
MQL5でONNXモデルをアンサンブルする方法の例
はじめに
安定した取引のためには、通常、取引される商品と取引戦略の両方を多様化することが推奨されます。同じことが機械学習モデルにも当てはまります。複雑なモデルを1つ作成するよりも、いくつかの単純なモデルを作成する方が簡単ですが、これらのモデルを1つのONNXモデルに組み立てるのは難しい場合があります。
ただし、1つのMQL5プログラムで複数の訓練済みONNXモデルを組み合わせることができます。この記事では、投票分類器と呼ばれるアンサンブルの1つを検討します。このようなアンサンブルを実装するのがいかに簡単かをお見せします。
プロジェクトのモデル
この例では、回帰価格予測モデルと分類価格変動予測モデルの2つの単純なモデルを使用します。モデル間の主な違いは、回帰が数量を予測するのに対し、分類はクラスを予測することです。
最初のモデルは回帰です。
このモデルは、2003年から2022年末までのEURUSD D1データを使用して訓練されています。訓練は、10個のOHLC価格のシリーズを使用して実行されます。モデルの訓練可能性を向上させるために、価格を正規化し、シリーズの平均価格をシリーズの標準偏差で割ります。したがって、シリーズを平均0とスプレッド1の特定の範囲に入れます。これにより、訓練中の収束が改善されます。
その結果、モデルは翌日の終値を予測します。
このモデルは非常に単純です。ここで提供されているのは、デモンストレーション目的のみです。
# Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. # https://www.mql5.com from datetime import datetime import MetaTrader5 as mt5 import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import pandas as pd import tf2onnx from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from tqdm import tqdm from sys import argv if not mt5.initialize(): print("initialize() failed, error code =",mt5.last_error()) quit() # we will save generated onnx-file near the our script data_path=argv[0] last_index=data_path.rfind("\\")+1 data_path=data_path[0:last_index] print("data path to save onnx model",data_path) # input parameters inp_model_name = "model.eurusd.D1.10.onnx" inp_history_size = 10 inp_start_date = datetime(2003, 1, 1, 0) inp_end_date = datetime(2023, 1, 1, 0) # get data from client terminal eurusd_rates = mt5.copy_rates_range("EURUSD", mt5.TIMEFRAME_D1, inp_start_date, inp_end_date) df = pd.DataFrame(eurusd_rates) # # collect dataset subroutine # def collect_dataset(df: pd.DataFrame, history_size: int): """ Collect dataset for the following regression problem: - input: history_size consecutive H1 bars; - output: close price for the next bar. :param df: D1 bars for a range of dates :param history_size: how many bars should be considered for making a prediction :return: features and labels """ n = len(df) xs = [] ys = [] for i in tqdm(range(n - history_size)): w = df.iloc[i: i + history_size + 1] x = w[['open', 'high', 'low', 'close']].iloc[:-1].values y = w.iloc[-1]['close'] xs.append(x) ys.append(y) X = np.array(xs) y = np.array(ys) return X, y ### # get prices X, y = collect_dataset(df, history_size=inp_history_size) # normalize prices m = X.mean(axis=1, keepdims=True) s = X.std(axis=1, keepdims=True) X_norm = (X - m) / s y_norm = (y - m[:, 0, 3]) / s[:, 0, 3] # split data to train and test sets X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_norm, y_norm, test_size=0.2, random_state=0) # define model model = tf.keras.Sequential([ tf.keras.layers.LSTM(64, input_shape=(inp_history_size, 4)), tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(), tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.1), tf.keras.layers.Dense(32, activation='relu'), tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(), tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.1), tf.keras.layers.Dense(32, activation='relu'), tf.keras.layers.Dense(1) ]) model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mse', metrics=['mae']) # model training for 50 epochs lr_reduction = tf.keras.callbacks.ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_loss', factor=0.1, patience=3, min_lr=0.000001) history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=50, verbose=2, validation_split=0.15, callbacks=[lr_reduction]) # model evaluation test_loss, test_mae = model.evaluate(X_test, y_test) print(f"test_loss={test_loss:.3f}") print(f"test_mae={test_mae:.3f}") # save model to onnx output_path = data_path+inp_model_name onnx_model = tf2onnx.convert.from_keras(model, output_path=output_path) print(f"saved model to {output_path}") # finish mt5.shutdown()回帰モデルが実行されると、結果の予測価格は価格が下がる、価格が変わらない、価格が上がるというクラスに変換されることが仮定されます。これは、投票分類器を編成するために必要です。
2番目のモデルは分類モデルです。
このモデルは、2010年から2022年末までのEURUSD D1で訓練されています。訓練は、63個の終値のシリーズを使用して実行されます。出力で、価格が下がる、価格が10ポイント以内にとどまる、価格が上がるの3つのクラスのいずれかを定義する必要があります。2010年以降のデータを使用してモデルを訓練する必要があったのは、2番目のクラスのためです。それ以前の2009年に、市場は4桁から5桁の精度に切り替わりました。したがって、古い1ポイントが新しい10ポイントになりました。
前のモデルと同様、価格は正規化されています。正規化も同じで、シリーズの平均価格からの偏差をシリーズの標準偏差で割ります。このモデルのアイデアは、「KerasでのMLPを使用した金融時系列予測」」(ロシア語)で説明されています。このモデルもデモンストレーションのみを目的として設計されています。
# Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. # https://www.mql5.com # # Classification model # 0,0,1 - predict price down # 0,1,0 - predict price same # 1,0,0 - predict price up # from datetime import datetime import MetaTrader5 as mt5 import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import pandas as pd import tf2onnx from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from tqdm import tqdm from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Activation,Dropout, BatchNormalization, LeakyReLU from keras.optimizers import SGD from keras import regularizers from sys import argv # initialize MetaTrader 5 client terminal if not mt5.initialize(): print("initialize() failed, error code =",mt5.last_error()) quit() # we will save the generated onnx-file near the our script data_path=argv[0] last_index=data_path.rfind("\\")+1 data_path=data_path[0:last_index] print("data path to save onnx model",data_path) # input parameters inp_model_name = "model.eurusd.D1.63.onnx" inp_history_size = 63 inp_start_date = datetime(2010, 1, 1, 0) inp_end_date = datetime(2023, 1, 1, 0) # get data from the client terminal eurusd_rates = mt5.copy_rates_range("EURUSD", mt5.TIMEFRAME_D1, inp_start_date, inp_end_date) df = pd.DataFrame(eurusd_rates) # # collect dataset subroutine # def collect_dataset(df: pd.DataFrame, history_size: int): """ Collect dataset for the following regression problem: - input: history_size consecutive H1 bars; - output: close price for the next bar. :param df: H1 bars for a range of dates :param history_size: how many bars should be considered for making a prediction :return: features and labels """ n = len(df) xs = [] ys = [] for i in tqdm(range(n - history_size)): w = df.iloc[i: i + history_size + 1] x = w[['close']].iloc[:-1].values delta = x[-1] - w.iloc[-1]['close'] if np.abs(delta)<=0.0001: y = 0, 1, 0 else: if delta<0: y = 1, 0, 0 else: y = 0, 0, 1 xs.append(x) ys.append(y) X = np.array(xs) Y = np.array(ys) return X, Y ### # get prices X, Y = collect_dataset(df, history_size=inp_history_size) # normalize prices m = X.mean(axis=1, keepdims=True) s = X.std(axis=1, keepdims=True) X_norm = (X - m) / s # split data to train and test sets X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X_norm, Y, test_size=0.1, random_state=0) # define model model = Sequential() model.add(Dense(64, input_dim=inp_history_size, activity_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.01))) model.add(BatchNormalization()) model.add(LeakyReLU()) model.add(Dropout(0.3)) model.add(Dense(16, activity_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.01))) model.add(BatchNormalization()) model.add(LeakyReLU()) model.add(Dense(3)) model.add(Activation('softmax')) opt = SGD(learning_rate=0.01, momentum=0.9) model.compile(optimizer=opt, loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) # model training for 300 epochs lr_reduction = tf.keras.callbacks.ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_loss', factor=0.9, patience=5, min_lr=0.00001) history = model.fit(X_train, Y_train, epochs=300, validation_data=(X_test, Y_test), shuffle = True, batch_size=128, verbose=2, callbacks=[lr_reduction]) # model evaluation test_loss, test_accuracy = model.evaluate(X_test, Y_test) print(f"test_loss={test_loss:.3f}") print(f"test_accuracy={test_accuracy:.3f}") # save model to onnx output_path = data_path+inp_model_name onnx_model = tf2onnx.convert.from_keras(model, output_path=output_path) print(f"saved model to {output_path}") # finish mt5.shutdown()モデルは2022年末までデータを使用して訓練されたため、ストラテジーテスターでの動作を実証する期間が残りました。
MQL5 EAにおけるONNXモデルのアンサンブル
以下は、モデルアンサンブルの可能性を示す簡単なEAです。MQL5でONNXモデルを使用する主な原則は、前の記事の第2部で説明されています。
前方宣言と定義
#include <Trade\Trade.mqh> input double InpLots = 1.0; // Lots amount to open position #resource "Python/model.eurusd.D1.10.onnx" as uchar ExtModel1[] #resource "Python/model.eurusd.D1.63.onnx" as uchar ExtModel2[] #define SAMPLE_SIZE1 10 #define SAMPLE_SIZE2 63 long ExtHandle1=INVALID_HANDLE; long ExtHandle2=INVALID_HANDLE; int ExtPredictedClass1=-1; int ExtPredictedClass2=-1; int ExtPredictedClass=-1; datetime ExtNextBar=0; CTrade ExtTrade; //--- price movement prediction #define PRICE_UP 0 #define PRICE_SAME 1 #define PRICE_DOWN 2
OnInit関数
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { if(_Symbol!="EURUSD" || _Period!=PERIOD_D1) { Print("model must work with EURUSD,D1"); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- create first model from static buffer ExtHandle1=OnnxCreateFromBuffer(ExtModel1,ONNX_DEFAULT); if(ExtHandle1==INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("First model OnnxCreateFromBuffer error ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- since not all sizes defined in the input tensor we must set them explicitly //--- first index - batch size, second index - series size, third index - number of series (OHLC) const long input_shape1[] = {1,SAMPLE_SIZE1,4}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(ExtHandle1,0,input_shape1)) { Print("First model OnnxSetInputShape error ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- since not all sizes defined in the output tensor we must set them explicitly //--- first index - batch size, must match the batch size of the input tensor //--- second index - number of predicted prices (we only predict Close) const long output_shape1[] = {1,1}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(ExtHandle1,0,output_shape1)) { Print("First model OnnxSetOutputShape error ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- create second model from static buffer ExtHandle2=OnnxCreateFromBuffer(ExtModel2,ONNX_DEFAULT); if(ExtHandle2==INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("Second model OnnxCreateFromBuffer error ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- since not all sizes defined in the input tensor we must set them explicitly //--- first index - batch size, second index - series size const long input_shape2[] = {1,SAMPLE_SIZE2}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(ExtHandle2,0,input_shape2)) { Print("Second model OnnxSetInputShape error ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- since not all sizes defined in the output tensor we must set them explicitly //--- first index - batch size, must match the batch size of the input tensor //--- second index - number of classes (up, same or down) const long output_shape2[] = {1,3}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(ExtHandle2,0,output_shape2)) { Print("Second model OnnxSetOutputShape error ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- ok return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
EURUSD、D1でのみ実行します。これは、モデルが毎日の価格を使用して訓練される一方で、現在の銘柄期間のデータを使用するためです。
モデルはEAにリソースとして含まれています。
入出力のデータ形状を明示的に定義することが重要です。
OnTick関数
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { //--- check new bar if(TimeCurrent()<ExtNextBar) return; //--- set next bar time ExtNextBar=TimeCurrent(); ExtNextBar-=ExtNextBar%PeriodSeconds(); ExtNextBar+=PeriodSeconds(); //--- predict price movement Predict(); //--- check trading according to prediction if(ExtPredictedClass>=0) if(PositionSelect(_Symbol)) CheckForClose(); else CheckForOpen(); }
すべての取引操作は、1日の初めにのみ実行されます。
予測機能
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Voting classification | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void Predict(void) { //--- evaluate first model ExtPredictedClass1=PredictPrice(ExtHandle1,SAMPLE_SIZE1); //--- evaluate second model ExtPredictedClass2=PredictPriceMovement(ExtHandle2,SAMPLE_SIZE2); //--- vote if(ExtPredictedClass1==ExtPredictedClass2) ExtPredictedClass=ExtPredictedClass1; else ExtPredictedClass=-1; }
両方のモデルが同じクラスを受け取った場合に、クラスが選択されたと見なされます。これは多数決です。アンサンブルにはモデルが2つしかないため、多数決による投票は「全会一致」を意味します。
過去10個のOHLC価格からの終値予測
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Predict next price (first model) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int PredictPrice(const long handle,const int sample_size) { static matrixf input_data(sample_size,4); // matrix for prepared input data static vectorf output_data(1); // vector to get result static matrix mm(sample_size,4); // matrix of horizontal vectors Mean static matrix ms(sample_size,4); // matrix of horizontal vectors Std static matrix x_norm(sample_size,4); // matrix for prices normalize //--- prepare input data matrix rates; //--- request last bars if(!rates.CopyRates(_Symbol,_Period,COPY_RATES_OHLC,1,sample_size)) return(-1); //--- get series Mean vector m=rates.Mean(1); //--- get series Std vector s=rates.Std(1); //--- prepare matrices for prices normalization for(int i=0; i<sample_size; i++) { mm.Row(m,i); ms.Row(s,i); } //--- the input of the model must be a set of vertical OHLC vectors x_norm=rates.Transpose(); //--- normalize prices x_norm-=mm; x_norm/=ms; //--- run the inference input_data.Assign(x_norm); if(!OnnxRun(handle,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,input_data,output_data)) return(-1); //--- denormalize the price from the output value double predicted=output_data[0]*s[3]+m[3]; //--- classify predicted price movement int predicted_class=-1; double delta=rates[3][sample_size-1]-predicted; if(fabs(delta)<=0.0001) predicted_class=PRICE_SAME; else { if(delta<0) predicted_class=PRICE_UP; else predicted_class=PRICE_DOWN; } return(predicted_class); }
入力データは、モデルを訓練するときと同じルールに従って準備します。モデルが実行された後、結果の値が価格に変換されます。クラスは、シリーズの最後の終値と結果の価格の差に基づいて計算されます。
63個の毎日の終値のシリーズに基づく価格変動予測:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Predict price movement (second model) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int PredictPriceMovement(const long handle,const int sample_size) { static vectorf input_data(sample_size); // vector for prepared input data static vectorf output_data(3); // vector to get result //--- request last bars if(!input_data.CopyRates(_Symbol,_Period,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,1,sample_size)) return(-1); //--- get series Mean float m=input_data.Mean(); //--- get series Std float s=input_data.Std(); //--- normalize prices input_data-=m; input_data/=s; //--- run the inference if(!OnnxRun(handle,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,input_data,output_data)) return(-1); //--- evaluate prediction return(int(output_data.ArgMax())); }
価格は、最初のモデルと同じルールを使用して正規化されます。ただし、今回は、入力が行列ではなくベクトルであるため、コードはよりコンパクトになります。クラスは3つの確率の最大値によって選択されます。
取引戦略は簡単です。取引操作は、毎日の初めに実行されます。予測が「価格が上がる」である場合は買って、「価格が下がる」なら売ります。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Check for open position conditions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CheckForOpen(void) { ENUM_ORDER_TYPE signal=WRONG_VALUE; //--- check signals if(ExtPredictedClass==PRICE_DOWN) signal=ORDER_TYPE_SELL; // sell condition else { if(ExtPredictedClass==PRICE_UP) signal=ORDER_TYPE_BUY; // buy condition } //--- open position if possible according to signal if(signal!=WRONG_VALUE && TerminalInfoInteger(TERMINAL_TRADE_ALLOWED)) ExtTrade.PositionOpen(_Symbol,signal,InpLots, SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol,signal==ORDER_TYPE_SELL ? SYMBOL_BID:SYMBOL_ASK), 0,0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Check for close position conditions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CheckForClose(void) { bool bsignal=false; //--- position already selected before long type=PositionGetInteger(POSITION_TYPE); //--- check signals if(type==POSITION_TYPE_BUY && ExtPredictedClass==PRICE_DOWN) bsignal=true; if(type==POSITION_TYPE_SELL && ExtPredictedClass==PRICE_UP) bsignal=true; //--- close position if possible if(bsignal && TerminalInfoInteger(TERMINAL_TRADE_ALLOWED)) { ExtTrade.PositionClose(_Symbol,3); //--- open opposite CheckForOpen(); } }
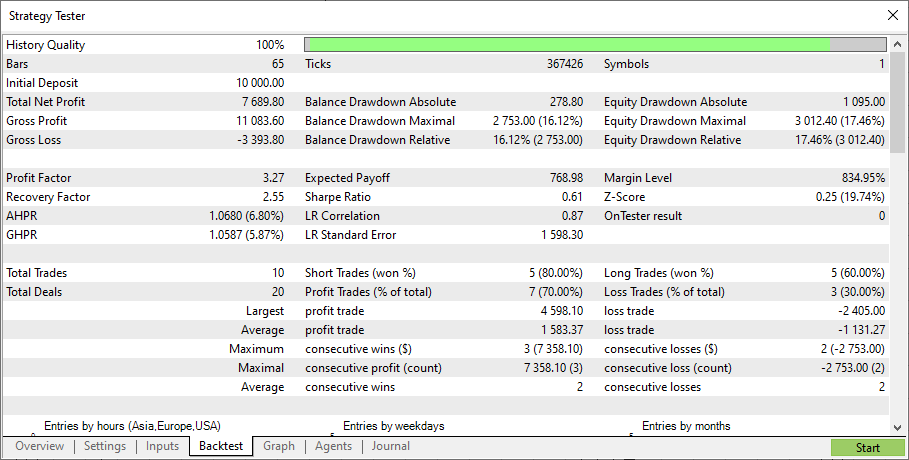
2023年の初めまで、データを使用してモデルを訓練しました。年初からテスト間隔を設定しましょう。
これは、年初からのデータに基づくテスト結果です。
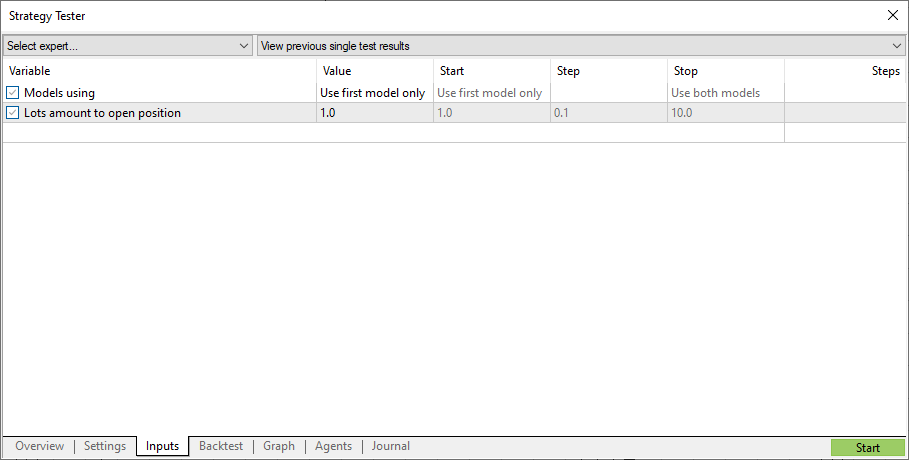
個々のモデルのテスト結果を知るのは面白いでしょう。
これを行うには、次のようにEAソースコードを変更します。
enum EnModels { USE_FIRST_MODEL, // Use first model only USE_SECOND_MODEL, // Use second model only USE_BOTH_MODELS // Use both models }; input EnModels InpModels = USE_BOTH_MODELS; // Models using input double InpLots = 1.0; // Lots amount to open position ... //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Voting classification | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void Predict(void) { //--- evaluate first model if(InpModels==USE_BOTH_MODELS || InpModels==USE_FIRST_MODEL) ExtPredictedClass1=PredictPrice(ExtHandle1,SAMPLE_SIZE1); //--- evaluate second model if(InpModels==USE_BOTH_MODELS || InpModels==USE_SECOND_MODEL) ExtPredictedClass2=PredictPriceMovement(ExtHandle2,SAMPLE_SIZE2); //--- check predictions switch(InpModels) { case USE_FIRST_MODEL : ExtPredictedClass=ExtPredictedClass1; break; case USE_SECOND_MODEL : ExtPredictedClass=ExtPredictedClass2; break; case USE_BOTH_MODELS : if(ExtPredictedClass1==ExtPredictedClass2) ExtPredictedClass=ExtPredictedClass1; else ExtPredictedClass=-1; } }
パラメータ「最初のモデルのみを使用」を有効にします。
最初のモデルのテスト結果
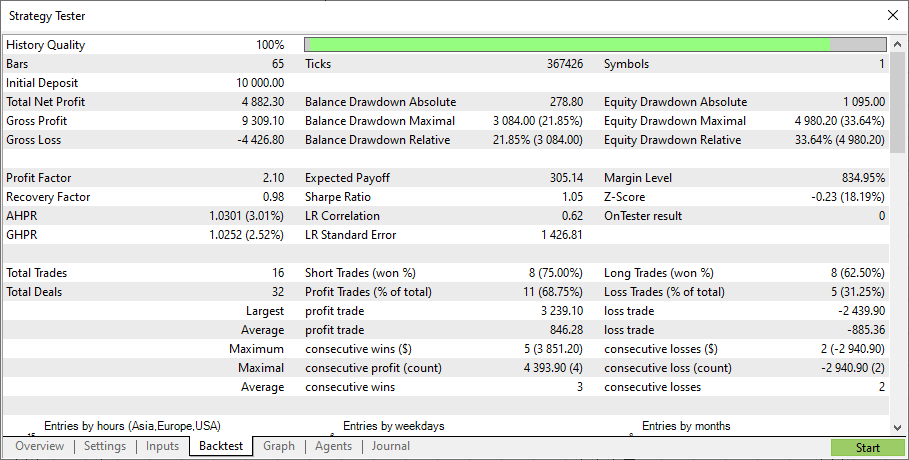
次に、2番目のモデルをテストします。2番目のモデルのテスト結果は次のとおりです。
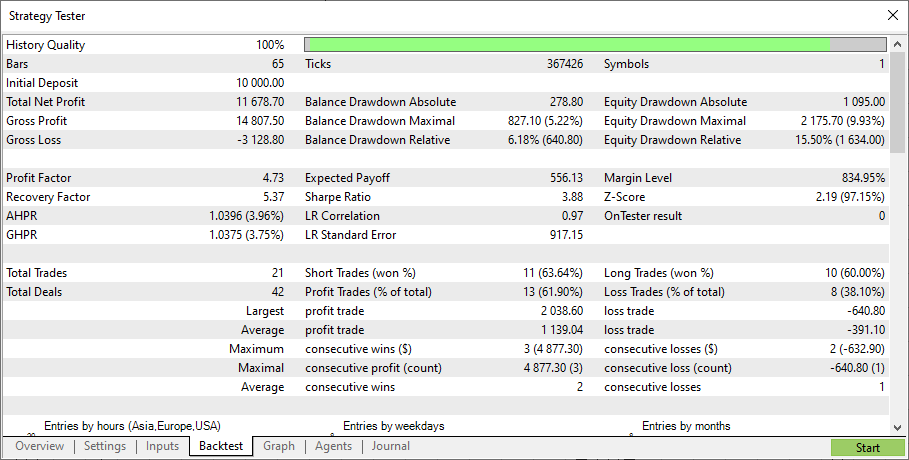
2番目のモデルは、最初のモデルよりもはるかに強力であることが判明しました。この結果は、弱いモデルはアンサンブルする必要があるという理論を裏付けています。ただし、この記事はアンサンブルの理論に関するものではなく、実際のアプリケーションに関するものでした。
重要な注意点:この記事で使用されているモデルは、MQL5言語を使用してONNXモデルを操作する方法を示すためにのみ提示されています。EAは、実際の口座での取引を意図したものではありません。
結論
2つのONNXモデルのアンサンブルの非常に単純でわかりやすい例を紹介しました。同時に使用できるモデルの数には制限があり、256モデルを超えることはできません。ただし、3つ以上のモデルを使用する場合でも、EAプログラミングに対して異なるアプローチが必要になります。つまり、オブジェクト指向プログラミングが必要になります。
これは別の記事のトピックになります。
MetaQuotes Ltdによってロシア語から翻訳されました。
元の記事: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/12433
警告: これらの資料についてのすべての権利はMetaQuotes Ltd.が保有しています。これらの資料の全部または一部の複製や再プリントは禁じられています。
- 無料取引アプリ
- 8千を超えるシグナルをコピー
- 金融ニュースで金融マーケットを探索
同じ日付、同じ設定にしたのですが、結果が違ってしまいました。どなたか理由をご存じですか?
第1モデルのテスト結果2回目のテスト結果
あなたの取引サーバーがMetaQuotes-Demoでないからかもしれません。
同じ日付、同じ設定にしたのですが、結果が違ってしまいました。どなたか理由をご存じですか?
最初のモデルのテスト結果2番目のモデルのテスト結果
まず、これをまとめてくれて本当にありがとう。フォローしやすく、よくまとまっています。
私の場合、デモ口座では同じような成功率で、取引回数も少し少ないのですが、メタトレーダーのデモ口座を使うと、同じような成功率で、取引回数も少し少なくなります。私の取引口座では一度しか取引しません。私のブローカーはオーストラリア(GMT+10) です。デモ口座からの最初の取引は; Core 1 2023.01.02 07:02:00 取引 #2 1.07016で1 EURUSDを売る 完了(注文#2に基づいて)
マイ・ブローカー・ オーストラリア (GMT+10)からの最初の 取引は ; Core 1 2023.01.03 00:00:00 failed market sell 1 EURUSD [Market closed]であり、これをどのように解決するか正確にはわからない。モデル全体がタイムゾーンに依存している可能性があります。もしそうであれば、時間は時間単位で表示されるはずですが、2023.01.02 07:02:00の 取引開始が、どのようにして 2023.01.03 00:00:00に なるのでしょうか。
この原因について何かご指摘があればお願いします。
トレードサーブ
こちらも同じで、MetaQuates-Demo口座のオリジナルのonnxファイルで 非常によく似た結果を再現することができました。
その後、PythonのMLスクリプトの再トレーニングを完了しました:
で終了:
次に、オリジナルの ONNX.Price.Prediction.2M.D1.mq5を 再コンパイルして、トレーニングした新しいMLを使用します。
同じMetaQuates-Demo口座を使ったバックテスト結果は、オリジナルとはかなり違っていました。
ありがとうございます。