
使用MQL5经济日历进行交易(第五部分):添加响应式控件和过滤按钮的增强型仪表盘
概述
在本文中,我们将在《MetaQuotes语言5(MQL5)系列教程》的第四部分前期工作的基础上继续展开,在此,我们为MQL5经济日历仪表盘添加了实时更新功能。本文的重点是通过添加按钮,使仪表盘更具交互性,这些按钮允许我们直接从面板上控制货币对过滤器、重要性级别以及时间范围过滤器,而无需修改代码中的设置。我们还将添加一个“取消”按钮,用于清除所选过滤器并移除仪表盘组件,从而让我们能够完全掌控显示的内容。最后,我们将通过使按钮能够对点击操作做出响应,提升用户体验,确保按钮运行流畅并提供即时反馈。本文将涵盖的主题包括:
- 创建过滤按钮及控件
- 实现按钮自动化并增强其响应性
- 测试增强型仪表盘
- 结论
这些新增功能将显著提升我们仪表盘的可用性,使用户能够更灵活、更动态地与之进行实时交互。借助这些交互元素,我们可以轻松地过滤和管理所显示的新闻数据,而无需每次都修改底层代码。现在,让我们开始创建过滤按钮,并将其集成到现有的仪表盘布局中。
创建过滤按钮及控件
在本节中,我们将专注于创建过滤按钮,这些按钮将允许我们直接从面板上控制仪表盘的不同方面,如货币对过滤器、重要性级别过滤器以及时间范围过滤器。通过添加这些按钮,我们将能够更轻松地与仪表盘进行交互,而无需每次更改过滤器设置时都访问或修改代码。我们的目标是设计一个直观的用户界面,在保持布局简洁明了的同时提供灵活性。
首先,我们将定义每个过滤按钮的位置和属性。把这些按钮放置在仪表盘面板内,以便能够在货币对、重要性级别和时间过滤器之间切换不同设置。例如,我们将把货币过滤器按钮放置在仪表盘的右上角,将货币、重要性和时间过滤器选择按钮放置在标题部分,并在定义完这些按钮后立即放置取消按钮。每个按钮都将对应一个特定的过滤器设置,我们可以点击这些按钮来设置偏好的过滤器。以下是仪表盘内过滤按钮初始布局的示意图:
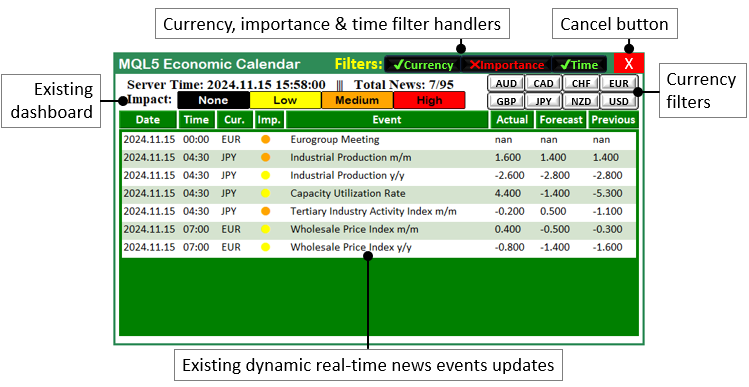
从图中可以看出,过滤按钮在仪表盘中进行了有序布局,便于用户轻松访问和管理。每个按钮都是为执行特定功能而设计,包括启用可用货币对、设置事件的重要性级别或按时间进行过滤。此外,这些按钮在视觉上也将彼此区分,以便我们能够轻松区分不同的控制组。
为了实现这一功能,我们需要为将要添加到仪表盘中的额外对象和控件定义常量。
#define FILTER_LABEL "FILTER_LABEL" //--- Define the label for the filter section on the dashboard #define FILTER_CURR_BTN "FILTER_CURR_BTN" //--- Define the button for filtering by currency pair #define FILTER_IMP_BTN "FILTER_IMP_BTN" //--- Define the button for filtering by event importance #define FILTER_TIME_BTN "FILTER_TIME_BTN" //--- Define the button for filtering by time range #define CANCEL_BTN "CANCEL_BTN" //--- Define the cancel button to reset or close the filters #define CURRENCY_BTNS "CURRENCY_BTNS" //--- Define the collection of currency buttons for user selection
在此,我们使用#define关键字定义一组string常量,这些常量代表将要添加到仪表盘中的各种元素(主要是按钮和标签)的名称。我们将利用这些常量来创建和管理用户界面组件,例如过滤按钮和取消按钮。首先,我们定义了“FILTER_LABEL”,它代表仪表盘上过滤部分的标签。
接下来,我们定义三个按钮:“FILTER_CURR_BTN”用于按货币对进行过滤,“FILTER_IMP_BTN”用于按事件重要性进行过滤,“FILTER_TIME_BTN”用于按事件时间范围进行过滤。我们还定义“CANCEL_BTN”,以便重置或关闭当前生效的过滤器并删除仪表盘组件。最后,“CURRENCY_BTNS”代表一组货币按钮,供我们选择特定的货币对。这些定义有助于创建一个动态且交互性强的仪表盘,使我们能够直接从界面上控制所显示的数据。为了增强动态性,我们将已定义的货币数组移至外部的全局作用域,如下所示:
string curr_filter[] = {"AUD","CAD","CHF","EUR","GBP","JPY","NZD","USD"}; string curr_filter_selected[];
在此,我们通过将函数内部预定义的货币列表移至全局作用域,增强了货币过滤器的灵活性和动态性。现在,我们定义一个新的全局数组“curr_filter”,用于存储可能的货币列表,如“AUD”(澳元)、“CAD”(加元)、“CHF”(瑞士法郎)、“EUR”(欧元)、“GBP”(英镑)、“JPY”(日元)、“NZD”(新西兰元)和“USD”(美元)。此外,我们还创建了一个空数组“curr_filter_selected”,该数组将在运行时动态存储用户选择的货币。最后,我们创建一个变量,用于跟踪是否需要进行更新,因为这次通过取消按钮移除仪表盘后,就不再需要更新操作了。轻而易举。
bool isDashboardUpdate = true;
我们只需定义一个布尔(boolean)变量“isDashboardUpdate”,并将其初始化为true。将使用此变量来跟踪仪表盘是否需要更新。将其设置为true,可以标记已经发生了需要仪表盘用新数据或设置进行刷新的更改或操作(如过滤器选择或按钮点击)。同样,将其设置为false则表示我们不需要执行更新过程,这样有助于高效管理仪表盘的状态,确保只在必要时进行更新,并避免不必要的重新渲染。
从全局作用域出发,我们可以进入初始化部分,并将附加的过滤组件映射到仪表盘上。我们将从最上方的按钮开始,这些按钮是过滤器启用按钮。
createLabel(FILTER_LABEL,370,55,"Filters:",clrYellow,16,"Impact"); //--- Create a label for the "Filters" section in the dashboard //--- Define the text, color, and state for the Currency filter button string filter_curr_text = enableCurrencyFilter ? ShortToString(0x2714)+"Currency" : ShortToString(0x274C)+"Currency"; //--- Set text based on filter state color filter_curr_txt_color = enableCurrencyFilter ? clrLime : clrRed; //--- Set text color based on filter state bool filter_curr_state = enableCurrencyFilter ? true : false; //--- Set button state (enabled/disabled) createButton(FILTER_CURR_BTN,430,55,110,26,filter_curr_text,filter_curr_txt_color,12,clrBlack); //--- Create Currency filter button ObjectSetInteger(0,FILTER_CURR_BTN,OBJPROP_STATE,filter_curr_state); //--- Set the state of the Currency button
这里,我们为仪表盘添加一个货币过滤器的标签和一个按钮。首先,我们使用“createLabel”函数在图表坐标(370,55)处放置一个标题为“Filters:”(过滤器:)的标签,该标签颜色为黄色,字体大小为16。此标签将作为过滤器部分的标题,清晰地向用户指示过滤器选项的位置。
接下来,我们定义并设置“Currency”(货币)过滤器的按钮。我们检查“enableCurrencyFilter”变量的状态,并根据其值,使用“filter_curr_text”变量动态设置按钮的文本。如果启用了货币过滤器(“enableCurrencyFilter”为true),按钮将显示一个带“Currency”(货币)文本的对勾标记(“0x2714”),表示过滤器处于激活状态;如果禁用,则显示一个叉号(“0x274C”),表示过滤器处于非激活状态。我们通过使用三元运算符来实现这一点,其功能与if运算符类似,但更加简洁和明了。
为了进一步从视觉上反映过滤器的状态,我们使用“filter_curr_txt_color”变量设置按钮的文本颜色。如果过滤器处于激活状态,文本将显示为绿色;如果处于非激活状态,文本将显示为红色。我们还使用“filter_curr_state”布尔变量来控制按钮的实际状态,该变量决定按钮是启用还是禁用。
然后,我们使用“createButton”函数创建按钮本身,将其放置在图表坐标(430,55)处,并设置适当的标签(“filter_curr_text”)、文本颜色(“filter_curr_txt_color”)和黑色背景。最后,我们使用ObjectSetInteger函数,通过引用“filter_curr_state”变量来设置按钮的状态(启用或禁用)。这确保了按钮的外观和功能与当前的过滤器设置相匹配。编译后,我们得到以下输出。
非常成功。现在,我们可以按照相同的逻辑继续添加过滤按钮。
//--- Define the text, color, and state for the Importance filter button string filter_imp_text = enableImportanceFilter ? ShortToString(0x2714)+"Importance" : ShortToString(0x274C)+"Importance"; //--- Set text based on filter state color filter_imp_txt_color = enableImportanceFilter ? clrLime : clrRed; //--- Set text color based on filter state bool filter_imp_state = enableImportanceFilter ? true : false; //--- Set button state (enabled/disabled) createButton(FILTER_IMP_BTN,430+110,55,120,26,filter_imp_text,filter_imp_txt_color,12,clrBlack); //--- Create Importance filter button ObjectSetInteger(0,FILTER_IMP_BTN,OBJPROP_STATE,filter_imp_state); //--- Set the state of the Importance button //--- Define the text, color, and state for the Time filter button string filter_time_text = enableTimeFilter ? ShortToString(0x2714)+"Time" : ShortToString(0x274C)+"Time"; //--- Set text based on filter state color filter_time_txt_color = enableTimeFilter ? clrLime : clrRed; //--- Set text color based on filter state bool filter_time_state = enableTimeFilter ? true : false; //--- Set button state (enabled/disabled) createButton(FILTER_TIME_BTN,430+110+120,55,70,26,filter_time_text,filter_time_txt_color,12,clrBlack); //--- Create Time filter button ObjectSetInteger(0,FILTER_TIME_BTN,OBJPROP_STATE,filter_time_state); //--- Set the state of the Time button //--- Create a Cancel button to reset all filters createButton(CANCEL_BTN,430+110+120+79,51,50,30,"X",clrWhite,17,clrRed,clrNONE); //--- Create the Cancel button with an "X" //--- Redraw the chart to update the visual elements ChartRedraw(0); //--- Redraw the chart to reflect all changes made above
在此,我们在仪表盘上为“重要性”(Importance)、“时间”(Time)和“取消”(Cancel)过滤器设置按钮。对于“重要性”(Importance)过滤器,我们首先使用“filter_imp_text”变量定义按钮的文本。根据“enableImportanceFilter”的值,如果过滤器处于激活状态,我们会在“Importance”(重要性)文本旁显示一个对勾标记(“0x2714”),表明该过滤器已启用;如果未激活,则显示一个叉号(“0x274C”)和相同文本,表明该过滤器已禁用。我们还使用“filter_imp_txt_color”设置按钮的文本颜色,启用时为绿色,禁用时为红色。“filter_imp_state”布尔变量用于控制按钮是启用还是禁用。
接下来,我们使用“createButton”函数创建“重要性”(Importance)过滤器按钮,并将其放置在坐标位置(430+110,55)处,同时设置合适的文本、颜色和状态。然后,我们使用ObjectSetInteger函数,根据“filter_imp_state”的值设置按钮的状态(“OBJPROP_STATE”),确保按钮能正确反映其状态。
对于“时间”(Time)过滤器按钮,我们采用类似的操作流程。我们在“filter_time_text”中定义其文本,并根据“enableTimeFilter”的值,使用“filter_time_txt_color”调整颜色。该按钮在坐标位置(430+110+120,55)处创建,并相应地使用“filter_time_state”设置其状态。
最后,我们使用“createButton”函数创建“取消”(Cancel)按钮,点击该按钮将重置所有过滤器并删除仪表盘。此按钮放置在坐标位置(430+110+120+79,51)处,背景为红色,上面有一个白色的“X”以表明其用途。最后,我们调用ChartRedraw函数刷新图表,使新创建的按钮和更改在视觉上得到更新。运行后,我们得到如下结果。
非常成功。现在,我们已经在仪表盘上添加了所有过滤器按钮。不过,在创建文本时,我们使用了被称为Unicode字符的非典型字符组合。下面让我们深入了解一下这些字符。
ShortToString(0x2714); ShortToString(0x274C);
在此,我们使用“ShortToString(0x2714)”和“ShortToString(0x274C)”函数在MQL5中表示Unicode字符,其中“0x2714”和“0x274C”是Unicode字符集中的特定符号编码。
- “0x2714”是“对勾标记(CHECK MARK)”符号的Unicode编码。它用于表示某事物已启用、已完成或正确。在过滤器按钮的上下文中,我们用它来表示某个过滤器(如货币过滤器或重要性过滤器)处于激活或启用状态。
- “0x274C”是“叉号标记(CROSS MARK)”符号的Unicode编码。它用于表示某事物已禁用、未完成或不正确。在此,我们用它来表示某个过滤器处于非激活或禁用状态。
您也可以使用其他字符,只要这些字符与MQL5编码环境兼容即可。以下是部分可用字符示例:
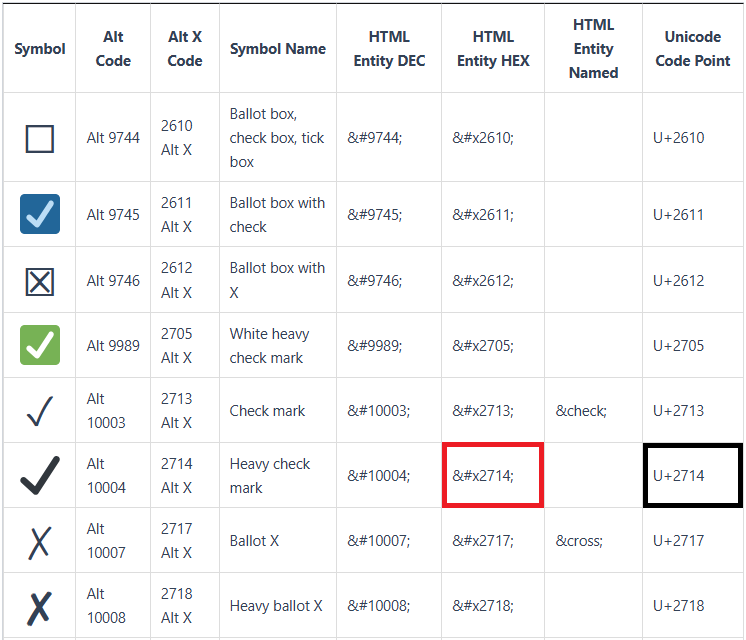
在代码中,ShortToString函数将这些Unicode编码点转换为对应的字符表示形式。随后,这些字符会被附加到过滤器按钮的文本上,从而以直观的方式显示过滤器是否处于激活状态。接下来,我们可以动态创建货币过滤器按钮。
int curr_size = 51; //--- Button width int button_height = 22; //--- Button height int spacing_x = 0; //--- Horizontal spacing int spacing_y = 3; //--- Vertical spacing int max_columns = 4; //--- Number of buttons per row for (int i = 0; i < ArraySize(curr_filter); i++){ int row = i / max_columns; //--- Determine the row int col = i % max_columns; //--- Determine the column int x_pos = 575 + col * (curr_size + spacing_x); //--- Calculate X position int y_pos = 83 + row * (button_height + spacing_y); //--- Calculate Y position //--- Create button with dynamic positioning createButton(CURRENCY_BTNS+IntegerToString(i),x_pos,y_pos,curr_size,button_height,curr_filter[i],clrBlack); } if (enableCurrencyFilter == true){ ArrayFree(curr_filter_selected); ArrayCopy(curr_filter_selected,curr_filter); Print("CURRENCY FILTER ENABLED"); ArrayPrint(curr_filter_selected); for (int i = 0; i < ArraySize(curr_filter_selected); i++) { // Set the button to "clicked" (selected) state by default ObjectSetInteger(0, CURRENCY_BTNS + IntegerToString(i), OBJPROP_STATE, true); // true means clicked } }
这里,我们动态创建货币过滤器按钮,并根据过滤器是否启用来管理它们的布局和状态。首先,我们定义按钮布局参数。我们将 整型变量“curr_size”设置为51,用于确定每个按钮的宽度;将“button_height”设置为22,用于确定按钮的高度。“spacing_x”和“spacing_y”分别设置为0和3,以控制按钮在水平和垂直方向上的间距。我们还定义“max_columns”为4,将每行的按钮数量限制为四个。
接下来,我们使用for循环 遍历包含货币对代码(如“AUD”、“CAD”等)的数组“curr_filter”。在每次迭代中,我们计算按钮应放置的行和列。我们通过“i / max_columns”计算行数,通过“i % max_columns”计算行内的列数。利用这些值,计算按钮在屏幕上的X轴位置(“x_pos”)和Y轴位置(“y_pos”)。然后,我们调用“createButton”函数,根据“curr_filter”数组中对应的货币代码动态创建每个按钮,并将其标签设置为相应的货币名称,颜色设置为黑色。
创建按钮后,我们通过评估“enableCurrencyFilter”的值来判断过滤器是否已启用。如果过滤器已经启用,我们使用ArrayFree函数清空已选货币数组,并使用ArrayCopy函数将“curr_filter”数组的内容复制到“curr_filter_selected”数组中。这样实际上是将所有货币复制到已选数组中。之后,我们打印“CURRENCY FILTER ENABLED”(货币过滤器已启用),并使用 ArrayPrint函数显示已选过滤器数组。最后,我们遍历“curr_filter_selected”数组中的已选货币,并使用ObjectSetInteger函数,通过设置相应参数,将每个对应按钮的状态设置为已选中。我们使用IntegerToString函数将选择项的索引与“CURRENCY_BTNS”宏拼接起来,并将状态设置为true,这样在视觉上就会将按钮标记为已点击。
编译后,我们得到以下结果。
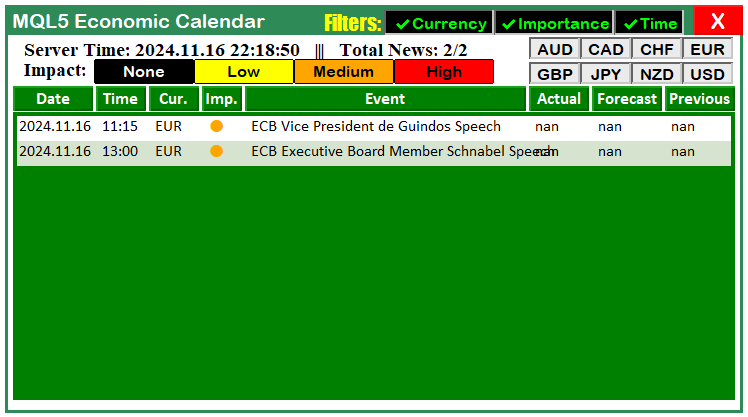
从图中可以看出,我们已经成功地将过滤器按钮添加到了仪表盘上。接下来,我们需要更新负责销毁仪表盘的函数,以确保该函数也能处理新添加的这些组件。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Function to destroy the Dashboard panel | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void destroy_Dashboard(){ //--- Delete the main rectangle that defines the dashboard background ObjectDelete(0,"MAIN_REC"); //--- Delete the sub-rectangles that separate sections in the dashboard ObjectDelete(0,"SUB_REC1"); ObjectDelete(0,"SUB_REC2"); //--- Delete the header label that displays the title of the dashboard ObjectDelete(0,"HEADER_LABEL"); //--- Delete the time and impact labels from the dashboard ObjectDelete(0,"TIME_LABEL"); ObjectDelete(0,"IMPACT_LABEL"); //--- Delete all calendar-related objects ObjectsDeleteAll(0,"ARRAY_CALENDAR"); //--- Delete all news-related objects ObjectsDeleteAll(0,"ARRAY_NEWS"); //--- Delete all data holder objects (for storing data within the dashboard) ObjectsDeleteAll(0,"DATA_HOLDERS"); //--- Delete the impact label objects (impact-related elements in the dashboard) ObjectsDeleteAll(0,"IMPACT_LABEL"); //--- Delete the filter label that identifies the filter section ObjectDelete(0,"FILTER_LABEL"); //--- Delete the filter buttons for Currency, Importance, and Time ObjectDelete(0,"FILTER_CURR_BTN"); ObjectDelete(0,"FILTER_IMP_BTN"); ObjectDelete(0,"FILTER_TIME_BTN"); //--- Delete the cancel button that resets or closes the filters ObjectDelete(0,"CANCEL_BTN"); //--- Delete all currency filter buttons dynamically created ObjectsDeleteAll(0,"CURRENCY_BTNS"); //--- Redraw the chart to reflect the removal of all dashboard components ChartRedraw(0); }
我们还需要更新OnTick事件处理程序的逻辑,使其仅在更新标识为true时才执行更新操作。我们可通过以下逻辑实现这一点。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick(){ //--- if (isDashboardUpdate){ update_dashboard_values(curr_filter_selected); } }
这里,我们检查条件“isDashboardUpdate”是否为true,该条件表明仪表盘需要使用最新数据进行更新。如果满足此条件,我们调用“update_dashboard_values”函数,利用存储在“curr_filter_selected”数组中的已选货币过滤器来更新仪表盘上显示的值。
“curr_filter_selected”数组包含已选择用于过滤的货币,通过将其传递给“update_dashboard_values”函数,我们确保仪表盘能够反映最新的过滤器选择。如果该变量标识为false,则不会考虑进行任何更新。创建过滤器按钮时,我们需要考虑的内容就是这些现在,我们只需继续为已创建的按钮添加响应功能,这部分内容将在下一节中介绍。
实现按钮自动化并增强其响应性
为使仪表盘具备交互响应能力,我们需要添加一个事件监听器来追踪用户点击操作,并根据点击事件执行相应动作。为此,我们将使用MQL5内置的OnChartEvent事件处理函数。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| OnChartEvent handler function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnChartEvent( const int id, // event ID const long& lparam, // long type event parameter const double& dparam, // double type event parameter const string& sparam // string type event parameter ){ //--- }
该函数专门用于识别图表上的各类活动,例如图表内容变更、用户点击操作、对象创建事件等。不过,我们仅需关注图表点击事件,因为当前目标是监听按钮的点击操作。我们将按照从简单到复杂的顺序逐步实现功能。其中,取消按钮的逻辑最为简单。
if (id == CHARTEVENT_OBJECT_CLICK){ //--- Check if the event is a click on an object if (sparam == CANCEL_BTN){ //--- If the Cancel button is clicked isDashboardUpdate = false; //--- Set dashboard update flag to false destroy_Dashboard(); //--- Call the function to destroy the dashboard } }
以下代码处理的是当检测到图表对象被点击时的场景——具体通过判断事件ID是否为CHARTEVENT_OBJECT_CLICK来识别点击事件。如果确认是点击事件,我们将进一步检查被点击的对象是否为"CANCEL_BTN"——通过判断字符串参数"sparam"的值是否等于"CANCEL_BTN"来实现。当该条件成立时,说明用户点击了仪表盘上的取消按钮。此时,我们将全局标识变量"isDashboardUpdate"设置为false,从而禁止仪表盘后续的更新操作。接着调用"destroy_Dashboard"函数,从图表中移除所有与仪表盘相关的图形元素,完成界面清理。通过这套逻辑,当用户点击取消按钮时,仪表盘界面将被重置并清空。以下是相关代码示例:
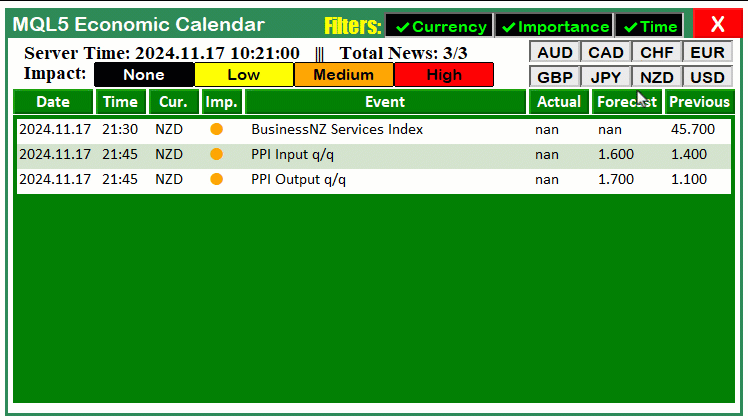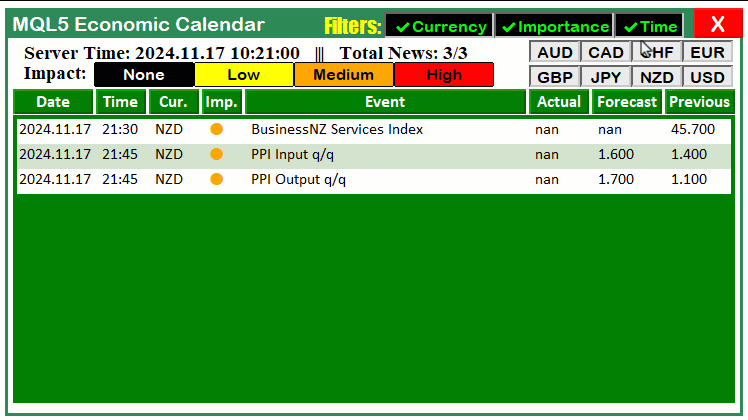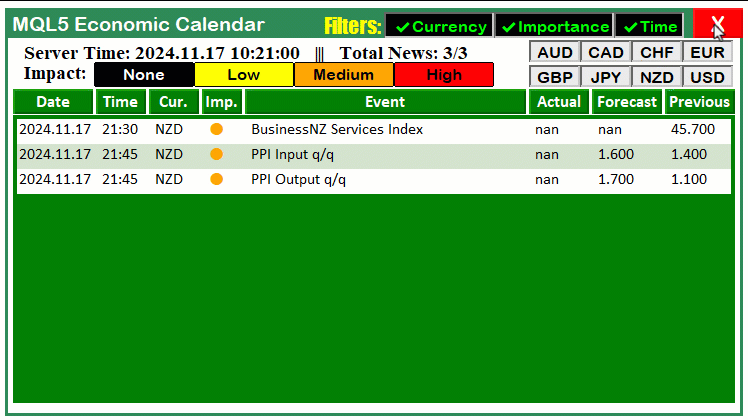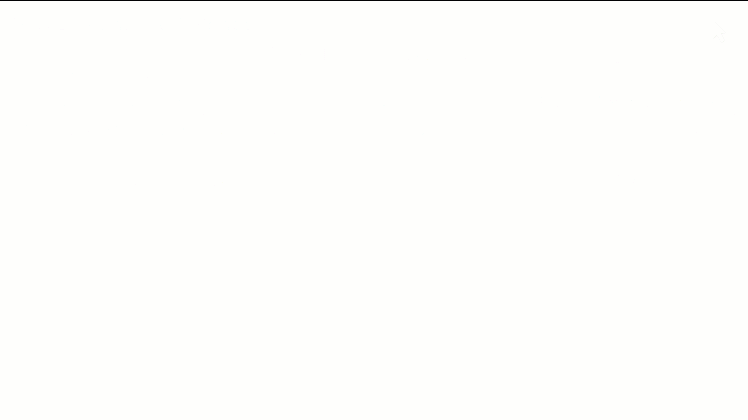
非常成功。现在我们可以将相同的逻辑应用于其他按钮的自动化操作。接下来将实现货币过滤器按钮的自动化功能。我们通过以下代码段来实现这一目标:
if (sparam == FILTER_CURR_BTN){ //--- If the Currency filter button is clicked bool btn_state = ObjectGetInteger(0,sparam,OBJPROP_STATE); //--- Get the button state (clicked/unclicked) enableCurrencyFilter = btn_state; //--- Update the Currency filter flag Print(sparam+" STATE = "+(string)btn_state+", FLAG = "+(string)enableCurrencyFilter); //--- Log the state string filter_curr_text = enableCurrencyFilter ? ShortToString(0x2714)+"Currency" : ShortToString(0x274C)+"Currency"; //--- Set button text based on state color filter_curr_txt_color = enableCurrencyFilter ? clrLime : clrRed; //--- Set button text color based on state ObjectSetString(0,FILTER_CURR_BTN,OBJPROP_TEXT,filter_curr_text); //--- Update the button text ObjectSetInteger(0,FILTER_CURR_BTN,OBJPROP_COLOR,filter_curr_txt_color); //--- Update the button text color Print("Success. Changes updated! State: "+(string)enableCurrencyFilter); //--- Log success ChartRedraw(0); //--- Redraw the chart to reflect changes }
以下代码处理当用户点击"FILTER_CURR_BTN"(货币过滤器按钮)时的交互逻辑。当检测到该按钮被点击时,我们通过ObjectGetInteger函数配合OBJPROP_STATE属性获取按钮的当前状态(选中/未选中),并将结果存储在"btn_state"变量中。随后,我们将"enableCurrencyFilter"标识变量的值更新为"btn_state"的当前值,以此同步货币过滤器的激活状态——当按钮被选中时启用过滤器,未选中时则禁用。
接下来,我们使用Print函数记录按钮状态和更新后的标识值,以提供操作反馈。根据货币过滤器的状态,我们通过 ShortToString函数动态地将按钮文本设为勾选符号或叉号,并将其颜色更新为绿色(启用)或红色(禁用)。使用ObjectSetString更新按钮文本,同时通过ObjectSetInteger设置颜色属性。
最后,我们打印一条成功消息以确认变更已生效,并调用ChartRedraw函数刷新图表,确保按钮的视觉变化立即呈现。这种交互设计实现了货币过滤器的动态切换功能,并能实时在仪表盘上反映状态变更。其他过滤器按钮也可采用相同的实现逻辑。
if (sparam == FILTER_IMP_BTN){ //--- If the Importance filter button is clicked bool btn_state = ObjectGetInteger(0,sparam,OBJPROP_STATE); //--- Get the button state enableImportanceFilter = btn_state; //--- Update the Importance filter flag Print(sparam+" STATE = "+(string)btn_state+", FLAG = "+(string)enableImportanceFilter); //--- Log the state string filter_imp_text = enableImportanceFilter ? ShortToString(0x2714)+"Importance" : ShortToString(0x274C)+"Importance"; //--- Set button text color filter_imp_txt_color = enableImportanceFilter ? clrLime : clrRed; //--- Set button text color ObjectSetString(0,FILTER_IMP_BTN,OBJPROP_TEXT,filter_imp_text); //--- Update the button text ObjectSetInteger(0,FILTER_IMP_BTN,OBJPROP_COLOR,filter_imp_txt_color); //--- Update the button text color Print("Success. Changes updated! State: "+(string)enableImportanceFilter); //--- Log success ChartRedraw(0); //--- Redraw the chart } if (sparam == FILTER_TIME_BTN){ //--- If the Time filter button is clicked bool btn_state = ObjectGetInteger(0,sparam,OBJPROP_STATE); //--- Get the button state enableTimeFilter = btn_state; //--- Update the Time filter flag Print(sparam+" STATE = "+(string)btn_state+", FLAG = "+(string)enableTimeFilter); //--- Log the state string filter_time_text = enableTimeFilter ? ShortToString(0x2714)+"Time" : ShortToString(0x274C)+"Time"; //--- Set button text color filter_time_txt_color = enableTimeFilter ? clrLime : clrRed; //--- Set button text color ObjectSetString(0,FILTER_TIME_BTN,OBJPROP_TEXT,filter_time_text); //--- Update the button text ObjectSetInteger(0,FILTER_TIME_BTN,OBJPROP_COLOR,filter_time_txt_color); //--- Update the button text color Print("Success. Changes updated! State: "+(string)enableTimeFilter); //--- Log success ChartRedraw(0); //--- Redraw the chart }
以下代码实现了对"FILTER_IMP_BTN"(重要性过滤器按钮)和"FILTER_TIME_BTN"(时间过滤器按钮)的点击交互处理,支持动态切换过滤器状态。对于"FILTER_IMP_BTN",当按钮被点击时,通过ObjectGetInteger配合OBJPROP_STATE属性获取按钮当前状态,并存入"btn_state"变量。更新"enableImportanceFilter"标识,以同步重要性过滤器是否处于激活状态。使用Print函数,记录按钮状态以及更新后的标识值。根据状态不同,我们通过ShortToString函数将按钮文本设置为勾选标记或叉号,并将其颜色更新为绿色(启用)或红色(禁用)。通过ObjectSetString设置按钮文本,并用ObjectSetInteger设置颜色属性。最后,我们打印一条成功消息,并调用ChartRedraw函数,以确保这些更新能够立即在界面上呈现。
同样地,对于 “FILTER_TIME_BTN”,我们采用完全相同的流程。使用ObjectGetInteger函数获取按钮的当前状态,并据此更新 “enableTimeFilter” 标识。记录状态及标识的更新结果,以便反馈。使用 ShortToString、ObjectSetString 以及ObjectSetInteger函数分别动态设置按钮的文本(✓/✗)和颜色(绿色/红色),以反映启用或禁用状态。更新完成后打印确认消息,并调用ChartRedraw函数重绘图表,确保视觉效果即时生效。该流程确保了过滤器按钮的实时响应能力,使用户在切换时能够获得流畅的操作体验。动态效果如下:
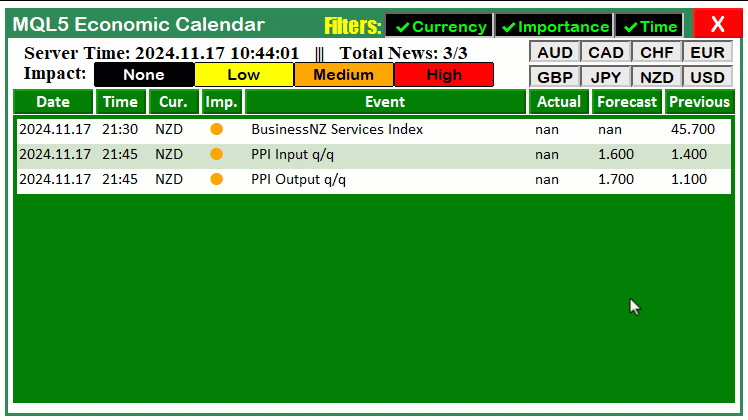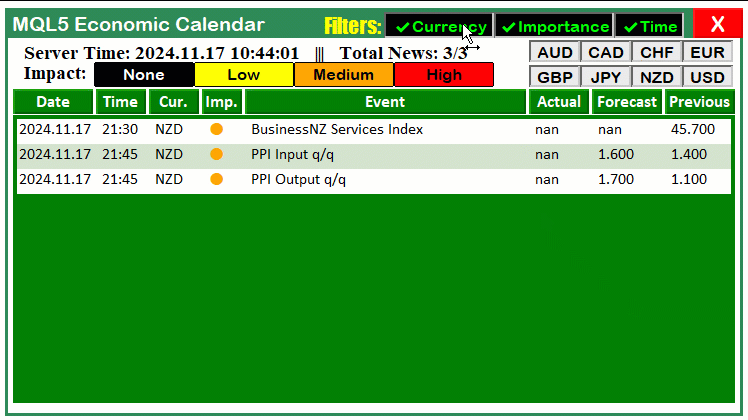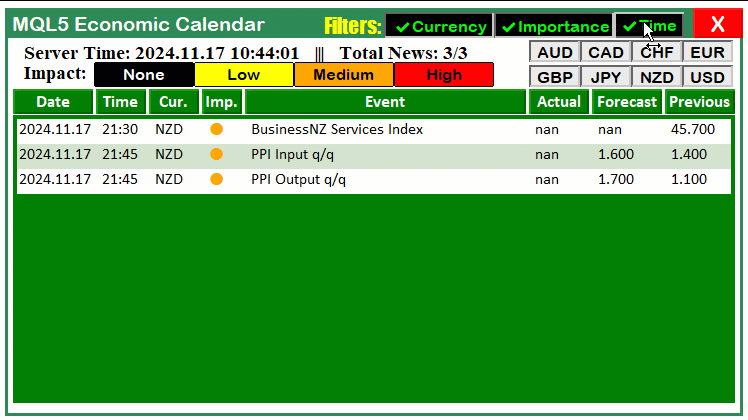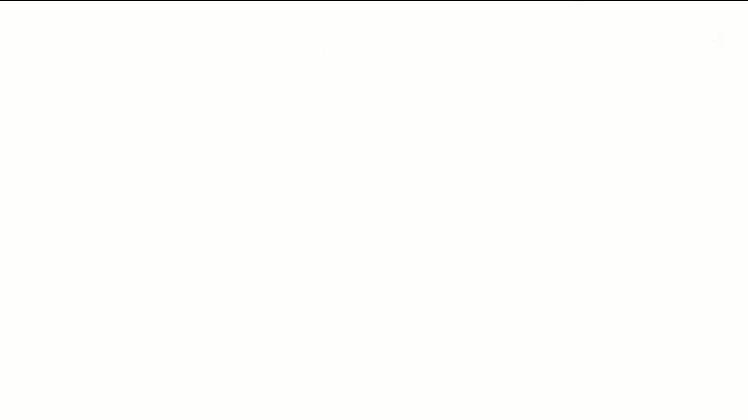
非常成功。现在,我们可以继续对货币按钮进行同样的自动化处理。
if (StringFind(sparam,CURRENCY_BTNS) >= 0){ //--- If a Currency button is clicked string selected_curr = ObjectGetString(0,sparam,OBJPROP_TEXT); //--- Get the text of the clicked button Print("BTN NAME = ",sparam,", CURRENCY = ",selected_curr); //--- Log the button name and currency bool btn_state = ObjectGetInteger(0,sparam,OBJPROP_STATE); //--- Get the button state if (btn_state == false){ //--- If the button is unselected Print("BUTTON IS IN UN-SELECTED MODE."); //--- Loop to find and remove the currency from the array for (int i = 0; i < ArraySize(curr_filter_selected); i++) { if (curr_filter_selected[i] == selected_curr) { //--- Shift elements to remove the selected currency for (int j = i; j < ArraySize(curr_filter_selected) - 1; j++) { curr_filter_selected[j] = curr_filter_selected[j + 1]; } ArrayResize(curr_filter_selected, ArraySize(curr_filter_selected) - 1); //--- Resize the array Print("Removed from selected filters: ", selected_curr); //--- Log removal break; } } } else if (btn_state == true){ //--- If the button is selected Print("BUTTON IS IN SELECTED MODE. TAKE ACTION"); //--- Check for duplicates bool already_selected = false; for (int j = 0; j < ArraySize(curr_filter_selected); j++) { if (curr_filter_selected[j] == selected_curr) { already_selected = true; break; } } //--- If not already selected, add to the array if (!already_selected) { ArrayResize(curr_filter_selected, ArraySize(curr_filter_selected) + 1); //--- Resize array curr_filter_selected[ArraySize(curr_filter_selected) - 1] = selected_curr; //--- Add the new currency Print("Added to selected filters: ", selected_curr); //--- Log addition } else { Print("Currency already selected: ", selected_curr); //--- Log already selected } } Print("SELECTED ARRAY SIZE = ",ArraySize(curr_filter_selected)); //--- Log the size of the selected array ArrayPrint(curr_filter_selected); //--- Print the selected array update_dashboard_values(curr_filter_selected); //--- Update the dashboard with the selected filters Print("SUCCESS. DASHBOARD UPDATED"); //--- Log success ChartRedraw(0); //--- Redraw the chart to reflect changes }
以下代码实现了对货币过滤器按钮的点击交互处理,用于动态管理已选货币列表并实时更新仪表盘。当检测到按钮被点击时,首先通过StringFind函数判断该按钮是否属于"CURRENCY_BTNS"货币按钮组。如果为true,我们调用ObjectGetString并传入 “OBJPROP_TEXT” 属性,获取按钮的文本标签,以识别其所代表的货币。接着,使用ObjectGetInteger并指定“OBJPROP_STATE”属性,判断按钮当前处于选中(true)还是未选中(false)状态。
若按钮处于未选中状态,我们将相应货币从 “curr_filter_selected” 数组中移除。具体做法是:遍历数组找到匹配的货币,把后续所有元素左移一格覆盖该元素,然后使用ArrayResize函数调整数组长度,去掉末尾多余的位置。每次移除都会写入日志以确认操作。相反,如果按钮处于选中状态,我们先检查是否已存在该货币,防止重复添加。若该货币尚未在数组中,则先用"ArrayResize"函数扩大数组,再将新货币追加到末尾,并记录添加日志。若该货币已存在,则记录一条消息表示无需再进行操作。
在更新完"curr_filter_selected"数组后,我们使用ArrayPrint函数记录数组的当前大小和内容,以便调试和状态追踪。随后调用"update_dashboard_values"函数,根据用户最新选择的货币过滤器重新计算并刷新仪表盘数据。最后,通过调用ChartRedraw函数强制重绘图表,确保所有界面变更(如按钮状态、数据展示等)立即生效,实现实时交互反馈。
由于用户交互后货币过滤器可能发生动态变化,我们需要同步更新负责数据处理的函数,使其始终基于当前用户选中的货币列表进行计算。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Function to update dashboard values | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void update_dashboard_values(string &curr_filter_array[]){ //--- //--- Check if the event’s currency matches any in the filter array (if the filter is enabled) bool currencyMatch = false; if (enableCurrencyFilter) { for (int j = 0; j < ArraySize(curr_filter_array); j++) { if (country.currency == curr_filter_array[j]) { currencyMatch = true; break; } } //--- If no match found, skip to the next event if (!currencyMatch) { continue; } } //--- }
这里,我们通过引入一个关键改进——利用按引用传递的 “curr_filter_array” 参数(使用 “&” 符号)——来更新 “update_dashboard_values” 函数。这种设计使函数能够直接操作已选货币过滤数组,确保仪表盘始终与用户偏好保持同步。
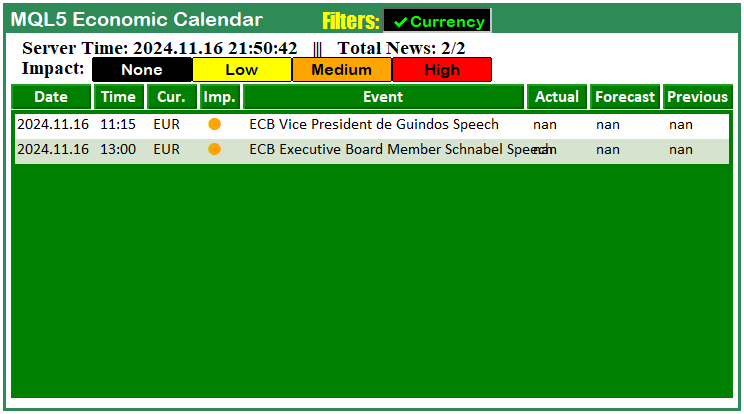
这就是"引用传递 (&)"的含义。“curr_filter_array” 参数以引用方式传入函数。这意味着函数访问的是内存中的实际数组,而非其副本。因此,函数内部对数组的任何修改都会直接反映到函数外部的原始数组。该方法在处理较大数组时效率更高,并且与用户当前的过滤选择保持一致。稍后,我们将直接采用这个按引用传递的最新数组(包含用户偏好),而不再使用初始数组。为了便于阅读,相关改动已用黄色高亮显示。编译后,显示出的效果如下:
从可视化结果可以看出,每次点击任一货币按钮时,仪表盘都会立即更新,说明功能已成功实现。然而,目前货币过滤器按钮与具体货币之间仍存在依赖问题:当我们单击单个货币过滤器后,仪表盘并未随之更新。为解决这一问题,只需在每个过滤器按钮的事件处理中都调用一次更新函数,如下所示。
if (sparam == FILTER_CURR_BTN){ //--- If the Currency filter button is clicked bool btn_state = ObjectGetInteger(0,sparam,OBJPROP_STATE); //--- Get the button state (clicked/unclicked) enableCurrencyFilter = btn_state; //--- Update the Currency filter flag Print(sparam+" STATE = "+(string)btn_state+", FLAG = "+(string)enableCurrencyFilter); //--- Log the state string filter_curr_text = enableCurrencyFilter ? ShortToString(0x2714)+"Currency" : ShortToString(0x274C)+"Currency"; //--- Set button text based on state color filter_curr_txt_color = enableCurrencyFilter ? clrLime : clrRed; //--- Set button text color based on state ObjectSetString(0,FILTER_CURR_BTN,OBJPROP_TEXT,filter_curr_text); //--- Update the button text ObjectSetInteger(0,FILTER_CURR_BTN,OBJPROP_COLOR,filter_curr_txt_color); //--- Update the button text color update_dashboard_values(curr_filter_selected); Print("Success. Changes updated! State: "+(string)enableCurrencyFilter); //--- Log success ChartRedraw(0); //--- Redraw the chart to reflect changes } if (sparam == FILTER_IMP_BTN){ //--- If the Importance filter button is clicked bool btn_state = ObjectGetInteger(0,sparam,OBJPROP_STATE); //--- Get the button state enableImportanceFilter = btn_state; //--- Update the Importance filter flag Print(sparam+" STATE = "+(string)btn_state+", FLAG = "+(string)enableImportanceFilter); //--- Log the state string filter_imp_text = enableImportanceFilter ? ShortToString(0x2714)+"Importance" : ShortToString(0x274C)+"Importance"; //--- Set button text color filter_imp_txt_color = enableImportanceFilter ? clrLime : clrRed; //--- Set button text color ObjectSetString(0,FILTER_IMP_BTN,OBJPROP_TEXT,filter_imp_text); //--- Update the button text ObjectSetInteger(0,FILTER_IMP_BTN,OBJPROP_COLOR,filter_imp_txt_color); //--- Update the button text color update_dashboard_values(curr_filter_selected); Print("Success. Changes updated! State: "+(string)enableImportanceFilter); //--- Log success ChartRedraw(0); //--- Redraw the chart } if (sparam == FILTER_TIME_BTN){ //--- If the Time filter button is clicked bool btn_state = ObjectGetInteger(0,sparam,OBJPROP_STATE); //--- Get the button state enableTimeFilter = btn_state; //--- Update the Time filter flag Print(sparam+" STATE = "+(string)btn_state+", FLAG = "+(string)enableTimeFilter); //--- Log the state string filter_time_text = enableTimeFilter ? ShortToString(0x2714)+"Time" : ShortToString(0x274C)+"Time"; //--- Set button text color filter_time_txt_color = enableTimeFilter ? clrLime : clrRed; //--- Set button text color ObjectSetString(0,FILTER_TIME_BTN,OBJPROP_TEXT,filter_time_text); //--- Update the button text ObjectSetInteger(0,FILTER_TIME_BTN,OBJPROP_COLOR,filter_time_txt_color); //--- Update the button text color update_dashboard_values(curr_filter_selected); Print("Success. Changes updated! State: "+(string)enableTimeFilter); //--- Log success ChartRedraw(0); //--- Redraw the chart }
这里,我们只需确保调用更新函数,以提升仪表盘事件的独立性。为便于查看,相关改动已用黄色高亮标示。通过这些调整,按钮功能实现完全独立化。直观效果显示如下:
至此,我们已经成功地整合了货币过滤器。采用同样的流程,接下来可以继续整合重要性过滤器。这一步会稍显复杂,因为我们需要在既有按钮上追加过滤效果,并为此准备两个重要性级别数组:一个主数组,以及一个用于比对的辅助字符串数组。首先,我们将所有重要性数组提升到全局作用域,使其在各处代码中都可以被访问。
//--- Define labels for impact levels and size of impact display areas string impact_labels[] = {"None","Low","Medium","High"}; string impact_filter_selected[]; // Define the levels of importance to filter (low, moderate, high) ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_IMPORTANCE allowed_importance_levels[] = {CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_NONE,CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_LOW, CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_MODERATE, CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_HIGH}; ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_IMPORTANCE imp_filter_selected[];
这里,我们定义字符串数组 “impact_labels”,用来保存可供用户选择的不同影响级别标签。这些标签依次为 “None”、“Low”、“Medium” 和 “High”。我们用该数组向用户展示选项,以便按感知影响力过滤日历事件。
接下来引入数组 “impact_filter_selected”,用于存放用户从 “impact_labels” 中实际选中的标签。每当用户通过界面选择某个影响级别时,相应的标签即被添加到该数组。由于采用字符串格式,我们可以轻松地解读所选级别,而无需依赖枚举列表。这样就能动态地追踪用户的过滤偏好。
随后,我们定义数组 “allowed_importance_levels”,其中包含ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_IMPORTANCE类型的枚举值。这些枚举值对应各影响级别:“CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_NONE”、“CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_LOW”、“CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_MODERATE” 以及 “CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_HIGH”。之前已定义过,现在只是将它们提升到全局作用域。这些值将用于按重要性程度过滤日历事件。
我们还定义数组 “imp_filter_selected”,用来存储与用户所选影响标签对应的重要性级别。当用户从 “impact_labels” 中选择标签时,我们将每个标签与 “allowed_importance_levels” 中的对应级别匹配,并将结果存入 “imp_filter_selected”。该数组随后用于过滤日历事件,确保仅显示符合所选重要性级别的事件。
现在进入初始化函数,我们将为这些按钮更新外观,以提升清晰度——因为它们不仅用于提示事件结果,还承担过滤功能。因此,当按钮被点击时,需要即时显示处于启用或禁用状态。
if (enableImportanceFilter == true) { ArrayFree(imp_filter_selected); //--- Clear the existing selections in the importance filter array ArrayCopy(imp_filter_selected, allowed_importance_levels); //--- Copy all allowed importance levels as default selections ArrayFree(impact_filter_selected); ArrayCopy(impact_filter_selected, impact_labels); Print("IMPORTANCE FILTER ENABLED"); //--- Log that importance filter is enabled ArrayPrint(imp_filter_selected); //--- Print the current selection of importance levels ArrayPrint(impact_filter_selected); // Loop through the importance levels and set their buttons to "selected" state for (int i = 0; i < ArraySize(imp_filter_selected); i++) { string btn_name = IMPACT_LABEL+IntegerToString(i); //--- Dynamically name the button for each importance level ObjectSetInteger(0, btn_name, OBJPROP_STATE, true); //--- Set the button state to "clicked" (selected) ObjectSetInteger(0, btn_name, OBJPROP_BORDER_COLOR, clrNONE); //--- Set the button state to "clicked" (selected) } }
这里,我们首先检查"enableImportanceFilter"变量是否为true。若条件成立,则继续配置重要性过滤系统。使用ArrayFree函数清空"imp_filter_selected"数组,移除之前的所有已选级别。随后,将"allowed_importance_levels"数组的全部数值复制到"imp_filter_selected"中,默认选择所有重要性级别。也就是说,在默认情况下,所有的级别一开始都被纳入过滤范围。
接着,同样用ArrayFree函数清空"impact_filter_selected" 数组,确保清除先前选择的影响程度标签。再将"impact_labels"数组的全部字符串标签复制到"impact_filter_selected"中。这样使得代表影响级别(如“None / Low / Medium / High”)标签可用于过滤。数组设置完成后,打印日志 “IMPORTANCE FILTER ENABLED”,确认重要性过滤器已激活。同时打印输出"imp_filter_selected"与"impact_filter_selected"数组的内容,以展示当前已选级别与标签。
最后,我们遍历"imp_filter_selected"数组(其中保存了当前已选的重要性级别),并为每个对应的重要性级别动态设置按钮状态。对于每一个重要性级别,我们使用“IMPACT_LABEL”和当前重要性级别的索引,通过IntegerToString函数动态生成按钮名称。接下来,使用ObjectSetInteger函数把该按钮的状态设为 true(表示已选中)。同时,将OBJPROP_BORDER_COLOR属性设为空值,去掉边框颜色,以视觉方式突出按钮已被选中。至此,所需初始化工作已全部完成。现在轮到事件监听函数,用于监听重要性按钮的点击并作出相应地处理。此处的逻辑与我们之前处理货币过滤按钮的方式类似。
if (StringFind(sparam, IMPACT_LABEL) >= 0) { //--- If an Importance button is clicked string selected_imp = ObjectGetString(0, sparam, OBJPROP_TEXT); //--- Get the importance level of the clicked button ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_IMPORTANCE selected_importance_lvl = get_importance_level(impact_labels,allowed_importance_levels,selected_imp); Print("BTN NAME = ", sparam, ", IMPORTANCE LEVEL = ", selected_imp,"(",selected_importance_lvl,")"); //--- Log the button name and importance level bool btn_state = ObjectGetInteger(0, sparam, OBJPROP_STATE); //--- Get the button state color color_border = btn_state ? clrNONE : clrBlack; if (btn_state == false) { //--- If the button is unselected Print("BUTTON IS IN UN-SELECTED MODE."); //--- Loop to find and remove the importance level from the array for (int i = 0; i < ArraySize(imp_filter_selected); i++) { if (impact_filter_selected[i] == selected_imp) { //--- Shift elements to remove the unselected importance level for (int j = i; j < ArraySize(imp_filter_selected) - 1; j++) { imp_filter_selected[j] = imp_filter_selected[j + 1]; impact_filter_selected[j] = impact_filter_selected[j + 1]; } ArrayResize(imp_filter_selected, ArraySize(imp_filter_selected) - 1); //--- Resize the array ArrayResize(impact_filter_selected, ArraySize(impact_filter_selected) - 1); //--- Resize the array Print("Removed from selected importance filters: ", selected_imp,"(",selected_importance_lvl,")"); //--- Log removal break; } } } else if (btn_state == true) { //--- If the button is selected Print("BUTTON IS IN SELECTED MODE. TAKE ACTION"); //--- Check for duplicates bool already_selected = false; for (int j = 0; j < ArraySize(imp_filter_selected); j++) { if (impact_filter_selected[j] == selected_imp) { already_selected = true; break; } } //--- If not already selected, add to the array if (!already_selected) { ArrayResize(imp_filter_selected, ArraySize(imp_filter_selected) + 1); //--- Resize the array imp_filter_selected[ArraySize(imp_filter_selected) - 1] = selected_importance_lvl; //--- Add the new importance level ArrayResize(impact_filter_selected, ArraySize(impact_filter_selected) + 1); //--- Resize the array impact_filter_selected[ArraySize(impact_filter_selected) - 1] = selected_imp; //--- Add the new importance level Print("Added to selected importance filters: ", selected_imp,"(",selected_importance_lvl,")"); //--- Log addition } else { Print("Importance level already selected: ", selected_imp,"(",selected_importance_lvl,")"); //--- Log already selected } } Print("SELECTED ARRAY SIZE = ", ArraySize(imp_filter_selected)," >< ",ArraySize(impact_filter_selected)); //--- Log the size of the selected array ArrayPrint(imp_filter_selected); //--- Print the selected array ArrayPrint(impact_filter_selected); update_dashboard_values(curr_filter_selected,imp_filter_selected); //--- Update the dashboard with the selected filters ObjectSetInteger(0,sparam,OBJPROP_BORDER_COLOR,color_border); Print("SUCCESS. DASHBOARD UPDATED"); //--- Log success ChartRedraw(0); //--- Redraw the chart to reflect changes }
这里,我们首先使用StringFind判断被点击的是否为重要性过滤按钮。该函数检查被点击按钮的名称(由"sparam"表示)是否包含字符串“IMPACT_LABEL”。如果包含,我们会继续调用ObjectGetString函数并传入文本属性,获取按钮上的文字(例如 “Low”、“Medium” 等)。随后,我们将该文字转换为对应的枚举值(如CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_LOW), 这是通过将所选标签传递给函数“get_importance_level(impact_labels, allowed_importance_levels, selected_imp)”来完成。该函数接收标签数组、允许的枚举值数组以及用户选中的文本标签,返回相应的枚举重要性级别。稍后我们会详细介绍这个自定义函数。
接下来,我们使用ObjectGetInteger函数并传入状态属性,检查按钮当前是选中(true)还是未选中(false)。根据该状态,我们对过滤数组执行“添加”或“移除”操作。若按钮变为未选中, 遍历"imp_filter_selected"数组,移除对应的重要性级别,并通过ArrayResize 函数调整数组长度。我们也会"impact_filter_selected"数组执行同样地操作,保持两个数组同步。若按钮变为选中,我们先通过循环检查该重要性级别是否已存在于过滤数组。如果不存在,则分别扩展两个数组并将新值追加到末尾。
数组更新完毕后,我们调用ArrayPrint函数记录过滤数组的当前内容,方便调试。随后,我们通过调用"update_dashboard_values(curr_filter_selected, imp_filter_selected) "函数,将新筛选条件同步至仪表盘,使筛选数组的变更实时反映在界面上。更新后的该函数现已支持两个数组参数,以实时反映用户偏好。我们将在稍后详细查看。最后,根据按钮是否被选中,计算出对应颜色并设置其边框颜色,从而更新按钮外观。随后调用ChartRedraw函数重绘图表,确保视觉效果即时生效。
现在我们来看一下负责获取对应的重要性枚举值的自定义函数。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Function to get the importance level based on the selected label | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_IMPORTANCE get_importance_level(string &impact_label[], ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_IMPORTANCE &importance_levels[], string selected_label) { // Loop through the impact_labels array to find the matching label for (int i = 0; i < ArraySize(impact_label); i++) { if (impact_label[i] == selected_label) { // Return the corresponding importance level return importance_levels[i]; } } // If no match found, return CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_NONE as the default return CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_NONE; }
这里,我们定义了一个枚举转换函数"get_importance_level",根据用户选中的标签返回对应的重要性级别。该函数接收三个参数:
- "impact_label":字符串数组,存放各影响程度级别标签(如 “None”、“Low”、“Medium”和“High”)。
- "importance_levels":存放对应重要性级别的枚举值的数组(如CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_NONE、CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_LOW 等)。
- "selected_label":传递给函数的标签字符串,代表用户选择的重要性级别(例如 “Medium”)。
函数内部使用 for循环遍历"impact_label"数组。对于每次迭代,我们都会检查数组中的当前项是否与“selected_label”匹配。如果匹配成功,则从"importance_levels" 数组中返回相同索引位置对应的重要性级别值。如果遍历所有标签后仍未找到匹配项,函数将默认返回CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_NONE。我们需要此函数来实现将用户选择的影响程度级别的字符串(如"Medium")转换为对应的重要性级别枚举值(如CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_MODERATE)的功能。
其他修改包括:将更新后的重要性筛选条件数组以引用传递的方式传入更新函数,使得筛选器能够根据用户的最新偏好动态生效。当前函数声明如下方代码段所示:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Function to update dashboard values | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void update_dashboard_values(string &curr_filter_array[], ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_IMPORTANCE &imp_filter_array[]){ //--- }
在完成该函数更新后,需同步重构其他同类函数,使其集成重要性筛选数组的处理逻辑。例如,“OnInit”事件处理函数的调用方式如下所示。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick(){ //--- if (isDashboardUpdate){ update_dashboard_values(curr_filter_selected,imp_filter_selected); } }
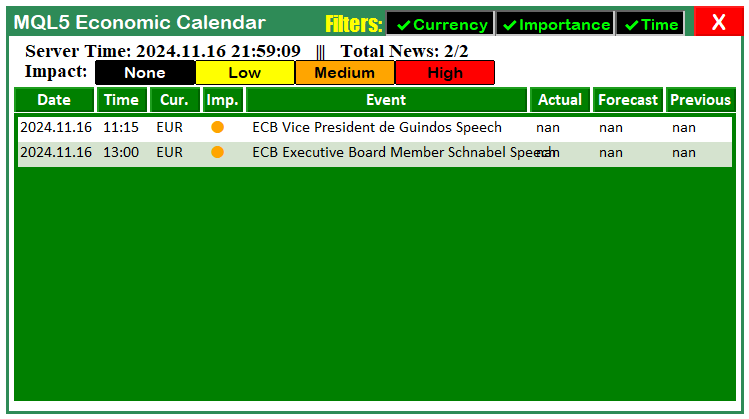
至此,我们已完成货币过滤器与重要性过滤器的全部集成。现在让我们查看当前阶段的成果,以确认重要性过滤器也如预期般正常工作。
由可视化结果可见,我们已成功实现了按重要性过滤的动态响应目标。最后,我们还可以更新所显示的事件信息。具体包括:过滤后的事件数量、图表上能够显示的总事件数上限和纳入统计的全部事件总数。以下是我们用来实现以上这些的逻辑。在全局作用域,我们可以定义若干用于跟踪的变量。
int totalEvents_Considered = 0; int totalEvents_Filtered = 0; int totalEvents_Displayable = 0;
在此,我们定义三个整型变量:"totalEvents_Considered"、"totalEvents_Filtered"和"totalEvents_Displayable"。这些变量将作为计数器,用于在处理过程中跟踪事件的状态:
- "totalEvents_Considered":记录在处理流程中最初纳入被考虑的事件总数。在任何过滤条件生效前,所有事件都被计算在内,作为起点。
- "totalEvents_Filtered":统计因满足过滤条件(货币、重要性、时间等)而被剔除的事件数量。它代表有多少事件被从数据集中被移除。
- "totalEvents_Displayable":记录过滤后仍保留、可以最终呈现在仪表盘上的事件数量。它代表符合全部过滤条件、可供呈现的最终版事件集合。
利用这三个计数器,我们能够监控并分析整个事件处理流程,确保过滤逻辑按预期工作,同时为数据流向提供清晰的脉络。接下来,在任何数据过滤开始之前,先将它们全部初始化为 0。
totalEvents_Displayable = 0; totalEvents_Filtered = 0; totalEvents_Considered = 0;
在进入首个循环前,需用最新值覆盖历史值,以确保所有事件均被纳入计算范围。具体示例如下:
//--- Loop through each calendar value up to the maximum defined total for (int i = 0; i < allValues; i++){ //--- }
我们不提前应用限制条件,而是先统计所有事件。这样可以完整显示溢出数据。因此在循环内部,将采用以下更新逻辑:
//--- Loop through each calendar value up to the maximum defined total for (int i = 0; i < allValues; i++){ MqlCalendarEvent event; //--- Declare event structure CalendarEventById(values[i].event_id,event); //--- Retrieve event details by ID //--- Other declarations totalEvents_Considered++; //--- Check if the event’s currency matches any in the filter array (if the filter is enabled) bool currencyMatch = false; if (enableCurrencyFilter) { for (int j = 0; j < ArraySize(curr_filter); j++) { if (country.currency == curr_filter[j]) { currencyMatch = true; break; } } //--- If no match found, skip to the next event if (!currencyMatch) { continue; } } //--- Other filters //--- If we reach here, the filters passed totalEvents_Filtered++; //--- Restrict the number of displayable events to a maximum of 11 if (totalEvents_Displayable >= 11) { continue; // Skip further processing if display limit is reached } //--- Increment total displayable events totalEvents_Displayable++; //--- Set alternating colors for data holders color holder_color = (totalEvents_Displayable % 2 == 0) ? C'213,227,207' : clrWhite; //--- Create rectangle label for the data holder createRecLabel(DATA_HOLDERS + string(totalEvents_Displayable), 62, startY - 1, 716, 26 + 1, holder_color, 1, clrNONE); //--- Initialize starting x-coordinate for each data entry int startX = 65; //--- Loop through calendar data columns for (int k=0; k<ArraySize(array_calendar); k++){ //--- Prepare news data array with time, country, and other event details string news_data[ArraySize(array_calendar)]; news_data[0] = TimeToString(values[i].time,TIME_DATE); //--- Event date news_data[1] = TimeToString(values[i].time,TIME_MINUTES); //--- Event time news_data[2] = country.currency; //--- Event country currency //--- Other fills and creations } ArrayResize(current_eventNames_data,ArraySize(current_eventNames_data)+1); current_eventNames_data[ArraySize(current_eventNames_data)-1] = event.name; //--- Increment y-coordinate for the next row of data startY += 25; } Print("CURRENT EVENT NAMES DATA SIZE = ",ArraySize(current_eventNames_data)); //--- Other logs updateLabel(TIME_LABEL,"Server Time: "+TimeToString(TimeCurrent(), TIME_DATE|TIME_SECONDS)+" ||| Total News: "+ IntegerToString(totalEvents_Displayable)+"/"+IntegerToString(totalEvents_Filtered)+"/"+IntegerToString(totalEvents_Considered)); //---
这里,我们只需同步更新事件计数器。需要特别注意以浅蓝色高亮的那段代码。其逻辑与过滤器一致:一旦达到可显示上限,则跳过后续处理。最后,我们将这三个计数值一并写入标签,方便日后查看数据溢出量。随后,在更新函数中也应用同样逻辑,确保实时同步。运行系统后,显示效果如下:
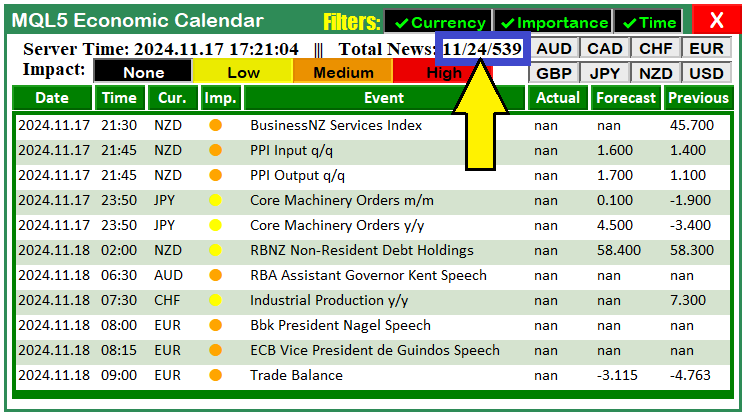
由上图可见,我们现在得到了3个新闻计数。第一个数字(本例中为11)表示可显示新闻总数;第二个数字24表示经筛选后的事件总数,只是仪表盘无法全部展示;第三个数字539代表可以纳入处理的新闻总数。至此,为启用时间过滤器,我们可以把期望的时间范围设为输入格式,以便在程序初始化时进行设定。实现该功能的逻辑如下:
sinput group "General Calendar Settings" input ENUM_TIMEFRAMES start_time = PERIOD_H12; input ENUM_TIMEFRAMES end_time = PERIOD_H12; input ENUM_TIMEFRAMES range_time = PERIOD_H8;
这里,我们定义一个名为 “General Calendar Settings” 的组,用于提供与日历相关的可配置选项。我们使用三个ENUM_TIMEFRAMES类型的输入参数,来控制过滤或分析日历事件时所处的时间范围。首先,我们定义 “start_time”,用于指定日历事件时间范围的起始点,默认值为12小时("PERIOD_H12")。
接着,我们引入 “end_time”,用于标记该时间范围的终点,同样默认设为 “PERIOD_H12”。最后,我们使用 “range_time” 来设定日历过滤或计算所需的时间跨度,默认值为8小时("PERIOD_H8")。这样一来,程序可依据用户自定义的时间框架灵活运行,使日历数据适配特定关注区间。这些设置实现了动态过滤,并赋予用户对显示或分析事件时间范围的全权掌控。
为使更改生效,我们将这些参数分别添加到对应承载函数与控制逻辑的输入项中,如下所示:
//--- Define start and end time for calendar event retrieval datetime startTime = TimeTradeServer() - PeriodSeconds(start_time); datetime endTime = TimeTradeServer() + PeriodSeconds(end_time); //--- Define time range for filtering news events based on daily period datetime timeRange = PeriodSeconds(range_time); datetime timeBefore = TimeTradeServer() - timeRange; datetime timeAfter = TimeTradeServer() + timeRange;
以上这些就是全部。编译后,我们得到以下输出。
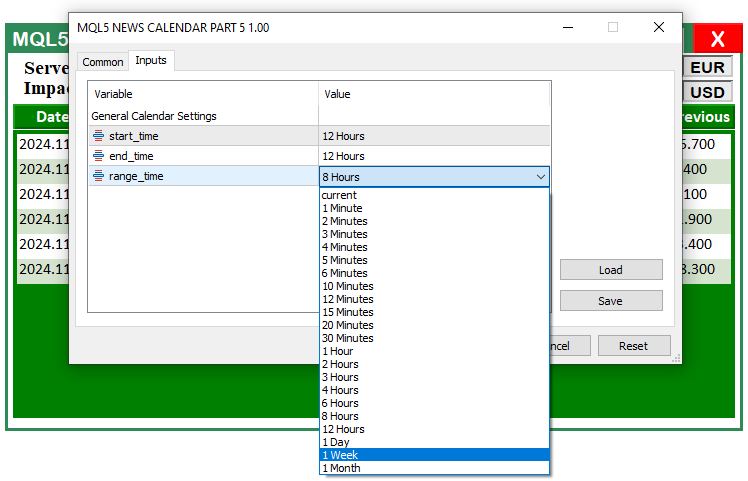
由上图可见,我们现在已经能够访问输入参数,并通过下拉列表启用所需的时间设置。至此,仪表盘完全可用且实时响应。接下来只需在各种条件与环境中进行测试,确保运行无误,如果发现问题,则加以修正。这将在下一部分中完成。
测试增强型仪表盘
在本节中,我们对增强型仪表盘进行了全面测试。目标是验证所有过滤器、事件跟踪及数据显示机制均能按预期运行。我们已实现货币、重要性与时间等多级过滤器,以便更高效地查看和分析日历事件。
测试仪表盘过程模拟用户操作:启用/禁用各类过滤器,并确保日历事件根据所选条件实时更新。同时验证事件数据(国家、货币、重要性级别、事件时间等)是否在指定时间范围内正确呈现。
经过多场景测试,逐一确认各功能:基于重要性或货币过滤事件、限制显示数量、数据标签即时更新等,均表现正常。下方视频展示了这些测试的运行过程。
结论
我们已成功完成增强型MQL5经济日历仪表盘的开发与测试,验证了过滤器、数据可视化及事件追踪系统的无缝协同能力。该仪表盘通过直观的界面追踪经济事件,可按货币、重要性与时间进行过滤,帮助我们随时掌握信息并依据市场数据做出决策。
接下来,在本系列的下一部分,我们将以此为基础,进一步整合信号生成与交易功能。通过充分利用增强型仪表盘的数据,我们将开发一套能够根据经济事件与市场状况自动生成交易信号的系统,从而实现更高效、更明智的交易策略。请您持续关注。
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/16404
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 交易中的神经网络:双曲型潜在扩散模型(终篇)
交易中的神经网络:双曲型潜在扩散模型(终篇)
 MQL5 交易工具包(第 3 部分):开发挂单管理 EX5 库
MQL5 交易工具包(第 3 部分):开发挂单管理 EX5 库
 在MQL5中创建交易管理员面板(第八部分):分析面板
在MQL5中创建交易管理员面板(第八部分):分析面板
 群体自适应矩估计(ADAM)优化算法
群体自适应矩估计(ADAM)优化算法