
矩阵实用工具,扩展矩阵和向量的标准库功能
“您永远不会达到完美,因为总有改进的余地。
然而,在通往完美的道路上,您会学会变得更好。”
概述
在 python 中,Utils 类是一个通用的实用工具类,含有函数和代码行,我们可以重用它们,而无需创建类的实例。
针对矩阵的标准库为我们提供了一些非常重要的功能和方法,我们可以用来初始化、转换、操纵矩阵、以及更多,但就像任何其它构建的函数库一样,它可以加以扩展,从而执行某些应用程序中也许必须/所需的额外内容。
下面介绍的函数和方法没有特定的顺序;
内容:
- 从 CSV 文件中读取矩阵
- 从 CSV 文件中读取编码值
- 将矩阵写入 CSV 文件
- 将矩阵转换为向量
- 将向量转换为矩阵
- 将数组转换为向量
- 向量到数组
- 从矩阵中删除单列
- 从矩阵中删除多列
- 从矩阵中删除单行
- 从向量中删除单个值
- 将矩阵拆分为训练矩阵和测试矩阵
- X 和 Y 矩阵拆分
- 创建设计矩阵
- 独热编码矩阵
- 从向量获取类
- 创建随机值向量
- 将一个向量附加到另一个向量
- 将一个向量复制到另一个向量
从 CSV 文件中读取矩阵
这是一个非常重要的功能,因为它允许我们从 CSV 文件加载数据库,并毫不费力地将它们存储在矩阵之中。 无需强调此功能的重要性,因为在交易系统编码过程中,我们经常需要程序能够加载包含交易信号或交易历史的 CSV 文件。
函数的第一步(您猜对了?)是读取一个 CSV 文件,假定 CSV 文件的第一行只有字符串,如此即使第一行中有数值,它们也不会包含在矩阵中,因为矩阵不能包含字符串值,第一行中的值将存储在 csv_header 数组之中。while(!FileIsEnding(handle)) { string data = FileReadString(handle); //--- if(rows ==0) { ArrayResize(csv_header,column+1); csv_header[column] = data; } if(rows>0) //Avoid the first column which contains the column's header mat_[rows-1,column] = (double(data)); column++; //---
此数组有助于跟踪我们刚刚读取的 CSV 文件中的列名。
完整代码:
matrix CMatrixutils::ReadCsv(string file_name,string delimiter=",") { matrix mat_ = {}; int rows_total=0; int handle = FileOpen(file_name,FILE_READ|FILE_CSV|FILE_ANSI,delimiter); ResetLastError(); if(handle == INVALID_HANDLE) { printf("Invalid %s handle Error %d ",file_name,GetLastError()); Print(GetLastError()==0?" TIP | File Might be in use Somewhere else or in another Directory":""); } else { int column = 0, rows=0; while(!FileIsEnding(handle)) { string data = FileReadString(handle); //--- if(rows ==0) { ArrayResize(csv_header,column+1); csv_header[column] = data; } if(rows>0) //Avoid the first column which contains the column's header mat_[rows-1,column] = (double(data)); column++; //--- if(FileIsLineEnding(handle)) { rows++; mat_.Resize(rows,column); column = 0; } } rows_total = rows; FileClose(handle); } mat_.Resize(rows_total-1,mat_.Cols()); return(mat_); }
用法:
这是我们想要加载到矩阵中的 CSV 文件将 CSV 文件加载到矩阵之中;
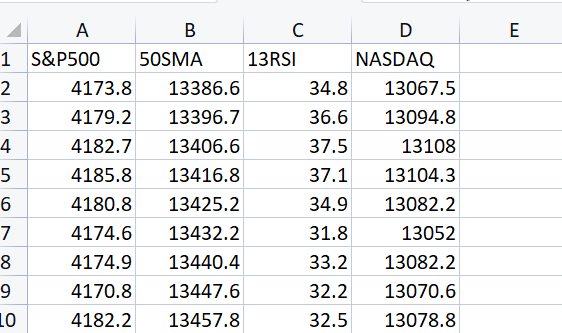
Print("---> Reading a CSV file to Matrix\n"); Matrix = matrix_utils.ReadCsv("NASDAQ_DATA.csv"); ArrayPrint(matrix_utils.csv_header); Print(Matrix);输出:
CS 0 06:48:21.228 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) "S&P500" "50SMA" "13RSI" "NASDAQ" CS 0 06:48:21.228 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [[4173.8,13386.6,34.8,13067.5] CS 0 06:48:21.228 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4179.2,13396.7,36.6,13094.8] CS 0 06:48:21.228 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4182.7,13406.6,37.5,13108] CS 0 06:48:21.228 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4185.8,13416.8,37.1,13104.3] CS 0 06:48:21.228 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4180.8,13425.2,34.9,13082.2] CS 0 06:48:21.228 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4174.6,13432.2,31.8,13052] CS 0 06:48:21.228 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4174.9,13440.4,33.2,13082.2] CS 0 06:48:21.228 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4170.8,13447.6,32.2,13070.6] CS 0 06:48:21.228 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4182.2,13457.8,32.5,13078.8]
我决定构建这个函数的原因,是我在标准库中找不到读取 CSV 文件的方法,我期待这是将数值从文件加载 CSV 的途径 Matrix.FromFile()。
但很失望,如果有人从文档中知道如何这样做的方式,请在本文的讨论部分告诉我。
从 CSV 文件中读取编码值
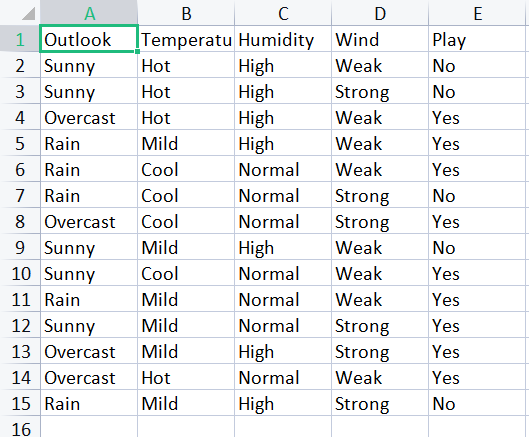
您可能经常需要读取包含字符串值的 CSV 文件,当人们希望制作分类算法时,经常会遇到这些包含字符串的 CSV 文件,譬如查看最流行的天气数据集;
为了能够对此 csv 文件进行编码,我们预计将其所有数据读取到单独的字符串值数组之中,因为矩阵不能携带字符串值, 在 ReadCsvEncode() 函数内, 我们先要做的第一件事是读取给定 CSV 文件中存在的已知列数,其次我们循环读取这些列,就像在每次迭代中打开 csv,并完全读取单列一样,并且该列的值将存储到名为 toArr[] 的数组当中。
//--- Obtaining the columns matrix Matrix={}; //--- Loading the entire Matrix to an Array int csv_columns=0, rows_total=0; int handle = CSVOpen(file_name,delimiter); if (handle != INVALID_HANDLE) { while (!FileIsEnding(handle)) { string data = FileReadString(handle); csv_columns++; //--- if (FileIsLineEnding(handle)) break; } } FileClose(handle); ArrayResize(csv_header,csv_columns); //--- string toArr[]; int counter=0; for (int i=0; i<csv_columns; i++) { if ((handle = CSVOpen(file_name,delimiter)) != INVALID_HANDLE) { int column = 0, rows=0; while (!FileIsEnding(handle)) { string data = FileReadString(handle); column++; //--- if (column==i+1) { if (rows>=1) //Avoid the first column which contains the column's header { counter++; ArrayResize(toArr,counter); //array size for all the columns toArr[counter-1]=data; } else csv_header[column-1] = data; } //--- if (FileIsLineEnding(handle)) { rows++; column = 0; } } rows_total += rows-1; } FileClose(handle); } //---
一旦结束,toArr[] 在打印时如下所示
CS 0 06:00:15.952 matrix test (US500,D1) [ 0] "Sunny" "Sunny" "Overcast" "Rain" "Rain" "Rain" "Overcast" "Sunny" "Sunny" "Rain" "Sunny" "Overcast" CS 0 06:00:15.952 matrix test (US500,D1) [12] "Overcast" "Rain" "Hot" "Hot" "Hot" "Mild" "Cool" "Cool" "Cool" "Mild" "Cool" "Mild" CS 0 06:00:15.952 matrix test (US500,D1) [24] "Mild" "Mild" "Hot" "Mild" "High" "High" "High" "High" "Normal" "Normal" "Normal" "High" CS 0 06:00:15.952 matrix test (US500,D1) [36] "Normal" "Normal" "Normal" "High" "Normal" "High" "Weak" "Strong" "Weak" "Weak" "Weak" "Strong" CS 0 06:00:15.952 matrix test (US500,D1) [48] "Strong" "Weak" "Weak" "Weak" "Strong" "Strong" "Weak" "Strong" "No" "No" "Yes" "Yes" CS 0 06:00:15.952 matrix test (US500,D1) [60] "Yes" "No" "Yes" "No" "Yes" "Yes" "Yes" "Yes" "Yes" "No"
如果您留意该数组,您会注意到 CSV 文件中的数值是按照从 CSV 文件获取的顺序排列的,从索引 0 到 13 是第一列,从索引 14 到 27 是第二列,等等,依此类推。 现在,从那里可以轻松提取数值,并对其进行编码,以便最终将它们存储到矩阵之中。
ulong mat_cols = 0,mat_rows = 0; if (ArraySize(toArr) % csv_columns !=0) printf("This CSV file named %s has unequal number of columns = %d and rows %d Its size = %d",file_name,csv_columns,ArraySize(toArr) / csv_columns,ArraySize(toArr)); else //preparing the number of columns and rows that out matrix needs { mat_cols = (ulong)csv_columns; mat_rows = (ulong)ArraySize(toArr)/mat_cols; } //--- Encoding the CSV Matrix.Resize(mat_rows,mat_cols); //--- string Arr[]; //temporary array to carry the values of a single column int start =0; vector v = {}; for (ulong j=0; j<mat_cols; j++) { ArrayCopy(Arr,toArr,0,start,(int)mat_rows); v = LabelEncoder(Arr); Matrix.Col(v, j); start += (int)mat_rows; } return (Matrix);
LabelEncoder() 函数就像它的名字一样,若特征相似,则它在列数组中贴上相同标签,这是它里面的内容。
vector CMatrixutils::LabelEncoder(string &Arr[]) { string classes[]; vector Encoded((ulong)ArraySize(Arr)); Classes(Arr,classes); for (ulong A=0; A<classes.Size(); A++) for (ulong i=0; i<Encoded.Size(); i++) { if (classes[A] == Arr[i]) Encoded[i] = (int)A; } return Encoded; }
这个函数很简单,它循环遍历整个数组查找给定的类,从而找到类似的特征,并为它们添加标签,大部分工作都是在以黑色高亮显示的函数 Classes() 中完成的。
void CMatrixutils::Classes(const string &Array[],string &classes_arr[]) { string temp_arr[]; ArrayResize(classes_arr,1); ArrayCopy(temp_arr,Array); classes_arr[0] = Array[0]; for(int i=0, count =1; i<ArraySize(Array); i++) //counting the different neighbors { for(int j=0; j<ArraySize(Array); j++) { if(Array[i] == temp_arr[j] && temp_arr[j] != "nan") { bool count_ready = false; for(int n=0; n<ArraySize(classes_arr); n++) if(Array[i] == classes_arr[n]) count_ready = true; if(!count_ready) { count++; ArrayResize(classes_arr,count); classes_arr[count-1] = Array[i]; temp_arr[j] = "nan"; //modify so that it can no more be counted } else break; //Print("t vectors vector ",v); } else continue; } } }
此函数获取给定数组中存在的类,并将它们传递给引用的数组 classes_arr[]。此函数有一个变体,能在向量中查找类。 有关此函数的更多详细信息,请参阅此处。
vector CMatrixutils::Classes(vector &v)
以下是如何使用此函数;
Matrix = matrix_utils.ReadCsvEncode("weather dataset.csv"); ArrayPrint(matrix_utils.csv_header); Print(Matrix);
输出:
CS 0 06:35:10.798 matrix test (US500,D1) "Outlook" "Temperature" "Humidity" "Wind" "Play" CS 0 06:35:10.798 matrix test (US500,D1) [[0,0,0,0,0] CS 0 06:35:10.798 matrix test (US500,D1) [0,0,0,1,0] CS 0 06:35:10.798 matrix test (US500,D1) [1,0,0,0,1] CS 0 06:35:10.798 matrix test (US500,D1) [2,1,0,0,1] CS 0 06:35:10.798 matrix test (US500,D1) [2,2,1,0,1] CS 0 06:35:10.798 matrix test (US500,D1) [2,2,1,1,0] CS 0 06:35:10.798 matrix test (US500,D1) [1,2,1,1,1] CS 0 06:35:10.798 matrix test (US500,D1) [0,1,0,0,0] CS 0 06:35:10.798 matrix test (US500,D1) [0,2,1,0,1] CS 0 06:35:10.798 matrix test (US500,D1) [2,1,1,0,1] CS 0 06:35:10.798 matrix test (US500,D1) [0,1,1,1,1] CS 0 06:35:10.798 matrix test (US500,D1) [1,1,0,1,1] CS 0 06:35:10.798 matrix test (US500,D1) [1,0,1,0,1] CS 0 06:35:10.798 matrix test (US500,D1) [2,1,0,1,0]]
将矩阵写入一个 CSV 文件
这是另一个重要的函数,它可以帮助将矩阵写入 CSV 文件,且无需在每次向矩阵添加新列时对内容进行硬编码。 对于论坛中的许多人来说,能够以灵活的方式写入 CSV 文件一直是一件困难的事情 > Post1, Post2, Post3。 以下是矩阵写入的方法;row = Matrix.Row(i); for(ulong j=0, cols =1; j<row.Size(); j++, cols++) { concstring += (string)NormalizeDouble(row[j],digits) + (cols == Matrix.Cols() ? "" : ","); }
在末尾,看起来就像 CSV 文件以手工写入不同一列。 由于矩阵不能携带字符串值,我不得不用字符串数组,来将标头写入此 csv 文件。
我们尝试把从 CSV 文件提取的矩阵再写回新的 CSV 文件。
string csv_name = "matrix CSV.csv"; Print("\n---> Writing a Matrix to a CSV File > ",csv_name); string header[4] = {"S&P500","SMA","RSI","NASDAQ"}; matrix_utils.WriteCsv(csv_name,Matrix,header);
以下是新编写的 CSV 文件;
很酷!
将矩阵转换为向量
有人可能会问自己为什么要将矩阵转换为向量? 这在许多领域都能派上用场,因为您可能不需要一直使用矩阵,因此此函数的作用是将矩阵转换为向量,例如,当您想要制作线性回归模型的时候,从 CSV 文件中读取矩阵,自变量是 nx1 或 1xn 矩阵, 当尝试使用损失函数(如 MSE)时,您无法用矩阵来评估模型,而是用此自变量的向量,以及模型预测值的向量。
下面是它的代码;vector CMatrixutils::MatrixToVector(const matrix &mat) { vector v = {}; if (!v.Assign(mat)) Print("Failed to turn the matrix to a vector"); return(v); }
用法:
matrix mat = { {1,2,3}, {4,5,6}, {7,8,9} }; Print("\nMatrix to play with\n",mat,"\n"); //--- Print("---> Matrix to Vector"); vector vec = matrix_utils.MatrixToVector(mat); Print(vec);
输出:
2022.12.20 05:39:00.286 matrix test (US500,D1) ---> Matrix to Vector 2022.12.20 05:39:00.286 matrix test (US500,D1) [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
将向量转换为矩阵
这与我们刚刚在上面看到的函数完全相反,但这比您想象的更重要。 大多数时候,在机器学习模型中,您需要在不同矩阵之间执行乘法运算,由于自变量通常存储在向量中,您可能需要将它们转换为 nx1 矩阵才能执行运算,故这两个逆反的函数很重要,因为它们通过调整现有变量令我们的代码更少。matrix CMatrixutils::VectorToMatrix(const vector &v) { matrix mat = {}; if (!mat.Assign(v)) Print("Failed to turn the vector to a 1xn matrix"); return(mat); }
用法:
Print("\n---> Vector ",vec," to Matrix"); mat = matrix_utils.VectorToMatrix(vec); Print(mat);
输出:
2022.12.20 05:50:05.680 matrix test (US500,D1) ---> Vector [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] to Matrix 2022.12.20 05:50:05.680 matrix test (US500,D1) [[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]]
将数组转换为向量
谁会在机器学习程序中需要使用大量数组? 数组非常有用,但它们对大小非常敏感。 经常调整并使用它们,也许会令终端加速将您的程序抛出图表,因为这些数组出现超界错误;即使向量做同样的事情,但它们比数组更灵活一些,更不用说它们是面向对象的,您可以从函数返回向量,但不能从数组返回向量,除非您想看到代码的编译错误和警告。
vector CMatrixutils::ArrayToVector(const double &Arr[]) { vector v((ulong)ArraySize(Arr)); for(ulong i=0; i<v.Size(); i++) v[i] = Arr[i]; return (v); }
用法:
Print("---> Array to vector"); double Arr[3] = {1,2,3}; vec = matrix_utils.ArrayToVector(Arr); Print(vec);
输出:
CS 0 05:51:58.853 matrix test (US500,D1) ---> Array to vector CS 0 05:51:58.853 matrix test (US500,D1) [1,2,3]
向量到数组
我们仍然不能彻底放弃数组,因为有时可能需要将向量转换为数组,以便按需要插入只接受数组参数的函数,或者我们可能需要执行一些数组排序、设置为系列、切片、以及我们无法用向量完成的更多操作。 bool CMatrixutils::VectorToArray(const vector &v,double &arr[]) { ArrayResize(arr,(int)v.Size()); if(ArraySize(arr) == 0) return(false); for(ulong i=0; i<v.Size(); i++) arr[i] = v[i]; return(true); }
用法:
Print("---> Vector to Array"); double new_array[]; matrix_utils.VectorToArray(vec,new_array); ArrayPrint(new_array);
输出:
CS 0 06:19:14.647 matrix test (US500,D1) ---> Vector to Array CS 0 06:19:14.647 matrix test (US500,D1) 1.0 2.0 3.0
矩阵删除列
仅仅因为我们已经将 CSV 列加载到矩阵之中,而这并不意味着我们需要其中的所有列,在创建监督式机器学习模型时,我们需要删除一些不相关的列,更不用说我们可能需要从充满自变量的矩阵中删除响应变量。
这是执行该操作的代码:
void CMatrixutils::MatrixRemoveCol(matrix &mat, ulong col) { matrix new_matrix(mat.Rows(),mat.Cols()-1); //Remove the one Column for (ulong i=0, new_col=0; i<mat.Cols(); i++) { if (i == col) continue; else { new_matrix.Col(mat.Col(i),new_col); new_col++; } } mat.Copy(new_matrix); }
函数内部没有什么神奇之处,我们创建一个新的矩阵,其大小与原始矩阵的行数相同,但少了一列。
matrix new_matrix(mat.Rows(),mat.Cols()-1); //Remove the one column在新矩阵中,我们忽略新矩阵中不再需要的列,其它所有内容都将被存储,仅此而已。
在函数结束时,我们将这个新矩阵复制到旧矩阵。
mat.Copy(new_matrix);
我们从刚刚自 CSV 文件中读取的矩阵中将列放在索引 1(第二列)处
Print("Col 1 ","Removed from Matrix"); matrix_utils.MatrixRemoveCol(Matrix,1); Print("New Matrix\n",Matrix);
输出:
CS 0 07:23:59.612 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) Column of index 1 removed new Matrix CS 0 07:23:59.612 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [[4173.8,34.8,13067.5] CS 0 07:23:59.612 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4179.2,36.6,13094.8] CS 0 07:23:59.612 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4182.7,37.5,13108] CS 0 07:23:59.612 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4185.8,37.1,13104.3] CS 0 07:23:59.612 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4180.8,34.9,13082.2] CS 0 07:23:59.612 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4174.6,31.8,13052] CS 0 07:23:59.612 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4174.9,33.2,13082.2] CS 0 07:23:59.612 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4170.8,32.2,13070.6] CS 0 07:23:59.612 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4182.2,32.5,13078.8]
从矩阵中删除多列
尝试删除单列时就是这种情况,但若有较大的矩阵包含大量我们想要一次性删除的列,为此,我们需要执行一些棘手的操作,避免误删所需的列,并避免尝试访问超界的数值, 基本上都是为了安全地删除列。
新矩阵的列数/大小要等于总列数减去我们要删除的列数,每列的行数保持不变(与旧矩阵相同)。
我们要做的第一件事是遍历我们要删除的所有选定列,以及旧矩阵中的所有可用列,如果要删除这些列,我们会将该列中的所有值设置为零。 这是一个明智的操作,可以最终得到一个干净的操作。vector zeros(mat.Rows()); zeros.Fill(0); for(ulong i=0; i<size; i++) for(ulong j=0; j<mat.Cols(); j++) { if(cols[i] == j) mat.Col(zeros,j); }我们要做的最后一件事是再次遍历矩阵两次,并检查所有填充零值的列,并将这些列逐个删除。
vector column_vector; for(ulong A=0; A<mat.Cols(); A++) for(ulong i=0; i<mat.Cols(); i++) { column_vector = mat.Col(i); if(column_vector.Sum()==0) MatrixRemoveCol(mat,i); }
注意到循环两次了吗? 它们非常重要,因为矩阵在删除每列后其大小都会调整,因此需再次循环,故再次返回检查我们是否跳过所需列非常必要。
下面是该函数的完整代码;void CMatrixutils::MatrixRemoveMultCols(matrix &mat,int &cols[]) { ulong size = (int)ArraySize(cols); if(size > mat.Cols()) { Print(__FUNCTION__," Columns to remove can't be more than the available columns"); return; } vector zeros(mat.Rows()); zeros.Fill(0); for(ulong i=0; i<size; i++) for(ulong j=0; j<mat.Cols(); j++) { if(cols[i] == j) mat.Col(zeros,j); } //--- vector column_vector; for(ulong A=0; A<mat.Cols(); A++) for(ulong i=0; i<mat.Cols(); i++) { column_vector = mat.Col(i); if(column_vector.Sum()==0) MatrixRemoveCol(mat,i); } }
我们看看这个函数的实际效果,我们尝试删除索引 0 和索引 2 处的列;
Print("\nRemoving multiple columns"); int cols[2] = {0,2}; matrix_utils.MatrixRemoveMultCols(Matrix,cols); Print("Columns at 0,2 index removed New Matrix\n",Matrix);
输出:
CS 0 07:32:10.923 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) Columns at 0,2 index removed New Matrix CS 0 07:32:10.923 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [[13386.6,13067.5] CS 0 07:32:10.923 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [13396.7,13094.8] CS 0 07:32:10.923 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [13406.6,13108] CS 0 07:32:10.923 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [13416.8,13104.3] CS 0 07:32:10.923 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [13425.2,13082.2] CS 0 07:32:10.923 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [13432.2,13052] CS 0 07:32:10.923 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [13440.4,13082.2] CS 0 07:32:10.923 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [13447.6,13070.6] CS 0 07:32:10.923 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [13457.8,13078.8]
从矩阵中删除单行
可能还需要从数据集中删除单独一行,因为它可能不相关,或者人为想要减少列数,只是为了看看有什么效果。 这并不像从矩阵中删除列那么重要,如此我们只有这个函数来删除单行,我们看不到删除多行的用处,如果您需要,您可自行编写。
与尝试从矩阵中删除行时所采用的思路相同,我们在制作的新矩阵中简单地忽略不需要的行。
void CMatrixutils::MatrixRemoveRow(matrix &mat, ulong row) { matrix new_matrix(mat.Rows()-1,mat.Cols()); //Remove the one Row for(ulong i=0, new_rows=0; i<mat.Rows(); i++) { if(i == row) continue; else { new_matrix.Row(mat.Row(i),new_rows); new_rows++; } } mat.Copy(new_matrix); }
用法:
Print("Removing row 1 from matrix"); matrix_utils.MatrixRemoveRow(Matrix,1); printf("Row %d Removed New Matrix[%d][%d]",0,Matrix.Rows(),Matrix.Cols()); Print(Matrix);
输出:
CS 0 06:36:36.773 matrix test (US500,D1) Removing row 1 from matrix CS 0 06:36:36.773 matrix test (US500,D1) Row 1 Removed New Matrix[743][4] CS 0 06:36:36.773 matrix test (US500,D1) [[4173.8,13386.6,34.8,13067.5] CS 0 06:36:36.773 matrix test (US500,D1) [4182.7,13406.6,37.5,13108] CS 0 06:36:36.773 matrix test (US500,D1) [4185.8,13416.8,37.1,13104.3] CS 0 06:36:36.773 matrix test (US500,D1) [4180.8,13425.2,34.9,13082.2] CS 0 06:36:36.773 matrix test (US500,D1) [4174.6,13432.2,31.8,13052] CS 0 06:36:36.773 matrix test (US500,D1) [4174.9,13440.4,33.2,13082.2] CS 0 06:36:36.773 matrix test (US500,D1) [4170.8,13447.6,32.2,13070.6]
向量删除索引
这是一个简短的函数,此函数可为从向量中删除特定索引处的单个项提供帮助。 它能够通过忽略位于向量中给定索引处的数字来实现这样的结果,其余值则被存储到新向量中,该向量最终从函数参数复制到主/引用向量。
void CMatrixutils::VectorRemoveIndex(vector &v, ulong index) { vector new_v(v.Size()-1); for(ulong i=0, count = 0; i<v.Size(); i++) if(i != index) { new_v[count] = v[i]; count++; } v.Copy(new_v); }
Below is how to use it:
vector v= {0,1,2,3,4}; Print("Vector remove index 3"); matrix_utils.VectorRemoveIndex(v,3); Print(v);
输出:
2022.12.20 06:40:30.928 matrix test (US500,D1) Vector remove index 3 2022.12.20 06:40:30.928 matrix test (US500,D1) [0,1,2,4]
将矩阵拆分为训练矩阵和测试矩阵
在制作监督式机器学习模型时,我无法强调这个函数有多重要。 我们通常需要将数据集拆分为训练数据集和测试数据集,以便我们可以在某个数据集上训练数据集,并在模型以前从未见过的另一个数据集上对其进行测试。
默认情况下,此函数将 70% 的数据集拆分为训练样本,其余 30% 拆分为测试样本,当中没有随机状态。 数据选择按矩阵的时间顺序,前 70% 的数据存储在训练矩阵之中,其余 30% 存储在测试矩阵之中。
Print("---> Train / Test Split"); matrix TrainMatrix, TestMatrix; matrix_utils.TrainTestSplitMatrices(Matrix,TrainMatrix,TestMatrix); Print("\nTrain Matrix(",TrainMatrix.Rows(),",",TrainMatrix.Cols(),")\n",TrainMatrix); Print("\nTestMatrix(",TestMatrix.Rows(),",",TestMatrix.Cols(),")\n",TestMatrix);
输出:
CS 0 07:38:46.011 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) Train Matrix(521,4) CS 0 07:38:46.011 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [[4173.8,13386.6,34.8,13067.5] CS 0 07:38:46.011 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4179.2,13396.7,36.6,13094.8] CS 0 07:38:46.011 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4182.7,13406.6,37.5,13108] CS 0 07:38:46.011 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4185.8,13416.8,37.1,13104.3] CS 0 07:38:46.011 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4180.8,13425.2,34.9,13082.2] .... .... CS 0 07:38:46.012 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) TestMatrix(223,4) CS 0 07:38:46.012 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [[4578.1,14797.9,65.90000000000001,15021.1] CS 0 07:38:46.012 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4574.9,14789.2,63.9,15006.2] CS 0 07:38:46.012 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4573.6,14781.4,63,14999] CS 0 07:38:46.012 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4571.4,14773.9,62.1,14992.6] CS 0 07:38:46.012 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [4572.8,14766.3,65.2,15007.1]
X 和 Y 拆分矩阵
当我们将数据集加载到矩阵之中,然后尝试制作监督学习模型时,接下来我们需要做的是从矩阵中提取目标变量,并单独存储它们,就像我们希望自变量存储在它们的数值矩阵中一样,这是执行此操作的函数:if(y_index == -1) value = matrix_.Cols()-1; //Last column in the matrix
用法:
Print("---> X and Y split matrices"); matrix x; vector y; matrix_utils.XandYSplitMatrices(Matrix,x,y); Print("independent vars\n",x); Print("Target variables\n",y);
输出:
CS 0 05:05:03.467 matrix test (US500,D1) ---> X and Y split matrices CS 0 05:05:03.467 matrix test (US500,D1) independent vars CS 0 05:05:03.468 matrix test (US500,D1) [[4173.8,13386.6,34.8] CS 0 05:05:03.468 matrix test (US500,D1) [4179.2,13396.7,36.6] CS 0 05:05:03.468 matrix test (US500,D1) [4182.7,13406.6,37.5] CS 0 05:05:03.468 matrix test (US500,D1) [4185.8,13416.8,37.1] CS 0 05:05:03.468 matrix test (US500,D1) [4180.8,13425.2,34.9] CS 0 05:05:03.468 matrix test (US500,D1) [4174.6,13432.2,31.8] CS 0 05:05:03.468 matrix test (US500,D1) [4174.9,13440.4,33.2] CS 0 05:05:03.468 matrix test (US500,D1) [4170.8,13447.6,32.2] CS 0 05:05:03.468 matrix test (US500,D1) [4182.2,13457.8,32.5] .... .... 2022.12.20 05:05:03.470 matrix test (US500,D1) Target variables 2022.12.20 05:05:03.470 matrix test (US500,D1) [13067.5,13094.8,13108,13104.3,13082.2,13052,13082.2,13070.6,13078.8,...]
在 X 和 Y 拆分函数中,所选列作为 y 变量存储在 Y 矩阵之中,而其余列存储在 X 矩阵之中。
void CMatrixutils::XandYSplitMatrices(const matrix &matrix_,matrix &xmatrix,vector &y_vector,int y_index=-1) { ulong value = y_index; if(y_index == -1) value = matrix_.Cols()-1; //Last column in the matrix //--- y_vector = matrix_.Col(value); xmatrix.Copy(matrix_); MatrixRemoveCol(xmatrix, value); //Remove the y column }
制作设计矩阵
设计矩阵对于最小二乘算法至关重要,它只是 x 矩阵(独立变量矩阵),第一列由数字 1 填充。 此设计矩阵可帮助我们获取线性回归模型的系数。 在函数 DesignMatrix() 中,创建向量,并填充数字 1,然后将其插入到矩阵的第一列,而其余列则仍然遵循原来顺序;完整代码:
matrix CMatrixutils::DesignMatrix(matrix &x_matrix) { matrix out_matrix(x_matrix.Rows(),x_matrix.Cols()+1); vector ones(x_matrix.Rows()); ones.Fill(1); out_matrix.Col(ones,0); vector new_vector; for(ulong i=1; i<out_matrix.Cols(); i++) { new_vector = x_matrix.Col(i-1); out_matrix.Col(new_vector,i); } return (out_matrix); }
用法:
Print("---> Design Matrix\n"); matrix design = matrix_utils.DesignMatrix(x); Print(design);
输出:
CS 0 05:28:51.786 matrix test (US500,D1) ---> Design Matrix CS 0 05:28:51.786 matrix test (US500,D1) CS 0 05:28:51.786 matrix test (US500,D1) [[1,4173.8,13386.6,34.8] CS 0 05:28:51.786 matrix test (US500,D1) [1,4179.2,13396.7,36.6] CS 0 05:28:51.786 matrix test (US500,D1) [1,4182.7,13406.6,37.5] CS 0 05:28:51.786 matrix test (US500,D1) [1,4185.8,13416.8,37.1] CS 0 05:28:51.786 matrix test (US500,D1) [1,4180.8,13425.2,34.9] CS 0 05:28:51.786 matrix test (US500,D1) [1,4174.6,13432.2,31.8] CS 0 05:28:51.786 matrix test (US500,D1) [1,4174.9,13440.4,33.2] CS 0 05:28:51.786 matrix test (US500,D1) [1,4170.8,13447.6,32.2] CS 0 05:28:51.786 matrix test (US500,D1) [1,4182.2,13457.8,32.5]
独热编码矩阵
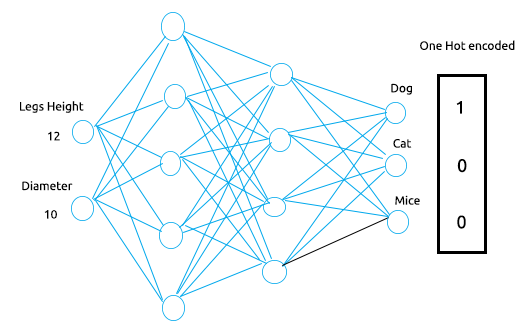
我们完成一些独热编码。 这是您在尝试创建分类神经网络时需要的一个非常重要的函数。 这个函数被证明非常重要,因为它清楚地表明 MLP 与最后一层神经元输出与实际值相关联。
在独热编码矩阵中,每行的向量由零值组成,除了一个值,该值用于我们要命中的正确值,其值为 1。
为了更好地理解这一点,我们来看下面的例子:
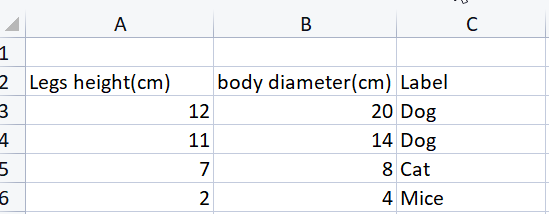
假设这是我们想要训练神经网络的数据集,以便能够在狗、猫和老鼠三类之间,基于它们的腿高和体径进行分类。
多层感知器会有 2 个输入节点/神经元,一个用于腿高,另一个则是输入层的身体直径,同时输出层将有 3 个节点代表 3 个结果:狗、猫和老鼠。
现在,假设我们给这个 MLP 投喂的高度和直径分别为 12 和 20,我们希望神经网络将其归类为狗,对不对? 独热编码的作用是将数字 1 放在给定训练数据集具有正确值的节点中,在这种情况下,在属于狗的节点上,将输入数字 1,其余位置则依然携带零值。
由于其余为零值,我们在计算成本函数时,可以将独热编码向量的值替代模型给我们的每个概率,然后该误差将传播回前一层各自之前节点中的网络。
好了,现在我们来看看独热编码在运行。
这是我们在 MetaEditor 中的矩阵;
matrix dataset = { {12,28, 1}, {11,14, 1}, {7,8, 2}, {2,4, 3} };
这与您从 CSV 中看到的数据集相同,只是目标以整数型标记,因为我们不能在矩阵中包含字符串,顺便问一下,何时何地可以在计算中使用字符串?
matrix dataset = { {12,28, 1}, {11,14, 1}, {7,8, 2}, {2,4, 3} }; vector y_vector = dataset.Col(2); //obtain the column to encode uint classes = 3; //number of classes in the column Print("One Hot encoded matrix \n",matrix_utils.OneHotEncoding(y_vector,classes));
下面是输出:
CS 0 08:54:04.744 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) One Hot encoded matrix CS 0 08:54:04.744 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [[1,0,0] CS 0 08:54:04.744 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [1,0,0] CS 0 08:54:04.744 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [0,1,0] CS 0 08:54:04.744 matrix test (EURUSD,H1) [0,0,1]]
从向量获取类
此函数返回包含给定向量中可用类的向量;例如,具有 [1,2,3] 的向量有 3 个不同的类,具有 [1,0,1,0] 的向量则有两个不同的类。 函数的作用是返回可用的非重复类。
vector v = {1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0}; Print("classes ",matrix_utils.Classes(v));
输出:
2022.12.27 06:41:54.758 matrix test (US500,D1) classes [1,0]
创建随机值向量。
有几回,我们需要生成一个充满随机变量的向量,那这个函数就可以提供帮助。 此函数最常见的用途是为神经网络生成权重和偏置向量。 您还可以用其来创建随机数据集样本。
vector Random(int min, int max, int size); vector Random(double min, double max, int size);
用法:
v = matrix_utils.Random(1.0,2.0,10); Print("v ",v);
输出:
2022.12.27 06:50:03.055 matrix test (US500,D1) v [1.717642750328074,1.276955473494675,1.346263008514664,1.32959990234077,1.006469924008911,1.992980742820521,1.788445692312387,1.218909268471328,1.732139042329173,1.512405774101993]
将一个向量附加到另一个向量。
这类似于字符串连接,但这里我们连接向量。 我发现自己在很多情况下都会想到用这个函数。 以下是它的组成,
vector CMatrixutils::Append(vector &v1, vector &v2) { vector v_out = v1; v_out.Resize(v1.Size()+v2.Size()); for (ulong i=v2.Size(),i2=0; i<v_out.Size(); i++, i2++) v_out[i] = v2[i2]; return (v_out); }
用法:
vector v1 = {1,2,3}, v2 = {4,5,6}; Print("Vector 1 & 2 ",matrix_utils.Append(v1,v2));
输出:
2022.12.27 06:59:25.252 matrix test (US500,D1) Vector 1 & 2 [1,2,3,4,5,6]
将一个向量复制到另一个向量
最后但同样重要的是,我们像 Arraycopy 一样操作把一个向量复制到另一个向量,我们通常不需要将整个向量复制到另一个向量,我们一般只需要其中的一大块,标准库提供的 Copy 方法在这种情况下就太平凡了。
bool CMatrixutils::Copy(const vector &src,vector &dst,ulong src_start,ulong total=WHOLE_ARRAY) { if (total == WHOLE_ARRAY) total = src.Size()-src_start; if ( total <= 0 || src.Size() == 0) { printf("Can't copy a vector | Size %d total %d src_start %d ",src.Size(),total,src_start); return (false); } dst.Resize(total); dst.Fill(0); for (ulong i=src_start, index =0; i<total+src_start; i++) { dst[index] = src[i]; index++; } return (true); }
用法:
vector all = {1,2,3,4,5,6}; matrix_utils.Copy(all,v,3); Print("copied vector ",v);
输出:
2022.12.27 07:15:41.420 matrix test (US500,D1) copied vector [4,5,6]
后记
我们可以做很多事情,我们可以向实用工具文件添加更多函数,但我认为本文中介绍的函数和方法是那些我认为您会需要的,如果您已经使用矩阵一段时间了,并且在尝试创建复杂的交易系统(例如受机器学习启发的系统)时,您会发现经常需要它们。
跟踪此矩阵类实用工具的开发,请查阅我的 GitHub 存储库 > https://github.com/MegaJoctan/MALE5
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/11858
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。


谢谢你的文章,它真的很有启发性。
顺便说一下,我发现很难处理的是在 Metatreader 上训练基于 NN 的 ea。
我曾尝试将权重和偏置值写入 CSV 文件,由 metatrader 优化器上的训练代理加载,但它只是在步骤少于 100 时停止。
你有什么办法训练这么多变量吗?
谢谢你的文章,它真的很鼓舞人心。
顺便说一下,我发现很难处理的是 Metatreader 上基于 NN 的 EA 训练。
我曾尝试将权重和偏置值写入 CSV 文件,由 metatrader 优化器上的训练代理加载,但它在步骤小于 100 时就停止了。除此之外,它看起来就像代理在破坏 CSV 文件。
你有什么办法训练这么多变量吗?
在没有看到代码和所有相关内容的情况下,很难说清楚。我不在策略测试器上训练 NN,我更喜欢在那里训练交易参数。我所有的 NN 都是自己训练的
谢谢你的文章,它真的很鼓舞人心。
顺便说一下,我发现很难处理的是 Metatreader 上基于 NN 的 EA 训练。
我曾尝试将权重和偏置值写入 CSV 文件,由 metatrader 优化器上的训练代理加载,但它在步骤小于 100 时就停止了。除此之外,它看起来就像代理在破坏 CSV 文件。
你有什么办法训练这么多变量吗?
如果你使用测试器的快速遗传算法,你必须小心,因为它有不同的 "动机",这取决于你设置奖励的方式。
正如 Msigwa 先生所说,最好使用反向传播来训练你的网络。您可以训练更多的权重,而网络的唯一奖励就是提高 "准确性"。