(prefix + "_Neckline_Label", necklineMidTime, necklineMidPrice, "NECKLINE", clrBlue, false, necklineAngle); //--- Draw "NECKLINE" label at midpoint with calculated angle
Concluímos anotando o padrão com a função 'DrawText', posicionando os rótulos vermelhos “LS”, “HEAD” e “RS” acima dos pontos do ombro esquerdo, da cabeça e do ombro direito, respectivamente, nos momentos e preços correspondentes, tornando o gráfico mais legível. Em seguida, calculamos o ponto médio da linha de pescoço, obtendo 'necklineMidTime' pela média entre 'extendedNecklineStartTime' e 'breakoutTime', e ajustamos 'extendedNecklineStartPrice' com base na inclinação (slope) e na diferença de barras por meio da função iBarShift para determinar 'necklineMidPrice'. Para alinhar o rótulo corretamente, convertemos o tempo em pixels no eixo x com a função 'ShiftToX' e os preços em pixels no eixo y com 'PriceToY', aplicando esses cálculos tanto no início da linha de pescoço quanto no ponto de rompimento, calculamos 'pixelSlope' e obtemos o ângulo da linha de pescoço ('necklineAngle') em graus, utilizando as funções atan e M_PI, registrando os valores para verificação com as funções 'Print' e DoubleToString.
Depois disso, desenhamos o rótulo azul “NECKLINE” (LINHA DE PESCOÇO) no ponto médio usando a função 'DrawText', posicionando-o abaixo da linha e inclinando-o de acordo com o valor de 'necklineAngle', garantindo que a anotação siga o mesmo ângulo da linha de pescoço. O resultado é apresentado abaixo.
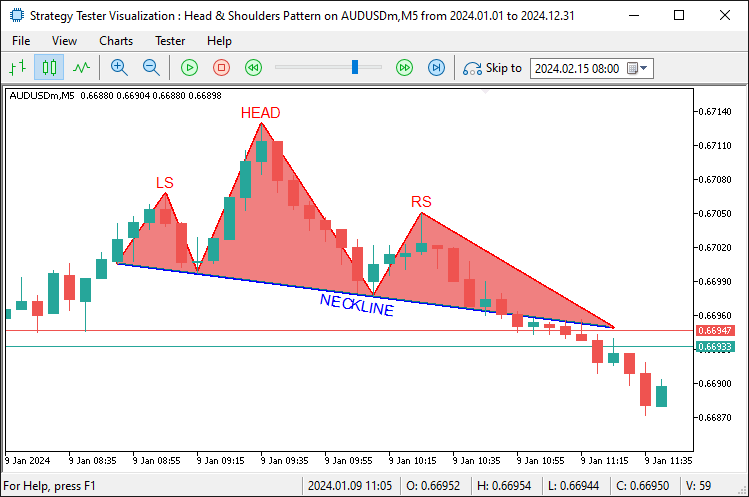
Na imagem, é possível observar o padrão completamente visualizado. Agora precisamos detectar o seu rompimento, especificamente o ponto em que a linha estendida é cruzada, para abrir uma posição de venda e ajustar o intervalo da extensão até a barra de rompimento. É um processo simples. Para isso aplicamos a seguinte lógica.
double entryPrice = 0; //--- Set entry price to 0 for market order (uses current price) double sl = extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price + BufferPoints * _Point; //--- Calculate stop-loss above right shoulder with buffer double patternHeight = extrema[headIdx].price - necklinePrice; //--- Calculate pattern height from head to neckline double tp = closePrice - patternHeight; //--- Calculate take-profit below close by pattern height if (sl > closePrice && tp < closePrice) { //--- Validate trade direction (SL above, TP below for sell) if (obj_Trade.Sell(LotSize, _Symbol, entryPrice, sl, tp, "Head and Shoulders")) { //--- Attempt to open a sell trade AddTradedPattern(lsTime, lsPrice); //--- Add pattern to traded list Print("Sell Trade Opened: SL ", DoubleToString(sl, _Digits), ", TP ", DoubleToString(tp, _Digits)); //--- Log successful trade opening } }
Assim que o padrão é confirmado, executamos uma operação de venda, definindo o valor de 'entryPrice' do ordem a mercado como 0, calculando o 'sl' (stop loss) acima do preço do ombro direito com o uso de BufferPoints, determinando patternHeight como a diferença entre os preços da cabeça e da linha de pescoço e configurando o 'tp' (take profit) abaixo do closePrice com base nessa altura do padrão.
Em seguida, verificamos a direção da operação, assegurando que o 'sl' esteja acima e o 'tp' esteja abaixo do closePrice, antes de utilizar a função 'Sell' do objeto 'obj_Trade' para abrir a posição, especificando 'LotSize', 'sl', 'tp' e o comentário descritivo. Se a execução for bem-sucedida, chamamos a função 'AddTradedPattern' passando 'lsTime' e 'lsPrice' para registrar o padrão no log e utilizamos a função 'Print' juntamente com 'DoubleToString' para registrar as informações de sl e tp. O trecho de código da função personalizada que marca o padrão como negociado está ilustrado a seguir.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Add pattern to traded list with size management | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void AddTradedPattern(datetime lsTime, double lsPrice) { //--- Function to add a new traded pattern to the list int size = ArraySize(tradedPatterns); //--- Get the current size of the tradedPatterns array if (size >= MaxTradedPatterns) { //--- Check if array size exceeds maximum allowed for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) { //--- Shift all elements left to remove the oldest tradedPatterns[i] = tradedPatterns[i + 1]; //--- Copy next element to current position } ArrayResize(tradedPatterns, size - 1); //--- Reduce array size by 1 size--; //--- Decrement size variable Print("Removed oldest traded pattern to maintain max size of ", MaxTradedPatterns); //--- Log removal of oldest pattern } ArrayResize(tradedPatterns, size + 1); //--- Increase array size to add new pattern tradedPatterns[size].leftShoulderTime = lsTime; //--- Store the left shoulder time of the new pattern tradedPatterns[size].leftShoulderPrice = lsPrice; //--- Store the left shoulder price of the new pattern Print("Added traded pattern: Left Shoulder Time ", TimeToString(lsTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(lsPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log addition of new pattern }
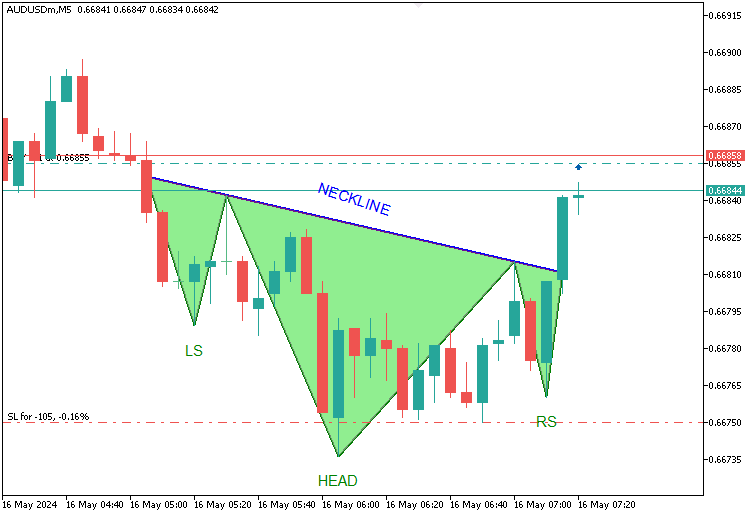
Definimos a função 'AddTradedPattern' para o rastreamento das configurações de negociação. Ela utiliza 'lsTime' e 'lsPrice' para registrar os detalhes do ombro esquerdo, já que esse ponto não é redesenhado. Verificamos o tamanho de 'tradedPatterns' usando a função 'ArraySize'. Caso o tamanho atinja o limite definido por 'MaxTradedPatterns', deslocamos os elementos para a esquerda a fim de remover os mais antigos. Redimensionamos o array 'tradedPatterns' com a função 'ArrayResize', reduzindo-o antes de expandi-lo novamente com outra chamada de ArrayResize para incluir o novo registro. Em seguida, definimos 'leftShoulderTime' como 'lsTime' e 'leftShoulderPrice' como 'lsPrice'. O registro da nova entrada é feito com a função Print, juntamente com TimeToString e DoubleToString. Após a compilação, obtemos o seguinte resultado.
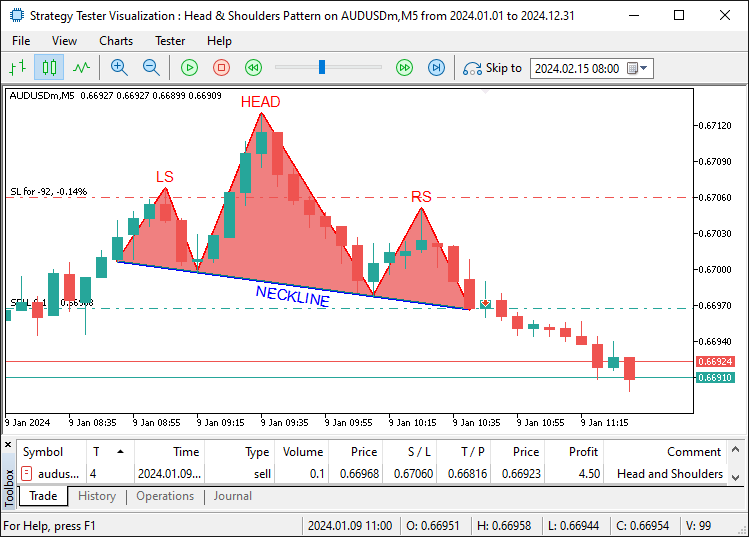
Na imagem, podemos observar que não apenas visualizamos as configurações, mas também as negociamos de forma coerente. O reconhecimento inverso do padrão “Cabeça e Ombros”, sua visualização e execução das negociações seguem a mesma lógica, apenas invertendo as condições. Essa é a estrutura.
// Inverse Head and Shoulders (Buy) if (DetectInverseHeadAndShoulders(extrema, leftShoulderIdx, headIdx, rightShoulderIdx, necklineStartIdx, necklineEndIdx)) { //--- Check for inverse H&S pattern double closePrice = iClose(_Symbol, _Period, 1); //--- Get the closing price of the previous bar double necklinePrice = extrema[necklineEndIdx].price; //--- Get the price of the neckline end point if (closePrice > necklinePrice) { //--- Check if price has broken above the neckline (buy signal) datetime lsTime = extrema[leftShoulderIdx].time; //--- Get the timestamp of the left shoulder double lsPrice = extrema[leftShoulderIdx].price; //--- Get the price of the left shoulder if (IsPatternTraded(lsTime, lsPrice)) return; //--- Exit if this pattern has already been traded datetime breakoutTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, 1); //--- Get the timestamp of the breakout bar (previous bar) int lsBar = extrema[leftShoulderIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the left shoulder int headBar = extrema[headIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the head int rsBar = extrema[rightShoulderIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the right shoulder int necklineStartBar = extrema[necklineStartIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the neckline start int necklineEndBar = extrema[necklineEndIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the neckline end int breakoutBar = 1; //--- Set breakout bar index (previous bar) int lsToHead = lsBar - headBar; //--- Calculate number of bars from left shoulder to head int headToRs = headBar - rsBar; //--- Calculate number of bars from head to right shoulder int rsToBreakout = rsBar - breakoutBar; //--- Calculate number of bars from right shoulder to breakout int lsToNeckStart = lsBar - necklineStartBar; //--- Calculate number of bars from left shoulder to neckline start double avgPatternRange = (lsToHead + headToRs) / 2.0; //--- Calculate average bar range of the pattern for uniformity check if (rsToBreakout > avgPatternRange * RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier) { //--- Check if breakout distance exceeds allowed range Print("Pattern rejected: Right Shoulder to Breakout (", rsToBreakout, ") exceeds ", RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier, "x average range (", avgPatternRange, ")"); //--- Log rejection due to excessive breakout range return; //--- Exit function if pattern is invalid } double necklineStartPrice = extrema[necklineStartIdx].price; //--- Get the price of the neckline start point double necklineEndPrice = extrema[necklineEndIdx].price; //--- Get the price of the neckline end point datetime necklineStartTime = extrema[necklineStartIdx].time; //--- Get the timestamp of the neckline start point datetime necklineEndTime = extrema[necklineEndIdx].time; //--- Get the timestamp of the neckline end point int barDiff = necklineStartBar - necklineEndBar; //--- Calculate bar difference between neckline points for slope double slope = (necklineEndPrice - necklineStartPrice) / barDiff; //--- Calculate the slope of the neckline (price change per bar) double breakoutNecklinePrice = necklineStartPrice + slope * (necklineStartBar - breakoutBar); //--- Calculate neckline price at breakout point // Extend neckline backwards int extendedBar = necklineStartBar; //--- Initialize extended bar index with neckline start datetime extendedNecklineStartTime = necklineStartTime; //--- Initialize extended neckline start time double extendedNecklineStartPrice = necklineStartPrice; //--- Initialize extended neckline start price bool foundCrossing = false; //--- Flag to track if neckline crosses a bar within range for (int i = necklineStartBar + 1; i < Bars(_Symbol, _Period); i++) { //--- Loop through bars to extend neckline backwards double checkPrice = necklineStartPrice - slope * (i - necklineStartBar); //--- Calculate projected neckline price at bar i if (NecklineCrossesBar(checkPrice, i)) { //--- Check if neckline intersects the bar's high-low range int distance = i - necklineStartBar; //--- Calculate distance from neckline start to crossing bar if (distance <= avgPatternRange * RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier) { //--- Check if crossing is within uniformity range extendedBar = i; //--- Update extended bar index extendedNecklineStartTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, i); //--- Update extended neckline start time extendedNecklineStartPrice = checkPrice; //--- Update extended neckline start price foundCrossing = true; //--- Set flag to indicate crossing found Print("Neckline extended to first crossing bar within uniformity: Bar ", extendedBar); //--- Log successful extension break; //--- Exit loop after finding valid crossing } else { //--- If crossing exceeds uniformity range Print("Crossing bar ", i, " exceeds uniformity (", distance, " > ", avgPatternRange * RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier, ")"); //--- Log rejection of crossing break; //--- Exit loop as crossing is too far } } } if (!foundCrossing) { //--- If no valid crossing found within range int barsToExtend = 2 * lsToNeckStart; //--- Set fallback extension distance as twice LS to neckline start extendedBar = necklineStartBar + barsToExtend; //--- Calculate extended bar index if (extendedBar >= Bars(_Symbol, _Period)) extendedBar = Bars(_Symbol, _Period) - 1; //--- Cap extended bar at total bars if exceeded extendedNecklineStartTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, extendedBar); //--- Update extended neckline start time extendedNecklineStartPrice = necklineStartPrice - slope * (extendedBar - necklineStartBar); //--- Update extended neckline start price Print("Neckline extended to fallback (2x LS to Neckline Start): Bar ", extendedBar, " (no crossing within uniformity)"); //--- Log fallback extension } Print("Inverse Head and Shoulders Detected:"); //--- Log detection of inverse H&S pattern Print("Left Shoulder: Bar ", lsBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(lsTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(lsPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log left shoulder details Print("Head: Bar ", headBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(extrema[headIdx].time), ", Price ", DoubleToString(extrema[headIdx].price, _Digits)); //--- Log head details Print("Right Shoulder: Bar ", rsBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time), ", Price ", DoubleToString(extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, _Digits)); //--- Log right shoulder details Print("Neckline Start: Bar ", necklineStartBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(necklineStartTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(necklineStartPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log neckline start details Print("Neckline End: Bar ", necklineEndBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(necklineEndTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(necklineEndPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log neckline end details Print("Close Price: ", DoubleToString(closePrice, _Digits)); //--- Log closing price at breakout Print("Breakout Time: ", TimeToString(breakoutTime)); //--- Log breakout timestamp Print("Neckline Price at Breakout: ", DoubleToString(breakoutNecklinePrice, _Digits)); //--- Log neckline price at breakout Print("Extended Neckline Start: Bar ", extendedBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(extendedNecklineStartTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(extendedNecklineStartPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log extended neckline start details Print("Bar Ranges: LS to Head = ", lsToHead, ", Head to RS = ", headToRs, ", RS to Breakout = ", rsToBreakout, ", LS to Neckline Start = ", lsToNeckStart); //--- Log bar ranges for pattern analysis string prefix = "IHS_" + TimeToString(extrema[headIdx].time, TIME_MINUTES); //--- Create unique prefix for chart objects based on head time // Lines DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_LeftToNeckStart", lsTime, lsPrice, necklineStartTime, necklineStartPrice, clrGreen, 2, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from left shoulder to neckline start DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_NeckStartToHead", necklineStartTime, necklineStartPrice, extrema[headIdx].time, extrema[headIdx].price, clrGreen, 2, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from neckline start to head DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_HeadToNeckEnd", extrema[headIdx].time, extrema[headIdx].price, necklineEndTime, necklineEndPrice, clrGreen, 2, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from head to neckline end DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_NeckEndToRight", necklineEndTime, necklineEndPrice, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, clrGreen, 2, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from neckline end to right shoulder DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_Neckline", extendedNecklineStartTime, extendedNecklineStartPrice, breakoutTime, breakoutNecklinePrice, clrBlue, 2, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw neckline from extended start to breakout DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_RightToBreakout", extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, breakoutTime, breakoutNecklinePrice, clrGreen, 2, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from right shoulder to breakout DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_ExtendedToLeftShoulder", extendedNecklineStartTime, extendedNecklineStartPrice, lsTime, lsPrice, clrGreen, 2, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from extended neckline to left shoulder // Triangles DrawTriangle(prefix + "_LeftShoulderTriangle", lsTime, lsPrice, necklineStartTime, necklineStartPrice, extendedNecklineStartTime, extendedNecklineStartPrice, clrLightGreen); //--- Draw triangle for left shoulder area DrawTriangle(prefix + "_HeadTriangle", extrema[headIdx].time, extrema[headIdx].price, necklineStartTime, necklineStartPrice, necklineEndTime, necklineEndPrice, clrLightGreen); //--- Draw triangle for head area DrawTriangle(prefix + "_RightShoulderTriangle", extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, necklineEndTime, necklineEndPrice, breakoutTime, breakoutNecklinePrice, clrLightGreen); //--- Draw triangle for right shoulder area // Text Labels DrawText(prefix + "_LS_Label", lsTime, lsPrice, "LS", clrGreen, false); //--- Draw "LS" label below left shoulder DrawText(prefix + "_Head_Label", extrema[headIdx].time, extrema[headIdx].price, "HEAD", clrGreen, false); //--- Draw "HEAD" label below head DrawText(prefix + "_RS_Label", extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, "RS", clrGreen, false); //--- Draw "RS" label below right shoulder datetime necklineMidTime = extendedNecklineStartTime + (breakoutTime - extendedNecklineStartTime) / 2; //--- Calculate midpoint time of the neckline double necklineMidPrice = extendedNecklineStartPrice + slope * (iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, extendedNecklineStartTime) - iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, necklineMidTime)); //--- Calculate midpoint price of the neckline // Calculate angle in pixel space int x1 = ShiftToX(iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, extendedNecklineStartTime)); //--- Convert extended neckline start to x-pixel coordinate int y1 = PriceToY(extendedNecklineStartPrice); //--- Convert extended neckline start price to y-pixel coordinate int x2 = ShiftToX(iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, breakoutTime)); //--- Convert breakout time to x-pixel coordinate int y2 = PriceToY(breakoutNecklinePrice); //--- Convert breakout price to y-pixel coordinate double pixelSlope = (y2 - y1) / (double)(x2 - x1); //--- Calculate slope in pixel space (rise over run) double necklineAngle = -atan(pixelSlope) * 180 / M_PI; //--- Calculate neckline angle in degrees, negated for visual alignment Print("Pixel X1: ", x1, ", Y1: ", y1, ", X2: ", x2, ", Y2: ", y2, ", Pixel Slope: ", DoubleToString(pixelSlope, 4), ", Neckline Angle: ", DoubleToString(necklineAngle, 2)); //--- Log pixel coordinates and angle DrawText(prefix + "_Neckline_Label", necklineMidTime, necklineMidPrice, "NECKLINE", clrBlue, true, necklineAngle); //--- Draw "NECKLINE" label at midpoint with calculated angle double entryPrice = 0; //--- Set entry price to 0 for market order (uses current price) double sl = extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price - BufferPoints * _Point; //--- Calculate stop-loss below right shoulder with buffer double patternHeight = necklinePrice - extrema[headIdx].price; //--- Calculate pattern height from neckline to head double tp = closePrice + patternHeight; //--- Calculate take-profit above close by pattern height if (sl < closePrice && tp > closePrice) { //--- Validate trade direction (SL below, TP above for buy) if (obj_Trade.Buy(LotSize, _Symbol, entryPrice, sl, tp, "Inverse Head and Shoulders")) { //--- Attempt to open a buy trade AddTradedPattern(lsTime, lsPrice); //--- Add pattern to traded list Print("Buy Trade Opened: SL ", DoubleToString(sl, _Digits), ", TP ", DoubleToString(tp, _Digits)); //--- Log successful trade opening } } } }
Agora, resta apenas gerenciar as posições abertas aplicando a lógica de trailing stop para maximizar o lucro. Criamos, então, uma função para processar essa lógica de acompanhamento, conforme descrito a seguir.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Apply trailing stop with minimum profit threshold | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void ApplyTrailingStop(int minTrailPoints, int trailingPoints, CTrade &trade_object, ulong magicNo = 0) { //--- Function to apply trailing stop to open positions double bid = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_BID); //--- Get current bid price double ask = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_ASK); //--- Get current ask price for (int i = PositionsTotal() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { //--- Loop through all open positions from last to first ulong ticket = PositionGetTicket(i); //--- Retrieve position ticket number if (ticket > 0 && PositionSelectByTicket(ticket)) { //--- Check if ticket is valid and select the position if (PositionGetString(POSITION_SYMBOL) == _Symbol && //--- Verify position is for the current symbol (magicNo == 0 || PositionGetInteger(POSITION_MAGIC) == magicNo)) { //--- Check if magic number matches or no magic filter applied double openPrice = PositionGetDouble(POSITION_PRICE_OPEN); //--- Get position opening price double currentSL = PositionGetDouble(POSITION_SL); //--- Get current stop-loss price double currentProfit = PositionGetDouble(POSITION_PROFIT) / (LotSize * SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_TRADE_TICK_VALUE)); //--- Calculate profit in points if (PositionGetInteger(POSITION_TYPE) == POSITION_TYPE_BUY) { //--- Check if position is a Buy double profitPoints = (bid - openPrice) / _Point; //--- Calculate profit in points for Buy position if (profitPoints >= minTrailPoints + trailingPoints) { //--- Check if profit exceeds minimum threshold for trailing double newSL = NormalizeDouble(bid - trailingPoints * _Point, _Digits); //--- Calculate new stop-loss price if (newSL > openPrice && (newSL > currentSL || currentSL == 0)) { //--- Ensure new SL is above open price and better than current SL if (trade_object.PositionModify(ticket, newSL, PositionGetDouble(POSITION_TP))) { //--- Attempt to modify position with new SL Print("Trailing Stop Updated: Ticket ", ticket, ", New SL: ", DoubleToString(newSL, _Digits)); //--- Log successful SL update } } } } else if (PositionGetInteger(POSITION_TYPE) == POSITION_TYPE_SELL) { //--- Check if position is a Sell double profitPoints = (openPrice - ask) / _Point; //--- Calculate profit in points for Sell position if (profitPoints >= minTrailPoints + trailingPoints) { //--- Check if profit exceeds minimum threshold for trailing double newSL = NormalizeDouble(ask + trailingPoints * _Point, _Digits); //--- Calculate new stop-loss price if (newSL < openPrice && (newSL < currentSL || currentSL == 0)) { //--- Ensure new SL is below open price and better than current SL if (trade_object.PositionModify(ticket, newSL, PositionGetDouble(POSITION_TP))) { //--- Attempt to modify position with new SL Print("Trailing Stop Updated: Ticket ", ticket, ", New SL: ", DoubleToString(newSL, _Digits)); //--- Log successful SL update } } } } } } } }
Aqui adicionamos a função de trailing stop denominada 'ApplyTrailingStop'. Para ajustar as posições abertas, ela utiliza os parâmetros 'minTrailPoints' e 'trailingPoints'. Obtemos os preços 'bid' e 'ask' através da função SymbolInfoDouble. Em seguida, percorremos todas as posições utilizando PositionsTotal. Para cada posição, obtemos o número do 'ticket' com PositionGetTicket e a selecionamos com PositionSelectByTicket. Verificamos o símbolo e o número mágico ('magicNo') por meio das funções 'PositionGetString' e 'PositionGetInteger'. Extraímos 'openPrice', 'currentSL' e 'currentProfit' usando PositionGetDouble.
Para operações de compra, calculamos o lucro com base no valor de bid e comparamos com a soma de 'minTrailPoints' e 'trailingPoints'. Se a condição for atendida, definimos o novo 'newSL' utilizando a função NormalizeDouble e o atualizamos através do método PositionModify do objeto 'trade_object'. Para operações de venda, usamos 'ask' em vez de 'bid' e ajustamos o 'newSL' para um valor inferior. A modificação bem-sucedida do stop é registrada no log. Depois disso, podemos chamar essa função dentro do manipulador de eventos OnTick.
// Apply trailing stop if enabled and positions exist if (UseTrailingStop && PositionsTotal() > 0) { //--- Check if trailing stop is enabled and there are open positions ApplyTrailingStop(MinTrailPoints, TrailingPoints, obj_Trade, MagicNumber); //--- Apply trailing stop to positions with specified parameters }
A chamada dessa função com os parâmetros de entrada é tudo o que precisamos para ativar o trailing stop. Agora, quando o programa deixar de ser utilizado, basta liberar os arrays de armazenamento e remover todos os objetos visuais criados. Isso é tratado dentro do manipulador de eventos OnDeinit.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { //--- Expert Advisor deinitialization function ArrayFree(tradedPatterns); //--- Free memory used by tradedPatterns array ObjectsDeleteAll(0, "HS_"); //--- Delete all chart objects with "HS_" prefix (standard H&S) ObjectsDeleteAll(0, "IHS_"); //--- Delete all chart objects with "IHS_" prefix (inverse H&S) ChartRedraw(); //--- Redraw the chart to remove deleted objects }
No manipulador de eventos OnDeinit, que é acionado quando o EA é desligado, limpamos tanto o programa quanto o gráfico ao qual ele está vinculado. Utilizamos a função ArrayFree para liberar a memória ocupada por 'tradedPatterns'. Em seguida, removemos todos os objetos visuais do gráfico. A função ObjectsDeleteAll exclui todos os elementos com o prefixo “HS_”, referentes aos padrões clássicos. Ela também apaga os padrões com o prefixo “IHS_”, correspondentes aos padrões invertidos. Por fim, atualizamos a visualização do gráfico. A função ChartRedraw atualiza o gráfico antes do encerramento completo. Após a compilação, obtemos o seguinte resultado.
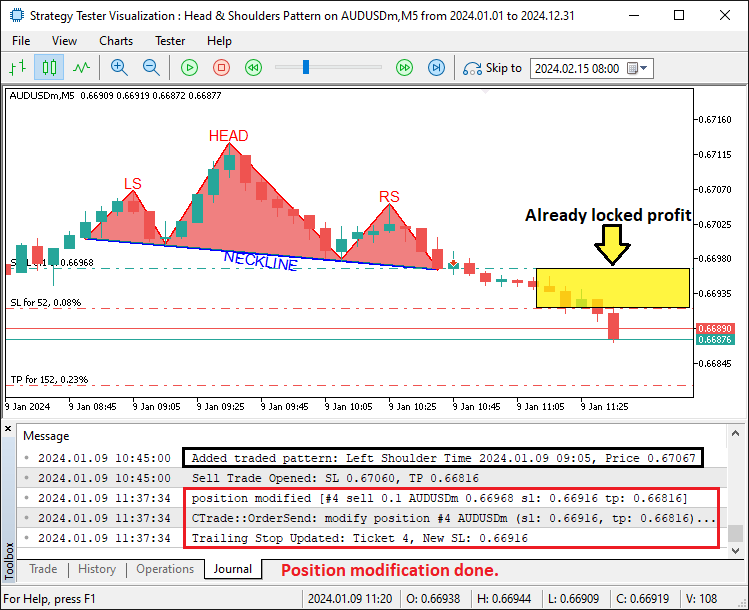
Na imagem, é possível observar a aplicação bem-sucedida do trailing stop às configurações de negociação, atingindo o objetivo proposto. Resta apenas realizar o reteste da estratégia, o que será feito na próxima etapa.
Testes em histórico
Após uma análise minuciosa em dados históricos, obtivemos os seguintes resultados.
Gráfico do teste em histórico:
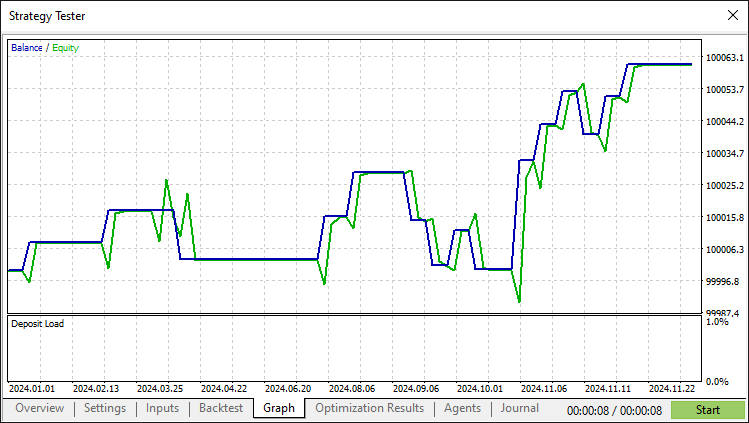
Relatório do teste em histórico:
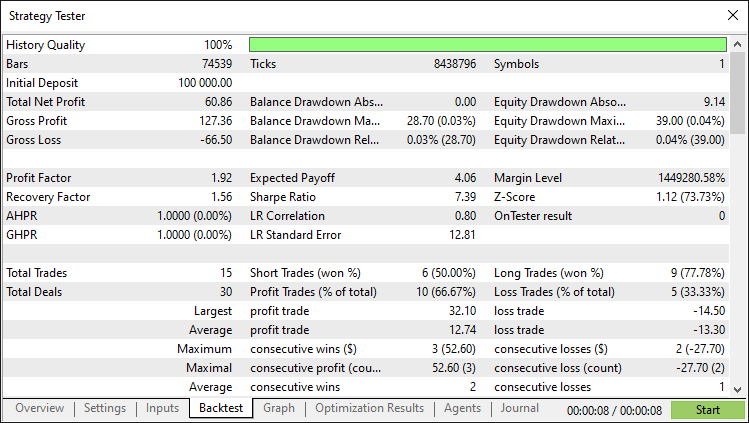
Considerações finais
Em conclusão, desenvolvemos com sucesso um algoritmo de negociação “Cabeça e Ombros” em MQL5. Ele oferece detecção precisa dos padrões, visualização detalhada e execução automática das operações baseadas no clássico sinal de reversão. Com o uso de regras de validação, construção da linha de pescoço e trailing stop, nosso EA adapta-se de forma eficiente às mudanças do mercado. As ilustrações apresentadas podem servir como ponto de partida para aprimoramentos adicionais, como ajustes de parâmetros ou um controle de risco mais avançado. Além disso, vale destacar que esta é uma configuração de padrão rara e altamente específica.
Aviso de responsabilidade: O conteúdo deste artigo é destinado exclusivamente para fins educacionais. A negociação envolve riscos financeiros significativos, e as condições de mercado podem ser imprevisíveis. Antes de aplicar qualquer estratégia em condições reais, é essencial realizar testes extensivos em histórico e implementar práticas adequadas de gerenciamento de risco.
Com essa base, você será capaz de aprimorar suas habilidades de negociação e aperfeiçoar ainda mais este algoritmo. Continue testando e otimizando o sistema para alcançar sucesso. Desejamos sucesso em sua jornada!
Traduzido do Inglês pela MetaQuotes Ltd.
Artigo original: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/17618
Aviso: Todos os direitos sobre esses materiais pertencem à MetaQuotes Ltd. É proibida a reimpressão total ou parcial.
Esse artigo foi escrito por um usuário do site e reflete seu ponto de vista pessoal. A MetaQuotes Ltd. não se responsabiliza pela precisão das informações apresentadas nem pelas possíveis consequências decorrentes do uso das soluções, estratégias ou recomendações descritas.
 Desenvolvimento de um sistema de monitoramento de entradas de swing (EA)
Desenvolvimento de um sistema de monitoramento de entradas de swing (EA)
 Reimaginando Estratégias Clássicas (Parte 13): Minimizando o Atraso em Cruzamentos de Médias Móveis
Reimaginando Estratégias Clássicas (Parte 13): Minimizando o Atraso em Cruzamentos de Médias Móveis
 Automatizando Estratégias de Negociação em MQL5 (Parte 3): O Sistema Zone Recovery RSI para Gestão Dinâmica de Operações
Automatizando Estratégias de Negociação em MQL5 (Parte 3): O Sistema Zone Recovery RSI para Gestão Dinâmica de Operações
- Aplicativos de negociação gratuitos
- 8 000+ sinais para cópia
- Notícias econômicas para análise dos mercados financeiros
Você concorda com a política do site e com os termos de uso