探索达瓦斯箱体突破策略中的高级机器学习技术
概述
达瓦斯箱体突破策略由尼古拉斯·达瓦斯(Nicolas Darvas)提出,是一种技术交易方法:当股价突破预设的"箱体"区间上沿时,视为潜在买入信号,表明强劲的上升动能。本文将以该策略为例,探讨三种高级机器学习技术的应用。其中包括:利用机器学习模型直接生成交易信号(而非仅过滤交易);采用连续型信号(而非离散型信号);使用基于不同时间框架训练的模型进行交易验证。这些方法为机器学习如何突破传统实践、提升算法交易效能提供了全新视角。
本文将深入探讨三种教育领域鲜少提及的高级技术背后的特征与理论,因其相较于传统方法更具创新性。同时,文章还将就模型训练过程中的特征工程和超参数调优等高级主题提供独到见解。然而,本文不会详细阐述机器学习模型训练流程的每一个步骤。对于对跳过步骤感兴趣的读者,请点击此文章链接查看完整实现过程。
信号生成
机器学习主要分为三种类型:监督学习、无监督学习和强化学习。在量化交易中,交易者主要使用监督学习,原因主要有两点。 - 无监督学习往往过于基础,难以捕捉交易结果与市场特征之间的复杂关系。由于缺乏标签,它难以与预测目标保持一致,更适合用于预测间接数据,而非交易策略的直接结果。
- 强化学习需要构建一个带有奖励函数的训练环境,旨在实现长期利润最大化,而非关注单个预测的准确性。这种方法在预测结果这一简单任务上设置复杂,对于散户交易者而言成本效益较低。
尽管如此,监督学习在算法交易中仍有许多应用。一种常见的方法是将其用作过滤器:先从一个能生成大量样本的原始策略入手,然后训练一个模型来识别该策略可能成功或失败的情况。模型的置信度有助于过滤掉模型预测会亏损的交易。
另一种方法(也是本文将探讨的方法)是使用监督学习生成信号。对于预测价格等典型的回归任务,操作很简单——当模型预测价格上涨时买入,预测价格下跌时卖出。但是如何将这种方法与达瓦斯箱体突破等核心策略相结合?
首先,我们将开发一个智能交易系统(EA),用于收集后续在Python中训练模型所需的特征数据和标签数据。
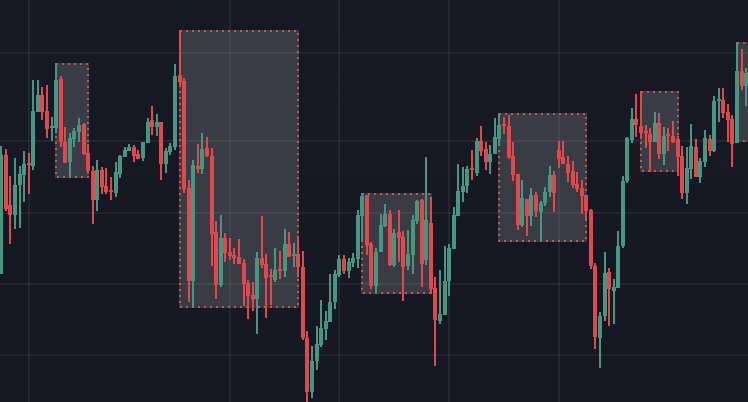
达瓦斯箱体突破策略通过一系列高点或低点后的拒绝K线来定义箱体,当价格突破该范围时触发交易。无论哪种情况,我们都需要一个信号来开始收集特征数据并预测未来结果。因此,我们将触发条件设定为价格突破箱体下限或上限的时刻。此函数用于检测给定回溯期和确认K线数量下是否存在达瓦斯箱体,将高低范围值分配给变量,并在图表上绘制箱体。
double high; double low; bool boxFormed = false; bool DetectDarvasBox(int n = 100, int M = 3) { // Clear previous Darvas box objects for (int k = ObjectsTotal(0, 0, -1) - 1; k >= 0; k--) { string name = ObjectName(0, k); if (StringFind(name, "DarvasBox_") == 0) ObjectDelete(0, name); } bool current_box_active = false; // Start checking from the oldest bar within the lookback period for (int i = M+1; i <= n; i++) { // Get high of current bar and previous bar double high_current = iHigh(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, i); double high_prev = iHigh(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, i + 1); // Check for a new high if (high_current > high_prev) { // Check if the next M bars do not exceed the high bool pullback = true; for (int k = 1; k <= M; k++) { if (i - k < 0) // Ensure we don't go beyond available bars { pullback = false; break; } double high_next = iHigh(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, i - k); if (high_next > high_current) { pullback = false; break; } } // If pullback condition is met, define the box if (pullback) { double top = high_current; double bottom = iLow(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, i); // Find the lowest low over the bar and the next M bars for (int k = 1; k <= M; k++) { double low_next = iLow(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, i - k); if (low_next < bottom) bottom = low_next; } // Check for breakout from i - M - 1 to the current bar (index 0) int j = i - M - 1; while (j >= 0) { double close_j = iClose(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, j); if (close_j > top || close_j < bottom) break; // Breakout found j--; } j++; // Adjust to the bar after breakout (or 0 if no breakout) // Create a unique object name string obj_name = "DarvasBox_" + IntegerToString(i); // Plot the box datetime time_start = iTime(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, i); datetime time_end; if (j > 0) { // Historical box: ends at breakout time_end = iTime(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, j); } else { // Current box: extends to the current bar time_end = iTime(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 0); current_box_active = true; } high = top; low = bottom; ObjectCreate(0, obj_name, OBJ_RECTANGLE, 0, time_start, top, time_end, bottom); ObjectSetInteger(0, obj_name, OBJPROP_COLOR, clrBlue); ObjectSetInteger(0, obj_name, OBJPROP_STYLE, STYLE_SOLID); ObjectSetInteger(0, obj_name, OBJPROP_WIDTH, 1); boxFormed = true; // Since we're only plotting the most recent box, break after finding it break; } } } return current_box_active; }
以下是图表中达瓦斯箱体的部分示例:
与将其用作过滤器的方法相比,这种方法存在缺点。我们需要预测结果均衡且概率相等的情况,例如判断接下来的10根K线是上涨还是下跌,或者价格是先上涨10个点还是先下跌10个点。另一个缺点是,我们失去了核心策略本身所具备的优势——此时的优势完全取决于模型的预测能力。不过,其优势在于,您不再受限于核心策略仅在触发时提供的样本,这样您可以获得更大的初始样本量,并且有更大的潜在上行空间。我们在onTick()函数中实现交易逻辑,如下所示:
input int checkBar = 30; input int lookBack = 100; input int countMax = 10; void OnTick() { int bars = iBars(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT); if (barsTotal!= bars){ barsTotal = bars; boxFormed = false; bool NotInPosition = true; lastClose = iClose(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 1); lastlastClose = iClose(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,2); for(int i = 0; i<PositionsTotal(); i++){ ulong pos = PositionGetTicket(i); string symboll = PositionGetSymbol(i); if(PositionGetInteger(POSITION_MAGIC) == Magic&&symboll== _Symbol)NotInPosition = false;} /*count++; if(count >=countMax ){ trade.PositionClose(pos); count = 0;} }}*/ DetectDarvasBox(lookBack,checkBar); if (NotInPosition&&boxFormed&&((lastlastClose<high&&lastClose>high)||(lastClose<low&&lastlastClose>low)))executeBuy(); } }
对于该策略而言,采用相同的止盈和止损幅度,比追踪接下来10根K线的结果更具一致性。前者将我们的预测直接与最终盈利挂钩,而后者则因每10根K线周期内的收益波动而增加了不确定性。值得注意的是,我们将止盈和止损设置为价格的一定百分比,这样能更好地适应不同资产,也更适合黄金或指数等趋势性资产。读者可以通过取消被注释代码的注释,并从买入函数中移除止盈和止损设置,来测试替代方案。
对于用作预测结果的特征数据,我选择了过去三个标准化收益率、与箱体高低点的标准化距离,以及一些常见的平稳指标。我们将这些数据存储在一个多维数组中,然后使用包含文件中的CFileCSV类将其保存到CSV文件中。请确保按照以下列表设置所有时间周期和交易品种,以便轻松切换不同时间周期和资产。string data[50000][12]; int indexx = 0; void getData(){ double close = iClose(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,1); double close2 = iClose(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,2); double close3 = iClose(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,3); double stationary = 1000*(close-iOpen(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,1))/close; double stationary2 = 1000*(close2-iOpen(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,2))/close2; double stationary3 = 1000*(close3-iOpen(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,3))/close3; double highDistance = 1000*(close-high)/close; double lowDistance = 1000*(close-low)/close; double boxSize = 1000*(high-low)/close; double adx[]; // Average Directional Movement Index double wilder[]; // Average Directional Movement Index by Welles Wilder double dm[]; // DeMarker double rsi[]; // Relative Strength Index double rvi[]; // Relative Vigor Index double sto[]; // Stochastic Oscillator CopyBuffer(handleAdx, 0, 1, 1, adx); // Average Directional Movement Index CopyBuffer(handleWilder, 0, 1, 1, wilder); // Average Directional Movement Index by Welles Wilder CopyBuffer(handleDm, 0, 1, 1, dm); // DeMarker CopyBuffer(handleRsi, 0, 1, 1, rsi); // Relative Strength Index CopyBuffer(handleRvi, 0, 1, 1, rvi); // Relative Vigor Index CopyBuffer(handleSto, 0, 1, 1, sto); // Stochastic Oscillator //2 means 2 decimal places data[indexx][0] = DoubleToString(adx[0], 2); // Average Directional Movement Index data[indexx][1] = DoubleToString(wilder[0], 2); // Average Directional Movement Index by Welles Wilder data[indexx][2] = DoubleToString(dm[0], 2); // DeMarker data[indexx][3] = DoubleToString(rsi[0], 2); // Relative Strength Index data[indexx][4] = DoubleToString(rvi[0], 2); // Relative Vigor Index data[indexx][5] = DoubleToString(sto[0], 2); // Stochastic Oscillator data[indexx][6] = DoubleToString(stationary,2); data[indexx][7] = DoubleToString(boxSize,2); data[indexx][8] = DoubleToString(stationary2,2); data[indexx][9] = DoubleToString(stationary3,2); data[indexx][10] = DoubleToString(highDistance,2); data[indexx][11] = DoubleToString(lowDistance,2); indexx++; }
数据获取型EA的最终代码将如下所示:
#include <Trade/Trade.mqh> CTrade trade; #include <FileCSV.mqh> CFileCSV csvFile; string fileName = "box.csv"; string headers[] = { "Average Directional Movement Index", "Average Directional Movement Index by Welles Wilder", "DeMarker", "Relative Strength Index", "Relative Vigor Index", "Stochastic Oscillator", "Stationary", "Box Size", "Stationary2", "Stationary3", "Distance High", "Distance Low" }; input double lott = 0.01; input int Magic = 0; input int checkBar = 30; input int lookBack = 100; input int countMax = 10; input double slp = 0.003; input double tpp = 0.003; input bool saveData = true; string data[50000][12]; int indexx = 0; int barsTotal = 0; int count = 0; double high; double low; bool boxFormed = false; double lastClose; double lastlastClose; int handleAdx; // Average Directional Movement Index - 3 int handleWilder; // Average Directional Movement Index by Welles Wilder - 3 int handleDm; // DeMarker - 1 int handleRsi; // Relative Strength Index - 1 int handleRvi; // Relative Vigor Index - 2 int handleSto; // Stochastic Oscillator - 2 int OnInit() { trade.SetExpertMagicNumber(Magic); handleAdx=iADX(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,14);//Average Directional Movement Index - 3 handleWilder=iADXWilder(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,14);//Average Directional Movement Index by Welles Wilder - 3 handleDm=iDeMarker(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,14);//DeMarker - 1 handleRsi=iRSI(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,14,PRICE_CLOSE);//Relative Strength Index - 1 handleRvi=iRVI(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,10);//Relative Vigor Index - 2 handleSto=iStochastic(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,5,3,3,MODE_SMA,STO_LOWHIGH);//Stochastic Oscillator - 2 return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } void OnDeinit(const int reason) { if (!saveData) return; if(csvFile.Open(fileName, FILE_WRITE|FILE_ANSI)) { //Write the header csvFile.WriteHeader(headers); //Write data rows csvFile.WriteLine(data); //Close the file csvFile.Close(); } else { Print("File opening error!"); } } void OnTick() { int bars = iBars(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT); if (barsTotal!= bars){ barsTotal = bars; boxFormed = false; bool NotInPosition = true; lastClose = iClose(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 1); lastlastClose = iClose(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,2); for(int i = 0; i<PositionsTotal(); i++){ ulong pos = PositionGetTicket(i); string symboll = PositionGetSymbol(i); if(PositionGetInteger(POSITION_MAGIC) == Magic&&symboll== _Symbol)NotInPosition = false;} /*count++; if(count >=countMax ){ trade.PositionClose(pos); count = 0;} }}*/ DetectDarvasBox(lookBack,checkBar); if (NotInPosition&&boxFormed&&((lastlastClose<high&&lastClose>high)||(lastClose<low&&lastlastClose>low)))executeBuy(); } } void executeBuy() { double ask = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_ASK); ask = NormalizeDouble(ask,_Digits); double sl = lastClose*(1-slp); double tp = lastClose*(1+tpp); trade.Buy(lott,_Symbol,ask,sl,tp); if(PositionsTotal()>0)getData(); } bool DetectDarvasBox(int n = 100, int M = 3) { // Clear previous Darvas box objects for (int k = ObjectsTotal(0, 0, -1) - 1; k >= 0; k--) { string name = ObjectName(0, k); if (StringFind(name, "DarvasBox_") == 0) ObjectDelete(0, name); } bool current_box_active = false; // Start checking from the oldest bar within the lookback period for (int i = M+1; i <= n; i++) { // Get high of current bar and previous bar double high_current = iHigh(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, i); double high_prev = iHigh(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, i + 1); // Check for a new high if (high_current > high_prev) { // Check if the next M bars do not exceed the high bool pullback = true; for (int k = 1; k <= M; k++) { if (i - k < 0) // Ensure we don't go beyond available bars { pullback = false; break; } double high_next = iHigh(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, i - k); if (high_next > high_current) { pullback = false; break; } } // If pullback condition is met, define the box if (pullback) { double top = high_current; double bottom = iLow(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, i); // Find the lowest low over the bar and the next M bars for (int k = 1; k <= M; k++) { double low_next = iLow(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, i - k); if (low_next < bottom) bottom = low_next; } // Check for breakout from i - M - 1 to the current bar (index 0) int j = i - M - 1; while (j >= 0) { double close_j = iClose(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, j); if (close_j > top || close_j < bottom) break; // Breakout found j--; } j++; // Adjust to the bar after breakout (or 0 if no breakout) // Create a unique object name string obj_name = "DarvasBox_" + IntegerToString(i); // Plot the box datetime time_start = iTime(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, i); datetime time_end; if (j > 0) { // Historical box: ends at breakout time_end = iTime(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, j); } else { // Current box: extends to the current bar time_end = iTime(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 0); current_box_active = true; } high = top; low = bottom; ObjectCreate(0, obj_name, OBJ_RECTANGLE, 0, time_start, top, time_end, bottom); ObjectSetInteger(0, obj_name, OBJPROP_COLOR, clrBlue); ObjectSetInteger(0, obj_name, OBJPROP_STYLE, STYLE_SOLID); ObjectSetInteger(0, obj_name, OBJPROP_WIDTH, 1); boxFormed = true; // Since we're only plotting the most recent box, break after finding it break; } } } return current_box_active; } void getData(){ double close = iClose(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,1); double close2 = iClose(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,2); double close3 = iClose(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,3); double stationary = 1000*(close-iOpen(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,1))/close; double stationary2 = 1000*(close2-iOpen(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,2))/close2; double stationary3 = 1000*(close3-iOpen(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,3))/close3; double highDistance = 1000*(close-high)/close; double lowDistance = 1000*(close-low)/close; double boxSize = 1000*(high-low)/close; double adx[]; // Average Directional Movement Index double wilder[]; // Average Directional Movement Index by Welles Wilder double dm[]; // DeMarker double rsi[]; // Relative Strength Index double rvi[]; // Relative Vigor Index double sto[]; // Stochastic Oscillator CopyBuffer(handleAdx, 0, 1, 1, adx); // Average Directional Movement Index CopyBuffer(handleWilder, 0, 1, 1, wilder); // Average Directional Movement Index by Welles Wilder CopyBuffer(handleDm, 0, 1, 1, dm); // DeMarker CopyBuffer(handleRsi, 0, 1, 1, rsi); // Relative Strength Index CopyBuffer(handleRvi, 0, 1, 1, rvi); // Relative Vigor Index CopyBuffer(handleSto, 0, 1, 1, sto); // Stochastic Oscillator //2 means 2 decimal places data[indexx][0] = DoubleToString(adx[0], 2); // Average Directional Movement Index data[indexx][1] = DoubleToString(wilder[0], 2); // Average Directional Movement Index by Welles Wilder data[indexx][2] = DoubleToString(dm[0], 2); // DeMarker data[indexx][3] = DoubleToString(rsi[0], 2); // Relative Strength Index data[indexx][4] = DoubleToString(rvi[0], 2); // Relative Vigor Index data[indexx][5] = DoubleToString(sto[0], 2); // Stochastic Oscillator data[indexx][6] = DoubleToString(stationary,2); data[indexx][7] = DoubleToString(boxSize,2); data[indexx][8] = DoubleToString(stationary2,2); data[indexx][9] = DoubleToString(stationary3,2); data[indexx][10] = DoubleToString(highDistance,2); data[indexx][11] = DoubleToString(lowDistance,2); indexx++; }
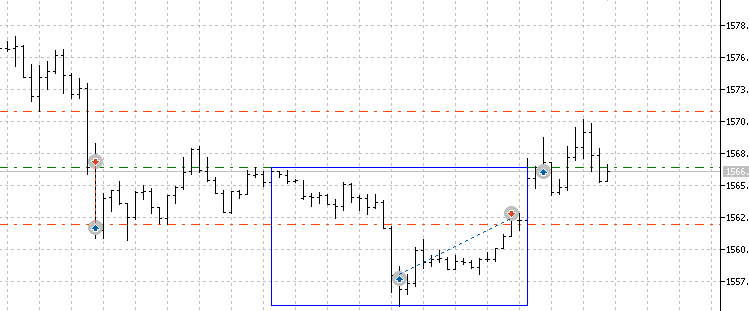
我们打算在黄金兑美元(XAUUSD)15分钟时间框架下运用该策略进行交易,原因在于该资产波动性平稳,且15分钟周期既能有效降低市场噪音,又能生成足够多的交易样本。一次典型交易示例如下:
我们使用2020年至2024年的数据作为训练数据和验证数据,后续将在MetaTrader 5终端中对2024年至2025年的数据进行测试。在策略测试器中运行该EA后,CSV文件将在EA去初始化后保存至/Tester/Agent-sth000目录中。
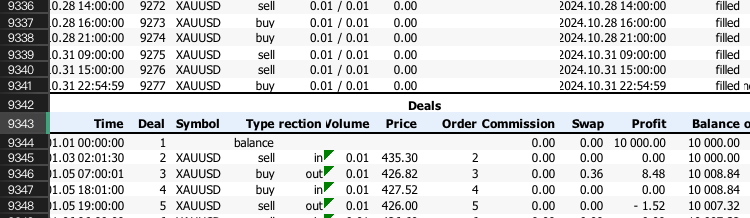
此外,右键单击可获取类似以下的回测Excel报告:
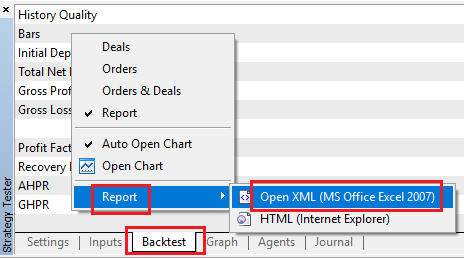
请注意“交易(Deals)”所在行的行号,我们后续将使用该行号作为输入。
之后,我们使用python训练模型。
本文所选模型是基于决策树的模型,这类模型非常适合处理分类问题,正如我们在本文中所使用的模型一样。
import pandas as pd # Replace 'your_file.xlsx' with the path to your file input_file = 'box.xlsx' # Load the Excel file and skip the first {skiprows} rows data1 = pd.read_excel(input_file, skiprows=4417) # Select the 'profit' column (assumed to be 'Unnamed: 10') and filter rows as per your instructions profit_data = data1["Profit"][1:-1] profit_data = profit_data[profit_data.index % 2 == 0] # Filter for rows with odd indices profit_data = profit_data.reset_index(drop=True) # Reset index # Convert to float, then apply the condition to set values to 1 if > 0, otherwise to 0 profit_data = pd.to_numeric(profit_data, errors='coerce').fillna(0) # Convert to float, replacing NaN with 0 profit_data = profit_data.apply(lambda x: 1 if x > 0 else 0) # Apply condition # Load the CSV file with semicolon separator file_path = 'box.csv' data2 = pd.read_csv(file_path, sep=';') # Drop rows with any missing or incomplete values data2.dropna(inplace=True) # Drop any duplicate rows if present data2.drop_duplicates(inplace=True) # Convert non-numeric columns to numerical format for col in data2.columns: if data2[col].dtype == 'object': # Convert categorical to numerical using label encoding data2[col] = data2[col].astype('category').cat.codes # Ensure all remaining columns are numeric and cleanly formatted for CatBoost data2 = data2.apply(pd.to_numeric, errors='coerce') data2.dropna(inplace=True) # Drop any rows that might still contain NaNs after conversion # Merge the two DataFrames on the index merged_data = pd.merge(profit_data, data2, left_index=True, right_index=True, how='inner') # Save the merged data to a new CSV file output_csv_path = 'merged_data.csv' merged_data.to_csv(output_csv_path) print(f"Merged data saved to {output_csv_path}")我们使用此段代码对Excel回测报告进行标签标注,将盈利的交易标记为1,未盈利的交易标记为0。随后,我们将这些标签数据与从数据获取型EA生成的CSV文件中收集的特征数据进行合并。请注意,skiprow参数的值需与“Deals”所在行的行号一致。
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import warnings warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") data = pd.read_csv("merged_data.csv",index_col=0) XX = data.drop(columns=['Profit']) yy = data['Profit'] y = yy.values X = XX.values pd.DataFrame(X,y)
接下来,我们将标签数组赋值给变量y,将特征数据帧赋值给变量X。
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import warnings import seaborn as sns warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split import catboost as cb from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, roc_auc_score import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Split data X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.1, shuffle=False) # Identify categorical features cat_feature_indices = [i for i, col in enumerate(XX.columns) if XX[col].dtype == 'object'] # Train CatBoost classifier model = cb.CatBoostClassifier( iterations=5000, # Number of trees (similar to n_estimators) learning_rate=0.02, # Learning rate depth=5, # Depth of each tree l2_leaf_reg=5, bagging_temperature=1, early_stopping_rounds=50, loss_function='Logloss', # Use 'MultiClass' if it's a multi-class problem verbose=1000) model.fit(X_train, y_train, cat_features=cat_feature_indices)
接着,我们将数据按9:1的比例划分为训练集和验证集,并开始训练模型。在sklearn中,train-test_split函数的默认设置包含数据打乱操作,这对于时间序列数据并不理想,因此务必在参数中设置shuffle=False。根据样本量大小,调整超参数以避免过拟合或欠拟合是个不错的主意。就我个人经验而言,当对数损失降至约0.1时停止迭代效果较好。
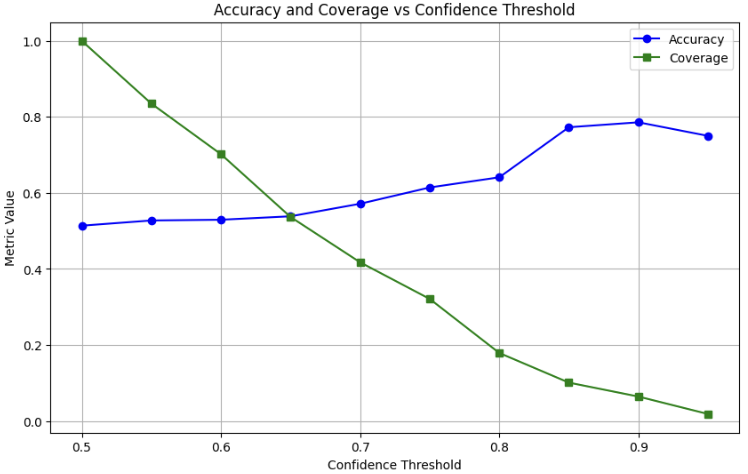
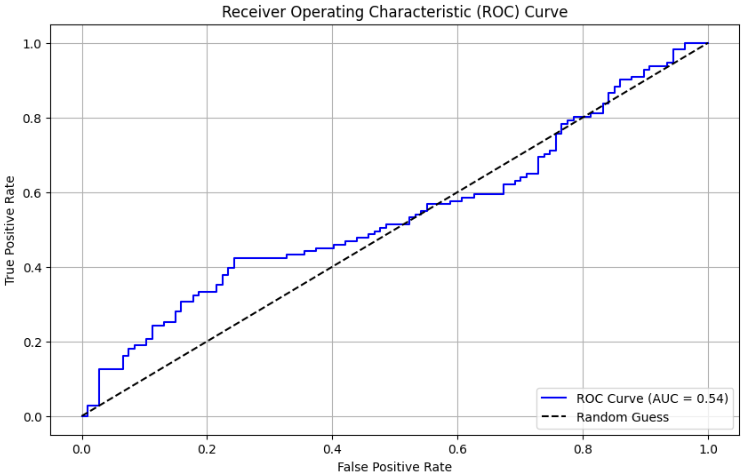
import numpy as np from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, roc_auc_score import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Assuming you already have y_test, X_test, and model defined # Predict probabilities y_prob = model.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1] # Probability for positive class # Compute ROC curve and AUC (for reference) fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_test, y_prob) auc_score = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_prob) print(f"AUC Score: {auc_score:.2f}") # Define confidence thresholds to test (e.g., 50%, 60%, 70%, etc.) confidence_thresholds = np.arange(0.5, 1.0, 0.05) # From 50% to 95% in steps of 5% accuracies = [] coverage = [] # Fraction of samples classified at each threshold for thresh in confidence_thresholds: # Classify only when probability is >= thresh (positive) or <= (1 - thresh) (negative) y_pred_confident = np.where(y_prob >= thresh, 1, np.where(y_prob <= (1 - thresh), 0, -1)) # Filter out unclassified samples (where y_pred_confident == -1) mask = y_pred_confident != -1 y_test_confident = y_test[mask] y_pred_confident = y_pred_confident[mask] # Calculate accuracy and coverage if len(y_test_confident) > 0: # Avoid division by zero acc = np.mean(y_pred_confident == y_test_confident) cov = len(y_test_confident) / len(y_test) else: acc = 0 cov = 0 accuracies.append(acc) coverage.append(cov) # Plot Accuracy vs Confidence Threshold plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) plt.plot(confidence_thresholds, accuracies, marker='o', label='Accuracy', color='blue') plt.plot(confidence_thresholds, coverage, marker='s', label='Coverage', color='green') plt.xlabel('Confidence Threshold') plt.ylabel('Metric Value') plt.title('Accuracy and Coverage vs Confidence Threshold') plt.legend(loc='best') plt.grid(True) plt.show() # Also show the original ROC curve for reference plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) plt.plot(fpr, tpr, label=f'ROC Curve (AUC = {auc_score:.2f})', color='blue') plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], 'k--', label='Random Guess') plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate') plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate') plt.title('Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve') plt.legend(loc='lower right') plt.grid(True) plt.show()
随后,我们将结果绘制为可视化图表,以检查验证测试情况。在典型的训练-验证-测试方法中,验证步骤有助于选择最优超参数,并初步评估训练好的模型是否具备预测能力。这是进入最终测试前的一个缓冲环节。
# Feature importance feature_importance = model.get_feature_importance() importance_df = pd.DataFrame({ 'feature': XX.columns, 'importance': feature_importance }).sort_values('importance', ascending=False) print("Feature Importances:") print(importance_df) plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) sns.barplot(x='importance', y='feature', data=importance_df) plt.title(' Feature Importance') plt.xlabel('Importance') plt.ylabel('Feature') x = 100/len(XX.columns) plt.axvline(x,color = 'red', linestyle = '--') plt.show()
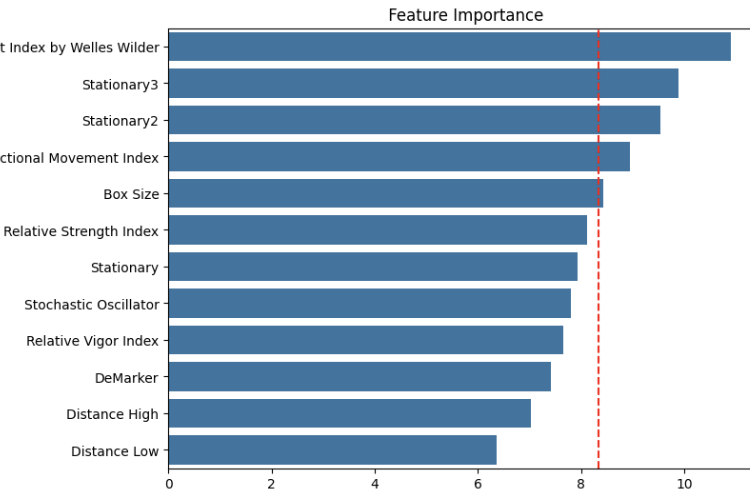
此段代码将绘制出特征重要性以及中位数线。在机器学习领域,定义特征重要性的方法有很多种,例如:
- 基于树模型的重要性:通过衡量决策树或集成模型(如随机森林和XGBoost)中的不纯度降低量(如基尼系数)来评估。
- 排列重要性:通过打乱某一特征的值后评估模型性能的下降程度来衡量。
- SHAP值:基于沙普利值计算每个特征对预测结果的贡献。
- 系数绝对值:利用线性模型中系数的绝对值来衡量。
在我们的示例中,我们使用的是CatBoost,一种基于决策树的模型。特征重要性展示了在样本内数据中,每个特征用于分割决策树时所减少的不纯度(混乱程度)有多少。关键要认识到,尽管选择最重要的特征作为最终特征集通常能提升模型效率,但并不总是能提高预测能力,原因如下:
- 特征重要性是根据样本内数据计算的,对样本外数据一无所知。
- 特征重要性取决于所考虑的其他特征。如果您选择的大多数特征都缺乏预测能力,那么剔除最弱的特征也无济于事。
- 重要性反映的是特征分割树的有效性,而不一定是其对最终决策结果的关键程度。
当我意外发现选择最不重要的特征反而提高了样本外准确率时,这些认知让我深受启发。但一般来说,选择最重要的特征并剔除不太重要的特征有助于减轻模型负担,整体上可能提高准确率。
from onnx.helper import get_attribute_value import onnxruntime as rt from skl2onnx import convert_sklearn, update_registered_converter from skl2onnx.common.shape_calculator import ( calculate_linear_classifier_output_shapes, ) # noqa from skl2onnx.common.data_types import ( FloatTensorType, Int64TensorType, guess_tensor_type, ) from skl2onnx._parse import _apply_zipmap, _get_sklearn_operator_name from catboost import CatBoostClassifier from catboost.utils import convert_to_onnx_object def skl2onnx_parser_castboost_classifier(scope, model, inputs, custom_parsers=None): options = scope.get_options(model, dict(zipmap=True)) no_zipmap = isinstance(options["zipmap"], bool) and not options["zipmap"] alias = _get_sklearn_operator_name(type(model)) this_operator = scope.declare_local_operator(alias, model) this_operator.inputs = inputs label_variable = scope.declare_local_variable("label", Int64TensorType()) prob_dtype = guess_tensor_type(inputs[0].type) probability_tensor_variable = scope.declare_local_variable( "probabilities", prob_dtype ) this_operator.outputs.append(label_variable) this_operator.outputs.append(probability_tensor_variable) probability_tensor = this_operator.outputs if no_zipmap: return probability_tensor return _apply_zipmap( options["zipmap"], scope, model, inputs[0].type, probability_tensor ) def skl2onnx_convert_catboost(scope, operator, container): """ CatBoost returns an ONNX graph with a single node. This function adds it to the main graph. """ onx = convert_to_onnx_object(operator.raw_operator) opsets = {d.domain: d.version for d in onx.opset_import} if "" in opsets and opsets[""] >= container.target_opset: raise RuntimeError("CatBoost uses an opset more recent than the target one.") if len(onx.graph.initializer) > 0 or len(onx.graph.sparse_initializer) > 0: raise NotImplementedError( "CatBoost returns a model initializers. This option is not implemented yet." ) if ( len(onx.graph.node) not in (1, 2) or not onx.graph.node[0].op_type.startswith("TreeEnsemble") or (len(onx.graph.node) == 2 and onx.graph.node[1].op_type != "ZipMap") ): types = ", ".join(map(lambda n: n.op_type, onx.graph.node)) raise NotImplementedError( f"CatBoost returns {len(onx.graph.node)} != 1 (types={types}). " f"This option is not implemented yet." ) node = onx.graph.node[0] atts = {} for att in node.attribute: atts[att.name] = get_attribute_value(att) container.add_node( node.op_type, [operator.inputs[0].full_name], [operator.outputs[0].full_name, operator.outputs[1].full_name], op_domain=node.domain, op_version=opsets.get(node.domain, None), **atts, ) update_registered_converter( CatBoostClassifier, "CatBoostCatBoostClassifier", calculate_linear_classifier_output_shapes, skl2onnx_convert_catboost, parser=skl2onnx_parser_castboost_classifier, options={"nocl": [True, False], "zipmap": [True, False, "columns"]}, ) model_onnx = convert_sklearn( model, "catboost", [("input", FloatTensorType([None, X.shape[1]]))], target_opset={"": 12, "ai.onnx.ml": 2}, ) # And save. with open("box2024.onnx", "wb") as f: f.write(model_onnx.SerializeToString())
最后,我们将导出ONNX格式文件,并将其保存至MQL5/Files目录。
现在,我们回到MetaTrader 5代码编辑器,创建EA。
我们只需对原始的数据获取型EA稍作修改,导入一些用于处理CatBoost模型的包含文件即可。
#resource "\\Files\\box2024.onnx" as uchar catboost_onnx[] #include <CatOnnx.mqh> CCatBoost cat_boost; string data[1][12]; vector xx; vector prob;
接着,我们将调整getData()函数,使其返回一个向量。
vector getData(){ double close = iClose(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,1); double close2 = iClose(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,2); double close3 = iClose(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,3); double stationary = 1000*(close-iOpen(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,1))/close; double stationary2 = 1000*(close2-iOpen(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,2))/close2; double stationary3 = 1000*(close3-iOpen(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,3))/close3; double highDistance = 1000*(close-high)/close; double lowDistance = 1000*(close-low)/close; double boxSize = 1000*(high-low)/close; double adx[]; // Average Directional Movement Index double wilder[]; // Average Directional Movement Index by Welles Wilder double dm[]; // DeMarker double rsi[]; // Relative Strength Index double rvi[]; // Relative Vigor Index double sto[]; // Stochastic Oscillator CopyBuffer(handleAdx, 0, 1, 1, adx); // Average Directional Movement Index CopyBuffer(handleWilder, 0, 1, 1, wilder); // Average Directional Movement Index by Welles Wilder CopyBuffer(handleDm, 0, 1, 1, dm); // DeMarker CopyBuffer(handleRsi, 0, 1, 1, rsi); // Relative Strength Index CopyBuffer(handleRvi, 0, 1, 1, rvi); // Relative Vigor Index CopyBuffer(handleSto, 0, 1, 1, sto); // Stochastic Oscillator data[0][0] = DoubleToString(adx[0], 2); // Average Directional Movement Index data[0][1] = DoubleToString(wilder[0], 2); // Average Directional Movement Index by Welles Wilder data[0][2] = DoubleToString(dm[0], 2); // DeMarker data[0][3] = DoubleToString(rsi[0], 2); // Relative Strength Index data[0][4] = DoubleToString(rvi[0], 2); // Relative Vigor Index data[0][5] = DoubleToString(sto[0], 2); // Stochastic Oscillator data[0][6] = DoubleToString(stationary,2); data[0][7] = DoubleToString(boxSize,2); data[0][8] = DoubleToString(stationary2,2); data[0][9] = DoubleToString(stationary3,2); data[0][10] = DoubleToString(highDistance,2); data[0][11] = DoubleToString(lowDistance,2); vector features(12); for(int i = 0; i < 12; i++) { features[i] = StringToDouble(data[0][i]); } return features; }
OnTick()函数中的最终交易逻辑会呈现为如下形式:
void OnTick() { int bars = iBars(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT); if (barsTotal!= bars){ barsTotal = bars; boxFormed = false; bool NotInPosition = true; lastClose = iClose(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 1); lastlastClose = iClose(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,2); for(int i = 0; i<PositionsTotal(); i++){ ulong pos = PositionGetTicket(i); string symboll = PositionGetSymbol(i); if(PositionGetInteger(POSITION_MAGIC) == Magic&&symboll== _Symbol)NotInPosition = false;} /*count++; if(count >=countMax){ trade.PositionClose(pos); count = 0;} }}*/ DetectDarvasBox(lookBack,checkBar); if (NotInPosition&&boxFormed&&((lastlastClose<high&&lastClose>high)||(lastClose<low&&lastlastClose>low))){ xx = getData(); prob = cat_boost.predict_proba(xx); if(prob[1]>threshold)executeBuy(); if(prob[0]>threshold)executeSell(); } } }
在信号逻辑中,首先会检查当前是否没有持仓,以确保每次只进行一笔交易。然后,其会检测价格是否突破了区间上下轨。之后,调用getData()函数获取特征向量。该向量会作为输入传递给CatBoost模型,模型会针对每个可能的结果输出预测置信度,并存入prob数组。根据每个结果的置信度水平,我们按预测结果下单交易。本质上,我们是在利用模型生成买入或卖出信号。
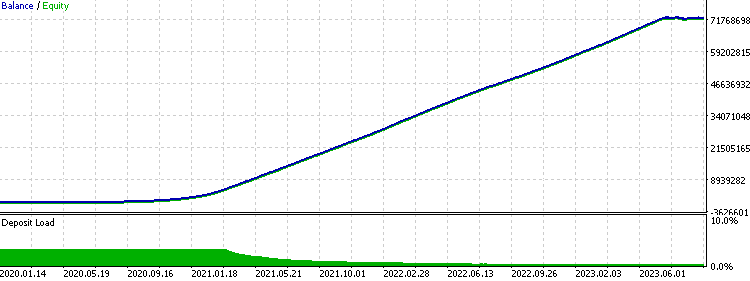
我们在MetaTrader 5策略测试器中,使用2020年至2024年的样本内数据进行了回测,以验证训练数据无错误,且特征与结果的合并正确无误。如果一切准确无误,资金曲线应呈现近乎完美的走势,如下所示:
随后,我们使用2024年至2025年的样本外数据进行了回测,以检验该策略在最近时间段内是否具备盈利能力。我们将置信阈值设定为0.7,即根据训练数据,只有当模型预测某一方向的止盈目标达成置信度达到70%或更高时,才会在该方向进行交易。
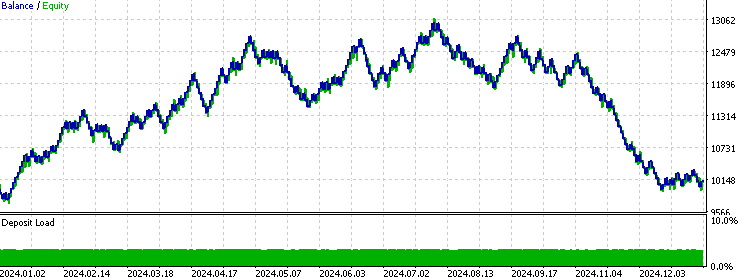
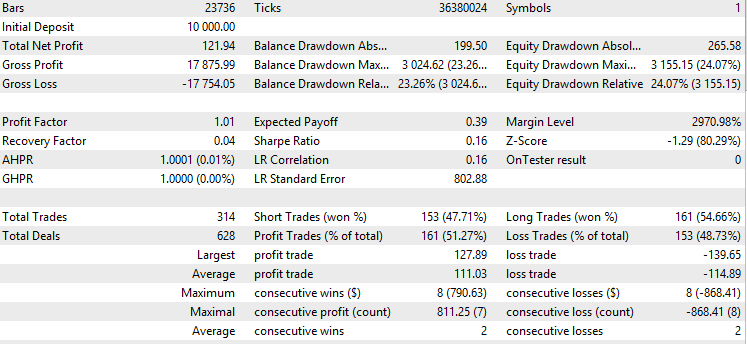
由此可见,该模型在上半年的表现极为出色,但随着时间的推移,表现逐渐下滑。这在机器学习模型中较为常见,因为从历史数据中获取的优势往往是暂时性的,且这种优势会随时间推移而逐渐减弱。这表明,在未来的实盘交易中,采用较小的测试集与训练集比例可能会取得更好的效果。总体而言,该模型展现出了一定的预测能力,因为即使在计入交易成本后,它仍能保持盈利。
连续信号
在算法交易中,交易者通常倾向于采用简单的离散信号方法——即每笔交易要么买入要么卖出,且风险固定。这种方法便于操作,也更利于分析策略表现。一些交易者尝试通过叠加信号来优化这种离散信号方法,即根据策略条件的满足程度来调整交易风险。连续信号则进一步拓展了这种加性方法,将其应用于更抽象的策略条件,并生成一个介于0和1之间的风险水平。
这一方法的基本理念是,并非所有满足入场条件的交易都同等重要。有些交易因其信号更强,基于与策略相关的非线性规则,似乎更有可能成功。这可以被视为一种风险管理工具——在信心充足时下重注,在交易前景不太明朗时则缩减仓位,即使该交易仍具有正的预期收益。然而,我们需要记住,这为策略表现引入了另一个因素,且如果在实施过程中不够谨慎,前瞻偏差和过拟合风险仍然是个问题。
要在交易EA中应用这一概念,我们首先需要调整买入/卖出函数,以便根据若触及止损我们愿意承担的损失来计算交易手数。手数计算函数如下所示:
double calclots(double slpoints, string symbol, double risk) { double balance = AccountInfoDouble(ACCOUNT_BALANCE); double riskAmount = balance* risk / 100; double ticksize = SymbolInfoDouble(symbol, SYMBOL_TRADE_TICK_SIZE); double tickvalue = SymbolInfoDouble(symbol, SYMBOL_TRADE_TICK_VALUE); double lotstep = SymbolInfoDouble(symbol, SYMBOL_VOLUME_STEP); double moneyperlotstep = slpoints / ticksize * tickvalue * lotstep; double lots = MathFloor(riskAmount / moneyperlotstep) * lotstep; lots = MathMin(lots, SymbolInfoDouble(symbol, SYMBOL_VOLUME_MAX)); lots = MathMax(lots, SymbolInfoDouble(symbol, SYMBOL_VOLUME_MIN)); return lots; }随后,我们更新买入/卖出函数,使其调用这个calclots()函数,并将风险乘数作为输入参数:
void executeSell(double riskMultiplier) { double bid = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_BID); bid = NormalizeDouble(bid,_Digits); double sl = lastClose*(1+slp); double tp = lastClose*(1-tpp); double lots = 0.1; lots = calclots(slp*lastClose,_Symbol,risks*riskMultiplier); trade.Sell(lots,_Symbol,bid,sl,tp); } void executeBuy(double riskMultiplier) { double ask = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_ASK); ask = NormalizeDouble(ask,_Digits); double sl = lastClose*(1-slp); double tp = lastClose*(1+tpp); double lots = 0.1; lots = calclots(slp*lastClose,_Symbol,risks*riskMultiplier); trade.Buy(lots,_Symbol,ask,sl,tp); }由于机器学习模型已经输出了置信度水平,我们可以直接将其用作风险乘数的输入。如果我们想调整置信度水平对每笔交易风险的影响程度,只需根据需要相应地放大或缩小置信度水平即可。
if(prob[1]>threshold)executeBuy(prob[1]); if(prob[0]>threshold)executeSell(prob[0]);
例如,如果我们想放大置信度水平差异的影响,可以将概率自乘三次(即进行三次方运算)。这将扩大不同概率之间的比例差异,使置信度水平的影响更加显著。
if(prob[1]>threshold)executeBuy(prob[1]*prob[1]*prob[1]); if(prob[0]>threshold)executeSell(prob[0]*prob[0]*prob[0]);
现在,我们尝试在回测中查看结果。
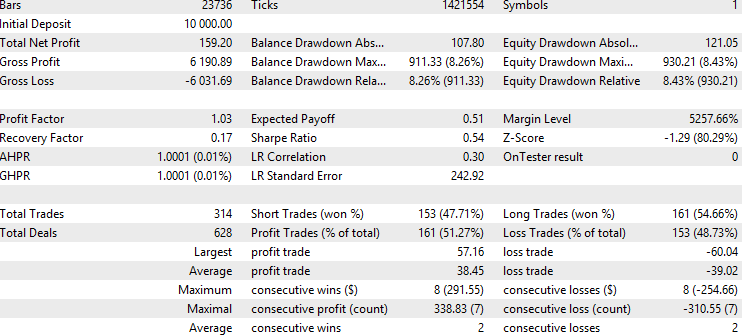
所执行的交易仍与离散信号版本相同,但盈利因子和夏普比率略有提升。这表明,在此特定场景下,连续信号提升了样本外测试的整体表现,且由于我们仅进行了一次测试,因此不存在前瞻偏差问题。然而,必须指出的是,只有当模型在置信度较高时预测准确率也更高时,这种方法才优于固定风险方法。否则,原始的固定风险方法可能更优。此外,由于我们应用了介于0和1之间的风险乘数,降低了平均交易手数,因此如果想获得与之前相似的总盈利,就需要提高风险变量值。
多时间周期验证
分别训练不同的机器学习模型,每个模型使用不同时间周期的特征来预测相同的结果,这为改进交易筛选和信号生成提供了一种有力方法。通过让一个模型专注于短期数据,另一个模型关注中期数据,或许还有第三个模型分析长期趋势,你可以获得专业化的洞察,这些洞察结合起来能够比单一模型更可靠地验证预测结果。这种多模型方法可以通过交叉验证信号来增强交易决策的信心,降低因单一时间周期的噪声而采取行动的风险,并且通过允许你根据共识强度调整交易规模或止损来支持风险管理。
另一方面,这种策略可能会使系统复杂化,尤其是当你为多个模型的预测分配不同权重时。如果调整不当,这样可能会引入自身的偏差或错误。每个模型也可能过度拟合其特定时间周期,忽略更广泛的市场动态,而且它们预测结果之间的差异可能会造成混淆,延误决策或削弱信心。
这种方法依赖于两个关键假设:较高时间周期不存在前瞻偏差(我们必须使用最后一根K线的值,而非当前值),且较高时间周期的模型具有自身的可预测性(在样本外测试中表现优于随机猜测)。
要实现这一点,我们首先修改数据获取型EA中的代码,将所有与特征提取相关的时间周期更改为更高的时间周期,例如1小时。包括指标、价格计算以及使用的任何其他特征。
int OnInit() { trade.SetExpertMagicNumber(Magic); handleAdx = iADX(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 14); // Average Directional Movement Index - 3 handleWilder = iADXWilder(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 14); // Average Directional Movement Index by Welles Wilder - 3 handleDm = iDeMarker(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 14); // DeMarker - 1 handleRsi = iRSI(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 14, PRICE_CLOSE); // Relative Strength Index - 1 handleRvi = iRVI(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 10); // Relative Vigor Index - 2 handleSto = iStochastic(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 5, 3, 3, MODE_SMA, STO_LOWHIGH); // Stochastic Oscillator - 2 return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } void getData() { double close = iClose(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 1); double close2 = iClose(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 2); double close3 = iClose(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 3); double stationary = 1000 * (close - iOpen(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 1)) / close; double stationary2 = 1000 * (close2 - iOpen(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 2)) / close2; double stationary3 = 1000 * (close3 - iOpen(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 3)) / close3; }
完成上述操作后,我们按照之前讨论的步骤进行:获取数据、训练模型并导出模型,步骤与前面完全一致。
之后,在交易EA中,我们创建第二个函数用于获取特征输入,并将该函数输入到我们导入的第二个机器学习模型中,以获取置信度输出。
vector getData2() { double close = iClose(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 1); double close2 = iClose(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 2); double close3 = iClose(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 3); double stationary = 1000 * (close - iOpen(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 1)) / close; double stationary2 = 1000 * (close2 - iOpen(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 2)) / close2; double stationary3 = 1000 * (close3 - iOpen(_Symbol, PERIOD_H1, 3)) / close3; double highDistance = 1000 * (close - high) / close; double lowDistance = 1000 * (close - low) / close; double boxSize = 1000 * (high - low) / close; double adx[]; // Average Directional Movement Index double wilder[]; // Average Directional Movement Index by Welles Wilder double dm[]; // DeMarker double rsi[]; // Relative Strength Index double rvi[]; // Relative Vigor Index double sto[]; // Stochastic Oscillator CopyBuffer(handleAdx, 0, 1, 1, adx); // Average Directional Movement Index CopyBuffer(handleWilder, 0, 1, 1, wilder); // Average Directional Movement Index by Welles Wilder CopyBuffer(handleDm, 0, 1, 1, dm); // DeMarker CopyBuffer(handleRsi, 0, 1, 1, rsi); // Relative Strength Index CopyBuffer(handleRvi, 0, 1, 1, rvi); // Relative Vigor Index CopyBuffer(handleSto, 0, 1, 1, sto); // Stochastic Oscillator data[0][0] = DoubleToString(adx[0], 2); // Average Directional Movement Index data[0][1] = DoubleToString(wilder[0], 2); // Average Directional Movement Index by Welles Wilder data[0][2] = DoubleToString(dm[0], 2); // DeMarker data[0][3] = DoubleToString(rsi[0], 2); // Relative Strength Index data[0][4] = DoubleToString(rvi[0], 2); // Relative Vigor Index data[0][5] = DoubleToString(sto[0], 2); // Stochastic Oscillator data[0][6] = DoubleToString(stationary, 2); data[0][7] = DoubleToString(boxSize, 2); data[0][8] = DoubleToString(stationary2, 2); data[0][9] = DoubleToString(stationary3, 2); data[0][10] = DoubleToString(highDistance, 2); data[0][11] = DoubleToString(lowDistance, 2); vector features(12); for(int i = 0; i < 12; i++) { features[i] = StringToDouble(data[0][i]); } return features; }
假设我们希望对两个模型的输出赋予相同权重,只需取它们输出的平均值,并将其视为我们之前使用的单一输出结果即可。
if (NotInPosition&&boxFormed&&((lastlastClose<high&&lastClose>high)||(lastClose<low&&lastlastClose>low))){ xx = getData(); xx2 = getData2(); prob = cat_boost.predict_proba(xx); prob2 = cat_boost.predict_proba(xx2); double probability_buy = (prob[1]+prob2[1])/2; double probability_sell = (prob[0]+prob2[0])/2; if(probability_buy>threshold)executeBuy(probability_buy); if(probability_sell>threshold)executeSell(probability_sell); } }
根据上述方法计算出这两个变量后,我们就可以将它们合并为一个单一的置信度水平,并按照之前使用的方法将其用于验证。
结论
在本文中,我们首先探讨了将机器学习模型用作信号生成器而非过滤器的理念,并通过达瓦斯箱体突破策略进行了演示。我们简要回顾了模型训练流程,并探讨了置信度阈值与显著型特征的重要性。接下来,我们引入了连续信号的概念,并将其性能与离散信号进行了比较。我们发现,在这个例子中,连续信号改善了回测表现,因为随着置信度水平的提升,模型的预测准确率也倾向于更高。最后,我们简要介绍了利用在不同时间周期上训练的多个机器学习模型共同验证信号的方案。
总体而言,本文旨在提出一些关于在管理期货(CTA)交易的监督学习中应用机器学习模型的非常规理念。本文的目标并非断言哪种方法效果最优,因为一切都取决于具体场景,而是旨在激发读者创造性思考,并在简单初始概念的基础上进行拓展。归根结底,没有什么是完全新颖的——创新往往源于将现有理念相结合,创造出全新的东西。
文件表
| 文件名 | 文件使用 |
|---|---|
| Darvas_Box.ipynb | 用于训练ML模型的Jupyter Notebook文件 |
| Darvas Box Data.mq5 | 用于训练模型的数据获取型EA |
| Darvas Box EA.mq5 | 本文中的交易EA |
| CatOnnx.mqh | 用于处理CatBoost模型的包含文件 |
| FileCSV.mqh | 用于将数据保存到CSV的包含文件 |
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/17466
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 市场模拟(第五部分):创建 C_Orders 类(二)
市场模拟(第五部分):创建 C_Orders 类(二)
 让手动回测变得简单:为MQL5策略测试器构建自定义工具包
让手动回测变得简单:为MQL5策略测试器构建自定义工具包
 市场模拟(第四部分):创建 C_Orders 类(一)
市场模拟(第四部分):创建 C_Orders 类(一)

感谢您的提醒。pip install 部分被忽略,但如果用户尚未安装相关库,则必须安装。
您的错误可能是由于模型训练中使用的维度与 EA 中使用的维度不同造成的。例如,如果您训练了一个具有 5 个特征的模型,那么您就应该在 EA 中输入 5 个特征,而不是 4 或 6 个。本文链接 提供了更详细的说明。希望对您有所帮助。如果没有,请提供更多信息。