
开发多币种 EA 交易(第 22 部分):开始向设置的热插拔过渡
概述
在本系列文章的前两部分中,我们为交易 EA 的自动优化的进一步实验做了认真的准备。主要重点是创建一个优化输送机,目前包括三个阶段:
- 针对特定交易品种和时间周期的组合,优化单个策略实例。
- 将第一阶段获得的最佳单个样本进行分组。
- 生成最终 EA 的初始化字符串,合并形成的组,并将其保存到库中。
为了确保输送机本身的创建能够自动化,我们开发了一个专门的 EA 脚本。它允许将优化项目填充到数据库中,并根据指定的参数和模板创建阶段、作业和任务。这种方法提供了按给定顺序进一步执行优化任务的可能性,从一个阶段移动到另一个阶段。
我们还寻找使用分析和代码优化来提高性能的方法。主要重点是与安排接收交易工具(交易品种)信息的对象合作。这大大减少了检索价格和交易品种规格数据所需的方法调用次数。
这项工作的结果是自动生成可用于进一步实验和分析的结果。这为检验关于重新优化的频率和顺序如何影响交易表现的假设开辟了道路。
在这篇新文章中,我们将深入研究加载最终 EA 参数的新机制的实现,该机制应允许在策略测试器的单次运行期间以及在交易账户上运行最终 EA 时,部分或完全替换交易策略的单个实例的组成和参数。
规划路径
让我们试着更详细地描述我们想要实现的目标。理想情况下,系统应该这样工作:
- 生成一个项目,将当前日期作为优化期的结束日期。
- 该项目在输送机上启动。其实施需要一些时间,从几天到几周不等。
- 结果加载到最终 EA 中。如果最终的 EA 还没有进行过交易,则会在真实账户上启动它。如果它已经在账户上运行,那么它的参数将被最后一个项目通过输送机后收到的新参数替换。
- 让我们继续回到第一步。
让我们逐一探讨这些要点。为了实现第一步,我们已经有了上一部分的项目生成脚本 EA,我们可以在其中使用参数来选择优化的结束日期。但目前它只能手动启动。这可以通过在项目执行输送机中添加一个额外的阶段来解决,该阶段在当前项目的所有其他阶段完成后生成一个新项目。然后我们只需要第一次手动运行它即可。
对于第二点,我们只需要一台安装了 Optimization.ex5 EA 的终端,该终端的参数中指定了所需的数据库。一旦新的未完成项目任务出现在其中,它们将按照队列的顺序启动执行。在创建新项目之前的最后一个阶段,应该以某种形式将项目优化的结果转移到最终的 EA 中。
第三点是最难的。我们已经实现了将参数传递给最终 EA 的单一选项,但这仍然需要手动操作:您需要运行一个单独的 EA,将参数库导出到一个文件,然后将该文件复制到项目文件夹,然后重新编译最终的 EA。虽然我们现在可以将这些操作的执行委托给程序代码,但结构本身开始显得不必要地繁琐。我想做一些更简单、更可靠的事情。
所实现的将参数传递给最终 EA 的方法的另一个缺点是无法部分替换参数。只有完全替换才能实现,这将导致所有未平仓头寸(如果有的话)被平仓,并从头开始交易。如果我们停留在现有方法的框架内,就无法从根本上消除这一缺点。
让我们记住,我们现在所说的参数是指在一个最终的 EA 中并行运行的大量单一交易策略实例的参数。如果旧参数立即被新参数替换,即使它们与旧参数基本相同,那么当前的实现很可能无法正确加载有关先前开立的虚拟仓位的信息。只有当最终 EA 初始化字符串中各个实例的参数数量和顺序完全相同时,这才有可能实现。
为了实现部分参数替换,有必要以某种方式管理新旧参数的同时存在。在这种情况下,可以开发一种平滑过渡算法,使一些单独的实例保持不变。它们的虚拟仓位应该继续运作。那些不在新参数范围内的实例的仓位应该正确关闭。新添加的实例应该从头开始工作。
看起来正在酝酿比我们希望的更重大的变化。但是,如果我们看不到实现预期结果的任何其他方法,我们能做什么呢?最好尽早接受变革的必要性。如果我们继续朝着一个不完全正确的方向前进,那么我们走得越远,从这个方向走到一条新路就越困难。
因此,是时候转向将 EA 工作的所有信息存储在数据库中的“黑暗面”了。此外,在单独的数据库中,由于用于优化的数据库非常大(每个项目几 GB),将它们提供给最终的 EA 是没有意义的,因为实际工作只需要它们提供的一小部分信息。
我们还希望能够重新安排自动优化阶段的顺序。我们在第 20 部分中提到过,它是按交易品种和时间周期分组的。但我们当时没有选择它,因为如果没有部分替换参数的可能性,就不需要这样的顺序。现在,如果一切顺利,结果会更好。但是,让我们首先尝试过渡到为最终的 EA 使用单独的数据库,确保交易策略的单个实例的参数的热交换。
转换初始化字符串
这项任务相当庞大,所以我们将分小步进行。首先,我们需要将有关交易策略各个实例的信息存储在 EA 数据库中。该信息现已在 EA 初始化字符串中提供。EA 可以从优化数据库中获取该值,也可以从 EA 代码内置的数据(字符串常量)中获取该值,这些数据是在编译阶段从参数库中获取的。第一种方法用于优化 EA( SimpleVolumesStage2.mq5 和 SimpleVolumesStage3.mq5 ),第二种方法用于最终 EA( SimpleVolumesExpert.mq5 )。
我们想增加第三种方法:初始化字符串应分为与交易策略的不同单个实例相关的部分,这些部分存储在 EA 数据库中。然后,EA 就可以从其数据库中读取这些信息,并根据这些信息组成一个完整的初始化字符串。它将用于创建一个 EA 对象,该对象将执行所有后续工作。
为了理解如何分割初始化字符串,让我们看一下上一篇文章中的一个典型示例。它相当大(约 200 个字符串),因此我们将仅显示最小的必要部分,以了解其结构。
class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CSimpleVolumesStrategy("GBPUSD",16385,12,1.00,1.30,80,3200.00,930.00,12000,3) ],8.428150), class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CSimpleVolumesStrategy("GBPUSD",16385,172,1.40,1.20,140,2200.00,1220.00,19000,3) ],12.357884), class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CSimpleVolumesStrategy("GBPUSD",16385,12,1.20,0.10,0,1800.00,780.00,8000,3) ],4.756016), class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CSimpleVolumesStrategy("GBPUSD",16385,172,0.30,0.10,150,4400.00,1000.00,1000,3) ],4.459508), class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CSimpleVolumesStrategy("GBPUSD",16385,12,0.50,1.10,200,2800.00,1030.00,32000,3) ],5.021593), class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CSimpleVolumesStrategy("GBPUSD",16385,172,1.40,1.70,100,200.00,1640.00,32000,3) ],18.155410), class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CSimpleVolumesStrategy("GBPUSD",16385,12,0.10,0.40,160,8400.00,1080.00,44000,3) ],4.313320), class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CSimpleVolumesStrategy("GBPUSD",16385,52,0.50,1.00,110,3600.00,1030.00,53000,3) ],4.490144), ],4.615527), class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CSimpleVolumesStrategy("GBPUSD",16385,12,0.10,0.80,240,4800.00,1620.00,57000,3) ],6.805962), class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CSimpleVolumesStrategy("GBPUSD",16385,52,0.50,1.80,40,400.00,930.00,53000,3) ],11.825922), class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CSimpleVolumesStrategy("GBPUSD",16385,212,1.30,1.50,160,600.00,1000.00,28000,3) ],16.866251), class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CSimpleVolumesStrategy("GBPUSD",16385,12,0.30,1.50,30,3000.00,1280.00,28000,3) ],5.824790), class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CSimpleVolumesStrategy("GBPUSD",16385,12,1.30,0.10,10,2000.00,780.00,1000,3) ],3.476085), class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CSimpleVolumesStrategy("GBPUSD",16385,12,0.10,0.10,0,16000.00,700.00,11000,3) ],4.522636), class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CSimpleVolumesStrategy("GBPUSD",16385,52,0.40,1.80,80,2200.00,360.00,25000,3) ],8.206812), class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ class CSimpleVolumesStrategy("GBPUSD",16385,12,0.10,0.10,0,19200.00,700.00,44000,3) ],2.698618), ],5.362505), class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ ... ],5.149065), ... class CVirtualStrategyGroup([ ... ],2.718278), ],2.072066)
该初始化字符串由第一级、第二级和第三级的嵌套交易策略组组成。单个交易策略实例仅嵌套在第三级组中。每个实例都指定了参数。每个组都有一个缩放因子,它存在于第一、第二和第三级别。第 5 部分讨论了缩放因子的使用。需要将它们标准化为测试期间达到的最大回撤值 10%。此外,包含多个嵌套组或多个嵌套策略实例的组的缩放因子值首先除以该组中的元素数量,然后将此新因子应用于所有嵌套元素。这是 VirtualStrategyGroup.mqh 文件代码中的样子:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CVirtualStrategyGroup::CVirtualStrategyGroup(string p_params) { // Save the initialization string m_params = p_params; ... // Read the scaling factor m_scale = ReadDouble(p_params); // Correct it if necessary if(m_scale <= 0.0) { m_scale = 1.0; } if(ArraySize(m_groups) > 0 && ArraySize(m_strategies) == 0) { // If we filled the array of groups, and the array of strategies is empty, then PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | Scale = %.2f, total groups = %d", m_scale, ArraySize(m_groups)); // Scale all groups Scale(m_scale / ArraySize(m_groups)); } else if(ArraySize(m_strategies) > 0 && ArraySize(m_groups) == 0) { // If we filled the array of strategies, and the array of groups is empty, then PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | Scale = %.2f, total strategies = %d", m_scale, ArraySize(m_strategies)); // Scale all strategies Scale(m_scale / ArraySize(m_strategies)); } else { // Otherwise, report an error in the initialization string SetInvalid(__FUNCTION__, StringFormat("Groups or strategies not found in Params:\n%s", p_params)); } }
因此,初始化字符串具有层次结构,其中上层由策略组占据,策略本身位于最底层。虽然一个策略组可以包含多个策略,但在项目开发过程中,我们得出的结论是,在一个组中使用多个策略对我们来说不是更方便,而是应该将一个策略的每个实例都包含在较低级别的个体组中。这就是第三层级的由来。前两个层级是将第一阶段优化结果分组,然后将输送机上第二阶段优化结果分组的结果。
当然,我们可以在数据库中创建一个表结构来保留策略和组之间的现有层次结构,但这真的有必要吗?并非如此。优化输送机需要分层结构。当谈到交易账户的最终 EA 表现时,最重要的是一系列具有正确计算的缩放因子的交易策略实例。这样的列表需要一个简单的表来存储在数据库中。因此,让我们添加一个从初始化字符串填充这样一个列表的方法,以及一个在使用具有相应乘数的交易策略的单个实例列表的同时执行为最终 EA 形成初始化字符串的反向任务的方法。
导出策略列表
我们先从获取 EA 策略列表的方法开始。这个方法应该是 EA 类的一个方法,因为在其中我们有所有想要转换为所需形式进行存储的信息。我们想为交易策略的每个实例存储什么信息呢?首先是它的初始化参数和缩放因子。
在写上一段时,甚至没有可以完成这项工作的代码的开头。似乎自由选择实施方式的不确定性根本不允许我确定任何具体的实施方式。关于如何在考虑未来使用的情况下使其更好,出现了很多问题。但是,由于缺乏对未来需要和不需要什么的明确认识,我们甚至无法做出最微不足道的选择。例如,EA 将使用的数据库文件名中是否必须包含版本号?还有幻数呢?这个名称应该在最终 EA 的参数中指定,还是应该根据指定的算法,由策略名称和幻数生成?或者还有其他的?
一般来说,对于这种情况,只有一种方法可以打破这种无休止的问题的恶性循环。我们至少需要做出一些选择,即使这不是最好的选择。在此基础上,我们将继续做出下一个选择,依此类推。否则,我们将无法起飞。现在代码已经编写完成,我们可以冷静地回顾并完成您在开发过程中必须经历的步骤。并非每个解决方案都能进入最终代码,也不是每个解决方案不需要调整,但它们都有助于达到当前状态,我们将尝试进一步描述。
那么,我们来处理策略列表的导出。首先,我们来决定从哪里调用它。假设这是第三阶段的 EA,它之前已经为最终的 EA 导出了一组策略。但正如上文所述,为了在最终的 EA 中使用这些信息,还需要进行其他一些操作。在第三阶段的输出中,我们只收到了优化数据库中 strategy_groups 表中具有已分配名称的通过的 ID。这是在制作第 21 部分期间进行优化后的内容:
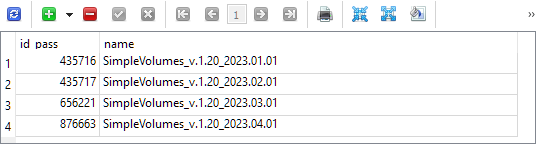
这四次迭代中的每一次都包含一个保存的初始化字符串,用于一组单个交易策略实例,这些实例是在测试间隔内优化时选择的,测试间隔的开始日期相同(2018.01.01),结束日期略有不同,并在组名称中指定。
在 SimpleVolumesStage3.mq5 文件中,将执行导出操作的函数调用替换为调用另一个(尚未存在的)函数:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Test results | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double OnTester(void) { // Handle the completion of the pass in the EA object double res = expert.Tester(); // If the group name is not empty, save the pass to the library if(groupName_ != "") { // CGroupsLibrary::Add(CTesterHandler::s_idPass, groupName_, fileName_); expert.Export(groupName_, advFileName_); } return res; }
向 CVirtualAdvisor EA 类添加一个新方法 Export() 。传递给它的参数将是新组的名称和要导出到的 EA 数据库文件的名称。请注意,这是一个新数据库,而不是以前使用的优化数据库。为了给这个参数赋值,我们将在第三阶段 EA 中添加一个输入参数:
input group "::: Saving to library" input string groupName_ = "SimpleVolumes_v.1.20_2023.01.01"; // - Version name (if empty - not saving) input string advFileName_ = "SimpleVolumes-27183.test.db.sqlite"; // - EA database name
我们从未在 EA 类级别直接操作过数据库。所有直接生成 SQL 查询的方法都移到了单独的静态类 CTesterHandler中。所以,我们不要破坏这个结构,并将接收到的参数重定向到新方法 CTesterHandler::Export() ,并将EA 策略数组添加到其中:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Export the current strategy group to the specified EA database | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualAdvisor::Export(string p_groupName, string p_advFileName) { CTesterHandler::Export(m_strategies, p_groupName, p_advFileName); }
为了实现这个方法,我们需要确定 EA 数据库中表的结构,而新数据库的存在将需要确保连接到不同数据库的能力。
访问不同数据库
经过长时间的考虑,我最终选择了以下方案。让我们修改现有的 CDatabase 类,这样我们不仅可以指定数据库文件的名称,还可以指定其类型。鉴于新的数据库类型,我们将需要使用三种不同的类型:
- 优化数据库。用于安排自动优化项目,并存储有关在自动优化输送机内执行的策略测试程序的信息。
- 用于分组选择的数据库(截断的优化数据库)。用于在自动优化流程的第二阶段将所需的优化数据库部分发送给远程测试代理。
- EA 数据库(最终 EA)。最终在交易账户上运行的 EA 将使用一个数据库来存储有关其工作的所有必要信息,包括所使用的交易策略的单个实例组的组成。
让我们创建三个文件来存储创建每种类型数据库的 SQL 代码,将它们作为资源连接到 Database.mqh 文件,并为这三种类型的数据库创建一个枚举:
// Import SQL files for creating database structures of different types #resource "db.opt.schema.sql" as string dbOptSchema #resource "db.cut.schema.sql" as string dbCutSchema #resource "db.adv.schema.sql" as string dbAdvSchema // Database type enum ENUM_DB_TYPE { DB_TYPE_OPT, // Optimization database DB_TYPE_CUT, // Database for group selection (stripped down optimization database) DB_TYPE_ADV, // EA (final EA) database };
由于我们现在可以访问创建这三种类型数据库中的任何一种的脚本(当然,当我们用适当的内容填充它们时),我们可以更改 Connect() 数据库连接方法的逻辑。如果事实证明传递名称的数据库不存在,那么我们将从脚本中创建它并连接到新创建的数据库,而不是错误消息。
但是,为了了解我们需要什么类型的数据库,让我们向连接方法添加一个输入参数,通过它我们可以传递所需的类型。为了减少编辑现有代码的需要,我们将此参数的默认值设置为优化数据库类型,因为我们之前在任何地方都连接过它:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Create an empty DB | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CDatabase::Create(string p_schema) { bool res = Execute(p_schema); if(res) { PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | Database successfully created from %s", "db.*.schema.sql"); } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Check connection to the database with the given name | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CDatabase::Connect(string p_fileName, ENUM_DB_TYPE p_dbType = DB_TYPE_OPT) { // If the database is open, close it Close(); // If a file name is specified, save it s_fileName = p_fileName; // Set the shared folder flag for the optimization and EA databases s_common = (p_dbType != DB_TYPE_CUT ? DATABASE_OPEN_COMMON : 0); // Open the database // Try to open an existing DB file s_db = DatabaseOpen(s_fileName, DATABASE_OPEN_READWRITE | s_common); // If the DB file is not found, try to create it when opening if(!IsOpen()) { s_db = DatabaseOpen(s_fileName, DATABASE_OPEN_READWRITE | DATABASE_OPEN_CREATE | s_common); // Report an error in case of failure if(!IsOpen()) { PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | ERROR: %s Connect failed with code %d", s_fileName, GetLastError()); return false; } if(p_dbType == DB_TYPE_OPT) { Create(dbOptSchema); } else if(p_dbType == DB_TYPE_CUT) { Create(dbCutSchema); } else { Create(dbAdvSchema); } } return true; }
请注意,我决定将优化和 EA 数据库存储在终端共享文件夹中,将组选择数据库存储在终端工作文件夹中。否则,将无法安排将其自动发送给测试代理。
EA 数据库
为了在EA数据库中存储有关生成的策略组的信息,我决定使用两个表: strategy_groups 和 strategies ,其结构如下:
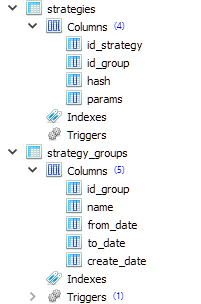
CREATE TABLE strategies ( id_strategy INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT NOT NULL, id_group INTEGER REFERENCES strategy_groups (id_group) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE, hash TEXT NOT NULL, params TEXT NOT NULL ); CREATE TABLE strategy_groups ( id_group INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT, name TEXT, from_date TEXT, to_date TEXT, create_date TEXT );
我们可以看到,strategies 表中的每个条目都对应 strategy_groups 表中的某个条目。因此,我们可以在这个数据库中同时存储许多不同的策略组。
strategies 表中的 hash 字段将存储交易策略单个实例的参数的哈希值。以后可以利用它来了解某个组中的单个实例是否与另一个组中的实例相同。
strategies 表中的 params 字段将存储交易策略单个实例的初始化字符串。从该实例出发,可以为整个策略组生成一个通用的初始化字符串,从而在最终的 EA 中创建一个 EA 对象( CVirtualAdvisor类)。
strategy_groups 表中的 from_date 和 to_date 字段将继续存储用于获取此组的优化间隔的开始日期和结束日期。目前它们将一直空置。
再次导出策略
现在我们准备在 TesterHandler.mqh 中实现将一组策略导出到 EA 数据库的方法。为此,我们需要连接到所需的数据库,在 strategy_groups 表中为新的策略组创建一个记录,为该组中的每个策略生成一个初始化字符串,其中包含其当前的归一化因子(包装在“ class CVirtualStrategyGroup([strategy], scale)”中),并将它们保存在 strategies 表中。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Export an array of strategies to the specified EA database | //| as a new group of strategies | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTesterHandler::Export(CStrategy* &p_strategies[], string p_groupName, string p_advFileName) { // Connect to the required EA database if(DB::Connect(p_advFileName, DB_TYPE_ADV)) { string fromDate = ""; // Start date of the optimization interval string toDate = ""; // End date of the optimization interval // Create an entry for a new strategy group string query = StringFormat("INSERT INTO strategy_groups VALUES(NULL, '%s', '%s', '%s', NULL) RETURNING rowid;", p_groupName, fromDate, toDate); ulong groupId = DB::Insert(query); PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | Export %d strategies into new group [%s] with ID=%I64u", ArraySize(p_strategies), p_groupName, groupId); // For each strategy FOREACH(p_strategies, { CVirtualStrategy *strategy = p_strategies[i]; // Form an initialization string as a group of one strategy with a normalizing factor string params = StringFormat("class CVirtualStrategyGroup([%s],%0.5f)", ~strategy, strategy.Scale()); // Save it in the EA database with the new group ID specified string query = StringFormat("INSERT INTO strategies " "VALUES (NULL, %I64u, '%s', '%s')", groupId, strategy.Hash(~strategy), params); DB::Execute(query); }); // Close the database DB::Close(); } }
为了根据策略参数计算哈希值,我们将现有方法从 EA 类移到了 CFactorable 父类。因此,它现在可供该类的所有子类使用,包括交易策略类。
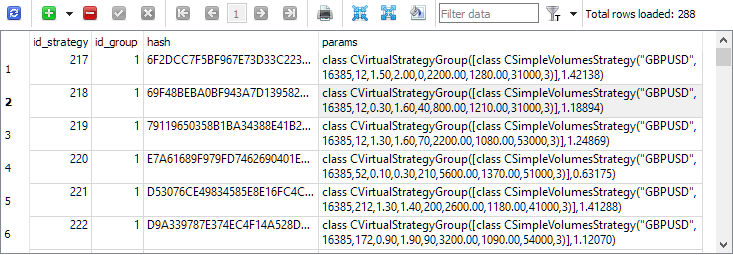
现在,如果我们重新运行优化项目的第三阶段,我们将看到 strategies 表中的条目只包含单个交易策略实例:
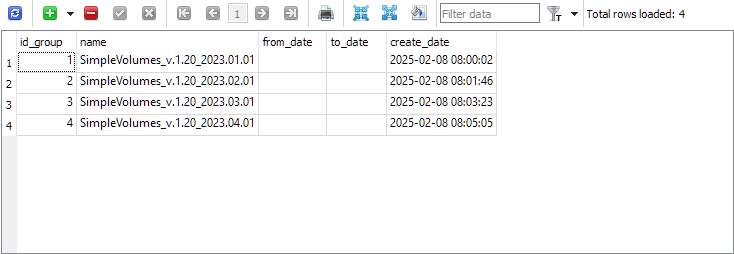
strategy_group 表现在包含了每个项目的最终分组信息:
我们已经完成了导出操作,现在让我们进行反向操作 —— 将这些组导入到最终的 EA 中。
导入策略
我暂时不会完全放弃之前实现的导出组的方法。让我们能够并行使用新旧方法。如果新方法被证明是成功的,那么我们可以考虑放弃旧方法。
让我们在最终的 EA SimpleVolumesExpert.mq5 文件中添加一个新的输入参数 newGroupId_ ,通过该输入参数我们可以设置来自新库的策略组 ID 的值:
input group "::: Use a strategy group" input ENUM_GROUPS_LIBRARY groupId_ = -1; // - Group from the old library OR: input int newGroupId_ = 0; // - ID of the group from the new library (0 - last)
让我们添加一个常量,用于存储最终 EA 的名称:
#define __NAME__ "SimpleVolumes"
在最终的 EA 初始化函数中,首先检查是否在 groupId_ 参数中选择了旧库中的任何组。如果不是,我们将从新库中获取初始化字符串。为此, CVirtualAdvisor EA 类新增了两个静态方法:FileName() 和 Import() 。它们可以在 EA 对象创建之前调用。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { // ... // Initialization string with strategy parameter sets string strategiesParams = NULL; // If the selected strategy group index from the library is valid, then if(groupId_ >= 0 && groupId_ < ArraySize(CGroupsLibrary::s_params)) { // Take the initialization string from the library for the selected group strategiesParams = CGroupsLibrary::s_params[groupId_]; } else { // Take the initialization string from the new library for the selected group // (from the EA database) strategiesParams = CVirtualAdvisor::Import( CVirtualAdvisor::FileName(__NAME__, magic_), newGroupId_ ); } // If the strategy group from the library is not specified, then we interrupt the operation if(strategiesParams == NULL) { return INIT_FAILED; } // ... // Successful initialization return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
我们将对 VirtualAdvisor.mqh 文件进行进一步修改。让我们添加上面提到的两个方法:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class of the EA handling virtual positions (orders) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CVirtualAdvisor : public CAdvisor { protected: // ... public: // ... // Name of the file with the EA database static string FileName(string p_name, ulong p_magic = 1); // Get the strategy group initialization string // from the EA database with the given ID static string Import(string p_fileName, int p_groupId = 0); };
在 FileName() 方法中,我们设置 EA 数据库文件名称的生成规则。它包含了最终 EA 的名称及其幻数,以便具有不同幻数的 EA 始终使用不同的数据库。如果在策略测试器中启动 EA,则还会自动添加后缀 “.test”。这样做是为了防止在测试器中运行的 EA 意外覆盖已在交易账户上运行的 EA 数据库中的信息。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Name of the file with the EA database | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string CVirtualAdvisor::FileName(string p_name, ulong p_magic = 1) { return StringFormat("%s-%d%s.db.sqlite", (p_name != "" ? p_name : "Expert"), p_magic, (MQLInfoInteger(MQL_TESTER) ? ".test" : "") ); }
在 Import() 方法中,我们从 EA 数据库中获取属于给定组的交易策略单个实例的初始化字符串列表。如果所需组的 ID 为 0,则加载最后创建的组的策略列表。
从结果列表中,我们通过将逗号分隔的策略初始化字符串连接起来,并将结果字符串插入到正在形成的组初始化字符串中的所需位置,形成策略组初始化字符串。初始化字符串中组的缩放因子设置为等于策略的数量。这是必要的,这样当使用这样的组初始化字符串创建 EA 时,所有策略的缩放因子都等于存储在 EA 数据库中的缩放因子。毕竟,在创建过程中,组中所有策略的乘数会自动除以组中策略的数量。在这种情况下,这正是困扰我们的问题,为了绕过这个障碍,我们特别将组乘数增加了与它应该减少的次数相同的次数。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Get the strategy group initialization string | //| from the EA database with the given ID | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string CVirtualAdvisor::Import(string p_fileName, int p_groupId = 0) { string params[]; // Array for strategy initialization strings // Request to get strategies of a given group or the last group string query = StringFormat("SELECT id_group, params " " FROM strategies" " WHERE id_group = %s;", (p_groupId > 0 ? (string) p_groupId : "(SELECT MAX(id_group) FROM strategy_groups)")); // Open EA database if(DB::Connect(p_fileName, DB_TYPE_ADV)) { // Execute the request int request = DatabasePrepare(DB::Id(), query); // If there is no error if(request != INVALID_HANDLE) { // Data structure for reading a single string of a query result struct Row { int groupId; string params; } row; // Read data from the first result string while(DatabaseReadBind(request, row)) { // Remember the strategy group ID // in the static property of the EA class s_groupId = row.groupId; // Add another strategy initialization string to the array APPEND(params, row.params); } } else { // Report an error if necessary PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | ERROR: request \n%s\nfailed with code %d", query, GetLastError()); } // Close the EA database DB::Close(); } // Strategy group initialization string string groupParams = NULL; // Total number of strategies in the group int totalStrategies = ArraySize(params); // If there are strategies, then if(totalStrategies > 0) { // Concatenate their initialization strings with commas JOIN(params, groupParams, ","); // Create a strategy group initialization string groupParams = StringFormat("class CVirtualStrategyGroup([%s], %.5f)", groupParams, totalStrategies); } // Return the strategy group initialization string return groupParams; }
这种方法并不完全纯粹,因为除了返回组初始化字符串之外,它还将 CVirtualAdvisor::s_groupId 类的静态属性的值设置为已加载策略组的 ID。这种记住从库中加载了哪个组的方法似乎很简单可靠,尽管不是很漂亮。
传输最终 EA 的数据
由于我们已经建立了一个单独的数据库来存储创建最终 EA 所使用的交易策略单个实例的参数,因此我们不会半途而废,而是会将最终 EA 在交易账户上运行的剩余信息的存储转移到同一个数据库中。以前,此类信息使用 CVitrualAdvisor::Save() 方法保存在单独的文件中,如有必要,可以使用 CVitrualAdvisor::Load() 方法从中加载。
文件中保存的信息包括:
- EA 通用参数:上次保存时间,以及 …… 目前就这些。但未来这个列表可能会扩充。
- 每个策略的数据:虚拟仓位列表以及该策略可能需要存储的任何数据。目前所采用的策略不需要存储任何额外的数据,但对于其他类型的策略,可能会出现这种需求。
- 风险管理器数据:当前状态、最新余额和净值水平、持仓规模倍数等。
先前选择的实现方法的缺点是数据文件只能完整地读取和解释。例如,如果我们想要增加初始化字符串中的策略数量并重新启动最终的 EA,它将无法无错误地读取保存的数据文件。读取时,最终的 EA 会期望文件中包含新增策略的信息,但它并不在那里。因此,加载方法将尝试把文件中接下来的数据(实际上已经与风险管理数据相关)解释为与另外的交易策略相关的数据。很明显,这样做不会有好结果。
为了解决这个问题,我们需要摆脱对最终 EA 工作的所有信息进行严格顺序存储的方式,而使用数据库在这里将非常有用。让我们以键值对(Key-Value)的形式在其中安排一个简单的任意数据存储。
键值存储
尽管我们在上面提到了存储任意数据,但任务不必设置得如此宽泛。在查看了最终 EA 数据文件中当前保存的内容后,我们可以将自己限制在确保保留单个数字(整数和实数)和虚拟仓位对象上。我们还要记住,每个策略都有一个固定大小的虚拟仓位数组。该大小在策略初始化参数中指定。因此,虚拟仓位对象总是作为某个数组的一部分存在。展望未来,我们将立即提供保存单个数字以及保存不同类型数字数组的功能。
考虑到上述情况,让我们创建一个新的静态类,其中包含以下方法:
- 连接到目标数据库:Connect()/Close()
- 设置不同类型的值:Set(...)
- 读取不同类型的值:Get(...)
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class for working with the EA database in the form of | //| Key-Value storage for properties and virtual positions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CStorage { protected: static bool s_res; // Result of all database read/write operations public: // Connect to the EA database static bool Connect(string p_fileName); // Close connection to the database static void Close(); // Save a virtual order/position static void Set(int i, CVirtualOrder* order); // Store a single value of an arbitrary simple type template<typename T> static void Set(string key, const T &value); // Store an array of values of an arbitrary simple type template<typename T> static void Set(string key, const T &values[]); // Get the value as a string for the given key static string Get(string key); // Get an array of virtual orders/positions for a given strategy hash static bool Get(string key, CVirtualOrder* &orders[]); // Get the value for a given key into a variable of an arbitrary simple type template<typename T> static bool Get(string key, T &value); // Get an array of values of a simple type by a given key into a variable template<typename T> static bool CStorage::Get(string key, T &values[]); // Result of operations static bool Res() { return s_res; } };
我们已向类中添加了静态属性 s_res 和读取其值的方法。它会记录数据库读/写操作过程中发生的任何错误。
由于此类仅用于保存和加载最终 EA 的状态,因此也将仅在这些时刻执行与数据库的连接。在连接关闭之前,不会对数据库执行任何其他有意义的操作。因此,在数据库连接方法中,将立即打开一个事务,在该事务中,将发生与数据库的所有操作,而在连接关闭方法中,该事务将被确认或取消:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Connect to the EA database | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CStorage::Connect(string p_fileName) { // Connect to the EA database if(DB::Connect(p_fileName, DB_TYPE_ADV)) { // No errors yet s_res = true; // Start a transaction DatabaseTransactionBegin(DB::Id()); return true; } return false; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Close the database connection | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CStorage::Close() { // If there are no errors, if(s_res) { // Confirm the transaction DatabaseTransactionCommit(DB::Id()); } else { // Otherwise, cancel the transaction DatabaseTransactionRollback(DB::Id()); } // Close connection to the database DB::Close(); }
让我们在最终的 EA 数据库结构中添加两个具有以下列的表:
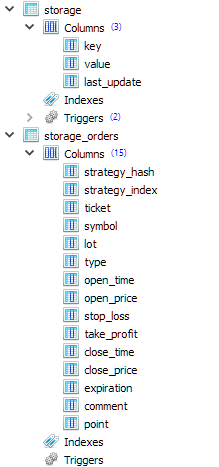
第一个表(storage)将用于存储单个数值和数值数组。但是,字符串也可以存储在那里。第二个表( storage_orders )将用于存储有关不同交易策略实例的虚拟仓位数组元素的信息。因此, strategy_hash 和 strategy_index 列位于表的开头,分别存储策略参数的哈希值(每个策略都是唯一的)和策略虚拟仓位数组中虚拟仓位的索引。
所有单独的数值都是通过调用 Set() 模板方法存储的,该方法接受一个包含键名的字符串和一个任意简单的 T 类型的变量作为参数。例如,这可以是 int 、 ulong 或 double 。在生成用于保存的 SQL 查询时,此变量的值将转换为 string 类型并以字符串形式存储在数据库中:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Store a single value of an arbitrary simple type | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> void CStorage::Set(string key, const T &value) { // Escape single quotes (can't avoid using them yet) // StringReplace(key, "'", "\\'"); // StringReplace(value, "'", "\\'"); // Request to save the value string query = StringFormat("REPLACE INTO storage(key, value) VALUES('%s', '%s');", key, (string) value); // Execute the request s_res &= DatabaseExecute(DB::Id(), query); if(!s_res) { // Report an error if necessary PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | ERROR: Execution failed in DB [adv], query:\n" "%s\n" "error code = %d", query, GetLastError()); } }
如果我们想为一个键存储一个简单类型的值数组,我们首先创建一个字符串,用分隔符将传递的数组中的所有值连接起来,逗号用作分隔符。这种情况也发生在另一个同名模板方法 Set() 中,只是它的第二个参数不是对简单类型变量的引用,而是对简单类型值数组的引用:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Store an array of values of an arbitrary simple type | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> void CStorage::Set(string key, const T &values[]) { string value = ""; // Concatenate all values from the array into one string separated by commas JOIN(values, value, ","); // Save a string with a specified key Set(key, value); }
为了执行相反的操作 —— 从数据库读取数据 —— 我们将添加 Get() 方法,该方法给定一个键值,返回数据库中存储的该键对应的行。为了获得所需的简单类型的值,我们将创建一个同名的模板方法,但该方法还会接受对任意简单类型变量的引用作为第二个参数。在这个方法中,我们将首先从数据库中接收一个字符串值,如果能够获取到该值,我们将把它从字符串转换为所需的类型,并将其写入传递的变量。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Get the value as a string for the given key | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string CStorage::Get(string key) { string value = NULL; // Return value // Request to get the value string query = StringFormat("SELECT value FROM storage WHERE key='%s'", key); // Execute the request int request = DatabasePrepare(DB::Id(), query); // If there is no error if(request != INVALID_HANDLE) { // Read data from the first result string DatabaseRead(request); if(!DatabaseColumnText(request, 0, value)) { // Report an error if necessary PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | ERROR: Reading row in DB [adv] for request \n%s\n" "failed with code %d", query, GetLastError()); } } else { // Report an error if necessary PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | ERROR: Request in DB [adv] \n%s\nfailed with code %d", query, GetLastError()); } return value; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Get the value for a given key into a variable | //| of an arbitrary simple type | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> bool CStorage::Get(string key, T &value) { // Get the value as a string string res = Get(key); // If the value is received if(res != NULL) { // Cast it to type T and assign it to the target variable value = (T) res; return true; } return false; }
让我们使用新增的方法来保存和加载最终 EA 的状态。
保存并下载 EA
在 CVirtualAdvisor::Save() EA 状态保存方法中,我们只需要连接到 EA 数据库,然后通过直接调用 CStorage 类方法或间接调用需要保存的对象的 Save()/Load() 方法来保存我们需要的所有内容。
我们目前仅直接存储两个值:虚拟仓位组成上次更改的时间和策略组 ID。接下来,对循环中的所有策略调用 Save() 方法。最后调用风险管理器的保存方法。我们还需要对上述方法进行修改,以便它们也能保存到 EA 数据库中。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Save status | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CVirtualAdvisor::Save() { // Save status if: if(true // later changes appeared && m_lastSaveTime < CVirtualReceiver::s_lastChangeTime // currently, there is no optimization && !MQLInfoInteger(MQL_OPTIMIZATION) // and there is no testing at the moment or there is a visual test at the moment && (!MQLInfoInteger(MQL_TESTER) || MQLInfoInteger(MQL_VISUAL_MODE)) ) { // If the connection to the EA database is established if(CStorage::Connect(m_fileName)) { // Save the last modification time CStorage::Set("CVirtualReceiver::s_lastChangeTime", CVirtualReceiver::s_lastChangeTime); CStorage::Set("CVirtualAdvisor::s_groupId", CVirtualAdvisor::s_groupId); // Save all strategies FOREACH(m_strategies, ((CVirtualStrategy*) m_strategies[i]).Save()); // Save the risk manager m_riskManager.Save(); // Update the last save time m_lastSaveTime = CVirtualReceiver::s_lastChangeTime; PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | OK at %s to %s", TimeToString(m_lastSaveTime, TIME_DATE | TIME_MINUTES | TIME_SECONDS), m_fileName); // Close the connection CStorage::Close(); // Return the result return CStorage::Res(); } else { PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | ERROR: Can't open database [%s], LastError=%d", m_fileName, GetLastError()); return false; } } return true; }
在 CVirtualAdvisor::Load() 下载方法中,执行相反的操作:从数据库中读取最后更改时间值和策略组 ID,然后每个策略和风险管理器加载其信息。如果最后修改时间在未来,那么我们就不再加载任何其他内容。当我们再次以可视化方式运行策略测试器时,可能会出现这种情况。上一次测试结束时保存了信息,当开始第二次测试时,EA 将使用与第一次测试相同的数据库。因此,我们只需要忽略之前的信息,再从头开始。
当调用加载方法时,EA 对象已经创建完成,并带有一个策略组,该策略组的 ID 取自 EA 的输入参数。该 ID 保存在 CVirtualAdvisor::Import() 方法的 CVirtualAdvisor::s_groupId 静态属性中。因此,当从 EA 数据库加载策略组 ID 时,我们可以将其与现有值进行比较。如果结果不同,则表示最终 EA 已使用一组新的策略重新启动,可能需要采取一些额外的操作。但目前还不完全清楚我们在这种情况下肯定需要采取什么行动。所以,让我们在代码中留下相应的注释,以备将来使用。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Load status | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CVirtualAdvisor::Load() { bool res = true; ulong groupId = 0; // Load status if: if(true // file exists && FileIsExist(m_fileName, FILE_COMMON) // currently, there is no optimization && !MQLInfoInteger(MQL_OPTIMIZATION) // and there is no testing at the moment or there is a visual test at the moment && (!MQLInfoInteger(MQL_TESTER) || MQLInfoInteger(MQL_VISUAL_MODE)) ) { // If the connection to the EA database is established if(CStorage::Connect(m_fileName)) { // Download the last modification time res &= CStorage::Get("CVirtualReceiver::s_lastChangeTime", m_lastSaveTime); // Download the saved strategy group ID res &= CStorage::Get("CVirtualAdvisor::s_groupId", groupId); // If the last modification time is in the future, then ignore the download if(m_lastSaveTime > TimeCurrent()) { PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | IGNORE LAST SAVE at %s in the future", TimeToString(m_lastSaveTime, TIME_DATE | TIME_MINUTES | TIME_SECONDS)); m_lastSaveTime = 0; return true; } PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | LAST SAVE at %s", TimeToString(m_lastSaveTime, TIME_DATE | TIME_MINUTES | TIME_SECONDS)); if(groupId != CVirtualAdvisor::s_groupId) { // Actions when launching an EA with a new group of strategies. // Nothing is happening here yet } // Load all strategies FOREACH(m_strategies, { res &= ((CVirtualStrategy*) m_strategies[i]).Load(); if(!res) break; }); if(!res) { PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | ERROR loading strategies from file %s", m_fileName); } // Download the risk manager res &= m_riskManager.Load(); if(!res) { PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | ERROR loading risk manager from file %s", m_fileName); } // Close the connection CStorage::Close(); return res; } } return true; }
现在,让我们深入了解保存和加载策略方法的实现。
保存并下载策略
在 CVirtualStrategy 类中,我们只在这些方法中实现所有使用虚拟仓位的策略共有的功能。它们各自包含一个虚拟仓位对象数组,需要保存和加载。我们将把详细的实现细节放到更低的层级,在这里我们只会调用专门创建的 CStorage 类方法:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Save status | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualStrategy::Save() { // Save virtual positions (orders) of the strategy FOREACH(m_orders, CStorage::Set(i, m_orders[i])); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Load status | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CVirtualStrategy::Load() { bool res = true; // Download virtual positions (orders) of the strategy res = CStorage::Get(this.Hash(), m_orders); return res; }
对于 CVirtualStrategy 类的子类(包括 CSimpleVolumnesStrategy ),我们也可能需要保存一些与虚拟仓位数组相关的额外数据。我们的模型策略过于简单,除了虚拟仓位列表之外,不需要存储任何其他内容。但假设出于某种原因,我们想要保存一个包含分时交易量和平均分时交易量的数组。由于保存和加载方法被声明为虚拟方法,我们可以在派生类中重写它们,添加对所需数据的操作,并调用基类方法来保存和加载虚拟仓位:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Save status | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CSimpleVolumesStrategy::Save() { double avrVolume = ArrayAverage(m_volumes); // Let's form the common part of the key with the type and hash of the strategy string key = "CSimpleVolumesStrategy[" + this.Hash() + "]"; // Save the average tick volume CStorage::Set(key + ".avrVolume", avrVolume); // Save the array of tick volumes CStorage::Set(key + ".m_volumes", m_volumes); // Call the base class method (to save virtual positions) CVirtualStrategy::Save(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Load status | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CSimpleVolumesStrategy::Load() { bool res = true; double avrVolume = 0; // Let's form the common part of the key with the type and hash of the strategy string key = "CSimpleVolumesStrategy[" + this.Hash() + "]"; // Load the tick volume array res &= CStorage::Get(key + ".avrVolume", avrVolume); // Load the tick volume array res &= CStorage::Get(key + ".m_volumes", m_volumes); // Call the base class method (to load virtual positions) res &= CVirtualStrategy::Load(); return res; }
剩下的就是实现虚拟仓位的保存和加载。
保存/加载虚拟仓位
以前, Save() 和 Load() 方法直接将当前虚拟仓位对象的必要信息保存到虚拟仓位类的数据文件中。现在我们稍微改变一下结构。添加一个简单的 CVirtualOrderStruct 结构,其中包含虚拟仓位所需的所有数据字段:
// Structure for reading/writing // basic properties of a virtual order/position from the database struct VirtualOrderStruct { string strategyHash; int strategyIndex; ulong ticket; string symbol; double lot; ENUM_ORDER_TYPE type; datetime openTime; double openPrice; double stopLoss; double takeProfit; datetime closeTime; double closePrice; datetime expiration; string comment; double point; };
与虚拟仓位对象不同,虚拟仓位对象的所有创建实例都会被严格记录并在交易量接收器模块中自动处理,而此类结构可以根据需要随时创建任意次数。我们将使用它们在虚拟仓位对象和在 CStorage 类中实现的 EA 数据库中保存/加载它们的方法之间传递信息。然后,虚拟仓位类中的保存和加载方法只会填充传递的结构,或者获取传递的结构的字段值并写入其属性:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Load status | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualOrder::Load(const VirtualOrderStruct &o) { m_ticket = o.ticket; m_symbol = o.symbol; m_lot = o.lot; m_type = o.type; m_openPrice = o.openPrice; m_stopLoss = o.stopLoss; m_takeProfit = o.takeProfit; m_openTime = o.openTime; m_closePrice = o.closePrice; m_closeTime = o.closeTime; m_expiration = o.expiration; m_comment = o.comment; m_point = o.point; PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | %s", ~this); s_ticket = MathMax(s_ticket, m_ticket); m_symbolInfo = m_symbols[m_symbol]; // Notify the recipient and the strategy that the position (order) is open if(IsOpen()) { m_receiver.OnOpen(&this); m_strategy.OnOpen(&this); } else { m_receiver.OnClose(&this); m_strategy.OnClose(&this); } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Save status | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualOrder::Save(VirtualOrderStruct &o) { o.ticket = m_ticket; o.symbol = m_symbol; o.lot = m_lot; o.type = m_type; o.openPrice = m_openPrice; o.stopLoss = m_stopLoss; o.takeProfit = m_takeProfit; o.openTime = m_openTime; o.closePrice = m_closePrice; o.closeTime = m_closeTime; o.expiration = m_expiration; o.comment = m_comment; o.point = m_point; }
最后,让我们使用在 EA 数据库中创建的 storage_orders 表来保存每个虚拟仓位的属性。处理它的方法是 CStorage::Set() 。此方法应该接收虚拟仓位索引和虚拟仓位对象本身:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Save a virtual order/position | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CStorage::Set(int i, CVirtualOrder* order) { VirtualOrderStruct o; // Structure for virtual position data order.Save(o); // Fill it // Escape quotes in the comment StringReplace(o.comment, "'", "\\'"); // Request to save string query = StringFormat("REPLACE INTO storage_orders VALUES(" "'%s',%d,%I64u," "'%s',%.2f,%d,%I64d,%f,%f,%f,%I64d,%f,%I64d,'%s',%f);", order.Strategy().Hash(), i, o.ticket, o.symbol, o.lot, o.type, o.openTime, o.openPrice, o.stopLoss, o.takeProfit, o.closeTime, o.closePrice, o.expiration, o.comment, o.point); // Execute the request s_res &= DatabaseExecute(DB::Id(), query); if(!s_res) { // Report an error if necessary PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | ERROR: Execution failed in DB [adv], query:\n" "%s\n" "error code = %d", query, GetLastError()); } }
CStorage::Get() 方法接收一个虚拟仓位对象数组作为其第二个参数,它从 storage_orders 表中下载第一个参数中指定的哈希值所对应的策略的虚拟仓位信息:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Get an array of virtual orders/positions | //| by the given strategy hash | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CStorage::Get(string key, CVirtualOrder* &orders[]) { // Request to obtain data on virtual positions string query = StringFormat("SELECT * FROM storage_orders " " WHERE strategy_hash = '%s' " " ORDER BY strategy_index ASC;", key); // Execute the request int request = DatabasePrepare(DB::Id(), query); // If there is no error if(request != INVALID_HANDLE) { // Structure for virtual position information VirtualOrderStruct row; // Read the data from the query result string by string while(DatabaseReadBind(request, row)) { orders[row.strategyIndex].Load(row); } } else { // Save the error and report it if necessary s_res = false; PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | ERROR: Execution failed in DB [adv], query:\n" "%s\n" "error code = %d", query, GetLastError()); } return s_res; }
至此,与将最终 EA 操作信息存储在单独的数据库中相关的变更大部分已经完成。
小测试
尽管进行了大量更改,但我们尚未达到可以在最终 EA 运行期间测试真正热插拔设置的能力。但我们现在可以确定,我们没有搞砸最终 EA 的初始化机制。
为此,我们使用旧方法和新方法从优化数据库中导出初始化字符串数组。现在, ExportedGroupsLibrary.mqh 文件和名为 SimpleVolumes-27183.test.db.sqlite 的 EA 数据库中都包含了有关四组策略的信息。让我们用最终的 SimpleVolumesExpert.mq5 EA 代码编译该文件。
如果我们按以下方式设置输入参数值,

然后,选定的初始化字符串将从最终 EA 的内部数组中加载。该数组在编译过程中从 ExportedGroupsLibrary.mqh 文件中的数据填充(旧方法)。
如果参数值以这种方式指定,

然后,将根据从 EA 数据库接收的信息生成初始化字符串(新方法)。
让我们使用旧的初始化方法对最终的EA进行一次较短时间间隔的测试,例如,测试上个月。我们将得到以下结果:
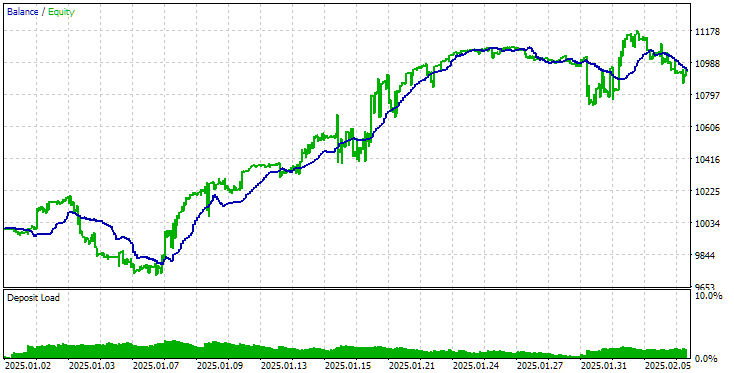
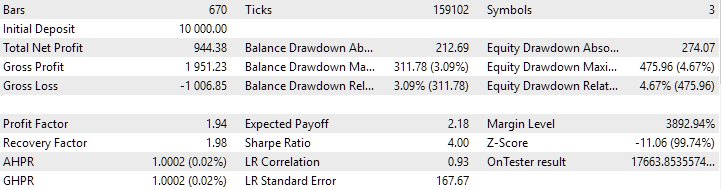
采用旧方法下载策略的最终EA操作结果
现在让我们使用新的初始化方法在相同的时间间隔内运行最终 EA。结果如下:
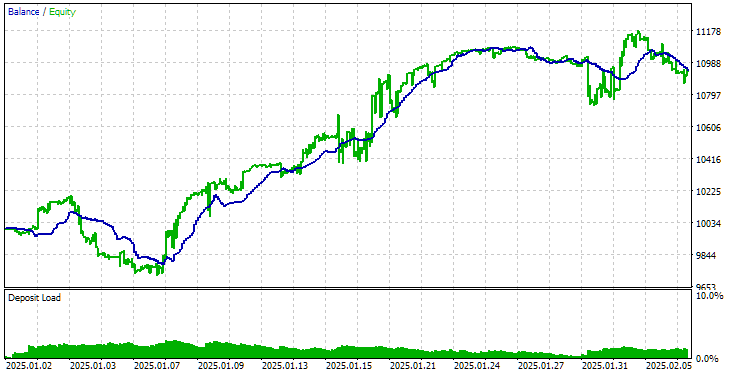
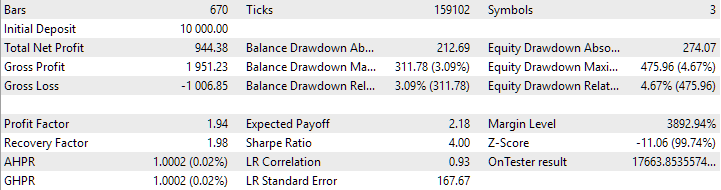
采用新的策略下载方法后,最终 EA 运行的结果
如您所见,使用旧方法和新方法得到的结果完全相同。
结论
我们承担的任务比最初想象的要困难得多。虽然我们还没有达到所有预期的结果,但我们已经获得了一个适合进一步测试和开发的全功能解决方案。我们现在可以通过将新的交易策略组直接导出到交易账户上运行的最终 EA 交易使用的数据库来运行优化项目。但这种机制的正确性仍有待测试。
我们将像往常一样,通过在策略测试器中运行的 EA 中模拟所需的行为来开始测试它。如果那里的结果令人满意,那么我们将继续在最终的 EA 中使用它,这将不再适用于测试器。下次再详细讨论。
感谢您的关注!期待很快与您见面!
重要警告:
本文和本系列之前的所有文章中的所有结果仅基于历史测试数据,并不保证未来会有任何利润。该项目中的工作具有研究性质。所有已发表的结果都可以由任何人使用,风险自负。
存档内容
| # | 名称 | 版本 | 描述 | 最近修改 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MQL5/Experts/Article.16452 | ||||
| 1 | Advisor.mqh | 1.04 | EA 基类 | 第 10 部分 |
| 2 | ClusteringStage1.py | 1.01 | 对第一阶段优化结果进行聚类的程序 | 第 20 部分 |
| 3 | CreateProject.mq5 | 1.00 | 用于创建具有阶段、作业和优化任务的项目的 EA 脚本。 | 第 21 部分 |
| 4 | Database.mqh | 1.10 | 处理数据库的类 | 第 22 部分 |
| 5 | db.adv.schema.sql | 1.00 | 最终 EA 的数据库结构 | 第 22 部分 |
| 6 | db.cut.schema.sql | 1.00 | 被截断的优化数据库的结构 | 第 22 部分 |
| 7 | db.opt.schema.sql | 1.05 | 优化数据库结构 | 第 22 部分 |
| 8 | ExpertHistory.mqh | 1.00 | 用于将交易历史导出到文件的类 | 第 16 部分 |
| 9 | ExportedGroupsLibrary.mqh | — | 生成的文件列出了策略组名称及其初始化字符串数组 | 第 22 部分 |
| 10 | Factorable.mqh | 1.03 | 从字符串创建的对象的基类 | 第 22 部分 |
| 11 | GroupsLibrary.mqh | 1.01 | 用于处理选定策略组库的类 | 第 18 部分 |
| 12 | HistoryReceiverExpert.mq5 | 1.00 | 用于与风险管理器回放交易历史的 EA | 第 16 部分 |
| 13 | HistoryStrategy.mqh | 1.00 | 用于回放交易历史的交易策略类 | 第 16 部分 |
| 14 | Interface.mqh | 1.00 | 可视化各种对象的基类 | 第 4 部分 |
| 15 | LibraryExport.mq5 | 1.01 | EA 将库中选定通过的初始化字符串保存到 ExportedGroupsLibrary.mqh 文件 | 第 18 部分 |
| 16 | Macros.mqh | 1.05 | 用于数组操作的有用的宏 | 第 22 部分 |
| 17 | Money.mqh | 1.01 | 资金管理基类 | 第 12 部分 |
| 18 | NewBarEvent.mqh | 1.00 | 用于定义特定交易品种的新柱形的类 | 第 8 部分 |
| 19 | Optimization.mq5 | 1.04 | EA 管理优化任务的启动 | 第 22 部分 |
| 20 | Optimizer.mqh | 1.03 | 项目自动优化管理器类 | 第 22 部分 |
| 21 | OptimizerTask.mqh | 1.03 | 优化任务类 | 第 22 部分 |
| 22 | Receiver.mqh | 1.04 | 将未平仓交易量转换为市场仓位的基类 | 第 12 部分 |
| 23 | SimpleHistoryReceiverExpert.mq5 | 1.00 | 简化的 EA,用于回放交易历史 | 第 16 部分 |
| 24 | SimpleVolumesExpert.mq5 | 1.21 | 最终 EA 的算法,用于并行运行多组模型策略。参数将从内置组库中获取。 | 第 22 部分 |
| 25 | SimpleVolumesStage1.mq5 | 1.18 | 交易策略单实例优化EA(第一阶段) | 第 19 部分 |
| 26 | SimpleVolumesStage2.mq5 | 1.02 | 交易策略实例组优化EA(第二阶段) | 第 19 部分 |
| 27 | SimpleVolumesStage3.mq5 | 1.03 | 将生成的标准化策略组保存到具有给定名称的组库中的 EA。 | 第 22 部分 |
| 28 | SimpleVolumesStrategy.mqh | 1.11 | 使用分时交易量的交易策略类 | 第 22 部分 |
| 29 | Storage.mqh | 1.00 | 用于处理最终 EA 的键值存储的类。 | 第 22 部分 |
| 30 | Strategy.mqh | 1.04 | 交易策略基类 | 第 10 部分 |
| 31 | SymbolsMonitor.mqh | 1.00 | 用于获取交易工具(交易品种)信息的类 | 第 21 部分 |
| 32 | TesterHandler.mqh | 1.06 | 优化事件处理类 | 第 22 部分 |
| 33 | VirtualAdvisor.mqh | 1.09 | 处理虚拟仓位(订单)的 EA 类 | 第 22 部分 |
| 34 | VirtualChartOrder.mqh | 1.01 | 图形虚拟仓位类 | 第 18 部分 |
| 35 | VirtualFactory.mqh | 1.04 | 对象工厂类 | 第 16 部分 |
| 36 | VirtualHistoryAdvisor.mqh | 1.00 | 交易历史回放 EA 类 | 第 16 部分 |
| 37 | VirtualInterface.mqh | 1.00 | EA GUI 类 | 第 4 部分 |
| 38 | VirtualOrder.mqh | 1.09 | 虚拟订单和仓位类 | 第 22 部分 |
| 39 | VirtualReceiver.mqh | 1.03 | 将未平仓交易量转换为市场仓位的类(接收方) | 第 12 部分 |
| 40 | VirtualRiskManager.mqh | 1.02 | 风险管理类(风险管理器) | 第 15 部分 |
| 41 | VirtualStrategy.mqh | 1.08 | 具有虚拟仓位的交易策略类 | 第 22 部分 |
| 42 | VirtualStrategyGroup.mqh | 1.00 | 交易策略组类 | 第 11 部分 |
| 43 | VirtualSymbolReceiver.mqh | 1.00 | 交易品种接收器类 | 第 3 部分 |
| MQL5/Common/Files | 共享终端文件夹 | |||
| 44 | SimpleVolumes-27183.test.db.sqlite | — | EA 数据库新增四个策略组 | |
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自俄文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/16452
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 开发多币种 EA 交易(第 23 部分):整理自动项目优化阶段的输送机(二)
开发多币种 EA 交易(第 23 部分):整理自动项目优化阶段的输送机(二)
 交易中的神经网络:针对加密货币市场的记忆扩充上下文感知学习(终篇)
交易中的神经网络:针对加密货币市场的记忆扩充上下文感知学习(终篇)
 MQL5中表格模型的实现:应用MVC概念
MQL5中表格模型的实现:应用MVC概念
 交易中的神经网络:针对加密货币市场的记忆扩充上下文感知学习(MacroHFT)
交易中的神经网络:针对加密货币市场的记忆扩充上下文感知学习(MacroHFT)