
在MQL5中构建带自定义画布图形的凯特纳通道(Keltner Channel)指标
概述
在本文中,我们将使用MQL5构建一个带有高级自定义画布图形的凯特纳通道指标 。凯特纳通道通过MA和ATR指标计算动态支撑与阻力位,帮助交易者识别趋势方向及潜在突破机会。本文将涵盖以下主题:
- 凯特纳通道指标详解
- 架构设计:指标逻辑拆解
- 在MQL5中的实现
- 集成自定义画布图形
- 凯特纳通道指标回测
- 结论
凯特纳通道指标详解
凯特纳通道指标是一种基于波动率的交易工具,它结合MA平滑价格数据,并利用ATR设定动态支撑与阻力位。该指标由三条线构成一个通道。中轨为MA,通常选择能反映当前趋势的周期。上轨和下轨则通过在中轨的基础上加减ATR的倍数生成。这种方法使指标能动态适应市场波动,帮助交易者更清晰地识别潜在突破点或价格反转区域。
这种方法使指标能动态适应市场波动,帮助交易者更清晰地识别潜在突破点或价格反转区域。当价格突破上轨或下轨时,表明市场可能超买/超卖,或即将出现反转,为趋势跟踪和均值回归策略提供可操作的信号。其动态意味着该指标能够能随市场波动率变化而调整,确保支撑位和阻力位在市场条件变化时始终保持相关性。一个直观示例如下:
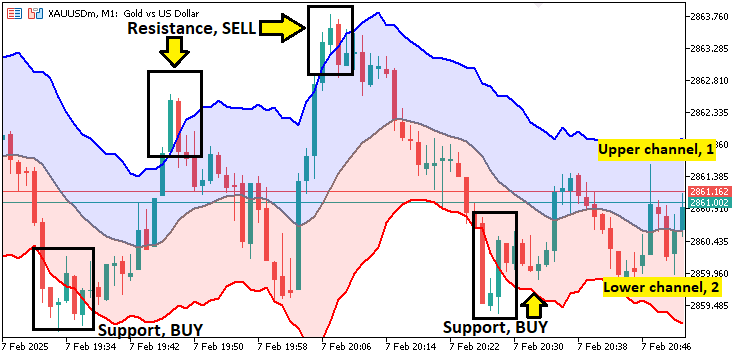
架构设计:指标逻辑拆解
我们将基于清晰的职责分离来构建该指标的架构,涵盖三大核心模块:输入参数、指标 缓冲区和图形属性。首先,我们将定义关键输入参数,例如移动平均周期、ATR周期和ATR乘数,这些参数将直接决定指标的行为表现。接着,我们将分配三个缓冲区,分别用于存储上轨、中轨和下轨的计算值。这些缓冲区将通过MQL5内置函数与图形绘图关联,并配置颜色、线宽、绘制偏移等属性。此外,我们将利用内置函数完成动态计算,确保指标能实时适应市场波动率的变化。
为保障稳定性,我们将加入错误处理机制,确保指标句柄创建成功,为后续的指标计算提供可靠基础。除核心逻辑外,我们还将集成自定义画布图形,通过创建叠加于图表上的位图标签提升视觉呈现效果。这种模块化设计不仅简化了调试与未来维护,还确保了从数据计算到图形输出的各组件协同运作,最终交付一款功能强大且视觉优化的交易工具。简言之,我们将实现三个目标。
在MQL5中的实现
要在MQL5中创建该指标,只需打开MetaEditor,进入导航,找到指标文件夹,点击“新建”选项卡,并按照提示完成文件创建。文件创建后,在编码环境中,我们将定义指标的属性与设置,包括缓冲区数量、绘图配置,以及每条线的颜色、线宽和标签等个性化属性。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Keltner Channel Canvas Indicator.mq5 | //| Copyright 2025, Forex Algo-Trader, Allan. | //| "https://t.me/Forex_Algo_Trader" | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Forex Algo-Trader, Allan" #property link "https://t.me/Forex_Algo_Trader" #property version "1.00" #property description "Description: Keltner Channel Indicator" #property indicator_chart_window //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Indicator properties and settings | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // Define the number of buffers used for plotting data on the chart #property indicator_buffers 3 // We will use 3 buffers: Upper Channel, Middle (MA) line, and Lower Channel // Define the number of plots on the chart #property indicator_plots 3 // We will plot 3 lines (Upper, Middle, and Lower) //--- Plot settings for the Upper Keltner Channel line #property indicator_type1 DRAW_LINE // Draw the Upper Channel as a line #property indicator_color1 clrBlue // Set the color of the Upper Channel to Blue #property indicator_label1 "Upper Keltner" // Label of the Upper Channel line in the Data Window #property indicator_width1 2 // Set the line width of the Upper Channel to 2 pixels //--- Plot settings for the Middle Keltner Channel line (the moving average) #property indicator_type2 DRAW_LINE // Draw the Middle (MA) Channel as a line #property indicator_color2 clrGray // Set the color of the Middle (MA) Channel to Gray #property indicator_label2 "Middle Keltner" // Label of the Middle (MA) line in the Data Window #property indicator_width2 2 // Set the line width of the Middle (MA) to 2 pixels //--- Plot settings for the Lower Keltner Channel line #property indicator_type3 DRAW_LINE // Draw the Lower Channel as a line #property indicator_color3 clrRed // Set the color of the Lower Channel to Red #property indicator_label3 "Lower Keltner" // Label of the Lower Channel line in the Data Window #property indicator_width3 2 // Set the line width of the Lower Channel to 2 pixels
我们首先使用#property关键字设置指标的基本信息(metadata),例如版本号。接下来,通过indicator_buffers属性分配三个指标缓冲区,用于存储并管理“上轨”、“中轨MA”和“下轨”的计算值。同时,我们将indicator_plots设置为3,定义图表上需绘制三个独立的图形。针对每个图形,我们进一步配置其可视化属性:
- 上凯特纳通道:我们将绘制类型设为DRAW_LINE宏,表示以连续线条的形式呈现。通过clrBlue设置颜色为蓝色,并在数据窗口中添加标签“Upper Keltner”以便识别。线宽设置为2像素,以增强可见性。
- 中凯特纳通道(MA)):同样将类型设为"DRAW_LINE",颜色选用"灰色",并分配标签"Middle Keltner"。该线代表核心移动平均线,作为上下轨计算的基准参考。
- 下凯特纳通道:此线也定义为DRAW_LINE类型,颜色设为"红色",与其他线条区分开。分配标签"Lower Keltner",线宽同样设置为2像素。
完成上述属性配置后,我们即可进入定义输入参数的环节。
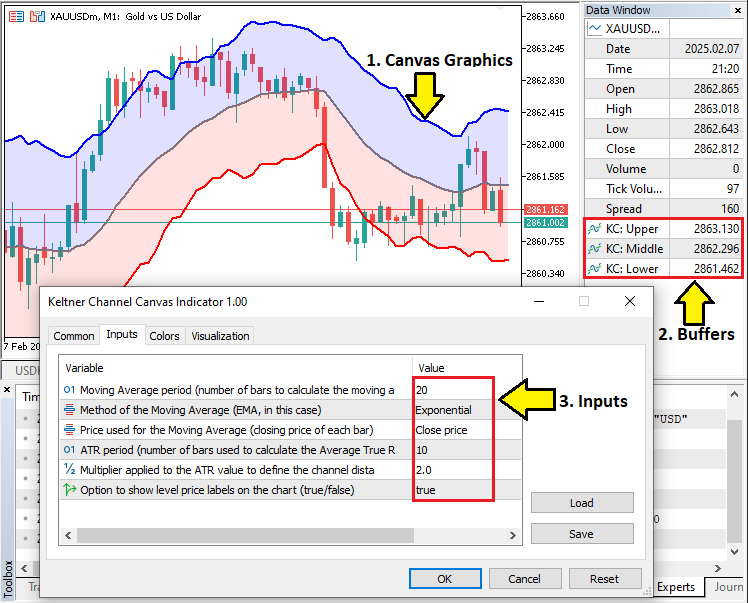
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Input parameters for the indicator | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Moving Average parameters input int maPeriod=20; // Moving Average period (number of bars to calculate the moving average) input ENUM_MA_METHOD maMethod=MODE_EMA; // Method of the Moving Average (EMA, in this case) input ENUM_APPLIED_PRICE maPrice=PRICE_CLOSE; // Price used for the Moving Average (closing price of each bar) //--- ATR parameters input int atrPeriod=10; // ATR period (number of bars used to calculate the Average True Range) input double atrMultiplier=2.0; // Multiplier applied to the ATR value to define the channel distance (upper and lower limits) input bool showPriceLabel=true; // Option to show level price labels on the chart (true/false)
接下来,我们定义输入参数属性。对于移动平均线,设置参数"maPeriod"(默认值20)以确定计算所用的K线数量。参数"maMethod"的数据类型为ENUM_MA_METHOD,设为"MODE_EMA",表示采用指数移动平均(EMA);参数"maPrice"的数据类型为ENUM_APPLIED_PRICE,设置为"PRICE_CLOSE",即计算基于收盘价。
对于ATR,参数"atrPeriod"(默认值10)决定计算波动率所用的K线数量,而参数"atrMultiplier"(默认值2.0)则设定上下轨与移动平均线的距离倍数。最后,参数"showPriceLabel"(默认值true)控制是否在图表上显示价格标签。这些设置将确保指标能够灵活适应不同的市场条件。最后,我们需要定义即将使用的指标句柄。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Indicator handle declarations | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Indicator handles for the Moving Average and ATR int maHandle = INVALID_HANDLE; // Handle for Moving Average (used to store the result of iMA) int atrHandle = INVALID_HANDLE; // Handle for ATR (used to store the result of iATR) //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Indicator buffers (arrays for storing calculated values) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Buffers for storing the calculated indicator values double upperChannelBuffer[]; // Buffer to store the Upper Channel values (Moving Average + ATR * Multiplier) double movingAverageBuffer[]; // Buffer to store the Moving Average values (middle of the channel) double lowerChannelBuffer[]; // Buffer to store the Lower Channel values (Moving Average - ATR * Multiplier) //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Global variables for the parameter values | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- These variables store the actual input parameter values, if necessary for any further use or calculations int maPeriodValue; // Store the Moving Average period value int atrPeriodValue; // Store the ATR period value double atrMultiplierValue; // Store the ATR multiplier value //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
接下来,我们声明凯特纳通道计算所需的指标句柄、缓冲区以及部分全局变量。这些句柄用于存储对其他指标的引用,使我们能够动态获取其计算值。我们将"maHandle"和"atrHandle"初始化为 INVALID_HANDLE,以确保在赋值前正确管理句柄资源。
随后,我们定义指标缓冲区,用这些数组存储计算值以便绘图。"upperChannelBuffer"存储上轨数值,"movingAverageBuffer"存储中轨移动平均线数值,而"lowerChannelBuffer"则存储下轨数值。这些缓冲区将确保凯特纳通道在图表上实现平滑可视化。最后,我们引入全局变量以存储输入参数,供后续计算使用。"maPeriodValue"和"atrPeriodValue"分别存储用户定义的MA和ATR周期,而"atrMultiplierValue"则存储用于确定通道宽度的倍数参数。现在,我们可以进入初始化事件处理程序,在此完成所有必要的指标绘图、数据映射以及指标句柄的初始化工作。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- Indicator buffers mapping // Indicator buffers are used to store calculated indicator values. // We link each buffer to a graphical plot for visual representation. SetIndexBuffer(0, upperChannelBuffer, INDICATOR_DATA); // Buffer for the upper channel line SetIndexBuffer(1, movingAverageBuffer, INDICATOR_DATA); // Buffer for the middle (moving average) line SetIndexBuffer(2, lowerChannelBuffer, INDICATOR_DATA); // Buffer for the lower channel line //--- Set the starting position for drawing each plot // The drawing for each line will only begin after a certain number of bars have passed // This is to avoid showing incomplete calculations at the start PlotIndexSetInteger(0, PLOT_DRAW_BEGIN, maPeriod + 1); // Start drawing Upper Channel after 'maPeriod + 1' bars PlotIndexSetInteger(1, PLOT_DRAW_BEGIN, maPeriod + 1); // Start drawing Middle (MA) after 'maPeriod + 1' bars PlotIndexSetInteger(2, PLOT_DRAW_BEGIN, maPeriod + 1); // Start drawing Lower Channel after 'maPeriod + 1' bars //--- Set an offset for the plots // This shifts the plotted lines by 1 bar to the right, ensuring that the values are aligned properly PlotIndexSetInteger(0, PLOT_SHIFT, 1); // Shift the Upper Channel by 1 bar to the right PlotIndexSetInteger(1, PLOT_SHIFT, 1); // Shift the Middle (MA) by 1 bar to the right PlotIndexSetInteger(2, PLOT_SHIFT, 1); // Shift the Lower Channel by 1 bar to the right //--- Define an "empty value" for each plot // Any buffer value set to this value will not be drawn on the chart // This is useful for gaps where there are no valid indicator values PlotIndexSetDouble(0, PLOT_EMPTY_VALUE, 0.0); // Empty value for Upper Channel PlotIndexSetDouble(1, PLOT_EMPTY_VALUE, 0.0); // Empty value for Middle (MA) PlotIndexSetDouble(2, PLOT_EMPTY_VALUE, 0.0); // Empty value for Lower Channel //--- Set the short name of the indicator (displayed in the chart and Data Window) // This sets the name of the indicator that appears on the chart IndicatorSetString(INDICATOR_SHORTNAME, "Keltner Channel"); //--- Customize the label for each buffer in the Data Window // This allows for better identification of the individual plots in the Data Window string short_name = "KC:"; // Shortened name of the indicator PlotIndexSetString(0, PLOT_LABEL, short_name + " Upper"); // Label for the Upper Channel PlotIndexSetString(1, PLOT_LABEL, short_name + " Middle"); // Label for the Middle (MA) PlotIndexSetString(2, PLOT_LABEL, short_name + " Lower"); // Label for the Lower Channel //--- Set the number of decimal places for the indicator values // _Digits is the number of decimal places used in the current chart symbol IndicatorSetInteger(INDICATOR_DIGITS, _Digits); // Ensures indicator values match the chart's price format //--- Create indicators (Moving Average and ATR) // These are handles (IDs) for the built-in indicators used to calculate the Keltner Channel // iMA = Moving Average (EMA in this case), iATR = Average True Range maHandle = iMA(NULL, 0, maPeriod, 0, maMethod, maPrice); // Create MA handle (NULL = current chart, 0 = current timeframe) atrHandle = iATR(NULL, 0, atrPeriod); // Create ATR handle (NULL = current chart, 0 = current timeframe) //--- Error handling for indicator creation // Check if the handle for the Moving Average (MA) is valid if(maHandle == INVALID_HANDLE) { // If the handle is invalid, print an error message and return failure code Print("UNABLE TO CREATE THE MA HANDLE REVERTING NOW!"); return (INIT_FAILED); // Initialization failed } // Check if the handle for the ATR is valid if(atrHandle == INVALID_HANDLE) { // If the handle is invalid, print an error message and return failure code Print("UNABLE TO CREATE THE ATR HANDLE REVERTING NOW!"); return (INIT_FAILED); // Initialization failed } //--- Return success code // If everything works correctly, we return INIT_SUCCEEDED to signal successful initialization return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
在OnInit事件处理程序中,我们通过配置缓冲区、绘图属性、偏移量以及句柄,完成凯特纳通道指标的初始化工作,以确保其可视化与计算正确性。首先,我们使用SetIndexBuffer函数将每个指标缓冲区与其对应的图形绘图关联起来,确保“上轨”、“中轨MA”、“下轨”能够正确地显示在图表上。
接下来,我们使用PlotIndexSetInteger函数定义绘图行为。我们设置绘图起始位置仅在“maPeriod + 1”根K线之后开始,以避免因计算不完整而显示错误数据。此外,通过 PLOT_SHIFT参数设置向右偏移量,确保绘制的数值与图表对齐。。为处理缺失数据,我们使用PlotIndexSetDouble函数为每个缓冲区分配空值“0.0”。
随后,我们配置显示设置。使用IndicatorSetString函数设置指标名称,并通过PlotIndexSetString函数为“数据窗口”(Data Window)中的每条线分配标签。通过"IndicatorSetInteger"函数,将指标数值的小数精度与图表的价格显示格式保持一致。最后,我们使用iMA和iATR函数创建指标句柄。若任一句柄创建失败,则通过Print函数输出错误信息,并返回INIT_FAILED以终止初始化。若所有操作均成功,则返回INIT_SUCCEEDED,完成初始化流程。接下来,我们可以进入核心事件处理程序,进行指标的具体计算。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator iteration function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnCalculate(const int rates_total, // Total number of bars in the price series const int prev_calculated, // Number of previously calculated bars const datetime &time[], // Array of time values for each bar const double &open[], // Array of open prices for each bar const double &high[], // Array of high prices for each bar const double &low[], // Array of low prices for each bar const double &close[], // Array of close prices for each bar const long &tick_volume[], // Array of tick volumes for each bar const long &volume[], // Array of trade volumes for each bar const int &spread[]) // Array of spreads for each bar { //--- Check if this is the first time the indicator is being calculated if(prev_calculated == 0) // If no previous bars were calculated, it means this is the first calculation { //--- Initialize indicator buffers (upper, middle, and lower) with zeros ArrayFill(upperChannelBuffer, 0, rates_total, 0); // Fill the entire upper channel buffer with 0s ArrayFill(movingAverageBuffer, 0, rates_total, 0); // Fill the moving average buffer with 0s ArrayFill(lowerChannelBuffer, 0, rates_total, 0); // Fill the lower channel buffer with 0s //--- Copy Exponential Moving Average (EMA) values into the moving average buffer // This function requests 'rates_total' values from the MA indicator (maHandle) and copies them into movingAverageBuffer if(CopyBuffer(maHandle, 0, 0, rates_total, movingAverageBuffer) < 0) return(0); // If unable to copy data, stop execution and return 0 //--- Copy Average True Range (ATR) values into a temporary array called atrValues double atrValues[]; if(CopyBuffer(atrHandle, 0, 0, rates_total, atrValues) < 0) return(0); // If unable to copy ATR data, stop execution and return 0 //--- Define the starting bar for calculations // We need to make sure we have enough data to calculate both the MA and ATR, so we start after the longest required period. int startBar = MathMax(maPeriod, atrPeriod) + 1; // Ensure sufficient bars for both EMA and ATR calculations //--- Loop from startBar to the total number of bars (rates_total) for(int i = startBar; i < rates_total; i++) { // Calculate the upper and lower channel boundaries for each bar upperChannelBuffer[i] = movingAverageBuffer[i] + atrMultiplier * atrValues[i]; // Upper channel = EMA + ATR * Multiplier lowerChannelBuffer[i] = movingAverageBuffer[i] - atrMultiplier * atrValues[i]; // Lower channel = EMA - ATR * Multiplier } //--- Calculation is complete, so we return the total number of rates (bars) calculated return(rates_total); } }
在OnCalculate事件处理程序中,我们实现了凯特纳通道指标的核心计算逻辑。该函数通过遍历价格数据来计算并更新指标缓冲区。首先,我们通过检查"prev_calculated"参数判断是否为首次计算。如果其值为0,则使用ArrayFill函数初始化“上轨”、“中轨MA”和“下轨”缓冲区,确保所有值初始化为0。接下来,我们使用CopyBuffer函数将MA的计算结果填充至"movingAverageBuffer"中。如果数据复制失败,则通过返回"0"终止执行。同理,我们将ATR的计算结果提取至临时数组"atrValues"中。
为确保MA和ATR均有足够的数据进行计算,我们使用MathMax函数确定起始K线位置。该函数返回指标周期中的较大值,并额外增加1根K线以避免包含当前未完成的K线数据。随后,通过for循环从"startBar"遍历至"rates_total",根据以下公式计算上下轨边界值:
- 上轨 = MA + (ATR × 倍数)
- 下轨 = MA - (ATR × 倍数)
最后,返回"rates_total"表示已计算的K线数量。如果非首次运行指标,则仅通过重新计算更新最近K线的数值。
//--- If this is NOT the first calculation, update only the most recent bars // This prevents re-calculating all bars, which improves performance int startBar = prev_calculated - 2; // Start 2 bars back to ensure smooth updating //--- Loop through the last few bars that need to be updated for(int i = startBar; i < rates_total; i++) { //--- Calculate reverse index to access recent bars from the end int reverseIndex = rates_total - i; // Reverse indexing ensures we are looking at the most recent bars first //--- Copy the latest Exponential Moving Average (EMA) value for this specific bar double emaValue[]; if(CopyBuffer(maHandle, 0, reverseIndex, 1, emaValue) < 0) return(prev_calculated); // If unable to copy, return the previous calculated value to avoid recalculation //--- Copy the latest Average True Range (ATR) value for this specific bar double atrValue[]; if(CopyBuffer(atrHandle, 0, reverseIndex, 1, atrValue) < 0) return(prev_calculated); // If unable to copy, return the previous calculated value to avoid recalculation //--- Update the indicator buffers with new values for the current bar movingAverageBuffer[i] = emaValue[0]; // Update the moving average buffer for this bar upperChannelBuffer[i] = emaValue[0] + atrMultiplier * atrValue[0]; // Calculate the upper channel boundary lowerChannelBuffer[i] = emaValue[0] - atrMultiplier * atrValue[0]; // Calculate the lower channel boundary } //--- Return the total number of calculated rates (bars) return(rates_total); // This informs MQL5 that all rates up to 'rates_total' have been successfully calculated
为了优化性能,我们仅更新最新K线数据,而非在每次价格变动时重新计算整个指标。如果非首次计算,我们将"startBar"设置为"prev_calculated - 2",确保仅更新最后几根K线,同时保持数据连续性。由于图表中已存储历史K线数据,此方法可避免重复计算。
使用for循环从"startBar"遍历至"rates_total"。通过计算"reverseIndex = rates_total - i",优先处理最新数据。使用CopyBuffer函数将最新EMA值存入"emaValue"数组。如果数据获取失败,返回"prev_calculated"以跳过冗余计算。同理,将ATR值存入"atrValue"数组中。检索后,我们更新缓冲区:
- "movingAverageBuffer[i] = emaValue[0];" 将EMA赋值给中线。
- "upperChannelBuffer[i] = emaValue[0] + atrMultiplier * atrValue[0];" 计算上轨。
- "lowerChannelBuffer[i] = emaValue[0] - atrMultiplier * atrValue[0];" 计算下轨。
最后,返回"rates_total",表示所有必要K线已处理完毕。程序运行后,输出如下:
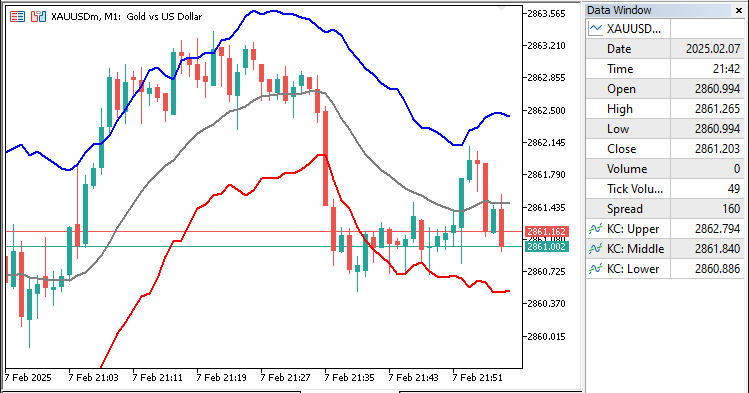
从图表中可以看出,指标线已经正确地映射至图表。接下来需完成通道的绘制,为此需借助画布(Canvas)功能。相关内容将在下一节展开说明。
集成自定义画布图形
要集成画布功能以实现图形绘制,需引入必要的画布类文件,因此我们要利用平台内置的图形结构。具体实现逻辑如下:
#include <Canvas/Canvas.mqh> CCanvas obj_Canvas;
我们使用#include关键字引入"Canvas.mqh"库,该库提供了在图表上进行图形渲染的功能。通过此库,我们能够直接在图表窗口中绘制自定义元素(如指标可视化图形和注释)。随后,我们声明一个"obj_Canvas"对象,作为CCanvas类的实例。该对象将用于与画布交互,支持动态创建、修改和管理图形元素。CCanvas类提供了绘制形状、线条和文本的方法,可显著增强指标的视觉呈现效果。接下来,我们需要获取图表的缩放比例等属性(因为后续需通过动态形状定位图表元素)。此操作需在全局作用域中完成。
int chart_width = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_WIDTH_IN_PIXELS); int chart_height = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_HEIGHT_IN_PIXELS); int chart_scale = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_SCALE); int chart_first_vis_bar = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_FIRST_VISIBLE_BAR); int chart_vis_bars = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_VISIBLE_BARS); double chart_prcmin = ChartGetDouble(0, CHART_PRICE_MIN, 0); double chart_prcmax = ChartGetDouble(0, CHART_PRICE_MAX, 0);
我们通过ChartGetInteger和ChartGetDouble函数获取当前图表窗口的多种属性,用于后续计算或图形元素的精准定位。首先,使用"ChartGetInteger"和参数CHART_WIDTH_IN_PIXELS获取图表宽度(像素)。将该值存储至"chart_width"变量中。同理,通过 "ChartGetInteger"和CHART_HEIGHT_IN_PIXELS获取高度,存储至"chart_height"变量中。
接下来,通过"CHART_SCALE"参数获取图表缩放比例,存储至"chart_scale"中。该值代表图表的缩放级别。使用"CHART_FIRST_VISIBLE_BAR"获取图表左侧第一根可见K线的索引,存储至"chart_first_vis_bar"中。通过CHART_VISIBLE_BARS参数计算当前窗口显示的K线总数,存储至"chart_vis_bars"中。所有返回值均需转换为整型,以确保兼容性。
最后,我们使用"ChartGetDouble"函数,分别通过"CHART_PRICE_MIN"和CHART_PRICE_MAX获取当前图表上可见的最低价和最高价。这些值存储在变量"chart_prcmin"和"chart_prcmax"中,它们提供了当前图表所显示的价格范围。借助这些变量,我们需要在初始化时在图表上创建一个位图标签(bitmap label),以便准备好我们的绘图区域。
// Create a obj_Canvas bitmap label for custom graphics on the chart obj_Canvas.CreateBitmapLabel(0, 0, short_name, 0, 0, chart_width, chart_height, COLOR_FORMAT_ARGB_NORMALIZE);
我们使用"obj_Canvas.CreateBitmapLabel"函数在图表上创建自定义的位图标签。该函数接收以下参数:定位坐标 ("0", "0")、内容 ("short_name")、尺寸 ("0", "0"表示自适应尺寸大小)和图表尺寸("chart_width", "chart_height") 。颜色格式设置为COLOR_FORMAT_ARGB_NORMALIZE,支持自定义透明度和颜色。借助该标签,我们现在可以绘制图形。然而,我们还需要一些辅助函数,用于将图表和K线坐标转换为价格和K线索引。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Converts the chart scale property to bar width/spacing | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int GetBarWidth(int chartScale) { // The width of each bar in pixels is determined using 2^chartScale. // This calculation is based on the MQL5 chart scale property, where larger chartScale values mean wider bars. return (int)pow(2, chartScale); // Example: chartScale = 3 -> bar width = 2^3 = 8 pixels } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Converts the bar index (as series) to x-coordinate in pixels | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int GetXCoordinateFromBarIndex(int barIndex) { // The chart starts from the first visible bar, and each bar has a fixed width. // To calculate the x-coordinate, we calculate the distance from the first visible bar to the given barIndex. // Each bar is shifted by 'bar width' pixels, and we subtract 1 to account for pixel alignment. return (chart_first_vis_bar - barIndex) * GetBarWidth(chart_scale) - 1; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Converts the price to y-coordinate in pixels | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int GetYCoordinateFromPrice(double price) { // To avoid division by zero, we check if chart_prcmax equals chart_prcmin. // If so, it means that all prices on the chart are the same, so we avoid dividing by zero. if(chart_prcmax - chart_prcmin == 0.0) return 0; // Return 0 to avoid undefined behavior // Calculate the relative position of the price in relation to the minimum and maximum price on the chart. // We then convert this to pixel coordinates based on the total height of the chart. return (int)round(chart_height * (chart_prcmax - price) / (chart_prcmax - chart_prcmin) - 1); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Converts x-coordinate in pixels to bar index (as series) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int GetBarIndexFromXCoordinate(int xCoordinate) { // Get the width of one bar in pixels int barWidth = GetBarWidth(chart_scale); // Check to avoid division by zero in case barWidth somehow equals 0 if(barWidth == 0) return 0; // Return 0 to prevent errors // Calculate the bar index using the x-coordinate position // This determines how many bar widths fit into the x-coordinate and converts it to a bar index return chart_first_vis_bar - (xCoordinate + barWidth / 2) / barWidth; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Converts y-coordinate in pixels to price | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double GetPriceFromYCoordinate(int yCoordinate) { // If the chart height is 0, division by zero would occur, so we avoid it. if(chart_height == 0) return 0; // Return 0 to prevent errors // Calculate the price corresponding to the y-coordinate // The y-coordinate is converted relative to the total height of the chart return chart_prcmax - yCoordinate * (chart_prcmax - chart_prcmin) / chart_height; }
我们编写了一系列函数,用于实现图表数据与像素坐标之间的映射。首先,在"GetBarWidth"函数中,我们利用图表缩放比例,通过"2的chart_scale次幂"公式计算每根K线的像素宽度。这样可以根据图表缩放自动调整K线粗细。这里使用pow函数完成2的幂运算。
接下来,"GetXCoordinateFromBarIndex"函数将K线索引转换为像素X的坐标。计算从第一根可见K线到目标索引的距离。乘以柱体宽度后再减1(像素对齐),即可得到X坐标。对于Y坐标,在"GetYCoordinateFromPrice"函数中,我们计算价格在图表上的相对位置。通过确定价格在图表最小值"chart_prcmin"与最大值"chart_prcmax"之间的相对位置,然后缩放该相对值以适应图表的高度。如果价格区间为0,我们要防止发生除0错误。
同样地,"GetBarIndexFromXCoordinate"函数执行反向操作。该函数接收一个X轴像素坐标,通过计算该坐标中包含多少个K线宽度,将其反向转换回对应的K线索引。这一过程使我们能够确定图表上某一特定位置所对应的K线。最后,"GetBarIndexFromXCoordinate"函数通过计算Y轴坐标在图表价格范围内的相对位置,将其转换回对应的价格值。同时,我们确保在图表高度为0时避免出现除0错误。
借助这些函数,我们可在像素坐标与数据值之间自由转换,从而将自定义图形精确对齐到价格与K线。因此,我们可以利用它们编写一个通用函数,用于在给定通道的两条边界线之间绘制所需图形。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Fill the area between two indicator lines | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void DrawFilledArea(double &upperSeries[], double &lowerSeries[], color upperColor, color lowerColor, uchar transparency = 255, int shift = 0) { int startBar = chart_first_vis_bar; // The first bar that is visible on the chart int totalBars = chart_vis_bars + shift; // The total number of visible bars plus the shift uint upperARGB = ColorToARGB(upperColor, transparency); // Convert the color to ARGB with transparency uint lowerARGB = ColorToARGB(lowerColor, transparency); // Convert the color to ARGB with transparency int seriesLimit = fmin(ArraySize(upperSeries), ArraySize(lowerSeries)); // Ensure series limits do not exceed array size int prevX = 0, prevYUpper = 0, prevYLower = 0; // Variables to store the previous bar's x, upper y, and lower y coordinates for(int i = 0; i < totalBars; i++) { int barPosition = startBar - i; // Current bar position relative to start bar int shiftedBarPosition = startBar - i + shift; // Apply the shift to the bar position int barIndex = seriesLimit - 1 - shiftedBarPosition; // Calculate the series index for the bar // Ensure the bar index is within the valid range of the array if(barIndex < 0 || barIndex >= seriesLimit || barIndex - 1 < 0) continue; // Skip this bar if the index is out of bounds // Check if the series contains valid data (not EMPTY_VALUE) if(upperSeries[barIndex] == EMPTY_VALUE || lowerSeries[barIndex] == EMPTY_VALUE || shiftedBarPosition >= seriesLimit) continue; // Skip this bar if the values are invalid or if the position exceeds the series limit int xCoordinate = GetXCoordinateFromBarIndex(barPosition); // Calculate x-coordinate of this bar int yUpper = GetYCoordinateFromPrice(upperSeries[barIndex]); // Calculate y-coordinate for upper line int yLower = GetYCoordinateFromPrice(lowerSeries[barIndex]); // Calculate y-coordinate for lower line uint currentARGB = upperSeries[barIndex] < lowerSeries[barIndex] ? lowerARGB : upperARGB; // Determine fill color based on which line is higher // If previous values are valid, draw triangles between the previous bar and the current bar if(i > 0 && upperSeries[barIndex - 1] != EMPTY_VALUE && lowerSeries[barIndex - 1] != EMPTY_VALUE) { if(prevYUpper != prevYLower) // Draw first triangle between the upper and lower parts of the two consecutive bars obj_Canvas.FillTriangle(prevX, prevYUpper, prevX, prevYLower, xCoordinate, yUpper, currentARGB); if(yUpper != yLower) // Draw the second triangle to complete the fill area obj_Canvas.FillTriangle(prevX, prevYLower, xCoordinate, yUpper, xCoordinate, yLower, currentARGB); } prevX = xCoordinate; // Store the x-coordinate for the next iteration prevYUpper = yUpper; // Store the y-coordinate of the upper series prevYLower = yLower; // Store the y-coordinate of the lower series } }
我们声明一个无返回值函数“DrawFilledArea”,用于填充图表上两条指标线之间的区域。首先,我们通过可选参数“shift”定义图表上的可见K线范围,以调整填充区域的起始点。同时,使用ColorToARGB函数将颜色参数(“upperColor”和“lowerColor”)转换为包含透明度的ARGB格式。接着,通过fmin函数确定数据序列的边界,避免超出上轨(“upperSeries”)和下轨(“lowerSeries”)指标数组的长度限制。我们初始化变量,存储上一根K线的上轨和下轨坐标,用于后续绘制填充区域。
随后,我们遍历所有可见K线,使用"GetXCoordinateFromBarIndex"函数计算每根K线在X轴上的像素坐标。通过"GetYCoordinateFromPrice"函数,根据"upperSeries"和"lowerSeries"的值计算上轨和下轨的Y轴坐标。比较两条线的上下位置,确定填充区域的颜色。
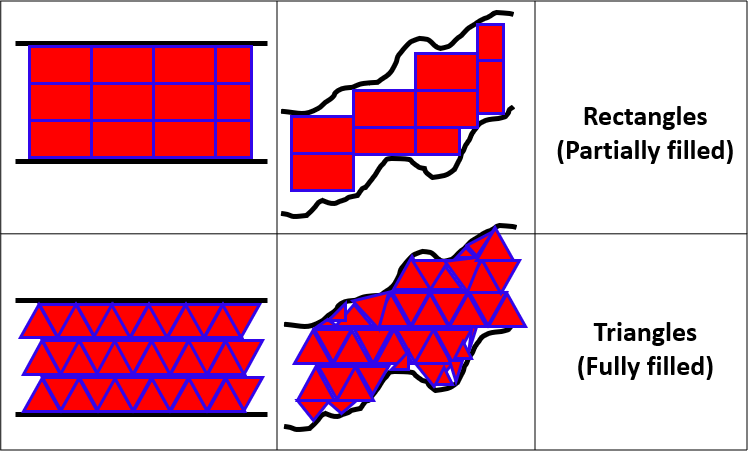
如果上一根K线数据有效,则使用obj_Canvas.FillTriangle填充两条线之间的区域。每对相邻K线之间绘制两个三角形:一个三角形连接上轨和下轨的当前点与上一根K线的对应点;另一个三角形补全填充区域的形状。三角形使用之前确定的颜色填充。采用三角形的原因是三角形能够更精确地连接不规则线段(尤其是当指标线与网格不对齐时)。相比矩形,三角形确保填充更平滑,渲染效率更高。图示如下:
最后,我们更新上一根K线的X、Y坐标,为下一次迭代做准备,确保填充区域能持续、无缝地衔接在两条指标线之间。完成上述函数定义后,我们进一步利用该函数在图表上绘制所需数量的通道,并按照要求为每个通道分配对应的颜色。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator redraw function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void RedrawChart(void) { uint defaultColor = 0; // Default color used to clear the canvas color colorUp = (color)PlotIndexGetInteger(0, PLOT_LINE_COLOR, 0); // Color of the upper indicator line color colorMid = (color)PlotIndexGetInteger(1, PLOT_LINE_COLOR, 0); // Color of the mid indicator line color colorDown = (color)PlotIndexGetInteger(2, PLOT_LINE_COLOR, 0); // Color of the lower indicator line //--- Clear the canvas by filling it with the default color obj_Canvas.Erase(defaultColor); //--- Draw the area between the upper channel and the moving average // This fills the area between the upper channel (upperChannelBuffer) and the moving average (movingAverageBuffer) DrawFilledArea(upperChannelBuffer, movingAverageBuffer, colorUp, colorMid, 128, 1); //--- Draw the area between the moving average and the lower channel // This fills the area between the moving average (movingAverageBuffer) and the lower channel (lowerChannelBuffer) DrawFilledArea(movingAverageBuffer, lowerChannelBuffer, colorDown, colorMid, 128, 1); //--- Update the canvas to reflect the new drawing obj_Canvas.Update(); }
我们声明“RedrawChart”函数,并首先定义默认颜色,随后,从指标属性中获取上轨、中轨和下轨通道的线条颜色。接下来,我们使用默认颜色清空画布,并调用“DrawFilledArea”函数填充以下区域:上轨通道与MA之间的区域(使用上轨颜色);MA与下轨通道之间的区域(使用下轨颜色)。最后,更新画布以应用所有变更,确保图表以新填充效果重新渲染。现在,我们可在OnCalculate事件处理器中调用该函数来绘制画布。
RedrawChart(); // This function clears and re-draws the filled areas between the indicator lines
由于我们创建了指标通道对象,需要在移除指标时将其删除。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason){ obj_Canvas.Destroy(); ChartRedraw(); }
在OnDeinit事件处理器中,我们使用"obj_Canvas.Destroy"方法清理并移除指标卸载时图表上的所有自定义绘图对象。最后,调用ChartRedraw函数刷新并重绘图表,确保所有自定义图形从显示中清除。程序运行后,最终效果如下:
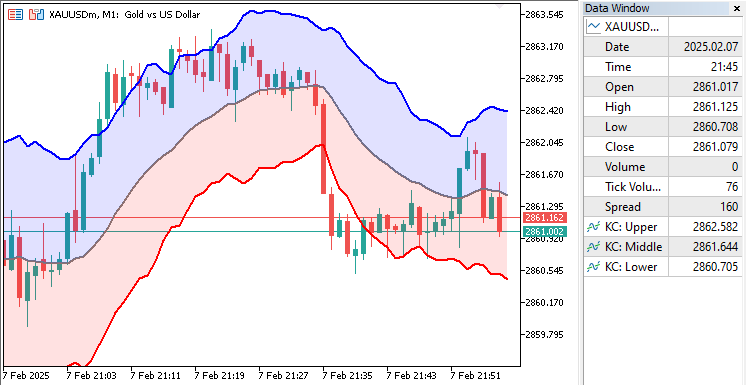
从可视化结果可以看出,我们成功实现了基于画布绘图的高级Keltner通道指标。我们现在需要对指标进行回测,以确保其正常工作。这将在下一部分中完成。
凯特纳通道指标回测
在回测过程中,我们发现当图表尺寸发生变化时,通道显示会出现卡顿,且无法更新至最新的图表坐标。以下是情况说明。
为了解决该问题,我们在OnChartEvent事件处理器上实现一个更新逻辑。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator chart event handler function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnChartEvent(const int id, const long& lparam, const double& dparam, const string& sparam){ if(id != CHARTEVENT_CHART_CHANGE) return; chart_width = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_WIDTH_IN_PIXELS); chart_height = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_HEIGHT_IN_PIXELS); chart_scale = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_SCALE); chart_first_vis_bar = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_FIRST_VISIBLE_BAR); chart_vis_bars = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_VISIBLE_BARS); chart_prcmin = ChartGetDouble(0, CHART_PRICE_MIN, 0); chart_prcmax = ChartGetDouble(0, CHART_PRICE_MAX, 0); if(chart_width != obj_Canvas.Width() || chart_height != obj_Canvas.Height()) obj_Canvas.Resize(chart_width, chart_height); //--- RedrawChart(); }
此处,我们处理OnChartEvent函数,用于监听CHARTEVENT_CHART_CHANGE事件。当图表尺寸发生变化(例如调整窗口大小)时,我们首先获取更新后的图表属性(如宽度CHART_WIDTH_IN_PIXELS)。接着,通过"obj_Canvas.Width"和"obj_Canvas.Height"检查图表的新宽高是否与当前画布尺寸不同。如果尺寸不同,则使用"obj_Canvas.Resize"调整画布大小。最后,调用"RedrawChart"函数更新图表,确保所有视觉元素都以新尺寸被正确渲染。效果如下:
参见可视化效果,当我们调整图表大小时,所有变化均能动态生效,从而实现了我们的目标。
结论
总而言之,本文阐述了如何基于移动平均线(MA)和 平均真实波幅( ATR)工具创建动态通道,在MQL5中构建自定义指标。我们重点解决了如何计算和展示这些通道,同时针对填充渲染、图表缩放适配及回测性能优化问题,确保为交易者提供高效、精准的技术分析工具。
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/17155
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 在 MQL5 中创建交易管理面板(第九部分):代码组织(二):模块化
在 MQL5 中创建交易管理面板(第九部分):代码组织(二):模块化
 分析交易所价格的二进制代码(第二部分):转换为 BIP39 并编写 GPT 模型
分析交易所价格的二进制代码(第二部分):转换为 BIP39 并编写 GPT 模型
 价格行为分析工具包开发(第十三部分):RSI 哨兵工具
价格行为分析工具包开发(第十三部分):RSI 哨兵工具
 开发先进的 ICT 交易系统:在订单块指标中实现信号
开发先进的 ICT 交易系统:在订单块指标中实现信号