
价格行为分析工具包开发(第十三部分):RSI 哨兵工具
内容
引言
背离是技术分析中的一个概念,指的是动量或震荡指标等指标的走势与价格的走势发生偏离。本质上,当价格形成未被指标反映的新高或新低时,这可能预示着当前趋势正在减弱,并可能预示着反转或动量的变化。RSI 背离是一种发现潜在市场反转的简单方法。当价格朝一个方向移动,而 RSI 却朝另一个方向移动时,这可能预示着趋势的变化。然而,手动在图表上扫描这些信号既缓慢又容易出错。这就是自动化发挥作用的地方。
在本文中,我们将构建一个 MQL5 EA,它可以自动检测 RSI 背离信号。该 EA 将在您的图表上用清晰的箭头标记这些信号,并提供简要摘要,以便您能快速了解正在发生的情况。无论您是初学者还是经验丰富的交易者,此工具都能帮助您发现交易机会,您可以在执行交易前进行验证,而无需花费数小时进行手动分析。让我们深入了解这个 RSI 背离 EA 如何简化您的交易过程。
策略概览
理解 RSI 背离
当相对强弱指数(RSI)的走势与资产价格的走势不同时,就会发生 RSI 背离,这预示着价格动量可能发生转变。RSI 与价格行为之间的这种对比是交易者用来预测市场反转或趋势延续的关键指标。通常,RSI 会跟随价格的动量,从而确认 prevailing trends(主导趋势)。然而,当背离出现时,它揭示了一种差异,这种差异通常发生在重大价格变动之前。及早识别这些信号对于把握市场进出场时机至关重要。
在 RSI 背离的背景下,主要有两种类型:
1. 常规 RSI 背离
常规 RSI 背离通常被视为反转信号。它表明当前趋势正在失去动力,可能即将反转。
- 常规看涨 RSI 背离
当价格形成更低的低点(LL),而 RSI 形成更高的低点(HL)时发生。这表明,尽管价格在下跌,但动量开始向上转变,暗示着可能反转至上升趋势。
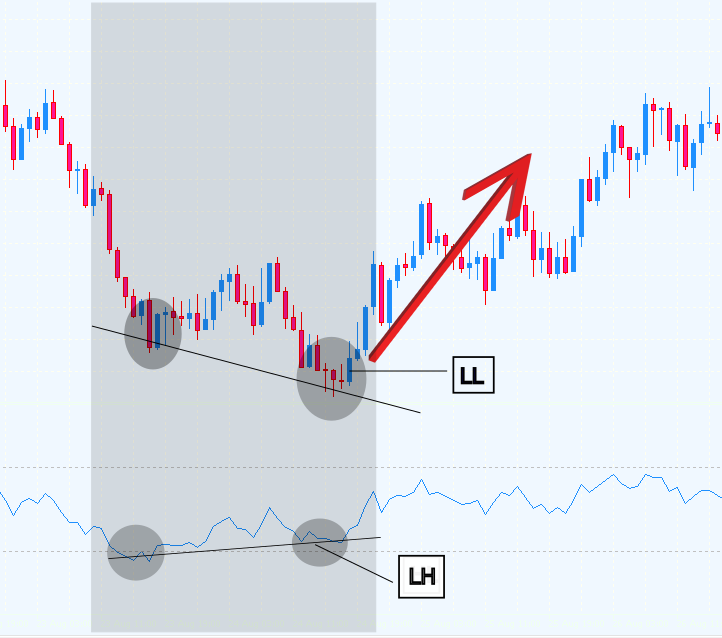
图 1. 看涨背离
- 常规看跌 RSI 背离
当价格形成更高的高点(HH),而 RSI 形成更低的高点(LH)时发生。尽管价格在上涨,但动量的减弱(如 RSI 所示)表明下跌可能即将到来。
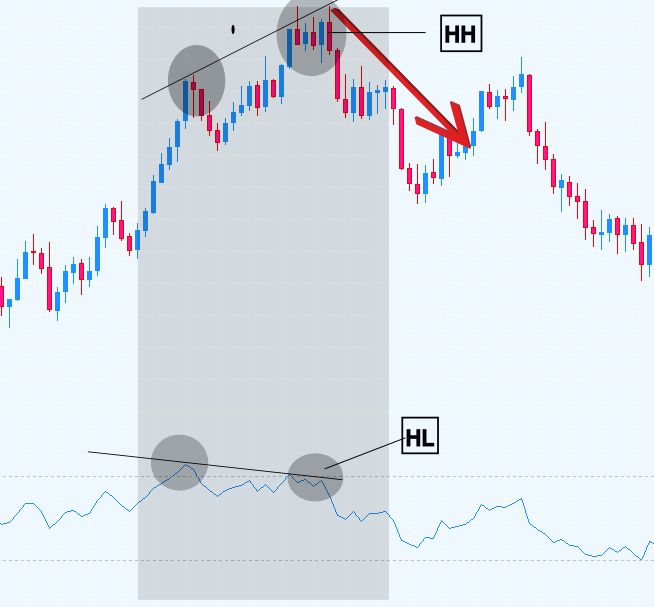
图 2. 看跌背离
2.隐藏 RSI 背离
隐藏 RSI 背离被解释为趋势延续的信号,而不是即将到来的反转。它证实了当前趋势仍然具有力量,即使 RSI 和价格暂时出现背离。
- 隐藏看涨 RSI 背离:在上升趋势中,如果价格形成更高的低点(HL),而 RSI 形成更低的低点(LL),这表明修正只是暂时的,上升趋势很可能继续。
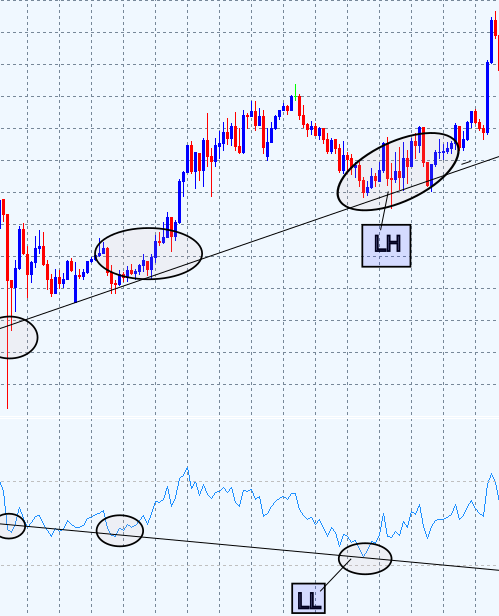
图 3. 隐藏看涨背离
- 隐藏看跌 RSI 背离:在下降趋势中,当价格形成更低的高点(LH),而 RSI 形成更高的高点(HH)时,这证实了下降趋势的强度,并表明下行运动很可能持续。
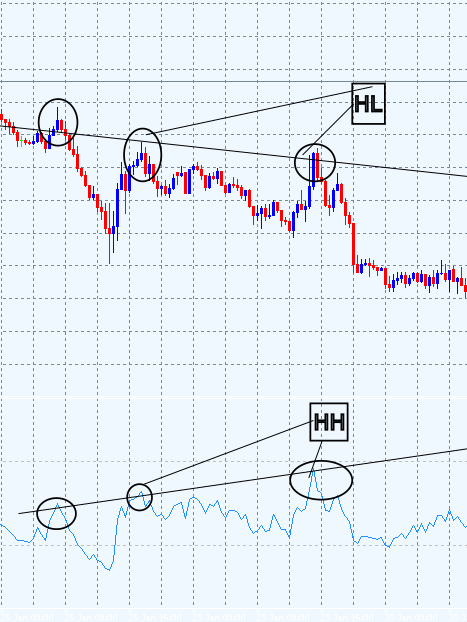
图 4. 隐藏看跌背离
下表总结了 RSI 背离类型之间的主要区别:
| RSI 背离类型 | 价格行为 | RSI 行为 | 信号类型 | 预期 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常规看涨 | 更低低点(LL) | 更高低点(HL) | 向上反转 | 下降趋势转上升趋势 |
| 常规看跌 | 更高高点(HH) | 更低高点(LH) | 向下反转 | 上升趋势转下降趋势 |
| 隐藏看涨 | 更高低点(HL) | 更低低点(LL) | 连续上涨 | 上升趋势延续 |
| 隐藏看跌 | 更低高点 (LH) | 更高高点(HH) | 连续下跌 | 下降趋势延续 |
总而言之,该 EA 在一个定义的回溯期内持续扫描价格和 RSI 数据,以检测它们走势之间的差异,我们称之为 RSI 背离。
以下是它的功能:
1. 数据收集与准备
该 EA 收集 RSI 值以及来自近期 K 线的相应价格数据(低点、高点、收盘价和时间)。这确保分析始终基于最新、完整的信息。2. 识别摆动点
然后,它确定价格和 RSI 数据中的局部摆动高点和低点。这些摆动点作为我们背离分析的参考标记。3. 检测常规背离
- 常规看涨背离:该 EA 寻找价格创出更低低点(LL),而 RSI 形成更高低点(HL)的情况,这预示着下降趋势可能正在失去动力,并可能向上反转。
- 常规看跌背离:它还检查价格创出更高高点(HH),而 RSI 形成更低高点(LH)的情况,这表明随着动量减弱,上升趋势可能即将结束。
- 隐藏看涨背离:在上升趋势中,如果价格形成更高的低点(HL),但 RSI 记录了更低的低点(LL),该 EA 将此识别为整体上升趋势尽管暂时回调但仍然强劲的迹象。
- 隐藏看跌背离:相反,在下降趋势期间,如果价格创出更低的高点(LH),而 RSI 显示更高的高点(HH),这证实了下降趋势很可能继续。
5. 视觉和日志信号生成
一旦检测到背离(无论是常规还是隐藏),EA 会在图表上直观地标记该事件(使用箭头和标签),并记录信号的详细信息以供进一步分析或回测。关于它如何执行上述过程的更多信息,请查看下面的代码剖析部分。
MQL5代码
//+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| RSI Divergence.mql5 | //| Copyright 2025, Christian Benjamin | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "2025, MetaQuotes Software Corp." #property link "https://www.mql5.com/en/users/lynnchris" #property version "1.0" #property strict //---- Input parameters input int InpRSIPeriod = 14; // RSI period input int InpSwingLeft = 1; // Bars to the left for swing detection (relaxed) input int InpSwingRight = 1; // Bars to the right for swing detection (relaxed) input int InpLookback = 100; // Number of bars to scan for divergence input int InpEvalBars = 5; // Bars after which to evaluate a signal input int InpMinBarsBetweenSignals = 1; // Minimum bars between same-type signals (allows frequent re-entry) input double InpArrowOffset = 3.0; // Arrow offset (in points) for display input double InpMinSwingDiffPct = 0.05; // Lower minimum % difference to qualify as a swing input double InpMinRSIDiff = 1.0; // Lower minimum difference in RSI between swing points // Optional RSI threshold filter for bullish divergence (disabled by default) input bool InpUseRSIThreshold = false; // If true, require earlier RSI swing to be oversold for bullish divergence input double InpRSIOversold = 30; // RSI oversold level input double InpRSIOverbought = 70; // RSI overbought level (if needed for bearish) //---- Global variables int rsiHandle; // Handle for the RSI indicator double rsiBuffer[]; // Buffer for RSI values double lowBuffer[]; // Buffer for low prices double highBuffer[]; // Buffer for high prices double closeBuffer[]; // Buffer for close prices datetime timeBuffer[]; // Buffer for bar times int g_totalBars = 0; // Number of bars in our copied arrays datetime lastBarTime = 0; // Time of last closed bar //---- Structure to hold signal information struct SignalInfo { string type; // e.g. "RegBearish Divergence", "HiddenBullish Divergence" int barIndex; // Bar index where the signal was generated datetime signalTime; // Time of the signal bar double signalPrice; // Price used for the signal (swing high for bearish, swing low for bullish) }; SignalInfo signals[]; // Global array to store signals //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { rsiHandle = iRSI(_Symbol, _Period, InpRSIPeriod, PRICE_CLOSE); if(rsiHandle == INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("Error creating RSI handle"); return(INIT_FAILED); } return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { if(rsiHandle != INVALID_HANDLE) IndicatorRelease(rsiHandle); EvaluateSignalsAndPrint(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { // Process once per new closed candle (using bar1's time) datetime currentBarTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, 1); if(currentBarTime == lastBarTime) return; lastBarTime = currentBarTime; //--- Copy RSI data ArrayResize(rsiBuffer, InpLookback); ArraySetAsSeries(rsiBuffer, true); if(CopyBuffer(rsiHandle, 0, 0, InpLookback, rsiBuffer) <= 0) { Print("Error copying RSI data"); return; } //--- Copy price and time data ArrayResize(lowBuffer, InpLookback); ArrayResize(highBuffer, InpLookback); ArrayResize(closeBuffer, InpLookback); ArraySetAsSeries(lowBuffer, true); ArraySetAsSeries(highBuffer, true); ArraySetAsSeries(closeBuffer, true); if(CopyLow(_Symbol, _Period, 0, InpLookback, lowBuffer) <= 0 || CopyHigh(_Symbol, _Period, 0, InpLookback, highBuffer) <= 0 || CopyClose(_Symbol, _Period, 0, InpLookback, closeBuffer) <= 0) { Print("Error copying price data"); return; } ArrayResize(timeBuffer, InpLookback); ArraySetAsSeries(timeBuffer, true); if(CopyTime(_Symbol, _Period, 0, InpLookback, timeBuffer) <= 0) { Print("Error copying time data"); return; } g_totalBars = InpLookback; //--- Identify swing lows and swing highs int swingLows[]; int swingHighs[]; int startIndex = InpSwingLeft; int endIndex = g_totalBars - InpSwingRight; for(int i = startIndex; i < endIndex; i++) { if(IsSignificantSwingLow(i, InpSwingLeft, InpSwingRight)) { ArrayResize(swingLows, ArraySize(swingLows) + 1); swingLows[ArraySize(swingLows) - 1] = i; } if(IsSignificantSwingHigh(i, InpSwingLeft, InpSwingRight)) { ArrayResize(swingHighs, ArraySize(swingHighs) + 1); swingHighs[ArraySize(swingHighs) - 1] = i; } } //--- Bearish Divergence (using swing highs) if(ArraySize(swingHighs) >= 2) { ArraySort(swingHighs); // ascending order: index 0 is most recent int recent = swingHighs[0]; int previous = swingHighs[1]; // Regular Bearish Divergence: Price makes a higher high while RSI makes a lower high if(highBuffer[recent] > highBuffer[previous] && rsiBuffer[recent] < rsiBuffer[previous] && (rsiBuffer[previous] - rsiBuffer[recent]) >= InpMinRSIDiff) { Print("Regular Bearish Divergence detected at bar ", recent); DisplaySignal("RegBearish Divergence", recent); } // Hidden Bearish Divergence: Price makes a lower high while RSI makes a higher high else if(highBuffer[recent] < highBuffer[previous] && rsiBuffer[recent] > rsiBuffer[previous] && (rsiBuffer[recent] - rsiBuffer[previous]) >= InpMinRSIDiff) { Print("Hidden Bearish Divergence detected at bar ", recent); DisplaySignal("HiddenBearish Divergence", recent); } } //--- Bullish Divergence (using swing lows) if(ArraySize(swingLows) >= 2) { ArraySort(swingLows); // ascending order: index 0 is most recent int recent = swingLows[0]; int previous = swingLows[1]; // Regular Bullish Divergence: Price makes a lower low while RSI makes a higher low if(lowBuffer[recent] < lowBuffer[previous] && rsiBuffer[recent] > rsiBuffer[previous] && (rsiBuffer[recent] - rsiBuffer[previous]) >= InpMinRSIDiff) { // Optionally require the earlier swing's RSI be oversold if(!InpUseRSIThreshold || rsiBuffer[previous] <= InpRSIOversold) { Print("Regular Bullish Divergence detected at bar ", recent); DisplaySignal("RegBullish Divergence", recent); } } // Hidden Bullish Divergence: Price makes a higher low while RSI makes a lower low else if(lowBuffer[recent] > lowBuffer[previous] && rsiBuffer[recent] < rsiBuffer[previous] && (rsiBuffer[previous] - rsiBuffer[recent]) >= InpMinRSIDiff) { Print("Hidden Bullish Divergence detected at bar ", recent); DisplaySignal("HiddenBullish Divergence", recent); } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| IsSignificantSwingLow: Determines if the bar at 'index' is a swing low | //+------------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool IsSignificantSwingLow(int index, int left, int right) { double currentLow = lowBuffer[index]; // Check left side for a local minimum condition for(int i = index - left; i < index; i++) { if(i < 0) continue; double pctDiff = MathAbs((lowBuffer[i] - currentLow) / currentLow) * 100.0; if(lowBuffer[i] < currentLow && pctDiff > InpMinSwingDiffPct) return false; } // Check right side for a local minimum condition for(int i = index + 1; i <= index + right; i++) { if(i >= g_totalBars) break; double pctDiff = MathAbs((lowBuffer[i] - currentLow) / currentLow) * 100.0; if(lowBuffer[i] < currentLow && pctDiff > InpMinSwingDiffPct) return false; } return true; } //+--------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| IsSignificantSwingHigh: Determines if the bar at 'index' is a swing high | //+--------------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool IsSignificantSwingHigh(int index, int left, int right) { double currentHigh = highBuffer[index]; // Check left side for a local maximum condition for(int i = index - left; i < index; i++) { if(i < 0) continue; double pctDiff = MathAbs((currentHigh - highBuffer[i]) / currentHigh) * 100.0; if(highBuffer[i] > currentHigh && pctDiff > InpMinSwingDiffPct) return false; } // Check right side for a local maximum condition for(int i = index + 1; i <= index + right; i++) { if(i >= g_totalBars) break; double pctDiff = MathAbs((currentHigh - highBuffer[i]) / currentHigh) * 100.0; if(highBuffer[i] > currentHigh && pctDiff > InpMinSwingDiffPct) return false; } return true; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| DisplaySignal: Draws an arrow on the chart and records the signal| //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void DisplaySignal(string signalText, int barIndex) { // Prevent duplicate signals on the same bar (or too close) for(int i = 0; i < ArraySize(signals); i++) { if(StringFind(signals[i].type, signalText) != -1) if(MathAbs(signals[i].barIndex - barIndex) < InpMinBarsBetweenSignals) return; } // Update a "LatestSignal" label for regular signals. if(StringFind(signalText, "Reg") != -1) { string labelName = "LatestSignal"; if(ObjectFind(0, labelName) == -1) { if(!ObjectCreate(0, labelName, OBJ_LABEL, 0, 0, 0)) { Print("Failed to create LatestSignal label"); return; } ObjectSetInteger(0, labelName, OBJPROP_CORNER, 0); ObjectSetInteger(0, labelName, OBJPROP_XDISTANCE, 10); ObjectSetInteger(0, labelName, OBJPROP_YDISTANCE, 20); ObjectSetInteger(0, labelName, OBJPROP_COLOR, clrWhite); } ObjectSetString(0, labelName, OBJPROP_TEXT, signalText); } // Create an arrow object for the signal. string arrowName = "Arrow_" + signalText + "_" + IntegerToString(barIndex); if(ObjectFind(0, arrowName) < 0) { int arrowCode = 0; double arrowPrice = 0.0; color arrowColor = clrWhite; double point = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_POINT); if(StringFind(signalText, "Bullish") != -1) { arrowCode = 233; // Wingdings up arrow arrowColor = clrLime; arrowPrice = lowBuffer[barIndex] - (InpArrowOffset * point); } else if(StringFind(signalText, "Bearish") != -1) { arrowCode = 234; // Wingdings down arrow arrowColor = clrRed; arrowPrice = highBuffer[barIndex] + (InpArrowOffset * point); } if(!ObjectCreate(0, arrowName, OBJ_ARROW, 0, timeBuffer[barIndex], arrowPrice)) { Print("Failed to create arrow object ", arrowName); return; } ObjectSetInteger(0, arrowName, OBJPROP_COLOR, arrowColor); ObjectSetInteger(0, arrowName, OBJPROP_ARROWCODE, arrowCode); } // Record the signal for evaluation. SignalInfo sig; sig.type = signalText; sig.barIndex = barIndex; sig.signalTime = timeBuffer[barIndex]; if(StringFind(signalText, "Bullish") != -1) sig.signalPrice = lowBuffer[barIndex]; else sig.signalPrice = highBuffer[barIndex]; ArrayResize(signals, ArraySize(signals) + 1); signals[ArraySize(signals) - 1] = sig; UpdateSignalCountLabel(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| UpdateSignalCountLabel: Updates a label showing signal counts | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void UpdateSignalCountLabel() { int regCount = 0, hidCount = 0; for(int i = 0; i < ArraySize(signals); i++) { if(StringFind(signals[i].type, "Reg") != -1) regCount++; else if(StringFind(signals[i].type, "Hidden") != -1) hidCount++; } string countText = "Regular Signals: " + IntegerToString(regCount) + "\nHidden Signals: " + IntegerToString(hidCount); string countLabel = "SignalCount"; if(ObjectFind(0, countLabel) == -1) { if(!ObjectCreate(0, countLabel, OBJ_LABEL, 0, 0, 0)) { Print("Failed to create SignalCount label"); return; } ObjectSetInteger(0, countLabel, OBJPROP_CORNER, 0); ObjectSetInteger(0, countLabel, OBJPROP_XDISTANCE, 10); ObjectSetInteger(0, countLabel, OBJPROP_YDISTANCE, 40); ObjectSetInteger(0, countLabel, OBJPROP_COLOR, clrYellow); } ObjectSetString(0, countLabel, OBJPROP_TEXT, countText); } //+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| EvaluateSignalsAndPrint: After backtesting, prints signal accuracy | //+--------------------------------------------------------------------+ void EvaluateSignalsAndPrint() { double closeAll[]; int totalBars = CopyClose(_Symbol, _Period, 0, WHOLE_ARRAY, closeAll); if(totalBars <= 0) { Print("Error copying complete close data for evaluation"); return; } ArraySetAsSeries(closeAll, true); int totalEvaluated = 0, regTotal = 0, hidTotal = 0; int regEval = 0, hidEval = 0; int regCorrect = 0, hidCorrect = 0; for(int i = 0; i < ArraySize(signals); i++) { int evalIndex = signals[i].barIndex - InpEvalBars; if(evalIndex < 0) continue; double evalClose = closeAll[evalIndex]; if(StringFind(signals[i].type, "Bullish") != -1) { if(StringFind(signals[i].type, "Reg") != -1) { regTotal++; regEval++; if(evalClose > signals[i].signalPrice) regCorrect++; } else if(StringFind(signals[i].type, "Hidden") != -1) { hidTotal++; hidEval++; if(evalClose > signals[i].signalPrice) hidCorrect++; } totalEvaluated++; } else if(StringFind(signals[i].type, "Bearish") != -1) { if(StringFind(signals[i].type, "Reg") != -1) { regTotal++; regEval++; if(evalClose < signals[i].signalPrice) regCorrect++; } else if(StringFind(signals[i].type, "Hidden") != -1) { hidTotal++; hidEval++; if(evalClose < signals[i].signalPrice) hidCorrect++; } totalEvaluated++; } } double overallAccuracy = (totalEvaluated > 0) ? (double)(regCorrect + hidCorrect) / totalEvaluated * 100.0 : 0.0; double regAccuracy = (regEval > 0) ? (double)regCorrect / regEval * 100.0 : 0.0; double hidAccuracy = (hidEval > 0) ? (double)hidCorrect / hidEval * 100.0 : 0.0; Print("----- Backtest Signal Evaluation -----"); Print("Total Signals Generated: ", ArraySize(signals)); Print("Signals Evaluated: ", totalEvaluated); Print("Overall Accuracy: ", DoubleToString(overallAccuracy, 2), "%"); Print("Regular Signals: ", regTotal, " | Evaluated: ", regEval, " | Accuracy: ", DoubleToString(regAccuracy, 2), "%"); Print("Hidden Signals: ", hidTotal, " | Evaluated: ", hidEval, " | Accuracy: ", DoubleToString(hidAccuracy, 2), "%"); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
代码分解
1. 头部信息和输入参数
在我们脚本的顶部,有一个定义良好的头部,它提供了关于代码的关键信息。
文件和作者信息
头部指定了文件名(RSI Divergence.mql5)、版权声明和作者个人资料的链接。这确保了正确的署名,并为用户提供了参考点,以便他们在需要检查更新或额外文档时使用。
版本控制和编译指令
#property 指令设置了重要的属性,如版本号和使用严格编译规则 (#property strict)。这有助于在开发和部署过程中保持一致性并减少潜在错误。接下来,输入参数部分对于定制化至关重要。这些参数允许您或任何用户在不修改核心代码的情况下,微调背离检测逻辑的行为。以下是几个要点:
RSI 和摆动点检测参数
- InpRSIPeriod: 设置 RSI 指标的周期。
- InpSwingLeft 和 InpSwingRight: 定义在检测摆动点时,每一侧需要考虑的 K 线数量。调整这些值可以使摆动点检测更宽松或更严格。
背离和信号评估设置
- InpLookback: 决定脚本将扫描过去多少根 K 线来寻找背离。
- InpEvalBars: 指定在评估一个信号是否成功之前需要等待的 K 线数量。
- InpMinBarsBetweenSignals: 通过在相似信号之间强制设置最小的 K 线间隔,有助于避免重复信号。
显示自定义
- InpArrowOffset: 设置箭头相对于摆动点的偏移距离(以点为单位),以增强图表上的视觉清晰度。
可选的 RSI 阈值过滤器
- InpUseRSIThreshold,以及 InpRSIOversold 和 InpRSIOverbought,提供了一个额外的过滤层。这确保了,对于看涨背离,较早的 RSI 摆动点处于超卖区域——前提是用户选择启用此过滤器。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| RSI Divergence.mql5 | //| Copyright 2025, Christian Benjamin | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "2025, MetaQuotes Software Corp." #property link "https://www.mql5.com/en/users/lynnchris" #property version "1.0" #property strict //---- Input parameters input int InpRSIPeriod = 14; // RSI period input int InpSwingLeft = 1; // Bars to the left for swing detection (relaxed) input int InpSwingRight = 1; // Bars to the right for swing detection (relaxed) input int InpLookback = 100; // Number of bars to scan for divergence input int InpEvalBars = 5; // Bars after which to evaluate a signal input int InpMinBarsBetweenSignals = 1; // Minimum bars between same-type signals (allows frequent re-entry) input double InpArrowOffset = 3.0; // Arrow offset (in points) for display input double InpMinSwingDiffPct = 0.05; // Lower minimum % difference to qualify as a swing input double InpMinRSIDiff = 1.0; // Lower minimum difference in RSI between swing points // Optional RSI threshold filter for bullish divergence (disabled by default) input bool InpUseRSIThreshold = false; // If true, require earlier RSI swing to be oversold for bullish divergence input double InpRSIOversold = 30; // RSI oversold level input double InpRSIOverbought = 70; // RSI overbought level (if needed for bearish)
2. 初始化指标
在这一部分,我们初始化我们的 RSI 指标。OnInit() 函数使用诸如交易品种、时间框架和用户指定的 RSI 周期等参数,为 RSI 指标创建一个句柄。这一步至关重要,因为所有后续操作都依赖于拥有一个有效的 RSI 句柄来获取指标数据。
- iRSI函数被调用并传入必要的参数。
- 实现了错误处理以捕获创建句柄时的任何失败。
- 初始化确保我们的指标已准备好进行数据采集和分析。
int OnInit() { // Create the RSI indicator handle with the specified period rsiHandle = iRSI(_Symbol, _Period, InpRSIPeriod, PRICE_CLOSE); if(rsiHandle == INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("Error creating RSI handle"); return(INIT_FAILED); } return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
3.在每根新 K 线上获取数据
在 OnTick() 函数中,我们在处理前检查是否有新的 K 线已经收盘。这确保了我们的分析始终基于已完成的完整数据。然后,我们复制在一个可配置的回溯期内的 RSI 值、低点、高点、收盘价和时间数据的数组。将数组设置为序列,确保数据按最近的 K 线在索引 0 的顺序排列。
- 代码等待下一根已收盘的 K 线,以避免处理不完整的数据。
- 使用 CopyBuffer 和 CopyLow/High/Close/Time 等函数来检索 RSI 和价格数据。
- 使用 ArraySetAsSeries 保留了时间序列分析的正确顺序。
void OnTick() { // Process only once per new closed candle by comparing bar times datetime currentBarTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, 1); if(currentBarTime == lastBarTime) return; lastBarTime = currentBarTime; // Copy RSI data for a given lookback period ArrayResize(rsiBuffer, InpLookback); ArraySetAsSeries(rsiBuffer, true); if(CopyBuffer(rsiHandle, 0, 0, InpLookback, rsiBuffer) <= 0) { Print("Error copying RSI data"); return; } // Copy price data (lows, highs, closes) and time data for analysis ArrayResize(lowBuffer, InpLookback); ArrayResize(highBuffer, InpLookback); ArrayResize(closeBuffer, InpLookback); ArraySetAsSeries(lowBuffer, true); ArraySetAsSeries(highBuffer, true); ArraySetAsSeries(closeBuffer, true); if(CopyLow(_Symbol, _Period, 0, InpLookback, lowBuffer) <= 0 || CopyHigh(_Symbol, _Period, 0, InpLookback, highBuffer) <= 0 || CopyClose(_Symbol, _Period, 0, InpLookback, closeBuffer) <= 0) { Print("Error copying price data"); return; } ArrayResize(timeBuffer, InpLookback); ArraySetAsSeries(timeBuffer, true); if(CopyTime(_Symbol, _Period, 0, InpLookback, timeBuffer) <= 0) { Print("Error copying time data"); return; } g_totalBars = InpLookback; // (Further processing follows here...) }
4. 摆动点检测(识别摆动低点和摆动高点)
在我们可以检测背离之前,必须首先精确定位重要的摆动点。两个辅助函数,IsSignificantSwingLow 和 IsSignificantSwingHigh,被用来识别局部最小值和最大值。它们通过将一根 K 线的低点或高点与给定窗口内的相邻 K 线进行比较,并检查百分比差异是否达到设定的阈值来实现这一点。- 这些函数会检查当前 K 线的左侧和右侧。
- 它们计算百分比差异,以确保只标记出显著的摆动。
- 这种过滤减少了噪音,确保我们的背离分析专注于有意义的市场变动。
bool IsSignificantSwingLow(int index, int left, int right) { double currentLow = lowBuffer[index]; // Check left side for local minimum condition for(int i = index - left; i < index; i++) { if(i < 0) continue; double pctDiff = MathAbs((lowBuffer[i] - currentLow) / currentLow) * 100.0; if(lowBuffer[i] < currentLow && pctDiff > InpMinSwingDiffPct) return false; } // Check right side for local minimum condition for(int i = index + 1; i <= index + right; i++) { if(i >= g_totalBars) break; double pctDiff = MathAbs((lowBuffer[i] - currentLow) / currentLow) * 100.0; if(lowBuffer[i] < currentLow && pctDiff > InpMinSwingDiffPct) return false; } return true; } bool IsSignificantSwingHigh(int index, int left, int right) { double currentHigh = highBuffer[index]; // Check left side for local maximum condition for(int i = index - left; i < index; i++) { if(i < 0) continue; double pctDiff = MathAbs((currentHigh - highBuffer[i]) / currentHigh) * 100.0; if(highBuffer[i] > currentHigh && pctDiff > InpMinSwingDiffPct) return false; } // Check right side for local maximum condition for(int i = index + 1; i <= index + right; i++) { if(i >= g_totalBars) break; double pctDiff = MathAbs((currentHigh - highBuffer[i]) / currentHigh) * 100.0; if(highBuffer[i] > currentHigh && pctDiff > InpMinSwingDiffPct) return false; } return true; }
5. 背离检测:看涨和看跌背离
一旦识别出摆动点,算法就会比较近期的摆动点以检测背离。对于看跌背离,代码会查看两个摆动高点,并检查价格是否创出更高的高点(HH),而 RSI 却显示出更低的高点(LH)(或者对于隐藏看跌背离则相反)。对于看涨背离,它会类似地比较两个摆动低点。一个可选的 RSI 阈值可以通过确保较早的 RSI 读数处于超卖区域,来进一步验证看涨信号。
- 使用两个近期的摆动点(高点或低点)进行背离分析。
- 常规背离和隐藏背离的条件被清晰地分开。
- 可选参数(如 RSI 超卖条件)为信号强度提供了额外的过滤。
// --- Bearish Divergence (using swing highs) if(ArraySize(swingHighs) >= 2) { ArraySort(swingHighs); // Ensure ascending order: index 0 is most recent int recent = swingHighs[0]; int previous = swingHighs[1]; // Regular Bearish Divergence: Price makes a higher high while RSI makes a lower high if(highBuffer[recent] > highBuffer[previous] && rsiBuffer[recent] < rsiBuffer[previous] && (rsiBuffer[previous] - rsiBuffer[recent]) >= InpMinRSIDiff) { Print("Regular Bearish Divergence detected at bar ", recent); DisplaySignal("RegBearish Divergence", recent); } // Hidden Bearish Divergence: Price makes a lower high while RSI makes a higher high else if(highBuffer[recent] < highBuffer[previous] && rsiBuffer[recent] > rsiBuffer[previous] && (rsiBuffer[recent] - rsiBuffer[previous]) >= InpMinRSIDiff) { Print("Hidden Bearish Divergence detected at bar ", recent); DisplaySignal("HiddenBearish Divergence", recent); } } // --- Bullish Divergence (using swing lows) if(ArraySize(swingLows) >= 2) { ArraySort(swingLows); // Ensure ascending order: index 0 is most recent int recent = swingLows[0]; int previous = swingLows[1]; // Regular Bullish Divergence: Price makes a lower low while RSI makes a higher low if(lowBuffer[recent] < lowBuffer[previous] && rsiBuffer[recent] > rsiBuffer[previous] && (rsiBuffer[recent] - rsiBuffer[previous]) >= InpMinRSIDiff) { // Optionally require the earlier RSI swing to be oversold if(!InpUseRSIThreshold || rsiBuffer[previous] <= InpRSIOversold) { Print("Regular Bullish Divergence detected at bar ", recent); DisplaySignal("RegBullish Divergence", recent); } } // Hidden Bullish Divergence: Price makes a higher low while RSI makes a lower low else if(lowBuffer[recent] > lowBuffer[previous] && rsiBuffer[recent] < rsiBuffer[previous] && (rsiBuffer[previous] - rsiBuffer[recent]) >= InpMinRSIDiff) { Print("Hidden Bullish Divergence detected at bar ", recent); DisplaySignal("HiddenBullish Divergence", recent); } }
6. 信号显示与记录
当检测到背离时,在视觉上标记信号并记录其详细信息以供后续评估,这一点非常重要。DisplaySignal() 函数不仅在图表上创建一个箭头(对看涨和看跌信号使用不同的箭头代码和颜色),还会更新最新信号的标签,并将信号的元数据存储在一个全局数组中。这种系统性的记录使得后续可以对策略进行回测。
- 通过检查相似 K 线的信号是否已存在,来防止重复信号。
- 箭头和标签等视觉提示增强了图表的可读性。
- 每个信号都连同其类型、K 线索引、时间和价格等详细信息一起存储,以便于后续的性能评估。
void DisplaySignal(string signalText, int barIndex) { // Prevent duplicate signals on the same or nearby bars for(int i = 0; i < ArraySize(signals); i++) { if(StringFind(signals[i].type, signalText) != -1) if(MathAbs(signals[i].barIndex - barIndex) < InpMinBarsBetweenSignals) return; } // Update a label for the latest regular signal if(StringFind(signalText, "Reg") != -1) { string labelName = "LatestSignal"; if(ObjectFind(0, labelName) == -1) { if(!ObjectCreate(0, labelName, OBJ_LABEL, 0, 0, 0)) { Print("Failed to create LatestSignal label"); return; } ObjectSetInteger(0, labelName, OBJPROP_CORNER, 0); ObjectSetInteger(0, labelName, OBJPROP_XDISTANCE, 10); ObjectSetInteger(0, labelName, OBJPROP_YDISTANCE, 20); ObjectSetInteger(0, labelName, OBJPROP_COLOR, clrWhite); } ObjectSetString(0, labelName, OBJPROP_TEXT, signalText); } // Create an arrow object to mark the signal on the chart string arrowName = "Arrow_" + signalText + "_" + IntegerToString(barIndex); if(ObjectFind(0, arrowName) < 0) { int arrowCode = 0; double arrowPrice = 0.0; color arrowColor = clrWhite; double point = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_POINT); if(StringFind(signalText, "Bullish") != -1) { arrowCode = 233; // Wingdings up arrow arrowColor = clrLime; arrowPrice = lowBuffer[barIndex] - (InpArrowOffset * point); } else if(StringFind(signalText, "Bearish") != -1) { arrowCode = 234; // Wingdings down arrow arrowColor = clrRed; arrowPrice = highBuffer[barIndex] + (InpArrowOffset * point); } if(!ObjectCreate(0, arrowName, OBJ_ARROW, 0, timeBuffer[barIndex], arrowPrice)) { Print("Failed to create arrow object ", arrowName); return; } ObjectSetInteger(0, arrowName, OBJPROP_COLOR, arrowColor); ObjectSetInteger(0, arrowName, OBJPROP_ARROWCODE, arrowCode); } // Record the signal details for later backtesting evaluation SignalInfo sig; sig.type = signalText; sig.barIndex = barIndex; sig.signalTime = timeBuffer[barIndex]; if(StringFind(signalText, "Bullish") != -1) sig.signalPrice = lowBuffer[barIndex]; else sig.signalPrice = highBuffer[barIndex]; ArrayResize(signals, ArraySize(signals) + 1); signals[ArraySize(signals) - 1] = sig; UpdateSignalCountLabel(); }
反初始化时的回测评估
最后,当EA反初始化时,会调用 EvaluateSignalsAndPrint() 函数。此函数通过将信号发出后几根 K 线的价格变动与信号记录的价格进行比较,来回顾性地评估所有已记录的信号。它会计算常规信号和隐藏信号的准确率,为我们的背离策略的性能提供宝贵的反馈。
- 该函数检索完整的历史收盘价数据。
- 每个信号在固定的 K 线数量(由 InpEvalBars 设置)之后被评估。
- 会为整体信号以及分别为常规信号和隐藏信号计算准确率指标,以辅助性能验证。
void EvaluateSignalsAndPrint() { double closeAll[]; int totalBars = CopyClose(_Symbol, _Period, 0, WHOLE_ARRAY, closeAll); if(totalBars <= 0) { Print("Error copying complete close data for evaluation"); return; } ArraySetAsSeries(closeAll, true); int totalEvaluated = 0, regTotal = 0, hidTotal = 0; int regEval = 0, hidEval = 0; int regCorrect = 0, hidCorrect = 0; for(int i = 0; i < ArraySize(signals); i++) { int evalIndex = signals[i].barIndex - InpEvalBars; if(evalIndex < 0) continue; double evalClose = closeAll[evalIndex]; if(StringFind(signals[i].type, "Bullish") != -1) { if(StringFind(signals[i].type, "Reg") != -1) { regTotal++; regEval++; if(evalClose > signals[i].signalPrice) regCorrect++; } else if(StringFind(signals[i].type, "Hidden") != -1) { hidTotal++; hidEval++; if(evalClose > signals[i].signalPrice) hidCorrect++; } totalEvaluated++; } else if(StringFind(signals[i].type, "Bearish") != -1) { if(StringFind(signals[i].type, "Reg") != -1) { regTotal++; regEval++; if(evalClose < signals[i].signalPrice) regCorrect++; } else if(StringFind(signals[i].type, "Hidden") != -1) { hidTotal++; hidEval++; if(evalClose < signals[i].signalPrice) hidCorrect++; } totalEvaluated++; } } double overallAccuracy = (totalEvaluated > 0) ? (double)(regCorrect + hidCorrect) / totalEvaluated * 100.0 : 0.0; double regAccuracy = (regEval > 0) ? (double)regCorrect / regEval * 100.0 : 0.0; double hidAccuracy = (hidEval > 0) ? (double)hidCorrect / hidEval * 100.0 : 0.0; Print("----- Backtest Signal Evaluation -----"); Print("Total Signals Generated: ", ArraySize(signals)); Print("Signals Evaluated: ", totalEvaluated); Print("Overall Accuracy: ", DoubleToString(overallAccuracy, 2), "%"); Print("Regular Signals: ", regTotal, " | Evaluated: ", regEval, " | Accuracy: ", DoubleToString(regAccuracy, 2), "%"); Print("Hidden Signals: ", hidTotal, " | Evaluated: ", hidEval, " | Accuracy: ", DoubleToString(hidAccuracy, 2), "%"); }
测试结果
使用 MetaEditor 成功编译您的 EA 后,将其拖到图表上进行测试。请确保您使用的是模拟账户,以避免真实资金的风险。您也可以在图表上添加 RSI 指标,以便在测试 EA 时轻松确认信号。为此,请导航到“指标”选项卡,在“面板”文件夹下选择 RSI 指标,并设置您偏好的参数,确保它们与您 EA 中的参数相匹配。查看下面的 GIF,它说明了如何在 MetaTrader 5 图表上添加 RSI 指标窗口。您还可以看到一个已确认的信号,即在一分钟时间框架上的常规看涨背离。
图 5. 设置指标与测试结果 1
以下是我们在 Boom 500 上进行的另一项测试,该测试得到了价格行为和 RSI 指标的双重确认,显示了一个卖出信号。
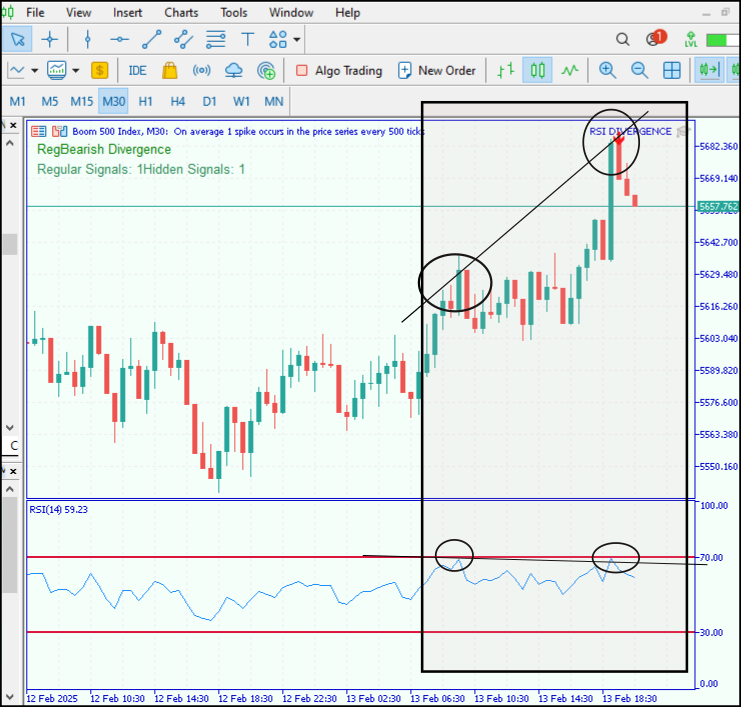
图 6. 测试结果 2
另一项测试使用了下面的 GIF 中的回测功能,其中显示了几个积极的变化。如果您仔细观察,会注意到既有隐藏的延续信号,也有常规信号。然而,尽管一些信号产生了积极影响,但由于缺乏确认,仍有少数信号需要被过滤掉。
图 7. 测试结果 3
结论
该工具已被证明与价格行为高度一致,这也是我们系列文章的核心目标,即创建尽可能多的价格行为分析工具。我非常欣赏 RSI 指标如何通过从背离中提取积极信号来有效地与价格行为互动。我们进行的测试显示了有希望的结果和积极的趋势。
然而,我认为现在是时候引入另一项增强了,即使用外部库来进行精确和准确的摆动点识别,从而提高信号的准确性。我的建议是彻底测试该工具,并调整其参数以适应您的交易风格。请记住,每个生成的信号在入场前都应进行交叉核对,因为该工具旨在帮助您监控市场并确认您的整体策略。
| 日期 | 工具名称 | 说明 | 版本 | 更新 | 提示 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01/10/24 | 图表投影仪 | 用于叠加前一天价格走势(带“幽灵”效果)的脚本。 | 1.0 | 首次发布 | Lynnchris工具箱中的第一款工具 |
| 18/11/24 | 分析评论 | 它以表格形式提供前一日的市场信息,并预测市场的未来走向。 | 1.0 | 首次发布 | Lynnchris工具箱中的第二款工具 |
| 27/11/24 | 分析大师 | 市场指标每两小时定期更新 | 1.01 | 第二版 | Lynnchris工具箱中的第三款工具 |
| 02/12/24 | 分析预测器 | 每两小时定期更新市场指标,并集成Telegram推送功能。 | 1.1 | 第三版 | 工具4 |
| 09/12/24 | 波动性导航工具 | 该EA使用布林带、RSI和ATR指标分析市场状况。 | 1.0 | 首次发布 | 工具5 |
| 19/12/24 | 均值回归信号收割器 | 使用均值回归策略分析市场并提供信号 | 1.0 | 首次发布 | 工具6 |
| 9/01/25 | 信号脉冲 | 多时间框架分析器 | 1.0 | 首次发布 | 工具7 |
| 17/01/25 | 指标看板 | 带按钮的分析面板 | 1.0 | 首次发布 | 工具8 |
| 21/01/25 | 外部资金流 | 通过外部库进行分析 | 1.0 | 首次发布 | 工具9 |
| 27/01/25 | VWAP | 成交量加权平均价格 | 1.3 | 首次发布 | 工具10 |
| 02/02/25 | Heikin Ashi | 势平滑与反转信号识别 | 1.0 | 首次发布 | 工具11 |
| 04/02/25 | FibVWAP | 通过 Python 分析生成信号 | 1.0 | 首次发布 | 工具12 |
| 14/02/25 | RSI 背离 | 价格走势与 RSI 背离的对比 | 1.0 | 首次发布 | 工具13 |
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/17198
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 在 MQL5 中创建交易管理面板(第九部分):代码组织(二):模块化
在 MQL5 中创建交易管理面板(第九部分):代码组织(二):模块化
 MQL5中的自动化交易策略(第七部分):构建具备仓位动态调整功能的网格交易EA
MQL5中的自动化交易策略(第七部分):构建具备仓位动态调整功能的网格交易EA
 在MQL5中构建带自定义画布图形的凯特纳通道(Keltner Channel)指标
在MQL5中构建带自定义画布图形的凯特纳通道(Keltner Channel)指标
