开发多币种 EA 交易(第 3 部分):架构修改
概述
在前几篇文章中,我们开始开发一种可同时使用多种交易策略的多币种 EA。第二篇文章中提供的解决方案与第一篇文章中提出的解决方案已经大相径庭。这表明我们仍在寻找最佳方案。
让我们试着从整体上审视已开发的系统,抽象出实现过程中的小细节,以了解改进的方法。为此,让我们追溯一下该系统虽然短暂、但仍然引人注目的演变过程。
第一个运行模式
我们分配了一个 EA 对象(CAdvisor 类或其子类),它是交易策略对象(CStrategy 类或其子类)的聚合器。在 EA 运行开始时,OnInit() 处理函数中会发生以下情况:
- 创建 EA 对象。
- 创建交易策略对象并将其添加到 EA 的交易策略数组中。
在 OnTick() 事件处理函数中会发生以下情况:
- 为 EA 对象调用 CAdvisor::Tick() 方法。
- 此方法遍历所有策略,并调用它们的 CStrategy::Tick() 方法。
- CStrategy::Tick() 中的策略执行所有必要操作,以打开和关闭市场仓位。
这可以用示意图来表示:
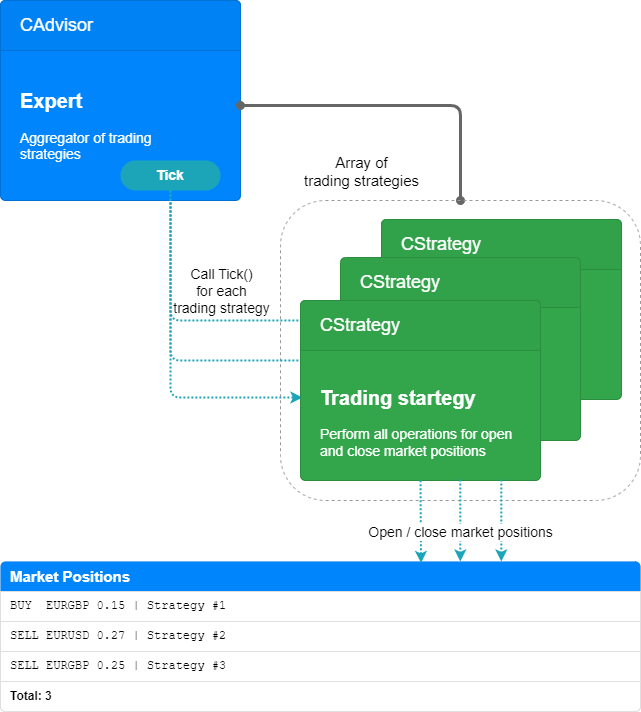
图 1.第一篇文章中的运行模式
这种模式的优势在于,只要拥有遵循某种交易策略的 EA 的源代码,就可以通过一些相对简单的操作,使 EA 与其他交易策略实例协同工作。
然而,主要的缺点很快就显现出来了:在组合多个策略时,我们必须或多或少地减少每个策略实例所开立仓位的大小。这可能导致某些甚至所有策略实例完全被排除在交易之外。由于公开市场仓位的最小规模是固定的,因此并行工作中包含的策略实例越多或初始存款越少,出现这种结果的可能性就越大。
此外,当多个策略实例一起工作时,会遇到相同大小的相反仓位被打开的情况。就总量而言,这相当于没有敞口头寸,但对立敞口头寸的库存费继续增加。
第二篇文章中的运行模式
为了消除这些缺陷,我们决定将所有与市场仓位有关的操作转移到一个单独的地方,取消交易策略直接打开市场仓位的能力。这在一定程度上使现成策略的重新设计变得复杂,但这并不是一个很大的损失,因为它弥补了第一种模式的主要缺点。
我们的操作模式中出现了两个新实体:虚拟仓位(CVirtualOrder 类)和策略交易量接收器(CReceiver 类及其子类)。
在 EA 运行开始时,OnInit() 处理函数中会发生以下情况:
- 创建一个接收器对象。
- 创建一个 EA 对象,并将创建的接收器传递给它。
- 创建交易策略对象并将其添加到 EA 的交易策略数组中。
- 每个策略都会创建自己的虚拟仓位对象数组,其中包含所需数量的虚拟仓位对象。
在 OnTick() 事件处理函数中会发生以下情况:
- 为 EA 对象调用 CAdvisor::Tick() 方法。
- 此方法遍历所有策略,并调用它们的 CStrategy::Tick() 方法。
- CStrategy::Tick() 中的策略会执行所有必要操作,以打开和关闭虚拟仓位。如果发生与未平仓虚拟仓位组成变化有关的事件,策略会通过设置标志来记住这一变化。
- 如果至少有一个策略设置了变更标志,则接收器会启动调整市场仓位未平仓合约量的方法。如果调整成功,则重置所有策略的更改标志。
这可以用示意图来表示:
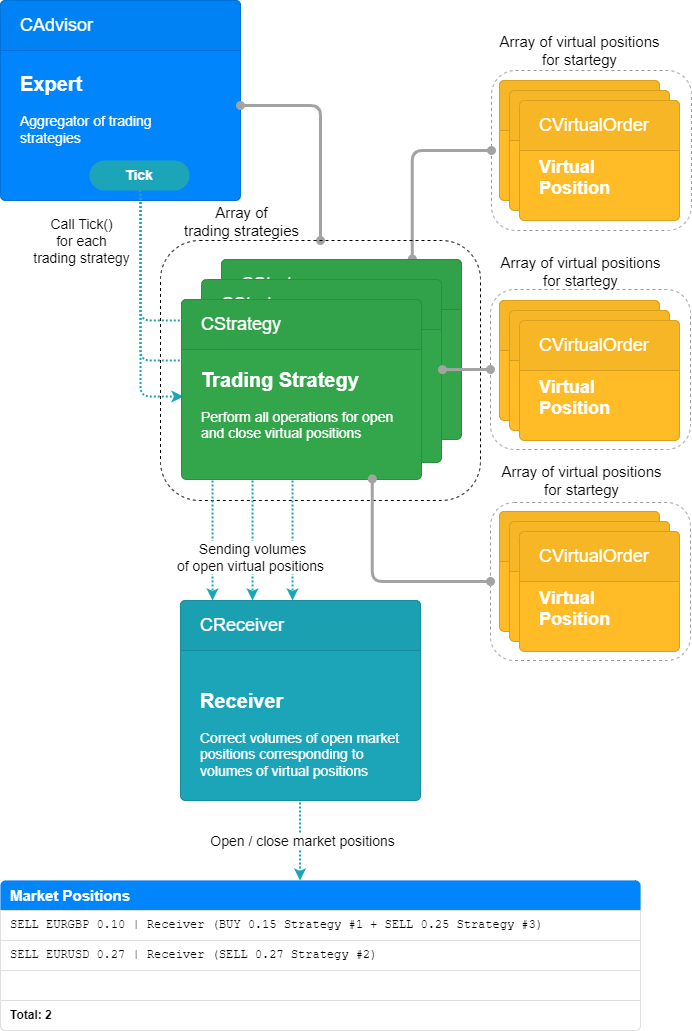
图 2.第二篇文章中的运行模式
在这种运行模式下,我们将不再面临某些策略实例不会以任何方式影响公开市场仓位大小的事实。相反,即使是一个虚拟交易量很小的开仓实例,也可能成为压倒多个策略实例虚拟仓位总交易量的一滴水,超过市场仓位的最小允许交易量。在这种情况下,真正的市场仓位将被打开。
同时,我们还获得了其他一些令人高兴的变化,包括可能节省库存费、减少存款负担、减少观察到的回撤以及改进交易质量评估(夏普比率、利润因子)。
在测试第二种模式时,我发现了以下问题:
- 每个策略首先处理已打开的虚拟仓位,以确定触发的止损和止盈水平。如果达到任何一个水平,则关闭该虚拟仓位。因此,这种处理方法被立即转移到 CVirtualOrder 类方法中。但这一解决方案似乎仍不够通用。
- 我们通过添加新的必需功能,扩展了基类的组成。如果我们不想处理虚拟仓位,也可以使用此类基类,只需将 "空" 对象传递给它们即可。例如,我们可以创建 CReceiver 类对象,其中只包含空 stub 方法。但这似乎也更像是一个需要重新修改的临时解决方案。
- 我们在 CStrategy 基类中添加了新方法和基类属性,用于跟踪未平仓虚拟仓位组成的变化,这些方法在 CAdvisor 基类中也有使用。同样,这看起来是朝着缩小功能和在基类中强加过于具体的实现迈出的一步。
- CStrategy 基类接收返回未平仓虚拟仓位总交易量的 Volume() 方法,因为开发的 CVolumeReceiver 类需要每个策略的未平仓虚拟交易量数据。不过,这样一来,我们就切断了在一个交易策略实例中为多个交易品种开立虚拟仓位的能力。在这种情况下,总交易量就失去了意义。这种解决方案适用于测试单交易品种策略,但仅此而已。
- 我们在 CReceiver 类中使用数组来存储 EA 策略的指针,这样接收器就可以使用它们来查找策略开启的虚拟交易量。这导致 EA 和接收器中填充策略数组的代码重复。
- 每个策略只对一个交易品种开仓:在策略数组中添加接收器时,会询问策略的交易品种,并将其添加到所用交易品种数组中。我们在 CVolumeReceiver 类中使用了这一功能。然后,接收器只处理添加到其交易品种数组中的交易品种。我们已经提到了这种行为产生的限制。
- 让我们尽可能地清理 CStrategy 和 CAdvisor 基类。让我们编写自定义派生的 CVirtualStrategy 和 CVirtualAdvisor 类,创建使用虚拟交易的 EA 开发分支。现在,它们将成为我们特定策略和 EA 的父类。
- 现在是扩大虚拟仓位类的时候了。每个虚拟仓位都应接收一个指向接收器对象和交易策略对象的指针,接收器对象负责将虚拟交易量带入市场,而交易策略对象则负责决定虚拟仓位的开仓/平仓。这样就可以通知有关实体虚拟仓位的打开/关闭操作。
- 让我们将所有虚拟仓位的存储移到一个数组中,而不是将它们分布在属于策略实例的多个数组中。每个策略实例都会请求从该数组中获取几个元素来进行操作。共同数组的所有者将是交易量的接收器。
- 一个 EA 只能有一个接收器。因此,我们将以单例的形式实现它。它的唯一实例将在所有必要的地方提供。我们将把这种实现形式化为 CVirtualReceiver 派生类。
- 我们将把新实体数组 - 交易品种接收器 (CVirtualSymbolReceiver类)- 添加到接收器中。每个交易品种接收器只能使用其交易品种的虚拟仓位,打开时会自动连接到交易品种接收器,关闭时会自动解除连接。
清理基类
让我们只在 CStrategy 和 CAdvisor 基类中留下基本要素。如果使用 CStartegy,只留下处理 OnTick 事件的方法,就能得到以下简洁的代码:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Base class of the trading strategy | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CStrategy { public: virtual void Tick() = 0; // Handle OnTick events };
其他一切都将位于类的子类中。
在 CAdvisor 基类中,包含一个小文件 Macros.mqh,其中包含几个有用的宏,用于对常规数组执行操作:
- APPEND(A, V) - 将 V 元素添加到 A 数组的末尾;
- FIND(A, V, I) - 将等于 A 的数组元素写入 I 变量。如果找不到元素,则在 I 变量中存储-1;
- ADD(A, V) - 如果 A 数组中还没有 V 元素,则将 V 元素添加到 A 数组的末尾;
- FOREACH(A, D) - 循环 A 数组索引(索引将位于 i 本地变量中),在主体中执行 D 操作;
- REMOVE_AT(A, I) - 从 A 数组的 I 索引位置移除一个元素,移除后续元素并减小数组大小;
- REMOVE(A, V) - 从 A 数组中删除等于 V 的元素
// Useful macros for array operations #ifndef __MACROS_INCLUDE__ #define APPEND(A, V) A[ArrayResize(A, ArraySize(A) + 1) - 1] = V; #define FIND(A, V, I) { for(I=ArraySize(A)-1;I>=0;I--) { if(A[I]==V) break; } } #define ADD(A, V) { int i; FIND(A, V, i) if(i==-1) { APPEND(A, V) } } #define FOREACH(A, D) { for(int i=0, im=ArraySize(A);i<im;i++) {D;} } #define REMOVE_AT(A, I) { int s=ArraySize(A);for(int i=I;i<s-1;i++) { A[i]=A[i+1]; } ArrayResize(A, s-1);} #define REMOVE(A, V) { int i; FIND(A, V, i) if(i>=0) REMOVE_AT(A, i) } #define __MACROS_INCLUDE__ #endif //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
这些宏将在其他文件中使用,因为这样可以使代码更简洁易读,并避免调用额外的函数。
我们将从 CAdvisor 类中删除所有遇到接收器的地方,并只在 OnTick 事件处理方法中调用相应的策略处理程序。我们将收到以下代码:
#include "Macros.mqh" #include "Strategy.mqh" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| EA base class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CAdvisor { protected: CStrategy *m_strategies[]; // Array of trading strategies public: ~CAdvisor(); // Destructor virtual void Tick(); // OnTick event handler virtual void Add(CStrategy *strategy); // Method for adding a strategy }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Destructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CAdvisor::~CAdvisor() { // Delete all strategy objects FOREACH(m_strategies, delete m_strategies[i]); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| OnTick event handler | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CAdvisor::Tick(void) { // Call OnTick handling for all strategies FOREACH(m_strategies, m_strategies[i].Tick()); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Strategy adding method | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CAdvisor::Add(CStrategy *strategy) { APPEND(m_strategies, strategy); // Add the strategy to the end of the array } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
这些类将保留在当前文件夹中的 Strategy.mqh 和 Advisor.mqh 文件中。
现在,让我们将必要的代码转移到派生的策略和 EA 类中,它们应与虚拟仓位一起工作。
创建继承自 CStrategy 的 CVirtualStrategy 类。让我们为它添加以下字段和方法:
- 虚拟仓位(订单)数组;
- 未关闭仓位和订单总数;
- 计算未关闭虚拟仓位和订单的方法;
- 处理打开/关闭虚拟仓位(订单)的方法。
#include "Strategy.mqh" #include "VirtualOrder.mqh" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class of a trading strategy with virtual positions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CVirtualStrategy : public CStrategy { protected: CVirtualOrder *m_orders[]; // Array of virtual positions (orders) int m_ordersTotal; // Total number of open positions and orders virtual void CountOrders(); // Calculate the number of open positions and orders public: virtual void OnOpen(); // Event handler for opening a virtual position (order) virtual void OnClose(); // Event handler for closing a virtual position (order) }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Counting open virtual positions and orders | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualStrategy::CountOrders() { m_ordersTotal = 0; FOREACH(m_orders, if(m_orders[i].IsOpen()) { m_ordersTotal += 1; }) } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Event handler for opening a virtual position (order) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualStrategy::OnOpen() { CountOrders(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Event handler for closing a virtual position (order) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualStrategy::OnClose() { CountOrders(); }
将代码保存到当前文件夹的 VirtualStrategy.mqh 文件中。
既然我们将接收器从 CAdvisor 基类中移除,那么它就应该转移到我们新的 CVirtualAdvisor 子类中。在该类中,我们将添加 m_receiver 字段,用于存储交易量接收器对象的指针。
在构造函数中,该字段将使用指向唯一可能的接收器对象的指针进行初始化,该对象将在调用 CVirtualReceiver::Instance() 静态方法时创建。析构函数将确保对象被正确删除。
我们还将在 OnTick 事件处理函数中添加新的操作。在策略中启动该事件的处理函数之前,我们首先要在接收器中启动该事件的处理函数。在策略处理完事件后,我们将启动接收器的方法来调整开仓量。如果接收器现在是所有虚拟仓位的所有者,那么它们自己就能确定是否存在变化。因此,交易策略类中没有跟踪变化的实现,所以我们不仅要从基础策略类中删除,还要完全删除。
#include "Advisor.mqh" #include "VirtualReceiver.mqh" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class of the EA handling virtual positions (orders) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CVirtualAdvisor : public CAdvisor { protected: CVirtualReceiver *m_receiver; // Receiver object that brings positions to the market public: CVirtualAdvisor(ulong p_magic = 1); // Constructor ~CVirtualAdvisor(); // Destructor virtual void Tick() override; // OnTick event handler }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CVirtualAdvisor::CVirtualAdvisor(ulong p_magic = 1) : // Initialize the receiver with a static receiver m_receiver(CVirtualReceiver::Instance(p_magic)) {}; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Destructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualAdvisor::~CVirtualAdvisor() { delete m_receiver; // Remove the recipient } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| OnTick event handler | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualAdvisor::Tick(void) { // Receiver handles virtual positions m_receiver.Tick(); // Start handling in strategies CAdvisor::Tick(); // Adjusting market volumes m_receiver.Correct(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
将代码保存到当前文件夹的 VirtualAdvisor.mqh 文件中。
扩展虚拟仓位类
虚拟仓位类接收指向 m_receiver 和 m_strategy 对象的指针。这些字段的值必须通过构造函数参数传递,因此我们也要对其进行修改。我还为虚拟仓位的私有属性添加了几个读取器(getter):Id() 和 Symbol() 。让我们在类描述中展示一下添加的代码:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class of virtual orders and positions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CVirtualOrder { private: //--- Static fields... //--- Related recipient objects and strategies CVirtualReceiver *m_receiver; CVirtualStrategy *m_strategy; //--- Order (position) properties ... //--- Closed order (position) properties ... //--- Private methods public: CVirtualOrder( CVirtualReceiver *p_receiver, CVirtualStrategy *p_strategy ); // Constructor //--- Methods for checking the position (order) status ... //--- Methods for receiving position (order) properties ... ulong Id() { // ID return m_id; } string Symbol() { // Symbol return m_symbol; } //--- Methods for handling positions (orders) ... };
在构造函数的实现中,我们只需在初始化列表中添加两行,就可以从构造函数参数中设置新字段的值:
CVirtualOrder::CVirtualOrder(CVirtualReceiver *p_receiver, CVirtualStrategy *p_strategy) : // Initialization list m_id(++s_count), // New ID = object counter + 1 m_receiver(p_receiver), m_strategy(p_strategy), ..., m_point(0) { }
只有在打开或关闭虚拟仓位时,才会通知接收器和策略。这只发生在 Open() 和 Close() 方法中,所以让我们为它们添加一点代码:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Open a virtual position | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CVirtualOrder::Open(...) { // If the position is already open, then do nothing ... if(s_symbolInfo.Name(symbol)) { // Select the desired symbol // Update information about current prices ... // Initialize position properties ... // Depending on the direction, set the opening price, as well as the SL and TP levels ... // Notify the recipient and the strategy that the position (order) is open m_receiver.OnOpen(GetPointer(this)); m_strategy.OnOpen(); ... return true; } return false; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Close a position | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualOrder::Close() { if(IsOpen()) { // If the position is open ... // Define the closure reason to be displayed in the log ... // Save the close price depending on the type ... // Notify the recipient and the strategy that the position (order) is open m_receiver.OnClose(GetPointer(this)); m_strategy.OnClose(); } }
将当前虚拟仓位对象的指针传递给 OnOpen() 和 OnClose() 接收处理函数。策略处理程序中还没有这方面的需求,因此在实现时不使用参数。
该代码保留在当前文件夹中的同名文件 VirtualOrder.mqh。
实现新的接收器
让我们开始实现 CVirtualReceiver 接收器类,以确保给定类实例的唯一性。为此,我们将使用一种名为 Singleton(单件)的标准设计模式。我们需要:
- 使类的构造函数非公有;
- 添加一个静态类字段,用于存储指向类对象的指针;
- 添加一个静态方法,在没有实例的情况下创建一个该类的实例,或者返回一个已经存在的实例。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class for converting open volumes to market positions (receiver) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CVirtualReceiver : public CReceiver { protected: // Static pointer to a single class instance static CVirtualReceiver *s_instance; ... CVirtualReceiver(ulong p_magic = 0); // Private constructor public: //--- Static methods static CVirtualReceiver *Instance(ulong p_magic = 0); // Singleton - creating and getting a single instance ... }; // Initializing a static pointer to a single class instance CVirtualReceiver *CVirtualReceiver::s_instance = NULL; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Singleton - creating and getting a single instance | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CVirtualReceiver* CVirtualReceiver::Instance(ulong p_magic = 0) { if(!s_instance) { s_instance = new CVirtualReceiver(p_magic); } return s_instance; }
接下来,在类中添加用于存储所有虚拟仓位的 m_orders 数组。每个策略实例都会向接收器请求一定数量的虚拟仓位。为此,请添加 Get() 静态方法,该方法将创建所需数量的虚拟仓位对象,并将指向这些对象的指针添加到接收器数组和策略虚拟仓位数组中:
class CVirtualReceiver : public CReceiver { protected: ... CVirtualOrder *m_orders[]; // Array of virtual positions ... public: //--- Static methods ... static void Get(CVirtualStrategy *strategy, CVirtualOrder *&orders[], int n); // Allocate the necessary amount of virtual positions to the strategy ... }; ... //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Allocate the necessary amount of virtual positions to strategy | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ static void CVirtualReceiver::Get(CVirtualStrategy *strategy, // Strategy CVirtualOrder *&orders[], // Array of strategy positions int n // Required number ) { CVirtualReceiver *self = Instance(); // Receiver singleton ArrayResize(orders, n); // Expand the array of virtual positions FOREACH(orders, orders[i] = new CVirtualOrder(self, strategy); // Fill the array with new objects APPEND(self.m_orders, orders[i])) // Register the created virtual position ... }
现在是时候在类中添加指向交易品种接收器对象(CVirtualSymbolReceiver 类)的指针数组了。该类尚未创建,但我们已经知道它应该做什么 - 根据单一交易品种的虚拟交易量直接打开和关闭市场仓位。因此,我们可以说,交易品种接收器对象的数量将等于 EA 中使用的不同交易品种的数量。我们将使它成为 CReceiver 的子类,因此它将拥有 Correct() 方法,该方法将完成主要的有用工作。我们还将添加必要的辅助方法。
我们稍后再讨论这个问题,现在回到 CVirtualReceiver 类,为它添加 Correct() 方法的虚拟重载。
class CVirtualReceiver : public CReceiver { protected: ... CVirtualSymbolReceiver *m_symbolReceivers[]; // Array of recipients for individual symbols public: ... //--- Public methods virtual bool Correct() override; // Adjustment of open volumes };
现在,Correct() 方法的实现非常简单,因为我们将主要工作转移到了层次结构的下一级。目前,我们只需循环浏览所有交易品种接收器,并调用它们的 Correct() 方法即可。
为了减少不必要的调用次数,我们将通过添加 IsTradeAllowed() 方法来初步检查现在是否允许交易,该方法可以回答这个问题。我们还将添加 m_isChanged 类字段,该字段将作为未关闭虚拟仓位变化的标志。我们也会在要求调整前进行检查。
class CVirtualReceiver : public CReceiver { ... bool m_isChanged; // Are there any changes in open positions? ... bool IsTradeAllowed(); // Is trading available? public: ... virtual bool Correct() override; // Adjustment of open volumes }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Adjust open volumes | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CVirtualReceiver::Correct() { bool res = true; if(m_isChanged && IsTradeAllowed()) { // If there are changes, then we call the adjustment of the recipients of individual symbols FOREACH(m_symbolReceivers, res &= m_symbolReceivers[i].Correct()); m_isChanged = !res; } return res; }
在 IsTradeAllowed() 方法中,检查终端和交易账户的状态,以确定是否可以进行真实交易:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Is trading available? | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CVirtualReceiver::IsTradeAllowed() { return (true && MQLInfoInteger(MQL_TRADE_ALLOWED) && TerminalInfoInteger(TERMINAL_TRADE_ALLOWED) && AccountInfoInteger(ACCOUNT_TRADE_EXPERT) && AccountInfoInteger(ACCOUNT_TRADE_ALLOWED) && TerminalInfoInteger(TERMINAL_CONNECTED) ); }
我们在 Correct() 方法中应用了更改标记。如果交易量调整成功,则重置该标记。但这个标志应该设置在哪里呢?显然,如果打开或关闭任何虚拟仓位,都会出现这种情况。在 CVirtualOrder 类中,我们特别将 CVirtualReceiver 类中尚未出现的 OnOpen() 和 OnClose() 方法的调用添加到打开/关闭方法 中。我们将在其中设置更改标志。
此外,我们还应将这些处理函数的更改通知所需的交易品种接收者。在为某个交易品种打开第一个虚拟仓位时,相应的交易品种接收者还不存在,因此我们需要创建并通知它。在为给定交易品种打开/关闭虚拟仓位的后续操作中,已经有相应的交易品种接收者,因此只需通知它即可。
class CVirtualReceiver : public CReceiver { ... public: ... //--- Public methods void OnOpen(CVirtualOrder *p_order); // Handle virtual position opening void OnClose(CVirtualOrder *p_order); // Handle virtual position closing ... }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Handle opening a virtual position | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualReceiver::OnOpen(CVirtualOrder *p_order) { string symbol = p_order.Symbol(); // Define position symbol CVirtualSymbolReceiver *symbolReceiver; int i; FIND(m_symbolReceivers, symbol, i); // Search for the symbol recipient if(i == -1) { // If not found, then create a new recipient for the symbol symbolReceiver = new CVirtualSymbolReceiver(m_magic, symbol); // and add it to the array of symbol recipients APPEND(m_symbolReceivers, symbolReceiver); } else { // If found, then take it symbolReceiver = m_symbolReceivers[i]; } symbolReceiver.Open(p_order); // Notify the symbol recipient about the new position m_isChanged = true; // Remember that there are changes } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Handle closing a virtual position | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualReceiver::OnClose(CVirtualOrder *p_order) { string symbol = p_order.Symbol(); // Define position symbol int i; FIND(m_symbolReceivers, symbol, i); // Search for the symbol recipient if(i != -1) { m_symbolReceivers[i].Close(p_order); // Notify the symbol recipient about closing a position m_isChanged = true; // Remember that there are changes } }
除了根据交易策略信号打开/关闭虚拟仓位外,还可以在达到止损或止盈水平时关闭虚拟仓位。在 CVirtualOrder 类中,我们专门为此提供了 Tick() 方法。它检查这些水平,并在必要时关闭虚拟位置。每个分时和所有虚拟仓位都应调用它。这正是 CVirtualReceiver 类中 Tick() 方法的作用。让我们添加类:
class CVirtualReceiver : public CReceiver { ... public: ... //--- Public methods void Tick(); // Handle a tick for the array of virtual orders (positions) ... }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Handle a tick for the array of virtual orders (positions) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualReceiver::Tick() { FOREACH(m_orders, m_orders[i].Tick()); }
最后,注意正确释放为虚拟仓位对象分配的内存。由于它们都在 m_orders 数组中,因此添加一个析构函数,我们将在其中删除它们:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Destructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CVirtualReceiver::~CVirtualReceiver() { FOREACH(m_orders, delete m_orders[i]); // Remove virtual positions }
将生成的代码保存到当前文件夹的 VirtualReceiver.mqh 文件中。
实现交易品种接收器
剩下的工作就是实现最后一个类 CVirtualSymbolReceiver,这样操作模式就能以适合使用的形式完成。我们将从上一篇文章中的 CVolumeReceiver 类中提取其主要内容,删除与确定每个虚拟仓位的交易品种和执行调整时枚举交易品种相关的地方。
该类对象也有自己的虚拟仓位对象指针数组,但其组成会不断变化。我们要求该数组只包含开启的虚拟仓位。这样,打开和关闭虚拟仓位时的操作就很清楚了:虚拟仓位打开后,我们应立即将其添加到相应交易品种接收者的数组中,而虚拟仓位关闭后,应立即将其从数组中移除。
此外,我们还可以方便地看到开启的虚拟仓位的构成是否发生了变化。这将有助于避免对每个分时进行不必要的检查。
让我们为该类添加一个交易品种字段、一个仓位数组和一个变化标记,以及两个处理打开/关闭的方法:
class CVirtualSymbolReceiver : public CReceiver { string m_symbol; // Symbol CVirtualOrder *m_orders[]; // Array of open virtual positions bool m_isChanged; // Are there any changes in the composition of virtual positions? ... public: ... void Open(CVirtualOrder *p_order); // Register opening a virtual position void Close(CVirtualOrder *p_order); // Register closing a virtual position ... };
这些方法本身的实现非常简单:我们从数组中添加/删除传入的虚拟仓位,并设置变化标志。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Register opening a virtual position | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualSymbolReceiver::Open(CVirtualOrder *p_order) { APPEND(m_orders, p_order); // Add a position to the array m_isChanged = true; // Set the changes flag } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Register closing a virtual position | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CVirtualSymbolReceiver::Close(CVirtualOrder *p_order) { REMOVE(m_orders, p_order); // Remove a position from the array m_isChanged = true; // Set the changes flag }
我们还需要通过交易品种名称搜索所需的交易品种接收者。为了使用FIND(A,V,I)宏中的普通线性搜索算法,让我们添加一个重载操作符,将交易品种接收器与字符串进行比较,如果实例交易品种与传递的字符串匹配,则返回 "true":
class CVirtualSymbolReceiver : public CReceiver { ... public: ... bool operator==(const string symbol) {// Operator for comparing by a symbol name return m_symbol == symbol; } ... };
下面是 CVirtualSymbolReceiver 类的完整描述。请在附件中查找所有方法的具体实现。
class CVirtualSymbolReceiver : public CReceiver { string m_symbol; // Symbol CVirtualOrder *m_orders[]; // Array of open virtual positions bool m_isChanged; // Are there any changes in the composition of virtual positions? bool m_isNetting; // Is this a netting account? double m_minMargin; // Minimum margin for opening CPositionInfo m_position; // Object for obtaining properties of market positions CSymbolInfo m_symbolInfo; // Object for getting symbol properties CTrade m_trade; // Object for performing trading operations double MarketVolume(); // Volume of open market positions double VirtualVolume(); // Volume of open virtual positions bool IsTradeAllowed(); // Is trading by symbol available? // Required volume difference double DiffVolume(double marketVolume, double virtualVolume); // Volume correction for the required difference bool Correct(double oldVolume, double diffVolume); // Auxiliary opening methods bool ClearOpen(double diffVolume); bool AddBuy(double volume); bool AddSell(double volume); // Auxiliary closing methods bool CloseBuyPartial(double volume); bool CloseSellPartial(double volume); bool CloseHedgingPartial(double volume, ENUM_POSITION_TYPE type); bool CloseFull(); // Check margin requirements bool FreeMarginCheck(double volume, ENUM_ORDER_TYPE type); public: CVirtualSymbolReceiver(ulong p_magic, string p_symbol); // Constructor bool operator==(const string symbol) {// Operator for comparing by a symbol name return m_symbol == symbol; } void Open(CVirtualOrder *p_order); // Register opening a virtual position void Close(CVirtualOrder *p_order); // Register closing a virtual position virtual bool Correct() override; // Adjustment of open volumes };
将代码保存在当前文件夹下的 VirtualSymbolReceiver.mqh 文件中。
比较结果
由此产生的运行模式可表示如下:
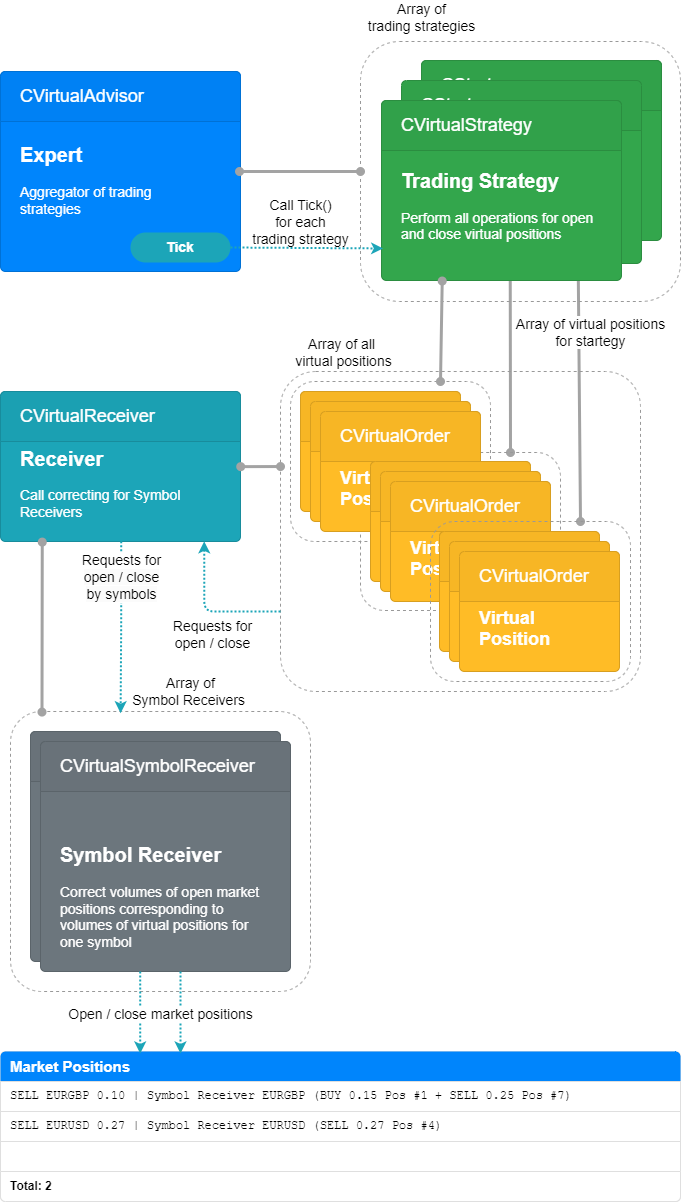
图 3.本文的运行模式
现在,最有趣的部分来了。让我们编译使用九个策略实例的 EA,参数与上一篇文章中的相同。让我们对上一篇文章中的类似 EA 和我们刚刚编译的 EA 进行测试运行:
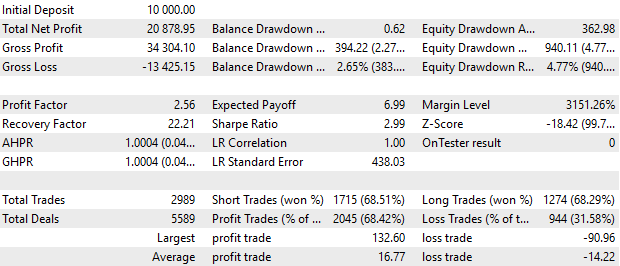
图 4.上一篇文章中的 EA 结果
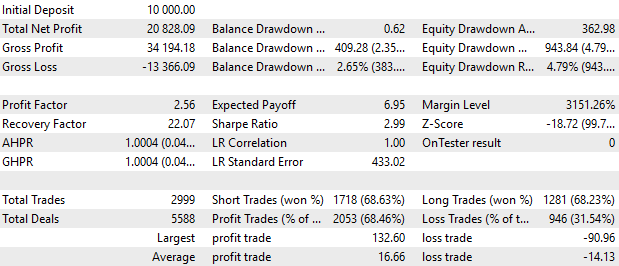
图 5.本文中的 EA 结果
总的来说,结果几乎相同。余额图一般没有区别。报告中可见的细微差别可能是由各种原因造成的,我们将进一步分析。
评估进一步的潜力
在上一篇文章的讨论中,我们提出了一个合乎逻辑的问题:使用相关方法可以获得怎样最有吸引力的交易结果?到目前为止,图表显示 5 年的回报率为 20%,看起来并不特别吸引人。
目前,对这个问题的回答可以如下。首先,有必要明确区分因选定的简单策略而取得的成果和因实现联合工作而取得的成果。
当把一种简单的策略改为另一种策略时,第一类的结果会发生变化。显然,简单策略的单个实例显示的结果越好,其整体结果也就越好。本文介绍的结果是在一个交易理念上取得的,最初正是由其质量和适用性决定的。我们仅通过测试区间的利润/回撤比率来评估这些结果。
第二类结果是联合工作和单独工作的比较结果。这里的评估基于其他参数:提高净值增长曲线图的线性度、减少回撤等。这些成果似乎更为重要,因为在它们的帮助下,有希望将第一类并不特别突出的成果提高到可以接受的水平。
但是,为了获得所有的结果,我们最好首先实现可变手数交易。如果不这样做,就更难根据测试结果估算盈利/亏损比率,尽管这仍然是可能的。
让我们尝试在 5 年内(2018.01.01 - 2023.01.01)存入少量初始资金,并为最大允许回撤 50%的未平仓仓位大小选择一个新的最佳值。以下是本文中的 EA 运行结果,采用了不同的仓位大小乘数,但在所有五年中都保持不变,初始存款为 1000 美元。在前一篇文章中,仓位大小是根据 10,000 美元的存款规模校准的,因此初始depoPart_值减少了约 10 倍。
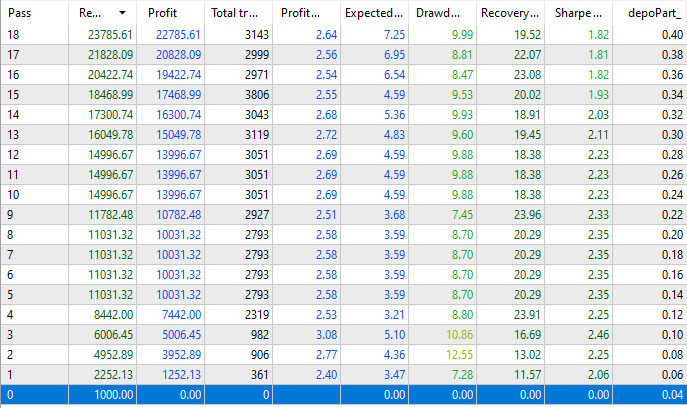
图 6.不同仓位大小的测试结果
我们可以看到,当最小的 depoPart_= 0.04 时,EA 并没有建立真实的仓位,因为在重新计算其交易量与余额的比例时,交易量小于 0.01。但从下一个乘数值 depoPart_= 0.06 开始,市场仓位被打开。
在最大的 depoPart_= 0.4 的情况下,我们可以获得约 22,800 美元的利润。不过,这里显示的回撤是整个运行过程中遇到的相对回撤。但是,23,000 的 10% 和 1000 的 10% 是完全不同的数值。因此,我们一定要看一次运行的结果:
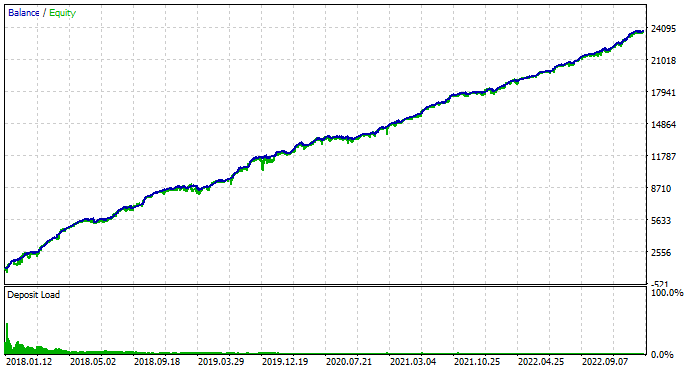
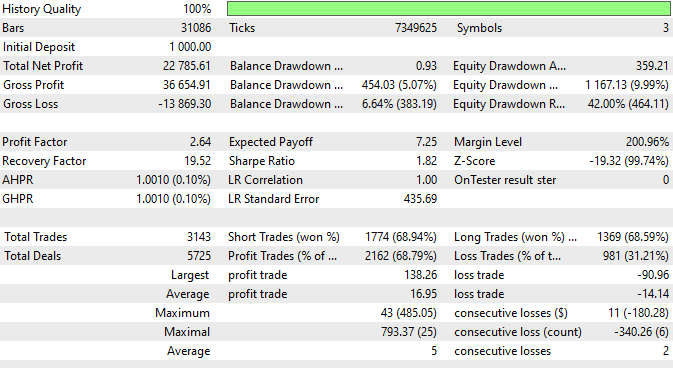
图 7.在最大depoPart_ = 0.4 条件下的测试结果
正如您所看到的,实际达到了 1167 美元的回撤,在达到缩水时仅为当前余额的 9.99%,但如果测试期的起始时间是在这一令人不快的时刻之前,那么我们就会损失全部存款。因此,我们不能使用这种仓位大小。
让我们看看 depoPart_= 0.2 时的结果
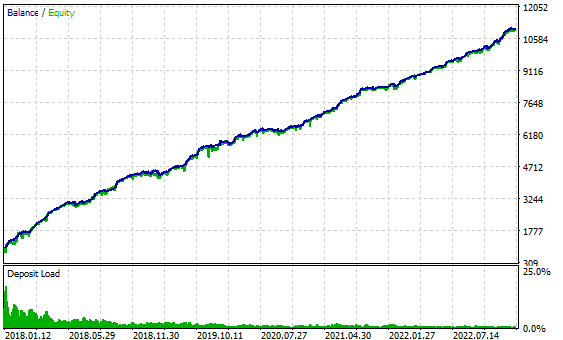
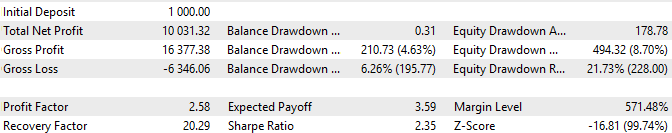
图 8.depoPart_= 0.2 时的测试结果
在这里,最大回撤额不超过 494 美元,约为初始存款 1000 美元的 50%。因此,有了这样的仓位大小,即使五年期间的期初选择得再差,也不会损失全部存款。
根据这一仓位大小,1 年(2022 年)的测试结果如下:
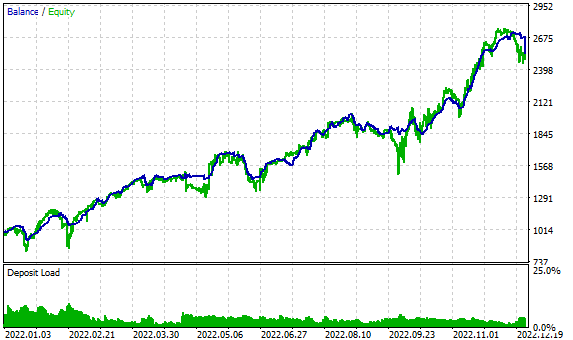
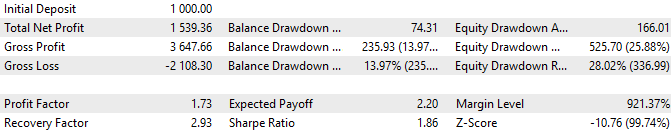
图 9.2022 年 depoPart_= 0.2 的测试结果
因此,在最大预期回撤约为 50%的情况下,我们看到每年的利润约为 150%。
这些结果看起来令人鼓舞,但其中也有缺陷。参数优化中未包括的 2023 年,其结果明显更差:
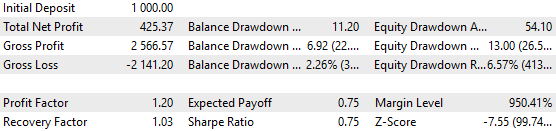
图 10.2023 年的测试结果,depoPart_ = 0.2
当然,我们在年底的测试结果中获得了 40% 的利润,但 12 个月中有 8 个月没有实现可持续增长。这个问题似乎是主要问题,本系列文章将专门探讨解决这个问题的不同方法。
结论
在本文中,我们通过简化和优化前一部分的代码,为进一步开发代码做好了准备。我们已经解决了之前发现的一些可能会限制我们利用各种交易策略的能力的缺陷。测试结果表明,新实现方案的效果并不比旧方案差。执行速度保持不变,但可能只有在策略实例数量成倍增加时才会出现增长。
为此,我们需要最终确定如何存储策略的输入参数,如何将这些参数组合成参数库,以及如何从优化单个策略实例后得到的参数中选出最佳组合。
我们将在下一篇文章中继续朝着选定的方向努力。
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自俄文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/14148
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 MQL5 简介(第 4 部分):掌握结构、类和时间函数
MQL5 简介(第 4 部分):掌握结构、类和时间函数
 数据科学和机器学习(第 18 部分):掌握市场复杂性博弈,截断型 SVD 对比 NMF
数据科学和机器学习(第 18 部分):掌握市场复杂性博弈,截断型 SVD 对比 NMF
 您应当知道的 MQL5 向导技术(第 10 部分):非常规 RBM
您应当知道的 MQL5 向导技术(第 10 部分):非常规 RBM
 种群优化算法:微人工免疫系统(Micro-AIS)
种群优化算法:微人工免疫系统(Micro-AIS)
最好添加一个开/关策略掩码,以考虑到体积计量器(虚拟体积的接收者)。
例如,您需要暂时关闭投资组合中的某些 TS:它将继续进行虚拟交易,但不会影响真实环境。同样,也可以反向打开。
要实现这一点并不难,但在不使用它的情况下,您需要为每个策略制定明确的开/关标准。这是一项比较复杂的任务,我还没有接触过,也许以后也不会接触。
而且,一定会有一个类似于这样的功能。
CAdvisor *m_advisors[]; // 虚拟投资组合阵列有自己的法师
目前还没有这方面的计划。合并到投资组合将在 CAdvisor 和 CStrategy 之间的中间层进行。目前已有一个解决方案草案,但在不断重构的过程中可能会发生很大变化。
交易量同步成功的标志可以帮您解决这个问题。
它似乎已经存在:
只有在每个符号成功打开所需的真实交易量时,才会重置该标志。
将一个完全不同的实体放入虚拟订单是一个值得商榷的解决方案。
我真的很想避免这种情况。我想尽一切办法让 CVirtualOrder 与这些实体无关。结果我更不喜欢了。所以现在就这样了。