MQL5自动化交易策略(第十一部分):开发多层级网格交易系统
概述
在前一篇文章(第十部分)中,我们使用MetaQuotes Language 5(MQL5)开发了一款EA,以结合移动平均线和动量过滤器的方式实现了趋势平移动量策略的自动化。现在,在第十一部分中,我们将重点构建一个多层级网格交易系统,该系统采用分层网格方法,以利用市场波动获利。本文将通过以下主题展开论述:
到本文结尾时,您将获得全面深入的理解,并拥有一套可直接用于实盘交易的功能完备的程序。让我们开始深入实践!
理解多级网格系统的体系架构
多层级网格交易系统是一种结构化策略,它通过在一系列价格水平上按预定间隔设置一系列买入和卖出订单,来利用市场波动获利。我们即将实施的这一策略并非旨在预测市场走向,而是着眼于从价格的自然变动中获利,无论市场上涨、下跌还是横盘,都能捕捉收益。
基于这一理念,我们的程序将通过模块化设计来实现多层级网格策略,该设计将信号检测、订单执行和风险管理分离开来。在系统开发过程中,我们首先将初始化关键参数,例如用于识别交易信号的移动平均线(MA),并设置相应的结构体,包含交易细节,如初始手数、网格间距和止盈水平。
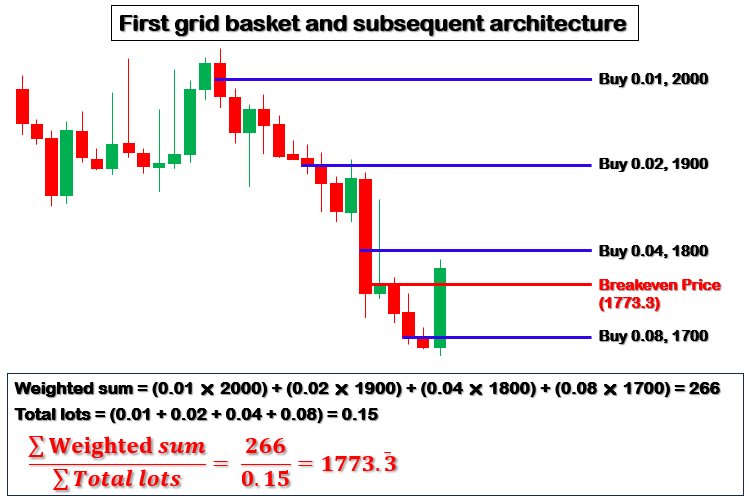
随着市场的发展,程序将监控价格走势以触发新交易并管理现有头寸,根据预定义条件在每个网格层级添加订单,并动态调整风险参数。该架构还将包括重新计算盈亏平衡点、修改止盈目标以及在达到盈利目标或风险阈值时平仓的功能。这一结构化计划不仅将程序组织成独立、易于管理的组件,还能确保网格的每一层级都为一个连贯、风险可控的交易策略做出贡献,该策略已准备好进行严格的回测和交易部署。简言之,架构将如下所示:
在MQL5中的实现
要在MQL5中创建该程序,请打开MetaEditor,进入导航器,找到“指标”文件夹,点击“新建”选项卡,并按照提示创建文件。文件创建完成后,在编码环境中,我们需要声明一些将在整个程序中使用的基础数据和全局变量。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Copyright 2025, Forex Algo-Trader, Allan. | //| "https://t.me/Forex_Algo_Trader" | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Forex Algo-Trader, Allan" #property link "https://t.me/Forex_Algo_Trader" #property version "1.00" #property description "This EA trades multiple signals with grid strategy using baskets" #property strict #include <Trade/Trade.mqh> //--- Includes the standard trading library for executing trades CTrade obj_Trade; //--- Instantiates the CTrade object used for managing trade operations //--- Closure Mode Enumeration and Inputs enum ClosureMode { CLOSE_BY_PROFIT, //--- Use total profit (in currency) to close positions CLOSE_BY_POINTS //--- Use points threshold from breakeven to close positions }; input group "General EA Settings" input ClosureMode closureMode = CLOSE_BY_POINTS; input double inpLotSize = 0.01; input long inpMagicNo = 1234567; input int inpTp_Points = 100; input int inpGridSize = 100; input double inpMultiplier = 2.0; input int inpBreakevenPts = 50; input int maxBaskets = 5; input group "MA Indicator Settings" //--- Begins the input group for Moving Average indicator settings input int inpMAPeriod = 21; //--- Period used for the Moving Average calculation
这里,我们构建程序的基础组件,以确保交易执行的顺畅性和头寸管理的战略性。我们首先引入“Trade/Trade.mqh”库,该库提供了访问基本交易执行功能的途径。为便于交易操作,我们将“CTrade”对象实例化为“obj_Trade”,以便在自动化策略中能够高效地下达、修改和关闭订单。
我们定义了“ClosureMode”枚举,以便灵活管理交易退出。程序有两种运行模式:“CLOSE_BY_PROFIT”,即当累计总利润达到账户货币中指定的阈值时触发平仓;“CLOSE_BY_POINTS”,即根据与盈亏平衡点的预定义距离平仓。这样确保了用户可以根据市场行为和风险承受能力动态调整退出策略。
接下来,我们在“通用EA设置”下引入了一个结构化的输入部分,以便用户自定义交易策略。我们指定了“inpLotSize”来控制初始交易量,并使用“inpMagicNo”来唯一标识EA的交易,防止与其他活跃策略产生冲突。对于基于网格的执行方式,我们设置了“inpTp_Points”来确定每笔交易的止盈水平,而“inpGridSize”则定义了连续网格订单之间的间距。“inpMultiplier”参数则按比例逐步扩大交易规模,实施自适应网格扩展策略,以在管理风险敞口的同时最大化利润潜力。为进一步优化风险控制,我们配置了“inpBreakevenPts”,该参数在达到一定阈值后将交易移至盈亏平衡点,以及“maxBaskets”,该参数限制了EA可以同时管理的独立网格结构的数量。
为增强交易过滤能力,我们在“移动平均线指标设置”下引入了移动平均线机制。这里,我们定义了“inpMAPeriod”,该参数用于确定计算移动平均线所使用的周期数。这样有助于使网格交易与当前市场趋势保持一致,过滤掉不利条件,并确保交易入场与更广泛的市场动量相契合。接下来,由于我们需要处理许多信号实例,因此可以定义相应的结构体。
//--- Basket Structure struct BasketInfo { int basketId; //--- Unique basket identifier (e.g., 1, 2, 3...) long magic; //--- Unique magic number for this basket to differentiate its trades int direction; //--- Direction of the basket: POSITION_TYPE_BUY or POSITION_TYPE_SELL double initialLotSize; //--- The initial lot size assigned to the basket double currentLotSize; //--- The current lot size for subsequent grid trades double gridSize; //--- The next grid level price for the basket double takeProfit; //--- The current take-profit price for the basket datetime signalTime; //--- Timestamp of the signal to avoid duplicate trade entries };
这里,我们定义“BasketInfo”结构体 ,以便独立地组织和管理每个网格篮子。我们为每个篮子分配一个唯一的“basketId”以进行追踪,并使用“magic”确保我们的交易与其他交易区分开来。我们通过“direction”确定交易方向,决定是执行买入策略还是卖出策略。
我们为篮子中的第一笔交易设置“initialLotSize”(初始手数),而“currentLotSize”(当前手数)则针对后续交易进行动态调整。我们使用“gridSize”(网格间距)来确定交易之间的间隔,并使用“takeProfit”(止盈)来定义我们的盈利目标。为防止重复入场,我们使用“signalTime”(信号时间)来追踪信号的发出时间。然后,可以使用所定义的结构体声明一个存储数组,并声明一些初始全局变量。
BasketInfo baskets[]; //--- Dynamic array to store active basket information int nextBasketId = 1; //--- Counter for assigning unique IDs to new baskets long baseMagic = inpMagicNo;//--- Base magic number obtained from user input double takeProfitPts = inpTp_Points * _Point; //--- Convert take profit points into price units double gridSize_Spacing = inpGridSize * _Point; //--- Convert grid size spacing from points into price units double profitTotal_inCurrency = 100; //--- Target profit in account currency for closing positions //--- Global Variables int totalBars = 0; //--- Stores the total number of bars processed so far int handle; //--- Handle for the Moving Average indicator double maData[]; //--- Array to store Moving Average indicator data
我们使用动态数组“baskets[]”来存储活跃篮子的信息,确保能够高效追踪多个持仓头寸。变量“nextBasketId”为每个新篮子分配唯一标识符,而“baseMagic”则确保系统内所有交易均可通过用户自定义的magic数字进行区分。我们将用户输入的点数转换为价格单位,通过将“inpTp_Points”(止盈点数)和“inpGridSize”(网格间距点数)乘以“_Point”(点值常量),从而精确控制“takeProfitPts”(止盈价格差值)和“gridSize_Spacing”(网格间距价格差值)。变量“profitTotal_inCurrency”定义了在使用基于货币金额的平仓模式时,关闭所有头寸要求的利润阈值。
在技术分析方面,我们初始化“totalBars”以追踪已处理的价格K线数量,使用“handle”存储移动平均线指标的句柄,并创建“maData[]”数组用于存储计算得出的移动平均线数值。至此,我们可以定义一部分任意函数原型,以便在程序后续需要时调用使用。
//--- Function Prototypes void InitializeBaskets(); //--- Prototype for basket initialization function (if used) void CheckAndCloseProfitTargets(); //--- Prototype to check and close positions if profit target is reached void CheckForNewSignal(double ask, double bid); //--- Prototype to check for new trading signals based on price bool ExecuteInitialTrade(int basketIdx, double ask, double bid, int direction); //--- Prototype to execute the initial trade for a basket void ManageGridPositions(int basketIdx, double ask, double bid); //--- Prototype to manage and add grid positions for an active basket void UpdateMovingAverage(); //--- Prototype to update the Moving Average indicator data bool IsNewBar(); //--- Prototype to check whether a new bar has formed double CalculateBreakevenPrice(int basketId); //--- Prototype to calculate the weighted breakeven price for a basket void CheckBreakevenClose(int basketIdx, double ask, double bid); //--- Prototype to check and close positions based on breakeven criteria void CloseBasketPositions(int basketId); //--- Prototype to close all positions within a basket string GetPositionComment(int basketId, bool isInitial); //--- Prototype to generate a comment for a position based on basket and trade type int CountBasketPositions(int basketId); //--- Prototype to count the number of open positions in a basket
这里,我们定义多层级网格交易系统的核心操作函数原型。这些函数将确保模块化设计,使我们能够高效地构建交易执行、头寸管理和风险控制流程。首先定义“InitializeBaskets()”函数,该函数负责初始化系统以跟踪活跃篮子。“CheckAndCloseProfitTargets()”函数确保在达到预设盈利条件时关闭头寸。为检测交易机会,“CheckForNewSignal()”函数会评估价格水平,以确定是否应执行新的交易信号。
“ExecuteInitialTrade()”函数将管理交易篮子中的首笔交易,而“ManageGridPositions()”函数则确保随着市场波动,网格层级能够系统性扩展。“UpdateMovingAverage()”函数获取并处理移动平均线指标数据,以支持信号生成。在交易管理方面,“IsNewBar()”函数通过确保仅在新的价格数据出现时执行操作,从而优化执行效率。“CalculateBreakevenPrice()”函数计算篮子的加权盈亏平衡价格,而“CheckBreakevenClose()”函数则根据盈亏平衡标准确定是否满足退出头寸的条件。
为管理篮子头寸,“CloseBasketPositions()”函数用于受控退出,确保在需要时关闭篮子内的所有头寸。“GetPositionComment()”函数提供结构化的交易注释,改善交易跟踪,而“CountBasketPositions()”函数则有助于监控篮子内的活跃头寸数量,确保系统在既定的风险限制内运行。
现在,可以从初始化移动平均线开始,因为我们仅将其用于信号生成。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Expert initialization function //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { handle = iMA(_Symbol, _Period, inpMAPeriod, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE); //--- Initialize the Moving Average indicator with specified period and parameters if(handle == INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("ERROR: Unable to initialize Moving Average indicator!"); //--- Log error if indicator initialization fails return(INIT_FAILED); //--- Terminate initialization with a failure code } ArraySetAsSeries(maData, true); //--- Set the moving average data array as a time series (newest data at index 0) ArrayResize(baskets, 0); //--- Initialize the baskets array as empty at startup obj_Trade.SetExpertMagicNumber(baseMagic); //--- Set the default magic number for trade operations return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); //--- Signal that initialization completed successfully }
在OnInit事件处理程序中,我们首先使用 iMA()函数初始化移动平均线指标,通过指定周期和参数来获取基于趋势的数据。如果指标句柄无效(INVALID_HANDLE),我们会记录错误信息,并使用INIT_FAILED终止初始化流程,以防止EA在数据缺失的情况下运行。
接下来,我们使用ArraySetAsSeries函数配置移动平均线数据数组,确保最新值存储在索引0处,以便高效地访问。随后,我们将“baskets”数组大小重置为0,那么当新交易开立时,可以为后续动态分配做好准备。最后,我们通过“SetExpertMagicNumber()”方法将基础magic数字分配给交易对象,使得EA能够通过唯一标识符跟踪和管理交易。若所有组件均成功初始化,我们返回 INIT_SUCCEEDED,确认EA已经准备好开始执行。
由于我们已经存储了数据,在 OnDeinit事件处理程序中,当不再需要该程序时,可通过调用IndicatorRelease函数释放相关资源。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Expert deinitialization function //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { IndicatorRelease(handle); //--- Release the indicator handle to free up resources when the EA is removed }
随后,我们可以在OnTick事件处理器中每个价格波动(tick)时处理数据。然而,我们希望每根K线仅运行一次程序,因此需要为此定义一个专用函数。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Expert tick function //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { if(IsNewBar()) { //--- Execute logic only when a new bar is detected } }
该函数的原型如下:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Check for New Bar //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool IsNewBar() { int bars = iBars(_Symbol, _Period); //--- Get the current number of bars on the chart for the symbol and period if(bars > totalBars) { //--- Compare the current number of bars with the previously stored total totalBars = bars; //--- Update the stored bar count to the new value return true; //--- Return true to indicate a new bar has formed } return false; //--- Return false if no new bar has been detected }
这部分中,我们定义“IsNewBar()”函数,该函数用于检查图表上是否已形成新的K线,这对于确保我们的EA仅在新K线出现时处理新的价格数据至关重要,可避免不必要的重复计算。我们首先使用iBars函数获取图表上当前的K线数量,该函数提供当前交易品种和时间框架下的历史K线总数。然后,我们将此值与存储先前记录的K线数量的变量“totalBars”进行比较。
如果当前K线数量大于“totalBars”变量中存储的值,则意味着已经出现新的K线。在此情况下,我们使用新的K线数量更新“totalBars”变量,并返回“true”,表示EA应当继续进行基于K线的计算或交易逻辑。如果未检测到新的K线柱,则函数返回“false”,确保EA不会对同一K线柱执行冗余操作。
现在,一旦检测到新的K线柱,我们就需要获取移动平均线数据,以便进一步处理。为此,我们使用一个函数。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Update Moving Average //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void UpdateMovingAverage() { if(CopyBuffer(handle, 0, 1, 3, maData) < 0) { //--- Copy the latest 3 values from the Moving Average indicator buffer into the maData array Print("Error: Unable to update Moving Average data."); //--- Log an error if copying the indicator data fails } }
对于“UpdateMovingAverage()”函数(该函数确保我们的EA从移动平均线指标中获取最新值),我们使用 CopyBuffer() 函数从移动平均线指标缓冲区中提取最近三个值,并将它们存储在“maData”数组中。参数分别指定了指标句柄(“handle”)、缓冲区索引(主线为0)、起始位置(1以跳过当前正在形成的K线)、获取值的数量(3)以及目标数组(“maData”)。
如果数据获取失败,我们使用Print()函数记录错误信息,以提醒我们注意指标数据获取过程中可能存在的问题,从而保护EA免受不完整或缺失的移动平均线值的影响,确保决策的可靠性。随后,我们可以调用该函数,并使用获取的数据生成交易信号。
UpdateMovingAverage(); //--- Update the Moving Average data for the current bar double ask = NormalizeDouble(SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_ASK), _Digits); //--- Get and normalize the current ask price double bid = NormalizeDouble(SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_BID), _Digits); //--- Get and normalize the current bid price //--- Check for new signals and create baskets accordingly CheckForNewSignal(ask, bid);
在获取指标数据后,我们分别使用SymbolInfoDouble()函数结合SYMBOL_ASK和SYMBOL_BID常量,获取当前的卖出价和买入价。由于价格值通常包含多位小数,我们使用 NormalizeDouble函数配合_Digits参数,确保价格按照交易品种的精度要求正确格式化。
最后,我们调用“CheckForNewSignal()”函数,并将规范化后的卖出价和买入价作为参数传入。以下是该函数的代码段。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Check for New Crossover Signal //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CheckForNewSignal(double ask, double bid) { double close1 = iClose(_Symbol, _Period, 1); //--- Retrieve the close price of the previous bar double close2 = iClose(_Symbol, _Period, 2); //--- Retrieve the close price of the bar before the previous one datetime currentBarTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, 1); //--- Get the time of the current bar if(ArraySize(baskets) >= maxBaskets) return; //--- Exit if the maximum allowed baskets are already active //--- Buy signal: current bar closes above the MA while the previous closed below it if(close1 > maData[1] && close2 < maData[1]) { //--- Check if this signal was already processed by comparing signal times in existing baskets for(int i = 0; i < ArraySize(baskets); i++) { if(baskets[i].signalTime == currentBarTime) return; //--- Signal already acted upon; exit the function } int basketIdx = ArraySize(baskets); //--- Index for the new basket equals the current array size ArrayResize(baskets, basketIdx + 1); //--- Increase the size of the baskets array to add a new basket if (ExecuteInitialTrade(basketIdx, ask, bid, POSITION_TYPE_BUY)){ baskets[basketIdx].signalTime = currentBarTime; //--- Record the time of the signal after a successful trade } } //--- Sell signal: current bar closes below the MA while the previous closed above it else if(close1 < maData[1] && close2 > maData[1]) { //--- Check for duplicate signals by verifying the signal time in active baskets for(int i = 0; i < ArraySize(baskets); i++) { if(baskets[i].signalTime == currentBarTime) return; //--- Signal already acted upon; exit the function } int basketIdx = ArraySize(baskets); //--- Determine the index for the new basket ArrayResize(baskets, basketIdx + 1); //--- Resize the baskets array to accommodate the new basket if (ExecuteInitialTrade(basketIdx, ask, bid, POSITION_TYPE_SELL)){ baskets[basketIdx].signalTime = currentBarTime; //--- Record the signal time for the new sell basket } } }
对于“CheckForNewSignal()”函数,我们首先使用iClose()函数获取前两根K线的收盘价。这样有助于我们判断是否发生了均线交叉。我们还使用iTime()函数获取最近一根K线的时间戳,以确保不会重复处理同一信号。
在继续执行前,我们会检查当前活跃的篮子数量是否已达到“maxBaskets”限制。如果是,则函数直接返回,以防止过度堆积交易。对于买入信号,我们会检查最近一根K线的收盘价是否高于移动平均线,而前一根K线的收盘价是否低于它。如果满足这一交叉条件,我们会遍历现有持仓组,以确保尚未处理过相同信号。如果信号是新的,我们会增加“baskets”数组的大小,将新持仓组存储在下一个可用索引处,并以POSITION_TYPE_BUY顺序调用“ExecuteInitialTrade()”函数执行买入交易。如果交易成功执行,我们会记录信号时间,以防止重复入场。
相类似地,对于卖出信号,我们会检查最近一根K线的收盘价是否低于移动平均线,而前一根K线的收盘价是否高于它。如果满足这一条件且未发现重复信号,我们会扩展“baskets”数组,使用POSITION_TYPE_SELL类型的“ExecuteInitialTrade()”函数执行初始卖出交易,并记录信号时间以确保唯一性。执行交易的具体函数如下:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Execute Initial Trade //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool ExecuteInitialTrade(int basketIdx, double ask, double bid, int direction) { baskets[basketIdx].basketId = nextBasketId++; //--- Assign a unique basket ID and increment the counter baskets[basketIdx].magic = baseMagic + baskets[basketIdx].basketId * 10000; //--- Calculate a unique magic number for the basket baskets[basketIdx].initialLotSize = inpLotSize; //--- Set the initial lot size for the basket from input baskets[basketIdx].currentLotSize = inpLotSize; //--- Initialize current lot size to the same as the initial lot size baskets[basketIdx].direction = direction; //--- Set the trade direction (buy or sell) for the basket bool isTradeExecuted = false; //--- Initialize flag to track if the trade was successfully executed string comment = GetPositionComment(baskets[basketIdx].basketId, true); //--- Generate a comment string indicating an initial trade obj_Trade.SetExpertMagicNumber(baskets[basketIdx].magic); //--- Set the trade object's magic number to the basket's unique value if(direction == POSITION_TYPE_BUY) { baskets[basketIdx].gridSize = ask - gridSize_Spacing; //--- Set the grid level for subsequent buy orders below the current ask price baskets[basketIdx].takeProfit = ask + takeProfitPts; //--- Calculate the take profit level for the buy order if(obj_Trade.Buy(baskets[basketIdx].currentLotSize, _Symbol, ask, 0, baskets[basketIdx].takeProfit, comment)) { Print("Basket ", baskets[basketIdx].basketId, ": Initial BUY at ", ask, " | Magic: ", baskets[basketIdx].magic); //--- Log the successful buy order details isTradeExecuted = true; //--- Mark the trade as executed successfully } else { Print("Basket ", baskets[basketIdx].basketId, ": Initial BUY failed, error: ", GetLastError()); //--- Log the error if the buy order fails ArrayResize(baskets, ArraySize(baskets) - 1); //--- Remove the basket if trade execution fails } } else if(direction == POSITION_TYPE_SELL) { baskets[basketIdx].gridSize = bid + gridSize_Spacing; //--- Set the grid level for subsequent sell orders above the current bid price baskets[basketIdx].takeProfit = bid - takeProfitPts; //--- Calculate the take profit level for the sell order if(obj_Trade.Sell(baskets[basketIdx].currentLotSize, _Symbol, bid, 0, baskets[basketIdx].takeProfit, comment)) { Print("Basket ", baskets[basketIdx].basketId, ": Initial SELL at ", bid, " | Magic: ", baskets[basketIdx].magic); //--- Log the successful sell order details isTradeExecuted = true; //--- Mark the trade as executed successfully } else { Print("Basket ", baskets[basketIdx].basketId, ": Initial SELL failed, error: ", GetLastError()); //--- Log the error if the sell order fails ArrayResize(baskets, ArraySize(baskets) - 1); //--- Remove the basket if trade execution fails } } return (isTradeExecuted); //--- Return the status of the trade execution }
我们定义“ExecuteInitialTrade()”函数,以确保每个篮子拥有唯一标识符、分配独立的magic数字,并在下单前初始化关键交易参数。首先,我们通过递增“nextBasketId”变量来分配一个“basketId”。接着,通过将缩放偏移量添加到“baseMagic”值上,为该持仓组生成一个唯一的magic数字,确保每个篮子独立运行。初始头寸规模和当前头寸规模均设置为“inpLotSize”,以确定该篮子的基础交易规模。最后,存储“direction”参数以区分买入持仓组和卖出持仓组。
为了确保交易能够被准确识别,我们调用“GetPositionComment()”函数生成描述性备注信息,并通过“SetExpertMagicNumber()”方法将持仓组的magic数字应用到交易对象中。该函数定义如下,其中我们使用StringFormat函数结合 三元运算符(ternary operator)生成备注信息。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Generate Position Comment //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string GetPositionComment(int basketId, bool isInitial) { return StringFormat("Basket_%d_%s", basketId, isInitial ? "Initial" : "Grid"); //--- Generate a standardized comment string for a position indicating basket ID and trade type }
若交易方向为POSITION_TYPE_BUY,我们通过从卖出价中减去“gridSize_Spacing”计算网格价位,并通过在卖出价基础上加上“takeProfitPts”确定止盈价位。随后,我们使用"CTrade"类中的“Buy()”函数下单。如果下单成功,我们通过 Print()函数记录交易详情,并标记该交易为已执行。如果下单失败,我们通过GetLastError()函数记录错误信息,并使用ArrayResize()函数缩小“baskets”数组规模,移除失败的篮子。
对于卖出交易(POSITION_TYPE_SELL),我们通过将“gridSize_Spacing”加至买入价计算网格价位,并通过从买入价中减去“takeProfitPts”确定止盈价位。交易通过“Sell()”函数执行。与买入交易类似,成功执行时使用“Print()”函数记录交易详情,失败时则通过GetLastError记录错误信息,并调用“ArrayResize()”缩小“baskets”数组规模,移除失败的篮子。
在执行任何交易前,该函数会先调用“ArrayResize()”扩大数组容量以确保有足够的空间。最后,如果交易成功执行,函数返回“true”;否则返回“false”。运行程序后,我们得到以下结果:
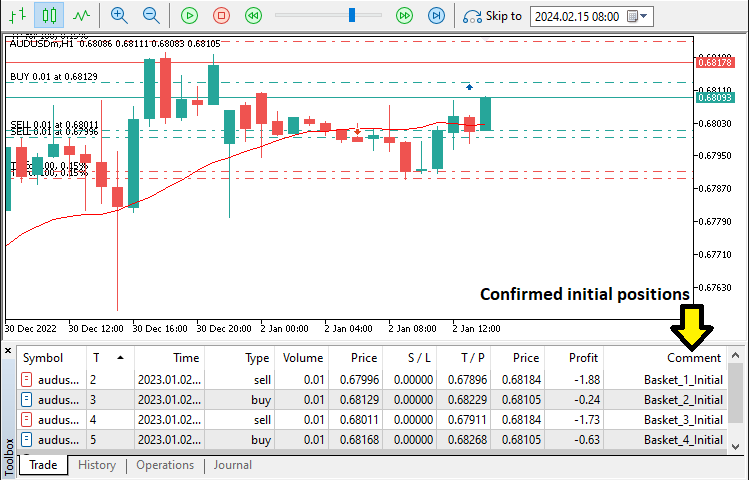
由图可见,我们已根据篮子或已触发的信号确认了初始头寸。接下来,我们需要通过逐个管理每个篮子来动态调控这些头寸。为实现这一目标,我们使用for循环进行迭代处理。
//--- Loop through all active baskets to manage grid positions and potential closures for(int i = 0; i < ArraySize(baskets); i++) { ManageGridPositions(i, ask, bid); //--- Manage grid trading for the current basket }
这部分中,我们通过for循环遍历所有活跃持仓组,确保每个持仓组均得到相应管理。ArraySize函数用于确定“baskets”数组中当前的篮子数量,以此设定循环的上限值。这一机制可确保我们处理所有现有篮子,同时避免超出数组边界。针对每个篮子,我们调用“ManageGridPositions()”函数,并传入该持仓组的索引及标准化后的“卖出价”和“买入价”。函数实现如下:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Manage Grid Positions //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void ManageGridPositions(int basketIdx, double ask, double bid) { bool newPositionOpened = false; //--- Flag to track if a new grid position has been opened string comment = GetPositionComment(baskets[basketIdx].basketId, false); //--- Generate a comment for grid trades in this basket obj_Trade.SetExpertMagicNumber(baskets[basketIdx].magic); //--- Ensure the trade object uses the basket's unique magic number if(baskets[basketIdx].direction == POSITION_TYPE_BUY) { if(ask <= baskets[basketIdx].gridSize) { //--- Check if the ask price has reached the grid level for a buy order baskets[basketIdx].currentLotSize *= inpMultiplier; //--- Increase the lot size based on the defined multiplier if(obj_Trade.Buy(baskets[basketIdx].currentLotSize, _Symbol, ask, 0, baskets[basketIdx].takeProfit, comment)) { newPositionOpened = true; //--- Set flag if the grid buy order is successfully executed Print("Basket ", baskets[basketIdx].basketId, ": Grid BUY at ", ask); //--- Log the grid buy execution details baskets[basketIdx].gridSize = ask - gridSize_Spacing; //--- Adjust the grid level for the next potential buy order } else { Print("Basket ", baskets[basketIdx].basketId, ": Grid BUY failed, error: ", GetLastError()); //--- Log an error if the grid buy order fails } } } else if(baskets[basketIdx].direction == POSITION_TYPE_SELL) { if(bid >= baskets[basketIdx].gridSize) { //--- Check if the bid price has reached the grid level for a sell order baskets[basketIdx].currentLotSize *= inpMultiplier; //--- Increase the lot size based on the multiplier for grid orders if(obj_Trade.Sell(baskets[basketIdx].currentLotSize, _Symbol, bid, 0, baskets[basketIdx].takeProfit, comment)) { newPositionOpened = true; //--- Set flag if the grid sell order is successfully executed Print("Basket ", baskets[basketIdx].basketId, ": Grid SELL at ", bid); //--- Log the grid sell execution details baskets[basketIdx].gridSize = bid + gridSize_Spacing; //--- Adjust the grid level for the next potential sell order } else { Print("Basket ", baskets[basketIdx].basketId, ": Grid SELL failed, error: ", GetLastError()); //--- Log an error if the grid sell order fails } } } //--- If a new grid position was opened and there are multiple positions, adjust the take profit to breakeven if(newPositionOpened && CountBasketPositions(baskets[basketIdx].basketId) > 1) { double breakevenPrice = CalculateBreakevenPrice(baskets[basketIdx].basketId); //--- Calculate the weighted breakeven price for the basket double newTP = (baskets[basketIdx].direction == POSITION_TYPE_BUY) ? breakevenPrice + (inpBreakevenPts * _Point) : //--- Set new TP for buy positions breakevenPrice - (inpBreakevenPts * _Point); //--- Set new TP for sell positions baskets[basketIdx].takeProfit = newTP; //--- Update the basket's take profit level with the new value for(int j = PositionsTotal() - 1; j >= 0; j--) { //--- Loop through all open positions to update TP where necessary ulong ticket = PositionGetTicket(j); //--- Get the ticket number for the current position if(PositionSelectByTicket(ticket) && PositionGetString(POSITION_SYMBOL) == _Symbol && PositionGetInteger(POSITION_MAGIC) == baskets[basketIdx].magic) { //--- Identify positions that belong to the current basket if(!obj_Trade.PositionModify(ticket, 0, newTP)) { //--- Attempt to modify the position's take profit level Print("Basket ", baskets[basketIdx].basketId, ": Failed to modify TP for ticket ", ticket); //--- Log error if modifying TP fails } } } Print("Basket ", baskets[basketIdx].basketId, ": Breakeven = ", breakevenPrice, ", New TP = ", newTP); //--- Log the new breakeven and take profit levels } }
这部分中,我们实现"ManageGridPositions()"函数,以动态管理每个活跃篮子内的网格交易策略。确保新网格头寸在正确价位执行,并在需要时进行盈利调整。首先,我们通过设置"newPositionOpened"布尔标识,跟踪是否已执行新的网格交易。调用"GetPositionComment()"函数,根据交易类型(初始或网格)生成专属备注字符串。然后通过"SetExpertMagicNumber()"函数分配持仓组唯一magic数字,确保组内所有交易可被准确追踪。
对于买入篮子,我们检测卖出价是否跌至或低于“gridSize”阈值。如果满足条件,通过将“currentLotSize”与输入参数“inpMultiplier”相乘调整头寸规模。随后,使用“obj_Trade”交易对象的“Buy()”方法尝试下单。如果交易成功,那么我们通过减去“gridSize_Spacing”更新“gridSize”,确保下一次买入交易定位准确。通过Print()函数记录成功执行信息。如果下单失败,则通过GetLastError()获取并记录错误信息。
对于卖出篮子,处理流程类似,但需检测买入价是否涨至或高于“gridSize”阈值。如果条件满足,通过“inpMultiplier”调整“currentLotSize”的头寸规模。随后,使用“Sell()”函数执行卖出订单,并更新“gridSize”:加上“gridSize_Spacing”以确定下一次卖出价位。如果订单成功,通过“Print()”记录详情;反之如果失败,则通过“GetLastError()”记录错误。
当新网格头寸开立且持仓组包含多个交易时,我们需要将止盈调整至盈亏平衡点。调用“CalculateBreakevenPrice()”函数计算盈亏平衡价格。之后根据篮子方向设置新的止盈价位。
- 对于买入篮子,将止盈价位设为盈亏平衡价格加上“inpBreakevenPts”(转换为价格点数)。
- 对于卖出篮子,将止盈价位设为盈亏平衡价格减去“inpBreakevenPts”。
接下来,我们通过PositionsTotal()函数遍历所有持仓,并使用PositionGetTicket()获取每个持仓的订单编号。再通过PositionSelectByTicket()选择目标持仓,并利用"PositionGetString"函数验证其交易品种。同时,通过检查持仓的带有"POSITION_MAGIC"参数的magic数字,确认其归属的篮子。验证通过后,尝试使用"PositionModify()"方法修改持仓的止盈价位。如果修改失败,则记录错误信息。
最终,通过Print()函数记录新计算的盈亏平衡价格及更新后的止盈价位。该机制确保网格交易策略能够动态调整,同时维持高效的离场点位。负责计算平均价的函数如下:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Calculate Weighted Breakeven Price for a Basket //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CalculateBreakevenPrice(int basketId) { double weightedSum = 0.0; //--- Initialize sum for weighted prices double totalLots = 0.0; //--- Initialize sum for total lot sizes for(int i = 0; i < PositionsTotal(); i++) { //--- Loop over all open positions ulong ticket = PositionGetTicket(i); //--- Retrieve the ticket for the current position if(PositionSelectByTicket(ticket) && PositionGetString(POSITION_SYMBOL) == _Symbol && StringFind(PositionGetString(POSITION_COMMENT), "Basket_" + IntegerToString(basketId)) >= 0) { //--- Check if the position belongs to the specified basket double lot = PositionGetDouble(POSITION_VOLUME); //--- Get the lot size of the position double openPrice = PositionGetDouble(POSITION_PRICE_OPEN); //--- Get the open price of the position weightedSum += openPrice * lot; //--- Add the weighted price to the sum totalLots += lot; //--- Add the lot size to the total lots } } return (totalLots > 0) ? (weightedSum / totalLots) : 0; //--- Return the weighted average price (breakeven) or 0 if no positions found }
我们实现 "CalculateBreakevenPrice()" 函数,用于计算持仓组内所有交易的加权盈亏平衡价格,确保止盈价位可根据组内所有持仓的成交量加权入场价动态调整。我们首先初始化"weightedSum"变量,用于存储加权价格总和,并且初始化"totalLots"变量,用于跟踪持仓组内所有持仓的总手数。之后,我们遍历所有未平仓头寸。
对于每一笔持仓,我们使用PositionGetTicket()获取其订单号,并通过PositionSelectByTicket()选中该持仓。随后验证该持仓是否属于当前交易品种。此外,我们使用StringFind()在注释字符串中搜索篮子ID,以判断该持仓是否属于指定篮子。注释必须包含"Basket_" + IntegerToString(basketId)才被归类放入同一篮子。
持仓验证通过后,我们用"PositionGetDouble(POSITION_VOLUME)"提取其手数,POSITION_PRICE_OPEN提取开仓价格。随后将开仓价乘以手数,结果累加到"weightedSum",确保大手数对最终盈亏平衡价影响更大。同时,把手数总和累积到"totalLots"。
遍历结束后,用"weightedSum" /"totalLots"计算加权平均盈亏平衡价。如果篮内无持仓("totalLots" = 0),结果返回0,以避免除零错误。运行程序后,我们得到以下结果:
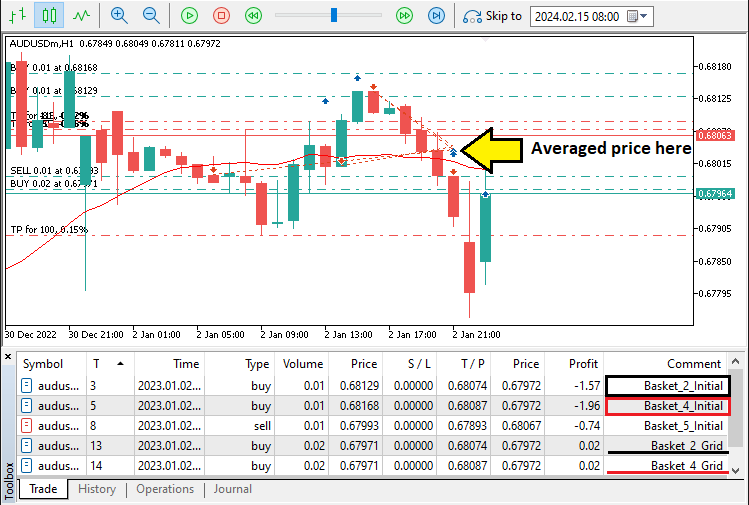
由图可见,通过开仓网格并将价格平均,实现各篮子的独立管理。例如,篮子2的统一止盈位为0.68074。我们可以在下方日志中确认。
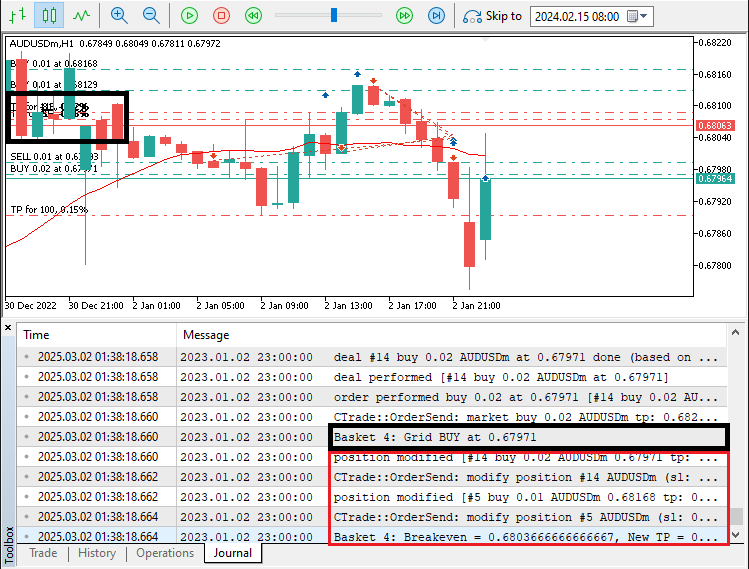
由图可见,一旦为篮子4开立网格买入仓位,我们也会同步修改止盈位。接下来,我们将根据模式平仓(尽管并非必须,因为止盈位已调整),具体如下:
if(closureMode == CLOSE_BY_PROFIT) CheckAndCloseProfitTargets(); //--- If using profit target closure mode, check for profit conditions if(closureMode == CLOSE_BY_POINTS && CountBasketPositions(baskets[i].basketId) > 1) { CheckBreakevenClose(i, ask, bid); //--- If using points-based closure and multiple positions exist, check breakeven conditions }
这部分中,我们根据所选的"closureMode"管理平仓逻辑:如果设置为"CLOSE_BY_PROFIT",则调用"CheckAndCloseProfitTargets()"来关闭达到止盈目标的篮子。如果设为 "CLOSE_BY_POINTS",则先通过"CountBasketPositions()"确保篮子内有多个持仓,再调用"CheckBreakevenClose()",在条件满足时以盈亏平衡点平仓。该函数的实现如下:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Check and Close Profit Targets (for CLOSE_BY_PROFIT mode) //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CheckAndCloseProfitTargets() { for(int i = 0; i < ArraySize(baskets); i++) { //--- Loop through each active basket int posCount = CountBasketPositions(baskets[i].basketId); //--- Count how many positions belong to the current basket if(posCount <= 1) continue; //--- Skip baskets with only one position as profit target checks apply to multiple positions double totalProfit = 0; //--- Initialize the total profit accumulator for the basket for(int j = PositionsTotal() - 1; j >= 0; j--) { //--- Loop through all open positions to sum their profits ulong ticket = PositionGetTicket(j); //--- Get the ticket for the current position if(PositionSelectByTicket(ticket) && StringFind(PositionGetString(POSITION_COMMENT), "Basket_" + IntegerToString(baskets[i].basketId)) >= 0) { //--- Check if the position is part of the current basket totalProfit += PositionGetDouble(POSITION_PROFIT); //--- Add the position's profit to the basket's total profit } } if(totalProfit >= profitTotal_inCurrency) { //--- Check if the accumulated profit meets or exceeds the profit target Print("Basket ", baskets[i].basketId, ": Profit target reached (", totalProfit, ")"); //--- Log that the profit target has been reached for the basket CloseBasketPositions(baskets[i].basketId); //--- Close all positions in the basket to secure the profits } } }
这部分中,我们检查并在篮子达到止盈目标时执行平仓("CLOSE_BY_PROFIT"模式)。遍历所有"baskets",先用"CountBasketPositions()"确保篮内存在多个持仓。随后对篮内所有持仓调用 "PositionGetDouble(POSITION_PROFIT)"累加总利润。如果总利润达到或超过"profitTotal_inCurrency",则记录日志并调用"CloseBasketPositions()"锁定盈利。"CountBasketPositions"函数定义如下:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Count Positions in a Basket //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int CountBasketPositions(int basketId) { int count = 0; //--- Initialize the counter for positions in the basket for(int i = 0; i < PositionsTotal(); i++) { //--- Loop through all open positions ulong ticket = PositionGetTicket(i); //--- Retrieve the ticket for the current position if(PositionSelectByTicket(ticket) && StringFind(PositionGetString(POSITION_COMMENT), "Basket_" + IntegerToString(basketId)) >= 0) { //--- Check if the position belongs to the specified basket count++; //--- Increment the counter if a matching position is found } } return count; //--- Return the total number of positions in the basket }
我们使用"CountBasketPositions()"函数统计指定篮子中的持仓数量。遍历所有持仓,通过 PositionGetTicket()获取每笔订单的"ticket",并检查其POSITION_COMMENT是否包含篮子ID。如果匹配成功,则计数器"count"递增。最后返回该篮子的总持仓数。"CloseBasketPositions()"函数定义如下所示:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Close All Positions in a Basket //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CloseBasketPositions(int basketId) { for(int i = PositionsTotal() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { //--- Loop backwards through all open positions ulong ticket = PositionGetTicket(i); //--- Retrieve the ticket of the current position if(PositionSelectByTicket(ticket) && StringFind(PositionGetString(POSITION_COMMENT), "Basket_" + IntegerToString(basketId)) >= 0) { //--- Identify if the position belongs to the specified basket if(obj_Trade.PositionClose(ticket)) { //--- Attempt to close the position Print("Basket ", basketId, ": Closed position ticket ", ticket); //--- Log the successful closure of the position } } } }
我们沿用相同的逻辑遍历所有持仓,逐一验证后,调用"PositionClose"方法平仓。最后,由指定函数负责在持仓超过预设目标位时强制执行平仓。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Check Breakeven Close //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CheckBreakevenClose(int basketIdx, double ask, double bid) { double breakevenPrice = CalculateBreakevenPrice(baskets[basketIdx].basketId); //--- Calculate the breakeven price for the basket if(baskets[basketIdx].direction == POSITION_TYPE_BUY) { if(bid >= breakevenPrice + (inpBreakevenPts * _Point)) { //--- Check if the bid price exceeds breakeven plus threshold for buy positions Print("Basket ", baskets[basketIdx].basketId, ": Closing BUY positions at breakeven + points"); //--- Log that breakeven condition is met for closing positions CloseBasketPositions(baskets[basketIdx].basketId); //--- Close all positions for the basket } } else if(baskets[basketIdx].direction == POSITION_TYPE_SELL) { if(ask <= breakevenPrice - (inpBreakevenPts * _Point)) { //--- Check if the ask price is below breakeven minus threshold for sell positions Print("Basket ", baskets[basketIdx].basketId, ": Closing SELL positions at breakeven + points"); //--- Log that breakeven condition is met for closing positions CloseBasketPositions(baskets[basketIdx].basketId); //--- Close all positions for the basket } } }
这部分中,我们通过"CheckBreakevenClose()"实现基于盈亏平衡的平仓逻辑。先用"CalculateBreakevenPrice()"计算出盈亏平衡价。如果篮子为买入方向,且当前买入价超过盈亏平衡价 + 阈值 (inpBreakevenPts * _Point),则记录日志并调用 CloseBasketPositions() 锁定利润。相类似地,对于卖出篮子,若当前卖出价低于盈亏平衡价 − 阈值,同样触发平仓。这样确保一旦价格达到盈亏平衡条件即平仓保护。
最后,由于我们优先通过止盈平仓,会留下空的“壳子”或持仓篮,造成系统冗余。因此需识别并移除这些不含任何元素的空篮子。实现逻辑如下:
//--- Remove inactive baskets that no longer have any open positions for(int i = ArraySize(baskets) - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if(CountBasketPositions(baskets[i].basketId) == 0) { Print("Removing inactive basket ID: ", baskets[i].basketId); //--- Log the removal of an inactive basket for(int j = i; j < ArraySize(baskets) - 1; j++) { baskets[j] = baskets[j + 1]; //--- Shift basket elements down to fill the gap } ArrayResize(baskets, ArraySize(baskets) - 1); //--- Resize the baskets array to remove the empty slot } }
这部分中,我们高效清理不再持有任何仓位的空篮子。逆向遍历"baskets"数组,避免删除时索引移位。使用"CountBasketPositions()"检查篮子是否已无任何持仓。如果为空,记录日志并将后续元素前移,保持数组连续。最后,调用ArrayResize()调整数组长度,防止内存浪费,确保仅保留活跃篮子。该方法使得篮子管理始终保持高效,避免系统冗余。运行后的结果如下:
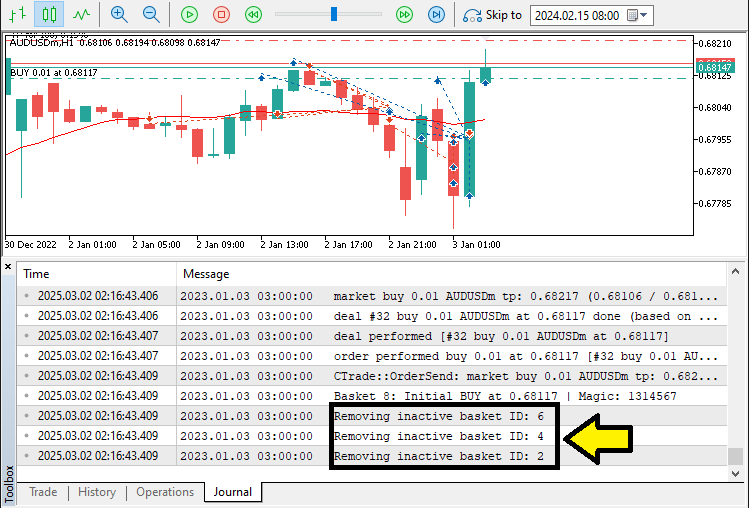
由图可见,我们高效完成了空篮子清理,并成功管理了网格头寸,从而达成了既定的目标。接下来需完成的工作是程序回测,相关内容将在下一章节详细阐述。
回测
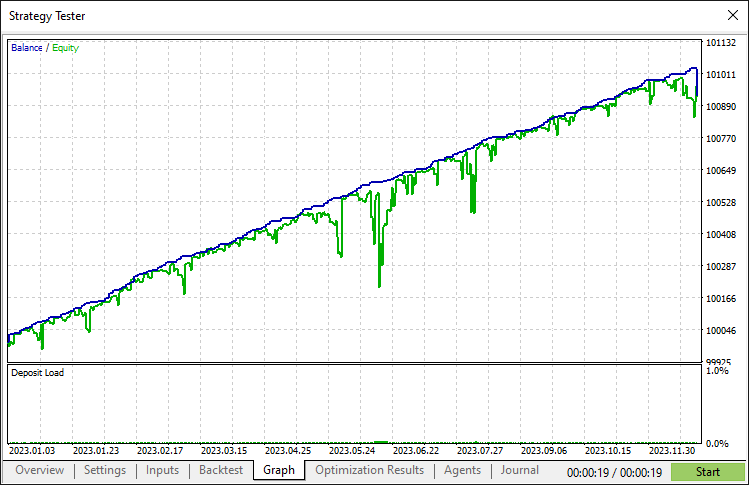
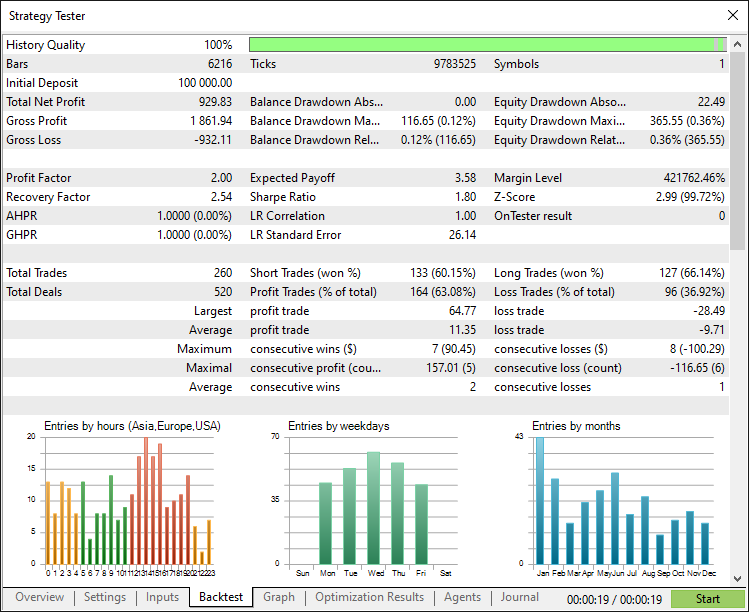
在2023一整年使用默认设置,经过完整的回测后,我们得到以下结果:
回测图:
回测报告:
结论
总而言之,我们已经开发出一款MQL5多级网格交易EA,能够高效管理分层入场、动态网格调整与结构化恢复。通过整合可扩展的网格间距、受控的手数递进以及盈亏平衡出场,该系统在适应市场波动的同时,优化了风险与收益的平衡。
免责声明:本文仅用于教学目的。交易涉及重大财务风险,且市场行情具有不可预测性。在实盘操作前,必须进行充分的回测与风险管理。
运用这些技巧,您可以提升算法交易能力,并进一步完善网格策略。持续测试与优化,方能取得长期的成功。祝您好运!
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/17350
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 价格行为分析工具包开发(第十八部分):四分位理论(3)——四分位看板
价格行为分析工具包开发(第十八部分):四分位理论(3)——四分位看板
 市场模拟(第三部分):性能问题
市场模拟(第三部分):性能问题
 时间演化旅行算法(TETA)
时间演化旅行算法(TETA)

非常好的代码,非常快的 EA!
遗憾的是,批量大小的计算有问题 - 带小数的乘数(如 1.3、1.5 等)可能会给 MQL 订单函数带来麻烦,因为当乘数不是 1 或 2 时,批量大小有时会给出错误代码 4756。
如果能对批量大小计算稍作修改,以确保批量大小计算得当,从而将所有乘数值输入订单函数,那就太好了。
如果能对批量大小计算稍作修改,以确保批量大小计算得当,从而将所有乘数值输入订单函数,那就太好了。
感谢您的反馈。当然可以。
你好、
读完这篇文章后,我觉得很有用,一定会进行测试。不过,我似乎没有看到,或者说我遗漏了文章中关于第一仓位 TP 分离的内容,我认为这对交易策略 也是有用和可持续的。
谢谢。
谢谢。
当然,谢谢。