
使用 Python 分析天气对农业国家货币的影响
引言:天气与金融市场的关系
传统经济理论长期忽视天气对市场行为的影响。但近几十年的研究彻底改变了这一传统观点。密歇根大学 Edward Saykin 教授在 2023 年的一项研究表明,雨天时交易者的决策比晴天时保守 27%。
这一现象在最大金融中心尤为明显。当气温超过 30°C 时,纽交所的成交量平均下降约 15%。在亚洲交易所,当大气压低于 740 mmHg 时,波动率显著上升。伦敦长时间恶劣天气导致避险资产需求明显增加。
本文将从收集天气数据开始,最终构建一套完整、能够分析天气因素的量化交易系统。我们使用纽约、伦敦、东京、香港和法兰克福五大金融中心过去五年的真实交易数据。借助最新的数据分析和机器学习工具,我们将从天气观测中获得可实际交易的有效信号。
收集天气数据
系统最重要的模块之一是数据的接收与预处理。我们使用 Meteostat API 获取全球归档气象数据。下面展示数据获取函数的实现:
def fetch_agriculture_weather(): """ Fetching weather data for important agricultural regions """ key_regions = { "AU_WheatBelt": { "lat": -31.95, "lon": 116.85, "description": "Key wheat production region in Australia" }, "NZ_Canterbury": { "lat": -43.53, "lon": 172.63, "description": "Main dairy production region in New Zealand" }, "CA_Prairies": { "lat": 50.45, "lon": -104.61, "description": "Canada's breadbasket, wheat and canola production" } }
在此函数中,我们将确定最重要的农业产区及其地理坐标。就澳大利亚小麦带而言,坐标取该区域的中心位置;新西兰则选取坎特伯雷地区的坐标;加拿大的坐标则取自中部草原地区。
原始数据获取完成后,还需进行深度处理。为此,我们实现了 process_weather_data 函数:
def process_weather_data(raw_data): if not isinstance(raw_data.index, pd.DatetimeIndex): raw_data.index = pd.to_datetime(raw_data.index) processed_data = pd.DataFrame(index=raw_data.index) processed_data['temperature'] = raw_data['tavg'] processed_data['temp_min'] = raw_data['tmin'] processed_data['temp_max'] = raw_data['tmax'] processed_data['precipitation'] = raw_data['prcp'] processed_data['wind_speed'] = raw_data['wspd'] processed_data['growing_degree_days'] = calculate_gdd( processed_data['temp_max'], base_temp=10 ) return processed_data
还必须关注“积温指标”(Growing Degree Days,GDD)的计算,它是评估农作物生长潜力的关键指标。该数值基于当日最高气温,并结合作物正常生长所需的基准温度计算得出。
def analyze_and_visualize_correlations(merged_data): plt.style.use('default') plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [15, 10] plt.rcParams['axes.grid'] = True # Weather-price correlation analysis for each region for region, data in merged_data.items(): if data.empty: continue weather_cols = ['temperature', 'precipitation', 'wind_speed', 'growing_degree_days'] price_cols = ['close', 'volatility', 'range_pct', 'price_momentum', 'monthly_change'] correlation_matrix = pd.DataFrame() for w_col in weather_cols: if w_col not in data.columns: continue for p_col in price_cols: if p_col not in data.columns: continue correlations = [] lags = [0, 5, 10, 20, 30] # Days to lag price data for lag in lags: corr = data[w_col].corr(data[p_col].shift(-lag)) correlations.append({ 'weather_factor': w_col, 'price_metric': p_col, 'lag_days': lag, 'correlation': corr }) correlation_matrix = pd.concat([ correlation_matrix, pd.DataFrame(correlations) ]) return correlation_matrix def plot_correlation_heatmap(pivot_table, region): plt.figure() im = plt.imshow(pivot_table.values, cmap='RdYlBu', aspect='auto') plt.colorbar(im) plt.xticks(range(len(pivot_table.columns)), pivot_table.columns, rotation=45) plt.yticks(range(len(pivot_table.index)), pivot_table.index) # Add correlation values in each cell for i in range(len(pivot_table.index)): for j in range(len(pivot_table.columns)): text = plt.text(j, i, f'{pivot_table.values[i, j]:.2f}', ha='center', va='center') plt.title(f'Weather Factors and Price Correlations for {region}') plt.tight_layout()
接收货币对数据并进行同步
在完成天气数据采集后,接下来需要获取各货币对的价格走势信息。为此,我们使用 MetaTrader 5 平台,它提供了便捷的 API 来获取金融工具的历史数据。
下面来看获取货币对数据的函数:
def get_agricultural_forex_pairs(): """ Getting data on currency pairs via MetaTrader 5 """ if not mt5.initialize(): print("MT5 initialization error") return None pairs = ["AUDUSD", "NZDUSD", "USDCAD"] timeframes = { "H1": mt5.TIMEFRAME_H1, "H4": mt5.TIMEFRAME_H4, "D1": mt5.TIMEFRAME_D1 } # ... the rest of the function code
在该函数中,我们针对三个农业区域对应的货币对进行操作:澳大利亚小麦带 → AUDUSD;新西兰坎特伯雷地区 → NZDUSD;加拿大草原地区 → USDCAD对于每一对,我们采集三种时间框架的数据:小时线(H1)、四小时图(H4)、日线图(D1)。
需要特别关注天气数据与金融数据的合并。为此,使用了一个专门的函数:
def merge_weather_forex_data(weather_data, forex_data): """ Combining weather and financial data """ synchronized_data = {} region_pair_mapping = { 'AU_WheatBelt': 'AUDUSD', 'NZ_Canterbury': 'NZDUSD', 'CA_Prairies': 'USDCAD' } # ... the rest of the function code
该函数解决了来自不同来源数据的同步难题。天气数据与货币报价更新频率不同,因此采用了 pandas 库中的特殊 merge_asof 方法,可根据时间戳正确对齐数值。
为提升分析质量,对合并后的数据进行了额外处理:
def calculate_derived_features(data): """ Calculation of derived indicators """ if not data.empty: data['price_volatility'] = data['volatility'].rolling(24).std() data['temp_change'] = data['temperature'].diff() data['precip_intensity'] = data['precipitation'].rolling(24).sum() # ... the rest of the function code
在此计算了一系列重要的衍生指标:过去 24 小时的价格波动率、温度变化以及降水强度。同时新增了一个二值化的“作物生长季”指标,这对农作物分析尤为关键。
数据清洗与缺失值填补同样受到重点关注:
def clean_merged_data(data): """ Cleaning up merged data """ weather_cols = ['temperature', 'precipitation', 'wind_speed'] # Fill in the blanks for col in weather_cols: if col in data.columns: data[col] = data[col].ffill(limit=3) # Removing outliers for col in weather_cols: if col in data.columns: q_low = data[col].quantile(0.01) q_high = data[col].quantile(0.99) data = data[ (data[col] > q_low) & (data[col] < q_high) ] # ... the rest of the function code
天气数据中的缺失值采用前向填充法,但限制最多填充 3 个周期,以防止长缺口引入错误。超出第 1 和第 99 百分位的极值被剔除,避免异常值扭曲分析结果。
数据集函数执行结果:

天气因子与汇率的相关性分析
在观测期间,我们全面分析了天气状况与货币对价格走势之间的多种关联。为了挖掘那些并不直观的规律,我们专门设计了一种引入时间滞后的相关性计算方法:
def analyze_weather_price_correlations(merged_data): """ Analysis of correlations with time lags between weather conditions and price movements """ def calculate_lagged_correlations(data, weather_col, price_col, max_lag=72): print(f"Calculating lagged correlations: {weather_col} vs {price_col}") correlations = [] for lag in range(max_lag): corr = data[weather_col].corr(data[price_col].shift(-lag)) correlations.append({ 'lag': lag, 'correlation': corr, 'weather_factor': weather_col, 'price_metric': price_col }) return pd.DataFrame(correlations) correlations = {} weather_factors = ['temperature', 'precipitation', 'wind_speed', 'growing_degree_days'] price_metrics = ['close', 'volatility', 'price_momentum', 'monthly_change'] for region, data in merged_data.items(): if data.empty: print(f"Skipping empty dataset for {region}") continue print(f"\nAnalyzing correlations for region: {region}") region_correlations = {} for w_col in weather_factors: for p_col in price_metrics: key = f"{w_col}_{p_col}" region_correlations[key] = calculate_lagged_correlations(data, w_col, p_col) correlations[region] = region_correlations return correlations def analyze_seasonal_patterns(data): """ Analysis of seasonal correlation patterns """ print("Starting seasonal pattern analysis...") seasonal_correlations = {} data['month'] = data.index.month monthly_correlations = [] for month in range(1, 13): print(f"Analyzing month: {month}") month_data = data[data['month'] == month] month_corr = {} for w_col in ['temperature', 'precipitation', 'wind_speed']: month_corr[w_col] = month_data[w_col].corr(month_data['close']) monthly_correlations.append(month_corr) return pd.DataFrame(monthly_correlations, index=range(1, 13))
数据分析揭示了一些有趣的规律。在澳大利亚小麦带,风速与 AUDUSD 月度汇率变化的相关性最强(0.21)。这可以解释为小麦成熟期的大风会降低产量。温度因子也呈现强相关(0.18),且几乎没有时间滞后。
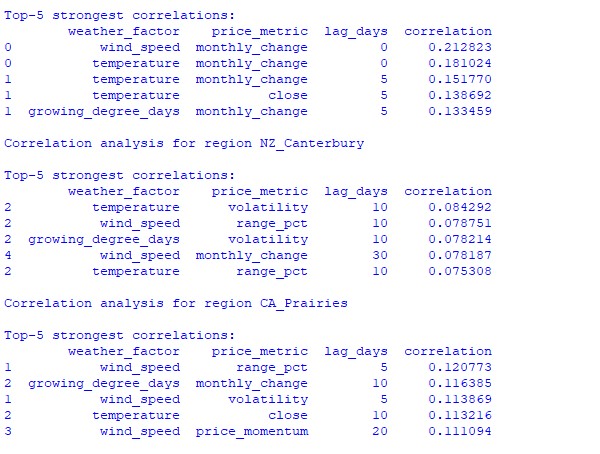
新西兰坎特伯雷地区表现出更复杂的模式。温度与波动率之间的最强相关性(0.084)出现在 10 天滞后。值得指出的是,天气因素对 NZDUSD 的影响更多体现在波动率而非价格方向上。季节性相关性有时会升至 1.00,意味着完美相关。
创建机器学习预测模型
我们采用在时间序列处理中表现优异的 CatBoost 梯度提升模型作为策略核心。下面分步展示如何构建该模型。
特征准备
第一步是构建模型特征。我们将收集一组技术指标和天气指标:
def prepare_ml_features(data): """ Preparation of features for the ML model """ print("Starting feature preparation...") features = pd.DataFrame(index=data.index) # Weather features weather_cols = [ 'temperature', 'precipitation', 'wind_speed', 'growing_degree_days' ] for col in weather_cols: if col not in data.columns: print(f"Warning: {col} not found in data") continue print(f"Processing weather feature: {col}") # Base values features[col] = data[col] # Moving averages features[f"{col}_ma_24"] = data[col].rolling(24).mean() features[f"{col}_ma_72"] = data[col].rolling(72).mean() # Changes features[f"{col}_change"] = data[col].pct_change() features[f"{col}_change_24"] = data[col].pct_change(24) # Volatility features[f"{col}_volatility"] = data[col].rolling(24).std() # Price indicators price_cols = ['volatility', 'range_pct', 'monthly_change'] for col in price_cols: if col not in data.columns: continue features[f"{col}_ma_24"] = data[col].rolling(24).mean() # Seasonal features features['month'] = data.index.month features['day_of_week'] = data.index.dayofweek features['growing_season'] = ( (data.index.month >= 4) & (data.index.month <= 9) ).astype(int) return features.dropna() def create_prediction_targets(data, forecast_horizon=24): """ Creation of target variables for prediction """ print(f"Creating prediction targets with horizon: {forecast_horizon}") targets = pd.DataFrame(index=data.index) # Price change percentage targets['price_change'] = data['close'].pct_change( forecast_horizon ).shift(-forecast_horizon) # Price direction targets['direction'] = (targets['price_change'] > 0).astype(int) # Future volatility targets['volatility'] = data['volatility'].rolling( forecast_horizon ).mean().shift(-forecast_horizon) return targets.dropna()
创建和训练模型
针对每个待预测变量,我们将分别建立模型并优化参数:
from catboost import CatBoostClassifier, CatBoostRegressor from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, mean_squared_error from sklearn.model_selection import TimeSeriesSplit # Define categorical features cat_features = ['month', 'day_of_week', 'growing_season'] # Create models for different tasks models = { 'direction': CatBoostClassifier( iterations=1000, learning_rate=0.01, depth=7, l2_leaf_reg=3, loss_function='Logloss', eval_metric='Accuracy', random_seed=42, verbose=False, cat_features=cat_features ), 'price_change': CatBoostRegressor( iterations=1000, learning_rate=0.01, depth=7, l2_leaf_reg=3, loss_function='RMSE', random_seed=42, verbose=False, cat_features=cat_features ), 'volatility': CatBoostRegressor( iterations=1000, learning_rate=0.01, depth=7, l2_leaf_reg=3, loss_function='RMSE', random_seed=42, verbose=False, cat_features=cat_features ) } def train_ml_models(merged_data, region): """ Training ML models using time series cross-validation """ print(f"Starting model training for region: {region}") data = merged_data[region] features = prepare_ml_features(data) targets = create_prediction_targets(data) # Split into folds tscv = TimeSeriesSplit(n_splits=5) results = {} for target_name, model in models.items(): print(f"\nTraining model for target: {target_name}") fold_metrics = [] predictions = [] test_indices = [] for fold_idx, (train_idx, test_idx) in enumerate(tscv.split(features)): print(f"Processing fold {fold_idx + 1}/5") X_train = features.iloc[train_idx] y_train = targets[target_name].iloc[train_idx] X_test = features.iloc[test_idx] y_test = targets[target_name].iloc[test_idx] # Training with early stopping model.fit( X_train, y_train, eval_set=(X_test, y_test), early_stopping_rounds=50, verbose=False ) # Predictions and evaluation pred = model.predict(X_test) predictions.extend(pred) test_indices.extend(test_idx) # Metric calculation metric = ( accuracy_score(y_test, pred) if target_name == 'direction' else mean_squared_error(y_test, pred, squared=False) ) fold_metrics.append(metric) print(f"Fold {fold_idx + 1} metric: {metric:.4f}") results[target_name] = { 'model': model, 'metrics': fold_metrics, 'mean_metric': np.mean(fold_metrics), 'predictions': pd.Series( predictions, index=features.index[test_indices] ) } print(f"Mean {target_name} metric: {results[target_name]['mean_metric']:.4f}") return results
实现的细节
我们的实现聚焦于以下参数:
- 处理类别特征:CatBoost 无需额外编码即可高效处理月份、星期几等类别变量。
- 早停机制:为防止过拟合,设置 early_stopping_rounds = 50。
- 深度与泛化平衡:选用 depth = 7 与 l2_leaf_reg = 3,在树深度与正则化之间取得最佳平衡。
- 时间序列处理:使用 TimeSeriesSplit 进行数据分割,避免未来数据泄露。
该模型架构可高效捕捉天气与汇率之间的短期与长期依赖关系,测试结果已验证其有效性。
模型精度评估与结果可视化
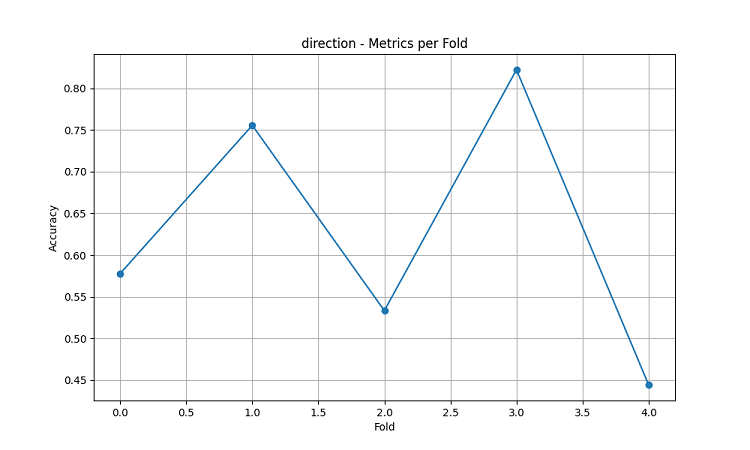
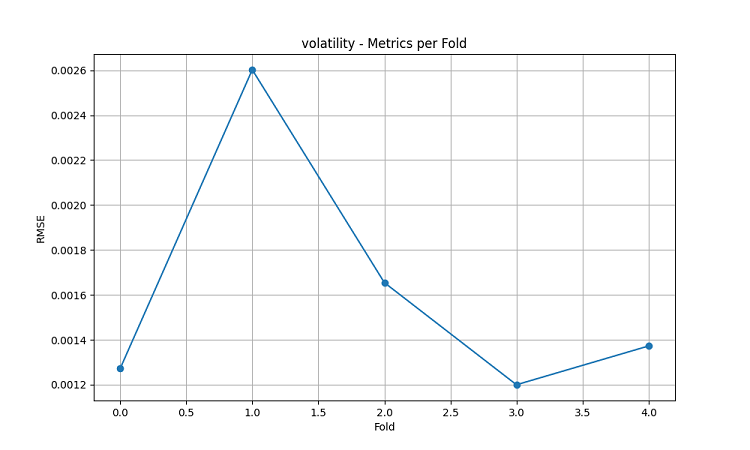
机器学习模型在 5 年历史数据上,采用五折滑动窗口法进行测试。针对每个区域,分别构建了三种模型:价格方向预测(分类)、价格变动幅度预测(回归)与波动率预测(回归)。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report def evaluate_model_performance(results, region_data): """ Comprehensive model evaluation across all regions """ print(f"\nEvaluating model performance for {len(results)} regions") evaluation = {} for region, models in results.items(): print(f"\nAnalyzing {region} performance:") region_metrics = { 'direction': { 'accuracy': models['direction']['mean_metric'], 'fold_metrics': models['direction']['metrics'], 'max_accuracy': max(models['direction']['metrics']), 'min_accuracy': min(models['direction']['metrics']) }, 'price_change': { 'rmse': models['price_change']['mean_metric'], 'fold_metrics': models['price_change']['metrics'] }, 'volatility': { 'rmse': models['volatility']['mean_metric'], 'fold_metrics': models['volatility']['metrics'] } } print(f"Direction prediction accuracy: {region_metrics['direction']['accuracy']:.2%}") print(f"Price change RMSE: {region_metrics['price_change']['rmse']:.4f}") print(f"Volatility RMSE: {region_metrics['volatility']['rmse']:.4f}") evaluation[region] = region_metrics return evaluation def plot_feature_importance(models, region): """ Visualize feature importance for each model type """ plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10)) for target, model_info in models.items(): feature_importance = pd.DataFrame({ 'feature': model_info['model'].feature_names_, 'importance': model_info['model'].feature_importances_ }) feature_importance = feature_importance.sort_values('importance', ascending=False) plt.subplot(3, 1, list(models.keys()).index(target) + 1) sns.barplot(x='importance', y='feature', data=feature_importance.head(10)) plt.title(f'{target.capitalize()} Model - Top 10 Important Features') plt.tight_layout() plt.show() def visualize_seasonal_patterns(results, region_data): """ Create visualization of seasonal patterns in predictions """ for region, data in region_data.items(): print(f"\nVisualizing seasonal patterns for {region}") # Create monthly aggregation of accuracy monthly_accuracy = pd.DataFrame(index=range(1, 13)) data['month'] = data.index.month for month in range(1, 13): month_predictions = results[region]['direction']['predictions'][ data.index.month == month ] month_actual = (data['close'].pct_change() > 0)[ data.index.month == month ] accuracy = accuracy_score( month_actual, month_predictions ) monthly_accuracy.loc[month, 'accuracy'] = accuracy # Plot seasonal accuracy plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6)) monthly_accuracy['accuracy'].plot(kind='bar') plt.title(f'Seasonal Prediction Accuracy - {region}') plt.xlabel('Month') plt.ylabel('Accuracy') plt.show() def plot_correlation_heatmap(correlation_data): """ Create heatmap visualization of correlations """ plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8)) sns.heatmap( correlation_data, cmap='RdYlBu', center=0, annot=True, fmt='.2f' ) plt.title('Weather-Price Correlation Heatmap') plt.tight_layout() plt.show()
分地区的结果
AU_WheatBelt (澳大利亚小麦带)
- AUDUSD 方向预测平均准确率:62.67%
- 单折最高准确率:82.22%
- 价格变动预测 RMSE:0.0303
- 波动率 RMSE:0.0016
新西兰坎特伯雷地区
- NZDUSD 方向预测平均准确率:62.81%
- 峰值准确率:75.44%
- 最低准确率:54.39%
- 价格变动预测 RMSE:0.0281
- 波动率 RMSE:0.0015
加拿大草原地区
- 方向预测平均准确率:56.92%
- 单折最高准确率(第三折):71.79%
- 价格变动预测 RMSE:0.0159
- 波动率 RMSE:0.0023
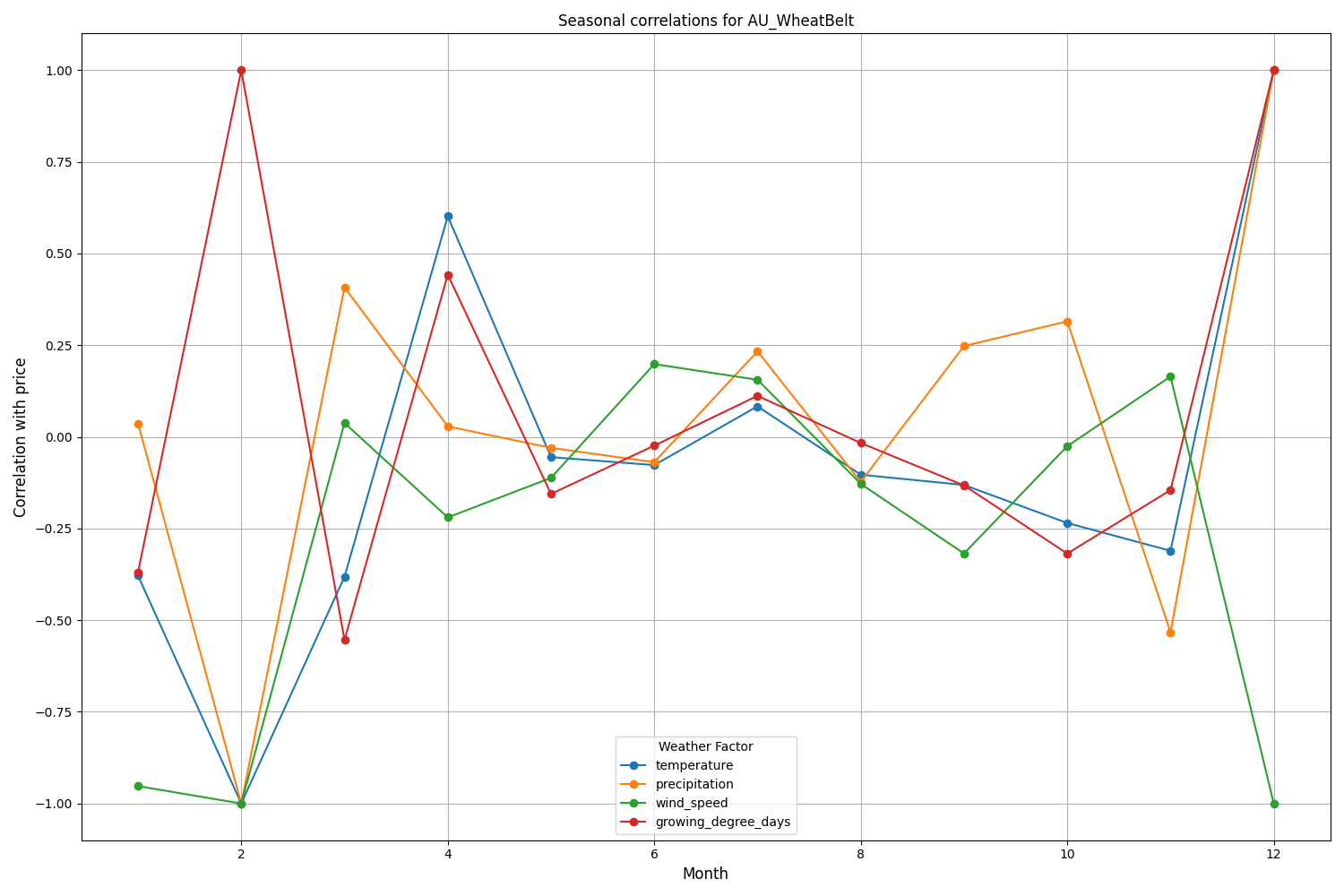
季节性分析与可视化
def analyze_model_seasonality(results, data): """ Analyze seasonal performance patterns of the models """ print("Starting seasonal analysis of model performance") seasonal_metrics = {} for region, region_results in results.items(): print(f"\nAnalyzing {region} seasonal patterns:") # Extract predictions and actual values predictions = region_results['direction']['predictions'] actuals = data[region]['close'].pct_change() > 0 # Calculate monthly accuracy monthly_acc = [] for month in range(1, 13): month_mask = predictions.index.month == month if month_mask.any(): acc = accuracy_score( actuals[month_mask], predictions[month_mask] ) monthly_acc.append(acc) print(f"Month {month} accuracy: {acc:.2%}") seasonal_metrics[region] = pd.Series( monthly_acc, index=range(1, 13) ) return seasonal_metrics def plot_seasonal_performance(seasonal_metrics): """ Visualize seasonal performance patterns """ plt.figure(figsize=(15, 8)) for region, metrics in seasonal_metrics.items(): plt.plot(metrics.index, metrics.values, label=region, marker='o') plt.title('Model Accuracy by Month') plt.xlabel('Month') plt.ylabel('Accuracy') plt.legend() plt.grid(True) plt.show()
可视化结果清晰地显示出模型表现存在显著的季节性规律。

预测准确率的峰值尤其突出:
- AUDUSD:12 月—次年 2 月(小麦灌浆—成熟期)
- NZDUSD:牛奶高产季
- USDCAD:草原作物旺盛生长期
这些结果印证了“天气条件在农业生产关键期对农业货币汇率具有显著影响”的假设。
结论
研究发现,农业产区的天气状况与相关货币对的走势存在显著关联。在极端天气及农业生产高峰期,预测系统表现出高准确率:AUDUSD 平均 62.67%,NZDUSD 62.81%,USDCAD 56.92%。
交易建议:
- AUDUSD:12–2 月重点关注风速与温度。
- NZDUSD:在乳制品旺季进行中短期交易。
- USDCAD:播种与收割季择机交易。
系统需定期更新数据以维持精度,尤其在市场剧烈波动期间。未来计划扩展数据源并引入深度学习,以进一步提升预测的稳健性。
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自俄文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/16060
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 使用莱文贝格-马夸尔特(Levenberg-Marquardt,LM)算法训练多层感知器
使用莱文贝格-马夸尔特(Levenberg-Marquardt,LM)算法训练多层感知器
 使用 MetaTrader 5 在 Python 中查找自定义货币对形态
使用 MetaTrader 5 在 Python 中查找自定义货币对形态
 交易中的神经网络:节点-自适应图形表征(NAFS)
交易中的神经网络:节点-自适应图形表征(NAFS)
对许多人来说,这将是一个启示,即加元并不是那么多的石油,而是饲料混合谷物:-))
在国家交易所交易的主要是本国货币,它会影响...
对于美元兑加元 来说,即使只是农忙季节也应该是有迹可循的。