
Artificial Electric Field Algorithm (AEFA)
The article presents an artificial electric field algorithm (AEFA) inspired by Coulomb's law of electrostatic force. The algorithm simulates electrical phenomena to solve complex optimization problems using charged particles and their interactions. AEFA exhibits unique properties in the context of other algorithms related to laws of nature.

Neural Networks in Trading: Two-Dimensional Connection Space Models (Final Part)
We continue to explore the innovative Chimera framework – a two-dimensional state-space model that uses neural network technologies to analyze multidimensional time series. This method provides high forecasting accuracy with low computational cost.

Neural Network in Practice: The First Neuron
In this article, we'll start building something simple and humble: a neuron. We will program it with a very small amount of MQL5 code. The neuron worked great in my tests. Let's go back a bit in this series of articles about neural networks to understand what I'm talking about.

Neural Networks in Trading: Memory Augmented Context-Aware Learning (MacroHFT) for Cryptocurrency Markets
I invite you to explore the MacroHFT framework, which applies context-aware reinforcement learning and memory to improve high-frequency cryptocurrency trading decisions using macroeconomic data and adaptive agents.

Black Hole Algorithm (BHA)
The Black Hole Algorithm (BHA) uses the principles of black hole gravity to optimize solutions. In this article, we will look at how BHA attracts the best solutions while avoiding local extremes, and why this algorithm has become a powerful tool for solving complex problems. Learn how simple ideas can lead to impressive results in the world of optimization.
Neural Networks in Trading: Lightweight Models for Time Series Forecasting
Lightweight time series forecasting models achieve high performance using a minimum number of parameters. This, in turn, reduces the consumption of computing resources and speeds up decision-making. Despite being lightweight, such models achieve forecast quality comparable to more complex ones.

Reimagining Classic Strategies (Part V): Multiple Symbol Analysis on USDZAR
In this series of articles, we revisit classical strategies to see if we can improve the strategy using AI. In today's article, we will examine a popular strategy of multiple symbol analysis using a basket of correlated securities, we will focus on the exotic USDZAR currency pair.
Neural networks made easy (Part 45): Training state exploration skills
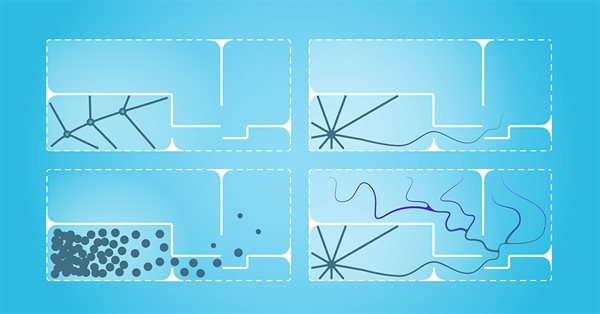
Training useful skills without an explicit reward function is one of the main challenges in hierarchical reinforcement learning. Previously, we already got acquainted with two algorithms for solving this problem. But the question of the completeness of environmental research remains open. This article demonstrates a different approach to skill training, the use of which directly depends on the current state of the system.

Neural networks made easy (Part 51): Behavior-Guided Actor-Critic (BAC)
The last two articles considered the Soft Actor-Critic algorithm, which incorporates entropy regularization into the reward function. This approach balances environmental exploration and model exploitation, but it is only applicable to stochastic models. The current article proposes an alternative approach that is applicable to both stochastic and deterministic models.

MQL5 Wizard Techniques you should know (Part 16): Principal Component Analysis with Eigen Vectors
Principal Component Analysis, a dimensionality reducing technique in data analysis, is looked at in this article, with how it could be implemented with Eigen values and vectors. As always, we aim to develop a prototype expert-signal-class usable in the MQL5 wizard.

MQL5 Wizard Techniques you should know (Part 61): Using Patterns of ADX and CCI with Supervised Learning
The ADX Oscillator and CCI oscillator are trend following and momentum indicators that can be paired when developing an Expert Advisor. We look at how this can be systemized by using all the 3 main training modes of Machine Learning. Wizard Assembled Expert Advisors allow us to evaluate the patterns presented by these two indicators, and we start by looking at how Supervised-Learning can be applied with these Patterns.
Developing an MQL5 Reinforcement Learning agent with RestAPI integration (Part 1): How to use RestAPIs in MQL5
In this article we will talk about the importance of APIs (Application Programming Interface) for interaction between different applications and software systems. We will see the role of APIs in simplifying interactions between applications, allowing them to efficiently share data and functionality.
Neural Networks in Trading: Contrastive Pattern Transformer
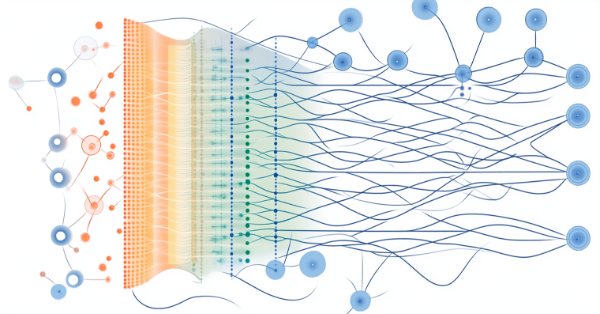
The Contrastive Transformer is designed to analyze markets both at the level of individual candlesticks and based on entire patterns. This helps improve the quality of market trend modeling. Moreover, the use of contrastive learning to align representations of candlesticks and patterns fosters self-regulation and improves the accuracy of forecasts.

Data Science and ML (Part 38): AI Transfer Learning in Forex Markets
The AI breakthroughs dominating headlines, from ChatGPT to self-driving cars, aren’t built from isolated models but through cumulative knowledge transferred from various models or common fields. Now, this same "learn once, apply everywhere" approach can be applied to help us transform our AI models in algorithmic trading. In this article, we are going to learn how we can leverage the information gained across various instruments to help in improving predictions on others using transfer learning.

Data Science and ML (Part 32): Keeping your AI models updated, Online Learning
In the ever-changing world of trading, adapting to market shifts is not just a choice—it's a necessity. New patterns and trends emerge everyday, making it harder even the most advanced machine learning models to stay effective in the face of evolving conditions. In this article, we’ll explore how to keep your models relevant and responsive to new market data by automatically retraining.

Neural Networks in Trading: Controlled Segmentation (Final Part)
We continue the work started in the previous article on building the RefMask3D framework using MQL5. This framework is designed to comprehensively study multimodal interaction and feature analysis in a point cloud, followed by target object identification based on a description provided in natural language.
Population ADAM (Adaptive Moment Estimation)
The article presents the transformation of the well-known and popular ADAM gradient optimization method into a population algorithm and its modification with the introduction of hybrid individuals. The new approach allows creating agents that combine elements of successful decisions using probability distribution. The key innovation is the formation of hybrid population individuals that adaptively accumulate information from the most promising solutions, increasing the efficiency of search in complex multidimensional spaces.

Market Simulation (Part 06): Transferring Information from MetaTrader 5 to Excel
Many people, especially non=programmers, find it very difficult to transfer information between MetaTrader 5 and other programs. One such program is Excel. Many use Excel as a way to manage and maintain their risk control. It is an excellent program and easy to learn, even for those who are not VBA programmers. Here we will look at how to establish a connection between MetaTrader 5 and Excel (a very simple method).
Matrix Factorization: A more practical modeling
You might not have noticed that the matrix modeling was a little strange, since only columns were specified, not rows and columns. This looks very strange when reading the code that performs matrix factorizations. If you were expecting to see the rows and columns listed, you might get confused when trying to factorize. Moreover, this matrix modeling method is not the best. This is because when we model matrices in this way, we encounter some limitations that force us to use other methods or functions that would not be necessary if the modeling were done in a more appropriate way.

Time series clustering in causal inference
Clustering algorithms in machine learning are important unsupervised learning algorithms that can divide the original data into groups with similar observations. By using these groups, you can analyze the market for a specific cluster, search for the most stable clusters using new data, and make causal inferences. The article proposes an original method for time series clustering in Python.
Neural Networks Made Easy (Part 86): U-Shaped Transformer
We continue to study timeseries forecasting algorithms. In this article, we will discuss another method: the U-shaped Transformer.
Neural Networks Made Easy (Part 85): Multivariate Time Series Forecasting
In this article, I would like to introduce you to a new complex timeseries forecasting method, which harmoniously combines the advantages of linear models and transformers.

Employing Game Theory Approaches in Trading Algorithms
We are creating an adaptive self-learning trading expert advisor based on DQN machine learning, with multidimensional causal inference. The EA will successfully trade simultaneously on 7 currency pairs. And agents of different pairs will exchange information with each other.
Price movement discretization methods in Python
We will look at price discretization methods using Python + MQL5. In this article, I will share my practical experience developing a Python library that implements a wide range of approaches to bar formation — from classic Volume and Range bars to more exotic methods like Renko and Kagi. We will consider three-line breakout candles and range bars analyzing their statistics and trying to define how else the prices can be represented discretely.

Neural networks made easy (Part 74): Trajectory prediction with adaptation
This article introduces a fairly effective method of multi-agent trajectory forecasting, which is able to adapt to various environmental conditions.

Neural Networks in Trading: Node-Adaptive Graph Representation with NAFS
We invite you to get acquainted with the NAFS (Node-Adaptive Feature Smoothing) method, which is a non-parametric approach to creating node representations that does not require parameter training. NAFS extracts features of each node given its neighbors and then adaptively combines these features to form a final representation.

Integrate Your Own LLM into EA (Part 5): Develop and Test Trading Strategy with LLMs(I)-Fine-tuning
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence today, language models (LLMs) are an important part of artificial intelligence, so we should think about how to integrate powerful LLMs into our algorithmic trading. For most people, it is difficult to fine-tune these powerful models according to their needs, deploy them locally, and then apply them to algorithmic trading. This series of articles will take a step-by-step approach to achieve this goal.
Data Science and Machine Learning (Part 16): A Refreshing Look at Decision Trees
Dive into the intricate world of decision trees in the latest installment of our Data Science and Machine Learning series. Tailored for traders seeking strategic insights, this article serves as a comprehensive recap, shedding light on the powerful role decision trees play in the analysis of market trends. Explore the roots and branches of these algorithmic trees, unlocking their potential to enhance your trading decisions. Join us for a refreshing perspective on decision trees and discover how they can be your allies in navigating the complexities of financial markets.
Atomic Orbital Search (AOS) algorithm
The article considers the Atomic Orbital Search (AOS) algorithm, which uses the concepts of the atomic orbital model to simulate the search for solutions. The algorithm is based on probability distributions and the dynamics of interactions in the atom. The article discusses in detail the mathematical aspects of AOS, including updating the positions of candidate solutions and the mechanisms of energy absorption and release. AOS opens new horizons for applying quantum principles to computing problems by offering an innovative approach to optimization.

Price Action Analysis Toolkit Development (Part 34): Turning Raw Market Data into Predictive Models Using an Advanced Ingestion Pipeline
Have you ever missed a sudden market spike or been caught off‑guard when one occurred? The best way to anticipate live events is to learn from historical patterns. Intending to train an ML model, this article begins by showing you how to create a script in MetaTrader 5 that ingests historical data and sends it to Python for storage—laying the foundation for your spike‑detection system. Read on to see each step in action.
MQL5 Wizard Techniques you should know (Part 57): Supervised Learning with Moving Average and Stochastic Oscillator
Moving Average and Stochastic Oscillator are very common indicators that some traders may not use a lot because of their lagging nature. In a 3-part ‘miniseries' that considers the 3 main forms of machine learning, we look to see if this bias against these indicators is justified, or they might be holding an edge. We do our examination in wizard assembled Expert Advisors.

Neural networks made easy (Part 71): Goal-Conditioned Predictive Coding (GCPC)
In previous articles, we discussed the Decision Transformer method and several algorithms derived from it. We experimented with different goal setting methods. During the experiments, we worked with various ways of setting goals. However, the model's study of the earlier passed trajectory always remained outside our attention. In this article. I want to introduce you to a method that fills this gap.
Self Optimizing Expert Advisors in MQL5 (Part 16): Supervised Linear System Identification
Linear system identifcation may be coupled to learn to correct the error in a supervised learning algorithm. This allows us to build applications that depend on statistical modelling techniques without necessarily inheriting the fragility of the model's restrictive assumptions. Classical supervised learning algorithms have many needs that may be supplemented by pairing these models with a feedback controller that can correct the model to keep up with current market conditions.
Neural Networks Made Easy (Part 83): The "Conformer" Spatio-Temporal Continuous Attention Transformer Algorithm
This article introduces the Conformer algorithm originally developed for the purpose of weather forecasting, which in terms of variability and capriciousness can be compared to financial markets. Conformer is a complex method. It combines the advantages of attention models and ordinary differential equations.

Time Evolution Travel Algorithm (TETA)
This is my own algorithm. The article presents the Time Evolution Travel Algorithm (TETA) inspired by the concept of parallel universes and time streams. The basic idea of the algorithm is that, although time travel in the conventional sense is impossible, we can choose a sequence of events that lead to different realities.

Neural networks made easy (Part 42): Model procrastination, reasons and solutions
In the context of reinforcement learning, model procrastination can be caused by several reasons. The article considers some of the possible causes of model procrastination and methods for overcoming them.

Neural Networks Made Easy (Part 95): Reducing Memory Consumption in Transformer Models
Transformer architecture-based models demonstrate high efficiency, but their use is complicated by high resource costs both at the training stage and during operation. In this article, I propose to get acquainted with algorithms that allow to reduce memory usage of such models.
Data label for time series mining (Part 6):Apply and Test in EA Using ONNX
This series of articles introduces several time series labeling methods, which can create data that meets most artificial intelligence models, and targeted data labeling according to needs can make the trained artificial intelligence model more in line with the expected design, improve the accuracy of our model, and even help the model make a qualitative leap!

Neural Network in Practice: Sketching a Neuron
In this article we will build a basic neuron. And although it looks simple, and many may consider this code completely trivial and meaningless, I want you to have fun studying this simple sketch of a neuron. Don't be afraid to modify the code, understanding it fully is the goal.

Population optimization algorithms: Differential Evolution (DE)
In this article, we will consider the algorithm that demonstrates the most controversial results of all those discussed previously - the differential evolution (DE) algorithm.