
Automating Trading Strategies in MQL5 (Part 21): Enhancing Neural Network Trading with Adaptive Learning Rates
Introduction
In our previous article (Part 20), we developed the Multi-Symbol Strategy Using Commodity Channel Index (CCI) and Awesome Oscillator (AO), automating trend reversal trades across multiple currency pairs with robust signal generation and risk management in MetaQuotes Language 5 (MQL5). In Part 21, we move on to a neural network-based trading strategy, which is enhanced with an adaptive learning rate mechanism to optimize prediction accuracy for market movements. We will cover the following topics:
- Understanding the Adaptive Neural Networks Learning Rate Strategy
- Implementation in MetaQuotes Language 5 (MQL5)
- Testing and Optimizing Learning Rate Adjustments
- Conclusion
By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive MetaQuotes Language 5 (MQL5) trading system leveraging neural networks with dynamic learning rate adjustments, ready for further refinement—let’s dive in!
Understanding the Adaptive Neural Networks Learning Rate Strategy
In Part 20, we developed a multi-symbol trading system that utilizes the Commodity Channel Index and Awesome Oscillator, enabling automated trend reversal trades across multiple currency pairs. Now, in Part 21, we dive into a dynamic neural network-based trading strategy, harnessing the power of neural networks—computational models mimicking the human brain’s interconnected neurons—to predict market price movements with greater precision by processing diverse market indicators and adapting the learning process to market volatility. Our goal is to build a flexible, high-performance trading system that leverages neural networks to analyze complex market patterns and execute trades with optimized accuracy through an adaptive learning rate mechanism.
Neural networks operate through layers of nodes, or neurons, structured as an input layer that captures market data, hidden layers that uncover intricate patterns, and an output layer that generates trade signals, such as predicting upward or downward price movements. Forward propagation drives data through these layers, where neurons apply weights and biases to inputs, transforming them into predictions. See below.
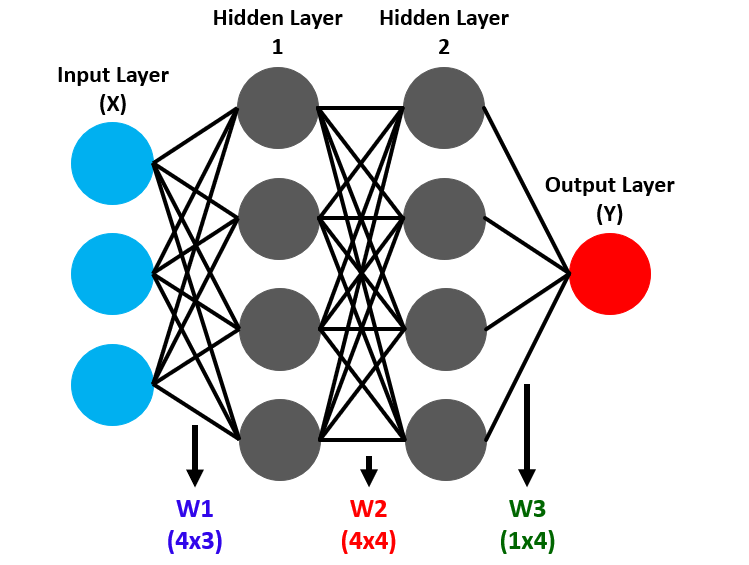
A critical component, the activation function, introduces non-linearity to these transformations, enabling the network to model complex relationships; for instance, the sigmoid activation function maps values to a 0-to-1 range, making it ideal for binary classification tasks like buy or sell decisions. Backpropagation refines this process by working backward from prediction errors and adjusting weights and biases to improve accuracy over time. See below.
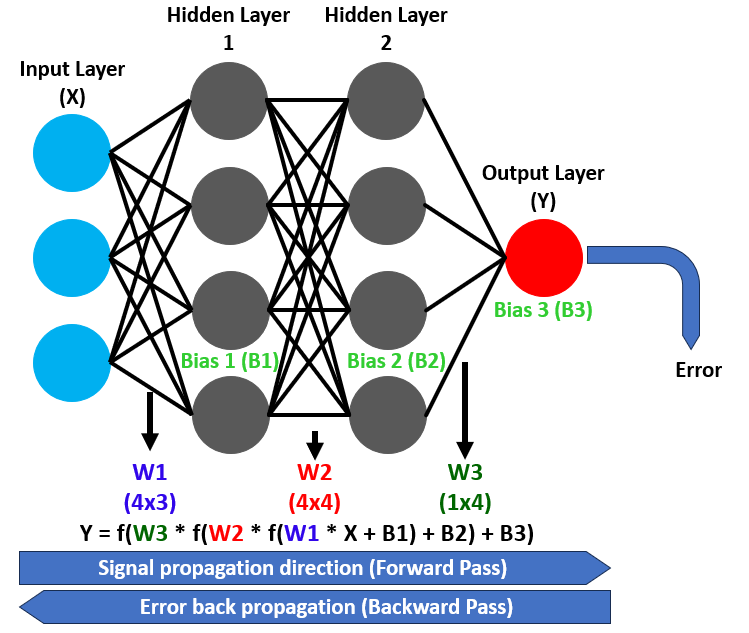
To make the network dynamic, we plan to implement an adaptive learning rate strategy that adjusts how quickly weights are updated during backpropagation—accelerating learning when predictions align with market outcomes and slowing it when errors spike to ensure stability.
We plan to design a system that feeds market indicators, such as moving averages and momentum metrics, into the neural network’s input layer, processes them through hidden layers to detect patterns, and produces reliable trade signals via the output layer. We plan to use the sigmoid activation function to transform neuron outputs, ensuring smooth, interpretable predictions for trading decisions. Our decision to use that is so that we can have 2 output options. Here is an example of other functions that you can use.
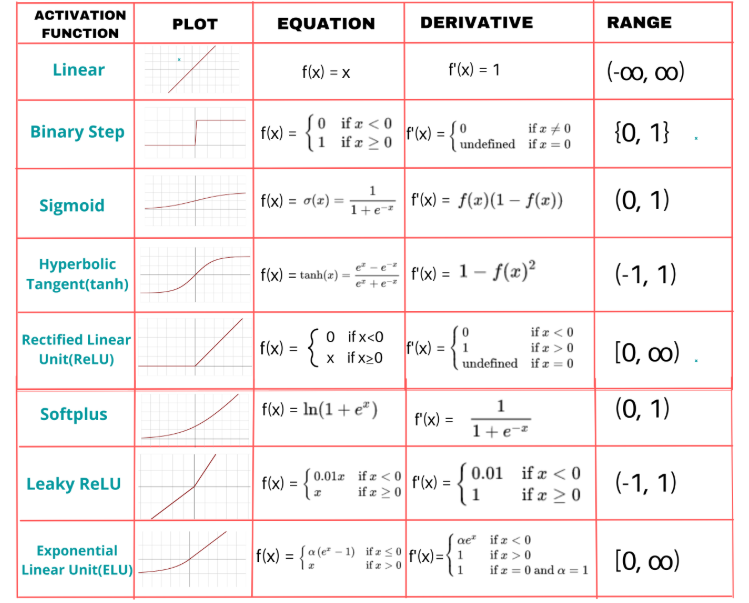
Additionally, we will dynamically adjust the learning rate based on training performance and adapt the number of hidden layer neurons to match market volatility, creating a responsive system that balances complexity and efficiency. This strategy sets the foundation for a robust implementation and thorough testing. We will use two moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Average True Range (ATR) to provide the inputs and once we have signals, we will open trades. Here is a visualization of what we aim to achieve after the implementation.
Implementation in MQL5
To create the program in MQL5, open the MetaEditor, go to the Navigator, locate the Indicators folder, click on the "New" tab, and follow the prompts to create the file. Once it is made, in the coding environment, we will start by declaring some input variables, structures and classes that we will use since we want to apply an Object Oriented Programming (OOP) approach.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Neural Networks Propagation EA.mq5 | //| Copyright 2025, Allan Munene Mutiiria. | //| https://t.me/Forex_Algo_Trader | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2025, Allan Munene Mutiiria." #property link "https://t.me/Forex_Algo_Trader" #property version "1.00" #include <Trade/Trade.mqh> CTrade tradeObject; //--- Instantiate trade object for executing trades // Input parameters with clear, meaningful names input double LotSize = 0.1; // Lot Size input int StopLossPoints = 100; // Stop Loss (points) input int TakeProfitPoints = 100; // Take Profit (points) input int MinHiddenNeurons = 10; // Minimum Hidden Neurons input int MaxHiddenNeurons = 50; // Maximum Hidden Neurons input int TrainingBarCount = 1000; // Training Bars input double MinPredictionAccuracy = 0.7; // Minimum Prediction Accuracy input double MinLearningRate = 0.01; // Minimum Learning Rate input double MaxLearningRate = 0.5; // Maximum Learning Rate input string InputToHiddenWeights = "0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1"; // Input-to-Hidden Weights input string HiddenToOutputWeights = "0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1"; // Hidden-to-Output Weights input string HiddenBiases = "0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1,0.1,-0.1"; // Hidden Biases input string OutputBiases = "0.1,-0.1"; // Output Biases // Neural Network Structure Constants const int INPUT_NEURON_COUNT = 10; //--- Define number of input neurons const int OUTPUT_NEURON_COUNT = 2; //--- Define number of output neurons const int MAX_HISTORY_SIZE = 10; //--- Define maximum history size for accuracy and error tracking // Indicator handles int ma20IndicatorHandle; //--- Handle for 20-period moving average int ma50IndicatorHandle; //--- Handle for 50-period moving average int rsiIndicatorHandle; //--- Handle for RSI indicator int atrIndicatorHandle; //--- Handle for ATR indicator // Training related structures struct TrainingData { double inputValues[]; //--- Array to store input values for training double targetValues[]; //--- Array to store target values for training };
Here, we lay the groundwork for our neural network-based trading strategy with adaptive learning rates by initializing essential components for trade execution and data processing. We include the "Trade.mqh" library and create the "tradeObject" instance of the "CTrade" class to manage trade operations, enabling the execution of buy and sell orders based on neural network predictions.
We define input parameters to configure the strategy, setting "LotSize" to control trade volume, "StopLossPoints" and "TakeProfitPoints" for risk management, and "MinHiddenNeurons" and "MaxHiddenNeurons" to define the range of hidden neurons in the neural network. Additionally, we specify "TrainingBarCount" for the number of historical bars used in training, "MinPredictionAccuracy" as the accuracy threshold, and "MinLearningRate" and "MaxLearningRate" to bound the adaptive learning rate. We also provide "InputToHiddenWeights", "HiddenToOutputWeights", "HiddenBiases", and "OutputBiases" as string inputs for initializing neural network weights and biases, allowing pre-set or default configurations.
Next, we establish constants for the neural network structure, defining "INPUT_NEURON_COUNT" as 10 for market data inputs, "OUTPUT_NEURON_COUNT" as 2 for buy/sell signal outputs, and "MAX_HISTORY_SIZE" as 10 to track training accuracy and errors. We create indicator handles "ma20IndicatorHandle", "ma50IndicatorHandle", "rsiIndicatorHandle", and "atrIndicatorHandle" to reference 20-period and 50-period moving averages, RSI, and Average True Range indicators, respectively, for feeding market data into the neural network. Finally, we define the "TrainingData" structure with "inputValues" and "targetValues" arrays to store input features and expected outputs for training, ensuring organized data management for the neural network’s learning process. We will store data like this below when we populate it with values.
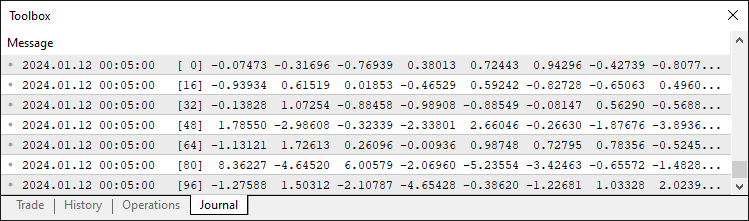
Next, we will need to define a class to hold most of the basic member variables that we will need to use frequently.
// Neural Network Class class CNeuralNetwork { private: int inputNeuronCount; //--- Number of input neurons int hiddenNeuronCount; //--- Number of hidden neurons int outputNeuronCount; //--- Number of output neurons double inputLayer[]; //--- Array for input layer values double hiddenLayer[]; //--- Array for hidden layer values double outputLayer[]; //--- Array for output layer values double inputToHiddenWeights[]; //--- Weights between input and hidden layers double hiddenToOutputWeights[];//--- Weights between hidden and output layers double hiddenLayerBiases[]; //--- Biases for hidden layer double outputLayerBiases[]; //--- Biases for output layer double outputDeltas[]; //--- Delta values for output layer double hiddenDeltas[]; //--- Delta values for hidden layer double trainingError; //--- Current training error double currentLearningRate; //--- Current learning rate double accuracyHistory[]; //--- History of training accuracy double errorHistory[]; //--- History of training errors int historyRecordCount; //--- Number of recorded history entries };
Here, we implement the core structure of our neural network by creating the "CNeuralNetwork" class. We define private member variables to manage the network’s architecture and training process, starting with "inputNeuronCount", "hiddenNeuronCount", and "outputNeuronCount" to set the number of neurons in the input, hidden, and output layers, respectively, aligning with the strategy’s design for processing market data and generating trade signals.
We establish arrays to store layer values, including "inputLayer" for market indicator inputs, "hiddenLayer" for processing intermediate patterns, and "outputLayer" for producing buy/sell predictions. To handle neural network computations, we create "inputToHiddenWeights" and "hiddenToOutputWeights" arrays for weight connections between layers, and "hiddenLayerBiases" and "outputLayerBiases" for bias adjustments in the hidden and output layers. For backpropagation, we define "outputDeltas" and "hiddenDeltas" to store error gradients, enabling weight and bias updates during training.
Additionally, we include "trainingError" to track the current error, "currentLearningRate" to manage the adaptive learning rate, "accuracyHistory" and "errorHistory" arrays to monitor training performance over time, and "historyRecordCount" to count recorded entries, ensuring the network can dynamically adjust its learning process based on performance trends. This class forms the foundation for implementing forward propagation, backpropagation, and adaptive learning rate adjustments in subsequent functions. Within the private access modifier, we can define a method to parse string inputs into an array for usage.
// Parse comma-separated string to array bool ParseStringToArray(string inputString, double &output[], int expectedSize) { //--- Check if input string is empty if(inputString == "") return false; string values[]; //--- Initialize array for parsed values ArrayResize(values, 0); //--- Split input string by comma int count = StringSplit(inputString, 44, values); //--- Check if string splitting failed if(count <= 0) { Print("Error: StringSplit failed for input: ", inputString, ". Error code: ", GetLastError()); return false; } //--- Verify correct number of values if(count != expectedSize) { Print("Error: Invalid number of values in input string. Expected: ", expectedSize, ", Got: ", count); return false; } //--- Resize output array to expected size ArrayResize(output, expectedSize); //--- Convert string values to doubles and normalize for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) { output[i] = StringToDouble(values[i]); //--- Clamp values between -1.0 and 1.0 if(MathAbs(output[i]) > 1.0) output[i] = MathMax(-1.0, MathMin(1.0, output[i])); } return true; }
We implement the "ParseStringToArray" function in the "CNeuralNetwork" class to process comma-separated strings for neural network weights and biases. We check if "inputString" is empty, returning "false" if invalid, and use StringSplit with a comma separator to split it into "values". If splitting fails or "count" mismatches "expectedSize", we log errors with Print and return "false". We resize "output" with ArrayResize, convert "values" to doubles using StringToDouble, normalize them between -1.0 and 1.0 with MathMax and MathMin, and return "true" for successful parsing. The rest of the helper functions can be declared in the public access modifier part as below, and then we can define them later.
public: CNeuralNetwork(int inputs, int hidden, int outputs); //--- Constructor void InitializeWeights(); //--- Initialize network weights double Sigmoid(double x); //--- Apply sigmoid activation function void ForwardPropagate(); //--- Perform forward propagation void Backpropagate(const double &targets[]); //--- Perform backpropagation void SetInput(double &inputs[]); //--- Set input values void GetOutput(double &outputs[]); //--- Retrieve output values double TrainOnHistoricalData(TrainingData &data[]); //--- Train on historical data void UpdateNetworkWithRecentData(); //--- Update with recent data void InitializeTraining(); //--- Initialize training arrays void ResizeNetwork(int newHiddenNeurons); //--- Resize network void AdjustLearningRate(); //--- Adjust learning rate dynamically double GetRecentAccuracy(); //--- Get recent training accuracy double GetRecentError(); //--- Get recent training error bool ShouldRetrain(); //--- Check if retraining is needed double CalculateDynamicNeurons(); //--- Calculate dynamic neuron count int GetHiddenNeurons() { return hiddenNeuronCount; //--- Get current hidden neuron count }
Here, we define the public interface of the "CNeuralNetwork" class. We create the "CNeuralNetwork" constructor with "inputs", "hidden", and "outputs" to set up the network, and "InitializeWeights" to configure weights and biases. We implement "Sigmoid" for activation, "ForwardPropagate" and "Backpropagate" for processing and updating based on "targets", and "SetInput" and "GetOutput" for handling "inputs" and "outputs".
We develop "TrainOnHistoricalData" using "TrainingData", "UpdateNetworkWithRecentData" for recent data, "InitializeTraining" for arrays, "ResizeNetwork" for "newHiddenNeurons", "AdjustLearningRate" for dynamic learning, and "GetRecentAccuracy", "GetRecentError", "ShouldRetrain", "CalculateDynamicNeurons", and "GetHiddenNeurons" for monitoring and adapting "hiddenNeuronCount". We can now begin the implementation and definition of the function as below.
// Constructor CNeuralNetwork::CNeuralNetwork(int inputs, int hidden, int outputs) { //--- Set input neuron count inputNeuronCount = inputs; //--- Set output neuron count outputNeuronCount = outputs; //--- Initialize learning rate to minimum currentLearningRate = MinLearningRate; //--- Set hidden neuron count hiddenNeuronCount = hidden; //--- Ensure hidden neurons within bounds if(hiddenNeuronCount < MinHiddenNeurons) hiddenNeuronCount = MinHiddenNeurons; if(hiddenNeuronCount > MaxHiddenNeurons) hiddenNeuronCount = MaxHiddenNeurons; //--- Resize input layer array ArrayResize(inputLayer, inputs); //--- Resize hidden layer array ArrayResize(hiddenLayer, hiddenNeuronCount); //--- Resize output layer array ArrayResize(outputLayer, outputs); //--- Resize input-to-hidden weights array ArrayResize(inputToHiddenWeights, inputs * hiddenNeuronCount); //--- Resize hidden-to-output weights array ArrayResize(hiddenToOutputWeights, hiddenNeuronCount * outputs); //--- Resize hidden biases array ArrayResize(hiddenLayerBiases, hiddenNeuronCount); //--- Resize output biases array ArrayResize(outputLayerBiases, outputs); //--- Resize accuracy history array ArrayResize(accuracyHistory, MAX_HISTORY_SIZE); //--- Resize error history array ArrayResize(errorHistory, MAX_HISTORY_SIZE); //--- Initialize history record count historyRecordCount = 0; //--- Initialize training error trainingError = 0.0; //--- Initialize network weights InitializeWeights(); //--- Initialize training arrays InitializeTraining(); } // Initialize training arrays void CNeuralNetwork::InitializeTraining() { //--- Resize output deltas array ArrayResize(outputDeltas, outputNeuronCount); //--- Resize hidden deltas array ArrayResize(hiddenDeltas, hiddenNeuronCount); } // Initialize weights void CNeuralNetwork::InitializeWeights() { //--- Track if weights and biases are set bool isInputToHiddenWeightsSet = false; bool isHiddenToOutputWeightsSet = false; bool isHiddenBiasesSet = false; bool isOutputBiasesSet = false; double tempInputToHiddenWeights[]; double tempHiddenToOutputWeights[]; double tempHiddenBiases[]; double tempOutputBiases[]; //--- Parse and set input-to-hidden weights if provided if(InputToHiddenWeights != "" && ParseStringToArray(InputToHiddenWeights, tempInputToHiddenWeights, inputNeuronCount * hiddenNeuronCount)) { //--- Copy parsed weights to main array ArrayCopy(inputToHiddenWeights, tempInputToHiddenWeights); isInputToHiddenWeightsSet = true; //--- Log weight initialization Print("Initialized input-to-hidden weights from input: ", InputToHiddenWeights); } //--- Parse and set hidden-to-output weights if provided if(HiddenToOutputWeights != "" && ParseStringToArray(HiddenToOutputWeights, tempHiddenToOutputWeights, hiddenNeuronCount * outputNeuronCount)) { //--- Copy parsed weights to main array ArrayCopy(hiddenToOutputWeights, tempHiddenToOutputWeights); isHiddenToOutputWeightsSet = true; //--- Log weight initialization Print("Initialized hidden-to-output weights from input: ", HiddenToOutputWeights); } //--- Parse and set hidden biases if provided if(HiddenBiases != "" && ParseStringToArray(HiddenBiases, tempHiddenBiases, hiddenNeuronCount)) { //--- Copy parsed biases to main array ArrayCopy(hiddenLayerBiases, tempHiddenBiases); isHiddenBiasesSet = true; //--- Log bias initialization Print("Initialized hidden biases from input: ", HiddenBiases); } //--- Parse and set output biases if provided if(OutputBiases != "" && ParseStringToArray(OutputBiases, tempOutputBiases, outputNeuronCount)) { //--- Copy parsed biases to main array ArrayCopy(outputLayerBiases, tempOutputBiases); isOutputBiasesSet = true; //--- Log bias initialization Print("Initialized output biases from input: ", OutputBiases); } //--- Initialize input-to-hidden weights randomly if not set if(!isInputToHiddenWeightsSet) { for(int i = 0; i < ArraySize(inputToHiddenWeights); i++) inputToHiddenWeights[i] = (MathRand() / 32767.0) * 2 - 1; } //--- Initialize hidden-to-output weights randomly if not set if(!isHiddenToOutputWeightsSet) { for(int i = 0; i < ArraySize(hiddenToOutputWeights); i++) hiddenToOutputWeights[i] = (MathRand() / 32767.0) * 2 - 1; } //--- Initialize hidden biases randomly if not set if(!isHiddenBiasesSet) { for(int i = 0; i < ArraySize(hiddenLayerBiases); i++) hiddenLayerBiases[i] = (MathRand() / 32767.0) * 2 - 1; } //--- Initialize output biases randomly if not set if(!isOutputBiasesSet) { for(int i = 0; i < ArraySize(outputLayerBiases); i++) outputLayerBiases[i] = (MathRand() / 32767.0) * 2 - 1; } } // Sigmoid activation function double CNeuralNetwork::Sigmoid(double x) { //--- Compute and return sigmoid value return 1.0 / (1.0 + MathExp(-x)); } // Set input void CNeuralNetwork::SetInput(double &inputs[]) { //--- Check for input array size mismatch if(ArraySize(inputs) != inputNeuronCount) { Print("Error: Input array size mismatch. Expected: ", inputNeuronCount, ", Got: ", ArraySize(inputs)); return; } //--- Copy inputs to input layer ArrayCopy(inputLayer, inputs); } // Forward propagation void CNeuralNetwork::ForwardPropagate() { //--- Compute hidden layer values for(int j = 0; j < hiddenNeuronCount; j++) { double sum = 0; //--- Calculate weighted sum for hidden neuron for(int i = 0; i < inputNeuronCount; i++) sum += inputLayer[i] * inputToHiddenWeights[i * hiddenNeuronCount + j]; //--- Apply sigmoid activation hiddenLayer[j] = Sigmoid(sum + hiddenLayerBiases[j]); } //--- Compute output layer values for(int j = 0; j < outputNeuronCount; j++) { double sum = 0; //--- Calculate weighted sum for output neuron for(int i = 0; i < hiddenNeuronCount; i++) sum += hiddenLayer[i] * hiddenToOutputWeights[i * outputNeuronCount + j]; //--- Apply sigmoid activation outputLayer[j] = Sigmoid(sum + outputLayerBiases[j]); } } // Get output void CNeuralNetwork::GetOutput(double &outputs[]) { //--- Resize output array ArrayResize(outputs, outputNeuronCount); //--- Copy output layer to outputs ArrayCopy(outputs, outputLayer); } // Backpropagation void CNeuralNetwork::Backpropagate(const double &targets[]) { //--- Calculate output layer deltas for(int i = 0; i < outputNeuronCount; i++) { double output = outputLayer[i]; //--- Compute delta for output neuron outputDeltas[i] = output * (1 - output) * (targets[i] - output); } //--- Calculate hidden layer deltas for(int i = 0; i < hiddenNeuronCount; i++) { double error = 0; //--- Sum weighted errors from output layer for(int j = 0; j < outputNeuronCount; j++) error += outputDeltas[j] * hiddenToOutputWeights[i * outputNeuronCount + j]; double output = hiddenLayer[i]; //--- Compute delta for hidden neuron hiddenDeltas[i] = output * (1 - output) * error; } //--- Update hidden-to-output weights for(int i = 0; i < hiddenNeuronCount; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < outputNeuronCount; j++) { int idx = i * outputNeuronCount + j; //--- Adjust weight based on learning rate and delta hiddenToOutputWeights[idx] += currentLearningRate * outputDeltas[j] * hiddenLayer[i]; } } //--- Update input-to-hidden weights for(int i = 0; i < inputNeuronCount; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < hiddenNeuronCount; j++) { int idx = i * hiddenNeuronCount + j; //--- Adjust weight based on learning rate and delta inputToHiddenWeights[idx] += currentLearningRate * hiddenDeltas[j] * inputLayer[i]; } } //--- Update hidden biases for(int i = 0; i < hiddenNeuronCount; i++) //--- Adjust bias based on learning rate and delta hiddenLayerBiases[i] += currentLearningRate * hiddenDeltas[i]; //--- Update output biases for(int i = 0; i < outputNeuronCount; i++) //--- Adjust bias based on learning rate and delta outputLayerBiases[i] += currentLearningRate * outputDeltas[i]; } // Resize network (adjust hidden neurons) void CNeuralNetwork::ResizeNetwork(int newHiddenNeurons) { //--- Clamp new neuron count within bounds newHiddenNeurons = MathMax(MinHiddenNeurons, MathMin(newHiddenNeurons, MaxHiddenNeurons)); //--- Check if resizing is necessary if(newHiddenNeurons == hiddenNeuronCount) return; //--- Log resizing information Print("Resizing network. New hidden neurons: ", newHiddenNeurons, ", Previous: ", hiddenNeuronCount); //--- Update hidden neuron count hiddenNeuronCount = newHiddenNeurons; //--- Resize hidden layer array ArrayResize(hiddenLayer, hiddenNeuronCount); //--- Resize input-to-hidden weights array ArrayResize(inputToHiddenWeights, inputNeuronCount * hiddenNeuronCount); //--- Resize hidden-to-output weights array ArrayResize(hiddenToOutputWeights, hiddenNeuronCount * outputNeuronCount); //--- Resize hidden biases array ArrayResize(hiddenLayerBiases, hiddenNeuronCount); //--- Resize hidden deltas array ArrayResize(hiddenDeltas, hiddenNeuronCount); //--- Reinitialize weights InitializeWeights(); }
Here, we implement critical components of the neural network. We create the "CNeuralNetwork" constructor, taking "inputs", "hidden", and "outputs" to set "inputNeuronCount", "outputNeuronCount", and "hiddenNeuronCount", clamping the latter between "MinHiddenNeurons" and "MaxHiddenNeurons". We don't need to actually spend much time explaining the class prototype as we had already done a similar thing from the previous part.
We then initialize "currentLearningRate" to "MinLearningRate", resize arrays like "inputLayer", "hiddenLayer", "outputLayer", "inputToHiddenWeights", "hiddenToOutputWeights", "hiddenLayerBiases", "outputLayerBiases", "accuracyHistory", and "errorHistory" using ArrayResize, and call "InitializeWeights" and "InitializeTraining" to set up the network.
We develop the "InitializeTraining" function to resize "outputDeltas" and "hiddenDeltas" arrays for backpropagation, ensuring proper error gradient storage. The "InitializeWeights" function sets up weights and biases, using "ParseStringToArray" to load "inputToHiddenWeights", "hiddenToOutputWeights", "hiddenLayerBiases", and "outputLayerBiases" from inputs like "InputToHiddenWeights" if provided, or randomizes them with MathRand between -1 and 1 if not, logging actions with "Print". We implement the "Sigmoid" function to compute the sigmoid activation value for a given "x" using the MathExp function.
The "SetInput" function copies "inputs" to "inputLayer" after verifying size with ArraySize, logging errors with "Print" if mismatched. We create the "ForwardPropagate" function to compute "hiddenLayer" and "outputLayer" values by applying weighted sums and "Sigmoid" activation with "hiddenLayerBiases" and "outputLayerBiases". The "GetOutput" function resizes "outputs" with "ArrayResize" and copies "outputLayer" values using ArrayCopy.
We implement the "Backpropagate" function to calculate "outputDeltas" and "hiddenDeltas" from "targets", updating "hiddenToOutputWeights", "inputToHiddenWeights", "hiddenLayerBiases", and "outputLayerBiases" using "currentLearningRate". Finally, the "ResizeNetwork" function adjusts "hiddenNeuronCount" within bounds, resizes arrays like "hiddenLayer" and "hiddenDeltas", and reinitializes weights with "InitializeWeights", logging changes with "Print". We need to then adjust the learning rate based on the error trend so let us take a deeper look at it carefully.
// Adjust learning rate based on error trend void CNeuralNetwork::AdjustLearningRate() { //--- Check if enough history exists if(historyRecordCount < 2) return; //--- Get last and previous errors double lastError = errorHistory[historyRecordCount - 1]; double prevError = errorHistory[historyRecordCount - 2]; //--- Calculate error difference double errorDiff = lastError - prevError; //--- Increase learning rate if error decreased if(lastError < prevError) currentLearningRate = MathMin(currentLearningRate * 1.05, MaxLearningRate); //--- Decrease learning rate if error increased significantly else if(lastError > prevError * 1.2) currentLearningRate = MathMax(currentLearningRate * 0.9, MinLearningRate); //--- Slightly decrease learning rate otherwise else currentLearningRate = MathMax(currentLearningRate * 0.99, MinLearningRate); //--- Log learning rate adjustment Print("Adjusted learning rate to: ", currentLearningRate, ", Last Error: ", lastError, ", Prev Error: ", prevError, ", Error Diff: ", errorDiff); }
We implement the adaptive learning rate mechanism by creating the "AdjustLearningRate" function within the "CNeuralNetwork" class. We check if "historyRecordCount" is at least 2 to ensure sufficient data in the "errorHistory" array, exiting if not to avoid invalid adjustments. We retrieve the latest error as "lastError" and the previous error as "prevError" from "errorHistory", then calculate their difference in "errorDiff" to assess training performance.
We use the MathMin function to increase "currentLearningRate" by 5% if "lastError" is less than "prevError", capping it at "MaxLearningRate", or use the MathMax function to decrease it by 10% if "lastError" exceeds "prevError" by 20%, ensuring it stays above "MinLearningRate". Otherwise, we slightly reduce "currentLearningRate" by 1% using "MathMax". Finally, we use the "Print" function to log the adjusted "currentLearningRate", "lastError", "prevError", and "errorDiff", enabling dynamic optimization of the neural network’s learning process. We then use the ATR indicator to dynamically calculate the number of hidden neurons so we can adjust based on volatility.
// Calculate dynamic number of hidden neurons based on ATR double CNeuralNetwork::CalculateDynamicNeurons() { double atrValues[]; //--- Set ATR array as series ArraySetAsSeries(atrValues, true); //--- Copy ATR buffer if(CopyBuffer(atrIndicatorHandle, 0, 0, 10, atrValues) < 10) { Print("Error: Failed to copy ATR for dynamic neurons. Using default: ", hiddenNeuronCount); return hiddenNeuronCount; } //--- Calculate average ATR double avgATR = 0; for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) avgATR += atrValues[i]; avgATR /= 10; //--- Get current close price double closePrice = iClose(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 0); //--- Check for valid close price if(MathAbs(closePrice) < 0.000001) { Print("Error: Invalid close price for ATR ratio. Using default: ", hiddenNeuronCount); return hiddenNeuronCount; } //--- Calculate ATR ratio double atrRatio = atrValues[0] / closePrice; //--- Compute new neuron count int newNeurons = MinHiddenNeurons + (int)((MaxHiddenNeurons - MinHiddenNeurons) * MathMin(atrRatio * 100, 1.0)); //--- Return clamped neuron count return MathMax(MinHiddenNeurons, MathMin(newNeurons, MaxHiddenNeurons)); }
To dynamically adjust the number of hidden neurons based on market volatility, we declare the "atrValues" array and use the ArraySetAsSeries function to configure it as a time-series array, then employ the CopyBuffer function to retrieve 10 bars of Average True Range data from "atrIndicatorHandle" into "atrValues". If "CopyBuffer" retrieves fewer than 10 values, we use the "Print" function to log an error and return "hiddenNeuronCount" as the default. We deeply need to set the array as a time series so that the newest data retrieved can be mapped in the initial indices and be used being the first. Here is a representation.
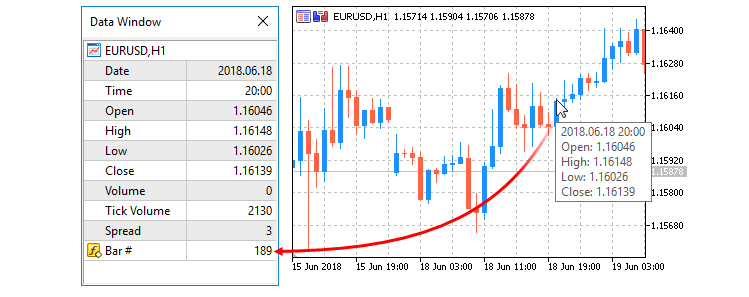
We calculate the average ATR by summing "atrValues" over 10 bars and dividing by 10, storing the result in "avgATR". We use the iClose function to obtain the current close price in "closePrice" for the _Symbol and "PERIOD_CURRENT". If "closePrice" is near zero, we use the "Print" function to log an error and return "hiddenNeuronCount". We compute the ATR ratio as "atrValues[0]" divided by "closePrice", then calculate "newNeurons" by scaling the range between "MinHiddenNeurons" and "MaxHiddenNeurons" using the MathMin function on the scaled "atrRatio". Finally, we use the MathMax and "MathMin" functions to clamp and return the adjusted neuron count, ensuring dynamic adaptation to market conditions. We can now define the rest of the training and update functions as below.
// Train network on historical data double CNeuralNetwork::TrainOnHistoricalData(TrainingData &data[]) { const int maxEpochs = 100; //--- Maximum training epochs const double targetError = 0.01; //--- Target error threshold double accuracy = 0; //--- Training accuracy //--- Reset learning rate currentLearningRate = MinLearningRate; //--- Iterate through epochs for(int epoch = 0; epoch < maxEpochs; epoch++) { double totalError = 0; //--- Total error for epoch int correctPredictions = 0; //--- Count of correct predictions //--- Process each training sample for(int i = 0; i < ArraySize(data); i++) { //--- Check target array size if(ArraySize(data[i].targetValues) != outputNeuronCount) { Print("Error: Mismatch in targets size for training data at index ", i); continue; } //--- Set input values SetInput(data[i].inputValues); //--- Perform forward propagation ForwardPropagate(); double error = 0; //--- Calculate error for(int j = 0; j < outputNeuronCount; j++) error += MathPow(data[i].targetValues[j] - outputLayer[j], 2); totalError += error; //--- Check prediction correctness if((outputLayer[0] > outputLayer[1] && data[i].targetValues[0] > data[i].targetValues[1]) || (outputLayer[0] < outputLayer[1] && data[i].targetValues[0] < data[i].targetValues[1])) correctPredictions++; //--- Perform backpropagation Backpropagate(data[i].targetValues); } //--- Calculate accuracy accuracy = (double)correctPredictions / ArraySize(data); //--- Update training error trainingError = totalError / ArraySize(data); //--- Update history if(historyRecordCount < MAX_HISTORY_SIZE) { accuracyHistory[historyRecordCount] = accuracy; errorHistory[historyRecordCount] = trainingError; historyRecordCount++; } else { //--- Shift history arrays for(int i = 1; i < MAX_HISTORY_SIZE; i++) { accuracyHistory[i - 1] = accuracyHistory[i]; errorHistory[i - 1] = errorHistory[i]; } //--- Add new values accuracyHistory[MAX_HISTORY_SIZE - 1] = accuracy; errorHistory[MAX_HISTORY_SIZE - 1] = trainingError; } //--- Log error history update Print("Error history updated: ", errorHistory[historyRecordCount - 1]); //--- Adjust learning rate AdjustLearningRate(); //--- Log progress every 10 epochs if(epoch % 10 == 0) Print("Epoch ", epoch, ": Error = ", trainingError, ", Accuracy = ", accuracy); //--- Check for early stopping if(trainingError < targetError && accuracy >= MinPredictionAccuracy) break; } //--- Return final accuracy return accuracy; } // Update network with recent data void CNeuralNetwork::UpdateNetworkWithRecentData() { const int recentBarCount = 10; //--- Number of recent bars to process TrainingData recentData[]; //--- Collect recent training data if(!CollectTrainingData(recentData, recentBarCount)) return; //--- Process each recent data sample for(int i = 0; i < ArraySize(recentData); i++) { //--- Set input values SetInput(recentData[i].inputValues); //--- Perform forward propagation ForwardPropagate(); //--- Perform backpropagation Backpropagate(recentData[i].targetValues); } } // Get recent accuracy double CNeuralNetwork::GetRecentAccuracy() { //--- Check if history exists if(historyRecordCount == 0) return 0.0; //--- Return most recent accuracy return accuracyHistory[historyRecordCount - 1]; } // Get recent error double CNeuralNetwork::GetRecentError() { //--- Check if history exists if(historyRecordCount == 0) return 0.0; //--- Return most recent error return errorHistory[historyRecordCount - 1]; } // Check if retraining is needed bool CNeuralNetwork::ShouldRetrain() { //--- Check if enough history exists if(historyRecordCount < 2) return false; //--- Get recent metrics double recentAccuracy = GetRecentAccuracy(); double recentError = GetRecentError(); double prevError = errorHistory[historyRecordCount - 2]; //--- Determine if retraining is needed return (recentAccuracy < MinPredictionAccuracy || recentError > prevError * 1.5); }
Here, we implement key training and updating mechanisms for the neural network. We create the "TrainOnHistoricalData" function to train the network using the "TrainingData" structure array, setting "maxEpochs" to 100 and "targetError" to 0.01, and resetting "currentLearningRate" to "MinLearningRate". For each epoch, we iterate through "data", verify "data[i].targetValues" size against "outputNeuronCount", and use the "SetInput" function to load "data[i].inputValues", followed by the "ForwardPropagate" function to compute predictions. We calculate the error using MathPow for "outputLayer" versus "data[i].targetValues", track "correctPredictions", and apply the "Backpropagate" function with "data[i].targetValues".
We update "accuracy" and "trainingError", store them in "accuracyHistory" and "errorHistory" using "historyRecordCount", shift arrays if full, log updates with the "Print" function, and use the "AdjustLearningRate" function to optimize learning, stopping early if "trainingError" and "accuracy" meet "targetError" and "MinPredictionAccuracy".
We develop the "UpdateNetworkWithRecentData" function to refine the network with "recentBarCount" set to 10, using the "CollectTrainingData" function to populate "recentData" and iterating to apply "SetInput", "ForwardPropagate", and "Backpropagate" for each sample. The "GetRecentAccuracy" function returns the latest "accuracyHistory" value or 0.0 if "historyRecordCount" is zero, and the "GetRecentError" function does the same for "errorHistory".
We create the "ShouldRetrain" function to check if "historyRecordCount" is at least 2, using "GetRecentAccuracy" and "GetRecentError" to compare "recentAccuracy" and "recentError" against "MinPredictionAccuracy" and 1.5 times the previous "errorHistory" value, returning true if retraining is needed. We can now create an instance of the class that we will use for the actual implementation.
// Global neural network instance CNeuralNetwork *neuralNetwork; //--- Global neural network object
We establish the global scope for the neural network by creating the "neuralNetwork" pointer to an instance of the "CNeuralNetwork" class. This global object will enable centralized access to the neural network’s functionality, including training, forward propagation, backpropagation, and adaptive learning rate adjustments, ensuring seamless integration across the Expert Advisor’s operations.
By defining "neuralNetwork" globally, we facilitate its use in initialization, tick processing, and deinitialization functions to manage the strategy’s predictive and trading capabilities. We can define functions to initialize the inputs and collect training data for modularity.
// Prepare inputs from market data void PrepareInputs(double &inputs[]) { //--- Resize inputs array if necessary if(ArraySize(inputs) != INPUT_NEURON_COUNT) ArrayResize(inputs, INPUT_NEURON_COUNT); double ma20Values[], ma50Values[], rsiValues[], atrValues[]; //--- Set arrays as series ArraySetAsSeries(ma20Values, true); ArraySetAsSeries(ma50Values, true); ArraySetAsSeries(rsiValues, true); ArraySetAsSeries(atrValues, true); //--- Copy MA20 buffer if(CopyBuffer(ma20IndicatorHandle, 0, 0, 2, ma20Values) <= 0) { Print("Error: Failed to copy MA20 buffer. Error code: ", GetLastError()); return; } //--- Copy MA50 buffer if(CopyBuffer(ma50IndicatorHandle, 0, 0, 2, ma50Values) <= 0) { Print("Error: Failed to copy MA50 buffer. Error code: ", GetLastError()); return; } //--- Copy RSI buffer if(CopyBuffer(rsiIndicatorHandle, 0, 0, 2, rsiValues) <= 0) { Print("Error: Failed to copy RSI buffer. Error code: ", GetLastError()); return; } //--- Copy ATR buffer if(CopyBuffer(atrIndicatorHandle, 0, 0, 2, atrValues) <= 0) { Print("Error: Failed to copy ATR buffer. Error code: ", GetLastError()); return; } //--- Check array sizes if(ArraySize(ma20Values) < 2 || ArraySize(ma50Values) < 2 || ArraySize(rsiValues) < 2 || ArraySize(atrValues) < 2) { Print("Error: Insufficient data in indicator arrays"); return; } //--- Get current market prices double closePrice = iClose(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 0); double openPrice = iOpen(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 0); double highPrice = iHigh(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 0); double lowPrice = iLow(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 0); //--- Calculate input features inputs[0] = (MathAbs(openPrice) > 0.000001) ? (closePrice - openPrice) / openPrice : 0; inputs[1] = (MathAbs(lowPrice) > 0.000001) ? (highPrice - lowPrice) / lowPrice : 0; inputs[2] = (MathAbs(ma20Values[0]) > 0.000001) ? (closePrice - ma20Values[0]) / ma20Values[0] : 0; inputs[3] = (MathAbs(ma50Values[0]) > 0.000001) ? (ma20Values[0] - ma50Values[0]) / ma50Values[0] : 0; inputs[4] = rsiValues[0] / 100.0; double highLowRange = highPrice - lowPrice; if(MathAbs(highLowRange) > 0.000001) { inputs[5] = (closePrice - lowPrice) / highLowRange; inputs[7] = MathAbs(closePrice - openPrice) / highLowRange; inputs[8] = (highPrice - closePrice) / highLowRange; inputs[9] = (closePrice - lowPrice) / highLowRange; } else { inputs[5] = 0; inputs[7] = 0; inputs[8] = 0; inputs[9] = 0; } inputs[6] = (MathAbs(closePrice) > 0.000001) ? atrValues[0] / closePrice : 0; //--- Log input preparation Print("Prepared inputs. Size: ", ArraySize(inputs)); } // Collect training data bool CollectTrainingData(TrainingData &data[], int barCount) { //--- Check output neuron count if(OUTPUT_NEURON_COUNT != 2) { Print("Error: OUTPUT_NEURON_COUNT must be 2 for binary classification."); return false; } //--- Resize data array ArrayResize(data, barCount); double ma20Values[], ma50Values[], rsiValues[], atrValues[]; //--- Set arrays as series ArraySetAsSeries(ma20Values, true); ArraySetAsSeries(ma50Values, true); ArraySetAsSeries(rsiValues, true); ArraySetAsSeries(atrValues, true); //--- Copy MA20 buffer if(CopyBuffer(ma20IndicatorHandle, 0, 0, barCount + 1, ma20Values) < barCount + 1) { Print("Error: Failed to copy MA20 buffer for training. Error code: ", GetLastError()); return false; } //--- Copy MA50 buffer if(CopyBuffer(ma50IndicatorHandle, 0, 0, barCount + 1, ma50Values) < barCount + 1) { Print("Error: Failed to copy MA50 buffer for training. Error code: ", GetLastError()); return false; } //--- Copy RSI buffer if(CopyBuffer(rsiIndicatorHandle, 0, 0, barCount + 1, rsiValues) < barCount + 1) { Print("Error: Failed to copy RSI buffer for training. Error code: ", GetLastError()); return false; } //--- Copy ATR buffer if(CopyBuffer(atrIndicatorHandle, 0, 0, barCount + 1, atrValues) < barCount + 1) { Print("Error: Failed to copy ATR buffer for training. Error code: ", GetLastError()); return false; } MqlRates priceData[]; //--- Set rates array as series ArraySetAsSeries(priceData, true); //--- Copy price data if(CopyRates(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 0, barCount + 1, priceData) < barCount + 1) { Print("Error: Failed to copy rates for training. Error code: ", GetLastError()); return false; } //--- Process each bar for(int i = 0; i < barCount; i++) { //--- Resize input and target arrays ArrayResize(data[i].inputValues, INPUT_NEURON_COUNT); ArrayResize(data[i].targetValues, OUTPUT_NEURON_COUNT); //--- Get price data double closePrice = priceData[i].close; double openPrice = priceData[i].open; double highPrice = priceData[i].high; double lowPrice = priceData[i].low; double highLowRange = highPrice - lowPrice; //--- Calculate input features data[i].inputValues[0] = (MathAbs(openPrice) > 0.000001) ? (closePrice - openPrice) / openPrice : 0; data[i].inputValues[1] = (MathAbs(lowPrice) > 0.000001) ? (highPrice - lowPrice) / lowPrice : 0; data[i].inputValues[2] = (MathAbs(ma20Values[i]) > 0.000001) ? (closePrice - ma20Values[i]) / ma20Values[i] : 0; data[i].inputValues[3] = (MathAbs(ma50Values[i]) > 0.000001) ? (ma20Values[i] - ma50Values[i]) / ma50Values[i] : 0; data[i].inputValues[4] = rsiValues[i] / 100.0; if(MathAbs(highLowRange) > 0.000001) { data[i].inputValues[5] = (closePrice - lowPrice) / highLowRange; data[i].inputValues[7] = MathAbs(closePrice - openPrice) / highLowRange; data[i].inputValues[8] = (highPrice - closePrice) / highLowRange; data[i].inputValues[9] = (closePrice - lowPrice) / highLowRange; } data[i].inputValues[6] = (MathAbs(closePrice) > 0.000001) ? atrValues[i] / closePrice : 0; //--- Set target values based on price movement if(i < barCount - 1) { double futureClose = priceData[i + 1].close; double priceChange = futureClose - closePrice; if(priceChange > 0) { data[i].targetValues[0] = 1; data[i].targetValues[1] = 0; } else { data[i].targetValues[0] = 0; data[i].targetValues[1] = 1; } } else { data[i].targetValues[0] = 0; data[i].targetValues[1] = 0; } } //--- Return success return true; }
Here, we implement data preparation by creating the "PrepareInputs" function to generate input features for the neural network. We use the ArrayResize function to ensure the "inputs" array matches "INPUT_NEURON_COUNT", then declare arrays "ma20Values", "ma50Values", "rsiValues", and "atrValues", setting them as time-series with the ArraySetAsSeries function. We use the CopyBuffer function to retrieve two bars of data from "ma20IndicatorHandle", "ma50IndicatorHandle", "rsiIndicatorHandle", and "atrIndicatorHandle", logging errors with the "Print" function and exit if any fail.
We verify array sizes with ArraySize, logging errors with "Print" if insufficient, and use iClose, "iOpen", "iHigh", and "iLow" to fetch current prices into "closePrice", "openPrice", "highPrice", and "lowPrice" for _Symbol and PERIOD_CURRENT. We calculate input features for "inputs", including normalized price differences, moving average deviations, RSI scaled to 0-1, and ATR relative to "closePrice", handling zero-division with MathAbs checks, and compute range-based features for "highLowRange". We log success with "Print" and "ArraySize".
Additionally, we create the "CollectTrainingData" function to prepare training data in the "TrainingData" structure array for "barCount" bars. We verify "OUTPUT_NEURON_COUNT" is 2, use "ArrayResize" to size "data", and use "CopyBuffer" to fetch data from indicator handles and "CopyRates" for price data in "priceData", logging errors with "Print" if any fail. For each bar, we use "ArrayResize" to set "data[i].inputValues" and "data[i].targetValues", compute input features similarly to "PrepareInputs", and set target values in "data[i].targetValues" based on price movement in "priceData", returning "true" on success. We then need to train the network based on the received data.
// Train the neural network bool TrainNetwork() { //--- Log training start Print("Starting neural network training..."); TrainingData trainingData[]; //--- Collect training data if(!CollectTrainingData(trainingData, TrainingBarCount)) { Print("Failed to collect training data"); return false; } //--- Train network double accuracy = neuralNetwork.TrainOnHistoricalData(trainingData); //--- Log training completion Print("Training completed. Final accuracy: ", accuracy); //--- Return training success return (accuracy >= MinPredictionAccuracy); }
We create the "TrainNetwork" function and use the "Print" function to log the start of training, then declare the "trainingData" array of the "TrainingData" structure to store input and target values. We call the "CollectTrainingData" function to populate "trainingData" with "TrainingBarCount" bars, logging an error with "Print" and returning "false" if data collection fails.
We use the "TrainOnHistoricalData" function of the "neuralNetwork" object to train the network, storing the result in "accuracy", log completion with "Print" including "accuracy", and return "true" if "accuracy" meets or exceeds "MinPredictionAccuracy", ensuring the network is adequately trained for trading. Finally, we can create a function to validate the trading signals as below.
// Validate Stop Loss and Take Profit levels bool CheckStopLossTakeprofit(ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, double price, double stopLoss, double takeProfit) { //--- Get minimum stop level double stopLevel = SymbolInfoInteger(_Symbol, SYMBOL_TRADE_STOPS_LEVEL) * _Point; //--- Validate buy order if(orderType == ORDER_TYPE_BUY) { //--- Check stop loss distance if(MathAbs(price - stopLoss) < stopLevel) { Print("Buy Stop Loss too close. Minimum distance: ", stopLevel); return false; } //--- Check take profit distance if(MathAbs(takeProfit - price) < stopLevel) { Print("Buy Take Profit too close. Minimum distance: ", stopLevel); return false; } } //--- Validate sell order else if(orderType == ORDER_TYPE_SELL) { //--- Check stop loss distance if(MathAbs(stopLoss - price) < stopLevel) { Print("Sell Stop Loss too close. Minimum distance: ", stopLevel); return false; } //--- Check take profit distance if(MathAbs(price - takeProfit) < stopLevel) { Print("Sell Take Profit too close. Minimum distance: ", stopLevel); return false; } } //--- Return validation success return true; }
Here, we just create a boolean function to validate the trading points to avoid potential errors with broker restrictions. We can now initialize the program on the OnInit event handler, technically initializing the indicators and instances of the neural class to do the heavy lifting as below.
// Expert initialization function int OnInit() { //--- Initialize 20-period MA indicator ma20IndicatorHandle = iMA(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 20, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE); //--- Initialize 50-period MA indicator ma50IndicatorHandle = iMA(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 50, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE); //--- Initialize RSI indicator rsiIndicatorHandle = iRSI(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 14, PRICE_CLOSE); //--- Initialize ATR indicator atrIndicatorHandle = iATR(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 14); //--- Check MA20 handle if(ma20IndicatorHandle == INVALID_HANDLE) Print("Error: Failed to initialize MA20 handle. Error code: ", GetLastError()); //--- Check MA50 handle if(ma50IndicatorHandle == INVALID_HANDLE) Print("Error: Failed to initialize MA50 handle. Error code: ", GetLastError()); //--- Check RSI handle if(rsiIndicatorHandle == INVALID_HANDLE) Print("Error: Failed to initialize RSI handle. Error code: ", GetLastError()); //--- Check ATR handle if(atrIndicatorHandle == INVALID_HANDLE) Print("Error: Failed to initialize ATR handle. Error code: ", GetLastError()); //--- Check for any invalid handles if(ma20IndicatorHandle == INVALID_HANDLE || ma50IndicatorHandle == INVALID_HANDLE || rsiIndicatorHandle == INVALID_HANDLE || atrIndicatorHandle == INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("Error initializing indicators"); return INIT_FAILED; } //--- Create neural network instance neuralNetwork = new CNeuralNetwork(INPUT_NEURON_COUNT, MinHiddenNeurons, OUTPUT_NEURON_COUNT); //--- Check neural network creation if(neuralNetwork == NULL) { Print("Failed to create neural network"); return INIT_FAILED; } //--- Log initialization Print("Initializing neural network..."); //--- Return success return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
We implement the initialization logic within the OnInit function. We use the iMA function to initialize "ma20IndicatorHandle" and "ma50IndicatorHandle" for 20-period and 50-period simple moving averages on "_Symbol" and PERIOD_CURRENT with "PRICE_CLOSE", and the "iRSI" and iATR function to set "rsiIndicatorHandle" and "atrIndicatorHandle" for 14-period RSI and ATR indicators. We check each handle against "INVALID_HANDLE", logging errors with the "Print" function and "GetLastError" if any fail, and return INIT_FAILED if any indicator initialization fails.
We create a new instance of the "CNeuralNetwork" class for "neuralNetwork" using "INPUT_NEURON_COUNT", "MinHiddenNeurons", and "OUTPUT_NEURON_COUNT" to set up the network structure. If "neuralNetwork" is "NULL", we use the "Print" function to log the failure and return "INIT_FAILED". Finally, we log successful initialization with "Print" and return INIT_SUCCEEDED, ensuring the Expert Advisor is properly set up for trading. Upon running the program, we have the following output.
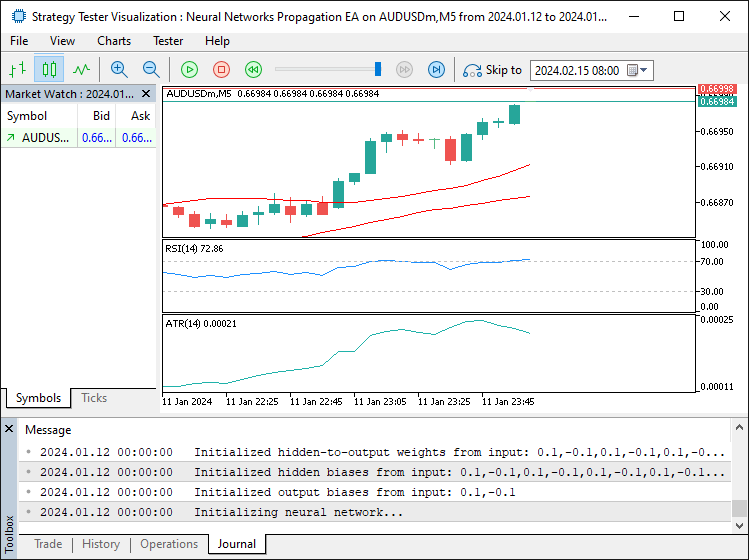
From the image, we can see that we initialized the program with success. Now since we have created an instance of the neural network, we need to delete it once we remove the program. Here is the logic we use to achieve that.
// Expert deinitialization function void OnDeinit(const int reason) { //--- Release MA20 indicator handle if(ma20IndicatorHandle != INVALID_HANDLE) IndicatorRelease(ma20IndicatorHandle); //--- Release MA50 indicator handle if(ma50IndicatorHandle != INVALID_HANDLE) IndicatorRelease(ma50IndicatorHandle); //--- Release RSI indicator handle if(rsiIndicatorHandle != INVALID_HANDLE) IndicatorRelease(rsiIndicatorHandle); //--- Release ATR indicator handle if(atrIndicatorHandle != INVALID_HANDLE) IndicatorRelease(atrIndicatorHandle); //--- Delete neural network instance if(neuralNetwork != NULL) delete neuralNetwork; //--- Log deinitialization Print("Expert Advisor deinitialized - ", EnumToString((ENUM_INIT_RETCODE)reason)); }
We implement the cleanup process within the OnDeinit function where we use the IndicatorRelease function to free resources for "ma20IndicatorHandle", "ma50IndicatorHandle", "rsiIndicatorHandle", and "atrIndicatorHandle" if each is not "INVALID_HANDLE", ensuring the proper release of moving average, RSI, and ATR indicator handles. We check if "neuralNetwork" is not "NULL" and use the "delete" operator to deallocate the "CNeuralNetwork" class instance, cleaning up the neural network. Finally, we use the "Print" function with EnumToString to log the deinitialization reason, confirming the Expert Advisor’s resources are properly released. Failure to delete the class instance will lead to memory leaks as seen below.
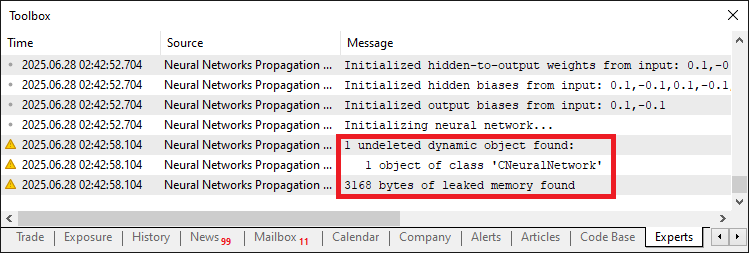
Once the memory leak issue is taken care of, we can implement the main data acquisition, training, and usage within the OnTick event handler.
// Expert tick function void OnTick() { static datetime lastBarTime = 0; //--- Track last processed bar time //--- Get current bar time datetime currentBarTime = iTime(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 0); //--- Skip if same bar if(lastBarTime == currentBarTime) return; //--- Update last bar time lastBarTime = currentBarTime; //--- Calculate dynamic neuron count int newNeuronCount = (int)neuralNetwork.CalculateDynamicNeurons(); //--- Resize network if necessary if(newNeuronCount != neuralNetwork.GetHiddenNeurons()) neuralNetwork.ResizeNetwork(newNeuronCount); //--- Check if retraining is needed if(TimeCurrent() - iTime(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, TrainingBarCount) >= 12 * 3600 || neuralNetwork.ShouldRetrain()) { //--- Log training start Print("Starting network training..."); //--- Train network if(!TrainNetwork()) { Print("Training failed or insufficient accuracy"); return; } } //--- Update network with recent data neuralNetwork.UpdateNetworkWithRecentData(); //--- Check for open positions if(PositionsTotal() > 0) { //--- Iterate through positions for(int i = PositionsTotal() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { //--- Skip if position is for current symbol if(PositionGetSymbol(i) == _Symbol) return; } } //--- Prepare input data double currentInputs[]; ArrayResize(currentInputs, INPUT_NEURON_COUNT); PrepareInputs(currentInputs); //--- Verify input array size if(ArraySize(currentInputs) != INPUT_NEURON_COUNT) { Print("Error: Inputs array not properly initialized. Size: ", ArraySize(currentInputs)); return; } //--- Set network inputs neuralNetwork.SetInput(currentInputs); //--- Perform forward propagation neuralNetwork.ForwardPropagate(); double outputValues[]; //--- Resize output array ArrayResize(outputValues, OUTPUT_NEURON_COUNT); //--- Get network outputs neuralNetwork.GetOutput(outputValues); //--- Verify output array size if(ArraySize(outputValues) != OUTPUT_NEURON_COUNT) { Print("Error: Outputs array not properly initialized. Size: ", ArraySize(outputValues)); return; } //--- Get market prices double askPrice = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_ASK); double bidPrice = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_BID); //--- Calculate stop loss and take profit levels double buyStopLoss = NormalizeDouble(askPrice - StopLossPoints * _Point, _Digits); double buyTakeProfit = NormalizeDouble(askPrice + TakeProfitPoints * _Point, _Digits); double sellStopLoss = NormalizeDouble(bidPrice + StopLossPoints * _Point, _Digits); double sellTakeProfit = NormalizeDouble(bidPrice - TakeProfitPoints * _Point, _Digits); //--- Validate stop loss and take profit if(!CheckStopLossTakeprofit(ORDER_TYPE_BUY, askPrice, buyStopLoss, buyTakeProfit) || !CheckStopLossTakeprofit(ORDER_TYPE_SELL, bidPrice, sellStopLoss, sellTakeProfit)) { return; } // Trading logic const double CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD = 0.8; //--- Confidence threshold for trading //--- Check for buy signal if(outputValues[0] > CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD && outputValues[1] < (1 - CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD)) { //--- Set trade magic number tradeObject.SetExpertMagicNumber(123456); //--- Place buy order if(tradeObject.Buy(LotSize, _Symbol, askPrice, buyStopLoss, buyTakeProfit, "Neural Buy")) { //--- Log successful buy order Print("Buy order placed - Signal Strength: ", outputValues[0]); } else { //--- Log buy order failure Print("Buy order failed. Error: ", GetLastError()); } } //--- Check for sell signal else if(outputValues[0] < (1 - CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD) && outputValues[1] > CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD) { //--- Set trade magic number tradeObject.SetExpertMagicNumber(123456); //--- Place sell order if(tradeObject.Sell(LotSize, _Symbol, bidPrice, sellStopLoss, sellTakeProfit, "Neural Sell")) { //--- Log successful sell order Print("Sell order placed - Signal Strength: ", outputValues[1]); } else { //--- Log sell order failure Print("Sell order failed. Error: ", GetLastError()); } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Here, we implement the core trading logic for the neural network strategy within the OnTick function. We declare "lastBarTime" to track the last processed bar and use the iTime function to get "currentBarTime" for "_Symbol" and PERIOD_CURRENT, exiting if unchanged to process new bars only. We update "lastBarTime" and use the "CalculateDynamicNeurons" function to compute "newNeuronCount", calling the "ResizeNetwork" function if it differs from the result of the "GetHiddenNeurons" function to adjust the network.
We check if retraining is needed by comparing TimeCurrent minus "iTime" for "TrainingBarCount" against 12 hours or using the "ShouldRetrain" function, then use the "TrainNetwork" function to retrain, exiting if it fails. We call the "UpdateNetworkWithRecentData" function to refine the network. If PositionsTotal indicates open positions, we use the "PositionGetSymbol" function to skip trading if any are for _Symbol. We declare "currentInputs", resize it with "ArrayResize" to "INPUT_NEURON_COUNT", and use the "PrepareInputs" function to populate it, verifying size with ArraySize and logging errors with "Print".
We use the "SetInput" function to load "currentInputs", call the "ForwardPropagate" function to generate predictions, and use the "GetOutput" function to retrieve "outputValues" after resizing with "ArrayResize" to "OUTPUT_NEURON_COUNT", logging errors with "Print" if invalid. We fetch "askPrice" and "bidPrice" with SymbolInfoDouble, calculate "buyStopLoss", "buyTakeProfit", "sellStopLoss", and "sellTakeProfit" using NormalizeDouble with "StopLossPoints", "TakeProfitPoints", "_Point", and "_Digits", and validate them with the "CheckStopLossTakeprofit" function.
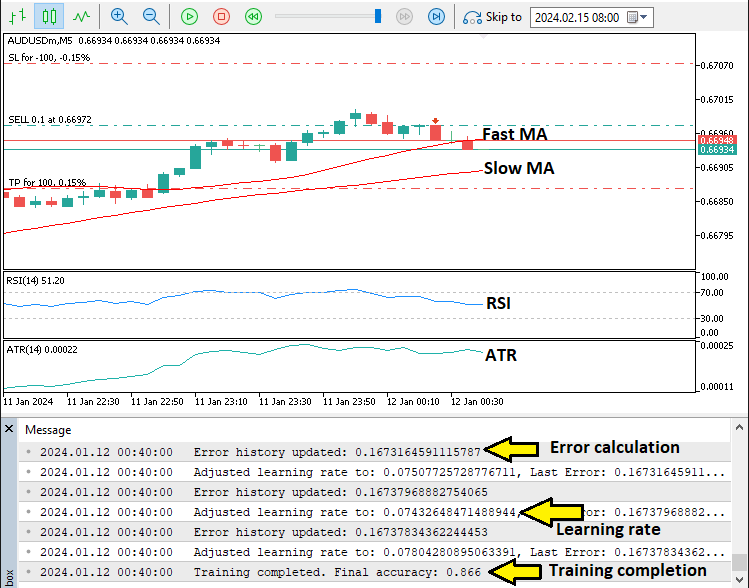
For trading, we set "CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD" to 0.8; if "outputValues[0]" exceeds it and "outputValues[1]" is below its complement, we use the "tradeObject.Buy" function after setting the magic number with "SetExpertMagicNumber", logging success or failure with "Print" and "GetLastError". Similarly, we use the "tradeObject.Sell" function for sell signals, ensuring robust trade execution. Upon compilation, we have the following output.
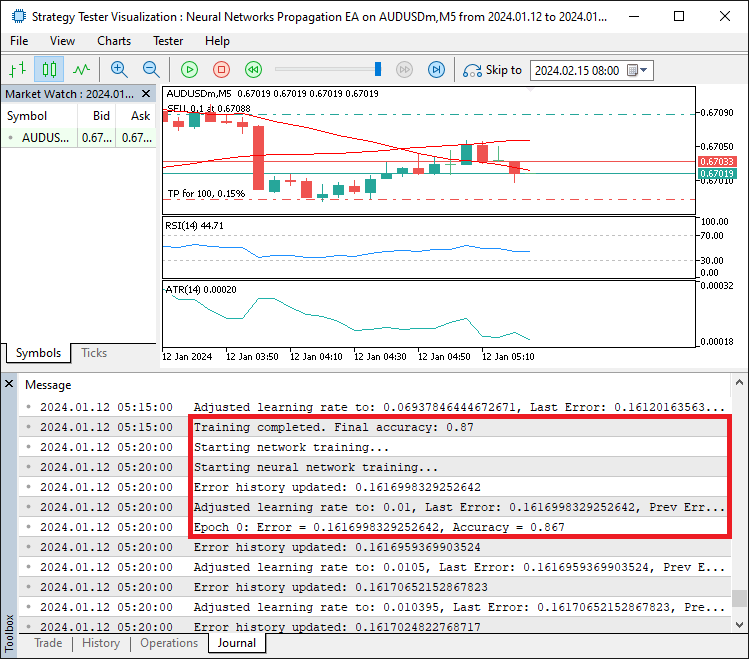
From the image, we can see that we train the neural network to get errors, propagate them within the epochs, and then adjust the learning rate based on the errors' accuracy. The thing that remains is backtesting the program, and that is handled in the next section.
Testing and Optimizing Learning Rate Adjustments
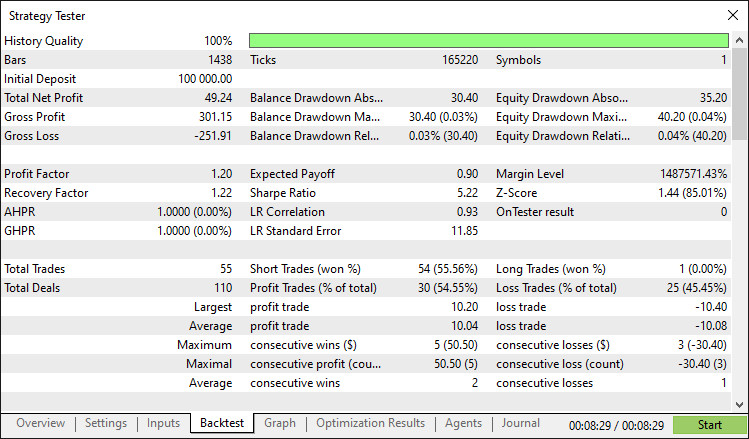
After thorough backtesting, we have the following results.
Backtest graph:
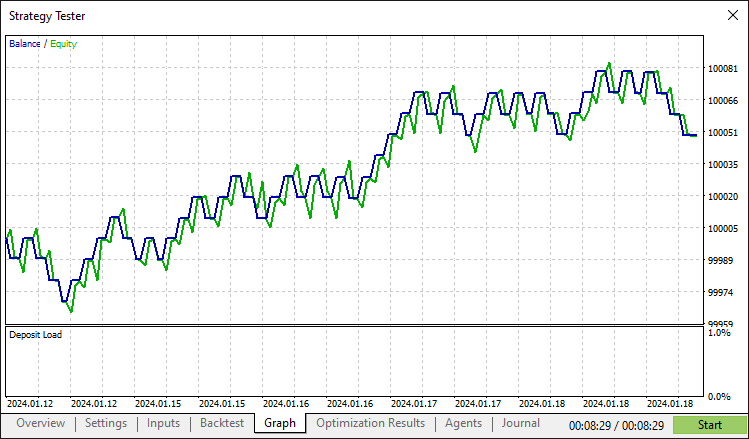
Backtest report:
Conclusion
In conclusion, we have developed an MQL5 program that implements a neural network-based trading strategy with adaptive learning rates, leveraging the "CNeuralNetwork" class to process market indicators and execute trades with dynamic adjustments to learning speed and network size for optimal performance. Through modular components like the "TrainingData" structure and functions such as "AdjustLearningRate" and "TrainNetwork", this system offers a flexible framework that you can enhance by fine-tuning parameters or integrating additional market indicators to suit your trading preferences.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only. Trading carries significant financial risks, and market volatility may result in losses. Thorough backtesting and careful risk management are crucial before deploying this program in live markets.
By leveraging the concepts and implementation presented, you can enhance this neural network trading system or adapt its architecture to create new strategies, empowering your journey in algorithmic trading. Happy trading!
Warning: All rights to these materials are reserved by MetaQuotes Ltd. Copying or reprinting of these materials in whole or in part is prohibited.
This article was written by a user of the site and reflects their personal views. MetaQuotes Ltd is not responsible for the accuracy of the information presented, nor for any consequences resulting from the use of the solutions, strategies or recommendations described.
 MQL5 Wizard Techniques you should know (Part 72): Using Patterns of MACD and the OBV with Supervised Learning
MQL5 Wizard Techniques you should know (Part 72): Using Patterns of MACD and the OBV with Supervised Learning
 Atomic Orbital Search (AOS) algorithm: Modification
Atomic Orbital Search (AOS) algorithm: Modification
 Price Action Analysis Toolkit Development (Part 30): Commodity Channel Index (CCI), Zero Line EA
Price Action Analysis Toolkit Development (Part 30): Commodity Channel Index (CCI), Zero Line EA
 Data Science and ML (Part 45): Forex Time series forecasting using PROPHET by Facebook Model
Data Science and ML (Part 45): Forex Time series forecasting using PROPHET by Facebook Model
- Free trading apps
- Over 8,000 signals for copying
- Economic news for exploring financial markets
You agree to website policy and terms of use