
开发多币种 EA 交易(第 8 部分):负载测试和处理新柱
概述
在第一篇文章中,我们开发了一个具有两个交易策略实例的 EA。在第二篇文章中,我们已经使用了 9 个实例,而在最后一篇文章中,这个数字跃升到了 32 个。测试时间没有问题。显然,单次测试通过的时间越短越好。但是,如果整体优化只需要几个小时,那也比几天或几周要好。同样,如果我们在一个 EA 中组合了多个策略实例,并希望查看其结果,那么一次通过应在几秒或几分钟内完成,而不是几小时或几天。
如果我们对选定的策略实例组进行优化,那么有几个实例已经参与了所有优化过程。这样,用于单个通过和整个优化的时间就会增加。因此,我们在进行优化时仅限于选择不超过 8 个实例的组。
让我们试着找出测试器中单次通过的时间如何取决于不同持续时间测试期的交易策略实例数量。我们再来看看消耗的内存。当然,我们需要了解在终端图表上启动不同数量的交易策略实例时,EA 的表现如何。
测试器中不同数量的实例
要进行这样的实验,我们将需要在现有 EA 的基础上编写一个新的 EA。让我们以 OptGroupExpert.mq5 EA 为基础,对其进行如下修改:
- 让我们移除指定八个参数集索引的输入参数,这八个参数集是从文件加载的全参数集数组中提取的。让我们留下 count_ 参数,它将指定从完整的集合数组中加载的集合数量。
- 让我们删除对已不存在的索引的唯一性检查。我们将在策略数组中添加新策略,参数集数组中的第一个 count_ 元素将作为新策略的参数集。如果数组中没有足够的实例,那么我们将在循环中从数组的开头开始获取新的实例。
- 让我们删除 OnTesterInit() 和 OntesterDeinit() 函数,因为我们还不会使用此 EA 进行任何优化。
我们将收到以下代码:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Inputs | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ input group "::: Money management" sinput double expectedDrawdown_ = 10; // - Maximum risk (%) sinput double fixedBalance_ = 10000; // - Used deposit (0 - use all) in the account currency sinput double scale_ = 1.00; // - Group scaling multiplier input group "::: Selection for the group" sinput string fileName_ = "Params_SV_EURGBP_H1.csv"; // - File with strategy parameters (*.csv) input int count_ = 8; // - Number of strategies in the group (1 .. 8) input group "::: Other parameters" sinput ulong magic_ = 27183; // - Magic ... //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { // Load strategy parameter sets int totalParams = LoadParams(fileName_, params); // If nothing is loaded, report an error if(totalParams == 0) { PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | ERROR: Can't load data from file %s.\n" "Check that it exists in data folder or in common data folder.", fileName_); return(INIT_PARAMETERS_INCORRECT); } // Report an error if if(count_ < 1) { // number of instances is less than 1 return INIT_PARAMETERS_INCORRECT; } ArrayResize(params, count_); // Set parameters in the money management class CMoney::DepoPart(expectedDrawdown_ / 10.0); CMoney::FixedBalance(fixedBalance_); // Create an EA handling virtual positions expert = new CVirtualAdvisor(magic_, "SimpleVolumes_BenchmarkInstances"); // Create and fill the array of all strategy instances CVirtualStrategy *strategies[]; FOREACH(params, APPEND(strategies, new CSimpleVolumesStrategy(params[i % totalParams]))); // Form and add a group of strategies to the EA expert.Add(CVirtualStrategyGroup(strategies, scale_)); return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
将生成的代码保存到当前文件夹下的 BenchmarkInstancesExpert.mq5 文件中。
现在,让我们尝试在测试器中使用不同数量的交易策略实例和不同的分时报价模拟模式多次运行该 EA。
不同模式的测试结果
让我们从熟悉的 "1 分钟 OHLC" 分时报价模拟模式开始,我们在之前的文章中都使用过这种模式。下一次启动时,我们将把实例数量增加一倍。让我们从 8 个实例开始。如果测试时间过长,我们将缩短测试时间段。
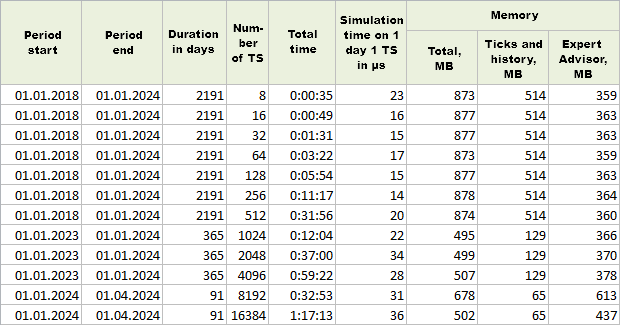
图 1."1 分钟 OHLC" 模式下的单次运行结果
正如您所看到的,在测试多达 512 个实例时,我们使用了 6 年的测试期,然后改为 1 年的测试期,最后两次测试仅使用了 3 个月。
为了能够比较不同测试时间段的时间成本,我们将计算一个单独的值:一个策略实例在一天的模拟时间。为此,将总时间除以策略实例的数量和测试期的天数。为了避免纠结于过小的数字,让我们把时间乘以 10^9 转换成纳秒。
在日志中,测试器会报告运行期间使用的内存信息,显示总使用量以及用于历史数据和分时报价数据的使用量。从内存总量中减去这些内存,我们就得到了 EA 本身所需的内存量。
根据测试结果,我们可以说,即使是最大副本数(16384 份),测试器的运行也不会耗费大量时间。一般来说,这样的副本数量足以安排一项联合工作,例如 15 个交易品种,每个交易品种上有 100 个实例。所以这已经很多了。与此同时,内存消耗并没有随着实例数量的增加而大幅增加。出于某种原因,EA 本身的内存消耗在 8192 个实例时达到峰值,但随后所需的内存又减少了。
为了获得更准确的结果,我们可以对每个实例数量重复几次通过,并计算平均时间和平均内存大小,因为在相同实例数量的情况下,不同通过的结果仍然不同。但这些差异并不是很大,因此进行更广泛的测试意义不大。我们只是想确保即使副本数量相对较少,也不会遇到限制。
现在,让我们试着看看在测试器中以 "每个分时报价" 模拟模式运行 EA 的结果。
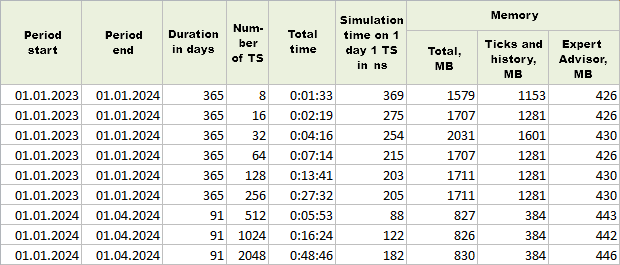
图 2."每个分时报价"模式下的单次运行结果
一次测试通过的时间增加了约 10 倍,因此与之前的模式相比,我们在相同数量的实例上缩短了测试时间段。分时报价内存的大小自然增加了,这也导致了分配内存总量的增加。但结果表明,在使用的所有实例数量下,分配给 EA 的内存量几乎相同。内存有一些增长,但相当缓慢。
512 和 1024 实例的运行时间异常短 - 几乎是其他实例数量大小的两倍快。可能的原因很可能与 CSV 数据文件中交易策略实例参数集的顺序有关。
最后一种模拟模式是 "基于真实分时的每个分时报价"。比起 "每个分时报价" 模式,我们多运行了几次。
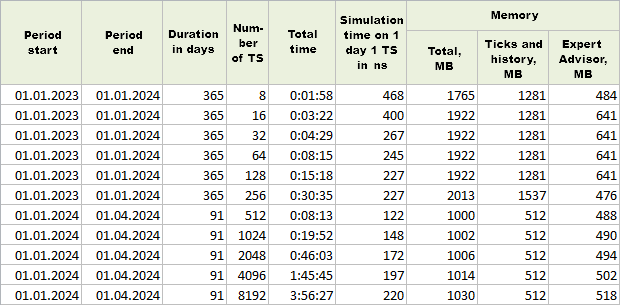
图 3。"基于真实分时的每个分时报价"模式下的单次运行结果
与之前的模式相比,时间增加了约 30%,使用的内存增加了约 20%。
值得注意的是,在测试期间,附在图表上的一个 EA 副本正在终端中运行。它使用了 8192 个实例。在这种情况下,终端内存消耗量约为 200 MB,而 CPU 资源消耗量在 0% 至 4% 之间。
总之,实验表明,我们为在一个 EA 中协同工作的交易策略实例的可能数量预留了相当大的空间。当然,这个数量在很大程度上取决于交易策略的具体内容。一个实例需要执行的计算越多,我们可以组合的计算就越少。
现在,让我们想想可以采取哪些简单的步骤来加快测试速度。
禁用输出
在目前的实现过程中,我们会在 EA 运行期间显示大量信息。在优化单个实例时,这不是问题,因为输出函数根本不会被执行。如果我们在测试器中运行一次 EA,所有信息都会发送到日志中。在应用的 VirtualOrder.mqh 库中,我们会显示关于处理每个虚拟订单事件的信息。当虚拟订单数量很少时,这对测试时间影响不大,但当虚拟订单数量开始达到数以万计时,就会产生明显的影响。
让我们试着测量一下,我们可以在 EA 文件开头添加以下的一行代码,禁止将所有信息输出到日志中:
#define PrintFormat StringFormat
由于这些函数的关联性,所有 PrintFormat() 调用都可以用 StringFormat() 函数代替。它们会生成一个字符串,但不会将其输出到日志中。
在进行了几次运行后,其中一些运行时间缩短了 5-10%,而另一些运行时间甚至略有增加。今后,我们可能仍然需要类似的 PrintFormat() 替换方法。
迁移至 1 分钟 OHLC
另一种加快单次测试通过和优化过程的方法是避免使用 "每个分时报价" 和 "基于真实分时的每个分时报价" 模拟模式。
显然,并非所有的交易策略都能承受这一点。如果策略涉及非常频繁的开仓/平仓(每分钟超过一次),那么就不可能放弃对所有分时报价的测试。即使是高频交易,也不会一直持续下去,而只会在指定的时间段内进行。但是,如果该策略不需要频繁开仓/平仓,对因止损和止盈水平触发不够准确而损失几个点也不那么敏感,那么为什么不利用这个机会呢?
作为示例的交易策略就是一种可以让我们摆脱使用全分时模式的交易策略。然而,这里又出现了另一个问题。如果我们只是在 "1 分钟 OHLC" 模式下优化单个实例的参数,然后将组装好的 EA 放到终端上运行,那么该 EA 就必须在每个 分时报价模式下运行。它不会每分钟收到固定的 4 个分时报价,而是会收到更多。因此,OnTick() 函数会被更频繁地调用,EA 处理的价格集也会更加多样化。
这种差异可能会改变 EA 所显示的结果。为了验证这种情况的真实性,让我们比较一下在 "1 分钟 OHLC" 和 "基于真实分时的每个分时报价" 模式下使用相同输入参数测试 EA 时的交易结果。

图 4.比较在
"基于真实分时的每个分时报价"(左)和 "1 分钟 OHLC"(右)
模式下的单个测试运行结果
我们可以看到,不同模式的开盘、收盘时间和价格略有不同。起初,这是唯一的区别,但后来,我们看到左边的交易开盘,而右边的交易却没有开盘:请看第 25 号交易的那一行。因此,"1 分钟 OHLC" 模式下的交易结果少于 "基于真实分时的每个分时报价" 模式下的交易结果。
在每种分时模式下,利润都会略微增加。如果我们看一下余额曲线,它们之间没有明显的差异:
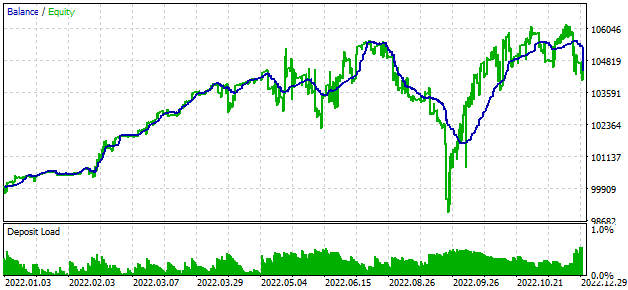

图 5.在 "1 分钟 OHLC"(顶部)和 "基于真实分时的每个分时报价"(底部)中的测试结果
因此,在终端运行该 EA 时,我们很可能会得到不比 "1 分钟 OHLC" 模式下的测试结果差的结果。这意味着可以使用更快的分时报价模拟模式进行优化。如果策略的某些计算只能在新柱开始时执行,那么我们可以在每个分时处拒绝此类计算,从而进一步加快 EA 的工作速度。为此,我们需要一种方法来确定 EA 中的新柱。
如果 "每个分时报价" 模式下的结果比 "1 分钟 OHLC" 模式下的结果差,我们可以尝试禁止 EA 不在柱形开始时执行交易。在这种情况下,我们应该在所有分时报价建模模式下得到尽可能接近的结果。为此,我们再次需要在 EA 中定义新的柱。
定义新柱
让我们先提出自己的愿望。我们希望有一个函数,在给定交易品种和给定时间框架上出现新的柱形时返回 true。在开发实现单个交易策略实例的 EA 时,通常会针对一个交易品种和时间框架(或针对一个交易品种和多个时间框架)执行这样的函数,使用变量来存储最后一个柱形的时间。通常可以看到,实现这一功能的代码并不是作为一个单独的函数分配的,而是在唯一需要它的地方实现的。
当需要为不同的交易策略实例执行多次新柱形出现检查时,这种方法就会变得很不方便。当然,也可以将这些代码直接嵌入到交易策略实例的执行中,但我们将采用不同的方式。
让我们创建 IsNewBar(symbol, timeframe) 公共函数,该函数应能按交易品种和时间框架报告当前分时是否出现新的柱形。除了调用该函数外,最好无需在策略的交易逻辑代码中添加其他变量或操作。此外,如果在当前分时上出现了新的柱形,并且函数被多次调用(例如,从不同的交易策略实例中调用),那么每次调用都应返回 "true",而不仅仅是第一次调用。
然后,我们需要存储每个交易品种和时间框架的最后一个柱形的时间信息。但是,我们所说的 "每一个" 并不是指终端中的所有交易品种,而是指只有在操作具体交易策略时才实际需要的部分。为了定义这些必要交易品种和时间框架的范围,我们将扩展 IsNewBar(symbol, timeframe) 函数执行的操作列表。首先检查给定交易品种和时间框架上的当前柱形是否有某种形式的记忆时间。如果不存在,函数将创建这样一个时间存储位置。如果存在,函数将返回检查新柱的结果。
为了让我们的 IsNewBar() 函数在单个分时上被多次调用,我们必须将其拆分成两个独立的函数。其中一个函数将在一个分时开始时检查所有感兴趣的交易品种和时间框架是否出现新的柱形,并将这些信息保存到第二个函数中,第二个函数将简单地找到新柱形出现事件的预期结果并返回。让我们将第一个函数命名为 UpdateNewBar()。我们将使它同时返回一个逻辑值,显示至少有一个交易品种和时间框架出现了新的柱形。
UpdateNewBar() 函数应在开始处理一个新分时报价时调用一次。例如,可以将其调用放在 CVirtualAdvisor::Tick() 方法的开头:
void CVirtualAdvisor::Tick(void) { // Define a new bar for all required symbols and timeframes UpdateNewBar(); ... // Start handling in strategies where IsNewBar(...) can already be used CAdvisor::Tick(); ... }
要存储最后一个柱形的时间,首先要创建 CNewBarEvent 静态类。这意味着我们不会创建该类的对象,而只会使用其静态属性和方法。这基本上等同于在专用命名空间中创建所需的全局变量和函数。
在这个类中,我们将有两个数组:交易品种名称数组(m_symbols)和指向新类对象的指针数组(m_symbolNewBarEvent)。第一个将包含我们用来跟踪新柱形事件的交易品种。第二个是指向新的 CSymbolNewBarEvent 类的指针,该类将存储一个交易品种的柱形时间,但时间框架不同。
这两个类将有三个方法:
- 注册新的受监控交易品种或交易品种时间框架的方法 Register(...)
- 更新新柱标记的方法 Update()
- 获取新柱形标志 IsNewBar(...) 的方法
如果需要注册跟踪新交易品种上的新柱形事件,则会创建一个新的类对象 CSymbolNewBarEvent。因此,有必要在 EA 完成工作时清理这些对象占用的内存。这项任务由 CNewBarEvent::Destroy() 静态方法和 DestroyNewBar() 全局函数完成。我们将在 EA 析构函数中添加函数调用:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Destructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualAdvisor::~CVirtualAdvisor() { delete m_receiver; // Remove the recipient delete m_interface; // Remove the interface DestroyNewBar(); // Remove the new bar tracking objects }
这些类的完整实现可能如下所示:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class for defining a new bar for a specific symbol | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CSymbolNewBarEvent { private: string m_symbol; // Tracked symbol long m_timeFrames[]; // Array of tracked symbol timeframes long m_timeLast[]; // Array of times of the last bars for timeframes bool m_res[]; // Array of flags of a new bar occurrence for timeframes // The method for registering a new tracked timeframe for a symbol int Register(ENUM_TIMEFRAMES p_timeframe) { APPEND(m_timeFrames, p_timeframe); // Add it to the timeframe array APPEND(m_timeLast, 0); // The last time bar for it is still unknown APPEND(m_res, false); // No new bar for it yet Update(); // Update new bar flags return ArraySize(m_timeFrames) - 1; } public: // Constructor CSymbolNewBarEvent(string p_symbol) : m_symbol(p_symbol) // Set a symbol {} // Method for updating new bar flags bool Update() { bool res = (ArraySize(m_res) == 0); FOREACH(m_timeFrames, { // Get the current bar time long time = iTime(m_symbol, (ENUM_TIMEFRAMES) m_timeFrames[i], 0); // If it does not match the saved one, it is a new bar m_res[i] = (time != m_timeLast[i]); res |= m_res[i]; // Save the new time m_timeLast[i] = time; }); return res; } // Method for getting the new bar flag bool IsNewBar(ENUM_TIMEFRAMES p_timeframe) { int index; // Search for the required timeframe index FIND(m_timeFrames, p_timeframe, index); // If not found, then register a new timeframe if(index == -1) { PrintFormat(__FUNCTION__" | Register new event handler for %s %s", m_symbol, EnumToString(p_timeframe)); index = Register(p_timeframe); } // Return the new bar flag for the necessary timeframe return m_res[index]; } }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Static class for defining a new bar for all | //| symbols and timeframes | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CNewBarEvent { private: // Array of objects to define a new bar for one symbol static CSymbolNewBarEvent *m_symbolNewBarEvent[]; // Array of required symbols static string m_symbols[]; // Method to register new symbol and timeframe to track a new bar static int Register(string p_symbol) { APPEND(m_symbols, p_symbol); APPEND(m_symbolNewBarEvent, new CSymbolNewBarEvent(p_symbol)); return ArraySize(m_symbols) - 1; } public: // There is no need to create objects of this class - delete the constructor CNewBarEvent() = delete; // Method for updating new bar flags static bool Update() { bool res = (ArraySize(m_symbolNewBarEvent) == 0); FOREACH(m_symbols, res |= m_symbolNewBarEvent[i].Update()); return res; } // Method to free memory for automatically created objects static void Destroy() { FOREACH(m_symbols, delete m_symbolNewBarEvent[i]); ArrayResize(m_symbols, 0); ArrayResize(m_symbolNewBarEvent, 0); } // Method for getting the new bar flag static bool IsNewBar(string p_symbol, ENUM_TIMEFRAMES p_timeframe) { int index; // Search for the required symbol index FIND(m_symbols, p_symbol, index); // If not found, then register a new symbol if(index == -1) index = Register(p_symbol); // Return the new bar flag for the necessary symbol and timeframe return m_symbolNewBarEvent[index].IsNewBar(p_timeframe); } }; // Initialize static members of the CSymbolNewBarEvent class members; CSymbolNewBarEvent* CNewBarEvent::m_symbolNewBarEvent[]; string CNewBarEvent::m_symbols[]; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Function for checking a new bar occurrence | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool IsNewBar(string p_symbol, ENUM_TIMEFRAMES p_timeframe) { return CNewBarEvent::IsNewBar(p_symbol, p_timeframe); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Function for updating information about new bars | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool UpdateNewBar() { return CNewBarEvent::Update(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Function for removing new bar tracking objects | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void DestroyNewBar() { CNewBarEvent::Destroy(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
将此代码保存在当前文件夹的 NewBarEvent.mqh 中。
现在让我们来看看如何在交易策略和 EA 中应用该库。但首先,让我们对交易策略做一些与处理新柱形无关的小调整。
交易策略改进
遗憾的是,在撰写本文的过程中,我们发现所使用的策略有两个错误。它们对之前的结果没有重大影响,但既然发现了,那就修正它们吧。
第一个错误的原因是,当参数中的 openDistance_ 设置为负值时,它会被重置为一个小的正数,等于当前交易品种的价差。换句话说,不是开立买入止损(BUY STOP)和卖出止损(SELL_STOP)挂单,而是开立市场仓位。这意味着在优化过程中,我们无法看到通过交易这些挂单所能取得的结果。这意味着我们错过了一些潜在的盈利参数集。
在 SimpleVolumesStrategy.mqh 文件的挂单开仓函数中的以下代码字符串中出现错误:
// Let's make sure that the opening distance is not less than the spread int distance = MathMax(m_openDistance, spread);
如果 m_openDistance 为负值,那么开盘价与当前价格的 distance 值就会变成正值。要在 distance 中保存与 m_openDistance 相同的符号,我们只需将下面的表达式乘以 m_openDistance:
// Let's make sure that the opening distance is not less than the spread int distance = MathMax(MathAbs(m_openDistance), spread) * (m_openDistance < 0 ? -1 : 1);
第二个错误是,在计算最近几条柱形的平均成交量时,当前柱形的成交量也被计算在内。虽然根据策略说明,我们不应该用它来计算平均值。不过,这一误差的影响可能也很小。成交量平均周期越长,最后一个柱对平均值的贡献就越小。
要解决这个错误,我们只需稍微修改计算平均值的函数,将传递数组的第一个元素排除在外:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Average value of the array of numbers from the second element | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CSimpleVolumesStrategy::ArrayAverage(const double &array[]) { double s = 0; int total = ArraySize(array) - 1; for(int i = 1; i <= total; i++) { s += array[i]; } return s / MathMax(1, total); }
将更改保存到当前文件夹的 SimpleVolumesStrategy.mqh 文件中。
考虑在策略中增设一个新柱
为了使交易策略中的某些操作只在出现新的柱形时执行,我们只需将该代码块放在这样的条件运算符中即可:
// If a new bar arrived on H1 for the current strategy symbol, then if(IsNewBar(m_symbol, PERIOD_H1)) { // perform the necessary actions ... }
如果策略中存在这样的代码,就会自动在 H1 和 m_symbol 策略交易品种中注册跟踪新柱事件。
我们可以很容易地在其他时间框架上添加对新柱形出现情况的检查。例如,如果策略使用某个平均价格范围(ATR 或 ADR)的值,那么可以通过以下方式轻松地每天只重新计算一次:
// If a new bar arrived on D1 for the current strategy symbol, then if(IsNewBar(m_symbol, PERIOD_H1)) { CalcATR(); // call our ATR calculation function }
在本系列文章所探讨的交易策略中,我们可以完全排除新柱形到达时刻之外的所有操作:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| "Tick" event handler function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CSimpleVolumesStrategy::Tick() override { // If there is no new bar on M1, if(!IsNewBar(m_symbol, PERIOD_M1)) return; // If their number is less than allowed if(m_ordersTotal < m_maxCountOfOrders) { // Get an open signal int signal = SignalForOpen(); if(signal == 1 /* || m_ordersTotal < 1 */) { // If there is a buy signal, then OpenBuyOrder(); // open the BUY_STOP order } else if(signal == -1) { // If there is a sell signal, then OpenSellOrder(); // open the SELL_STOP order } } }
我们还可以在 EA 的 OnTick 事件处理函数中,禁止在不符合所使用的任何交易品种或时间框架的新柱形开始时间的分时上进行任何处理。为此,我们可以对 CVirtualAdvisor::Tick() 方法进行如下修改:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| OnTick event handler | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualAdvisor::Tick(void) { // Define a new bar for all required symbols and timeframes bool isNewBar = UpdateNewBar(); // If there is no new bar anywhere, and we only work on new bars, then exit if(!isNewBar && m_useOnlyNewBar) { return; } // Receiver handles virtual positions m_receiver.Tick(); // Start handling in strategies CAdvisor::Tick(); // Adjusting market volumes m_receiver.Correct(); // Save status Save(); // Render the interface m_interface.Redraw(); }
在这段代码中,我们添加了一个新的 m_useOnlyNewBar EA 属性,可以在创建 EA 对象时设置:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class of the EA handling virtual positions (orders) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CVirtualAdvisor : public CAdvisor { protected: ... bool m_useOnlyNewBar; // Handle only new bar ticks public: CVirtualAdvisor(ulong p_magic = 1, string p_name = "", bool p_useOnlyNewBar = false); // Constructor ... }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CVirtualAdvisor::CVirtualAdvisor(ulong p_magic = 1, string p_name = "", bool p_useOnlyNewBar = false) : // Initialize the receiver with a static receiver m_receiver(CVirtualReceiver::Instance(p_magic)), // Initialize the interface with the static interface m_interface(CVirtualInterface::Instance(p_magic)), m_lastSaveTime(0), m_useOnlyNewBar(p_useOnlyNewBar) { m_name = StringFormat("%s-%d%s.csv", (p_name != "" ? p_name : "Expert"), p_magic, (MQLInfoInteger(MQL_TESTER) ? ".test" : "") ); };
我们本可以通过继承 CVirtualAdvisor 来创建一个新的 EA 类,并为其添加一个新的属性和新的柱形存在验证。但我们可以保持原样,因为 m_useOnlyNewBar 的默认值为 false,无需在 EA 类中添加此功能,一切都能正常运行。
如果我们以这种方式扩展了 EA 类,那么在交易策略类中,我们就可以不在 Tick() 方法中检查新的分钟柱形事件。只需在策略构造函数中使用当前交易品种和 M1 时限调用一次 IsNewBar() 函数,就可以开始跟踪使用此类交易品种和时限的新柱形事件。在这种情况下,m_useOnlyNewBar = true 的 EA 将不会触发策略实例的分时报价处理,除非 M1 上出现新的柱形:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CSimpleVolumesStrategy::CSimpleVolumesStrategy( ...) : // Initialization list ... { CVirtualReceiver::Get(GetPointer(this), m_orders, m_maxCountOfOrders); // Load the indicator to get tick volumes m_iVolumesHandle = iVolumes(m_symbol, m_timeframe, VOLUME_TICK); // Set the size of the tick volume receiving array and the required addressing ArrayResize(m_volumes, m_signalPeriod); ArraySetAsSeries(m_volumes, true); // Register the event handler for a new bar on the minimum timeframe IsNewBar(m_symbol, PERIOD_M1); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| "Tick" event handler function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CSimpleVolumesStrategy::Tick() override { // If their number is less than allowed if(m_ordersTotal < m_maxCountOfOrders) { // Get an open signal int signal = SignalForOpen(); if(signal == 1 /* || m_ordersTotal < 1 */) { // If there is a buy signal, then OpenBuyOrder(); // open the BUY_STOP order } else if(signal == -1) { // If there is a sell signal, then OpenSellOrder(); // open the SELL_STOP order } } }
将更改保存到当前文件夹的 SimpleVolumesStrategy.mqh 文件中。
结果
BenchmarkInstancesExpert.mq5 EA 获得了一个新输入参数 useOnlyNewBars_,我们在其中设置了它是否应该处理与新柱形开始不匹配的分时。初始化 EA 时,将参数值传递给 EA 的构造函数:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Inputs | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ... input group "::: Other parameters" sinput ulong magic_ = 27183; // - Magic input bool useOnlyNewBars_ = true; // - Work only at bar opening ... //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { ... // Create an EA handling virtual positions expert = new CVirtualAdvisor(magic_, "SimpleVolumes_BenchmarkInstances", useOnlyNewBars_); ... }
让我们用 256 个交易策略实例在 "基于真实分时的每个分时报价" 模式下对一个小周期进行测试 - 首先使用 useOnlyNewBars_ = false,然后使用 useOnlyNewBars_ = true。
在第一种情况下,当 EA 在每个分时运行时,利润为 296 美元,运行时间为 04:15。在第二种情况下,当 EA 跳过所有分时(新柱开始时的分时除外)时,利润为 434 美元,交易在 00:25 时完成。因此,在第二种情况下,我们不仅将计算成本降低了 10 倍,还获得了略高的利润。
但我们也不能过于乐观。对于其他交易策略来说,重复类似的结果绝非保证。每种交易策略都应单独研究。
结论
让我们再来看看取得的成果。我们测试了 EA 在大量交易策略实例同时运行时的性能。这为不同交易品种、时间框架和交易策略的多样化交易开辟了良好的前景,因为我们可以将它们结合到一个 EA 中。
我们还为类库添加了新功能 - 跟踪新的柱形事件。虽然在我们正在探讨的策略中并不真正需要这一功能,但它的存在对于实现其他交易策略非常有用。此外,将 EA 的运行限制在新的柱形开始时,有助于降低计算成本,并在不同的分时模拟模式下获得更相似的测试结果。
但是,我们又一次偏离了预定的项目轨迹。嗯,这也能帮助我们实现最终目标。稍事休息之后,让我们重新振作起来,回到 EA 自动测试的道路上来。看来,是时候重新使用字符串常量来初始化交易策略实例,并建立一个存储优化结果的系统了。
感谢您的关注!期待很快与您见面!
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自俄文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/14574
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 最负盛名的人工协作搜索算法的改进版本(AXSm)
最负盛名的人工协作搜索算法的改进版本(AXSm)
 人工协作搜索算法 (ACS)
人工协作搜索算法 (ACS)
 使用图表可视化交易(第一部分):选择分析时段
使用图表可视化交易(第一部分):选择分析时段

你好,尤里、
感谢您的文章。我附上了 csv 文件,只是想知道我的思路是否正确。
你好,菲利帕。
感谢您的反馈。
从所附文件来看,您的想法是对的。它应该是这样的