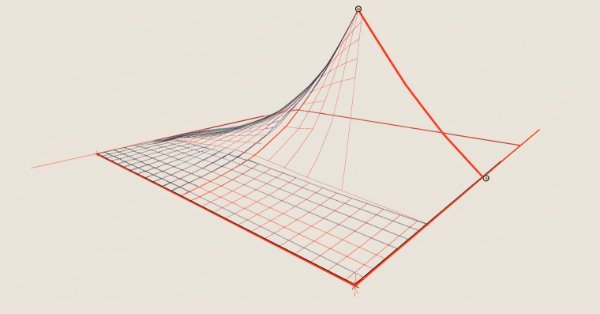
Neural Network in Practice: Least Squares
In this article, we'll look at a few ideas, including how mathematical formulas are more complex in appearance than when implemented in code. In addition, we will consider how to set up a chart quadrant, as well as one interesting problem that may arise in your MQL5 code. Although, to be honest, I still don't quite understand how to explain it. Anyway, I'll show you how to fix it in code.
Biological neuron for forecasting financial time series
We will build a biologically correct system of neurons for time series forecasting. The introduction of a plasma-like environment into the neural network architecture creates a kind of "collective intelligence," where each neuron influences the system's operation not only through direct connections, but also through long-range electromagnetic interactions. Let's see how the neural brain modeling system will perform in the market.

Exploring Machine Learning in Unidirectional Trend Trading Using Gold as a Case Study
This article discusses an approach to trading only in the chosen direction (buy or sell). For this purpose, the technique of causal inference and machine learning are used.

Overcoming The Limitation of Machine Learning (Part 1): Lack of Interoperable Metrics
There is a powerful and pervasive force quietly corrupting the collective efforts of our community to build reliable trading strategies that employ AI in any shape or form. This article establishes that part of the problems we face, are rooted in blind adherence to "best practices". By furnishing the reader with simple real-world market-based evidence, we will reason to the reader why we must refrain from such conduct, and rather adopt domain-bound best practices if our community should stand any chance of recovering the latent potential of AI.

African Buffalo Optimization (ABO)
The article presents the African Buffalo Optimization (ABO) algorithm, a metaheuristic approach developed in 2015 based on the unique behavior of these animals. The article describes in detail the stages of the algorithm implementation and its efficiency in finding solutions to complex problems, which makes it a valuable tool in the field of optimization.
MQL5 Wizard Techniques you should know (Part 68): Using Patterns of TRIX and the Williams Percent Range with a Cosine Kernel Network
We follow up our last article, where we introduced the indicator pair of TRIX and Williams Percent Range, by considering how this indicator pairing could be extended with Machine Learning. TRIX and William’s Percent are a trend and support/ resistance complimentary pairing. Our machine learning approach uses a convolution neural network that engages the cosine kernel in its architecture when fine-tuning the forecasts of this indicator pairing. As always, this is done in a custom signal class file that works with the MQL5 wizard to assemble an Expert Advisor.
Brain Storm Optimization algorithm (Part I): Clustering
In this article, we will look at an innovative optimization method called BSO (Brain Storm Optimization) inspired by a natural phenomenon called "brainstorming". We will also discuss a new approach to solving multimodal optimization problems the BSO method applies. It allows finding multiple optimal solutions without the need to pre-determine the number of subpopulations. We will also consider the K-Means and K-Means++ clustering methods.
Overcoming The Limitation of Machine Learning (Part 2): Lack of Reproducibility
The article explores why trading results can differ significantly between brokers, even when using the same strategy and financial symbol, due to decentralized pricing and data discrepancies. The piece helps MQL5 developers understand why their products may receive mixed reviews on the MQL5 Marketplace, and urges developers to tailor their approaches to specific brokers to ensure transparent and reproducible outcomes. This could grow to become an important domain-bound best practice that will serve our community well if the practice were to be widely adopted.

Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for Synthetic Data in Financial Modeling (Part 2): Creating Synthetic Symbol for Testing
In this article we are creating a synthetic symbol using a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) involves generating realistic Financial data that mimics the behavior of actual market instruments, such as EURUSD. The GAN model learns patterns and volatility from historical market data and creates synthetic price data with similar characteristics.

Causal inference in time series classification problems
In this article, we will look at the theory of causal inference using machine learning, as well as the custom approach implementation in Python. Causal inference and causal thinking have their roots in philosophy and psychology and play an important role in our understanding of reality.

Overcoming The Limitation of Machine Learning (Part 9): Correlation-Based Feature Learning in Self-Supervised Finance
Self-supervised learning is a powerful paradigm of statistical learning that searches for supervisory signals generated from the observations themselves. This approach reframes challenging unsupervised learning problems into more familiar supervised ones. This technology has overlooked applications for our objective as a community of algorithmic traders. Our discussion, therefore, aims to give the reader an approachable bridge into the open research area of self-supervised learning and offers practical applications that provide robust and reliable statistical models of financial markets without overfitting to small datasets.

MQL5 Wizard Techniques you should know (14): Multi Objective Timeseries Forecasting with STF
Spatial Temporal Fusion which is using both ‘space’ and time metrics in modelling data is primarily useful in remote-sensing, and a host of other visual based activities in gaining a better understanding of our surroundings. Thanks to a published paper, we take a novel approach in using it by examining its potential to traders.

Applying Localized Feature Selection in Python and MQL5
This article explores a feature selection algorithm introduced in the paper 'Local Feature Selection for Data Classification' by Narges Armanfard et al. The algorithm is implemented in Python to build binary classifier models that can be integrated with MetaTrader 5 applications for inference.

MQL5 Wizard Techniques you should know (Part 47): Reinforcement Learning with Temporal Difference
Temporal Difference is another algorithm in reinforcement learning that updates Q-Values basing on the difference between predicted and actual rewards during agent training. It specifically dwells on updating Q-Values without minding their state-action pairing. We therefore look to see how to apply this, as we have with previous articles, in a wizard assembled Expert Advisor.

Analyzing weather impact on currencies of agricultural countries using Python
What is the relationship between weather and Forex? Classical economic theory has long ignored the influence of such factors as weather on market behavior. But everything has changed. Let's try to find connections between the weather conditions and the position of agricultural currencies on the market.

Reimagining Classic Strategies (Part 14): High Probability Setups
High probability Setups are well known in our trading community, but regrettably they are not well-defined. In this article, we will aim to find an empirical and algorithmic way of defining exactly what is a high probability setup, identifying and exploiting them. By using Gradient Boosting Trees, we demonstrated how the reader can improve the performance of an arbitrary trading strategy and better communicate the exact job to be done to our computer in a more meaningful and explicit manner.
Integrating MQL5 with data processing packages (Part 3): Enhanced Data Visualization
In this article, we will perform Enhanced Data Visualization by going beyond basic charts by incorporating features like interactivity, layered data, and dynamic elements, enabling traders to explore trends, patterns, and correlations more effectively.

Data Science and ML (Part 44): Forex OHLC Time series Forecasting using Vector Autoregression (VAR)
Explore how Vector Autoregression (VAR) models can forecast Forex OHLC (Open, High, Low, and Close) time series data. This article covers VAR implementation, model training, and real-time forecasting in MetaTrader 5, helping traders analyze interdependent currency movements and improve their trading strategies.

Population optimization algorithms: Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA)
Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA) is a metaheuristic algorithm inspired by the behavior and hunting strategies of humpback whales. The main idea of WOA is to mimic the so-called "bubble-net" feeding method, in which whales create bubbles around prey and then attack it in a spiral motion.

Neural Networks in Trading: Hierarchical Dual-Tower Transformer (Final Part)
We continue to build the Hidformer hierarchical dual-tower transformer model designed for analyzing and forecasting complex multivariate time series. In this article, we will bring the work we started earlier to its logical conclusion — we will test the model on real historical data.

Neural Networks in Trading: Memory Augmented Context-Aware Learning for Cryptocurrency Markets (Final Part)
The MacroHFT framework for high-frequency cryptocurrency trading uses context-aware reinforcement learning and memory to adapt to dynamic market conditions. At the end of this article, we will test the implemented approaches on real historical data to assess their effectiveness.

Mutual information as criteria for Stepwise Feature Selection
In this article, we present an MQL5 implementation of Stepwise Feature Selection based on the mutual information between an optimal predictor set and a target variable.

Exploring Machine Learning in Unidirectional Trend Trading Using Gold as a Case Study
This article discusses an approach to trading only in the chosen direction (buy or sell). For this purpose, the technique of causal inference and machine learning are used.

Ensemble methods to enhance classification tasks in MQL5
In this article, we present the implementation of several ensemble classifiers in MQL5 and discuss their efficacy in varying situations.

Artificial Tribe Algorithm (ATA)
The article provides a detailed discussion of the key components and innovations of the ATA optimization algorithm, which is an evolutionary method with a unique dual behavior system that adapts depending on the situation. ATA combines individual and social learning while using crossover for explorations and migration to find solutions when stuck in local optima.

Population optimization algorithms: Evolution of Social Groups (ESG)
We will consider the principle of constructing multi-population algorithms. As an example of this type of algorithm, we will have a look at the new custom algorithm - Evolution of Social Groups (ESG). We will analyze the basic concepts, population interaction mechanisms and advantages of this algorithm, as well as examine its performance in optimization problems.

Neural Networks in Trading: Reducing Memory Consumption with Adam-mini Optimization
One of the directions for increasing the efficiency of the model training and convergence process is the improvement of optimization methods. Adam-mini is an adaptive optimization method designed to improve on the basic Adam algorithm.

Role of random number generator quality in the efficiency of optimization algorithms
In this article, we will look at the Mersenne Twister random number generator and compare it with the standard one in MQL5. We will also find out the influence of the random number generator quality on the results of optimization algorithms.
Population optimization algorithms: Charged System Search (CSS) algorithm
In this article, we will consider another optimization algorithm inspired by inanimate nature - Charged System Search (CSS) algorithm. The purpose of this article is to present a new optimization algorithm based on the principles of physics and mechanics.

Population optimization algorithms: Artificial Multi-Social Search Objects (MSO)
This is a continuation of the previous article considering the idea of social groups. The article explores the evolution of social groups using movement and memory algorithms. The results will help to understand the evolution of social systems and apply them in optimization and search for solutions.

MQL5 Wizard Techniques you should know (Part 20): Symbolic Regression
Symbolic Regression is a form of regression that starts with minimal to no assumptions on what the underlying model that maps the sets of data under study would look like. Even though it can be implemented by Bayesian Methods or Neural Networks, we look at how an implementation with Genetic Algorithms can help customize an expert signal class usable in the MQL5 wizard.

MQL5 Wizard Techniques you should know (Part 85): Using Patterns of Stochastic-Oscillator and the FrAMA with Beta VAE Inference Learning
This piece follows up ‘Part-84’, where we introduced the pairing of Stochastic and the Fractal Adaptive Moving Average. We now shift focus to Inference Learning, where we look to see if laggard patterns in the last article could have their fortunes turned around. The Stochastic and FrAMA are a momentum-trend complimentary pairing. For our inference learning, we are revisiting the Beta algorithm of a Variational Auto Encoder. We also, as always, do the implementation of a custom signal class designed for integration with the MQL5 Wizard.

MQL5 Wizard Techniques you should know (Part 54): Reinforcement Learning with hybrid SAC and Tensors
Soft Actor Critic is a Reinforcement Learning algorithm that we looked at in a previous article, where we also introduced python and ONNX to these series as efficient approaches to training networks. We revisit the algorithm with the aim of exploiting tensors, computational graphs that are often exploited in Python.

Neural networks made easy (Part 63): Unsupervised Pretraining for Decision Transformer (PDT)
We continue to discuss the family of Decision Transformer methods. From previous article, we have already noticed that training the transformer underlying the architecture of these methods is a rather complex task and requires a large labeled dataset for training. In this article we will look at an algorithm for using unlabeled trajectories for preliminary model training.
Bacterial Chemotaxis Optimization (BCO)
The article presents the original version of the Bacterial Chemotaxis Optimization (BCO) algorithm and its modified version. We will take a closer look at all the differences, with a special focus on the new version of BCOm, which simplifies the bacterial movement mechanism, reduces the dependence on positional history, and uses simpler math than the computationally heavy original version. We will also conduct the tests and summarize the results.
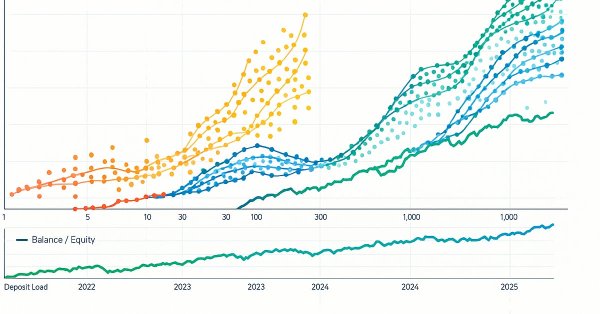
Overcoming The Limitation of Machine Learning (Part 4): Overcoming Irreducible Error Using Multiple Forecast Horizons
Machine learning is often viewed through statistical or linear algebraic lenses, but this article emphasizes a geometric perspective of model predictions. It demonstrates that models do not truly approximate the target but rather map it onto a new coordinate system, creating an inherent misalignment that results in irreducible error. The article proposes that multi-step predictions, comparing the model’s forecasts across different horizons, offer a more effective approach than direct comparisons with the target. By applying this method to a trading model, the article demonstrates significant improvements in profitability and accuracy without changing the underlying model.
Population optimization algorithms: Micro Artificial immune system (Micro-AIS)
The article considers an optimization method based on the principles of the body's immune system - Micro Artificial Immune System (Micro-AIS) - a modification of AIS. Micro-AIS uses a simpler model of the immune system and simple immune information processing operations. The article also discusses the advantages and disadvantages of Micro-AIS compared to conventional AIS.

Population optimization algorithms: Binary Genetic Algorithm (BGA). Part I
In this article, we will explore various methods used in binary genetic and other population algorithms. We will look at the main components of the algorithm, such as selection, crossover and mutation, and their impact on the optimization. In addition, we will study data presentation methods and their impact on optimization results.

Quantization in machine learning (Part 2): Data preprocessing, table selection, training CatBoost models
The article considers the practical application of quantization in the construction of tree models. The methods for selecting quantum tables and data preprocessing are considered. No complex mathematical equations are used.

MQL5 Wizard Techniques you should know (Part 35): Support Vector Regression
Support Vector Regression is an idealistic way of finding a function or ‘hyper-plane’ that best describes the relationship between two sets of data. We attempt to exploit this in time series forecasting within custom classes of the MQL5 wizard.