Automatización de estrategias de trading en MQL5 (Parte 13): Algoritmo de trading para patrón Hombro-Cabeza-Hombro
Introducción
En nuestro artículo anterior (Parte 12), implementamos la estrategia Mitigation Order Blocks (MOB) en MetaQuotes Language 5 (MQL5) para aprovechar las zonas de precios institucionales para operar. Ahora, en la parte 13, centramos nuestra atención en crear un algoritmo de trading «Hombro-Cabeza-Hombro», automatizando un patrón de reversión clásico para capturar los giros del mercado con precisión. Abordaremos los siguientes temas:
- Comprender la arquitectura del patrón Hombro-Cabeza-Hombro
- Implementación en MQL5
- Prueba retrospectiva
- Conclusión
Al finalizar este artículo tendrás un Asesor Experto totalmente funcional listo para operar el patrón Hombro-Cabeza-Hombro. Vamos a ello.
Comprender la arquitectura del patrón Hombro-Cabeza-Hombro
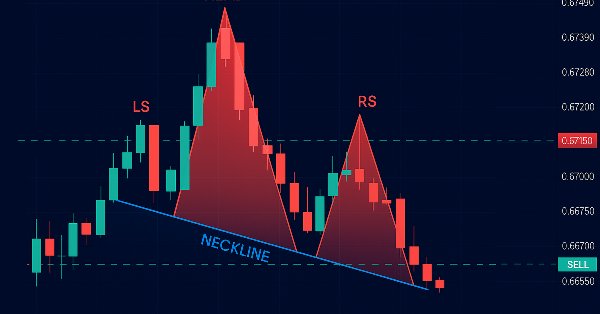
El patrón Hombro-Cabeza-Hombro es una formación clásica del análisis técnico usada para anticipar cambios de tendencia. Puede ser estándar (bajista) o invertido (alcista), según la secuencia de picos o valles que dibuja el precio. En el patrón estándar, en nuestro programa, una tendencia alcista dará paso a tres picos: el hombro izquierdo establecerá un máximo, la cabeza se elevará claramente más alto como clímax de la tendencia (superando significativamente a ambos hombros), y el hombro derecho se formará por debajo de la cabeza, pero con una altura cercana a la del izquierdo, todo ello unido por una línea de cuello que conecta los dos valles. Una vez que el precio rompa por debajo de esta línea, entraremos en una operación bajista en la ruptura, estableceremos un stop-loss por encima del hombro derecho y fijaremos un objetivo de take-profit proyectando la altura de la cabeza a la línea de cuello hacia abajo, como se ilustra a continuación.
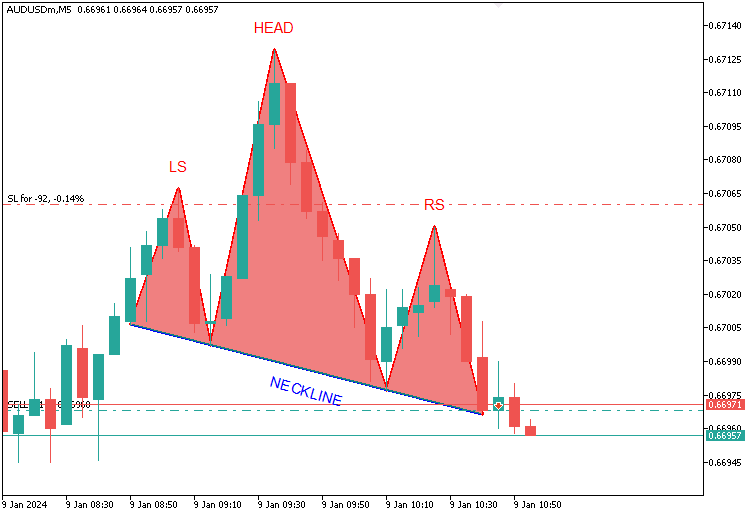
Para el patrón inverso, una tendencia bajista producirá tres mínimos: el hombro izquierdo marcará un mínimo, la cabeza caerá notablemente más (por debajo de ambos hombros) y el hombro derecho se alineará cerca del nivel del izquierdo, con una línea de cuello que atraviesa los picos; si el precio la supera, se activará una entrada alcista, con un stop-loss por debajo del hombro derecho y un take-profit que se extenderá hacia arriba por la distancia entre la línea de cuello y la cabeza, todo ello basado en la altura destacada de la cabeza y la casi simetría de los hombros como reglas orientativas. Aquí está su visualización.
En cuanto a la gestión de riesgos, integraremos una función opcional de trailing stop para asegurar las ganancias y maximizar los beneficios. Allá vamos.
Implementación en MQL5
Para crear el programa en MQL5, abra el MetaEditor, vaya al Navegador, localice la carpeta Indicadores, haga clic en la pestaña «Nuevo» y siga las instrucciones para crear el archivo. Una vez creado, en el entorno de programación, tendremos que declarar algunas variables globales que utilizaremos a lo largo del programa.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Head & Shoulders Pattern EA.mq5 | //| Copyright 2025, Allan Munene Mutiiria. | //| https://t.me/Forex_Algo_Trader | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2025, Allan Munene Mutiiria." #property link "https://youtube.com/@ForexAlgo-Trader?" #property version "1.00" #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> //--- Include the Trade.mqh library for trading functions CTrade obj_Trade; //--- Trade object for executing and managing trades // Input Parameters input int LookbackBars = 50; // Number of historical bars to analyze for pattern detection input double ThresholdPoints = 70.0; // Minimum price movement in points to identify a reversal input double ShoulderTolerancePoints = 15.0; // Maximum allowable price difference between left and right shoulders input double TroughTolerancePoints = 30.0; // Maximum allowable price difference between neckline troughs or peaks input double BufferPoints = 10.0; // Additional points added to stop-loss for safety buffer input double LotSize = 0.1; // Volume of each trade in lots input ulong MagicNumber = 123456; // Unique identifier for trades opened by this EA input int MaxBarRange = 30; // Maximum number of bars allowed between key pattern points input int MinBarRange = 5; // Minimum number of bars required between key pattern points input double BarRangeMultiplier = 2.0; // Maximum multiple of the smallest bar range for pattern uniformity input int ValidationBars = 3; // Number of bars after right shoulder to validate breakout input double PriceTolerance = 5.0; // Price tolerance in points for matching traded patterns input double RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier = 1.5; // Maximum multiple of pattern range for right shoulder to breakout distance input int MaxTradedPatterns = 20; // Maximum number of patterns stored in traded history input bool UseTrailingStop = false; // Toggle to enable or disable trailing stop functionality input int MinTrailPoints = 50; // Minimum profit in points before trailing stop activates input int TrailingPoints = 30; // Distance in points to maintain behind current price when trailing
Aquí, comenzamos con «#include <Trade\Trade.mqh>» y un objeto «CTrade», «obj_Trade», para incluir archivos de negociación adicionales para la gestión de operaciones. Establecemos entradas como «LookbackBars» (por defecto 50) para el análisis histórico, «ThresholdPoints» (por defecto 70,0) para la confirmación de la reversión, y «ShoulderTolerancePoints» (por defecto 15,0) y «TroughTolerancePoints» (por defecto 30,0) para la simetría. El resto de entradas se explican por sí mismas. Hemos añadido comentarios detallados para facilitar la comprensión. A continuación, debemos definir algunas estructuras que utilizaremos para encontrar los patrones y gestionar las operaciones consideradas.
// Structure to store peaks and troughs struct Extremum { int bar; //--- Bar index where extremum occurs datetime time; //--- Timestamp of the bar double price; //--- Price at extremum (high for peak, low for trough) bool isPeak; //--- True if peak (high), false if trough (low) }; // Structure to store traded patterns struct TradedPattern { datetime leftShoulderTime; //--- Timestamp of the left shoulder double leftShoulderPrice; //--- Price of the left shoulder };
Definimos dos estructuras clave con la palabra clave struct para impulsar nuestro algoritmo de Hombro-Cabeza-Hombro: "Extremum" guardará picos y valles con "bar" (index), "time" (marca temporal), "price" (valor) y "isPeak" (true para picos, false para valles) para identificar los componentes del patrón; mientras que "TradedPattern" registrará las operaciones ejecutadas usando "leftShoulderTime" y "leftShoulderPrice" para evitar duplicados. Para asegurarnos de que operamos una vez por barra y hacemos un seguimiento de las operaciones en curso, declaramos una variable y una matriz (array) como se indica a continuación.
// Global Variables static datetime lastBarTime = 0; //--- Tracks the timestamp of the last processed bar to avoid reprocessing TradedPattern tradedPatterns[]; //--- Array to store details of previously traded patterns
Con esto, ya estamos listos. Sin embargo, dado que tendremos que mostrar el patrón en el gráfico, necesitaremos obtener la arquitectura del gráfico y los componentes de las barras para asegurarnos de que se adapta a los requisitos del patrón.
int chart_width = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_WIDTH_IN_PIXELS); //--- Width of the chart in pixels for visualization int chart_height = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_HEIGHT_IN_PIXELS); //--- Height of the chart in pixels for visualization int chart_scale = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_SCALE); //--- Zoom level of the chart (0-5) int chart_first_vis_bar = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_FIRST_VISIBLE_BAR); //--- Index of the first visible bar on the chart int chart_vis_bars = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_VISIBLE_BARS); //--- Number of visible bars on the chart double chart_prcmin = ChartGetDouble(0, CHART_PRICE_MIN, 0); //--- Minimum price visible on the chart double chart_prcmax = ChartGetDouble(0, CHART_PRICE_MAX, 0); //--- Maximum price visible on the chart //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Converts the chart scale property to bar width/spacing | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int BarWidth(int scale) { return (int)pow(2, scale); } //--- Calculates bar width in pixels based on chart scale (zoom level) //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Converts the bar index (as series) to x in pixels | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int ShiftToX(int shift) { return (chart_first_vis_bar - shift) * BarWidth(chart_scale) - 1; } //--- Converts bar index to x-coordinate in pixels on the chart //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Converts the price to y in pixels | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int PriceToY(double price) { //--- Function to convert price to y-coordinate in pixels if (chart_prcmax - chart_prcmin == 0.0) return 0; //--- Return 0 if price range is zero to avoid division by zero return (int)round(chart_height * (chart_prcmax - price) / (chart_prcmax - chart_prcmin) - 1); //--- Calculate y-pixel position based on price and chart dimensions }
Preparamos y equipamos el programa con visualización definiendo variables como «chart_width» y «chart_height» utilizando la función ChartGetInteger para las dimensiones del gráfico, «chart_scale» para el zoom, «chart_first_vis_bar» y «chart_vis_bars» para los detalles de las barras, y «chart_prcmin» y «chart_prcmax» mediante ChartGetDouble para el rango de precios. Utilizamos la función «BarWidth» con pow para calcular el espaciado entre barras a partir de «chart_scale», la función «ShiftToX» para convertir los índices de las barras en coordenadas x utilizando «chart_first_vis_bar» y «chart_scale», y la función «PriceToY» con round para asignar los precios a las coordenadas y basándose en «chart_height», «chart_prcmax» y «chart_prcmin», lo que permite una visualización precisa de los patrones. Ya estamos listos. Ahora podemos proceder a inicializar el programa en el controlador de eventos OnInit.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- Expert Advisor initialization function obj_Trade.SetExpertMagicNumber(MagicNumber); //--- Set the magic number for trades opened by this EA ArrayResize(tradedPatterns, 0); //--- Initialize tradedPatterns array with zero size return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); //--- Return success code to indicate successful initialization }
En OnInit, utilizamos el método «SetExpertMagicNumber» en el objeto «obj_Trade» para asignar «MagicNumber» como identificador único para todas las operaciones, lo que garantiza que las posiciones de nuestro programa sean distinguibles, y llamamos a la función ArrayResize para establecer el tamaño de la matriz «tradedPatterns» en cero, borrando cualquier dato anterior para empezar de cero. A continuación, concluimos devolviendo INIT_SUCCEEDED para confirmar que la configuración se ha realizado correctamente, preparando el Asesor Experto para detectar y operar con el patrón de forma eficaz. Ahora podemos pasar al controlador de eventos OnTick y asegurarnos de que realizamos el análisis una vez por barra.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { //--- Main tick function executed on each price update datetime currentBarTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, 0); //--- Get the timestamp of the current bar if (currentBarTime == lastBarTime) return; //--- Exit if the current bar has already been processed lastBarTime = currentBarTime; //--- Update the last processed bar time // Update chart properties chart_width = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_WIDTH_IN_PIXELS); //--- Update chart width in pixels chart_height = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_HEIGHT_IN_PIXELS); //--- Update chart height in pixels chart_scale = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_SCALE); //--- Update chart zoom level chart_first_vis_bar = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_FIRST_VISIBLE_BAR); //--- Update index of the first visible bar chart_vis_bars = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_VISIBLE_BARS); //--- Update number of visible bars chart_prcmin = ChartGetDouble(0, CHART_PRICE_MIN, 0); //--- Update minimum visible price on chart chart_prcmax = ChartGetDouble(0, CHART_PRICE_MAX, 0); //--- Update maximum visible price on chart // Skip pattern detection if a position is already open if (PositionsTotal() > 0) return; //--- Exit function if there are open positions to avoid multiple trades }
En el controlador de eventos OnTick, que se activa con cada actualización de precios para supervisar y responder a los cambios del mercado, utilizamos la función iTime para obtener «currentBarTime» para la última barra y compararlo con «lastBarTime» para evitar volver a procesar, actualizando «lastBarTime» solo para las nuevas barras; a continuación, actualizamos los gráficos llamando a ChartGetInteger para actualizar «chart_width», «chart_height», «chart_scale», «chart_first_vis_bar» y «chart_vis_bars», y a ChartGetDouble para «chart_prcmin» y «chart_prcmax». También utilizamos la función PositionsTotal para comprobar si hay operaciones abiertas y, en caso de que las haya, salir antes de tiempo para evitar la superposición de posiciones, preparando el terreno para la detección de patrones y la negociación. A continuación, podemos definir una función para encontrar los puntos extremos o los puntos clave del patrón.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Find extrema in the last N bars | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void FindExtrema(Extremum &extrema[], int lookback) { //--- Function to identify peaks and troughs in price history ArrayFree(extrema); //--- Clear the extrema array to start fresh int bars = Bars(_Symbol, _Period); //--- Get total number of bars available if (lookback >= bars) lookback = bars - 1; //--- Adjust lookback if it exceeds available bars double highs[], lows[]; //--- Arrays to store high and low prices ArraySetAsSeries(highs, true); //--- Set highs array as time series (newest first) ArraySetAsSeries(lows, true); //--- Set lows array as time series (newest first) CopyHigh(_Symbol, _Period, 0, lookback + 1, highs); //--- Copy high prices for lookback period CopyLow(_Symbol, _Period, 0, lookback + 1, lows); //--- Copy low prices for lookback period bool isUpTrend = highs[lookback] < highs[lookback - 1]; //--- Determine initial trend based on first two bars double lastHigh = highs[lookback]; //--- Initialize last high price double lastLow = lows[lookback]; //--- Initialize last low price int lastExtremumBar = lookback; //--- Initialize last extremum bar index for (int i = lookback - 1; i >= 0; i--) { //--- Loop through bars from oldest to newest if (isUpTrend) { //--- If currently in an uptrend if (highs[i] > lastHigh) { //--- Check if current high exceeds last high lastHigh = highs[i]; //--- Update last high price lastExtremumBar = i; //--- Update last extremum bar index } else if (lows[i] < lastHigh - ThresholdPoints * _Point) { //--- Check if current low indicates a reversal (trough) int size = ArraySize(extrema); //--- Get current size of extrema array ArrayResize(extrema, size + 1); //--- Resize array to add new extremum extrema[size].bar = lastExtremumBar; //--- Store bar index of the peak extrema[size].time = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, lastExtremumBar); //--- Store timestamp of the peak extrema[size].price = lastHigh; //--- Store price of the peak extrema[size].isPeak = true; //--- Mark as a peak //Print("Extrema added: Bar ", lastExtremumBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(extrema[size].time), ", Price ", DoubleToString(lastHigh, _Digits), ", IsPeak true"); //--- Log new peak isUpTrend = false; //--- Switch trend to downtrend lastLow = lows[i]; //--- Update last low price lastExtremumBar = i; //--- Update last extremum bar index } } else { //--- If currently in a downtrend if (lows[i] < lastLow) { //--- Check if current low is below last low lastLow = lows[i]; //--- Update last low price lastExtremumBar = i; //--- Update last extremum bar index } else if (highs[i] > lastLow + ThresholdPoints * _Point) { //--- Check if current high indicates a reversal (peak) int size = ArraySize(extrema); //--- Get current size of extrema array ArrayResize(extrema, size + 1); //--- Resize array to add new extremum extrema[size].bar = lastExtremumBar; //--- Store bar index of the trough extrema[size].time = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, lastExtremumBar); //--- Store timestamp of the trough extrema[size].price = lastLow; //--- Store price of the trough extrema[size].isPeak = false; //--- Mark as a trough //Print("Extrema added: Bar ", lastExtremumBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(extrema[size].time), ", Price ", DoubleToString(lastLow, _Digits), ", IsPeak false"); //--- Log new trough isUpTrend = true; //--- Switch trend to uptrend lastHigh = highs[i]; //--- Update last high price lastExtremumBar = i; //--- Update last extremum bar index } } } }
Aquí, identificamos los picos y valles que definen nuestro patrón de cabeza y hombros mediante la implementación de la función «FindExtrema», que analiza las últimas barras «retrospectivas» para construir una matriz «extrema» de puntos críticos de precios. Comenzamos restableciendo la matriz «extrema» con la función ArrayFree para garantizar un borrado completo, y luego utilizamos la función «Bars» para obtener el total de barras disponibles y limitar el «lookback» si supera este límite, lo que garantiza que nos mantengamos dentro del rango de datos del gráfico. A continuación, preparamos matrices «altas» y «bajas» para almacenar los datos de precios, configurándolas como series temporales con la función ArraySetAsSeries (las más recientes primero), y las rellenamos utilizando CopyHigh y CopyLow para extraer los precios altos y bajos en «lookback + 1» barras.
En un bucle desde la barra más antigua hasta la más reciente, determinamos la tendencia con «isUpTrend» basándonos en el movimiento inicial del precio, luego rastreamos «lastHigh» o «lastLow» y su «lastExtremumBar»; cuando una reversión supera «ThresholdPoints», ampliamos «extrema» con la función ArrayResize, almacenamos detalles como «bar», «time» (a través de «iTime»), «price» e «isPeak» (verdadero para picos, falso para valles) y cambiamos la tendencia, lo que permite una identificación precisa del patrón. Ahora podemos tomar los niveles de precios identificados y almacenarlos para su uso posterior.
Extremum extrema[]; //--- Array to store identified peaks and troughs FindExtrema(extrema, LookbackBars); //--- Find extrema in the last LookbackBars bars
Aquí, declaramos una «extrema» matriz de tipo «Extremum» para contener los picos y valles identificados, que almacenarán los hombros y la cabeza del patrón. A continuación, llamamos a la función «FindExtrema», pasando «extrema» y «LookbackBars» como argumentos, para escanear las últimas barras «LookbackBars» y rellenar la matriz con los extremos clave, sentando las bases para el reconocimiento de patrones y las decisiones comerciales posteriores. Cuando imprimimos los valores de la matriz utilizando la función ArrayPrint, obtenemos algo que representa la siguiente estructura.
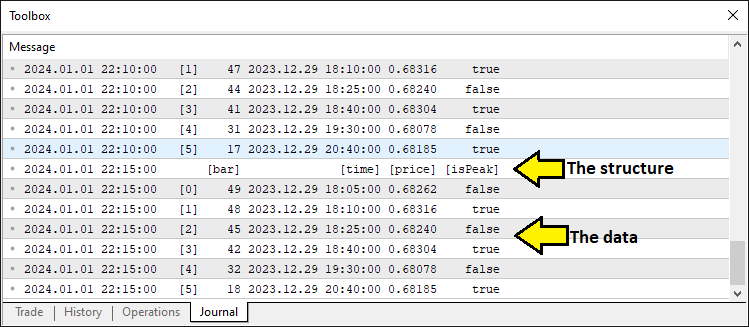
Esto confirma que disponemos de los datos necesarios. Así que podemos proceder a identificar los componentes del patrón. Para modularizar el código, utilizamos funciones.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Detect standard Head and Shoulders pattern | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool DetectHeadAndShoulders(Extremum &extrema[], int &leftShoulderIdx, int &headIdx, int &rightShoulderIdx, int &necklineStartIdx, int &necklineEndIdx) { //--- Function to detect standard H&S pattern int size = ArraySize(extrema); //--- Get the size of the extrema array if (size < 6) return false; //--- Return false if insufficient extrema for pattern (need at least 6 points) for (int i = size - 6; i >= 0; i--) { //--- Loop through extrema to find H&S pattern (start at size-6 to ensure enough points) if (!extrema[i].isPeak && extrema[i+1].isPeak && !extrema[i+2].isPeak && //--- Check sequence: trough, peak (LS), trough extrema[i+3].isPeak && !extrema[i+4].isPeak && extrema[i+5].isPeak) { //--- Check sequence: peak (head), trough, peak (RS) double leftShoulder = extrema[i+1].price; //--- Get price of left shoulder double head = extrema[i+3].price; //--- Get price of head double rightShoulder = extrema[i+5].price; //--- Get price of right shoulder double trough1 = extrema[i+2].price; //--- Get price of first trough (neckline start) double trough2 = extrema[i+4].price; //--- Get price of second trough (neckline end) bool isHeadHighest = true; //--- Flag to verify head is the highest peak in range for (int j = MathMax(0, i - 5); j < MathMin(size, i + 10); j++) { //--- Check surrounding bars (5 before, 10 after) for higher peaks if (extrema[j].isPeak && extrema[j].price > head && j != i + 3) { //--- If another peak is higher than head isHeadHighest = false; //--- Set flag to false break; //--- Exit loop as head is not highest } } int lsBar = extrema[i+1].bar; //--- Get bar index of left shoulder int headBar = extrema[i+3].bar; //--- Get bar index of head int rsBar = extrema[i+5].bar; //--- Get bar index of right shoulder int lsToHead = lsBar - headBar; //--- Calculate bars from left shoulder to head int headToRs = headBar - rsBar; //--- Calculate bars from head to right shoulder if (lsToHead < MinBarRange || lsToHead > MaxBarRange || headToRs < MinBarRange || headToRs > MaxBarRange) continue; //--- Skip if bar ranges are out of bounds int minRange = MathMin(lsToHead, headToRs); //--- Get the smaller of the two ranges for uniformity check if (lsToHead > minRange * BarRangeMultiplier || headToRs > minRange * BarRangeMultiplier) continue; //--- Skip if ranges exceed uniformity multiplier bool rsValid = false; //--- Flag to validate right shoulder breakout int rsBarIndex = extrema[i+5].bar; //--- Get bar index of right shoulder for validation for (int j = rsBarIndex - 1; j >= MathMax(0, rsBarIndex - ValidationBars); j--) { //--- Check bars after right shoulder for breakout if (iLow(_Symbol, _Period, j) < rightShoulder - ThresholdPoints * _Point) { //--- Check if price drops below RS by threshold rsValid = true; //--- Set flag to true if breakout confirmed break; //--- Exit loop once breakout is validated } } if (!rsValid) continue; //--- Skip if right shoulder breakout not validated if (isHeadHighest && head > leftShoulder && head > rightShoulder && //--- Verify head is highest and above shoulders MathAbs(leftShoulder - rightShoulder) < ShoulderTolerancePoints * _Point && //--- Check shoulder price difference within tolerance MathAbs(trough1 - trough2) < TroughTolerancePoints * _Point) { //--- Check trough price difference within tolerance leftShoulderIdx = i + 1; //--- Set index for left shoulder headIdx = i + 3; //--- Set index for head rightShoulderIdx = i + 5; //--- Set index for right shoulder necklineStartIdx = i + 2; //--- Set index for neckline start (first trough) necklineEndIdx = i + 4; //--- Set index for neckline end (second trough) Print("Bar Ranges: LS to Head = ", lsToHead, ", Head to RS = ", headToRs); //--- Log bar ranges for debugging return true; //--- Return true to indicate pattern found } } } return false; //--- Return false if no pattern detected }
Aquí, detectamos el patrón estándar mediante la función «DetectHeadAndShoulders», que examina la matriz «extrema» para encontrar una secuencia válida de seis puntos: un valle, un pico (hombro izquierdo), un valle, un pico (cabeza), un valle y un pico (hombro derecho), lo que requiere al menos seis entradas, tal y como comprueba la función ArraySize. Recorremos "extrema" comenzando en "size - 6", verificando la alternancia "pico–valle" del patrón. Luego extraemos los precios de "leftShoulder", "head", "rightShoulder" y los valles "trough1" y "trough2". Un bucle interno asegura que la cabeza sea el pico más alto del tramo usando "MathMax" y "MathMin". Además, las distancias en barras entre puntos se limitan con "MinBarRange" y "MaxBarRange", y la uniformidad con "BarRangeMultiplier".
Confirmamos la ruptura del hombro derecho comprobando la función iLow con respecto a «ThresholdPoints» sobre «ValidationBars», y si la cabeza supera ambos hombros y tolerancias («ShoulderTolerancePoints», «TroughTolerancePoints»), asignamos índices como «leftShoulderIdx», «headIdx» y «necklineStartIdx», registramos los rangos de barras con la función Print para la depuración y devolvemos verdadero para señalar un patrón detectado; de lo contrario, devolvemos falso. Utilizamos la misma lógica para encontrar el patrón inverso.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Detect inverse Head and Shoulders pattern | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool DetectInverseHeadAndShoulders(Extremum &extrema[], int &leftShoulderIdx, int &headIdx, int &rightShoulderIdx, int &necklineStartIdx, int &necklineEndIdx) { //--- Function to detect inverse H&S pattern int size = ArraySize(extrema); //--- Get the size of the extrema array if (size < 6) return false; //--- Return false if insufficient extrema for pattern (need at least 6 points) for (int i = size - 6; i >= 0; i--) { //--- Loop through extrema to find inverse H&S pattern if (extrema[i].isPeak && !extrema[i+1].isPeak && extrema[i+2].isPeak && //--- Check sequence: peak, trough (LS), peak !extrema[i+3].isPeak && extrema[i+4].isPeak && !extrema[i+5].isPeak) { //--- Check sequence: trough (head), peak, trough (RS) double leftShoulder = extrema[i+1].price; //--- Get price of left shoulder double head = extrema[i+3].price; //--- Get price of head double rightShoulder = extrema[i+5].price; //--- Get price of right shoulder double peak1 = extrema[i+2].price; //--- Get price of first peak (neckline start) double peak2 = extrema[i+4].price; //--- Get price of second peak (neckline end) bool isHeadLowest = true; //--- Flag to verify head is the lowest trough in range int headBar = extrema[i+3].bar; //--- Get bar index of head for range check for (int j = MathMax(0, headBar - 5); j <= MathMin(Bars(_Symbol, _Period) - 1, headBar + 5); j++) { //--- Check 5 bars before and after head if (iLow(_Symbol, _Period, j) < head) { //--- If any low is below head isHeadLowest = false; //--- Set flag to false break; //--- Exit loop as head is not lowest } } int lsBar = extrema[i+1].bar; //--- Get bar index of left shoulder int rsBar = extrema[i+5].bar; //--- Get bar index of right shoulder int lsToHead = lsBar - headBar; //--- Calculate bars from left shoulder to head int headToRs = headBar - rsBar; //--- Calculate bars from head to right shoulder if (lsToHead < MinBarRange || lsToHead > MaxBarRange || headToRs < MinBarRange || headToRs > MaxBarRange) continue; //--- Skip if bar ranges are out of bounds int minRange = MathMin(lsToHead, headToRs); //--- Get the smaller of the two ranges for uniformity check if (lsToHead > minRange * BarRangeMultiplier || headToRs > minRange * BarRangeMultiplier) continue; //--- Skip if ranges exceed uniformity multiplier bool rsValid = false; //--- Flag to validate right shoulder breakout int rsBarIndex = extrema[i+5].bar; //--- Get bar index of right shoulder for validation for (int j = rsBarIndex - 1; j >= MathMax(0, rsBarIndex - ValidationBars); j--) { //--- Check bars after right shoulder for breakout if (iHigh(_Symbol, _Period, j) > rightShoulder + ThresholdPoints * _Point) { //--- Check if price rises above RS by threshold rsValid = true; //--- Set flag to true if breakout confirmed break; //--- Exit loop once breakout is validated } } if (!rsValid) continue; //--- Skip if right shoulder breakout not validated if (isHeadLowest && head < leftShoulder && head < rightShoulder && //--- Verify head is lowest and below shoulders MathAbs(leftShoulder - rightShoulder) < ShoulderTolerancePoints * _Point && //--- Check shoulder price difference within tolerance MathAbs(peak1 - peak2) < TroughTolerancePoints * _Point) { //--- Check peak price difference within tolerance leftShoulderIdx = i + 1; //--- Set index for left shoulder headIdx = i + 3; //--- Set index for head rightShoulderIdx = i + 5; //--- Set index for right shoulder necklineStartIdx = i + 2; //--- Set index for neckline start (first peak) necklineEndIdx = i + 4; //--- Set index for neckline end (second peak) Print("Bar Ranges: LS to Head = ", lsToHead, ", Head to RS = ", headToRs); //--- Log bar ranges for debugging return true; //--- Return true to indicate pattern found } } } return false; //--- Return false if no pattern detected }
Definimos la función «DetectInverseHeadAndShoulders» para identificar el patrón inverso, que examina la matriz «extrema» para localizar una secuencia de seis puntos (pico, valle [hombro izquierdo], pico, valle [cabeza], pico, valle [hombro derecho]) que necesita al menos seis entradas, según lo verifica la función ArraySize. Iteramos desde "size - 6" hacia atrás, confirmando la alternancia "pico–valle" del patrón. Luego obtenemos los precios de "leftShoulder", "head", "rightShoulder" y los picos "peak1" y "peak2". Un bucle interno comprueba si la cabeza es el valle más bajo dentro de un rango de cinco barras alrededor de "headBar" usando "MathMax", "MathMin" y "iLow". Además, "Bars" garantiza que no salgamos de los límites del gráfico.
Forzamos la separación entre barras con "MinBarRange" y "MaxBarRange", calculamos la uniformidad con "MathMin" y "BarRangeMultiplier", y validamos la ruptura del hombro derecho usando "iHigh" contra "ThresholdPoints" durante "ValidationBars". Si la "head" queda por debajo de ambos hombros y se cumplen las tolerancias ("ShoulderTolerancePoints", "TroughTolerancePoints"), guardamos índices como "leftShoulderIdx" y "necklineStartIdx", registramos los rangos y devolvemos true; en caso contrario devolvemos false. Con estas dos funciones, ahora podemos proceder a identificar los patrones como se muestra a continuación.
int leftShoulderIdx, headIdx, rightShoulderIdx, necklineStartIdx, necklineEndIdx; //--- Indices for pattern components // Standard Head and Shoulders (Sell) if (DetectHeadAndShoulders(extrema, leftShoulderIdx, headIdx, rightShoulderIdx, necklineStartIdx, necklineEndIdx)) { //--- Check for standard H&S pattern double closePrice = iClose(_Symbol, _Period, 1); //--- Get the closing price of the previous bar double necklinePrice = extrema[necklineEndIdx].price; //--- Get the price of the neckline end point if (closePrice < necklinePrice) { //--- Check if price has broken below the neckline (sell signal) datetime lsTime = extrema[leftShoulderIdx].time; //--- Get the timestamp of the left shoulder double lsPrice = extrema[leftShoulderIdx].price; //--- Get the price of the left shoulder //--- } }
Aquí, avanzamos declarando las variables «leftShoulderIdx», «headIdx», «rightShoulderIdx», «necklineStartIdx» y «necklineEndIdx» para almacenar los índices de los componentes del patrón, y luego utilizamos la función «DetectHeadAndShoulders» para comprobar la matriz «extrema» en busca de un patrón estándar, pasando estos índices como referencias. Si se detecta, recuperamos «closePrice» con la función iClose para la barra anterior y «necklinePrice» de «extrema[necklineEndIdx].price», lo que activa una señal de venta si «closePrice» cae por debajo de «necklinePrice»; a continuación, extraemos «lsTime» y «lsPrice» de «extrema[leftShoulderIdx]» para prepararnos para la ejecución de la operación basándonos en la posición del hombro izquierdo. En este punto, debemos asegurarnos de que el patrón no se comercialice. Definimos una función para realizar la comprobación.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Check if pattern has already been traded | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool IsPatternTraded(datetime lsTime, double lsPrice) { //--- Function to check if a pattern has already been traded int size = ArraySize(tradedPatterns); //--- Get the current size of the tradedPatterns array for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { //--- Loop through all stored traded patterns if (tradedPatterns[i].leftShoulderTime == lsTime && //--- Check if left shoulder time matches MathAbs(tradedPatterns[i].leftShoulderPrice - lsPrice) < PriceTolerance * _Point) { //--- Check if left shoulder price is within tolerance Print("Pattern already traded: Left Shoulder Time ", TimeToString(lsTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(lsPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log that pattern was previously traded return true; //--- Return true to indicate pattern has been traded } } return false; //--- Return false if no match found }
Aquí, nos aseguramos de que nuestro programa evite operaciones duplicadas mediante la implementación de la función «IsPatternTraded», que comprueba si un patrón, identificado por «lsTime» y «lsPrice», ya existe en la matriz «tradedPatterns». Utilizamos la función ArraySize para obtener el «tamaño» de la matriz y, a continuación, la recorremos comparando el «leftShoulderTime» de cada entrada con «lsTime» y el «leftShoulderPrice» con «lsPrice» dentro de un rango «PriceTolerance» mediante la función MathAbs. si se encuentra una coincidencia, la registramos con la función Print, incluyendo TimeToString y DoubleToString para facilitar la lectura, y devolvemos verdadero; de lo contrario, devolvemos falso para permitir una nueva operación. A continuación, llamamos a la función para realizar la comprobación y continuamos si no se encuentra ninguna.
if (IsPatternTraded(lsTime, lsPrice)) return; //--- Exit if this pattern has already been traded datetime breakoutTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, 1); //--- Get the timestamp of the breakout bar (previous bar) int lsBar = extrema[leftShoulderIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the left shoulder int headBar = extrema[headIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the head int rsBar = extrema[rightShoulderIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the right shoulder int necklineStartBar = extrema[necklineStartIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the neckline start int necklineEndBar = extrema[necklineEndIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the neckline end int breakoutBar = 1; //--- Set breakout bar index (previous bar) int lsToHead = lsBar - headBar; //--- Calculate number of bars from left shoulder to head int headToRs = headBar - rsBar; //--- Calculate number of bars from head to right shoulder int rsToBreakout = rsBar - breakoutBar; //--- Calculate number of bars from right shoulder to breakout int lsToNeckStart = lsBar - necklineStartBar; //--- Calculate number of bars from left shoulder to neckline start double avgPatternRange = (lsToHead + headToRs) / 2.0; //--- Calculate average bar range of the pattern for uniformity check if (rsToBreakout > avgPatternRange * RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier) { //--- Check if breakout distance exceeds allowed range Print("Pattern rejected: Right Shoulder to Breakout (", rsToBreakout, ") exceeds ", RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier, "x average range (", avgPatternRange, ")"); //--- Log rejection due to excessive breakout range return; //--- Exit function if pattern is invalid } double necklineStartPrice = extrema[necklineStartIdx].price; //--- Get the price of the neckline start point double necklineEndPrice = extrema[necklineEndIdx].price; //--- Get the price of the neckline end point datetime necklineStartTime = extrema[necklineStartIdx].time; //--- Get the timestamp of the neckline start point datetime necklineEndTime = extrema[necklineEndIdx].time; //--- Get the timestamp of the neckline end point int barDiff = necklineStartBar - necklineEndBar; //--- Calculate bar difference between neckline points for slope double slope = (necklineEndPrice - necklineStartPrice) / barDiff; //--- Calculate the slope of the neckline (price change per bar) double breakoutNecklinePrice = necklineStartPrice + slope * (necklineStartBar - breakoutBar); //--- Calculate neckline price at breakout point // Extend neckline backwards int extendedBar = necklineStartBar; //--- Initialize extended bar index with neckline start datetime extendedNecklineStartTime = necklineStartTime; //--- Initialize extended neckline start time double extendedNecklineStartPrice = necklineStartPrice; //--- Initialize extended neckline start price bool foundCrossing = false; //--- Flag to track if neckline crosses a bar within range for (int i = necklineStartBar + 1; i < Bars(_Symbol, _Period); i++) { //--- Loop through bars to extend neckline backwards double checkPrice = necklineStartPrice - slope * (i - necklineStartBar); //--- Calculate projected neckline price at bar i if (NecklineCrossesBar(checkPrice, i)) { //--- Check if neckline intersects the bar's high-low range int distance = i - necklineStartBar; //--- Calculate distance from neckline start to crossing bar if (distance <= avgPatternRange * RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier) { //--- Check if crossing is within uniformity range extendedBar = i; //--- Update extended bar index extendedNecklineStartTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, i); //--- Update extended neckline start time extendedNecklineStartPrice = checkPrice; //--- Update extended neckline start price foundCrossing = true; //--- Set flag to indicate crossing found Print("Neckline extended to first crossing bar within uniformity: Bar ", extendedBar); //--- Log successful extension break; //--- Exit loop after finding valid crossing } else { //--- If crossing exceeds uniformity range Print("Crossing bar ", i, " exceeds uniformity (", distance, " > ", avgPatternRange * RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier, ")"); //--- Log rejection of crossing break; //--- Exit loop as crossing is too far } } } if (!foundCrossing) { //--- If no valid crossing found within range int barsToExtend = 2 * lsToNeckStart; //--- Set fallback extension distance as twice LS to neckline start extendedBar = necklineStartBar + barsToExtend; //--- Calculate extended bar index if (extendedBar >= Bars(_Symbol, _Period)) extendedBar = Bars(_Symbol, _Period) - 1; //--- Cap extended bar at total bars if exceeded extendedNecklineStartTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, extendedBar); //--- Update extended neckline start time extendedNecklineStartPrice = necklineStartPrice - slope * (extendedBar - necklineStartBar); //--- Update extended neckline start price Print("Neckline extended to fallback (2x LS to Neckline Start): Bar ", extendedBar, " (no crossing within uniformity)"); //--- Log fallback extension } Print("Standard Head and Shoulders Detected:"); //--- Log detection of standard H&S pattern Print("Left Shoulder: Bar ", lsBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(lsTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(lsPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log left shoulder details Print("Head: Bar ", headBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(extrema[headIdx].time), ", Price ", DoubleToString(extrema[headIdx].price, _Digits)); //--- Log head details Print("Right Shoulder: Bar ", rsBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time), ", Price ", DoubleToString(extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, _Digits)); //--- Log right shoulder details Print("Neckline Start: Bar ", necklineStartBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(necklineStartTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(necklineStartPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log neckline start details Print("Neckline End: Bar ", necklineEndBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(necklineEndTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(necklineEndPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log neckline end details Print("Close Price: ", DoubleToString(closePrice, _Digits)); //--- Log closing price at breakout Print("Breakout Time: ", TimeToString(breakoutTime)); //--- Log breakout timestamp Print("Neckline Price at Breakout: ", DoubleToString(breakoutNecklinePrice, _Digits)); //--- Log neckline price at breakout Print("Extended Neckline Start: Bar ", extendedBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(extendedNecklineStartTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(extendedNecklineStartPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log extended neckline start details Print("Bar Ranges: LS to Head = ", lsToHead, ", Head to RS = ", headToRs, ", RS to Breakout = ", rsToBreakout, ", LS to Neckline Start = ", lsToNeckStart); //--- Log bar ranges for pattern analysis
Aquí, mejoramos la detección de patrones validando un patrón estándar detectado y configurando una operación de venta, comenzando con la función «IsPatternTraded» para comprobar si «lsTime» y «lsPrice» coinciden con una operación anterior en «tradedPatterns», saliendo si es cierto para evitar duplicados. A continuación, utilizamos la función iTime para asignar «breakoutTime» como la marca de tiempo de la barra anterior y recuperar índices de barra como «lsBar», «headBar», «rsBar», «necklineStartBar» y «necklineEndBar» de «extrema», calculando rangos como «lsToHead», «headToRs» y «rsToBreakout»; si «rsToBreakout» supera «avgPatternRange» multiplicado por «RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier», rechazamos el patrón y lo registramos con la función Print.
A continuación, determinamos la «pendiente» de la línea de cuello utilizando «necklineStartPrice» y «necklineEndPrice» sobre «barDiff», calculamos «breakoutNecklinePrice» y extendemos la línea de cuello hacia atrás con un bucle, utilizando la función «NecklineCrossesBar» para encontrar un cruce dentro de «avgPatternRange * RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier», actualizando «extendedBar», «extendedNecklineStartTime» (a través de «iTime») y «extendedNecklineStartPrice»; si no hay ningún cruce que encaje, recurrimos a «2 * lsToNeckStart», con un límite máximo de «Bars» en total, y registramos todos los detalles (índices de barras, precios y rangos) con las funciones Print, TimeToString y DoubleToString para obtener una documentación exhaustiva. El fragmento de código de la función personalizada es el siguiente.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Check if neckline crosses a bar's high-low range | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool NecklineCrossesBar(double necklinePrice, int barIndex) { //--- Function to check if neckline price intersects a bar's range double high = iHigh(_Symbol, _Period, barIndex); //--- Get the high price of the specified bar double low = iLow(_Symbol, _Period, barIndex); //--- Get the low price of the specified bar return (necklinePrice >= low && necklinePrice <= high); //--- Return true if neckline price is within bar's high-low range }
El fragmento de código de la función personalizada es el siguiente. Utilizamos la función iHigh para obtener el precio «alto» de la barra y la función «iLow» para obtener su precio «bajo», y luego devolvemos verdadero si «necklinePrice» se encuentra entre «bajo» y «alto», lo que confirma que la línea de cuello cruza el rango de la barra para la validación del patrón. Si se valida el patrón, lo visualizamos en el gráfico. Necesitaremos funciones para dibujarlo y etiquetarlo.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Draw a trend line for visualization | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void DrawTrendLine(string name, datetime timeStart, double priceStart, datetime timeEnd, double priceEnd, color lineColor, int width, int style) { //--- Function to draw a trend line on the chart if (ObjectCreate(0, name, OBJ_TREND, 0, timeStart, priceStart, timeEnd, priceEnd)) { //--- Create a trend line object if possible ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_COLOR, lineColor); //--- Set the color of the trend line ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_STYLE, style); //--- Set the style (e.g., solid, dashed) of the trend line ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_WIDTH, width); //--- Set the width of the trend line ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_BACK, true); //--- Set the line to draw behind chart elements ChartRedraw(); //--- Redraw the chart to display the new line } else { //--- If line creation fails Print("Failed to create line: ", name, ". Error: ", GetLastError()); //--- Log the error with the object name and error code } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Draw a filled triangle for visualization | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void DrawTriangle(string name, datetime time1, double price1, datetime time2, double price2, datetime time3, double price3, color fillColor) { //--- Function to draw a filled triangle on the chart if (ObjectCreate(0, name, OBJ_TRIANGLE, 0, time1, price1, time2, price2, time3, price3)) { //--- Create a triangle object if possible ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_COLOR, fillColor); //--- Set the fill color of the triangle ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_STYLE, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Set the border style to solid ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_WIDTH, 1); //--- Set the border width to 1 pixel ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_FILL, true); //--- Enable filling of the triangle ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_BACK, true); //--- Set the triangle to draw behind chart elements ChartRedraw(); //--- Redraw the chart to display the new triangle } else { //--- If triangle creation fails Print("Failed to create triangle: ", name, ". Error: ", GetLastError()); //--- Log the error with the object name and error code } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Draw text label for visualization | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void DrawText(string name, datetime time, double price, string text, color textColor, bool above, double angle = 0) { //--- Function to draw a text label on the chart int chartscale = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_SCALE); //--- Get the current chart zoom level int dynamicFontSize = 5 + int(chartscale * 1.5); //--- Calculate font size based on zoom level for visibility double priceOffset = (above ? 10 : -10) * _Point; //--- Set price offset above or below the point for readability if (ObjectCreate(0, name, OBJ_TEXT, 0, time, price + priceOffset)) { //--- Create a text object if possible ObjectSetString(0, name, OBJPROP_TEXT, text); //--- Set the text content of the label ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_COLOR, textColor); //--- Set the color of the text ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_FONTSIZE, dynamicFontSize); //--- Set the font size based on chart scale ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_ANCHOR, ANCHOR_CENTER); //--- Center the text at the specified point ObjectSetDouble(0, name, OBJPROP_ANGLE, angle); //--- Set the rotation angle of the text in degrees ObjectSetInteger(0, name, OBJPROP_BACK, false); //--- Set the text to draw in front of chart elements ChartRedraw(); //--- Redraw the chart to display the new text Print("Text created: ", name, ", Angle: ", DoubleToString(angle, 2)); //--- Log successful creation of the text with its angle } else { //--- If text creation fails Print("Failed to create text: ", name, ". Error: ", GetLastError()); //--- Log the error with the object name and error code } }
Aquí, enriquecemos el programa con herramientas de visualización para resaltar el patrón en el gráfico, comenzando con la función «DrawTrendLine», que utiliza la función ObjectCreate para trazar una línea desde «timeStart» y «priceStart» hasta «timeEnd» y «priceEnd», estableciendo propiedades como «lineColor», «style» y «width» mediante ObjectSetInteger, dibujándola detrás de las barras con OBJPROP_BACK y actualizando la visualización con la función ChartRedraw, registrando los fallos con «Print» y GetLastError si es necesario.
A continuación, implementamos la función «DrawTriangle» para sombrear la estructura del patrón, llamando a la función «ObjectCreate» con tres puntos («time1», «price1», etc.), aplicando «fillColor» y un borde sólido utilizando ObjectSetInteger, rellenándolo con OBJPROP_FILL, colocándolo detrás del gráfico y actualizando la vista con ChartRedraw, registrando de nuevo los errores con «Print» si falla la creación.
Por último, añadimos la función «DrawText» para etiquetar los puntos clave, utilizando la función ChartGetInteger para ajustar «dynamicFontSize» en función de «chartscale», colocando el texto en «time» y «price» más un desplazamiento mediante «ObjectCreate», personalizándolo con «ObjectSetString» para «text», «ObjectSetInteger» para «textColor» y «FONTSIZE», y «ObjectSetDouble» para «angle», dibujándolo delante con ChartRedraw y confirmando la creación con «Print» y «DoubleToString» o anotando los errores. Ahora podemos llamar a las funciones para añadir la función de visibilidad, y lo primero que hacemos es añadir las líneas de la siguiente manera.
string prefix = "HS_" + TimeToString(extrema[headIdx].time, TIME_MINUTES); //--- Create unique prefix for chart objects based on head time // Lines DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_LeftToNeckStart", lsTime, lsPrice, necklineStartTime, necklineStartPrice, clrRed, 3, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from left shoulder to neckline start DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_NeckStartToHead", necklineStartTime, necklineStartPrice, extrema[headIdx].time, extrema[headIdx].price, clrRed, 3, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from neckline start to head DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_HeadToNeckEnd", extrema[headIdx].time, extrema[headIdx].price, necklineEndTime, necklineEndPrice, clrRed, 3, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from head to neckline end DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_NeckEndToRight", necklineEndTime, necklineEndPrice, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, clrRed, 3, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from neckline end to right shoulder DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_Neckline", extendedNecklineStartTime, extendedNecklineStartPrice, breakoutTime, breakoutNecklinePrice, clrBlue, 2, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw neckline from extended start to breakout DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_RightToBreakout", extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, breakoutTime, breakoutNecklinePrice, clrRed, 3, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from right shoulder to breakout DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_ExtendedToLeftShoulder", extendedNecklineStartTime, extendedNecklineStartPrice, lsTime, lsPrice, clrRed, 3, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from extended neckline to left shoulder
Aquí, representamos visualmente el patrón estándar creando un prefijo único basado en la marca de tiempo de la cabeza utilizando la función TimeToString y dibujando líneas de tendencia con la función «DrawTrendLine» para conectar el hombro izquierdo con el inicio del cuello, el inicio del cuello a la cabeza, la cabeza al final del cuello y el final del cuello al hombro derecho en rojo con un ancho de 3, mientras que el cuello desde su inicio extendido hasta el punto de ruptura utiliza azul con un ancho de 2, y líneas adicionales conectan el hombro derecho a la ruptura y el cuello extendido de vuelta al hombro izquierdo en rojo, todo en estilo sólido para mostrar el patrón en el gráfico. Tras la compilación, obtenemos el siguiente resultado.
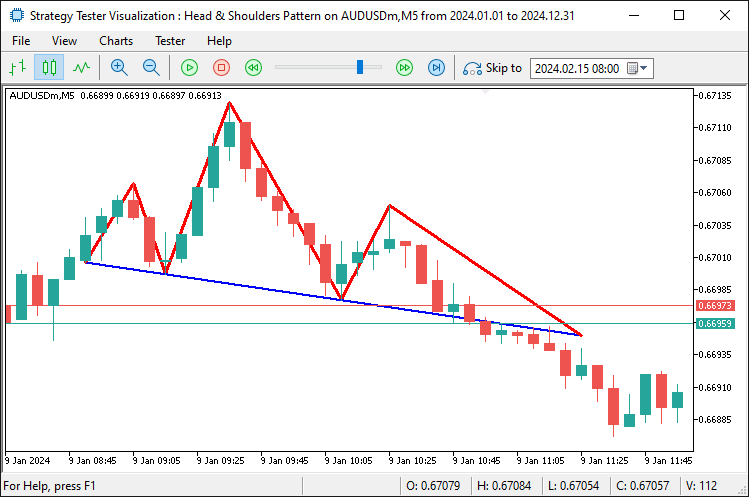
Para añadir los triángulos, utilizamos la función «DrawTriangle». Técnicamente, lo construimos dentro de los hombros y la cabeza.
// Triangles DrawTriangle(prefix + "_LeftShoulderTriangle", lsTime, lsPrice, necklineStartTime, necklineStartPrice, extendedNecklineStartTime, extendedNecklineStartPrice, clrLightCoral); //--- Draw triangle for left shoulder area DrawTriangle(prefix + "_HeadTriangle", extrema[headIdx].time, extrema[headIdx].price, necklineStartTime, necklineStartPrice, necklineEndTime, necklineEndPrice, clrLightCoral); //--- Draw triangle for head area DrawTriangle(prefix + "_RightShoulderTriangle", extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, necklineEndTime, necklineEndPrice, breakoutTime, breakoutNecklinePrice, clrLightCoral); //--- Draw triangle for right shoulder area
Aquí, mejoramos la visualización utilizando la función «DrawTriangle» para sombrear áreas clave en coral claro, formando un triángulo para el hombro izquierdo desde el punto del hombro izquierdo hasta el inicio del escote y el inicio del escote extendido, otro para la cabeza desde el punto de la cabeza hasta el inicio y el final del escote, y un tercero para el hombro derecho desde el punto del hombro derecho hasta el final del escote y el punto de ruptura, resaltando la estructura del patrón en el gráfico. Tras la compilación, obtenemos el siguiente resultado.
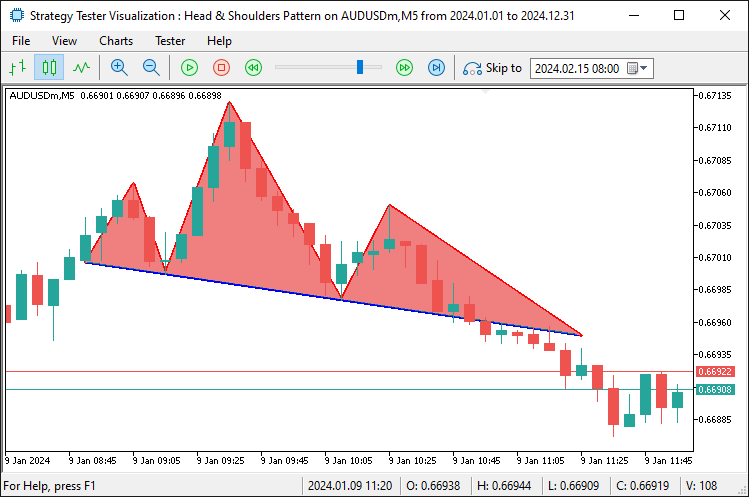
Por último, debemos añadir etiquetas al patrón para que resulte totalmente atractivo a la vista y se explique por sí mismo.
// Text Labels DrawText(prefix + "_LS_Label", lsTime, lsPrice, "LS", clrRed, true); //--- Draw "LS" label above left shoulder DrawText(prefix + "_Head_Label", extrema[headIdx].time, extrema[headIdx].price, "HEAD", clrRed, true); //--- Draw "HEAD" label above head DrawText(prefix + "_RS_Label", extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, "RS", clrRed, true); //--- Draw "RS" label above right shoulder datetime necklineMidTime = extendedNecklineStartTime + (breakoutTime - extendedNecklineStartTime) / 2; //--- Calculate midpoint time of the neckline double necklineMidPrice = extendedNecklineStartPrice + slope * (iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, extendedNecklineStartTime) - iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, necklineMidTime)); //--- Calculate midpoint price of the neckline // Calculate angle in pixel space int x1 = ShiftToX(iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, extendedNecklineStartTime)); //--- Convert extended neckline start to x-pixel coordinate int y1 = PriceToY(extendedNecklineStartPrice); //--- Convert extended neckline start price to y-pixel coordinate int x2 = ShiftToX(iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, breakoutTime)); //--- Convert breakout time to x-pixel coordinate int y2 = PriceToY(breakoutNecklinePrice); //--- Convert breakout price to y-pixel coordinate double pixelSlope = (y2 - y1) / (double)(x2 - x1); //--- Calculate slope in pixel space (rise over run) double necklineAngle = -atan(pixelSlope) * 180 / M_PI; //--- Calculate neckline angle in degrees, negated for visual alignment Print("Pixel X1: ", x1, ", Y1: ", y1, ", X2: ", x2, ", Y2: ", y2, ", Pixel Slope: ", DoubleToString(pixelSlope, 4), ", Neckline Angle: ", DoubleToString(necklineAngle, 2)); //--- Log pixel coordinates and angle DrawText(prefix + "_Neckline_Label", necklineMidTime, necklineMidPrice, "NECKLINE", clrBlue, false, necklineAngle); //--- Draw "NECKLINE" label at midpoint with calculated angle
Por último, anotamos el patrón utilizando la función «DrawText» para colocar las etiquetas rojas «LS», «HEAD» y «RS» sobre los puntos del hombro izquierdo, la cabeza y el hombro derecho en sus respectivos momentos y precios, lo que mejora la legibilidad del gráfico. A continuación, calculamos el punto medio de la línea de cuello promediando «extendedNecklineStartTime» y «breakoutTime» para «necklineMidTime» y ajustamos «extendedNecklineStartPrice» con «slope» y las diferencias de barras mediante la función iBarShift para «necklineMidPrice»; para alinear la etiqueta, convertimos los tiempos a píxeles x con la función «ShiftToX» y los precios a píxeles y con la función «PriceToY» en el inicio y la ruptura de la línea de cuello, calculamos una «pixelSlope» y derivamos «necklineAngle» en grados utilizando la función atan y «M_PI», registrando estos datos con la función «Print» y la función DoubleToString para su verificación.
A continuación, dibujamos una etiqueta azul «NECKLINE» en el punto medio con la función «DrawText», situada debajo y girada para que coincida con «necklineAngle», asegurándonos de que la anotación siga la inclinación de la línea del cuello. Este es el resultado.
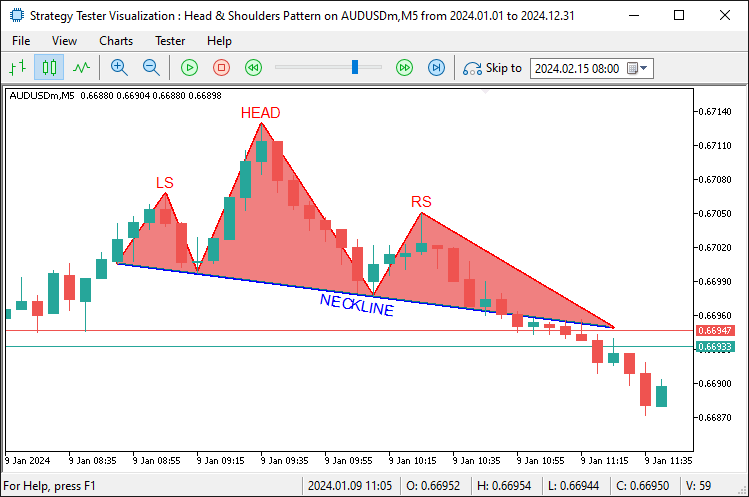
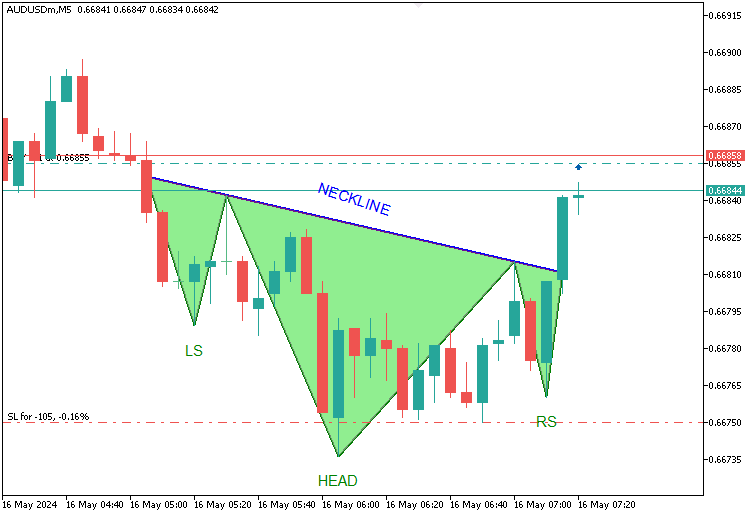
En la imagen podemos ver que el patrón se visualiza completamente. Ahora necesitamos detectar su ruptura, básicamente, la línea extendida, abrir una posición de venta y modificar el rango de extensión a la barra de ruptura. Pan comido. Lo conseguimos mediante la siguiente lógica.
double entryPrice = 0; //--- Set entry price to 0 for market order (uses current price) double sl = extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price + BufferPoints * _Point; //--- Calculate stop-loss above right shoulder with buffer double patternHeight = extrema[headIdx].price - necklinePrice; //--- Calculate pattern height from head to neckline double tp = closePrice - patternHeight; //--- Calculate take-profit below close by pattern height if (sl > closePrice && tp < closePrice) { //--- Validate trade direction (SL above, TP below for sell) if (obj_Trade.Sell(LotSize, _Symbol, entryPrice, sl, tp, "Head and Shoulders")) { //--- Attempt to open a sell trade AddTradedPattern(lsTime, lsPrice); //--- Add pattern to traded list Print("Sell Trade Opened: SL ", DoubleToString(sl, _Digits), ", TP ", DoubleToString(tp, _Digits)); //--- Log successful trade opening } }
Una vez confirmado el patrón, ejecutamos una operación de venta estableciendo «entryPrice» en 0 para una orden de mercado, calculando «sl» por encima del precio del hombro derecho con «BufferPoints», determinando «patternHeight» como la diferencia entre los precios de la cabeza y la línea del cuello, y estableciendo «tp» por debajo de «closePrice» por «patternHeight».
Validamos la dirección de la operación, asegurándonos de que «sl» esté por encima y «tp» por debajo de «closePrice», antes de utilizar la función «Sell» en «obj_Trade» para abrir la operación con «LotSize», «sl», «tp» y comentario. si tiene éxito, llamamos a la función «AddTradedPattern» con «lsTime» y «lsPrice» para registrar el patrón y utilizamos la función Print con DoubleToString para registrar los detalles de «sl» y «tp». El fragmento de código de la función personalizada para marcar el patrón como negociado es el siguiente.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Add pattern to traded list with size management | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void AddTradedPattern(datetime lsTime, double lsPrice) { //--- Function to add a new traded pattern to the list int size = ArraySize(tradedPatterns); //--- Get the current size of the tradedPatterns array if (size >= MaxTradedPatterns) { //--- Check if array size exceeds maximum allowed for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) { //--- Shift all elements left to remove the oldest tradedPatterns[i] = tradedPatterns[i + 1]; //--- Copy next element to current position } ArrayResize(tradedPatterns, size - 1); //--- Reduce array size by 1 size--; //--- Decrement size variable Print("Removed oldest traded pattern to maintain max size of ", MaxTradedPatterns); //--- Log removal of oldest pattern } ArrayResize(tradedPatterns, size + 1); //--- Increase array size to add new pattern tradedPatterns[size].leftShoulderTime = lsTime; //--- Store the left shoulder time of the new pattern tradedPatterns[size].leftShoulderPrice = lsPrice; //--- Store the left shoulder price of the new pattern Print("Added traded pattern: Left Shoulder Time ", TimeToString(lsTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(lsPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log addition of new pattern }
Definimos la función «AddTradedPattern» para realizar un seguimiento de las configuraciones negociadas. Utiliza «lsTime» y «lsPrice» para registrar los detalles del hombro izquierdo, ya que este no se repinta. Comprobamos el tamaño de «tradedPatterns» con la función ArraySize. Si alcanza «MaxTradedPatterns», desplazamos los elementos hacia la izquierda para eliminar los más antiguos. Cambiamos el tamaño de «tradedPatterns» con la función «ArrayResize» para reducirlo. Registramos esto y luego ampliamos «tradedPatterns» utilizando la función ArrayResize para una nueva entrada. Establecemos «leftShoulderTime» en «lsTime» y «leftShoulderPrice» en «lsPrice». Registramos la suma con la función Print, la función TimeToString y la función DoubleToString. Tras la compilación, obtenemos el siguiente resultado.
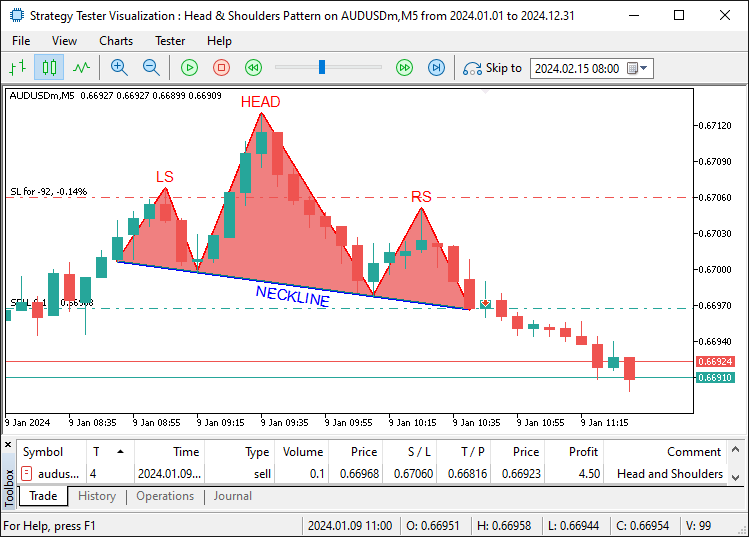
En la imagen podemos ver que no solo visualizamos la configuración, sino que también operamos en consecuencia. El reconocimiento del patrón inverso de cabeza y hombros, la visualización y la operación comercial emplean la misma lógica, pero de manera inversa. Esta es su lógica.
// Inverse Head and Shoulders (Buy) if (DetectInverseHeadAndShoulders(extrema, leftShoulderIdx, headIdx, rightShoulderIdx, necklineStartIdx, necklineEndIdx)) { //--- Check for inverse H&S pattern double closePrice = iClose(_Symbol, _Period, 1); //--- Get the closing price of the previous bar double necklinePrice = extrema[necklineEndIdx].price; //--- Get the price of the neckline end point if (closePrice > necklinePrice) { //--- Check if price has broken above the neckline (buy signal) datetime lsTime = extrema[leftShoulderIdx].time; //--- Get the timestamp of the left shoulder double lsPrice = extrema[leftShoulderIdx].price; //--- Get the price of the left shoulder if (IsPatternTraded(lsTime, lsPrice)) return; //--- Exit if this pattern has already been traded datetime breakoutTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, 1); //--- Get the timestamp of the breakout bar (previous bar) int lsBar = extrema[leftShoulderIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the left shoulder int headBar = extrema[headIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the head int rsBar = extrema[rightShoulderIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the right shoulder int necklineStartBar = extrema[necklineStartIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the neckline start int necklineEndBar = extrema[necklineEndIdx].bar; //--- Get the bar index of the neckline end int breakoutBar = 1; //--- Set breakout bar index (previous bar) int lsToHead = lsBar - headBar; //--- Calculate number of bars from left shoulder to head int headToRs = headBar - rsBar; //--- Calculate number of bars from head to right shoulder int rsToBreakout = rsBar - breakoutBar; //--- Calculate number of bars from right shoulder to breakout int lsToNeckStart = lsBar - necklineStartBar; //--- Calculate number of bars from left shoulder to neckline start double avgPatternRange = (lsToHead + headToRs) / 2.0; //--- Calculate average bar range of the pattern for uniformity check if (rsToBreakout > avgPatternRange * RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier) { //--- Check if breakout distance exceeds allowed range Print("Pattern rejected: Right Shoulder to Breakout (", rsToBreakout, ") exceeds ", RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier, "x average range (", avgPatternRange, ")"); //--- Log rejection due to excessive breakout range return; //--- Exit function if pattern is invalid } double necklineStartPrice = extrema[necklineStartIdx].price; //--- Get the price of the neckline start point double necklineEndPrice = extrema[necklineEndIdx].price; //--- Get the price of the neckline end point datetime necklineStartTime = extrema[necklineStartIdx].time; //--- Get the timestamp of the neckline start point datetime necklineEndTime = extrema[necklineEndIdx].time; //--- Get the timestamp of the neckline end point int barDiff = necklineStartBar - necklineEndBar; //--- Calculate bar difference between neckline points for slope double slope = (necklineEndPrice - necklineStartPrice) / barDiff; //--- Calculate the slope of the neckline (price change per bar) double breakoutNecklinePrice = necklineStartPrice + slope * (necklineStartBar - breakoutBar); //--- Calculate neckline price at breakout point // Extend neckline backwards int extendedBar = necklineStartBar; //--- Initialize extended bar index with neckline start datetime extendedNecklineStartTime = necklineStartTime; //--- Initialize extended neckline start time double extendedNecklineStartPrice = necklineStartPrice; //--- Initialize extended neckline start price bool foundCrossing = false; //--- Flag to track if neckline crosses a bar within range for (int i = necklineStartBar + 1; i < Bars(_Symbol, _Period); i++) { //--- Loop through bars to extend neckline backwards double checkPrice = necklineStartPrice - slope * (i - necklineStartBar); //--- Calculate projected neckline price at bar i if (NecklineCrossesBar(checkPrice, i)) { //--- Check if neckline intersects the bar's high-low range int distance = i - necklineStartBar; //--- Calculate distance from neckline start to crossing bar if (distance <= avgPatternRange * RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier) { //--- Check if crossing is within uniformity range extendedBar = i; //--- Update extended bar index extendedNecklineStartTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, i); //--- Update extended neckline start time extendedNecklineStartPrice = checkPrice; //--- Update extended neckline start price foundCrossing = true; //--- Set flag to indicate crossing found Print("Neckline extended to first crossing bar within uniformity: Bar ", extendedBar); //--- Log successful extension break; //--- Exit loop after finding valid crossing } else { //--- If crossing exceeds uniformity range Print("Crossing bar ", i, " exceeds uniformity (", distance, " > ", avgPatternRange * RightShoulderBreakoutMultiplier, ")"); //--- Log rejection of crossing break; //--- Exit loop as crossing is too far } } } if (!foundCrossing) { //--- If no valid crossing found within range int barsToExtend = 2 * lsToNeckStart; //--- Set fallback extension distance as twice LS to neckline start extendedBar = necklineStartBar + barsToExtend; //--- Calculate extended bar index if (extendedBar >= Bars(_Symbol, _Period)) extendedBar = Bars(_Symbol, _Period) - 1; //--- Cap extended bar at total bars if exceeded extendedNecklineStartTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, extendedBar); //--- Update extended neckline start time extendedNecklineStartPrice = necklineStartPrice - slope * (extendedBar - necklineStartBar); //--- Update extended neckline start price Print("Neckline extended to fallback (2x LS to Neckline Start): Bar ", extendedBar, " (no crossing within uniformity)"); //--- Log fallback extension } Print("Inverse Head and Shoulders Detected:"); //--- Log detection of inverse H&S pattern Print("Left Shoulder: Bar ", lsBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(lsTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(lsPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log left shoulder details Print("Head: Bar ", headBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(extrema[headIdx].time), ", Price ", DoubleToString(extrema[headIdx].price, _Digits)); //--- Log head details Print("Right Shoulder: Bar ", rsBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time), ", Price ", DoubleToString(extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, _Digits)); //--- Log right shoulder details Print("Neckline Start: Bar ", necklineStartBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(necklineStartTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(necklineStartPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log neckline start details Print("Neckline End: Bar ", necklineEndBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(necklineEndTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(necklineEndPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log neckline end details Print("Close Price: ", DoubleToString(closePrice, _Digits)); //--- Log closing price at breakout Print("Breakout Time: ", TimeToString(breakoutTime)); //--- Log breakout timestamp Print("Neckline Price at Breakout: ", DoubleToString(breakoutNecklinePrice, _Digits)); //--- Log neckline price at breakout Print("Extended Neckline Start: Bar ", extendedBar, ", Time ", TimeToString(extendedNecklineStartTime), ", Price ", DoubleToString(extendedNecklineStartPrice, _Digits)); //--- Log extended neckline start details Print("Bar Ranges: LS to Head = ", lsToHead, ", Head to RS = ", headToRs, ", RS to Breakout = ", rsToBreakout, ", LS to Neckline Start = ", lsToNeckStart); //--- Log bar ranges for pattern analysis string prefix = "IHS_" + TimeToString(extrema[headIdx].time, TIME_MINUTES); //--- Create unique prefix for chart objects based on head time // Lines DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_LeftToNeckStart", lsTime, lsPrice, necklineStartTime, necklineStartPrice, clrGreen, 2, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from left shoulder to neckline start DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_NeckStartToHead", necklineStartTime, necklineStartPrice, extrema[headIdx].time, extrema[headIdx].price, clrGreen, 2, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from neckline start to head DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_HeadToNeckEnd", extrema[headIdx].time, extrema[headIdx].price, necklineEndTime, necklineEndPrice, clrGreen, 2, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from head to neckline end DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_NeckEndToRight", necklineEndTime, necklineEndPrice, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, clrGreen, 2, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from neckline end to right shoulder DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_Neckline", extendedNecklineStartTime, extendedNecklineStartPrice, breakoutTime, breakoutNecklinePrice, clrBlue, 2, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw neckline from extended start to breakout DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_RightToBreakout", extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, breakoutTime, breakoutNecklinePrice, clrGreen, 2, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from right shoulder to breakout DrawTrendLine(prefix + "_ExtendedToLeftShoulder", extendedNecklineStartTime, extendedNecklineStartPrice, lsTime, lsPrice, clrGreen, 2, STYLE_SOLID); //--- Draw line from extended neckline to left shoulder // Triangles DrawTriangle(prefix + "_LeftShoulderTriangle", lsTime, lsPrice, necklineStartTime, necklineStartPrice, extendedNecklineStartTime, extendedNecklineStartPrice, clrLightGreen); //--- Draw triangle for left shoulder area DrawTriangle(prefix + "_HeadTriangle", extrema[headIdx].time, extrema[headIdx].price, necklineStartTime, necklineStartPrice, necklineEndTime, necklineEndPrice, clrLightGreen); //--- Draw triangle for head area DrawTriangle(prefix + "_RightShoulderTriangle", extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, necklineEndTime, necklineEndPrice, breakoutTime, breakoutNecklinePrice, clrLightGreen); //--- Draw triangle for right shoulder area // Text Labels DrawText(prefix + "_LS_Label", lsTime, lsPrice, "LS", clrGreen, false); //--- Draw "LS" label below left shoulder DrawText(prefix + "_Head_Label", extrema[headIdx].time, extrema[headIdx].price, "HEAD", clrGreen, false); //--- Draw "HEAD" label below head DrawText(prefix + "_RS_Label", extrema[rightShoulderIdx].time, extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price, "RS", clrGreen, false); //--- Draw "RS" label below right shoulder datetime necklineMidTime = extendedNecklineStartTime + (breakoutTime - extendedNecklineStartTime) / 2; //--- Calculate midpoint time of the neckline double necklineMidPrice = extendedNecklineStartPrice + slope * (iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, extendedNecklineStartTime) - iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, necklineMidTime)); //--- Calculate midpoint price of the neckline // Calculate angle in pixel space int x1 = ShiftToX(iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, extendedNecklineStartTime)); //--- Convert extended neckline start to x-pixel coordinate int y1 = PriceToY(extendedNecklineStartPrice); //--- Convert extended neckline start price to y-pixel coordinate int x2 = ShiftToX(iBarShift(_Symbol, _Period, breakoutTime)); //--- Convert breakout time to x-pixel coordinate int y2 = PriceToY(breakoutNecklinePrice); //--- Convert breakout price to y-pixel coordinate double pixelSlope = (y2 - y1) / (double)(x2 - x1); //--- Calculate slope in pixel space (rise over run) double necklineAngle = -atan(pixelSlope) * 180 / M_PI; //--- Calculate neckline angle in degrees, negated for visual alignment Print("Pixel X1: ", x1, ", Y1: ", y1, ", X2: ", x2, ", Y2: ", y2, ", Pixel Slope: ", DoubleToString(pixelSlope, 4), ", Neckline Angle: ", DoubleToString(necklineAngle, 2)); //--- Log pixel coordinates and angle DrawText(prefix + "_Neckline_Label", necklineMidTime, necklineMidPrice, "NECKLINE", clrBlue, true, necklineAngle); //--- Draw "NECKLINE" label at midpoint with calculated angle double entryPrice = 0; //--- Set entry price to 0 for market order (uses current price) double sl = extrema[rightShoulderIdx].price - BufferPoints * _Point; //--- Calculate stop-loss below right shoulder with buffer double patternHeight = necklinePrice - extrema[headIdx].price; //--- Calculate pattern height from neckline to head double tp = closePrice + patternHeight; //--- Calculate take-profit above close by pattern height if (sl < closePrice && tp > closePrice) { //--- Validate trade direction (SL below, TP above for buy) if (obj_Trade.Buy(LotSize, _Symbol, entryPrice, sl, tp, "Inverse Head and Shoulders")) { //--- Attempt to open a buy trade AddTradedPattern(lsTime, lsPrice); //--- Add pattern to traded list Print("Buy Trade Opened: SL ", DoubleToString(sl, _Digits), ", TP ", DoubleToString(tp, _Digits)); //--- Log successful trade opening } } } }
Ahora solo queda gestionar las posiciones abiertas aplicando una lógica de trailing stop para maximizar los beneficios. Creamos una función para gestionar la lógica final como se muestra a continuación.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Apply trailing stop with minimum profit threshold | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void ApplyTrailingStop(int minTrailPoints, int trailingPoints, CTrade &trade_object, ulong magicNo = 0) { //--- Function to apply trailing stop to open positions double bid = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_BID); //--- Get current bid price double ask = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_ASK); //--- Get current ask price for (int i = PositionsTotal() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { //--- Loop through all open positions from last to first ulong ticket = PositionGetTicket(i); //--- Retrieve position ticket number if (ticket > 0 && PositionSelectByTicket(ticket)) { //--- Check if ticket is valid and select the position if (PositionGetString(POSITION_SYMBOL) == _Symbol && //--- Verify position is for the current symbol (magicNo == 0 || PositionGetInteger(POSITION_MAGIC) == magicNo)) { //--- Check if magic number matches or no magic filter applied double openPrice = PositionGetDouble(POSITION_PRICE_OPEN); //--- Get position opening price double currentSL = PositionGetDouble(POSITION_SL); //--- Get current stop-loss price double currentProfit = PositionGetDouble(POSITION_PROFIT) / (LotSize * SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_TRADE_TICK_VALUE)); //--- Calculate profit in points if (PositionGetInteger(POSITION_TYPE) == POSITION_TYPE_BUY) { //--- Check if position is a Buy double profitPoints = (bid - openPrice) / _Point; //--- Calculate profit in points for Buy position if (profitPoints >= minTrailPoints + trailingPoints) { //--- Check if profit exceeds minimum threshold for trailing double newSL = NormalizeDouble(bid - trailingPoints * _Point, _Digits); //--- Calculate new stop-loss price if (newSL > openPrice && (newSL > currentSL || currentSL == 0)) { //--- Ensure new SL is above open price and better than current SL if (trade_object.PositionModify(ticket, newSL, PositionGetDouble(POSITION_TP))) { //--- Attempt to modify position with new SL Print("Trailing Stop Updated: Ticket ", ticket, ", New SL: ", DoubleToString(newSL, _Digits)); //--- Log successful SL update } } } } else if (PositionGetInteger(POSITION_TYPE) == POSITION_TYPE_SELL) { //--- Check if position is a Sell double profitPoints = (openPrice - ask) / _Point; //--- Calculate profit in points for Sell position if (profitPoints >= minTrailPoints + trailingPoints) { //--- Check if profit exceeds minimum threshold for trailing double newSL = NormalizeDouble(ask + trailingPoints * _Point, _Digits); //--- Calculate new stop-loss price if (newSL < openPrice && (newSL < currentSL || currentSL == 0)) { //--- Ensure new SL is below open price and better than current SL if (trade_object.PositionModify(ticket, newSL, PositionGetDouble(POSITION_TP))) { //--- Attempt to modify position with new SL Print("Trailing Stop Updated: Ticket ", ticket, ", New SL: ", DoubleToString(newSL, _Digits)); //--- Log successful SL update } } } } } } } }
Aquí, añadimos una función de stop dinámico con la función «ApplyTrailingStop». Utiliza «minTrailPoints» y «trailingPoints» para ajustar las posiciones abiertas. Obtenemos los precios de «compra» y «venta» con la función SymbolInfoDouble. Recorremos las posiciones utilizando la función PositionsTotal. Para cada uno, obtenemos el «ticket» con la función PositionGetTicket y lo seleccionamos con la función PositionSelectByTicket. Verificamos el símbolo y «magicNo» utilizando las funciones «PositionGetString» y «PositionGetInteger». Recuperamos «openPrice», «currentSL» y «currentProfit» con la función PositionGetDouble.
Para una compra, calculamos la ganancia con la «oferta» y la comparamos con «minTrailPoints» más «trailingPoints». Si se cumple, establecemos un nuevo «newSL» con la función NormalizeDouble y lo actualizamos mediante el método «PositionModify» en el objeto «trade_object». Para una venta, utilizamos «ask» en su lugar y ajustamos «newSL» a continuación. Se registra la modificación de precio correcta. A continuación, podemos llamar a esta función en el controlador de eventos OnTick.
// Apply trailing stop if enabled and positions exist if (UseTrailingStop && PositionsTotal() > 0) { //--- Check if trailing stop is enabled and there are open positions ApplyTrailingStop(MinTrailPoints, TrailingPoints, obj_Trade, MagicNumber); //--- Apply trailing stop to positions with specified parameters }
Lo único que necesitamos para asegurarnos de que el trailing stop esté habilitado es llamar a la función con los parámetros de entrada. Lo que queda ahora es liberar las matrices de almacenamiento una vez que el programa ya no se utilice y eliminar los objetos visuales que hemos mapeado. Nos ocupamos de eso en el controlador de eventos OnDeinit.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { //--- Expert Advisor deinitialization function ArrayFree(tradedPatterns); //--- Free memory used by tradedPatterns array ObjectsDeleteAll(0, "HS_"); //--- Delete all chart objects with "HS_" prefix (standard H&S) ObjectsDeleteAll(0, "IHS_"); //--- Delete all chart objects with "IHS_" prefix (inverse H&S) ChartRedraw(); //--- Redraw the chart to remove deleted objects }
En el controlador de eventos OnDeinit, que se ejecuta cuando se cierra el Asesor Experto, limpiamos el programa y el gráfico al que está vinculado. Utilizamos la función ArrayFree para liberar memoria de «tradedPatterns». A continuación, eliminamos todos los objetos del gráfico. La función ObjectsDeleteAll borra los elementos con el prefijo «HS_» para los patrones estándar. También elimina aquellos con el prefijo «IHS_» para patrones inversos. Por último, actualizamos el gráfico. La función ChartRedraw actualiza la visualización para reflejar estos cambios antes del cierre total. Tras la compilación, obtenemos el siguiente resultado.
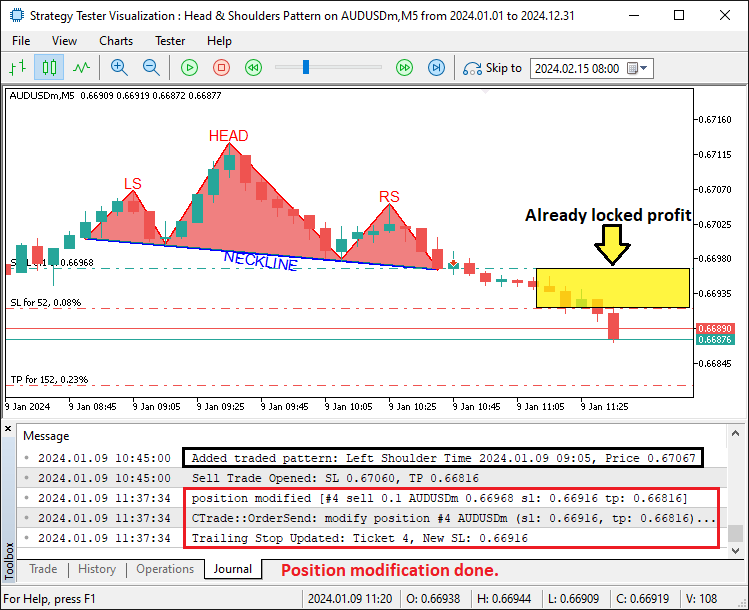
En la imagen podemos ver que aplicamos un trailing stop a la configuración negociada, logrando así nuestro objetivo. Lo que queda por hacer es realizar pruebas retrospectivas del programa, lo cual se aborda en la siguiente sección.
Prueba retrospectiva
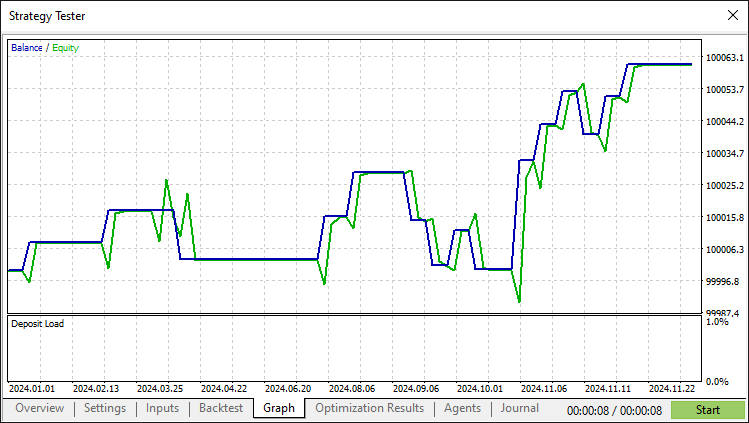
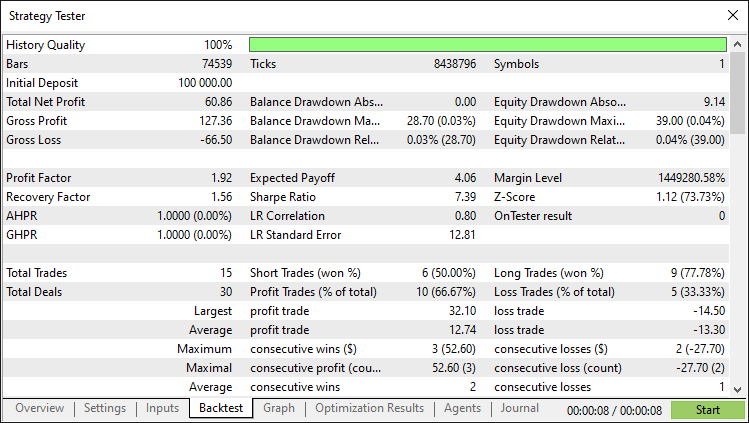
Tras realizar exhaustivas pruebas retrospectivas, hemos obtenido los siguientes resultados.
Gráfico de prueba retrospectiva:
Informe de prueba retrospectiva:
Conclusión
En conclusión, hemos creado con éxito un algoritmo de trading Hombro-Cabeza-Hombro en MQL5. Cuenta con detección precisa de patrones, visualización detallada y ejecución automatizada de operaciones para la señal de reversión clásica. Mediante el uso de reglas de validación, trazado de cuellos y stops dinámicos, nuestro Asesor Experto se adapta eficazmente a los cambios del mercado. Puede utilizar las ilustraciones como punto de partida para mejorarlo con pasos adicionales, como el ajuste de parámetros o controles de riesgo avanzados. Además, hay que tener en cuenta que se trata de una configuración de patrón poco habitual.
Descargo de responsabilidad: Este artículo tiene fines exclusivamente educativos. El trading conlleva un riesgo financiero significativo y las condiciones del mercado pueden ser impredecibles. Es esencial realizar pruebas retrospectivas adecuadas y gestionar los riesgos antes de la implementación en vivo.
Con esta base, podrá perfeccionar sus habilidades comerciales y mejorar este algoritmo. Siga probando y optimizando para alcanzar el éxito. ¡Mucha suerte!
Traducción del inglés realizada por MetaQuotes Ltd.
Artículo original: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/17618
Advertencia: todos los derechos de estos materiales pertenecen a MetaQuotes Ltd. Queda totalmente prohibido el copiado total o parcial.
Este artículo ha sido escrito por un usuario del sitio web y refleja su punto de vista personal. MetaQuotes Ltd. no se responsabiliza de la exactitud de la información ofrecida, ni de las posibles consecuencias del uso de las soluciones, estrategias o recomendaciones descritas.
 Asesor experto de scalping Ilan 3.0 Ai con aprendizaje automático
Asesor experto de scalping Ilan 3.0 Ai con aprendizaje automático
 Redes neuronales en el trading: Detección de anomalías en el dominio de la frecuencia (Final)
Redes neuronales en el trading: Detección de anomalías en el dominio de la frecuencia (Final)
 Implementación de un modelo de tabla en MQL5: Aplicación del concepto MVC (Modelo-Vista-Controlador)
Implementación de un modelo de tabla en MQL5: Aplicación del concepto MVC (Modelo-Vista-Controlador)
 Estrategias de reversión a la media con RSI2 de Larry Connors para operativa intradía
Estrategias de reversión a la media con RSI2 de Larry Connors para operativa intradía
- Aplicaciones de trading gratuitas
- 8 000+ señales para copiar
- Noticias económicas para analizar los mercados financieros
Usted acepta la política del sitio web y las condiciones de uso