
MQL5 Trading Tools (Part 11): Correlation Matrix Dashboard (Pearson, Spearman, Kendall) with Heatmap and Standard Modes
Introduction
In our previous article (Part 10), we developed a strategy tracker system in MetaQuotes Language 5 (MQL5) with visual levels and success metrics that detected moving average crossover signals, tracked trades with multiple take-profit levels and stop-losses, and visualized outcomes on the chart. In Part 11, we develop a correlation matrix dashboard with Pearson, Spearman, and Kendall methods featuring a heatmap and standard modes. This dashboard computes asset relationships using the selected method over a configurable timeframe and bars. It supports standard mode with color thresholds and p-value significance stars, as well as heatmap mode with gradient visuals. Additionally, it includes an interactive user interface with timeframe selectors, mode toggles, and a dynamic legend. We will cover the following topics:
By the end, you’ll have a functional MQL5 correlation matrix dashboard for analyzing asset interdependencies, ready for customization—let’s dive in!
Understanding the Correlation Matrix Dashboard Framework
The correlation matrix dashboard framework analyzes relationships between financial assets by computing correlation coefficients, helping us identify interdependencies that influence portfolio diversification, hedging, or multi-asset strategies. It processes price changes across user-selected symbols over a defined period and timeframe, applying one of three statistical methods—Pearson for linear relationships, Spearman for rank-based monotonic associations, or Kendall for concordance in rankings—to quantify how assets move together or in opposite directions. Significance is evaluated through p-values to indicate reliability, with visual cues like color thresholds or gradients highlighting strong positive, strong negative, mild, or neutral correlations, enabling quick pattern recognition without manual calculations.
In standard mode, the dashboard uses predefined thresholds to categorize correlations, applying distinct colors for strong positives or negatives and adding stars for p-value significance levels to denote statistical confidence. Heatmap mode employs a continuous color gradient for finer visualization of correlation intensities from negative to positive, making subtle variations more apparent. The interface includes interactive elements such as timeframe selectors for switching analysis periods, toggle buttons for modes or themes, and a dynamic legend to interpret colors and values, all arranged in a grid with symbols on axes and cells showing pairwise correlations.
Our plan is to parse a list of symbols, compute correlations and p-values using the chosen method on price deltas, render a user interface with panels for headers, timeframes, symbols, cells, and legends, and update visuals dynamically based on modes and thresholds. We will incorporate event handling for interactions like mode switching or timeframe changes, ensuring the dashboard refreshes on new data for real-time insights. In brief, here is a visual representation of our objectives.

Implementation in MQL5
To create the program in MQL5, open the MetaEditor, go to the Navigator, locate the Experts folder, click on the "New" tab, and follow the prompts to create the file. Once it is made, in the coding environment, we will need to declare some input parameters and global variables that we will use throughout the program.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Correlation Matrix Dashboard PART1.mq5 | //| Copyright 2026, Allan Munene Mutiiria. | //| https://t.me/Forex_Algo_Trader | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2026, Allan Munene Mutiiria." #property link "https://t.me/Forex_Algo_Trader" #property version "1.00" #include <Math\Stat\Math.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Inputs | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ input string SymbolsList = "EURUSDm,GBPUSDm,USDJPYm,AUDUSDm,BTCUSDm,NZDUSDm,US500m,XAUUSDm"; // Comma-separated symbols (up to 30) input ENUM_TIMEFRAMES CorrelationTimeframe = PERIOD_CURRENT; // Timeframe for correlation calculation input int CorrelationBars = 100; // Number of bars for correlation calculation (min 20) input double StrongPositiveThresholdPct = 70.0; // Strong positive threshold in % (e.g., 70.0 for >=0.70) input double StrongNegativeThresholdPct = -70.0; // Strong negative threshold in % (e.g., -70.0 for <=-0.70) input double PValueThreshold1 = 0.01; // P-value for *** significance input double PValueThreshold2 = 0.05; // P-value for ** significance input double PValueThreshold3 = 0.10; // P-value for * significance input color ColorStrongPositiveBg = clrLimeGreen; // Background for strong positive input color ColorStrongNegativeBg = clrOrangeRed; // Background for strong negative input color ColorNeutralBg = C'70,70,70'; // Background for neutral/mild/zero/diagonal cells input color ColorDiagonalBg = C'40,40,40'; // Background for diagonal cells input color ColorTextStrong = clrWhite; // Text color for strong correlations input color ColorTextPositive = clrDeepSkyBlue; // Text color for mild positive input color ColorTextNegative = clrRed; // Text color for mild negative input color ColorTextZero = clrWhite; // Text color for zero or diagonal //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Enumerations | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum DisplayMode { MODE_STANDARD, // Standard Thresholds MODE_HEATMAP // Heatmap Gradient }; input DisplayMode DashboardMode = MODE_STANDARD; // Dashboard Display Mode enum CorrelationMethod { PEARSON, // Pearson correlation SPEARMAN, // Spearman rank correlation KENDALL // Kendall tau correlation }; input CorrelationMethod CorrMethod = PEARSON; // Correlation calculation method //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Defines | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #define MAIN_PANEL "PANEL_MAIN" // Define main panel rectangle identifier #define HEADER_PANEL "PANEL_HEADER" // Define header panel rectangle identifier #define LEGEND_PANEL "PANEL_LEGEND" // Define legend panel rectangle identifier #define HEADER_PANEL_ICON "PANEL_HEADER_ICON" // Define header icon label identifier #define HEADER_PANEL_TEXT "PANEL_HEADER_TEXT" // Define header title label identifier #define CLOSE_BUTTON "BUTTON_CLOSE" // Define close button identifier #define TOGGLE_BUTTON "BUTTON_TOGGLE" // Define toggle (minimize/maximize) button identifier #define HEATMAP_BUTTON "BUTTON_HEATMAP" // Define heatmap toggle button identifier #define PVAL_BUTTON "BUTTON_PVAL" // Define P-value toggle button identifier #define SORT_BUTTON "BUTTON_SORT" // Define sort button identifier #define THEME_BUTTON "BUTTON_THEME" // Define theme toggle button identifier #define TF_CELL_RECT "TF_CELL_RECT_" // Define timeframe cell rectangle prefix #define TF_CELL_TEXT "TF_CELL_TEXT_" // Define timeframe cell text prefix #define SYMBOL_ROW_RECTANGLE "SYMBOL_ROW_" // Define row symbol rectangle prefix #define SYMBOL_ROW_TEXT "SYMBOL_ROW_TEXT_" // Define row symbol text label prefix #define SYMBOL_COL_RECTANGLE "SYMBOL_COL_" // Define column symbol rectangle prefix #define SYMBOL_COL_TEXT "SYMBOL_COL_TEXT_" // Define column symbol text label prefix #define CELL_RECTANGLE "CELL_" // Define correlation cell rectangle prefix #define CELL_TEXT "CELL_TEXT_" // Define correlation cell text label prefix #define LEGEND_CELL_RECTANGLE "LEGEND_CELL_" // Define legend cell rectangle prefix #define LEGEND_CELL_TEXT "LEGEND_CELL_TEXT_" // Define legend cell text prefix #define WIDTH_SYMBOL 80 // Define width of symbol rectangles #define WIDTH_CELL 80 // Define width of correlation cells #define WIDTH_TF_CELL 45 // Define width of TF cells #define WIDTH_LEGEND_CELL 45 // Define width of legend cells #define HEIGHT_RECTANGLE 30 // Define height of all rectangles #define HEIGHT_HEADER 27 // Define height of header #define HEIGHT_TF_CELL 25 // Define height of TF cells #define HEIGHT_LEGEND 30 // Define height of legend cells #define HEIGHT_LEGEND_PANEL 34 // Define height of legend panel (with padding) #define LEGEND_SPACING 5 // Define spacing between legend cells #define NUM_LEGEND_ITEMS 15 // Define increased to cover max possible (e.g., 11 in heatmap) #define GAP_HEIGHT 8 // Define gap between sections #define GAP_MAIN_LEGEND 2 // Define vertical gap between main panel and legend #define COLOR_WHITE clrWhite // Define white color for text and backgrounds #define COLOR_BLACK clrBlack // Define black color for borders and text #define COLOR_LIGHT_GRAY C'230,230,230' // Define light gray for neutral cells #define COLOR_DARK_GRAY C'105,105,105' // Define dark gray for headers #define MAX_SYMBOLS 30 // Define maximum symbols supported #define NUM_TF 8 // Define number of timeframes //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Global Variables | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int panel_x = 20, panel_y = 40; //--- Initialize panel position coordinates string symbols_array[MAX_SYMBOLS]; //--- Declare array to store symbols int num_symbols = 0; //--- Initialize number of valid symbols double correlation_matrix[MAX_SYMBOLS][MAX_SYMBOLS]; //--- Declare matrix to store correlations double pvalue_matrix[MAX_SYMBOLS][MAX_SYMBOLS]; //--- Declare matrix to store p-values DisplayMode global_display_mode; //--- Declare runtime display mode ENUM_TIMEFRAMES global_correlation_tf; //--- Declare runtime timeframe int current_tf_index = -1; //--- Initialize index of current TF int num_tf_visible; //--- Declare dynamic number of visible TF cells int num_legend_visible; //--- Declare dynamic number of visible legend items double visible_corr_vals[]; //--- Declare array of visible correlation values for legend ENUM_TIMEFRAMES tf_list[NUM_TF] = {PERIOD_M1, PERIOD_M5, PERIOD_M15, PERIOD_M30, PERIOD_H1, PERIOD_H4, PERIOD_D1, PERIOD_W1}; //--- Initialize timeframe list string tf_strings[NUM_TF] = {"M1", "M5", "M15", "M30", "H1", "H4", "D1", "W1"}; //--- Initialize timeframe strings // Enhanced gradient colors for heatmap color heatmap_colors[] = {clrRed, clrOrangeRed, clrOrange, clrYellow, clrLightGray, clrLime, clrLimeGreen, clrGreen}; //--- Initialize heatmap color gradient array
We begin the implementation by including the Math library with "#include <Math\Stat\Math.mqh>", which provides statistical functions essential for correlation calculations. Next, we define the input parameters that allow us to customize the dashboard. These include the "SymbolsList" as a comma-separated string for up to thirty symbols, "CorrelationTimeframe" using the ENUM_TIMEFRAMES enumeration for the calculation period, "CorrelationBars" as an integer specifying the number of bars with a minimum of twenty, thresholds like "StrongPositiveThresholdPct" and "StrongNegativeThresholdPct" in percentage for categorizing correlations, p-value thresholds such as "PValueThreshold1" for significance levels, and color inputs like "ColorStrongPositiveBg" set to lime green for strong positive backgrounds, along with others for negative, neutral, diagonal, and text colors.
We then create enumerations for configuration options. The "DisplayMode" enumeration offers "MODE_STANDARD" for threshold-based displays and "MODE_HEATMAP" for gradient visuals, with "DashboardMode" as an input defaulting to standard. Similarly, the "CorrelationMethod" enumeration provides "PEARSON" for linear correlations, "SPEARMAN" for rank-based, and "KENDALL" for tau, with "CorrMethod" as an input defaulting to Pearson. Following that, we use defines to set constants for user interface elements and layout using the #define directive. These include identifiers like "MAIN_PANEL" for the main rectangle, "HEADER_PANEL" for the header, and prefixes such as "TF_CELL_RECT" for timeframe cells, along with dimensions like "WIDTH_SYMBOL" at eighty pixels, "HEIGHT_RECTANGLE" at thirty, gaps such as "GAP_HEIGHT" at eight, and color defines like "COLOR_WHITE" aliased to white.
We declare global variables to manage state and data. These include "panel_x" and "panel_y" initialized to twenty and forty for position, "symbols_array" as a string array of maximum symbols size, "num_symbols" starting at zero, two-dimensional double arrays "correlation_matrix" and "pvalue_matrix" for storing values, "global_display_mode" from the display enumeration, "global_correlation_tf" from timeframes, "current_tf_index" at negative one, and integers like "num_tf_visible" and "num_legend_visible", plus a double array "visible_corr_vals" for legend values. Finally, we initialize arrays for timeframes and colors: "tf_list" as an "ENUM_TIMEFRAMES" array with values from one-minute to weekly, "tf_strings" as corresponding string labels, and "heatmap_colors" as a color array for gradients ranging from red to green. The next thing we will do is define some helper functions to do the statistical analysis.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Approximate Normal CDF | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool NormalCDF(double mean, double stddev, double x, double &cdf) { if (stddev <= 0.0) return false; //--- Check for invalid standard deviation double z = (x - mean) / stddev; //--- Compute z-score if (z < -10) { //--- Handle extreme low z-value cdf = 0.0; //--- Set CDF to 0 return true; //--- Return success } if (z > 10) { //--- Handle extreme high z-value cdf = 1.0; //--- Set CDF to 1 return true; //--- Return success } double t = 1 / (1 + 0.2316419 * MathAbs(z)); //--- Compute t for approximation double d = 0.3989423 * MathExp(-z * z / 2); //--- Compute density d cdf = d * t * (0.3193815 + t * (-0.3565638 + t * (1.7814779 + t * (-1.821256 + t * 1.3302744)))); //--- Calculate CDF approximation if (z > 0) cdf = 1 - cdf; //--- Adjust for positive z return true; //--- Return success } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Approximate Student t CDF | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool StudentCDF(int df, double x, double &cdf) { if (df <= 0) return false; //--- Check for invalid degrees of freedom double a = df / 2.0; //--- Compute alpha parameter double b = 0.5; //--- Set beta parameter double xt = df / (df + x * x); //--- Compute xt for incomplete beta double ib = MathBetaIncomplete(xt, a, b); //--- Compute incomplete beta double beta = MathExp(MathGammaLog(a) + MathGammaLog(b) - MathGammaLog(a + b)); //--- Compute beta function double regularized = ib / beta; //--- Compute regularized incomplete beta if (x >= 0) { //--- Handle non-negative x cdf = 1 - 0.5 * regularized; //--- Set CDF for positive side } else { //--- Handle negative x cdf = 0.5 * regularized; //--- Set CDF for negative side } return true; //--- Return success } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Calculate p-value based on method and correlation | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double calculate_pvalue(double corr, CorrelationMethod method, int n) { if (n < 3) return 1.0; //--- Return invalid if insufficient samples double cdf = 0.0; //--- Initialize CDF variable if (method == KENDALL) { //--- Handle Kendall method double sigma = MathSqrt((4.0 * n + 10.0) / (9.0 * n * (n - 1.0))); //--- Compute sigma if (sigma == 0) return 1.0; //--- Return invalid if sigma zero double z = corr / sigma; //--- Compute z-score if (!NormalCDF(0, 1, MathAbs(z), cdf)) return 1.0; //--- Compute Normal CDF or return invalid return 2 * (1 - cdf); //--- Return two-tailed p-value } else { //--- Handle PEARSON or SPEARMAN double r2 = corr * corr; //--- Compute squared correlation if (r2 >= 1.0) return 0.0; //--- Return zero for perfect correlation double denom = 1.0 - r2; //--- Compute denominator if (denom <= 0.0) return 0.0; //--- Avoid division by zero double t = corr * MathSqrt((n - 2.0) / denom); //--- Compute t-statistic if (!StudentCDF(n - 2, MathAbs(t), cdf)) return 1.0; //--- Compute Student CDF or return invalid return 2 * (1 - cdf); //--- Return two-tailed p-value } }
First, we define the "NormalCDF" function to approximate the cumulative distribution function (CDF) for a normal distribution, which is used in p-value calculations. It takes parameters for mean, standard deviation, the value x, and a reference to store the CDF result. We first check if the standard deviation is invalid and return false if so. Then, we compute the z-score by standardizing x. For extreme z values below negative ten or above ten, we set the CDF to zero or one, respectively, and return true. Otherwise, we calculate an approximation using a polynomial expansion based on t and density d, adjusting the CDF for positive z before returning true. A normal CDF graph would look as follows.

Next, we implement the "StudentCDF" function to approximate the cumulative distribution function (CDF) for Student's t-distribution, essential for p-values in Pearson and Spearman methods, which we will define later. It accepts degrees of freedom df, the value x, and a reference for the CDF. We validate df and return false if invalid. We then compute parameters a and b, followed by xt for the incomplete beta function. Using "MathBetaIncomplete" to get ib and calculating the full beta with gamma logs, we derive the regularized incomplete beta. Depending on whether x is non-negative or negative, we adjust the CDF accordingly and return true. A student CDF graph would look as follows.

We then create the "calculate_pvalue" function to compute the p-value based on the correlation coefficient, method, and sample size n. If n is less than three, we return one to indicate invalidity. We initialize a cumulative distribution function variable and handle Kendall separately by computing sigma, checking for zero, deriving z, and using "NormalCDF" to get the two-tailed p-value. For Pearson or Spearman, we calculate the squared correlation r2, handle perfect correlations by returning zero, compute the denominator and t-statistic, then use "StudentCDF" with adjusted df to obtain the two-tailed p-value. The next thing we need to do is create a function to parse the symbols' list into arrays that we can manage. Here is the logic we used to achieve that.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Parse symbols list into array | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void parse_symbols() { string temp = SymbolsList; //--- Copy input symbols list num_symbols = 0; //--- Reset symbol count while (StringFind(temp, ",") >= 0 && num_symbols < MAX_SYMBOLS) { //--- Loop through comma-separated symbols int pos = StringFind(temp, ","); //--- Find comma position string sym = StringSubstr(temp, 0, pos); //--- Extract symbol if (SymbolSelect(sym, true)) { //--- Select symbol if available symbols_array[num_symbols] = sym; //--- Store valid symbol num_symbols++; //--- Increment count } else { //--- Handle unavailable symbol Print("Warning: Symbol ", sym, " not available."); //--- Print warning } temp = StringSubstr(temp, pos + 1); //--- Update remaining string } if (StringLen(temp) > 0 && num_symbols < MAX_SYMBOLS) { //--- Handle last symbol if (SymbolSelect(temp, true)) { //--- Select last symbol if available symbols_array[num_symbols] = temp; //--- Store last valid symbol num_symbols++; //--- Increment count } else { //--- Handle unavailable last symbol Print("Warning: Symbol ", temp, " not available."); //--- Print warning } } if (num_symbols < 2) { //--- Check minimum symbols Print("Error: At least 2 valid symbols required. Found: ", num_symbols); //--- Print error ExpertRemove(); //--- Remove expert } }
Here, we implement the "parse_symbols" function to process the user-provided list of symbols into a usable array for the dashboard. It starts by copying the "SymbolsList" input to a temporary string variable and resetting the "num_symbols" counter to zero. We then enter a loop that continues as long as a comma is found in the temporary string and the symbol count is below the "MAX_SYMBOLS" limit. Inside the loop, we locate the position of the next comma using StringFind, extract the symbol substring from the start to that position with StringSubstr, and attempt to select the symbol in the market watch using SymbolSelect with true to add it if necessary. If successful, we store the symbol in the "symbols_array" at the current index and increment "num_symbols"; otherwise, we print a warning message for unavailable symbols. We update the temporary string to the remainder after the comma using another "StringSubstr".
After the loop, we check if any remaining text exists in the temporary string—indicating the last symbol—and if the count is still under the limit. We attempt to select and store this final symbol similarly, printing a warning if unavailable. Finally, if fewer than two valid symbols were found, we print an error message and remove the program with ExpertRemove to ensure the matrix requires at least two assets for correlations. Printing the array gives us the following outcome.

We can now move on to defining our statistical functions for use in calculations.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Rank data for Spearman correlation | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void rank_data(const double &data[], double &ranks[]) { int size = ArraySize(data); //--- Get data size int indices[]; //--- Declare indices array ArrayResize(indices, size); //--- Resize indices for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) indices[i] = i; //--- Initialize indices // Sort indices based on data values for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) { //--- Loop outer for sorting for (int j = i + 1; j < size; j++) { //--- Loop inner for comparison if (data[indices[i]] > data[indices[j]]) { //--- Check if swap needed int temp = indices[i]; //--- Store temporary indices[i] = indices[j]; //--- Swap indices indices[j] = temp; //--- Complete swap } } } // Assign ranks, handling ties for (int i = 0; i < size; ) { //--- Loop through sorted indices int start = i; //--- Set start of tie group double value = data[indices[i]]; //--- Get current value while (i < size && data[indices[i]] == value) i++; //--- Skip ties double rank = (start + i - 1) / 2.0 + 1.0; //--- Compute average rank for (int k = start; k < i; k++) { //--- Assign rank to group ranks[indices[k]] = rank; //--- Set rank } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Calculate Pearson correlation | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double pearson_correlation(const double &deltas1[], const double &deltas2[], int size) { double mean1 = 0, mean2 = 0; //--- Initialize means for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { //--- Loop to compute sums mean1 += deltas1[i]; //--- Accumulate first deltas mean2 += deltas2[i]; //--- Accumulate second deltas } mean1 /= size; //--- Compute first mean mean2 /= size; //--- Compute second mean double var1 = 0, var2 = 0, cov = 0; //--- Initialize variances and covariance for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { //--- Loop to compute deviations double dev1 = deltas1[i] - mean1; //--- Compute first deviation double dev2 = deltas2[i] - mean2; //--- Compute second deviation var1 += dev1 * dev1; //--- Accumulate first variance var2 += dev2 * dev2; //--- Accumulate second variance cov += dev1 * dev2; //--- Accumulate covariance } if (var1 == 0 || var2 == 0) return 0.0; //--- Return zero if no variance return cov / MathSqrt(var1 * var2); //--- Return correlation } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Calculate Spearman correlation | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double spearman_correlation(const double &deltas1[], const double &deltas2[], int size) { double ranks1[], ranks2[]; //--- Declare rank arrays ArrayResize(ranks1, size); //--- Resize first ranks ArrayResize(ranks2, size); //--- Resize second ranks rank_data(deltas1, ranks1); //--- Rank first deltas rank_data(deltas2, ranks2); //--- Rank second deltas return pearson_correlation(ranks1, ranks2, size); //--- Return Pearson on ranks } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Calculate Kendall correlation | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double kendall_correlation(const double &deltas1[], const double &deltas2[], int size) { int concordant = 0, discordant = 0; //--- Initialize pair counts for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) { //--- Loop outer pairs for (int j = i + 1; j < size; j++) { //--- Loop inner pairs double sign1 = deltas1[i] - deltas1[j]; //--- Compute first sign double sign2 = deltas2[i] - deltas2[j]; //--- Compute second sign if (sign1 * sign2 > 0) concordant++; //--- Increment concordant else if (sign1 * sign2 < 0) discordant++; //--- Increment discordant // Ties are ignored in basic Kendall tau } } int total_pairs = size * (size - 1) / 2; //--- Compute total pairs if (total_pairs == 0) return 0.0; //--- Return zero if no pairs return (concordant - discordant) / (double)total_pairs; //--- Return tau }
First, we implement the "rank_data" function to assign ranks to an array of data values, which is crucial for the Spearman correlation method to handle non-parametric ranking. It takes a constant reference to the data array and a reference to the ranks array. We first determine the size using ArraySize and declare an indices array, resizing it to match and initializing it with sequential values from zero to size minus one. We then perform a bubble sort on the indices based on the corresponding data values, swapping indices if the data at the current index is greater than that at the next. After sorting, we loop through the sorted indices to assign ranks, handling ties by identifying groups with the same value, computing an average rank for the group using the formula (start + end - 1) / 2.0 + 1.0, and applying that rank back to the original positions via the indices.
Next, we define the "pearson_correlation" function to calculate the Pearson correlation coefficient between two arrays of price deltas over a given size. It initializes means for both arrays to zero, then loops to sum the deltas and computes the means by dividing by the size. We then initialize variances and covariance to zero and loop again to calculate deviations from the means, accumulating squared deviations for variances and the product for covariance. If either variance is zero, we return 0.0 to avoid division by zero; otherwise, we return the covariance divided by the square root of the product of variances using the MathSqrt function. We then create the "spearman_correlation" function to compute Spearman's rank correlation. It declares and resizes two rank arrays to the input size, calls "rank_data" on each deltas array to populate the ranks, and returns the result of "pearson_correlation" applied to these rank arrays instead of the original deltas.
Finally, we implement the "kendall_correlation" function for Kendall's tau coefficient. Counters for concordant and discordant pairs are initialized to zero. We use nested loops over the data size to compare every pair of elements and compute signs as differences in each array. If the product of signs is positive, concordant is incremented; if negative, discordant—ignoring ties. Total pairs are calculated as size times (size - 1) / 2. We return 0.0 if there are no pairs, or the difference between concordant and discordant divided by the total pairs. In a normal bivariate population comparison, they look as follows.
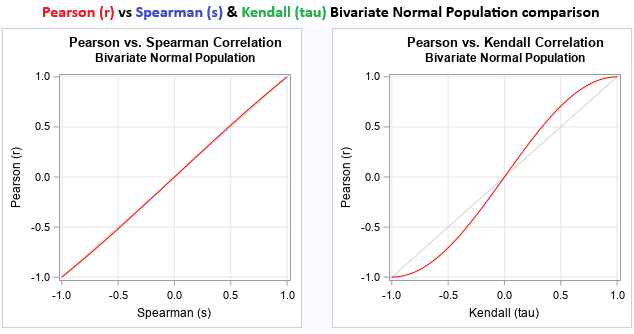
Using the analysis functions, we can create helper functions to handle the standardised correlation computations now as follows.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Calculate correlation based on method | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double calculate_correlation(string sym1, string sym2) { if (sym1 == sym2) return 1.0; //--- Return self-correlation double prices1[], prices2[]; //--- Declare price arrays ArrayResize(prices1, CorrelationBars); //--- Resize first prices ArrayResize(prices2, CorrelationBars); //--- Resize second prices if (CopyClose(sym1, global_correlation_tf, 0, CorrelationBars, prices1) < CorrelationBars || //--- Copy first closes or check failure CopyClose(sym2, global_correlation_tf, 0, CorrelationBars, prices2) < CorrelationBars) { return 0.0; //--- Return insufficient data } // Compute price changes (deltas) double deltas1[], deltas2[]; //--- Declare delta arrays ArrayResize(deltas1, CorrelationBars - 1); //--- Resize first deltas ArrayResize(deltas2, CorrelationBars - 1); //--- Resize second deltas for (int i = 0; i < CorrelationBars - 1; i++) { //--- Loop to compute deltas deltas1[i] = prices1[i + 1] - prices1[i]; //--- Set first delta deltas2[i] = prices2[i + 1] - prices2[i]; //--- Set second delta } int size = CorrelationBars - 1; //--- Set effective size switch (CorrMethod) { //--- Switch on method case PEARSON: //--- Handle Pearson return pearson_correlation(deltas1, deltas2, size); //--- Return Pearson result case SPEARMAN: //--- Handle Spearman return spearman_correlation(deltas1, deltas2, size); //--- Return Spearman result case KENDALL: //--- Handle Kendall return kendall_correlation(deltas1, deltas2, size); //--- Return Kendall result default: //--- Handle default return 0.0; //--- Return zero } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Update correlation matrix values | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void update_correlations() { int n = CorrelationBars - 1; //--- Set sample size if (n < 2) { //--- Check minimum bars Print("Error: Insufficient bars for correlation (need at least 3)."); //--- Print error return; //--- Exit function } for (int i = 0; i < num_symbols; i++) { //--- Loop rows for (int j = 0; j < num_symbols; j++) { //--- Loop columns double corr = calculate_correlation(symbols_array[i], symbols_array[j]); //--- Compute correlation correlation_matrix[i][j] = corr; //--- Store correlation if (i == j) { //--- Handle diagonal pvalue_matrix[i][j] = 0.0; //--- Set p-value to zero } else if (corr == 0.0 && n < 3) { //--- Handle insufficient data pvalue_matrix[i][j] = 1.0; //--- Set p-value to one } else { //--- Handle normal case pvalue_matrix[i][j] = calculate_pvalue(corr, CorrMethod, n); //--- Compute and store p-value } } } }
We create the "calculate_correlation" function to compute the correlation coefficient between two symbols, returning a double value. It takes string parameters for sym1 and sym2. If they are identical, it immediately returns 1.0 to represent perfect self-correlation. We declare and resize two double arrays "prices1" and "prices2" to the size of "CorrelationBars". We use CopyClose to fetch closing prices for each symbol from the "global_correlation_tf" timeframe, starting from the current bar zero. If either copy fails to retrieve the full amount, we return 0.0 to indicate insufficient data.
To focus on price changes, we declare and resize delta arrays "deltas1" and "deltas2" to one less than "CorrelationBars". We loop to calculate each delta as the difference between consecutive prices. The effective size is set to "CorrelationBars" minus one. A switch statement on the "CorrMethod" enumeration calls the relevant correlation function. For "PEARSON", we call "pearson_correlation" with the deltas and size. For "SPEARMAN", we call "spearman_correlation". For "KENDALL", we call "kendall_correlation". The default case returns 0.0.
Next, we implement the "update_correlations" function to populate the correlation and p-value matrices with fresh calculations. It computes the sample size n as "CorrelationBars" minus one and checks if it's less than two, printing an error if so, since at least three bars are needed for meaningful correlations, then exits early. We use nested loops over "num_symbols" for rows i and columns j, calling "calculate_correlation" with the corresponding symbols from "symbols_array" to get corr and storing it in "correlation_matrix" at [i][j]. For p-values, if i equals j for the diagonal, we set "pvalue_matrix" at [i][j] to 0.0; if corr is 0.0 and n is less than three, set it to 1.0; otherwise, compute it using "calculate_pvalue" with corr, "CorrMethod", and n, storing the result. Next, we will need helpers for the heatmap.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Get significance stars based on p-value | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string get_significance_stars(double pval) { if (pval < PValueThreshold1) return "***"; //--- Return three stars if (pval < PValueThreshold2) return "**"; //--- Return two stars if (pval < PValueThreshold3) return "*"; //--- Return one star return ""; //--- Return empty } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Interpolate between multiple colors based on value (-1 to 1) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ color interpolate_heatmap_color(double value) { if (value == 0.0) return ColorNeutralBg; //--- Return neutral for zero double abs_val = MathAbs(value); //--- Compute absolute value int num_stops = ArraySize(heatmap_colors) / 2; //--- Compute stops per side double step = 1.0 / (num_stops - 1); //--- Compute step size if (value > 0.0) { //--- Handle positive int idx = (int)MathFloor(abs_val / step); //--- Compute index if (idx >= num_stops - 1) idx = num_stops - 2; //--- Clamp index double factor = (abs_val - idx * step) / step; //--- Compute factor return interpolate_color(heatmap_colors[idx + num_stops], heatmap_colors[idx + num_stops + 1], factor); //--- Interpolate positive } else { //--- Handle negative int idx = (int)MathFloor(abs_val / step); //--- Compute index if (idx >= num_stops - 1) idx = num_stops - 2; //--- Clamp index double factor = (abs_val - idx * step) / step; //--- Compute factor return interpolate_color(heatmap_colors[idx], heatmap_colors[idx + 1], factor); //--- Interpolate negative } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Interpolate between two colors based on factor (0 to 1) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ color interpolate_color(color c1, color c2, double factor) { uchar r1 = (uchar)(c1 & 0xFF), g1 = (uchar)((c1 >> 8) & 0xFF), b1 = (uchar)((c1 >> 16) & 0xFF); //--- Extract RGB from first color uchar r2 = (uchar)(c2 & 0xFF), g2 = (uchar)((c2 >> 8) & 0xFF), b2 = (uchar)((c2 >> 16) & 0xFF); //--- Extract RGB from second color uchar r = (uchar)MathMax(0, MathMin(255, r1 + factor * (r2 - r1) + 0.5)); //--- Interpolate red uchar g = (uchar)MathMax(0, MathMin(255, g1 + factor * (g2 - g1) + 0.5)); //--- Interpolate green uchar b = (uchar)MathMax(0, MathMin(255, b1 + factor * (b2 - b1) + 0.5)); //--- Interpolate blue return (color)((b << 16) | (g << 8) | r); //--- Return interpolated color }
We define the "get_significance_stars" function to determine the number of asterisk symbols representing statistical significance based on a given p-value, returning a string. It takes a double parameter "pval" and uses conditional checks: if "pval" is less than "PValueThreshold1", we return "***" for the highest significance; if less than "PValueThreshold2", return "**"; if less than "PValueThreshold3", return "*"; otherwise, return an empty string for no significance.
Next, we implement the "interpolate_heatmap_color" function to generate a color for the heatmap mode by interpolating within the gradient array based on a correlation value between negative one and one, returning a color type. It handles zero by returning "ColorNeutralBg" directly. We compute the absolute value "abs_val", determine the number of stops per side by dividing the "heatmap_colors" array size by two, and calculate the step size as one divided by stops minus one. For positive values, we find the index with MathFloor of "abs_val" over step, clamp it if at or beyond the last interval, compute a factor as the remainder over step, and call "interpolate_color" with colors from the positive half of the array plus the factor. For negative values, we do similarly but use the negative half of the array.
We then create the "interpolate_color" function to blend two colors linearly based on a factor from zero to one, returning the resulting color. It extracts red, green, and blue components as unsigned chars from "c1" and "c2" using bitwise operations: masking with 0xFF for red, shifting right by eight and masking for green, and shifting by sixteen for blue. We interpolate each channel by starting from the first color's value, adding the factor times the difference to the second, adding 0.5 for rounding, and clamping between zero and 255 with the MathMax and MathMin functions. Finally, we combine the interpolated components into a single color value using bit shifts: blue left by sixteen, green by eight, and red, then bitwise OR them together. We can now begin the creation of the dashboard since we have most of the helper functions that we need to do the computations.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Create rectangle for UI | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool create_rectangle(string object_name, int x_distance, int y_distance, int x_size, int y_size, color background_color, color border_color = clrNONE) { if (!ObjectCreate(0, object_name, OBJ_RECTANGLE_LABEL, 0, 0, 0)) { //--- Create rectangle or check failure Print(__FUNCTION__, ": failed to create Rectangle: ", GetLastError()); //--- Print error return false; //--- Return failure } ObjectSetInteger(0, object_name, OBJPROP_XDISTANCE, x_distance); //--- Set x distance ObjectSetInteger(0, object_name, OBJPROP_YDISTANCE, y_distance); //--- Set y distance ObjectSetInteger(0, object_name, OBJPROP_XSIZE, x_size); //--- Set x size ObjectSetInteger(0, object_name, OBJPROP_YSIZE, y_size); //--- Set y size ObjectSetInteger(0, object_name, OBJPROP_CORNER, CORNER_LEFT_UPPER); //--- Set corner ObjectSetInteger(0, object_name, OBJPROP_BGCOLOR, background_color); //--- Set background ObjectSetInteger(0, object_name, OBJPROP_COLOR, border_color); //--- Set border color ObjectSetInteger(0, object_name, OBJPROP_BORDER_TYPE, BORDER_FLAT); //--- Set border type ObjectSetInteger(0, object_name, OBJPROP_BACK, false); //--- Set back property return true; //--- Return success } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Create text label for UI | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool create_label(string object_name, string text, int x_distance, int y_distance, int font_size = 10, color text_color = COLOR_WHITE, string font = "Arial Rounded MT Bold") { if (!ObjectCreate(0, object_name, OBJ_LABEL, 0, 0, 0)) { //--- Create label or check failure Print(__FUNCTION__, ": failed to create Label: ", GetLastError()); //--- Print error return false; //--- Return failure } ObjectSetInteger(0, object_name, OBJPROP_XDISTANCE, x_distance); //--- Set x distance ObjectSetInteger(0, object_name, OBJPROP_YDISTANCE, y_distance); //--- Set y distance ObjectSetInteger(0, object_name, OBJPROP_CORNER, CORNER_LEFT_UPPER); //--- Set corner ObjectSetString(0, object_name, OBJPROP_TEXT, text); //--- Set text ObjectSetString(0, object_name, OBJPROP_FONT, font); //--- Set font ObjectSetInteger(0, object_name, OBJPROP_FONTSIZE, font_size); //--- Set font size ObjectSetInteger(0, object_name, OBJPROP_COLOR, text_color); //--- Set text color ObjectSetInteger(0, object_name, OBJPROP_ANCHOR, ANCHOR_CENTER); //--- Set anchor return true; //--- Return success } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Create full dashboard UI | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void create_full_dashboard() { color main_bg = C'30,30,30'; //--- Set main background color header_bg = C'60,60,60'; //--- Set header background color text_color = COLOR_WHITE; //--- Set text color color neutral_bg = ColorNeutralBg; //--- Set neutral background color button_text = clrGold; //--- Set button text color color theme_icon_color = clrWhite; //--- Set theme icon color color close_text = clrWhite; //--- Set close text color color header_icon_color = clrAqua; //--- Set header icon color int panel_width = WIDTH_SYMBOL + num_symbols * (WIDTH_CELL - 1) + 4; //--- Compute panel width int panel_height = HEIGHT_HEADER + HEIGHT_TF_CELL + GAP_HEIGHT + HEIGHT_RECTANGLE * (num_symbols + 1) - num_symbols + 2; //--- Compute panel height create_rectangle(MAIN_PANEL, panel_x, panel_y, panel_width, panel_height, main_bg); //--- Create main panel create_rectangle(HEADER_PANEL, panel_x, panel_y, panel_width, HEIGHT_HEADER, header_bg); //--- Create header panel create_label(HEADER_PANEL_ICON, CharToString(181), panel_x + 12, panel_y + 14, 18, header_icon_color, "Wingdings"); //--- Create header icon create_label(HEADER_PANEL_TEXT, "Correlation Matrix", panel_x + 90, panel_y + 12, 13, text_color); //--- Create header text create_label(CLOSE_BUTTON, CharToString('r'), panel_x + (panel_width - 17), panel_y + 14, 18, close_text, "Webdings"); //--- Create close button create_label(TOGGLE_BUTTON, CharToString('r'), panel_x + (panel_width - 47), panel_y + 14, 18, button_text, "Wingdings"); //--- Create toggle button string heatmap_icon = CharToString(global_display_mode == MODE_STANDARD ? (uchar)82 : (uchar)110); //--- Set heatmap icon create_label(HEATMAP_BUTTON, heatmap_icon, panel_x + (panel_width - 77), panel_y + 14, 18, button_text, "Wingdings"); //--- Create heatmap button create_label(PVAL_BUTTON, CharToString('X'), panel_x + (panel_width - 107), panel_y + 14, 18, button_text, "Wingdings"); //--- Create PVAL button string sort_icon = CharToString('N'); //--- Set sort icon create_label(SORT_BUTTON, sort_icon, panel_x + (panel_width - 137), panel_y + 14, 18, button_text, "Wingdings 3"); //--- Create sort button create_label(THEME_BUTTON, CharToString('['), panel_x + (panel_width - 167), panel_y + 14, 18, theme_icon_color, "Wingdings"); //--- Create theme button // Timeframe cells row int tf_y = panel_y + HEIGHT_HEADER; //--- Compute TF y position int tf_x_start = panel_x + 2; //--- Set TF start x for (int i = 0; i < num_tf_visible; i++) { //--- Loop visible TFs int x_offset = tf_x_start + i * WIDTH_TF_CELL; //--- Compute offset string rect_name = TF_CELL_RECT + IntegerToString(i); //--- Get rectangle name string text_name = TF_CELL_TEXT + IntegerToString(i); //--- Get text name color bg = (i == current_tf_index) ? ColorStrongPositiveBg : header_bg; //--- Set background create_rectangle(rect_name, x_offset, tf_y, WIDTH_TF_CELL, HEIGHT_TF_CELL, bg); //--- Create TF rectangle create_label(text_name, tf_strings[i], x_offset + (WIDTH_TF_CELL / 2), tf_y + (HEIGHT_TF_CELL / 2), 10, text_color, "Arial Bold"); //--- Create TF text } // Create row symbols (left column), pushed down int matrix_y = tf_y + HEIGHT_TF_CELL + GAP_HEIGHT; //--- Compute matrix y create_rectangle("SYMBOL_ROW_HEADER", panel_x + 2, matrix_y, WIDTH_SYMBOL, HEIGHT_RECTANGLE, header_bg); //--- Create row header rectangle create_label("SYMBOL_ROW_HEADER_TEXT", "Symbols", panel_x + (WIDTH_SYMBOL / 2 + 2), matrix_y + (HEIGHT_RECTANGLE / 2), 10, text_color, "Arial Bold"); //--- Create row header text for (int i = 0; i < num_symbols; i++) { //--- Loop row symbols int y_offset = matrix_y + HEIGHT_RECTANGLE * (i + 1) - (1 + i); //--- Compute y offset create_rectangle(SYMBOL_ROW_RECTANGLE + IntegerToString(i), panel_x + 2, y_offset, WIDTH_SYMBOL, HEIGHT_RECTANGLE, header_bg); //--- Create row rectangle create_label(SYMBOL_ROW_TEXT + IntegerToString(i), symbols_array[i], panel_x + (WIDTH_SYMBOL / 2 + 2), y_offset + (HEIGHT_RECTANGLE / 2 - 1), 10, text_color, "Arial Bold"); //--- Create row text } // Create column symbols (top row), pushed down for (int j = 0; j < num_symbols; j++) { //--- Loop column symbols int x_offset = panel_x + WIDTH_SYMBOL + j * WIDTH_CELL - j + 1; //--- Compute x offset create_rectangle(SYMBOL_COL_RECTANGLE + IntegerToString(j), x_offset, matrix_y, WIDTH_CELL, HEIGHT_RECTANGLE, header_bg); //--- Create column rectangle create_label(SYMBOL_COL_TEXT + IntegerToString(j), symbols_array[j], x_offset + (WIDTH_CELL / 2), matrix_y + (HEIGHT_RECTANGLE / 2), 10, text_color, "Arial Bold"); //--- Create column text } // Create correlation cells, pushed down for (int i = 0; i < num_symbols; i++) { //--- Loop rows for cells int y_offset = matrix_y + HEIGHT_RECTANGLE * (i + 1) - (1 + i); //--- Compute y offset for (int j = 0; j < num_symbols; j++) { //--- Loop columns for cells string cell_name = CELL_RECTANGLE + IntegerToString(i) + "_" + IntegerToString(j); //--- Get cell name string text_name = CELL_TEXT + IntegerToString(i) + "_" + IntegerToString(j); //--- Get text name int x_offset = panel_x + WIDTH_SYMBOL + j * WIDTH_CELL - j + 1; //--- Compute x offset create_rectangle(cell_name, x_offset, y_offset, WIDTH_CELL, HEIGHT_RECTANGLE, neutral_bg); //--- Create cell rectangle create_label(text_name, "0.00", x_offset + (WIDTH_CELL / 2), y_offset + (HEIGHT_RECTANGLE / 2 - 1), 10, text_color, "Arial"); //--- Create cell text } } ChartRedraw(0); //--- Redraw chart }
Here, we define the "create_rectangle" function to generate a rectangular graphical object for the user interface, returning a boolean for success. It takes parameters including object name as a string, integers for x and y distances, sizes, background color, and an optional border color defaulting to none. We attempt to create the object using ObjectCreate with subwindow zero, the name OBJ_RECTANGLE_LABEL type, and default coordinates, printing an error with the function name and last error code if it fails, and returning false. If successful, we configure properties with ObjectSetInteger: x and y distances, sizes, corner to left upper, background color, border color, border type to flat, and back to false, then return true.
Next, we implement the "create_label" function to produce a text label object for the user interface, also returning boolean success. It accepts object name and text as strings, x and y distances, optional font size defaulting to ten, text color defaulting to white, and font defaulting to Arial Rounded MT Bold. We use "ObjectCreate" with OBJ_LABEL type, printing an error if failed. On success, we set x and y distances, corner to left upper, text, font, font size, text color, and anchor to center using appropriate "ObjectSetInteger" and ObjectSetString calls, returning true.
We then create the "create_full_dashboard" function to build the entire user interface structure using the above helpers. It sets local colors such as the main background to a dark gray, the header background to a medium gray, the text color to white, the neutral background from input, the button text to gold, the theme and close icons to white, and the header icon to aqua. We calculate panel width based on symbol width plus cells adjusted for the number of symbols, and height incorporating the header, timeframe row, gap, and matrix rows.
We call "create_rectangle" for the main and header panels, then "create_label" for elements like header icon with character 181 from Wingdings, title as Correlation Matrix, close button with 'r' from Webdings, toggle button similarly, heatmap button with dynamic icon based on display mode using CharToString and uchar casts, p-value button with 'X' from Wingdings, sort button with 'N' from Wingdings 3, and theme button with '[' from Wingdings. You can use any of your choosing from the font symbols list below.

For the timeframe row, we compute y position below the header and starting x, then loop over visible timeframes to create rectangles and labels: calculating offsets, forming names with timeframe cell prefix and index string, setting background conditionally to strong positive or header color based on current index, and labeling with timeframe strings in Arial Bold. We set the matrix y position below the timeframe row plus gap, then create the row header rectangle and label it as Symbols. For row symbols on the left, we loop to compute y offsets, create rectangles with row prefix and index, and labels with symbol names from the array in Arial Bold. Similarly, for column symbols on top, we loop to compute x offsets, create rectangles with column prefixes, and labels with symbol names.
For correlation cells, we nest loops over rows and columns, computing offsets, forming cell names with rectangle prefix and indices separated by underscore, and text names similarly, then calling "create_rectangle" with neutral background and "create_label" initialized to 0.00 in Arial. Finally, we redraw the chart with ChartRedraw at subwindow zero. We can now call this function in the "OnInit" event handler to do the heavy lifting.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Initialize expert | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { global_display_mode = DashboardMode; //--- Set display mode global_correlation_tf = (CorrelationTimeframe == PERIOD_CURRENT ? (ENUM_TIMEFRAMES)_Period : CorrelationTimeframe); //--- Set timeframe for (int i = 0; i < NUM_TF; i++) { //--- Loop to find index if (tf_list[i] == global_correlation_tf) { //--- Check match current_tf_index = i; //--- Set index break; //--- Exit loop } } if (current_tf_index == -1) current_tf_index = 3; //--- Default to H1 global_correlation_tf = tf_list[current_tf_index]; //--- Update timeframe parse_symbols(); //--- Parse symbols int panel_width = WIDTH_SYMBOL + num_symbols * (WIDTH_CELL - 1) + 4; //--- Compute width num_tf_visible = MathMin(NUM_TF, (panel_width - 2) / WIDTH_TF_CELL); //--- Set visible TFs if (current_tf_index >= num_tf_visible) current_tf_index = num_tf_visible - 1; //--- Clamp index global_correlation_tf = tf_list[current_tf_index]; //--- Update timeframe ArrayInitialize(pvalue_matrix, 1.0); //--- Initialize p-values create_full_dashboard(); //--- Create dashboard return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); //--- Return success }
In the OnInit event handler, we initialize the program's runtime settings and user interface. We set the "global_display_mode" to the input "DashboardMode" and determine the "global_correlation_tf" by checking if "CorrelationTimeframe" is PERIOD_CURRENT, in which case we cast the current chart period _Period to ENUM_TIMEFRAMES; otherwise, we use the input directly. We then loop through the "tf_list" array to find the index matching "global_correlation_tf" and assign it to "current_tf_index", exiting early on a match. If no match is found—leaving "current_tf_index" at negative one—we default it to three, corresponding to the hourly timeframe. We update "global_correlation_tf" to the value at that index in "tf_list" for consistency.
Next, we call "parse_symbols" to process the symbol list. We compute the "panel_width" based on "WIDTH_SYMBOL" plus an adjustment for the number of symbols times "WIDTH_CELL". The "num_tf_visible" is set to the minimum of "NUM_TF" and the available space in the panel divided by "WIDTH_TF_CELL". If "current_tf_index" exceeds this visible count, we clamp it to the last visible index minus one, and update "global_correlation_tf" again accordingly. We initialize the "pvalue_matrix" array to 1.0 using ArrayInitialize as a default state before calculations. Finally, we call "create_full_dashboard" to build the user interface and return INIT_SUCCEEDED to indicate successful initialization. Upon compilation, we get the following outcome.

From the image, we can see that the dashboard was created successfully. What we need to do is extend it by adding the legend panel so it is created in conjunction with the dashboard.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Recreate legend objects based on current mode | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void recreate_legend() { // Delete existing legend objects for (int i = 0; i < NUM_LEGEND_ITEMS; i++) { //--- Loop legend items ObjectDelete(0, LEGEND_CELL_RECTANGLE + IntegerToString(i)); //--- Delete rectangle ObjectDelete(0, LEGEND_CELL_TEXT + IntegerToString(i)); //--- Delete text } // Define full correlation values based on mode (more points for finer legend) double full_corr_vals[]; //--- Declare full values array if (global_display_mode == MODE_HEATMAP) { //--- Handle heatmap mode double heatmap_vals[] = {-1.0, -0.8, -0.6, -0.4, -0.2, 0.0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0}; //--- Set heatmap values ArrayCopy(full_corr_vals, heatmap_vals); //--- Copy to full } else { //--- Handle standard mode double standard_vals[] = {StrongNegativeThresholdPct / 100.0, -0.75, -0.5, -0.25, 0.0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, StrongPositiveThresholdPct / 100.0, 1.0}; //--- Set standard values ArrayCopy(full_corr_vals, standard_vals); //--- Copy to full } // Copy to visible and reduce dynamically if needed ArrayCopy(visible_corr_vals, full_corr_vals); //--- Copy to visible int panel_width = WIDTH_SYMBOL + num_symbols * (WIDTH_CELL - 1) + 4; //--- Compute panel width int available_width = panel_width - 4; //--- Compute available width double item_cost = WIDTH_LEGEND_CELL + LEGEND_SPACING; //--- Compute item cost int max_fit = (int)MathFloor((available_width + LEGEND_SPACING) / item_cost); //--- Compute max fit if (max_fit < 1) max_fit = 1; //--- Ensure minimum fit while (ArraySize(visible_corr_vals) > max_fit) { //--- Loop to reduce int sz = ArraySize(visible_corr_vals); //--- Get current size int zero_pos = -1; //--- Initialize zero position for (int p = 0; p < sz; p++) { //--- Loop to find zero if (visible_corr_vals[p] == 0.0) { //--- Check for zero zero_pos = p; //--- Set position break; //--- Exit loop } } if (zero_pos >= 0) { //--- Handle found zero ArrayRemove(visible_corr_vals, zero_pos, 1); //--- Remove zero continue; //--- Continue reduction } // Find min abs > 0 double min_abs = DBL_MAX; //--- Initialize min abs for (int p = 0; p < sz; p++) { //--- Loop to find min double av = MathAbs(visible_corr_vals[p]); //--- Get absolute if (av > 0 && av < min_abs) min_abs = av; //--- Update min } if (min_abs == DBL_MAX) break; //--- Exit if no more // Remove all == ±min_abs for (int p = sz - 1; p >= 0; p--) { //--- Loop backward to remove if (MathAbs(visible_corr_vals[p]) == min_abs) ArrayRemove(visible_corr_vals, p, 1); //--- Remove match } } num_legend_visible = ArraySize(visible_corr_vals); //--- Set visible count // Calculate positions int panel_height = HEIGHT_HEADER + HEIGHT_TF_CELL + GAP_HEIGHT + HEIGHT_RECTANGLE * (num_symbols + 1) - num_symbols + 2; //--- Compute panel height int legend_y = panel_y + panel_height + GAP_MAIN_LEGEND; //--- Compute legend y int total_legend_width = num_legend_visible * WIDTH_LEGEND_CELL + (num_legend_visible - 1) * LEGEND_SPACING; //--- Compute total width int x_start = panel_x + (panel_width - total_legend_width) / 2; //--- Compute start x color neutral_bg = ColorNeutralBg; //--- Set neutral background color text_color = COLOR_WHITE; //--- Set text color // Create new legend objects for (int i = 0; i < num_legend_visible; i++) { //--- Loop to create int x_offset = x_start + i * (WIDTH_LEGEND_CELL + LEGEND_SPACING); //--- Compute offset string rect_name = LEGEND_CELL_RECTANGLE + IntegerToString(i); //--- Get rectangle name string text_name = LEGEND_CELL_TEXT + IntegerToString(i); //--- Get text name create_rectangle(rect_name, x_offset, legend_y + 2, WIDTH_LEGEND_CELL, HEIGHT_LEGEND, neutral_bg); //--- Create rectangle create_label(text_name, "0%", x_offset + WIDTH_LEGEND_CELL / 2, legend_y + 2 + HEIGHT_LEGEND / 2 - 1, 10, text_color, "Arial"); //--- Create label } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Create full dashboard UI | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void create_full_dashboard() { //--- Other dashboard creation logic // Create separate legend panel int legend_y = panel_y + panel_height + GAP_MAIN_LEGEND; //--- Compute legend y create_rectangle(LEGEND_PANEL, panel_x, legend_y, panel_width, HEIGHT_LEGEND_PANEL, main_bg); //--- Create legend panel recreate_legend(); //--- Recreate legend ChartRedraw(0); //--- Redraw chart }
We implement the "recreate_legend" function to dynamically rebuild the legend objects based on the current display mode, ensuring it fits the panel and reflects appropriate correlation values. We loop to delete existing legend rectangles and text labels using ObjectDelete with names formed from prefixes and index strings.
We declare a full correlation values array and populate it conditionally: for heatmap mode, using a local array with values from negative 1.0 to 1.0 in 0.2 increments copied over; for standard mode, using thresholds converted to decimals and fixed points like negative 0.75. To fit the space, we copy to the visible array, compute panel width, available width, item cost including spacing, and maximum fit with a floor division, ensuring at least one. In a loop while oversized, we remove zero if present, or find and remove all instances of the smallest non-zero absolute value by scanning and using ArrayRemove backward.
We set the visible count to the updated array size. For positioning, we calculate panel height from constants and rows, legend y below the panel with a gap, total legend width with cells and spacings, and starting x for centering. We set a neutral background and text color, then loop to create rectangles and labels: computing offsets, forming names, using "create_rectangle" with a neutral background, and "create_label" initialized to 0% in Arial. In the "create_full_dashboard" function, after other interface logic, we compute legend y and create the legend panel rectangle with main background, call "recreate_legend" to populate it, and redraw the chart. On compilation, we get the following outcome.

With the legend added, we now just need to update the dashboard and the legend so the computations take effect.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Update TF highlights | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void update_tf_highlights() { color inactive_bg = C'60,60,60'; //--- Set inactive background for (int i = 0; i < num_tf_visible; i++) { //--- Loop visible TFs string rect_name = TF_CELL_RECT + IntegerToString(i); //--- Get rectangle name color bg = (i == current_tf_index) ? ColorStrongPositiveBg : inactive_bg; //--- Set background ObjectSetInteger(0, rect_name, OBJPROP_BGCOLOR, bg); //--- Update background } ChartRedraw(0); //--- Redraw chart } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Update legend colors and texts based on mode | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void update_legend() { color default_txt = ColorTextStrong; //--- Set default text color for (int i = 0; i < num_legend_visible; i++) { //--- Loop visible legends string rect_name = LEGEND_CELL_RECTANGLE + IntegerToString(i); //--- Get rectangle name string text_name = LEGEND_CELL_TEXT + IntegerToString(i); //--- Get text name double corr = visible_corr_vals[i]; //--- Get correlation value int decimals = (MathAbs(corr) == 0.5 || corr == 0.0 || MathAbs(corr) == 1.0) ? 0 : 1; //--- Set decimals string txt_str = DoubleToString(corr * 100, decimals) + "%"; //--- Format text color bg_color = ColorNeutralBg; //--- Initialize background color txt_color = default_txt; //--- Initialize text color if (corr == 1.0) { //--- Handle perfect positive bg_color = ColorDiagonalBg; //--- Set diagonal background txt_color = default_txt; //--- Set text color } else if (corr == 0.0) { //--- Handle zero bg_color = ColorNeutralBg; //--- Set neutral background txt_color = default_txt; //--- Set text color } else { //--- Handle other values if (global_display_mode == MODE_STANDARD) { //--- Handle standard mode double strong_pos = StrongPositiveThresholdPct / 100.0; //--- Set positive threshold double strong_neg = StrongNegativeThresholdPct / 100.0; //--- Set negative threshold if (corr >= strong_pos) { //--- Check strong positive bg_color = ColorStrongPositiveBg; //--- Set positive background txt_color = default_txt; //--- Set text color } else if (corr <= strong_neg) { //--- Check strong negative bg_color = ColorStrongNegativeBg; //--- Set negative background txt_color = default_txt; //--- Set text color } else { //--- Handle mild bg_color = ColorNeutralBg; //--- Set neutral background txt_color = (corr > 0.0) ? ColorTextPositive : ColorTextNegative; //--- Set mild text color } } else { //--- Handle heatmap mode txt_color = default_txt; //--- Set text color bg_color = interpolate_heatmap_color(corr); //--- Interpolate background } } ObjectSetInteger(0, rect_name, OBJPROP_BGCOLOR, bg_color); //--- Update background ObjectSetString(0, text_name, OBJPROP_TEXT, txt_str); //--- Update text ObjectSetInteger(0, text_name, OBJPROP_COLOR, txt_color); //--- Update text color } ChartRedraw(0); //--- Redraw chart } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Update dashboard cells with correlation values and colors | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void update_dashboard() { update_correlations(); //--- Update correlations double strong_pos = StrongPositiveThresholdPct / 100.0; //--- Set positive threshold double strong_neg = StrongNegativeThresholdPct / 100.0; //--- Set negative threshold color text_base = ColorTextStrong; //--- Set base text color for (int i = 0; i < num_symbols; i++) { //--- Loop rows for (int j = 0; j < num_symbols; j++) { //--- Loop columns double corr = correlation_matrix[i][j]; //--- Get correlation double pval = pvalue_matrix[i][j]; //--- Get p-value string text = DoubleToString(corr * 100, 1) + "%" + get_significance_stars(pval); //--- Format text color bg_color = ColorNeutralBg; //--- Initialize background color txt_color = ColorTextZero; //--- Initialize text color if (i == j) { //--- Handle diagonal bg_color = ColorDiagonalBg; //--- Set diagonal background txt_color = text_base; //--- Set text color } else { //--- Handle off-diagonal if (global_display_mode == MODE_STANDARD) { //--- Handle standard mode if (corr >= strong_pos) { //--- Check strong positive bg_color = ColorStrongPositiveBg; //--- Set positive background txt_color = text_base; //--- Set text color } else if (corr <= strong_neg) { //--- Check strong negative bg_color = ColorStrongNegativeBg; //--- Set negative background txt_color = text_base; //--- Set text color } else { //--- Handle mild bg_color = ColorNeutralBg; //--- Set neutral background if (corr > 0.0) { //--- Check positive mild txt_color = ColorTextPositive; //--- Set positive text } else if (corr < 0.0) { //--- Check negative mild txt_color = ColorTextNegative; //--- Set negative text } else { //--- Handle zero txt_color = text_base; //--- Set base text } } } else { //--- Handle heatmap mode txt_color = text_base; //--- Set text color bg_color = interpolate_heatmap_color(corr); //--- Set interpolated background } } string cell_name = CELL_RECTANGLE + IntegerToString(i) + "_" + IntegerToString(j); //--- Get cell name string text_name = CELL_TEXT + IntegerToString(i) + "_" + IntegerToString(j); //--- Get text name ObjectSetInteger(0, cell_name, OBJPROP_BGCOLOR, bg_color); //--- Update background ObjectSetString(0, text_name, OBJPROP_TEXT, text); //--- Update text ObjectSetInteger(0, text_name, OBJPROP_COLOR, txt_color); //--- Update text color } } update_legend(); //--- Update legend ChartRedraw(0); //--- Redraw chart }
Here, we implement the "update_tf_highlights" function to visually highlight the selected timeframe cell in the dashboard. We set an inactive background color to a medium gray and loop over the number of visible timeframes. For each, we form the rectangle name using the "TF_CELL_RECT" prefix and index string, then conditionally set the background color to "ColorStrongPositiveBg" if it matches the "current_tf_index" or to the inactive color otherwise. We update the object's background property with ObjectSetInteger using "OBJPROP_BGCOLOR" and redraw the chart.
Next, we define the "update_legend" function to refresh the legend's colors and texts according to the mode. We set a default text color from "ColorTextStrong" and loop over visible legend items. For each, we retrieve names for rectangle and text using prefixes and index, get the correlation value from "visible_corr_vals", determine decimals based on absolute value checks for clean formatting, and format the text string as a percentage with the DoubleToString function.
We initialize background and text colors, then handle special cases: for 1.0, use a diagonal background; for 0.0, a neutral background—both with default text. For others, in standard mode, we compute strong thresholds from percentages, setting backgrounds and text colors for strong positive, strong negative, or mild based on comparisons, using positive or negative mild text for non-zero. In heatmap mode, we set the default text and interpolate the background with "interpolate_heatmap_color". We update the rectangle's "OBJPROP_BGCOLOR", text's "OBJPROP_TEXT", and "OBJPROP_COLOR" using object setters, then redraw the chart.
We then create the "update_dashboard" function to refresh all cells with current correlations and visuals. We call "update_correlations" first, compute strong thresholds from percentages, and set a base text color from "ColorTextStrong".
In nested loops over symbols for rows and columns, we retrieve correlation and p-value from matrices, format cell text as percentage plus significance stars from "get_significance_stars", and initialize colors. For diagonal cells where indices match, we use a diagonal background and base text. For off-diagonal, in standard mode, we set backgrounds and text for strong positive, strong negative, or mild with conditional positive/negative/zero text; in heatmap mode, base text and interpolated background from "interpolate_heatmap_color". We form cell and text names with prefixes and indices, update background with OBJPROP_BGCOLOR, text content with "OBJPROP_TEXT", and text color with "OBJPROP_COLOR" via setters.
Finally, we call "update_legend" and redraw the chart. We call these functions in the initialization as tick events to apply the full effects as below.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Initialize expert | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { global_display_mode = DashboardMode; //--- Set display mode global_correlation_tf = (CorrelationTimeframe == PERIOD_CURRENT ? (ENUM_TIMEFRAMES)_Period : CorrelationTimeframe); //--- Set timeframe for (int i = 0; i < NUM_TF; i++) { //--- Loop to find index if (tf_list[i] == global_correlation_tf) { //--- Check match current_tf_index = i; //--- Set index break; //--- Exit loop } } if (current_tf_index == -1) current_tf_index = 3; //--- Default to H1 global_correlation_tf = tf_list[current_tf_index]; //--- Update timeframe parse_symbols(); //--- Parse symbols int panel_width = WIDTH_SYMBOL + num_symbols * (WIDTH_CELL - 1) + 4; //--- Compute width num_tf_visible = MathMin(NUM_TF, (panel_width - 2) / WIDTH_TF_CELL); //--- Set visible TFs if (current_tf_index >= num_tf_visible) current_tf_index = num_tf_visible - 1; //--- Clamp index global_correlation_tf = tf_list[current_tf_index]; //--- Update timeframe ArrayInitialize(pvalue_matrix, 1.0); //--- Initialize p-values create_full_dashboard(); //--- Create dashboard update_tf_highlights(); //--- Update highlights update_dashboard(); //--- Update initial return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); //--- Return success } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Handle tick event | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { update_dashboard(); //--- Update on tick }
In the OnInit event handler, we call "update_tf_highlights" for timeframe visuals, and "update_dashboard" for initial data population, returning INIT_SUCCEEDED. In the OnTick event handler, we simply call "update_dashboard" to refresh correlations and visuals on each new tick. If you want to handle the calculations on every bar, you can add a control logic but for now, we leave it as is since we only have a few symbol sets. Upon compilation, we get the following outcome.

From the image, we can see that we have correctly set up the correlation matrix dashboard with all the populations done, hence achieving our objectives. What now remains is testing the workability of the system, and that is handled in the preceding section.
Backtesting
We did the testing, and below is the compiled visualization in a single Graphics Interchange Format (GIF) bitmap image format.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we’ve developed a correlation matrix dashboard in MQL5 that computes relationships between user-specified symbols using Pearson, Spearman, or Kendall methods over a configurable timeframe and bars, incorporating p-value significance testing for reliability. The system supports standard mode with threshold-based coloring and stars for significance levels, as well as heatmap mode with gradient interpolation for visual representation of correlation strengths, featuring an interactive user interface with timeframe selectors, mode toggles, and a dynamic legend for analyzing asset interdependencies. In the next parts, we will bring life to the dashboard to make it hoverable, draggable, and make the clicking icons responsive by performing their respective functions. Keep tuned!
Warning: All rights to these materials are reserved by MetaQuotes Ltd. Copying or reprinting of these materials in whole or in part is prohibited.
This article was written by a user of the site and reflects their personal views. MetaQuotes Ltd is not responsible for the accuracy of the information presented, nor for any consequences resulting from the use of the solutions, strategies or recommendations described.
 Reimagining Classic Strategies (Part 21): Bollinger Bands And RSI Ensemble Strategy Discovery
Reimagining Classic Strategies (Part 21): Bollinger Bands And RSI Ensemble Strategy Discovery
 Forex arbitrage trading: Analyzing synthetic currencies movements and their mean reversion
Forex arbitrage trading: Analyzing synthetic currencies movements and their mean reversion
 Neural Networks in Trading: Two-Dimensional Connection Space Models (Final Part)
Neural Networks in Trading: Two-Dimensional Connection Space Models (Final Part)
 Optimizing Trend Strength: Trading in Trend Direction and Strength
Optimizing Trend Strength: Trading in Trend Direction and Strength
- Free trading apps
- Over 8,000 signals for copying
- Economic news for exploring financial markets
You agree to website policy and terms of use
Hello Allan Munene Mutiiria,
Thank you for sharing a brillant idea through your article. In return, I made your source code ready for production use
.ex5 file removed by moderator - only source code is allowed on the forum