Ação de preço. Como automatizar a estratégia de negociação de padrão de engolfo
Introdução
Todos os negociadores Forex cruzam com a Ação de preço em algum momento. Essa não é uma mera técnica de análise de gráficos, mas sim o sistema completo para definir a possível direção de movimento de preço futuro. Neste artigo, analisaremos o padrão de engolfo e criaremos um Expert Advisor que seguirá este padrão e tomará decisões de negociação relevantes com base nele.
Anteriormente, examinamos a negociação automatizada com padrões de Ação de preço, especificamente com a negociação Inside Bar, no artigo Ação de preço. Como automatizar a estratégia de negociação Inside Bar.
Regras do padrão de engolfo
O padrão de engolfo se dá quando o corpo e as sombras de uma barra engolfam por completo o corpo e as sombras da barra anterior. Há dois tipos de padrões disponíveis:
- BUOVB — Bullish Outside Vertical Bar (Barra vertical externa alta);
- BEOVB — Bearish Outside Vertical Bar (Barra vertical externa baixa).
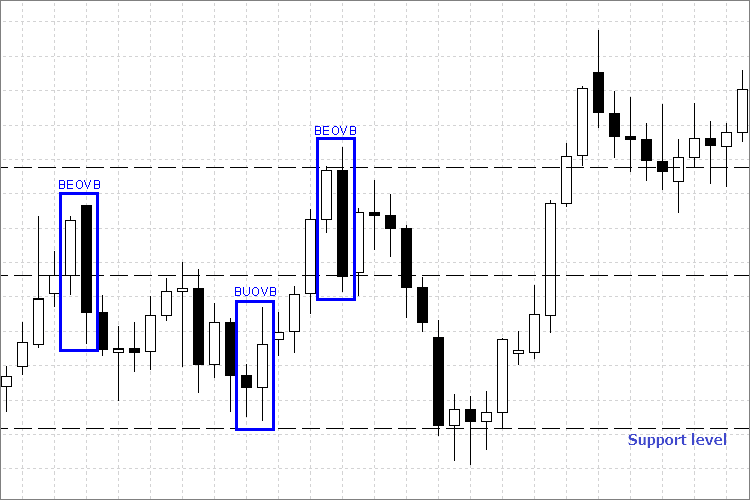
Fig. 1. Tipos de padrão exibidos no gráfico
BUOVB. O gráfico mostra que o High da barra externa está acima do High da barra anterior, e que o Low da barra externa está abaixo do Low da anterior.
BEOVB. Este padrão também pode ser facilmente identificado no gráfico. O Alto da barra externa está acima do Alto da barra anterior, e o Baixo da barra externa está abaixo do Baixo da barra anterior.
Suas diferenças são que cada padrão dá um entendimento claro sobre as direções possíveis do mercado.
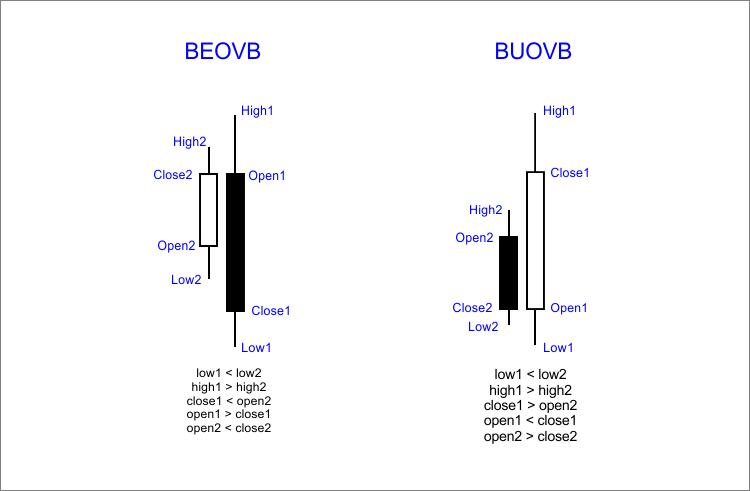
Fig. 2. Estrutura do padrão
Regras do padrão de engolfo:- É necessário operar com este padrão em períodos de tempo mais altos. H4, D1.
- Para uma entrada mais refinada, elementos adicionais de análises gráficas devem ser aplicados como linhas de tendência, níveis de resistência/suporte, níveis de Fibonacci, outros padrões de ação de preço etc.
- Use ordens pendentes para evitar entradas de mercado falsas ou prematuras.
- Padrões repetidos em negociações planas não devem ser usados como um sinal para entrada no mercado.
Como estabelecer pontos de entrada para "BUOVB", como efetuar uma ordem de parada
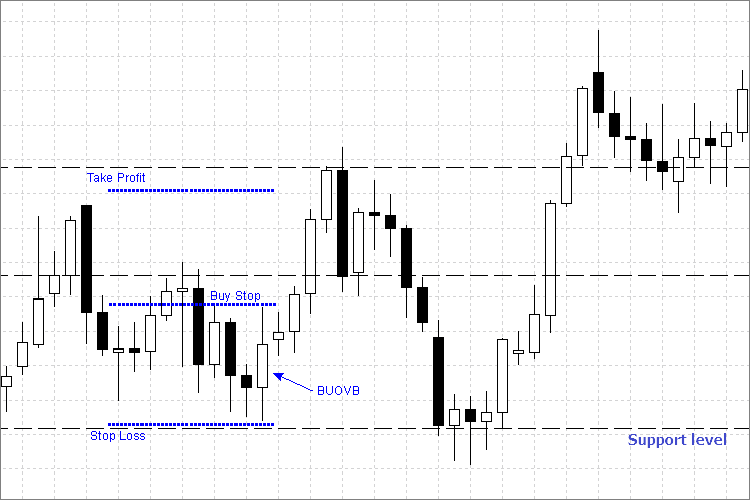
Fig. 3. Como definir ordens de Buy Stop e de parada
Analisaremos as regras de entrada e o posicionamento das ordens de parada para BUOVB (barra vertical externa alta) usando o exemplo acima:
- Definimos a ordem pendente Buy Stop a um preço um pouco acima do preço Alto (por alguns pontos, para confirmação) da barra externa.
- O nível de Stop Loss é definido abaixo do preço Baixo da barra externa.
- E o nível Take Profit é definido antes de alcançar o próximo nível de resistência.
Como estabelecer pontos de entrada para "BEOVB", como efetuar uma ordem de parada
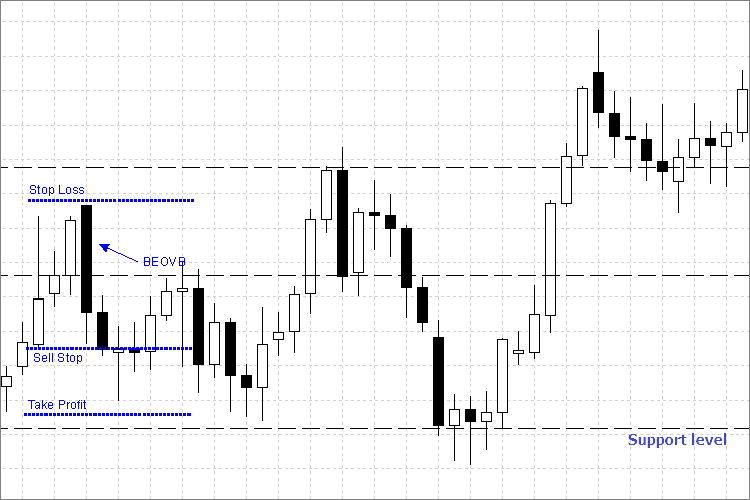
Fig. 4. Como definir ordens de Sell Stop e de parada
Vamos examinar as regras de entrada e posicionamento de ordens de parada de BEOVB (barra vertical externa baixa) do exemplo acima:
- Colocamos a ordem Sell Stop pendente a um preço um pouco abaixo do preço Baixo (por alguns pontos, para confirmação) de uma barra externa.
- O nível de Stop Loss é definido acima do preço Alto da barra externa.
- E o nível Take Profit é definido antes de alcançar o próximo nível de suporte.
Como criar um Expert Advisor para negociar o padrão de engolfo
Revisamos o padrão de engolfo, aprendemos a entrar no mercado com segurança e também a determinar os níveis de ordens de parada para limitar as perdas ou bloqueios de lucros.
A seguir, tentaremos implementar algoritmos de um Expert Advisor e automatizar o padrão de negociação de engolfo.
Abrimos o MetaEditor do terminal MetaTrader 4 e criamos um novo Expert Advisor (não entraremos em detalhes sobre como criar Expert Advisors, pois há informações suficientes disponíveis no site). Na etapa de criação, deixamos todos os parâmetros em branco. É possível nomeá-los da forma que quiser. Eventualmente, você obterá os seguintes resultados:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| BEOVB_BUOVB_Bar.mq4 | //| Copyright 2015, Iglakov Dmitry. | //| cjdmitri@gmail.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2015, Iglakov Dmitry." #property link "cjdmitri@gmail.com" #property version "1.00" #property strict //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- //--- return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { //--- } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { //--- } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Como converter o padrão no algoritmo MQL4
Após criar um Expert Advisor, devemos definir o padrão de engolfo após uma vela ser fechada. Para isso, introduzimos novas variáveis e valores designados a elas. Veja o código abaixo:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| BEOVB_BUOVB_Bar.mq4 | //| Copyright 2015, Iglakov Dmitry. | //| cjdmitri@gmail.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2015, Iglakov Dmitry." #property link "cjdmitri@gmail.com" #property version "1.00" #property strict double open1,//first candle Open price open2, //second candle Open price close1, //first candle Close price close2, //second candle Close price low1, //first candle Low price low2, //second candle Low price high1, //first candle High price high2; //second candle High price //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { //--- define prices of necessary bars open1 = NormalizeDouble(iOpen(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); open2 = NormalizeDouble(iOpen(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); close1 = NormalizeDouble(iClose(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); close2 = NormalizeDouble(iClose(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); low1 = NormalizeDouble(iLow(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); low2 = NormalizeDouble(iLow(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); high1 = NormalizeDouble(iHigh(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); high2 = NormalizeDouble(iHigh(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Encontramos os dois tipos de padrão de engolfo:
void OnTick() { //--- define prices of necessary bars open1 = NormalizeDouble(iOpen(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); open2 = NormalizeDouble(iOpen(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); close1 = NormalizeDouble(iClose(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); close2 = NormalizeDouble(iClose(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); low1 = NormalizeDouble(iLow(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); low2 = NormalizeDouble(iLow(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); high1 = NormalizeDouble(iHigh(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); high2 = NormalizeDouble(iHigh(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); //--- Finding bearish pattern BEOVB if(low1 < low2 &&// First bar's Low is below second bar's Low high1 > high2 &&// First bar's High is above second bar's High close1 < open2 && //First bar's Close price is below second bar's Open open1 > close1 && //First bar is a bearish bar open2 < close2) //Second bar is a bullish bar { //--- we have described all conditions indicating that the first bar completely engulfs the second bar and is a bearish bar }
Da mesma forma, encontramos um padrão bullish (alto):
//--- Finding bullish pattern BUOVB if(low1 < low2 &&// First bar's Low is below second bar's Low high1 > high2 &&// First bar's High is above second bar's High close1 > open2 && //First bar's Close price is higher than second bar's Open open1 < close1 && //First bar is a bullish bar open2 > close2) //Second bar is a bearish bar { //--- we have described all conditions indicating that the first bar completely engulfs the second bar and is a bullish bar }
- Criamos variáveis personalizadas: ordens de parada, deslizamento, tempo de expiração de ordem, número mágico do EA, lote de negociação. A Stop loss pode ser omitida, como será definido de acordo com as regras de padrão.
- Introduzimos variáveis locais para converter variáveis em uma forma normal.
- Além disso, mantemos em mente que as ordens de parada são definidas a uma certa distância dos valores de preço da barra. Para implementar isso, adicionamos a variável Intervalo responsável pelo intervalo entre os preços Altos/Baixos de barras e níveis de ordem de parada, assim como níveis de ordem pendentes.
- Inserimos a variável timeBUOVB_BEOVB para evitar a reabertura da ordem neste padrão.
- Inserimos a variável bar1size para verificar se a barra externa é grande o suficiente. Assim, assumimos que o mercado atual não está plano.
Como resultado, obtemos o seguinte código:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| BEOVB_BUOVB_bar.mq4 | //| Copyright 2015, Iglakov Dmitry. | //| cjdmitri@gmail.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2015, Iglakov Dmitry." #property link "cjdmitri@gmail.com" #property version "1.00" #property strict extern int interval = 25; //Interval extern double lot = 0.1; //Lot Size extern int TP = 400; //Take Profit extern int magic = 962231; //Magic number extern int slippage = 2; //Slippage extern int ExpDate = 48; //Expiration Hour Order extern int bar1size = 900; //Bar 1 Size double buyPrice,//define BuyStop setting price buyTP, //Take Profit BuyStop buySL, //Stop Loss BuyStop sellPrice, //define SellStop setting price sellTP, //Take Profit SellStop sellSL; //Stop Loss SellStop double open1,//first candle Open price open2, //second candle Open price close1, //first candle Close price close2, //second candle Close price low1, //first candle Low price low2, //second candle Low price high1, //first candle High price high2; //second candle High price datetime _ExpDate =0; // local variable for defining pending orders expiration time double _bar1size;// local variable required to avoid a flat market datetime timeBUOVB_BEOVB;// time of a bar when pattern orders were opened, to avoid re-opening //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { double _bid = NormalizeDouble(MarketInfo (Symbol(), MODE_BID), Digits); // define Low price double _ask = NormalizeDouble(MarketInfo(Symbol(), MODE_ASK), Digits); //define High price double _point = MarketInfo(Symbol(), MODE_POINT); //--- define prices of necessary bars open1 = NormalizeDouble(iOpen(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); open2 = NormalizeDouble(iOpen(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); close1 = NormalizeDouble(iClose(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); close2 = NormalizeDouble(iClose(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); low1 = NormalizeDouble(iLow(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); low2 = NormalizeDouble(iLow(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); high1 = NormalizeDouble(iHigh(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); high2 = NormalizeDouble(iHigh(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); //--- _bar1size=NormalizeDouble(((high1-low1)/_point),0); //--- Finding bearish pattern BEOVB if(timeBUOVB_BEOVB!=iTime(Symbol(),Period(),1) && //orders are not yet opened for this pattern _bar1size > bar1size && //first bar is big enough, so the market is not flat low1 < low2 &&//First bar's Low is below second bar's Low high1 > high2 &&//First bar's High is above second bar's High close1 < open2 && //First bar's Сlose price is lower than second bar's Open price open1 > close1 && //First bar is a bearish bar open2 < close2) //Second bar is a bullish bar { //--- we have described all conditions indicating that the first bar completely engulfs the second bar and is a bearish bar timeBUOVB_BEOVB=iTime(Symbol(),Period(),1); // indicate that orders are already placed on this pattern } //--- Finding bullish pattern BUOVB if(timeBUOVB_BEOVB!=iTime(Symbol(),Period(),1) && //orders are not yet opened for this pattern _bar1size > bar1size && //first bar is big enough not to consider a flat market low1 < low2 &&//First bar's Low is below second bar's Low high1 > high2 &&//First bar's High is above second bar's High close1 > open2 && //First bar's Close price is higher than second bar's Open price open1 < close1 && //First bar is a bullish bar open2 > close2) //Second bar is a bearish bar { //--- we have described all conditions indicating that the first bar completely engulfs the second bar and is a bullish bar timeBUOVB_BEOVB=iTime(Symbol(),Period(),1); // indicate that orders are already placed on this pattern } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Como definir níveis de ordem de parada
Preenchemos todas as condições e encontramos padrões de qualidade altos. Agora, é necessário definir os níveis de ordem padrão, preços de ordem pendentes assim como datas de expiração de ordens para cada padrão.
Vamos adicionar o seguinte código ao corpo da função OnTick() :
//--- Define prices for placing orders and stop orders buyPrice =NormalizeDouble(high1 + interval * _point,Digits); //define a price of order placing with intervals buySL =NormalizeDouble(low1-interval * _point,Digits); //define stop-loss with an interval buyTP =NormalizeDouble(buyPrice + TP * _point,Digits); //define take profit _ExpDate =TimeCurrent() + ExpDate*60*60; //pending order expiration time calculation //--- We also calculate sell orders sellPrice=NormalizeDouble(low1-interval*_point,Digits); sellSL=NormalizeDouble(high1+interval*_point,Digits); sellTP=NormalizeDouble(sellPrice-TP*_point,Digits);
Correção de erros de execução
Se você já se envolveu no desenvolvimento de Expert Advisors, provavelmente sabe que erros ocorrem com frequência ao fechar e definir ordens, incluindo tempo de espera, paradas incorretas etc. Para eliminar tais erros, devemos escrever uma função separada com um pequeno handler de erros básicos incorporado.
//+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| The function opens or sets an order | //| symbol - symbol, at which a deal is performed. | //| cmd - a deal (may be equal to any of the deal values). | //| volume - amount of lots. | //| price - Open price. | //| slippage - maximum price deviation for market buy or sell orders. | //| stoploss - position close price when an unprofitability level is reached (0 if there is no unprofitability level).| //| takeprofit - position close price when a profitability level is reached (0 if there is no profitability level). | //| comment - order comment. The last part of comment can be changed by the trade server. | //| magic - order magic number. It can be used as a user-defined ID. | //| expiration - pending order expiration time. | //| arrow_color - open arrow color on a chart. If the parameter is absent or equal to CLR_NONE, | //| the open arrow is not displayed on a chart. | //+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OrderOpenF(string OO_symbol, int OO_cmd, double OO_volume, double OO_price, int OO_slippage, double OO_stoploss, double OO_takeprofit, string OO_comment, int OO_magic, datetime OO_expiration, color OO_arrow_color) { int result = -1;// result of opening an order int Error = 0; // error when opening an order int attempt = 0; // amount of performed attempts int attemptMax = 3; // maximum amount of attempts bool exit_loop = false; // exit the loop string lang =TerminalInfoString(TERMINAL_LANGUAGE);// trading terminal language for defining the language of the messages double stopllvl =NormalizeDouble(MarketInfo (OO_symbol, MODE_STOPLEVEL) * MarketInfo (OO_symbol, MODE_POINT),Digits);// minimum stop loss/take profit level, in points //the module provides safe order opening //--- checking stop orders for buying if(OO_cmd==OP_BUY || OO_cmd==OP_BUYLIMIT || OO_cmd==OP_BUYSTOP) { double tp = (OO_takeprofit - OO_price)/MarketInfo(OO_symbol, MODE_POINT); double sl = (OO_price - OO_stoploss)/MarketInfo(OO_symbol, MODE_POINT); if(tp>0 && tp<=stopllvl) { OO_takeprofit=OO_price+stopllvl+2*MarketInfo(OO_symbol,MODE_POINT); } if(sl>0 && sl<=stopllvl) { OO_stoploss=OO_price -(stopllvl+2*MarketInfo(OO_symbol,MODE_POINT)); } } //--- checking stop orders for selling if(OO_cmd==OP_SELL || OO_cmd==OP_SELLLIMIT || OO_cmd==OP_SELLSTOP) { double tp = (OO_price - OO_takeprofit)/MarketInfo(OO_symbol, MODE_POINT); double sl = (OO_stoploss - OO_price)/MarketInfo(OO_symbol, MODE_POINT); if(tp>0 && tp<=stopllvl) { OO_takeprofit=OO_price -(stopllvl+2*MarketInfo(OO_symbol,MODE_POINT)); } if(sl>0 && sl<=stopllvl) { OO_stoploss=OO_price+stopllvl+2*MarketInfo(OO_symbol,MODE_POINT); } } //--- while loop while(!exit_loop) { result=OrderSend(OO_symbol,OO_cmd,OO_volume,OO_price,OO_slippage,OO_stoploss,OO_takeprofit,OO_comment,OO_magic,OO_expiration,OO_arrow_color); //attempt to open an order using the specified parameters //--- if there is an error when opening an order if(result<0) { Error = GetLastError(); //assign a code to an error switch(Error) //error enumeration { //order closing error enumeration and an attempt to fix them case 2: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; //define one more attempt Sleep(3000); //3 seconds of delay RefreshRates(); break; //exit switch } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt=0; //reset the amount of attempts to zero exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch } case 3: RefreshRates(); exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch case 4: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; //define one more attempt Sleep(3000); //3 seconds of delay RefreshRates(); break; //exit switch } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt = 0; //reset the amount of attempts to zero exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch } case 5: exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch case 6: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; //define one more attempt Sleep(5000); //3 seconds of delay break; //exit switch } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt = 0; //reset the amount of attempts to zero exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch } case 8: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; //define one more attempt Sleep(7000); //3 seconds of delay break; //exit switch } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt = 0; //reset the amount of attempts to zero exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch } case 64: exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch case 65: exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch case 128: Sleep(3000); RefreshRates(); continue; //exit switch case 129: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; //define one more attempt Sleep(3000); //3 seconds of delay RefreshRates(); break; //exit switch } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt = 0; //reset the amount of attempts to zero exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch } case 130: exit_loop=true; //exit while break; case 131: exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch case 132: Sleep(10000); //sleep for 10 seconds RefreshRates(); //update data //exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch case 133: exit_loop=true; //exit while break; //exit switch case 134: exit_loop=true; //exit while break; //exit switch case 135: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; //define one more attempt RefreshRates(); break; //exit switch } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt = 0; //set the number of attempts to zero exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch } case 136: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; //define one more attempt RefreshRates(); break; //exit switch } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt = 0; //set the amount of attempts to zero exit_loop = true; //exit while break; //exit switch } case 137: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; Sleep(2000); RefreshRates(); break; } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt=0; exit_loop=true; break; } case 138: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; Sleep(1000); RefreshRates(); break; } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt=0; exit_loop=true; break; } case 139: exit_loop=true; break; case 141: Sleep(5000); exit_loop=true; break; case 145: exit_loop=true; break; case 146: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; Sleep(2000); RefreshRates(); break; } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt=0; exit_loop=true; break; } case 147: if(attempt<attemptMax) { attempt=attempt+1; OO_expiration=0; break; } if(attempt==attemptMax) { attempt=0; exit_loop=true; break; } case 148: exit_loop=true; break; default: Print("Error: ",Error); exit_loop=true; //exit while break; //other options } } //--- if no errors detected else { if(lang == "Russian") {Print("Ордер успешно открыт. ", result);} if(lang == "English") {Print("The order is successfully opened.", result);} Error = 0; //reset the error code to zero break; //exit while //errorCount =0; //reset the amount of attempts to zero } } return(result); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Como resultado, obtemos o seguinte código:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| BEOVB_BUOVB_bar.mq4 | //| Copyright 2015, Iglakov Dmitry. | //| cjdmitri@gmail.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2015, Iglakov Dmitry." #property link "cjdmitri@gmail.com" #property version "1.00" #property strict extern int interval = 25; //Interval extern double lot = 0.1; //Lot Size extern int TP = 400; //Take Profit extern int magic = 962231; //Magic number extern int slippage = 2; //Slippage extern int ExpDate = 48; //Expiration Hour Order extern int bar1size = 900; //Bar 1 Size double buyPrice,//define BuyStop price buyTP, //Take Profit BuyStop buySL, //Stop Loss BuyStop sellPrice, //define SellStop price sellTP, //Take Profit SellStop sellSL; //Stop Loss SellStop double open1,//first candle Open price open2, //second candle Open price close1, //first candle Close price close2, //second candle Close price low1, //first candle Low price low2, //second candle Low price high1, //first candle High price high2; //second candle High price datetime _ExpDate =0; // local variable for defining pending orders expiration time double _bar1size;// local variable required to avoid a flat market datetime timeBUOVB_BEOVB;// time of a bar when pattern orders were opened, to avoid re-opening //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { double _bid = NormalizeDouble(MarketInfo (Symbol(), MODE_BID), Digits); // define Low price double _ask = NormalizeDouble(MarketInfo(Symbol(), MODE_ASK), Digits); //define High price double _point = MarketInfo(Symbol(), MODE_POINT); //--- define prices of necessary bars open1 = NormalizeDouble(iOpen(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); open2 = NormalizeDouble(iOpen(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); close1 = NormalizeDouble(iClose(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); close2 = NormalizeDouble(iClose(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); low1 = NormalizeDouble(iLow(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); low2 = NormalizeDouble(iLow(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); high1 = NormalizeDouble(iHigh(Symbol(), Period(), 1), Digits); high2 = NormalizeDouble(iHigh(Symbol(), Period(), 2), Digits); //--- Define prices for placing orders and stop orders buyPrice =NormalizeDouble(high1 + interval * _point,Digits); //define a price of order placing with intervals buySL =NormalizeDouble(low1-interval * _point,Digits); //define stop loss with an interval buyTP =NormalizeDouble(buyPrice + TP * _point,Digits); //define take profit _ExpDate =TimeCurrent() + ExpDate*60*60; //pending order expiration time calculation //--- We also calculate sell orders sellPrice=NormalizeDouble(low1-interval*_point,Digits); sellSL=NormalizeDouble(high1+interval*_point,Digits); sellTP=NormalizeDouble(sellPrice-TP*_point,Digits); //--- _bar1size=NormalizeDouble(((high1-low1)/_point),0); //--- Finding bearish pattern BEOVB if(timeBUOVB_BEOVB!=iTime(Symbol(),Period(),1) && //orders are not yet opened for this pattern _bar1size > bar1size && //first bar is big enough, so the market is not flat low1 < low2 &&//First bar's Low is below second bar's Low high1 > high2 &&//First bar's High is above second bar's High close1 < open2 && //First bar's Close price is lower than second bar's Open price open1 > close1 && //First bar is a bearish bar open2 < close2) //Second bar is a bullish bar { //--- we have described all conditions indicating that the first bar completely engulfs the second bar and is a bearish bar OrderOpenF(Symbol(),OP_SELLSTOP,lot,sellPrice,slippage,sellSL,sellTP,NULL,magic,_ExpDate,Blue); timeBUOVB_BEOVB=iTime(Symbol(),Period(),1); //indicate that orders are already placed on this pattern } //--- Finding bullish pattern BUOVB if(timeBUOVB_BEOVB!=iTime(Symbol(),Period(),1) && //orders are not yet opened for this pattern _bar1size > bar1size && //first bar is big enough, so the market is not flat low1 < low2 &&//First bar's Low is below second bar's Low high1 > high2 &&//First bar's High is above second bar's High close1 > open2 && //First bar's Close price is higher than second bar's Open price open1 < close1 && //First bar is a bullish bar open2 > close2) //Second bar is a bearish bar { //--- we have described all conditions indicating that the first bar completely engulfs the second bar and is a bullish bar OrderOpenF(Symbol(),OP_BUYSTOP,lot,buyPrice,slippage,buySL,buyTP,NULL,magic,_ExpDate,Blue); timeBUOVB_BEOVB = iTime(Symbol(),Period(),1); //indicate that orders are already placed on this pattern } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Agora, vamos executar a compilação e verificar as mensagens de erro no log.
Como testar o Expert Advisor
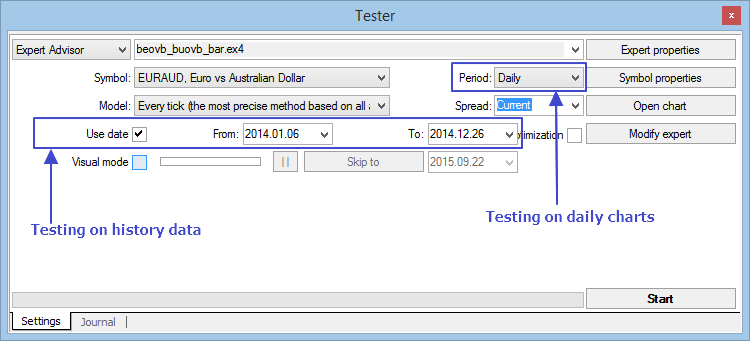
É hora de testar nosso Expert Advisor. Vamos iniciar o provador de estratégia e definir os parâmetros de entrada.
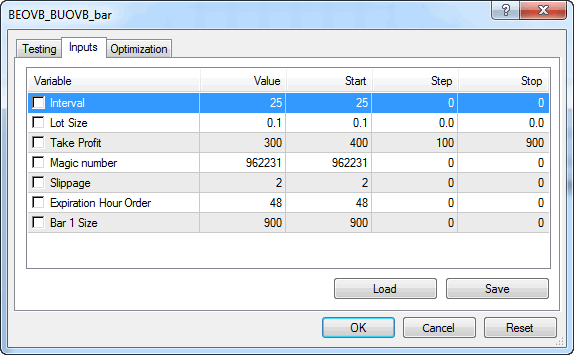
Fig. 5. Parâmetros de entrada para teste
- Escolha um par de moedas para teste. Escolhi EURAUD.
- Verifique se configurou o modo "Cada tick" e definiu que o teste será executado em dados históricos. Selecionei todo o ano de 2014.
- Defina o período de tempo D1.
- Inicie o teste.
- Após a conclusão do teste, verifique o log. Como podemos ver, nenhum erro de execução ocorreu no processo.
Abaixo está o diário de testes do EA:
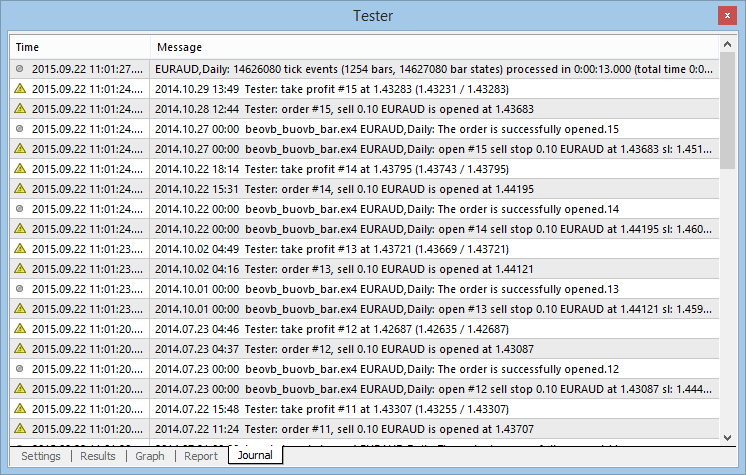
Fig. 7. Diário de testes do Expert Advisor
Tenha certeza de que não há erros e otimize o EA.
Otimização
Selecionei os seguintes parâmetros para otimização:
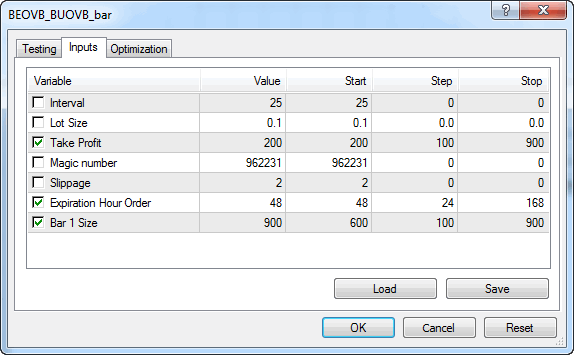
Fig. 8. Parâmetros de otimização
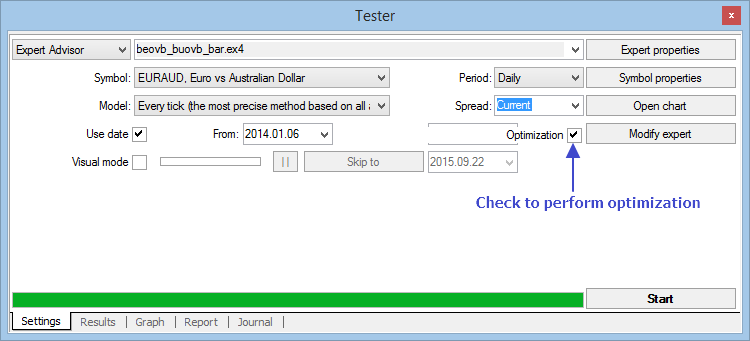
Fig. 9. Configurações de otimização
Dessa forma, como um resultado de otimização e teste, agora temos o robô pronto para uso.
Resultados de testes e otimização
Após a otimização dos pares de moeda mais populares, obtivemos os seguintes resultados:
| Par de moeda | Lucro da rede | Fator de lucro | Rebaixamento (%) | Lucro bruto | Perda bruta |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EURAUD | 523,90 $ | 3,70 | 2,13 | 727,98 $ | 196,86 $ |
| USDCHF | 454,19 $ | - | 2,25 | 454,19 $ | 0,00 $ |
| GBPUSD | 638,71 $ | - | 1,50 | 638,71 $ | 0,00 $ |
| EURUSD | 638,86 $ | - | 1,85 | 638,86 $ | 0,00 $ |
| USDJPY | 423,85 $ | 5,15 | 2,36 | 525,51 $ | 102,08 $ |
| USDCAD | 198,82 $ | 2,41 | 2,74 | 379,08 $ | 180,26 $ |
| AUDUSD | 136,14 $ | 1,67 | 2,39 | 339,26 $ | 203,12 $ |
Tabela 1. Resultados da otimização
Mais resultados de testes detalhados foram obtidos no par de moeda EURAUD:
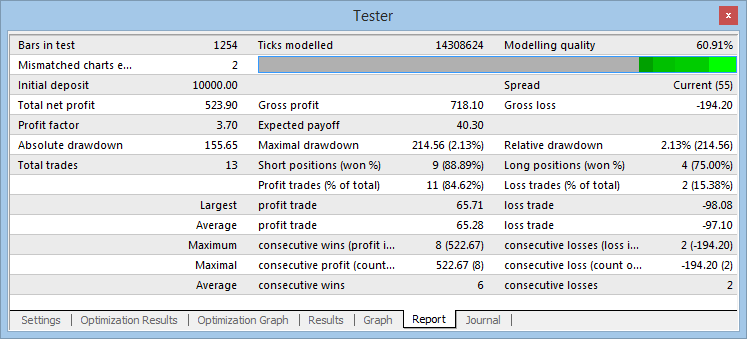
Fig. 10. Resultados do teste
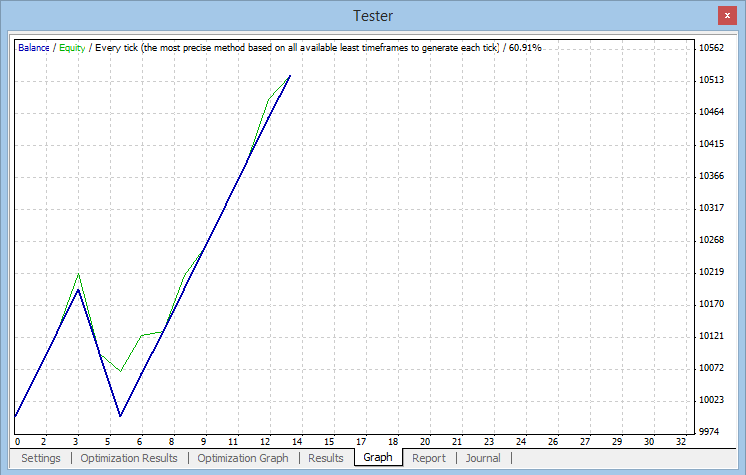
Fig. 11. Gráfico dos resultados do teste
Conclusão
- Neste artigo, criamos uma negociação de padrão de engolfo.
- Garantimos que os padrões de ação de preço podem funcionar mesmo sem filtros de entrada de mercado adicionais.
- Nenhum truque (como Martingale ou médias) foi usado.
- O rebaixamento foi minimizado através da configuração correta de ordens de parada.
- Nenhum indicador técnico foi usado. O EA foi baseado apenas na leitura de um gráfico "vazio".
Agradecemos pela leitura e esperamos que ache este artigo útil.
Traduzido do russo pela MetaQuotes Ltd.
Artigo original: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/1946
Aviso: Todos os direitos sobre esses materiais pertencem à MetaQuotes Ltd. É proibida a reimpressão total ou parcial.
Esse artigo foi escrito por um usuário do site e reflete seu ponto de vista pessoal. A MetaQuotes Ltd. não se responsabiliza pela precisão das informações apresentadas nem pelas possíveis consequências decorrentes do uso das soluções, estratégias ou recomendações descritas.
 Sobreposição e interferência de valores mobiliários financeiros
Sobreposição e interferência de valores mobiliários financeiros
 Uma pausa entre operações
Uma pausa entre operações
 Kit do trader: Indicadores de decoração
Kit do trader: Indicadores de decoração
- Aplicativos de negociação gratuitos
- 8 000+ sinais para cópia
- Notícias econômicas para análise dos mercados financeiros
Você concorda com a política do site e com os termos de uso