
Trabajamos con modelos ONNX en formato float16 y float8
Contenido
- 1. Nuevos tipos de datos para trabajar con modelos ONNX
- 1.1. Formato FP16
- 1.1.1. Pruebas de ejecución del operador ONNX Cast para FLOAT16
- 1.1.2. Pruebas de ejecución del operador ONNX Cast para BFLOAT16
- 1.2. Formato FP8
- 1.2.1. Formatos fp8_e5m2 y fp8_e4m3
- 1.2.2. Pruebas de ejecución del operador ONNX Cast para FLOAT8
- 2. Ejemplo de uso de ONNX para aumentar la resolución de las imágenes
- 2.1. Ejemplo de ejecución del modelo ONNX con float32
- 2.2. Ejemplo de ejecución del modelo ONNX con float16
- Conclusiones
Con el desarrollo de las tecnologías de aprendizaje automático e inteligencia artificial, resulta necesario optimizar los procesos de trabajo con modelos. El rendimiento de los modelos está directamente relacionado con los formatos de datos usados para representarlos. En los últimos años, han surgido varios tipos de datos nuevos diseñados específicamente para trabajar con modelos de aprendizaje profundo.
En este artículo, nos centraremos en dos de estos nuevos formatos de datos, float16 y float8, que están empezando a utilizarse activamente en los modelos ONNX modernos. Estos formatos suponen una alternativa a los formatos de datos con coma flotante, más precisos pero que consumen más recursos. Ofrecen una combinación óptima de rendimiento y precisión, lo cual los hace especialmente atractivos para diversas tareas de aprendizaje automático. Hoy estudiaremos las principales características y ventajas de los formatos float16 y float8, y presentaremos funciones para convertirlos en float y double estándar.
Esto ayudará a los desarrolladores e investigadores a comprender mejor cómo utilizar estos formatos de forma eficaz en sus proyectos y modelos. Como ejemplo, analizaremos el rendimiento del modelo ESRGAN de ONNX, que se utiliza para la mejora de imágenes.
1. Nuevos tipos de datos para trabajar con modelos ONNX
Para acelerar los cálculos, algunos modelos usan tipos de datos con menor precisión, como Float16 e incluso Float8.
Para trabajar con modelos ONNX, en el lenguaje MQL5 se ha añadido soporte para nuevos tipos de datos que permiten trabajar con representaciones de 8 y 16 bits de números con coma flotante.
El script genera la lista completa de elementos de la enumeración ENUM_ONNX_DATA_TYPE.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ONNX_Data_Types.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- for(int i=0; i<21; i++) PrintFormat("%2d %s",i,EnumToString(ENUM_ONNX_DATA_TYPE(i))); }
Resultado:
0: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_UNDEFINED 1: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT 2: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_UINT8 3: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_INT8 4: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_UINT16 5: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_INT16 6: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_INT32 7: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_INT64 8: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_STRING 9: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_BOOL 10: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT16 11: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_DOUBLE 12: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_UINT32 13: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_UINT64 14: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_COMPLEX64 15: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_COMPLEX128 16: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_BFLOAT16 17: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT8E4M3FN 18: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT8E4M3FNUZ 19: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT8E5M2 20: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT8E5M2FNUZ
Así pues, ahora podremos ejecutar modelos ONNX que trabajen con dichos datos.
Además, en MQL5 han aparecido funciones adicionales para la conversión de datos:
bool ArrayToFP16(ushort &dst_array[],const float &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT16_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayToFP16(ushort &dst_array[],const double &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT16_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayToFP8(uchar &dst_array[],const float &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayToFP8(uchar &dst_array[],const double &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayFromFP16(float &dst_array[],const ushort &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT16_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayFromFP16(double &dst_array[],const ushort &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT16_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayFromFP8(float &dst_array[],const uchar &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayFromFP8(double &dst_array[],const uchar &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT fmt);
Como los formatos de los números reales para 16 y 8 bits pueden diferir, el parámetro fmt de las funciones de conversión deberá especificar qué formato de número debe procesarse.
Para las versiones de 16 bits, se usará una nueva enumeración ENUM_FLOAT16_FORMAT, que actualmente tiene los siguientes valores:
- FLOAT_FP16 es un formato estándar de 16 bits, también conocido como half.
- FLOAT_BFP16 es un formato especial brain float point
- FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FN es un número con coma flotante de 8 bits, 4 bits de orden y 3 bits de mantisa. Suelen usarse como coeficientes.
- FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FNUZ es un número con coma flotante de 8 bits, 4 bits de orden y 3 bits de mantisa. Admite NaN; cero negativo e Inf no están soportados. Suelen usarse como coeficientes.
- FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FN es un número con coma flotante de 8 bits, 5 bits de orden y 2 bits de mantisa. Admite NaN e Inf. Se usa normalmente para gradientes.
- FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FNUZ es un número con coma flotante de 8 bits, 5 bits de orden y 2 bits de mantisa. Admite NaN e Inf; no soporta cero negativo. También se utiliza para gradientes.
1.1. Formato FP16
Los formatos FLOAT16 y BFLOAT16 son tipos de datos usados para representar números de coma flotante.
FLOAT16, también conocido como formato "half-precision float" o media precisión utiliza 16 bits para representar un número con coma flotante. Este formato logra un equilibrio entre precisión y eficacia de cálculo. FLOAT16 se usa ampliamente en el aprendizaje profundo y las redes neuronales, donde se requiere un alto rendimiento para procesar grandes cantidades de datos. Este formato permite un cálculo más rápido al reducir el tamaño de los números, lo cual resulta especialmente importante cuando se entrenan redes neuronales profundas en unidades de procesamiento gráfico (GPU).
BFLOAT16 (o Brain Floating Point 16) también utiliza 16 bits, pero difiere de FLOAT16 en la forma de representar los números. En este formato, se asignan 8 bits para representar el exponente, mientras que los 7 bits restantes se utilizan para representar la mantisa. Este formato se desarrolló para su uso en aprendizaje profundo e inteligencia artificial, especialmente en los procesadores Tensor Processing Unit (TPU) de Google. BFLOAT16 muestra un buen rendimiento en el entrenamiento de redes neuronales y puede utilizarse eficazmente para acelerar el cálculo.
Ambos formatos tienen sus ventajas y desventajas. FLOAT16 ofrece una mayor precisión, pero requiere más recursos de almacenamiento y cálculo. BFLOAT16, por su parte, ofrece un mayor rendimiento y eficacia en el procesamiento de datos, pero puede resultar menos preciso.
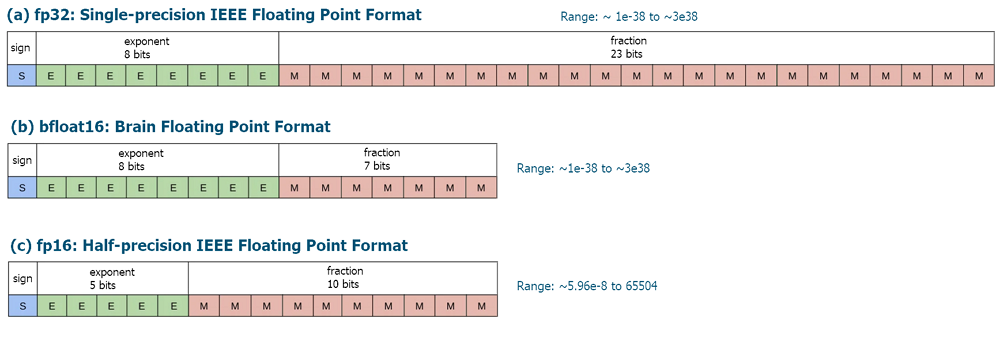
Figura 1. Formatos de bits con coma flotante FLOAT16 y BFLOAT16
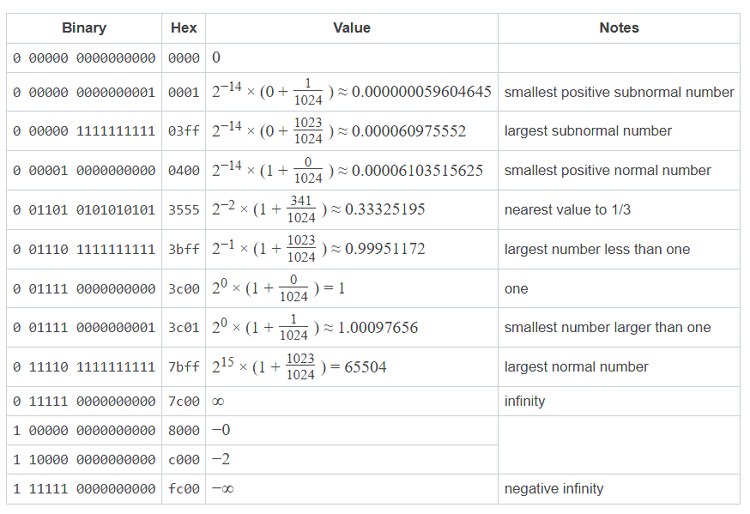
Tabla 1. Números con coma flotante en formato FLOAT16
1.1.1. Pruebas de ejecución del operador ONNX Cast para FLOAT16
A modo de ilustración, analizaremos la tarea de convertir datos de tipo FLOAT16 en tipos float y double.
Modelos ONNX con operación Cast:
- https://github.com/onnx/onnx/tree/main/onnx/backend/test/data/node/test_cast_FLOAT16_to_FLOAT
- https://github.com/onnx/onnx/tree/main/onnx/backend/test/data/node/test_cast_FLOAT16_to_DOUBLE
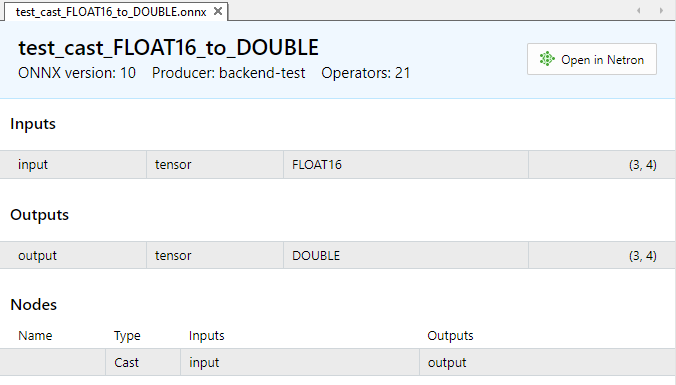
Figura 2. Parámetros de entrada y salida del modelo test_cast_FLOAT16_to_DOUBLE.onnx
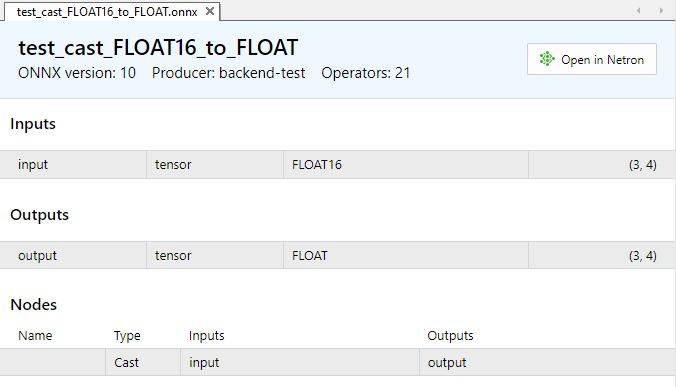
Figura 3. Parámetros de entrada y salida del modelo test_cast_FLOAT16_to_FLOAT.onnx
Como podemos ver en la descripción de las propiedades de los modelos ONNX, la entrada requiere datos de tipo ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT16, el modelo retornará los datos de salida en formato ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT.
Para convertir los valores, usaremos las funciones ArrayToFP16() y ArrayFromFP16() con el parámetro FLOAT_FP16.
Ejemplo:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TestCastFloat16.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #resource "models\\test_cast_FLOAT16_to_DOUBLE.onnx" as const uchar ExtModel1[]; #resource "models\\test_cast_FLOAT16_to_FLOAT.onnx" as const uchar ExtModel2[]; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| union for data conversion | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> union U { uchar uc[sizeof(T)]; T value; }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ArrayToString | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> string ArrayToString(const T &data[],uint length=16) { string res; for(uint n=0; n<MathMin(length,data.Size()); n++) res+="," + StringFormat("%.2x",data[n]); StringSetCharacter(res,0,'['); return res+"]"; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PatchONNXModel | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void PatchONNXModel(const uchar &original_model[],uchar &patched_model[]) { ArrayCopy(patched_model,original_model,0,0,WHOLE_ARRAY); //--- special ONNX model patch(IR=9,Opset=20) patched_model[1]=0x09; patched_model[ArraySize(patched_model)-1]=0x14; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| CreateModel | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CreateModel(long &model_handle,const uchar &model[]) { model_handle=INVALID_HANDLE; ulong flags=ONNX_DEFAULT; //ulong flags=ONNX_DEBUG_LOGS; //--- model_handle=OnnxCreateFromBuffer(model,flags); if(model_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) return(false); //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PrepareShapes | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool PrepareShapes(long model_handle) { ulong input_shape1[]= {3,4}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(model_handle,0,input_shape1)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetInputShape for input1. error code=%d",GetLastError()); //-- OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } //--- ulong output_shape[]= {3,4}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(model_handle,0,output_shape)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetOutputShape for output. error code=%d",GetLastError()); //-- OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| RunCastFloat16ToDouble | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool RunCastFloat16ToDouble(long model_handle) { PrintFormat("test=%s",__FUNCTION__); double test_data[12]= {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12}; ushort data_uint16[12]; if(!ArrayToFP16(data_uint16,test_data,FLOAT_FP16)) { Print("error in ArrayToFP16. error code=",GetLastError()); return(false); } Print("test array:"); ArrayPrint(test_data); Print("ArrayToFP16:"); ArrayPrint(data_uint16); U<ushort> input_float16_values[3*4]; U<double> output_double_values[3*4]; float test_data_float[]; if(!ArrayFromFP16(test_data_float,data_uint16,FLOAT_FP16)) { Print("error in ArrayFromFP16. error code=",GetLastError()); return(false); } for(int i=0; i<12; i++) { input_float16_values[i].value=data_uint16[i]; PrintFormat("%d input value =%f Hex float16 = %s ushort value=%d",i,test_data_float[i],ArrayToString(input_float16_values[i].uc),input_float16_values[i].value); } Print("ONNX input array:"); ArrayPrint(input_float16_values); bool res=OnnxRun(model_handle,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,input_float16_values,output_double_values); if(!res) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxRun. error code=%d",GetLastError()); return(false); } Print("ONNX output array:"); ArrayPrint(output_double_values); //--- double sum_error=0.0; for(int i=0; i<12; i++) { double delta=test_data[i]-output_double_values[i].value; sum_error+=MathAbs(delta); PrintFormat("%d output double %f = %s difference=%f",i,output_double_values[i].value,ArrayToString(output_double_values[i].uc),delta); } //--- PrintFormat("test=%s sum_error=%f",__FUNCTION__,sum_error); //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| RunCastFloat16ToFloat | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool RunCastFloat16ToFloat(long model_handle) { PrintFormat("test=%s",__FUNCTION__); double test_data[12]= {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12}; ushort data_uint16[12]; if(!ArrayToFP16(data_uint16,test_data,FLOAT_FP16)) { Print("error in ArrayToFP16. error code=",GetLastError()); return(false); } Print("test array:"); ArrayPrint(test_data); Print("ArrayToFP16:"); ArrayPrint(data_uint16); U<ushort> input_float16_values[3*4]; U<float> output_float_values[3*4]; float test_data_float[]; if(!ArrayFromFP16(test_data_float,data_uint16,FLOAT_FP16)) { Print("error in ArrayFromFP16. error code=",GetLastError()); return(false); } for(int i=0; i<12; i++) { input_float16_values[i].value=data_uint16[i]; PrintFormat("%d input value =%f Hex float16 = %s ushort value=%d",i,test_data_float[i],ArrayToString(input_float16_values[i].uc),input_float16_values[i].value); } Print("ONNX input array:"); ArrayPrint(input_float16_values); bool res=OnnxRun(model_handle,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,input_float16_values,output_float_values); if(!res) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxRun. error code=%d",GetLastError()); return(false); } Print("ONNX output array:"); ArrayPrint(output_float_values); //--- double sum_error=0.0; for(int i=0; i<12; i++) { double delta=test_data[i]-(double)output_float_values[i].value; sum_error+=MathAbs(delta); PrintFormat("%d output float %f = %s difference=%f",i,output_float_values[i].value,ArrayToString(output_float_values[i].uc),delta); } //--- PrintFormat("test=%s sum_error=%f",__FUNCTION__,sum_error); //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TestCastFloat16ToFloat | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool TestCastFloat16ToFloat(const uchar &res_model[]) { uchar model[]; PatchONNXModel(res_model,model); //--- get model handle long model_handle=INVALID_HANDLE; //--- get model handle if(!CreateModel(model_handle,model)) return(false); //--- prepare input and output shapes if(!PrepareShapes(model_handle)) return(false); //--- run ONNX model if(!RunCastFloat16ToFloat(model_handle)) return(false); //--- release model handle OnnxRelease(model_handle); //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TestCastFloat16ToDouble | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool TestCastFloat16ToDouble(const uchar &res_model[]) { uchar model[]; PatchONNXModel(res_model,model); //--- long model_handle=INVALID_HANDLE; //--- get model handle if(!CreateModel(model_handle,model)) return(false); //--- prepare input and output shapes if(!PrepareShapes(model_handle)) return(false); //--- run ONNX model if(!RunCastFloat16ToDouble(model_handle)) return(false); //--- release model handle OnnxRelease(model_handle); //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnStart(void) { if(!TestCastFloat16ToDouble(ExtModel1)) return 1; if(!TestCastFloat16ToFloat(ExtModel2)) return 1; //--- return 0; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Resultado:
TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test=RunCastFloat16ToDouble TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test array: TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1.00000 2.00000 3.00000 4.00000 5.00000 6.00000 7.00000 8.00000 9.00000 10.00000 11.00000 12.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ArrayToFP16: TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 15360 16384 16896 17408 17664 17920 18176 18432 18560 18688 18816 18944 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 0 input value =1.000000 Hex float16 = [00,3c] ushort value=15360 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1 input value =2.000000 Hex float16 = [00,40] ushort value=16384 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 2 input value =3.000000 Hex float16 = [00,42] ushort value=16896 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 3 input value =4.000000 Hex float16 = [00,44] ushort value=17408 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 4 input value =5.000000 Hex float16 = [00,45] ushort value=17664 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 5 input value =6.000000 Hex float16 = [00,46] ushort value=17920 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 6 input value =7.000000 Hex float16 = [00,47] ushort value=18176 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 7 input value =8.000000 Hex float16 = [00,48] ushort value=18432 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 8 input value =9.000000 Hex float16 = [80,48] ushort value=18560 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 9 input value =10.000000 Hex float16 = [00,49] ushort value=18688 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 10 input value =11.000000 Hex float16 = [80,49] ushort value=18816 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 11 input value =12.000000 Hex float16 = [00,4a] ushort value=18944 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX input array: TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [uc] [value] TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 0] ... 15360 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 1] ... 16384 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 2] ... 16896 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 3] ... 17408 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 4] ... 17664 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 5] ... 17920 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 6] ... 18176 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 7] ... 18432 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 8] ... 18560 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 9] ... 18688 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [10] ... 18816 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [11] ... 18944 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX output array: TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [uc] [value] TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 0] ... 1.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 1] ... 2.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 2] ... 3.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 3] ... 4.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 4] ... 5.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 5] ... 6.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 6] ... 7.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 7] ... 8.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 8] ... 9.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 9] ... 10.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [10] ... 11.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [11] ... 12.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 0 output double 1.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,f0,3f] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1 output double 2.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,00,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 2 output double 3.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,08,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 3 output double 4.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,10,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 4 output double 5.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,14,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 5 output double 6.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,18,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 6 output double 7.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,1c,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 7 output double 8.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,20,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 8 output double 9.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,22,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 9 output double 10.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,24,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 10 output double 11.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,26,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 11 output double 12.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,28,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test=RunCastFloat16ToDouble sum_error=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test=RunCastFloat16ToFloat TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test array: TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1.00000 2.00000 3.00000 4.00000 5.00000 6.00000 7.00000 8.00000 9.00000 10.00000 11.00000 12.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ArrayToFP16: TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 15360 16384 16896 17408 17664 17920 18176 18432 18560 18688 18816 18944 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 0 input value =1.000000 Hex float16 = [00,3c] ushort value=15360 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1 input value =2.000000 Hex float16 = [00,40] ushort value=16384 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 2 input value =3.000000 Hex float16 = [00,42] ushort value=16896 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 3 input value =4.000000 Hex float16 = [00,44] ushort value=17408 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 4 input value =5.000000 Hex float16 = [00,45] ushort value=17664 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 5 input value =6.000000 Hex float16 = [00,46] ushort value=17920 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 6 input value =7.000000 Hex float16 = [00,47] ushort value=18176 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 7 input value =8.000000 Hex float16 = [00,48] ushort value=18432 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 8 input value =9.000000 Hex float16 = [80,48] ushort value=18560 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 9 input value =10.000000 Hex float16 = [00,49] ushort value=18688 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 10 input value =11.000000 Hex float16 = [80,49] ushort value=18816 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 11 input value =12.000000 Hex float16 = [00,4a] ushort value=18944 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX input array: TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [uc] [value] TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 0] ... 15360 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 1] ... 16384 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 2] ... 16896 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 3] ... 17408 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 4] ... 17664 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 5] ... 17920 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 6] ... 18176 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 7] ... 18432 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 8] ... 18560 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 9] ... 18688 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [10] ... 18816 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [11] ... 18944 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX output array: TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [uc] [value] TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 0] ... 1.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 1] ... 2.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 2] ... 3.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 3] ... 4.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 4] ... 5.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 5] ... 6.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 6] ... 7.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 7] ... 8.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 8] ... 9.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 9] ... 10.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [10] ... 11.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [11] ... 12.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 0 output float 1.000000 = [00,00,80,3f] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1 output float 2.000000 = [00,00,00,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 2 output float 3.000000 = [00,00,40,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 3 output float 4.000000 = [00,00,80,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 4 output float 5.000000 = [00,00,a0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 5 output float 6.000000 = [00,00,c0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 6 output float 7.000000 = [00,00,e0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 7 output float 8.000000 = [00,00,00,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 8 output float 9.000000 = [00,00,10,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 9 output float 10.000000 = [00,00,20,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 10 output float 11.000000 = [00,00,30,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 11 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test=RunCastFloat16ToFloat sum_error=0.000000
1.1.2. Pruebas de ejecución del operador ONNX Cast para BFLOAT16
Este ejemplo analiza la conversión del tipo BFLOAT16 a float.
Modelo ONNX con la operación Cast:
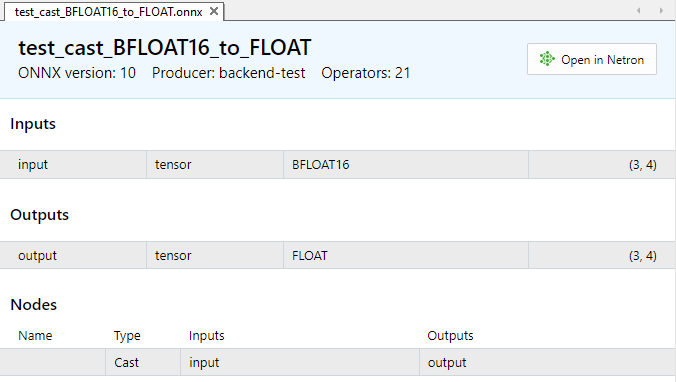
Fig.4. Parámetros de entrada y salida del modelo test_cast_BFLOAT16_to_FLOAT.onnx
La entrada requiere datos de tipo ONNX_DATA_TYPE_BFLOAT16, el modelo retornará datos de salida en formato ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT.
Para convertir los valores usaremos las funciones ArrayToFP16() y ArrayFromFP16() con el parámetro BFLOAT_FP16.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TestCastBFloat16.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #resource "models\\test_cast_BFLOAT16_to_FLOAT.onnx" as const uchar ExtModel1[]; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| union for data conversion | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> union U { uchar uc[sizeof(T)]; T value; }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ArrayToString | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> string ArrayToString(const T &data[],uint length=16) { string res; for(uint n=0; n<MathMin(length,data.Size()); n++) res+="," + StringFormat("%.2x",data[n]); StringSetCharacter(res,0,'['); return res+"]"; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PatchONNXModel | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void PatchONNXModel(const uchar &original_model[],uchar &patched_model[]) { ArrayCopy(patched_model,original_model,0,0,WHOLE_ARRAY); //--- special ONNX model patch(IR=9,Opset=20) patched_model[1]=0x09; patched_model[ArraySize(patched_model)-1]=0x14; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| CreateModel | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CreateModel(long &model_handle,const uchar &model[]) { model_handle=INVALID_HANDLE; ulong flags=ONNX_DEFAULT; //ulong flags=ONNX_DEBUG_LOGS; //--- model_handle=OnnxCreateFromBuffer(model,flags); if(model_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) return(false); //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PrepareShapes | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool PrepareShapes(long model_handle) { ulong input_shape1[]= {3,4}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(model_handle,0,input_shape1)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetInputShape for input1. error code=%d",GetLastError()); //-- OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } //--- ulong output_shape[]= {3,4}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(model_handle,0,output_shape)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetOutputShape for output. error code=%d",GetLastError()); //-- OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| RunCastBFloat16ToFloat | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool RunCastBFloat16ToFloat(long model_handle) { PrintFormat("test=%s",__FUNCTION__); double test_data[12]= {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12}; ushort data_uint16[12]; if(!ArrayToFP16(data_uint16,test_data,FLOAT_BFP16)) { Print("error in ArrayToFP16. error code=",GetLastError()); return(false); } Print("test array:"); ArrayPrint(test_data); Print("ArrayToFP16:"); ArrayPrint(data_uint16); U<ushort> input_float16_values[3*4]; U<float> output_float_values[3*4]; float test_data_float[]; if(!ArrayFromFP16(test_data_float,data_uint16,FLOAT_BFP16)) { Print("error in ArrayFromFP16. error code=",GetLastError()); return(false); } for(int i=0; i<12; i++) { input_float16_values[i].value=data_uint16[i]; PrintFormat("%d input value =%f Hex float16 = %s ushort value=%d",i,test_data_float[i],ArrayToString(input_float16_values[i].uc),input_float16_values[i].value); } Print("ONNX input array:"); ArrayPrint(input_float16_values); bool res=OnnxRun(model_handle,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,input_float16_values,output_float_values); if(!res) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxRun. error code=%d",GetLastError()); return(false); } Print("ONNX output array:"); ArrayPrint(output_float_values); //--- double sum_error=0.0; for(int i=0; i<12; i++) { double delta=test_data[i]-(double)output_float_values[i].value; sum_error+=MathAbs(delta); PrintFormat("%d output float %f = %s difference=%f",i,output_float_values[i].value,ArrayToString(output_float_values[i].uc),delta); } //--- PrintFormat("test=%s sum_error=%f",__FUNCTION__,sum_error); //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnStart(void) { uchar model[]; PatchONNXModel(ExtModel1,model); //--- get model handle long model_handle=INVALID_HANDLE; //--- get model handle if(!CreateModel(model_handle,model)) return 1; //--- prepare input and output shapes if(!PrepareShapes(model_handle)) return 1; //--- run ONNX model if(!RunCastBFloat16ToFloat(model_handle)) return 1; //--- release model handle OnnxRelease(model_handle); //--- return 0; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+Resultado:
TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test=RunCastBFloat16ToFloat TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test array: TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1.00000 2.00000 3.00000 4.00000 5.00000 6.00000 7.00000 8.00000 9.00000 10.00000 11.00000 12.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ArrayToFP16: TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 16256 16384 16448 16512 16544 16576 16608 16640 16656 16672 16688 16704 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 0 input value =1.000000 Hex float16 = [80,3f] ushort value=16256 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1 input value =2.000000 Hex float16 = [00,40] ushort value=16384 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 2 input value =3.000000 Hex float16 = [40,40] ushort value=16448 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 3 input value =4.000000 Hex float16 = [80,40] ushort value=16512 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 4 input value =5.000000 Hex float16 = [a0,40] ushort value=16544 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 5 input value =6.000000 Hex float16 = [c0,40] ushort value=16576 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 6 input value =7.000000 Hex float16 = [e0,40] ushort value=16608 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 7 input value =8.000000 Hex float16 = [00,41] ushort value=16640 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 8 input value =9.000000 Hex float16 = [10,41] ushort value=16656 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 9 input value =10.000000 Hex float16 = [20,41] ushort value=16672 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 10 input value =11.000000 Hex float16 = [30,41] ushort value=16688 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 11 input value =12.000000 Hex float16 = [40,41] ushort value=16704 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX input array: TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [uc] [value] TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 0] ... 16256 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 1] ... 16384 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 2] ... 16448 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 3] ... 16512 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 4] ... 16544 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 5] ... 16576 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 6] ... 16608 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 7] ... 16640 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 8] ... 16656 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 9] ... 16672 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [10] ... 16688 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [11] ... 16704 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX output array: TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [uc] [value] TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 0] ... 1.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 1] ... 2.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 2] ... 3.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 3] ... 4.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 4] ... 5.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 5] ... 6.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 6] ... 7.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 7] ... 8.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 8] ... 9.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 9] ... 10.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [10] ... 11.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [11] ... 12.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 0 output float 1.000000 = [00,00,80,3f] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1 output float 2.000000 = [00,00,00,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 2 output float 3.000000 = [00,00,40,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 3 output float 4.000000 = [00,00,80,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 4 output float 5.000000 = [00,00,a0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 5 output float 6.000000 = [00,00,c0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 6 output float 7.000000 = [00,00,e0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 7 output float 8.000000 = [00,00,00,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 8 output float 9.000000 = [00,00,10,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 9 output float 10.000000 = [00,00,20,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 10 output float 11.000000 = [00,00,30,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 11 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test=RunCastBFloat16ToFloat sum_error=0.000000
1.2. Formato FP8
Los modelos lingüísticos modernos pueden contener miles de millones de parámetros. El entrenamiento de modelos con números FP16 ya ha demostrado su eficacia. El paso de la coma flotante de 16 bits a FP8 reduce a la mitad los requisitos de memoria, mientras que acelera el entrenamiento y la ejecución de los modelos.
El formato FP8 (coma flotante de 8 bits) es uno de los tipos de datos usados para representar números con coma flotante. En FP8, cada número se representa mediante 8 bits de datos, que suelen dividirse en tres componentes: signo, exponente y mantisa. Este formato ofrece un compromiso entre precisión y eficiencia de almacenamiento de datos, lo cual lo hace atractivo para su uso en aplicaciones en las que sea necesario conservar memoria y recursos computacionales.
Una de las principales ventajas del 8PM es su eficacia a la hora de procesar grandes volúmenes de datos. Con su representación compacta de los números, FP8 puede reducir los requisitos de memoria y acelerar los cálculos. Esto resulta especialmente importante en las aplicaciones de aprendizaje automático e inteligencia artificial, donde el procesamiento de grandes conjuntos de datos es algo habitual.
Además, el FP8 puede ser útil para implementar operaciones de bajo nivel, como cálculos aritméticos y procesamiento de señales. Su formato compacto lo hace adecuado para su uso en sistemas incorporados y aplicaciones con recursos limitados. No obstante, debemos señalar que el FP8 tiene ciertas limitaciones debido a su escasa precisión. En algunas aplicaciones en las que se requiere computación de alta precisión, como la computación científica o el análisis financiero, el uso del 8PM puede no resultar suficiente.
1.2.1. Formatos fp8_e5m2 y fp8_e4m3
En 2022 se publicaron dos artículos que introducían los números con coma flotante almacenados en un byte, frente a los números float32 almacenados en 4 bytes.
En el artículo FP8 Formats for Deep Learning (2022) de NVIDIA, Intel y ARM se introducen dos tipos, siguiendo las especificaciones IEEE. El primer tipo es E4M3, 1 bit para el signo, 4 bits para el exponente y 3 bits para la mantisa. El segundo tipo es E5M2, 1 bit para el signo, 5 bits para el exponente y 2 para la mantisa. El primer tipo suele utilizarse para pesos, el segundo para gradientes.
El segundo artículo "8-bit Numerical Formats For Deep Neural Networks" presenta tipos similares. La norma IEEE asigna el mismo valor a +0 (o entero 0) y -0 (o entero 128). El artículo propone asignar diferentes valores flotantes a estos dos números. Además, también se investigan diferentes separaciones entre exponente y mantisa y se demuestra que E4M3 y E5M2 son las mejores.
Como resultado, se han introducido 4 nuevos tipos en ONNX (desde la versión 1.15.0):
- E4M3FN: 1 bit para el signo, 4 bits para el exponente, 3 bits para la mantisa, solo valores NaN y ningún valor infinito (FN),
- E4M3FNUZ: 1 bit para el signo, 4 bits para el exponente, 3 bits para la mantisa, solo valores NaN y ningún valor infinito (FN), ningún cero negativo (UZ)
- E5M2: 1 bit para el signo, 5 bits para el exponente, 2 bits para la mantisa,
- E5M2FNUZ: 1 bit para el signo, 5 bits para el exponente, 2 bits para la mantisa, solo valores NaN y ningún valor infinito (FN), ningún cero negativo (UZ)
La implementación suele depender del hardware. NVIDIA, Intel y Arm implementan E4M3FN, mientras que E5M2 se implementa en las GPU modernas. GraphCore hace lo mismo solo con E4M3FNUZ y E5M2FNUZ.
Vamos a resumir la información básica sobre el tipo FP8 según el artículo NVIDIA Hopper: H100 and FP8 Support.
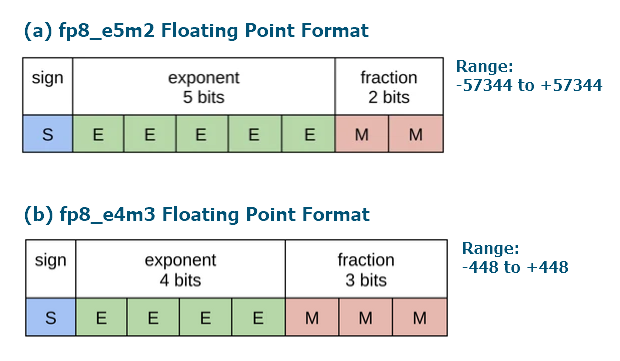
Fig.5. Formato de la representación en bits de los números con coma flotante FP8_E4M3
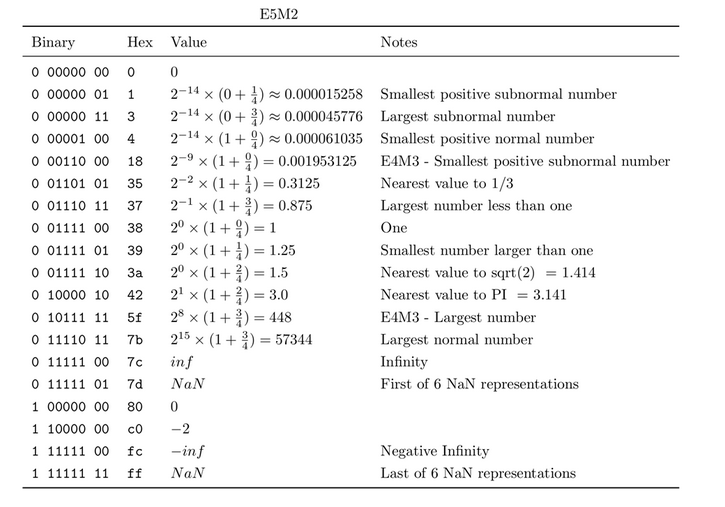
Tabla 3. Números con coma flotante en formato E5M2
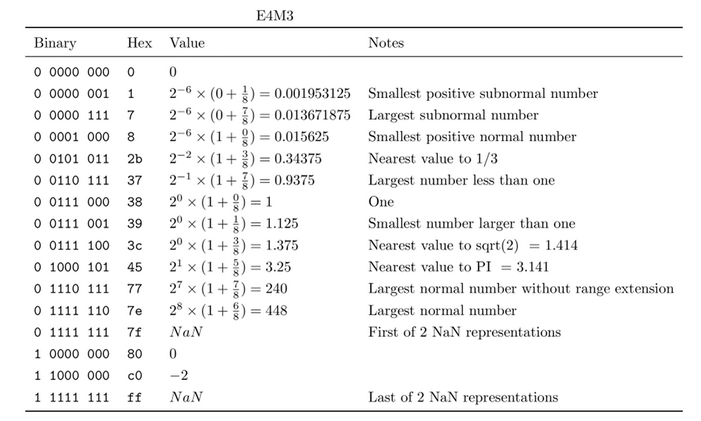
Tabla 4. Números con coma flotante en formato E4M3
La comparación de los rangos de números positivos de FP8_E4M3 y FP8_E5M2 se muestra en la figura
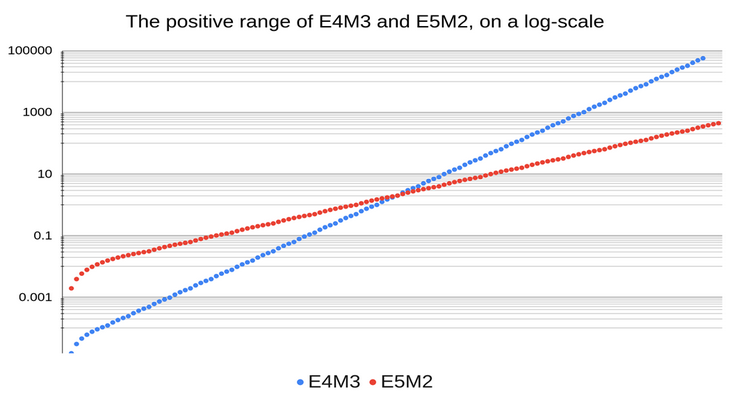
Fig.6. Comparación de los rangos de valores positivos de números FP8 (fuente)
La comparación de la precisión de las operaciones aritméticas (Add, Mul, Div) para números en formatos FP8_E5M2 y FP8_E4M3 se muestra en la siguiente figura:
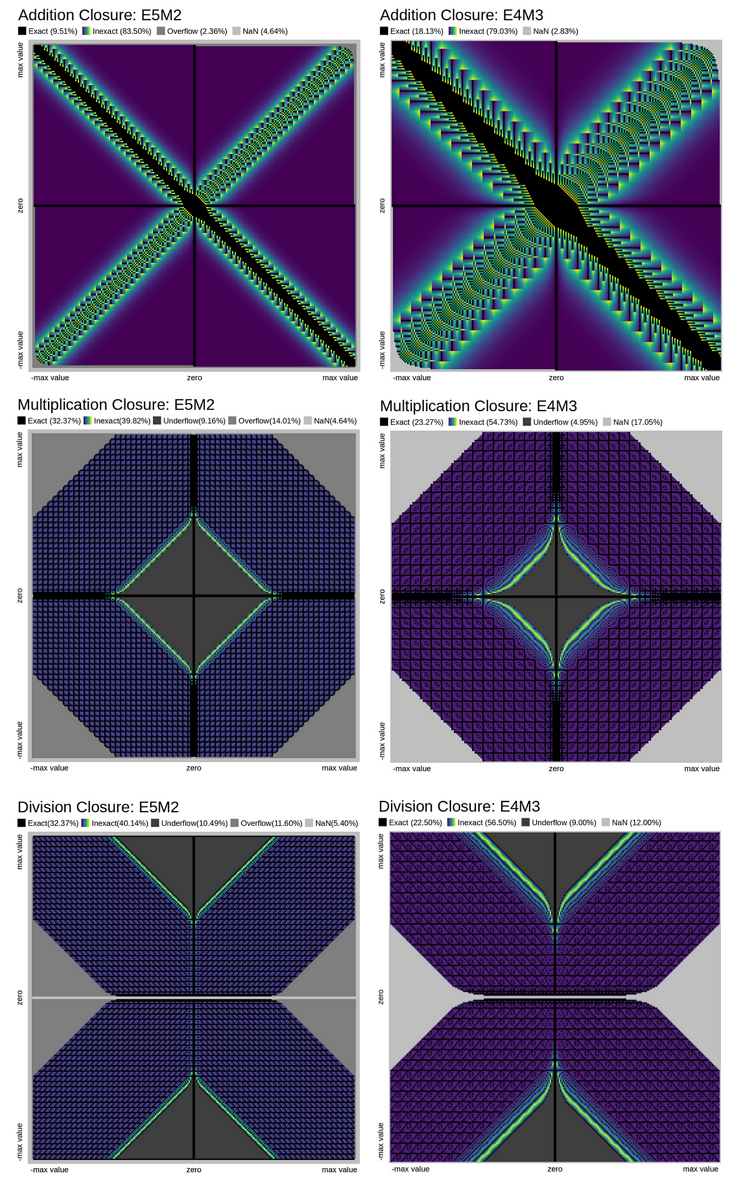
Fig.7. Comparación de la precisión de las operaciones aritméticas con números en formato float8_e5m2 y float8_e4m3 (fuente)
Uso recomendado de números en formato FP8:
- E4M3 para tensores de escala y activación;
- E5M2 para los tensores de gradiente.
1.2.2. Pruebas de ejecución del operador ONNX Cast para FLOAT8
Este ejemplo muestra la conversión de varios tipos FLOAT8 a float.
Modelos ONNX con operación Cast:
- https://github.com/onnx/onnx/tree/main/onnx/backend/test/data/node/test_cast_FLOAT8E4M3FN_to_FLOAT.onnx
- hgithub.com/onnx/onnx/tree/main/onnx/backend/test/data/node/test_cast_FLOAT8E4M3FNUZ_to_FLOAT.onnxhttps://github.com/onnx/onnx/tree/main/onnx/backend/test/data/node/test_cast_FLOAT8E4M3FNUZ_to_FLOAT.onnx
- https://github.com/onnx/onnx/tree/main/onnx/backend/test/data/node/test_cast_FLOAT8E5M2_to_FLOAT.onnx
- https://github.com/onnx/onnx/tree/main/onnx/backend/test/data/node/test_cast_FLOAT8E5M2FNUZ_to_FLOAT.onnx
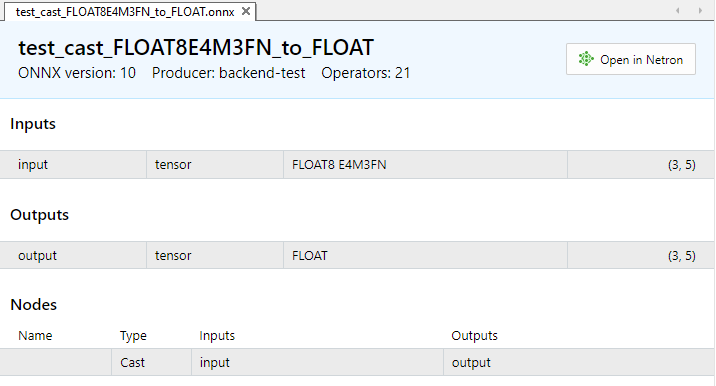
Fig.8. Parámetros de entrada y salida del modelo test_cast_FLOAT8E4M3FN_to_FLOAT.onnx en el MetaEditor
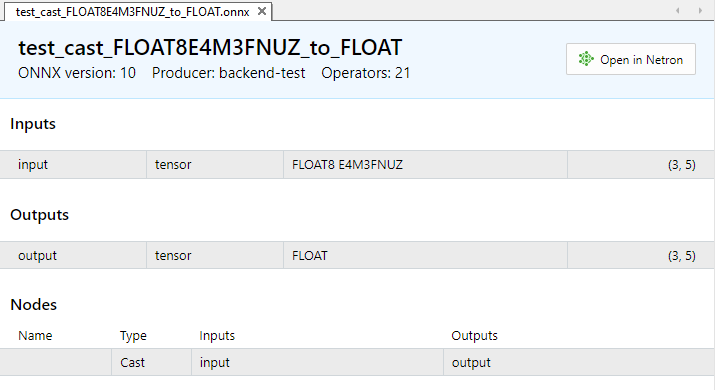
Fig.9. Parámetros de entrada y salida del modelo test_cast_FLOAT8E4M3FNUZ_to_FLOAT.onnx en el MetaEditor
Figura 10. Parámetros de entrada y salida del modelo test_cast_FLOAT8E5M2_to_FLOAT.onnx en el MetaEditor
Fig. 11. Parámetros de entrada y salida del modelo test_cast_FLOAT8E5M2FNUZ_to_FLOAT.onnx en el MetaEditor
Ejemplo:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TestCastBFloat8.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #resource "models\\test_cast_FLOAT8E4M3FN_to_FLOAT.onnx" as const uchar ExtModel_FLOAT8E4M3FN_to_FLOAT[]; #resource "models\\test_cast_FLOAT8E4M3FNUZ_to_FLOAT.onnx" as const uchar ExtModel_FLOAT8E4M3FNUZ_to_FLOAT[]; #resource "models\\test_cast_FLOAT8E5M2_to_FLOAT.onnx" as const uchar ExtModel_FLOAT8E5M2_to_FLOAT[]; #resource "models\\test_cast_FLOAT8E5M2FNUZ_to_FLOAT.onnx" as const uchar ExtModel_FLOAT8E5M2FNUZ_to_FLOAT[]; #define TEST_PASSED 0 #define TEST_FAILED 1 //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| union for data conversion | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> union U { uchar uc[sizeof(T)]; T value; }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ArrayToHexString | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> string ArrayToHexString(const T &data[],uint length=16) { string res; for(uint n=0; n<MathMin(length,data.Size()); n++) res+="," + StringFormat("%.2x",data[n]); StringSetCharacter(res,0,'['); return(res+"]"); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ArrayToString | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> string ArrayToString(const U<T> &data[],uint length=16) { string res; for(uint n=0; n<MathMin(length,data.Size()); n++) res+="," + (string)data[n].value; StringSetCharacter(res,0,'['); return(res+"]"); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PatchONNXModel | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ long CreatePatchedModel(const uchar &original_model[]) { uchar patched_model[]; ArrayCopy(patched_model,original_model); //--- special ONNX model patch(IR=9,Opset=20) patched_model[1]=0x09; patched_model[ArraySize(patched_model)-1]=0x14; return(OnnxCreateFromBuffer(patched_model,ONNX_DEFAULT)); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PrepareShapes | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool PrepareShapes(long model_handle) { //--- configure input shape ulong input_shape[]= {3,5}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(model_handle,0,input_shape)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetInputShape for input1. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } //--- configure output shape ulong output_shape[]= {3,5}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(model_handle,0,output_shape)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetOutputShape for output. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| RunCastFloat8Float | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool RunCastFloat8ToFloat(long model_handle,const ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT fmt) { PrintFormat("TEST: %s(%s)",__FUNCTION__,EnumToString(fmt)); //--- float test_data[15] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15}; uchar data_float8[15] = {}; if(!ArrayToFP8(data_float8,test_data,fmt)) { Print("error in ArrayToFP8. error code=",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } U<uchar> input_float8_values[3*5]; U<float> output_float_values[3*5]; float test_data_float[]; //--- convert float8 to float if(!ArrayFromFP8(test_data_float,data_float8,fmt)) { Print("error in ArrayFromFP8. error code=",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } for(uint i=0; i<data_float8.Size(); i++) { input_float8_values[i].value=data_float8[i]; PrintFormat("%d input value =%f Hex float8 = %s ushort value=%d",i,test_data_float[i],ArrayToHexString(input_float8_values[i].uc),input_float8_values[i].value); } Print("ONNX input array: ",ArrayToString(input_float8_values)); //--- execute model (convert float8 to float using ONNX) if(!OnnxRun(model_handle,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,input_float8_values,output_float_values)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxRun. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } Print("ONNX output array: ",ArrayToString(output_float_values)); //--- calculate error (compare ONNX and ArrayFromFP8 results) double sum_error=0.0; for(uint i=0; i<test_data.Size(); i++) { double delta=test_data_float[i]-(double)output_float_values[i].value; sum_error+=MathAbs(delta); PrintFormat("%d output float %f = %s difference=%f",i,output_float_values[i].value,ArrayToHexString(output_float_values[i].uc),delta); } //--- PrintFormat("%s(%s): sum_error=%f\n",__FUNCTION__,EnumToString(fmt),sum_error); return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TestModel | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool TestModel(const uchar &model[],const ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT fmt) { //--- create patched model long model_handle=CreatePatchedModel(model); if(model_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) return(false); //--- prepare input and output shapes if(!PrepareShapes(model_handle)) return(false); //--- run ONNX model if(!RunCastFloat8ToFloat(model_handle,fmt)) return(false); //--- release model handle OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnStart(void) { //--- run ONNX model if(!TestModel(ExtModel_FLOAT8E4M3FN_to_FLOAT,FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FN)) return(TEST_FAILED); //--- run ONNX model if(!TestModel(ExtModel_FLOAT8E4M3FNUZ_to_FLOAT,FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FNUZ)) return(TEST_FAILED); //--- run ONNX model if(!TestModel(ExtModel_FLOAT8E5M2_to_FLOAT,FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FN)) return(TEST_FAILED); //--- run ONNX model if(!TestModel(ExtModel_FLOAT8E5M2FNUZ_to_FLOAT,FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FNUZ)) return(TEST_FAILED); return(TEST_PASSED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Resultado:
TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) TEST: RunCastFloat8ToFloat(FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FN) TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 0 input value =1.000000 Hex float8 = [38] ushort value=56 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 1 input value =2.000000 Hex float8 = [40] ushort value=64 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 2 input value =3.000000 Hex float8 = [44] ushort value=68 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 3 input value =4.000000 Hex float8 = [48] ushort value=72 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 4 input value =5.000000 Hex float8 = [4a] ushort value=74 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 5 input value =6.000000 Hex float8 = [4c] ushort value=76 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 6 input value =7.000000 Hex float8 = [4e] ushort value=78 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 7 input value =8.000000 Hex float8 = [50] ushort value=80 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 8 input value =9.000000 Hex float8 = [51] ushort value=81 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 9 input value =10.000000 Hex float8 = [52] ushort value=82 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 10 input value =11.000000 Hex float8 = [53] ushort value=83 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 11 input value =12.000000 Hex float8 = [54] ushort value=84 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 12 input value =13.000000 Hex float8 = [55] ushort value=85 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 13 input value =14.000000 Hex float8 = [56] ushort value=86 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 14 input value =15.000000 Hex float8 = [57] ushort value=87 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX input array: [56,64,68,72,74,76,78,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87] TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX output array: [1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0,7.0,8.0,9.0,10.0,11.0,12.0,13.0,14.0,15.0] TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 0 output float 1.000000 = [00,00,80,3f] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 1 output float 2.000000 = [00,00,00,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 2 output float 3.000000 = [00,00,40,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 3 output float 4.000000 = [00,00,80,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 4 output float 5.000000 = [00,00,a0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 5 output float 6.000000 = [00,00,c0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 6 output float 7.000000 = [00,00,e0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 7 output float 8.000000 = [00,00,00,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 8 output float 9.000000 = [00,00,10,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 9 output float 10.000000 = [00,00,20,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 10 output float 11.000000 = [00,00,30,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 11 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 12 output float 13.000000 = [00,00,50,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 13 output float 14.000000 = [00,00,60,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 14 output float 15.000000 = [00,00,70,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) RunCastFloat8ToFloat(FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FN): sum_error=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) TEST: RunCastFloat8ToFloat(FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FNUZ) TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 0 input value =1.000000 Hex float8 = [40] ushort value=64 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 1 input value =2.000000 Hex float8 = [48] ushort value=72 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 2 input value =3.000000 Hex float8 = [4c] ushort value=76 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 3 input value =4.000000 Hex float8 = [50] ushort value=80 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 4 input value =5.000000 Hex float8 = [52] ushort value=82 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 5 input value =6.000000 Hex float8 = [54] ushort value=84 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 6 input value =7.000000 Hex float8 = [56] ushort value=86 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 7 input value =8.000000 Hex float8 = [58] ushort value=88 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 8 input value =9.000000 Hex float8 = [59] ushort value=89 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 9 input value =10.000000 Hex float8 = [5a] ushort value=90 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 10 input value =11.000000 Hex float8 = [5b] ushort value=91 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 11 input value =12.000000 Hex float8 = [5c] ushort value=92 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 12 input value =13.000000 Hex float8 = [5d] ushort value=93 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 13 input value =14.000000 Hex float8 = [5e] ushort value=94 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 14 input value =15.000000 Hex float8 = [5f] ushort value=95 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX input array: [64,72,76,80,82,84,86,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95] TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX output array: [1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0,7.0,8.0,9.0,10.0,11.0,12.0,13.0,14.0,15.0] TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 0 output float 1.000000 = [00,00,80,3f] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 1 output float 2.000000 = [00,00,00,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 2 output float 3.000000 = [00,00,40,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 3 output float 4.000000 = [00,00,80,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 4 output float 5.000000 = [00,00,a0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 5 output float 6.000000 = [00,00,c0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 6 output float 7.000000 = [00,00,e0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 7 output float 8.000000 = [00,00,00,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 8 output float 9.000000 = [00,00,10,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 9 output float 10.000000 = [00,00,20,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 10 output float 11.000000 = [00,00,30,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 11 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 12 output float 13.000000 = [00,00,50,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 13 output float 14.000000 = [00,00,60,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 14 output float 15.000000 = [00,00,70,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) RunCastFloat8ToFloat(FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FNUZ): sum_error=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) TEST: RunCastFloat8ToFloat(FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FN) TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 0 input value =1.000000 Hex float8 = [3c] ushort value=60 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 1 input value =2.000000 Hex float8 = [40] ushort value=64 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 2 input value =3.000000 Hex float8 = [42] ushort value=66 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 3 input value =4.000000 Hex float8 = [44] ushort value=68 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 4 input value =5.000000 Hex float8 = [45] ushort value=69 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 5 input value =6.000000 Hex float8 = [46] ushort value=70 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 6 input value =7.000000 Hex float8 = [47] ushort value=71 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 7 input value =8.000000 Hex float8 = [48] ushort value=72 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 8 input value =8.000000 Hex float8 = [48] ushort value=72 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 9 input value =10.000000 Hex float8 = [49] ushort value=73 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 10 input value =12.000000 Hex float8 = [4a] ushort value=74 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 11 input value =12.000000 Hex float8 = [4a] ushort value=74 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 12 input value =12.000000 Hex float8 = [4a] ushort value=74 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 13 input value =14.000000 Hex float8 = [4b] ushort value=75 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 14 input value =16.000000 Hex float8 = [4c] ushort value=76 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX input array: [60,64,66,68,69,70,71,72,72,73,74,74,74,75,76] TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX output array: [1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0,7.0,8.0,8.0,10.0,12.0,12.0,12.0,14.0,16.0] TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 0 output float 1.000000 = [00,00,80,3f] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 1 output float 2.000000 = [00,00,00,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 2 output float 3.000000 = [00,00,40,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 3 output float 4.000000 = [00,00,80,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 4 output float 5.000000 = [00,00,a0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 5 output float 6.000000 = [00,00,c0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 6 output float 7.000000 = [00,00,e0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 7 output float 8.000000 = [00,00,00,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 8 output float 8.000000 = [00,00,00,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 9 output float 10.000000 = [00,00,20,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 10 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 11 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 12 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 13 output float 14.000000 = [00,00,60,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 14 output float 16.000000 = [00,00,80,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) RunCastFloat8ToFloat(FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FN): sum_error=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) TEST: RunCastFloat8ToFloat(FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FNUZ) TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 0 input value =1.000000 Hex float8 = [40] ushort value=64 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 1 input value =2.000000 Hex float8 = [44] ushort value=68 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 2 input value =3.000000 Hex float8 = [46] ushort value=70 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 3 input value =4.000000 Hex float8 = [48] ushort value=72 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 4 input value =5.000000 Hex float8 = [49] ushort value=73 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 5 input value =6.000000 Hex float8 = [4a] ushort value=74 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 6 input value =7.000000 Hex float8 = [4b] ushort value=75 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 7 input value =8.000000 Hex float8 = [4c] ushort value=76 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 8 input value =8.000000 Hex float8 = [4c] ushort value=76 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 9 input value =10.000000 Hex float8 = [4d] ushort value=77 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 10 input value =12.000000 Hex float8 = [4e] ushort value=78 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 11 input value =12.000000 Hex float8 = [4e] ushort value=78 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 12 input value =12.000000 Hex float8 = [4e] ushort value=78 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 13 input value =14.000000 Hex float8 = [4f] ushort value=79 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 14 input value =16.000000 Hex float8 = [50] ushort value=80 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX input array: [64,68,70,72,73,74,75,76,76,77,78,78,78,79,80] TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX output array: [1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0,7.0,8.0,8.0,10.0,12.0,12.0,12.0,14.0,16.0] TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 0 output float 1.000000 = [00,00,80,3f] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 1 output float 2.000000 = [00,00,00,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 2 output float 3.000000 = [00,00,40,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 3 output float 4.000000 = [00,00,80,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 4 output float 5.000000 = [00,00,a0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 5 output float 6.000000 = [00,00,c0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 6 output float 7.000000 = [00,00,e0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 7 output float 8.000000 = [00,00,00,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 8 output float 8.000000 = [00,00,00,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 9 output float 10.000000 = [00,00,20,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 10 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 11 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 12 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 13 output float 14.000000 = [00,00,60,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 14 output float 16.000000 = [00,00,80,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) RunCastFloat8ToFloat(FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FNUZ): sum_error=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1)
2. Ejemplo de uso de ONNX para aumentar la resolución de las imágenes
En esta sección, describiremos un ejemplo de uso de modelos ESRGAN para aumentar la resolución de las imágenes.
ESRGAN, o Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Networks, es una potente arquitectura de redes neuronales diseñada para resolver el problema de la superresolución de imágenes. ESRGAN está diseñado para mejorar la calidad de las imágenes aumentando su resolución a un nivel superior. Para ello, se entrena una red neuronal profunda con un gran conjunto de datos de baja resolución y sus correspondientes imágenes de alta calidad. ESRGAN usa una arquitectura de redes generativas adversativas (GAN), que consta de dos componentes principales: un generador y un discriminador. El generador se encarga de crear imágenes de alta resolución, mientras que el discriminador está entrenado para distinguir las imágenes generadas a partir de las reales.
La arquitectura ESRGAN se basa en bloques residuales que ayudan a extraer y almacenar características importantes de las imágenes en distintos niveles de abstracción, lo cual permite a la red recuperar eficazmente los detalles y las texturas de las imágenes con gran calidad.
Para lograr una alta calidad y generalidad en el problema de la superresolución, ESRGAN necesita amplios conjuntos de datos de entrenamiento. Esto permite a la red aprender diferentes estilos y características de las imágenes y la hace más adaptable a los distintos tipos de datos de entrada. ESRGAN puede usarse para mejorar la calidad de las imágenes en muchos campos, como la fotografía, el diagnóstico médico, la producción de películas y vídeos, el diseño gráfico y muchos más. Su flexibilidad y eficacia lo convierten en uno de los métodos punteros en el campo de la superresolución de imágenes.
ESRGAN supone un importante paso adelante en el procesamiento de imágenes y la inteligencia artificial, abriendo nuevas posibilidades de creación y mejora de imágenes.
2.1. Ejemplo de ejecución del modelo ONNX con float32
Para ejecutar el ejemplo, descaremos el archivo https://github.com/amannm/super-resolution-service/blob/main/models/esrgan.onnx y lo copiaremos en la carpeta \MQL5\Scripts\models.
El modelo ESRGAN.onnx contiene ~1200 operaciones ONNX; las iniciales se muestran en la figura12
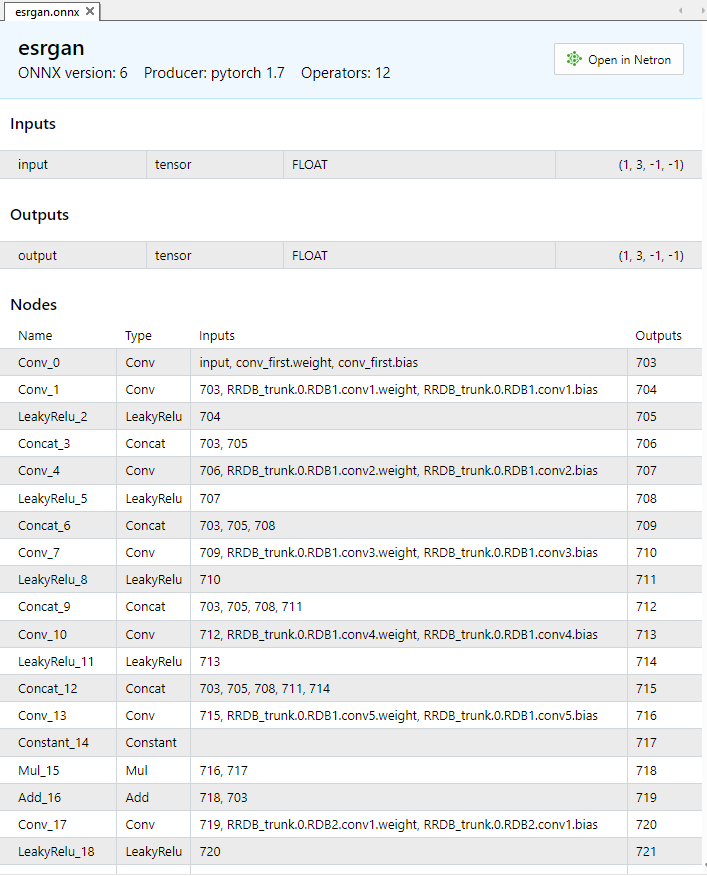
Fig. 12. Modelo ESRGAN en el MetaEditor
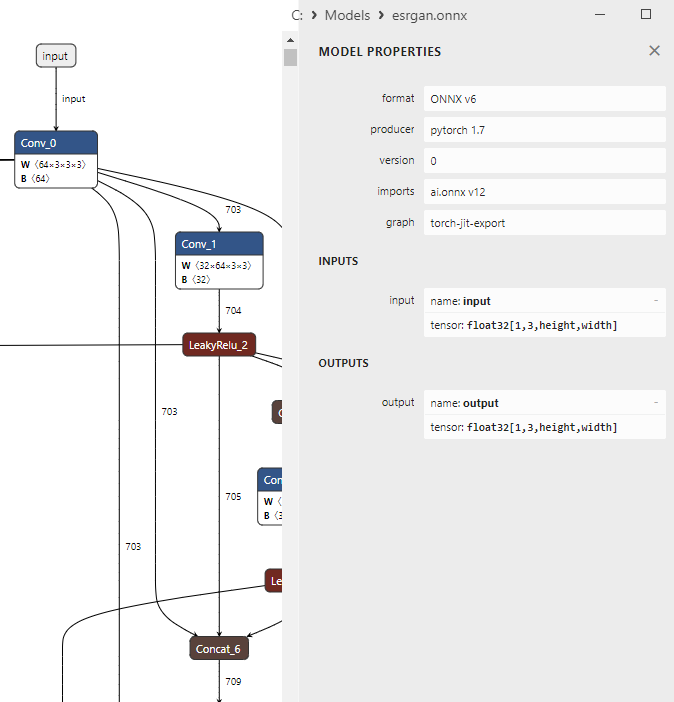
Fig. 13. Modelo ESRGAN en Netron
Comenzaremos cargando el modelo esrgan.onnxm. A continuación, seleccionaremos y cargaremos la imagen de origen en formato BMP. Luego la imagen se convertirá en canales RGB individuales que se introducirán en la entrada del modelo. El modelo realizará el proceso de ampliación del tamaño de la imagen en 4 veces, tras lo cual la imagen ampliada resultante se someterá a una transformación inversa y se preparará para su visualización.
La biblioteca Canvas se utilizará para la visualización, mientras que la biblioteca ONNX Runtime se usará para ejecutar el modelo. Una vez ejecutado el programa, la imagen ampliada se guardará en un archivo añadiendo "_upscaled" al nombre del archivo original. Las funciones principales incluyen el preprocesamiento y postprocesamiento de imágenes, así como la ejecución de un modelo para aumentar el tamaño de la imagen.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ESRGAN.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| 4x image upscaling demo using ESRGAN | //| esrgan.onnx model from | //| https://github.com/amannm/super-resolution-service/ | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Xintao Wang et al (2018) | //| ESRGAN: Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Networks| //| https://arxiv.org/abs/1809.00219 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #resource "models\\esrgan.onnx" as uchar ExtModel[]; #include <Canvas\Canvas.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| clamp | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ float clamp(float value, float minValue, float maxValue) { return MathMin(MathMax(value, minValue), maxValue); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Preprocessing | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool Preprocessing(float &data[],uint &image_data[],int &image_width,int &image_height) { //--- checkup if(image_height==0 || image_width==0) return(false); //--- prepare destination array with separated RGB channels for ONNX model int data_count=3*image_width*image_height; if(ArrayResize(data,data_count)!=data_count) { Print("ArrayResize failed"); return(false); } //--- converting for(int y=0; y<image_height; y++) for(int x=0; x<image_width; x++) { //--- load source RGB int offset=y*image_width+x; uint clr =image_data[offset]; uchar r =GETRGBR(clr); uchar g =GETRGBG(clr); uchar b =GETRGBB(clr); //--- store RGB components as separated channels int offset_ch1=0*image_width*image_height+offset; int offset_ch2=1*image_width*image_height+offset; int offset_ch3=2*image_width*image_height+offset; data[offset_ch1]=r/255.0f; data[offset_ch2]=g/255.0f; data[offset_ch3]=b/255.0f; } //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PostProcessing | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool PostProcessing(const float &data[], uint &image_data[], const int &image_width, const int &image_height) { //--- checks if(image_height == 0 || image_width == 0) return(false); int data_count=image_width*image_height; if(ArraySize(data)!=3*data_count) return(false); if(ArrayResize(image_data,data_count)!=data_count) return(false); //--- for(int y=0; y<image_height; y++) for(int x=0; x<image_width; x++) { int offset =y*image_width+x; int offset_ch1=0*image_width*image_height+offset; int offset_ch2=1*image_width*image_height+offset; int offset_ch3=2*image_width*image_height+offset; //--- rescale to [0..255] float r=clamp(data[offset_ch1]*255,0,255); float g=clamp(data[offset_ch2]*255,0,255); float b=clamp(data[offset_ch3]*255,0,255); //--- set color image_data image_data[offset]=XRGB(uchar(r),uchar(g),uchar(b)); } //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ShowImage | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool ShowImage(CCanvas &canvas,const string name,const int x0,const int y0,const int image_width,const int image_height, const uint &image_data[]) { if(ArraySize(image_data)==0 || name=="") return(false); //--- prepare canvas canvas.CreateBitmapLabel(name,x0,y0,image_width,image_height,COLOR_FORMAT_XRGB_NOALPHA); //--- copy image to canvas for(int y=0; y<image_height; y++) for(int x=0; x<image_width; x++) canvas.PixelSet(x,y,image_data[y*image_width+x]); //--- ready to draw canvas.Update(true); return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnStart(void) { //--- select BMP from <data folder>\MQL5\Files string image_path[1]; if(FileSelectDialog("Select BMP image",NULL,"Bitmap files (*.bmp)|*.bmp",FSD_FILE_MUST_EXIST,image_path,"lenna-original4.bmp")!=1) { Print("file not selected"); return(-1); } //--- load BMP into array uint image_data[]; int image_width; int image_height; if(!CCanvas::LoadBitmap(image_path[0],image_data,image_width,image_height)) { PrintFormat("CCanvas::LoadBitmap failed with error %d",GetLastError()); return(-1); } //--- convert RGB image to separated RGB channels float input_data[]; Preprocessing(input_data,image_data,image_width,image_height); PrintFormat("input array size=%d",ArraySize(input_data)); //--- load model long model_handle=OnnxCreateFromBuffer(ExtModel,ONNX_DEFAULT); if(model_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) { PrintFormat("OnnxCreate error %d",GetLastError()); return(-1); } PrintFormat("model loaded successfully"); PrintFormat("original: width=%d, height=%d Size=%d",image_width,image_height,ArraySize(image_data)); //--- set input shape ulong input_shape[]={1,3,image_height,image_width}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(model_handle,0,input_shape)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetInputShape. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(-1); } //--- upscaled image size int new_image_width =4*image_width; int new_image_height=4*image_height; ulong output_shape[]= {1,3,new_image_height,new_image_width}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(model_handle,0,output_shape)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetOutputShape. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(-1); } //--- run the model float output_data[]; int new_data_count=3*new_image_width*new_image_height; if(ArrayResize(output_data,new_data_count)!=new_data_count) { OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(-1); } if(!OnnxRun(model_handle,ONNX_DEBUG_LOGS,input_data,output_data)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxRun. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(-1); } Print("model successfully executed, output data size ",ArraySize(output_data)); OnnxRelease(model_handle); //--- postprocessing uint new_image[]; PostProcessing(output_data,new_image,new_image_width,new_image_height); //--- show images CCanvas canvas_original,canvas_scaled; ShowImage(canvas_original,"original_image",new_image_width,0,image_width,image_height,image_data); ShowImage(canvas_scaled,"upscaled_image",0,0,new_image_width,new_image_height,new_image); //--- save upscaled image StringReplace(image_path[0],".bmp","_upscaled.bmp"); Print(ResourceSave(canvas_scaled.ResourceName(),image_path[0])); //--- while(!IsStopped()) Sleep(100); return(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Resultado:
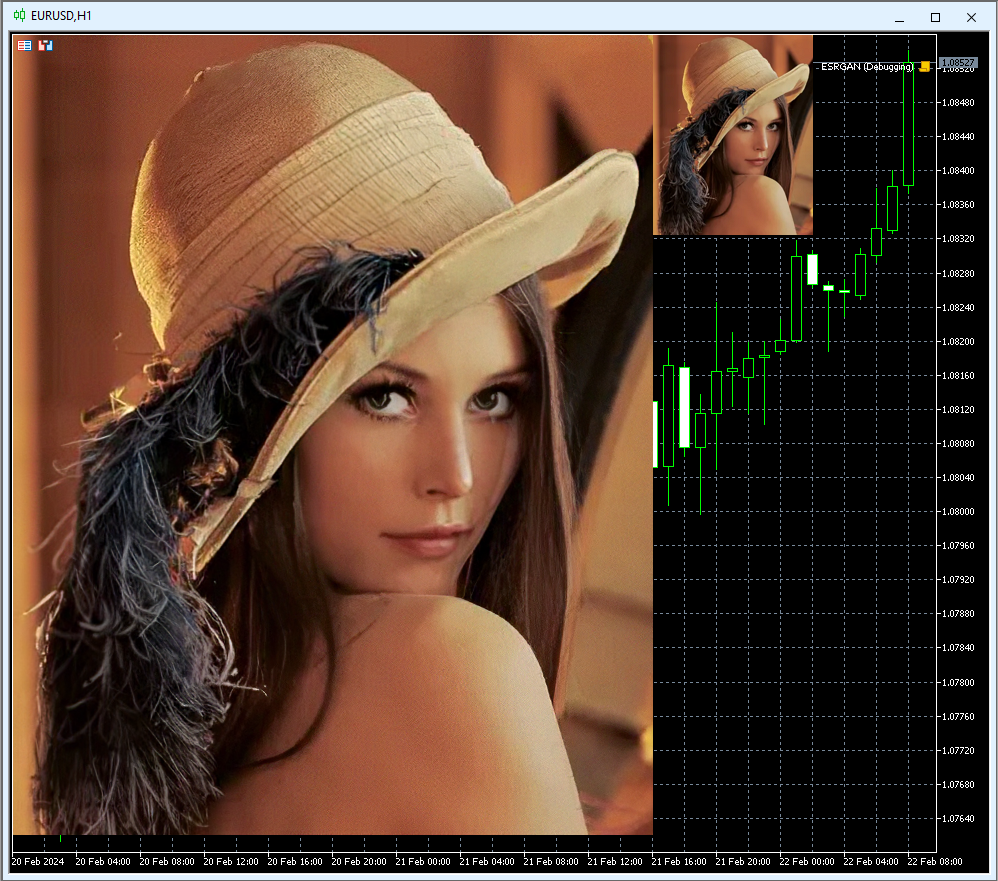
Fig. 14. Resultado del funcionamiento de ESRGAN.onnx (160x200 -> 640x800)
En este ejemplo, la imagen de 160x200 se ha ampliado en 4 veces (a 640x800) utilizando el modelo ESRGAN.onnx.
2.2. Ejemplo de ejecución del modelo ONNX con float16
Para convertir los modelos a float16 usaremos el método descrito en Create Float16 and Mixed Precision Models.
# Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. # https://www.mql5.com import onnx from onnxconverter_common import float16 from sys import argv # Define the path for saving the model data_path = argv[0] last_index = data_path.rfind("\\") + 1 data_path = data_path[0:last_index] # conversión de modelos en float16 model_path = data_path+'\\models\\esrgan.onnx' modelfp16_path = data_path+'\\models\\esrgan_float16.onnx' model = onnx.load(model_path) model_fp16 = float16.convert_float_to_float16(model) onnx.save(model_fp16, modelfp16_path)
Tras la conversión, el tamaño del archivo se ha reducido a la mitad (de 64 Mb a 32 Mb).
Los cambios en el código son mínimos:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ESRGAN_float16.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| 4x image upscaling demo using ESRGAN | //| esrgan.onnx model from | //| https://github.com/amannm/super-resolution-service/ | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Xintao Wang et al (2018) | //| ESRGAN: Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Networks| //| https://arxiv.org/abs/1809.00219 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #resource "models\\esrgan_float16.onnx" as uchar ExtModel[]; #include <Canvas\Canvas.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| clamp | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ float clamp(float value, float minValue, float maxValue) { return MathMin(MathMax(value, minValue), maxValue); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Preprocessing | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool Preprocessing(float &data[],uint &image_data[],int &image_width,int &image_height) { //--- checkup if(image_height==0 || image_width==0) return(false); //--- prepare destination array with separated RGB channels for ONNX model int data_count=3*image_width*image_height; if(ArrayResize(data,data_count)!=data_count) { Print("ArrayResize failed"); return(false); } //--- converting for(int y=0; y<image_height; y++) for(int x=0; x<image_width; x++) { //--- load source RGB int offset=y*image_width+x; uint clr =image_data[offset]; uchar r =GETRGBR(clr); uchar g =GETRGBG(clr); uchar b =GETRGBB(clr); //--- store RGB components as separated channels int offset_ch1=0*image_width*image_height+offset; int offset_ch2=1*image_width*image_height+offset; int offset_ch3=2*image_width*image_height+offset; data[offset_ch1]=r/255.0f; data[offset_ch2]=g/255.0f; data[offset_ch3]=b/255.0f; } //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PostProcessing | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool PostProcessing(const float &data[], uint &image_data[], const int &image_width, const int &image_height) { //--- checks if(image_height == 0 || image_width == 0) return(false); int data_count=image_width*image_height; if(ArraySize(data)!=3*data_count) return(false); if(ArrayResize(image_data,data_count)!=data_count) return(false); //--- for(int y=0; y<image_height; y++) for(int x=0; x<image_width; x++) { int offset =y*image_width+x; int offset_ch1=0*image_width*image_height+offset; int offset_ch2=1*image_width*image_height+offset; int offset_ch3=2*image_width*image_height+offset; //--- rescale to [0..255] float r=clamp(data[offset_ch1]*255,0,255); float g=clamp(data[offset_ch2]*255,0,255); float b=clamp(data[offset_ch3]*255,0,255); //--- set color image_data image_data[offset]=XRGB(uchar(r),uchar(g),uchar(b)); } //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ShowImage | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool ShowImage(CCanvas &canvas,const string name,const int x0,const int y0,const int image_width,const int image_height, const uint &image_data[]) { if(ArraySize(image_data)==0 || name=="") return(false); //--- prepare canvas canvas.CreateBitmapLabel(name,x0,y0,image_width,image_height,COLOR_FORMAT_XRGB_NOALPHA); //--- copy image to canvas for(int y=0; y<image_height; y++) for(int x=0; x<image_width; x++) canvas.PixelSet(x,y,image_data[y*image_width+x]); //--- ready to draw canvas.Update(true); return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnStart(void) { //--- select BMP from <data folder>\MQL5\Files string image_path[1]; if(FileSelectDialog("Select BMP image",NULL,"Bitmap files (*.bmp)|*.bmp",FSD_FILE_MUST_EXIST,image_path,"lenna.bmp")!=1) { Print("file not selected"); return(-1); } //--- load BMP into array uint image_data[]; int image_width; int image_height; if(!CCanvas::LoadBitmap(image_path[0],image_data,image_width,image_height)) { PrintFormat("CCanvas::LoadBitmap failed with error %d",GetLastError()); return(-1); } //--- convert RGB image to separated RGB channels float input_data[]; Preprocessing(input_data,image_data,image_width,image_height); PrintFormat("input array size=%d",ArraySize(input_data)); ushort input_data_float16[]; if(!ArrayToFP16(input_data_float16,input_data,FLOAT_FP16)) { Print("error in ArrayToFP16. error code=",GetLastError()); return(false); } //--- load model long model_handle=OnnxCreateFromBuffer(ExtModel,ONNX_DEFAULT); if(model_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) { PrintFormat("OnnxCreate error %d",GetLastError()); return(-1); } PrintFormat("model loaded successfully"); PrintFormat("original: width=%d, height=%d Size=%d",image_width,image_height,ArraySize(image_data)); //--- set input shape ulong input_shape[]={1,3,image_height,image_width}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(model_handle,0,input_shape)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetInputShape. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(-1); } //--- upscaled image size int new_image_width =4*image_width; int new_image_height=4*image_height; ulong output_shape[]= {1,3,new_image_height,new_image_width}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(model_handle,0,output_shape)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetOutputShape. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(-1); } //--- run the model float output_data[]; ushort output_data_float16[]; int new_data_count=3*new_image_width*new_image_height; if(ArrayResize(output_data_float16,new_data_count)!=new_data_count) { OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(-1); } if(!OnnxRun(model_handle,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,input_data_float16,output_data_float16)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxRun. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(-1); } Print("model successfully executed, output data size ",ArraySize(output_data)); OnnxRelease(model_handle); if(!ArrayFromFP16(output_data,output_data_float16,FLOAT_FP16)) { Print("error in ArrayFromFP16. error code=",GetLastError()); return(false); } //--- postprocessing uint new_image[]; PostProcessing(output_data,new_image,new_image_width,new_image_height); //--- show images CCanvas canvas_original,canvas_scaled; ShowImage(canvas_original,"original_image",new_image_width,0,image_width,image_height,image_data); ShowImage(canvas_scaled,"upscaled_image",0,0,new_image_width,new_image_height,new_image); //--- save upscaled image StringReplace(image_path[0],".bmp","_upscaled.bmp"); Print(ResourceSave(canvas_scaled.ResourceName(),image_path[0])); //--- while(!IsStopped()) Sleep(100); return(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Los cambios de código necesarios para ejecutar el modelo convertido al formato float16 se han resaltado en color.
Resultado:
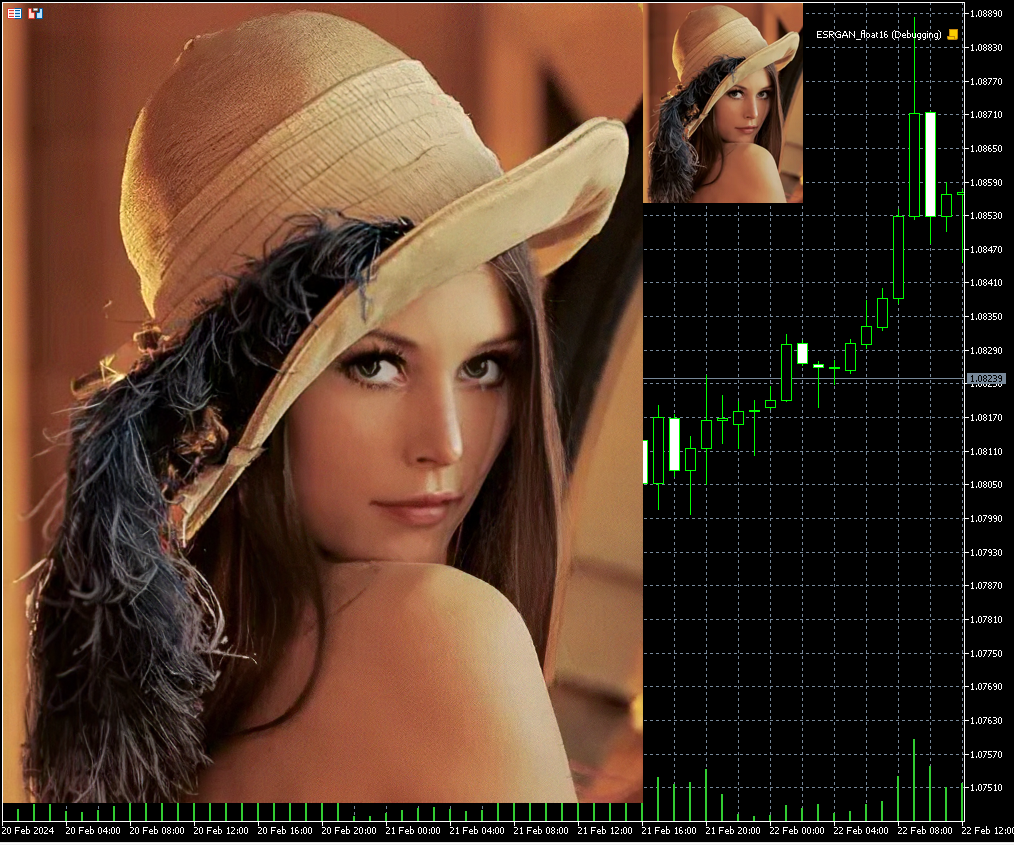
Figura 15. Resultado del modelo ESRGAN_float16.onnx (160x200 -> 640x800)
Así, el uso de números float16 en lugar de float32 permite reducir el tamaño del archivo del modelo ONNX en 2 veces (de 64Mb a 32Mb).
Al ejecutar los modelos en números float16, la calidad de las imágenes sigue siendo la misma, visualmente resulta difícil encontrar diferencias:
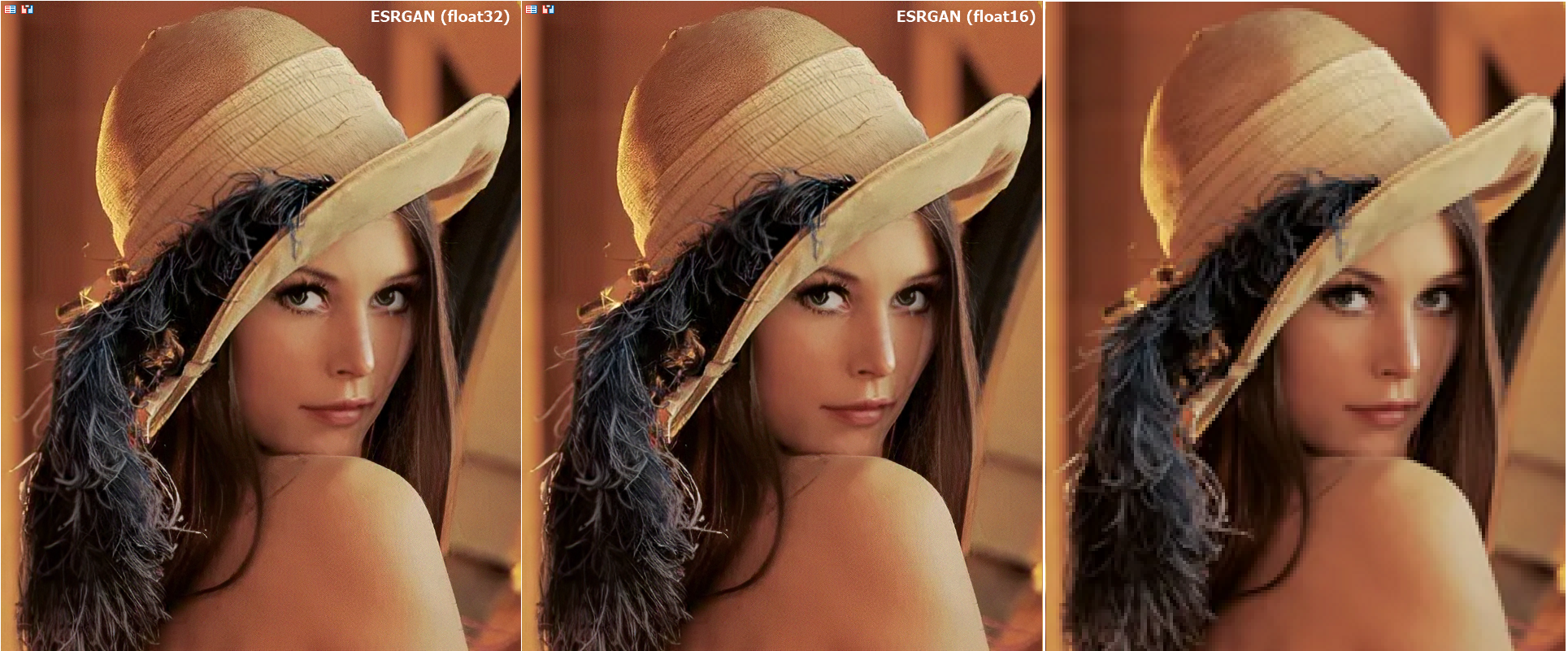

Fig.16. Comparación de los resultados del modelo ESRGAN para float y float16
Los cambios en el código son mínimos, solo hay que ocuparse de convertir los datos de entrada y salida.
En este caso, tras la conversión a float16 la calidad del rendimiento del modelo no ha cambiado significativamente, pero al analizar datos financieros, debemos esforzarnos por realizar cálculos con la mayor precisión posible.
Conclusiones
El uso de nuevos tipos de datos para números de coma flotante permite reducir el tamaño de los modelos ONNX sin padecer una pérdida significativa de calidad.
Las funciones de conversión de datos ArrayToFP16/ArrayFromFP16 y ArrayToFP8/ArrayFromFP8 simplifican enormemente el preprocesamiento y postprocesamiento de los datos.
Para trabajar con los modelos ONNX convertidos, los cambios requeridos en el código son mínimos.
Traducción del ruso hecha por MetaQuotes Ltd.
Artículo original: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/14330
Advertencia: todos los derechos de estos materiales pertenecen a MetaQuotes Ltd. Queda totalmente prohibido el copiado total o parcial.
 Creación de un modelo de restricción de tendencia de velas (Parte 1): Para EAs e Indicadores Técnicos
Creación de un modelo de restricción de tendencia de velas (Parte 1): Para EAs e Indicadores Técnicos
 Algoritmos de optimización de la población: Resiliencia ante el estancamiento en los extremos locales (Parte I)
Algoritmos de optimización de la población: Resiliencia ante el estancamiento en los extremos locales (Parte I)
 Desarrollamos un Asesor Experto multidivisas (Parte 4): Órdenes pendientes virtuales y guardado del estado
Desarrollamos un Asesor Experto multidivisas (Parte 4): Órdenes pendientes virtuales y guardado del estado
 Superar los retos de integración de ONNX
Superar los retos de integración de ONNX
- Aplicaciones de trading gratuitas
- 8 000+ señales para copiar
- Noticias económicas para analizar los mercados financieros
Usted acepta la política del sitio web y las condiciones de uso
Por favor, añada otra imagen del mismo tamaño a la derecha - cuadruplicado (en lugar de un píxel - cuatro (2x2) del mismo color) imagen original.
Puede reemplazar el código para mostrarlo:
Puede sustituir el código para darle salida:
¡Gracias! Reducido por un factor de dos en cada coordenada, obteniendo la imagen correcta como el original.
Pensé que float16/32 se acercaría al original con esta transformación. ¡Pero son notablemente mejores! Es decir, UpScale+DownScale >> Original.
ZY Sorprendido. Parece razonable pasar todas las imágenes/vídeos antiguos por este modelo onnx.
Si a la entrada del modelo onnx se le dan los mismos datos, ¿la salida será siempre la misma?
¿Existe algún elemento de aleatoriedad en el modelo onnx?
Si el modelo onnx recibe los mismos datos como entrada, ¿pero la salida tendrá siempre el mismo resultado?
¿Existe un elemento de aleatoriedad en el modelo onnx?
En general, depende de los operadores que se utilicen dentro del modelo ONNX.
Para este modelo el resultado debería ser el mismo, contiene operaciones deterministas (1195 en total)
Описание float16
https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%A7%D0%B8%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%BE_%D0%BF%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B8%D0%BD%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B9_%D1%82%D0%BE%D1%87%D0%BD%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B8
Примеры чисел половинной точности
En estos ejemplos, los números en coma flotante se representan en binario. Incluyen el bit de signo, el exponente y la mantisa.
0 01111 0000000000 = +1 *215-15 = 1
0 01111 0000000001 = +1.0000000001 2 *215-15=1+ 2-10 = 1.0009765625 (el número inmediatamente superior después de 1)
Es decir, para números con 5 decimales (la mayoría de las divisas) sólo se puede aplicar 1,00098 después de 1,00000.
¡Genial! Pero no para operar y trabajar con cotizaciones.