
MQL5中的自动化交易策略(第七部分):构建具备仓位动态调整功能的网格交易EA
引言
在 上一篇文章(第六部分) 中,我们用 MetaQuotes Language 5 (MQL5) 开发了一个自动化的订单块检测系统。现在,在第七部分中,我们将专注于网格交易,这是一种以固定价格间隔下单的策略,并结合动态仓位缩放来优化风险回报。这种方法根据市场状况调整仓位大小,旨在提高盈利能力和风险管理水平。我们将涵盖:
在本文结束时,您将拥有一个功能齐全的、带有动态仓位缩放的网格交易程序,准备好进行测试和优化。让我们开始吧!
策略的具体实现
网格交易是一种系统性的方法,它在预定的价格间隔下放置买入和卖出订单,使交易者能够利用市场波动,而无需精确的趋势预测。该策略通过在定义的价格范围内持续开仓和平仓来从市场波动中获益。为了增强其性能,我们将集成动态仓位缩放,它会根据预定条件(如账户余额、波动率或先前交易的结果)来调整仓位大小。我们的网格交易系统将由以下关键部分组成:
- 网格结构 – 我们将定义订单之间的间距。
- 入场和执行规则 – 我们将根据使用移动平均线指标策略的固定距离,来决定何时开立网格交易。
- 动态仓位缩放 – 我们将实现一个自适应的仓位调整机制,根据市场状况或预定义的风险参数来调整仓位大小。
- 交易管理 – 我们将引入止损、止盈和可选的保本机制,以有效管理风险。
- 退出策略 – 我们将开发基于盈利目标、风险限制或趋势反转来平仓的逻辑。
简而言之,为了便于理解,这里是整个策略方案的可视化展示。
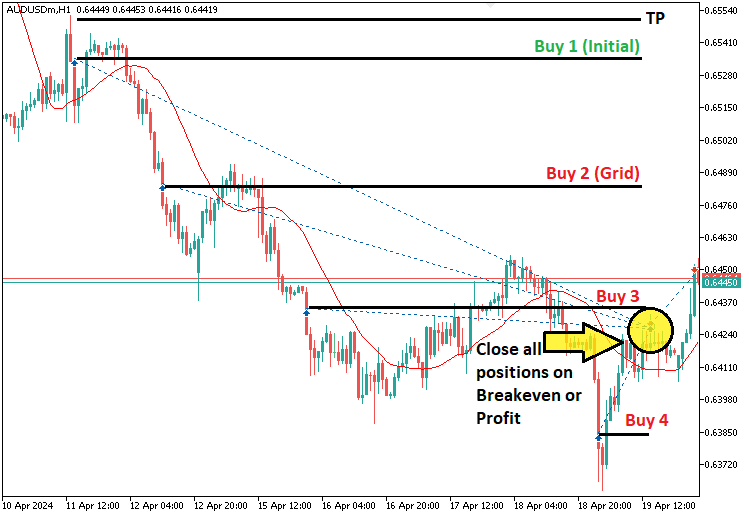
通过将结构化的网格系统与自适应的仓位调整相结合,我们将创建一个能在有效管理风险的同时最大化回报的 EA。接下来,我们将在 MQL5 中实现这些概念。
在MQL5中的实现
要在 MQL5 中创建程序,请打开 MetaEditor,转到“导航器”窗口,找到“指标”文件夹,点击“新建”选项卡,然后按照提示创建文件。文件创建完成后,在代码编环境下,我们需要声明一些将在整个程序中使用的全局变量。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Copyright 2025, Forex Algo-Trader, Allan. | //| "https://t.me/Forex_Algo_Trader" | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Forex Algo-Trader, Allan" #property link "https://t.me/Forex_Algo_Trader" #property version "1.00" #property description "This EA trades based on Grid Strategy" #property strict #include <Trade/Trade.mqh> //--- Include trading library CTrade obj_Trade; //--- Trading object instance //--- Closure Mode Enumeration and Inputs enum ClosureMode { CLOSE_BY_PROFIT, //--- Use total profit (in currency) to close positions CLOSE_BY_POINTS //--- Use a points threshold from breakeven to close positions }; input group "General EA Inputs" input ClosureMode closureMode = CLOSE_BY_POINTS; //Select closure mode double breakevenPoints = 50 * _Point; //--- Points offset to add/subtract to/from breakeven //--- Global Variables double TakeProfit; //--- Current take profit level double initialLotsize = 0.1; //--- Initial lot size for the first trade double takeProfitPts = 200 * _Point; //--- Take profit distance in points double profitTotal_inCurrency = 100; //--- Profit target (in currency) to close positions double gridSize; //--- Price level at which grid orders are triggered double gridSize_Spacing = 500 * _Point; //--- Grid spacing in points double LotSize; //--- Current lot size (increased with grid orders) bool isTradeAllowed = true; //--- Flag to allow trade on a new bar int totalBars = 0; //--- Count of bars seen so far int handle; //--- Handle for the Moving Average indicator double maData[]; //--- Array for Moving Average data
在这里,我们使用 #include 包含了“Trade/Trade.mqh”库,并实例化了“obj_Trade”对象来处理我们的交易。我们定义了一个“ClosureMode”枚举,其中包含平仓的选项,并设置了诸如“closureMode”和“breakevenPoints”之类的用户输入。接下来,我们声明了用于管理我们的止盈水平、初始手数、网格间距和动态仓位缩放的变量,以及用于交易控制和移动平均线指标数据的标志和计数器。然后,我们需要声明我们关键函数的原型,以构建程序结构如下:
//--- Function Prototypes void CheckAndCloseProfitTargets(); //--- Closes all positions if total profit meets target void ExecuteInitialTrade(double ask, double bid); //--- Executes the initial BUY/SELL trade (initial positions) void ManageGridPositions(double ask, double bid); //--- Adds grid orders when market moves to grid level (grid positions) void UpdateMovingAverage(); //--- Updates MA indicator data from its buffer bool IsNewBar(); //--- Checks if a new bar has formed double CalculateWeightedBreakevenPrice(); //--- Calculates the weighted average entry price for positions void CheckBreakevenClose(double ask, double bid); //--- Closes positions if price meets breakeven+/- threshold void CloseAllPositions(); //--- Closes all open positions
对于这些函数,我们将实现“CheckAndCloseProfitTargets”来监控整体盈利能力,并在达到目标时平仓;以及实现“ExecuteInitialTrade”来通过初始的买入或卖出订单启动策略。“ManageGridPositions”将随着市场移动,在设定的网格间隔处添加额外的订单,而“UpdateMovingAverage”则确保我们的指标数据是最新的,以便做出决策。“IsNewBar”检测新的 K 线,以防止在同一根K线上多次交易;“CalculateWeightedBreakevenPrice”计算所有持仓的平均入场价格;“CheckBreakevenClose”则利用该信息在满足有利条件时退出交易。最后,“CloseAllPositions”将在必要时系统地关闭所有未平仓的交易。
在“全局作用域”中设置好所有这些之后,我们就可以继续进行程序初始化,即在“OnInit”事件处理程序中进行。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Expert initialization function //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit(){ //--- Initialize the Moving Average indicator (Period: 21, SMA, Price: Close) handle = iMA(_Symbol, _Period, 21, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE); if (handle == INVALID_HANDLE){ Print("ERROR: UNABLE TO INITIALIZE THE INDICATOR. REVERTING NOW!"); return (INIT_FAILED); } ArraySetAsSeries(maData, true); //--- Ensure MA data array is in series order return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
在这里,我们通过使用 iMA 函数设置移动平均线指标来初始化程序,该指标周期为 21,类型为 SMA,价格为 PRICE_CLOSE(收盘价)。我们检查指标句柄是否有效——如果无效(INVALID_HANDLE),我们打印一条错误消息并返回 INIT_FAILED 来阻止程序运行。最后,我们在“maData”数组上调用 ArraySetAsSeries 函数,以确保移动平均线数据按正确的顺序排列,然后返回 INIT_SUCCEEDED 以确认初始化成功。一旦正确初始化,我们就可以进入 OnTick 事件处理程序来构建开仓和管理仓位的逻辑。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Expert tick function //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick(){ //--- Allow new trade signals on a new bar if(IsNewBar()) isTradeAllowed = true; //--- Update the Moving Average data UpdateMovingAverage(); }
由于我们不希望在每一个 tick 上都检查交易,而是在每一根 K 线上检查,因此我们调用函数“IsNewBar”,并在形成新 K 线时用它将“isTradeAllowed”变量设置为 true。然后,我们调用负责获取移动平均线值的函数。这些函数的定义如下:
//+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Function: UpdateMovingAverage //--- Description: Copies the latest data from the MA indicator buffer. //+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ void UpdateMovingAverage(){ if(CopyBuffer(handle, 0, 1, 3, maData) < 0) Print("Error: Unable to update Moving Average data."); } //+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Function: IsNewBar //--- Description: Checks if a new bar has been formed. //+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool IsNewBar(){ int bars = iBars(_Symbol, _Period); if(bars > totalBars){ totalBars = bars; return true; } return false; }
在这里,我们实现了“UpdateMovingAverage”,通过使用 CopyBuffer 函数从移动平均线缓冲区复制最新值来刷新我们的指标数据。如果此函数调用失败,我们会打印一条错误消息,以提醒我们更新未成功。在“IsNewBar”函数中,我们通过使用 iBars 函数获取的当前 K 线数量与我们存储的“totalBars”计数进行比较,来检查是否形成了新的 K 线;如果数量增加了,我们就更新“totalBars”并返回“true”,表示有新的 K 线可用于交易决策。然后我们继续在 tick 函数中,根据检索到的指标值执行交易。
//--- Reset lot size if no positions are open if(PositionsTotal() == 0) LotSize = initialLotsize; //--- Retrieve recent bar prices for trade signal logic double low1 = iLow(_Symbol, _Period, 1); double low2 = iLow(_Symbol, _Period, 2); double high1 = iHigh(_Symbol, _Period, 1); double high2 = iHigh(_Symbol, _Period, 2); //--- Get current Ask and Bid prices (normalized) double ask = NormalizeDouble(SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_ASK), _Digits); double bid = NormalizeDouble(SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_BID), _Digits); //--- If no positions are open and trading is allowed, check for an initial trade signal if(PositionsTotal() == 0 && isTradeAllowed){ ExecuteInitialTrade(ask, bid); }
在这里,我们首先使用 PositionsTotal 函数检查是否有未平仓位,如果没有,我们就将“LotSize”重置为“initialLotsize”。接下来,我们通过调用 iLow 和 iHigh 来获取最近 K 线的价格,以捕获前两根 K 线的最高价和最低价,这将有助于形成我们的交易信号。然后,我们使用 SymbolInfoDouble 获取当前的“ask”(卖价)和“bid”(买价),并使用 NormalizeDouble 对其进行标准化,以确保准确性。最后,如果允许交易(由“isTradeAllowed”指示)并且当前没有未平仓位,我们就调用“ExecuteInitialTrade”函数,并传入“ask”和“bid”价格来启动我们的第一笔交易。该函数的定义如下:
//+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Function: ExecuteInitialTrade //--- Description: Executes the initial BUY or SELL trade based on MA criteria. //--- (These are considered "initial positions.") //+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+ void ExecuteInitialTrade(double ask, double bid){ //--- BUY Signal: previous bar's low above MA and bar before that below MA if(iLow(_Symbol, _Period, 1) > maData[1] && iLow(_Symbol, _Period, 2) < maData[1]){ gridSize = ask - gridSize_Spacing; //--- Set grid trigger below current ask TakeProfit = ask + takeProfitPts; //--- Set TP for BUY if(obj_Trade.Buy(LotSize, _Symbol, ask, 0, TakeProfit,"Initial Buy")) Print("Initial BUY order executed at ", ask, " with LotSize: ", LotSize); else Print("Initial BUY order failed at ", ask); isTradeAllowed = false; } //--- SELL Signal: previous bar's high below MA and bar before that above MA else if(iHigh(_Symbol, _Period, 1) < maData[1] && iHigh(_Symbol, _Period, 2) > maData[1]){ gridSize = bid + gridSize_Spacing; //--- Set grid trigger above current bid TakeProfit = bid - takeProfitPts; //--- Set TP for SELL if(obj_Trade.Sell(LotSize, _Symbol, bid, 0, TakeProfit,"Initial Sell")) Print("Initial SELL order executed at ", bid, " with LotSize: ", LotSize); else Print("Initial SELL order failed at ", bid); isTradeAllowed = false; } }
在这里,我们实现了“ExecuteInitialTrade”函数,以根据“maData”的值开立一笔初始交易。我们使用函数 iLow 获取前两根 K 线的最低价,并使用函数 iHigh 获取最高价。对于买入信号,我们检查前一根 K 线的最低价是否高于“maData”,而再前一根 K 线的最低价低于它。如果满足此条件,我们使用“gridSize_Spacing”在当前“ask”价下方设置“gridSize”以确定下一个网格水平,通过将“takeProfitPts”加到“ask”价上来计算“TakeProfit”,并使用“obj_Trade.Buy”方法执行一笔买入交易。
对于卖出信号,我们检查前一根 K 线的最高价是否低于“maData”,而再前一根 K 线的最高价高于它。如果为真,我们在“bid”价上方设置“gridSize”,通过从“bid”价中减去“takeProfitPts”来确定“TakeProfit”,并尝试使用“obj_Trade.Sell”执行一笔卖出交易。一旦交易执行,我们将“isTradeAllowed”设置为 false,以防止在满足进一步条件之前有额外的入场。结果如下。
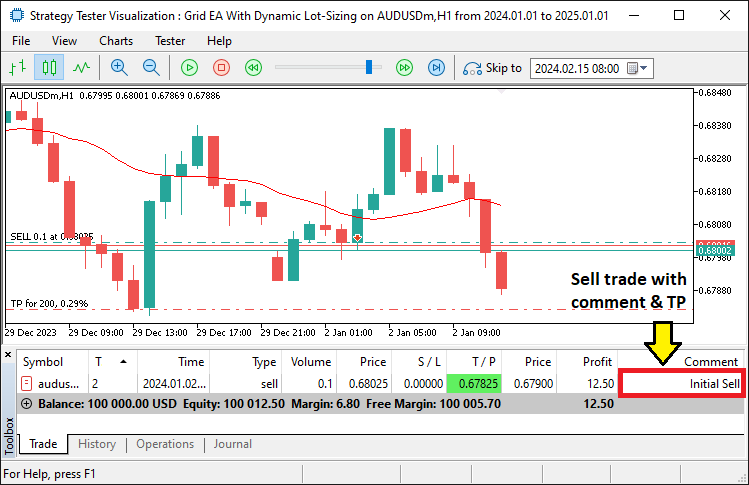
从图片中,我们可以看到已确认的交易正在执行。我们现在需要继续通过开立网格仓位来管理这些交易。
//--- If positions exist, manage grid orders if(PositionsTotal() > 0){ ManageGridPositions(ask, bid); }
我们使用函数 PositionsTotal 检查是否有未平仓位。如果仓位数量大于零,我们就调用“ManageGridPositions”函数来处理额外的网格交易。该函数接收“ask”和“bid”作为参数,以根据市场移动确定放置新网格订单的合适价格水平。该函数的代码片段实现如下:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Function: ManageGridPositions //--- Description: When an initial position exists, grid orders are added //--- if the market moves to the grid level. (These orders are //--- considered "grid positions.") The lot size is doubled //--- with each grid order. //+------------------------------------------------------------------------+ void ManageGridPositions(double ask, double bid){ for(int i = PositionsTotal()-1; i >= 0; i--){ ulong ticket = PositionGetTicket(i); if(PositionSelectByTicket(ticket)){ int positionType = (int)PositionGetInteger(POSITION_TYPE); //--- Grid management for BUY positions if(positionType == POSITION_TYPE_BUY){ if(ask <= gridSize){ LotSize *= 2; //--- Increase lot size for grid order if(obj_Trade.Buy(LotSize, _Symbol, ask, 0, TakeProfit,"Grid Position BUY")) Print("Grid BUY order executed at ", ask, " with LotSize: ", LotSize); else Print("Grid BUY order failed at ", ask); gridSize = ask - gridSize_Spacing; //--- Update grid trigger } } //--- Grid management for SELL positions else if(positionType == POSITION_TYPE_SELL){ if(bid >= gridSize){ LotSize *= 2; //--- Increase lot size for grid order if(obj_Trade.Sell(LotSize, _Symbol, bid, 0, TakeProfit,"Grid Position SELL")) Print("Grid SELL order executed at ", bid, " with LotSize: ", LotSize); else Print("Grid SELL order failed at ", bid); gridSize = bid + gridSize_Spacing; //--- Update grid trigger } } } } }
我们实现了“ManageGridPositions”函数来管理网格订单。我们使用for 循环逆序遍历所有未平仓位,并使用函数 PositionGetTicket 获取每个仓位的编号。然后,我们使用 PositionSelectByTicket 选择该仓位,并使用 PositionGetInteger 函数配合参数 POSITION_TYPE 来判断它是买入还是卖出交易。如果该仓位是买入(BUY),我们检查市场价格“ask”是否已达到或跌破“gridSize”。如果为真,我们将“LotSize”加倍,并使用“obj_Trade.Buy”函数执行一笔新的网格买入订单。如果订单成功,我们打印一条确认消息;否则,我们打印一条错误消息。然后,我们将“gridSize”更新为下一个更低的网格水平。
类似地,如果该仓位是卖出(SELL),我们检查“bid”是否已达到或超过“gridSize”。如果为真,我们将“LotSize”加倍,并使用“obj_Trade.Sell”放置一笔新的网格卖出订单。然后,网格触发点“gridSize”被更新到上一个更高的水平。在开立网格仓位后,我们需要通过在达到以下定义的条件时平仓来跟踪和管理这些仓位。
//--- Check if total profit meets the target (only used if closureMode == CLOSE_BY_PROFIT) if(closureMode == CLOSE_BY_PROFIT) CheckAndCloseProfitTargets();
如果“closureMode”被设置为“CLOSE_BY_PROFIT”,我们就调用“CheckAndCloseProfitTargets”函数来检查总利润是否已达到预定义的目标,并相应地关闭所有仓位。该函数的声明如下:
//+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Function: CheckAndCloseProfitTargets //--- Description: Closes all positions if the combined profit meets or exceeds //--- the user-defined profit target. //+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CheckAndCloseProfitTargets(){ if(PositionsTotal() > 1){ double totalProfit = 0; for(int i = PositionsTotal()-1; i >= 0; i--){ ulong tkt = PositionGetTicket(i); if(PositionSelectByTicket(tkt)) totalProfit += PositionGetDouble(POSITION_PROFIT); } if(totalProfit >= profitTotal_inCurrency){ Print("Profit target reached (", totalProfit, "). Closing all positions."); CloseAllPositions(); } } }
为确保在累计总利润达到或超过预定义的盈利目标时关闭所有仓位,我们首先使用 PositionsTotal 检查是否有超过一个未平仓位。我们初始化“totalProfit”来跟踪所有仓位的综合利润。然后,我们循环遍历所有未平仓位,使用 PositionGetTicket 获取每个仓位的编号,并使用 PositionSelectByTicket 选择该仓位。对于每个选中的仓位,我们使用 PositionGetDouble 函数配合参数 POSITION_PROFIT 来获取其利润,并将其加到“totalProfit”上。如果“totalProfit”达到或超过“profitTotal_inCurrency”,我们打印一条消息表明利润目标已达成,并调用“CloseAllPositions”函数(其定义如下)来关闭所有未平仓的交易。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Function: CloseAllPositions //--- Description: Iterates through and closes all open positions. //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CloseAllPositions(){ for(int i = PositionsTotal()-1; i >= 0; i--){ ulong posTkt = PositionGetTicket(i); if(PositionSelectByTicket(posTkt)){ if(obj_Trade.PositionClose(posTkt)) Print("Closed position ticket: ", posTkt); else Print("Failed to close position ticket: ", posTkt); } } }
该函数只是遍历所有未平仓位,对于每个选中的仓位,使用“obj_Trade.PositionClose”方法将其关闭。最后,我们定义了在保本时平仓的逻辑。
//--- If using CLOSE_BY_POINTS and more than one position exists (i.e. grid), check breakeven closure if(closureMode == CLOSE_BY_POINTS && PositionsTotal() > 1) CheckBreakevenClose(ask, bid);
如果“closureMode”被设置为“CLOSE_BY_POINTS”并且存在超过一个未平仓位,我们就调用“CheckBreakevenClose”函数,并传入参数“ask”和“bid”,以判断价格是否已达到保本阈值,从而允许根据预设的保本点数来平仓。以下是该函数的定义。
//+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Function: CalculateWeightedBreakevenPrice //--- Description: Calculates the weighted average entry price (breakeven) //--- of all open positions (assumed to be in the same direction). //+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CalculateWeightedBreakevenPrice(){ double totalCost = 0; double totalVolume = 0; int posType = -1; //--- Determine the type from the first position for(int i = 0; i < PositionsTotal(); i++){ ulong ticket = PositionGetTicket(i); if(PositionSelectByTicket(ticket)){ posType = (int)PositionGetInteger(POSITION_TYPE); break; } } //--- Sum the cost and volume for positions matching the type for(int i = 0; i < PositionsTotal(); i++){ ulong ticket = PositionGetTicket(i); if(PositionSelectByTicket(ticket)){ if(PositionGetInteger(POSITION_TYPE) == posType){ double price = PositionGetDouble(POSITION_PRICE_OPEN); double volume = PositionGetDouble(POSITION_VOLUME); totalCost += price * volume; totalVolume += volume; } } } if(totalVolume > 0) return(totalCost / totalVolume); else return(0); } //+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- Function: CheckBreakevenClose //--- Description: When using CLOSE_BY_POINTS and multiple positions exist, //--- calculates the weighted breakeven price and checks if the //--- current price has moved the specified points in a profitable //--- direction relative to breakeven. If so, closes all positions. //+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CheckBreakevenClose(double ask, double bid){ //--- Ensure we have more than one position (grid positions) if(PositionsTotal() <= 1) return; double weightedBreakeven = CalculateWeightedBreakevenPrice(); int posType = -1; //--- Determine the trade type from one of the positions for(int i = 0; i < PositionsTotal(); i++){ ulong ticket = PositionGetTicket(i); if(PositionSelectByTicket(ticket)){ posType = (int)PositionGetInteger(POSITION_TYPE); break; } } if(posType == -1) return; //--- For BUY positions, profit when Bid >= breakeven + threshold if(posType == POSITION_TYPE_BUY){ if(bid >= weightedBreakeven + breakevenPoints){ Print("Closing BUY positions: Bid (", bid, ") >= Breakeven (", weightedBreakeven, ") + ", breakevenPoints); CloseAllPositions(); } } //--- For SELL positions, profit when Ask <= breakeven - threshold else if(posType == POSITION_TYPE_SELL){ if(ask <= weightedBreakeven - breakevenPoints){ Print("Closing SELL positions: Ask (", ask, ") <= Breakeven (", weightedBreakeven, ") - ", breakevenPoints); CloseAllPositions(); } } }
在这里,我们计算所有未平仓位的保本价格,并判断市场价格是否已移动到超出该价格的指定距离,以便平仓获利。在“CalculateWeightedBreakevenPrice”函数中,我们通过使用 POSITION_PRICE_OPEN 将所有未平仓位的总成本相加,并按“POSITION_VOLUME”(仓位手数)进行加权,来计算加权保本价格。我们首先使用 POSITION_TYPE 从第一个未平仓位确定其类型(买入或卖出)。然后,我们遍历所有仓位,将与已识别类型匹配的仓位的总成本和总手数相加。如果总手数大于零,我们通过将总成本除以总手数来返回加权保本价格。否则,我们返回零。
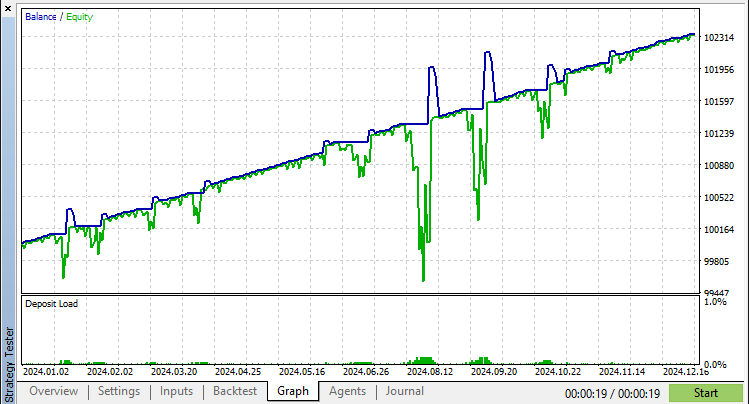
在“CheckBreakevenClose”函数中,我们首先使用 PositionsTotal 函数确认存在多个未平仓位。然后,我们通过调用“CalculateWeightedBreakevenPrice”来获取加权保本价格。我们通过选择一个仓位并获取其 POSITION_TYPE 来确定仓位类型。如果类型无效,我们退出该函数。对于买入(BUY)仓位,我们检查“bid”价格是否已达到或超过“weightedBreakeven”加上“breakevenPoints”。如果是,我们打印一条消息并调用“CloseAllPositions”。对于卖出(SELL)仓位,我们检查“ask”价格是否已跌破“weightedBreakeven”减去“breakevenPoints”。如果满足此条件,我们同样打印一条消息并调用“CloseAllPositions”函数来锁定利润。在编译并运行程序后,我们得到以下结果。
从可视化结果中,我们可以看到仓位通过网格系统被开立和管理,并在达到定义的平仓水平时被关闭,从而实现了我们创建带有动态仓位调整的网格系统的目标。剩下的事情就是对该程序进行回测,这将在下一节中处理。
回测
经过彻底的回测后,我们得到以下结果。
回测结果图形:
回测报告:
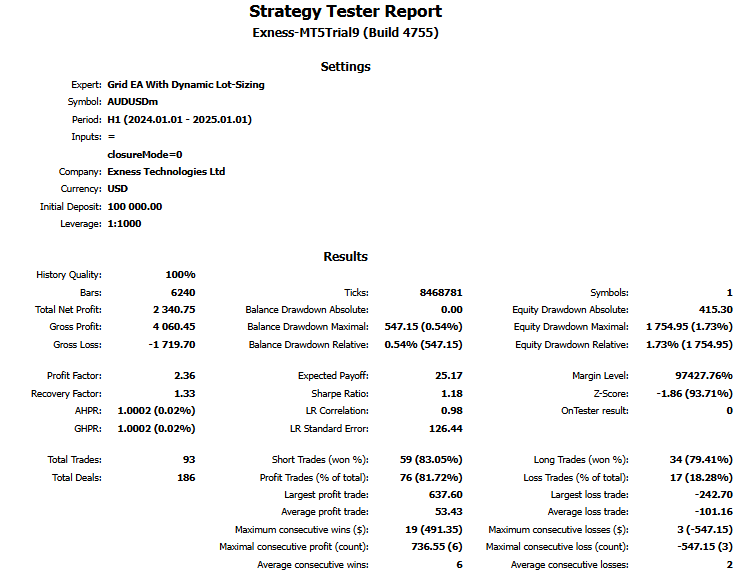
结论
总之,我们演示了开发一个利用动态网格交易策略的 MQL5 EA的过程。通过结合网格订单放置、动态仓位缩放以及有针对性的盈利和保本管理等关键要素,我们创建了一个能够适应市场波动的系统,旨在优化风险回报比,并从不利的价格变动中恢复。
免责声明:本文仅用于教学目的。交易涉及重大的财务风险,市场行为可能高度不可预测。虽然概述的策略为网格交易提供了一种结构化的方法,但它们并不保证未来的盈利性。在实盘交易之前,严格的回测和风险管理是必不可少的。
通过实施这些技术,您可以优化您的网格交易系统,增强您的市场分析,并提升您的算法交易策略。祝您在交易之旅中好运!
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/17190
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 您应当知道的 MQL5 向导技术(第 52 部分):加速器振荡器
您应当知道的 MQL5 向导技术(第 52 部分):加速器振荡器
 价格行为分析工具包开发(第十三部分):RSI 哨兵工具
价格行为分析工具包开发(第十三部分):RSI 哨兵工具


is ok.....best EA。
对于新手来说,这 4 行很容易混淆
is ok.....best EA .
对于新手来说,这 4 行很容易混淆
好的
好文章 - 非常感谢...我正在学习交易方法,我将在自己的交易中对自定义 散列符号 进行编辑!
检查....
检查....
Great article - thank you so much... I'm learning trading methods and I'll be editing custom hash symbols in my own trading!
examine....