
Arbeiten mit ONNX-Modellen in den Datenformaten float16 und float8
Inhalt
- 1. Neue Datentypen für die Arbeit mit ONNX-Modellen
- 1.1. FP16-Format
- 1.1.1. Ausführungstests des ONNX-Cast-Operators für FLOAT16
- 1.1.2. Ausführungstests des ONNX-Cast-Operators für BFLOAT16
- 1.2. FP8-Format
- 1.2.1. FP8-Formate fp8_e5m2 und fp8_e4m3
- 1.2.2. Ausführungstests des ONNX-Cast-Operators für FLOAT8
- 2. Verwendung von ONNX für die Super-Resolution von Bildern
- 2.1. Ausführen des ONNX-Modells mit float32
- 2.2. Ausführen eines ONNX-Modells mit float16
- Schlussfolgerungen
Mit der Weiterentwicklung des maschinellen Lernens und der Technologien der künstlichen Intelligenz wächst der Bedarf, die Prozesse für die Arbeit mit Modellen zu optimieren. Die Effizienz des Modellbetriebs hängt direkt von den Datenformaten ab, in denen sie dargestellt werden. In den letzten Jahren sind mehrere neue Datentypen entstanden, die speziell für die Arbeit mit Deep-Learning-Modellen entwickelt wurden.
In diesem Artikel werden wir uns auf zwei dieser neuen Datenformate konzentrieren - float16 und float8, die allmählich aktiv in modernen ONNX-Modellen verwendet werden. Diese Formate sind eine Alternative zu den präziseren, aber ressourcenintensiven Fließkommadatenformaten. Sie bieten ein optimales Gleichgewicht zwischen Leistung und Genauigkeit, was sie für verschiedene Aufgaben des maschinellen Lernens besonders attraktiv macht. Wir werden die wichtigsten Eigenschaften und Vorteile der Formate float16 und float8 kennenlernen und Funktionen für die Konvertierung in die Standardformate float und double vorstellen.
Dies wird Entwicklern und Forschern helfen, besser zu verstehen, wie sie diese Formate in ihren Projekten und Modellen effektiv nutzen können. Als Beispiel wird die Funktionsweise des ESRGAN ONNX-Modells untersucht, das zur Verbesserung der Bildqualität eingesetzt wird.
1. Neue Datentypen für die Arbeit mit ONNX-Modellen
Um die Berechnungen zu beschleunigen, verwenden einige Modelle Datentypen mit geringerer Genauigkeit, wie Float16 und sogar Float8.
Die Unterstützung für diese neuen Datentypen wurde hinzugefügt, um mit ONNX-Modellen in der MQL5-Sprache zu arbeiten, was die Manipulation von 8-Bit- und 16-Bit-Gleitkomma-Darstellungen ermöglicht.
Das Skript gibt die vollständige Liste der Elemente der Enumeration ENUM_ONNX_DATA_TYPE aus.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ONNX_Data_Types.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- for(int i=0; i<21; i++) PrintFormat("%2d %s",i,EnumToString(ENUM_ONNX_DATA_TYPE(i))); }
Ausgabe:
0: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_UNDEFINED 1: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT 2: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_UINT8 3: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_INT8 4: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_UINT16 5: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_INT16 6: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_INT32 7: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_INT64 8: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_STRING 9: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_BOOL 10: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT16 11: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_DOUBLE 12: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_UINT32 13: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_UINT64 14: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_COMPLEX64 15: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_COMPLEX128 16: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_BFLOAT16 17: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT8E4M3FN 18: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT8E4M3FNUZ 19: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT8E5M2 20: ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT8E5M2FNUZ
Somit ist es nun möglich, ONNX-Modelle mit solchen Daten auszuführen.
Außerdem wurden in MQL5 zusätzliche Funktionen zur Datenkonvertierung hinzugefügt:
bool ArrayToFP16(ushort &dst_array[],const float &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT16_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayToFP16(ushort &dst_array[],const double &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT16_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayToFP8(uchar &dst_array[],const float &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayToFP8(uchar &dst_array[],const double &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayFromFP16(float &dst_array[],const ushort &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT16_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayFromFP16(double &dst_array[],const ushort &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT16_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayFromFP8(float &dst_array[],const uchar &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT fmt); bool ArrayFromFP8(double &dst_array[],const uchar &src_array[],ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT fmt);
Da die Fließkommaformate für 16 und 8 Bit unterschiedlich sein können, muss der Parameter 'fmt' in den Konvertierungsfunktionen angeben, welches Zahlenformat verarbeitet werden muss.
Für 16-Bit-Versionen wird eine neue Enumeration ENUM_FLOAT16_FORMAT verwendet, die derzeit die folgenden Werte hat:
- FLOAT_FP16 — Standard 16-Bit-Format, auch bekannt als Half Float.
- FLOAT_BFP16 — spezielles Gleitkommaformat brain float point.
- FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FN — 8-Bit-Gleitkommazahl, 4-Bit-Exponent und 3-Bit-Mantisse. Normalerweise als Koeffizienten verwendet.
- FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FNUZ — 8-Bit-Gleitkommazahl, 4-Bit-Exponent und 3-Bit-Mantisse. Unterstützt NaN, aber nicht die negative Null und Inf. Normalerweise als Koeffizienten verwendet.
- FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FN — 8-Bit-Gleitkommazahl, 5-Bit-Exponent und 2-Bit-Mantisse. Unterstützt NaN und Inf. Wird normalerweise für Farbverläufe verwendet.
- FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FNUZ — 8-Bit-Gleitkommazahl, 5-Bit-Exponent und 2-Bit-Mantisse. Unterstützt NaN und Inf, nicht aber negative Null. Wird auch für Gradienten verwendet.
1.1. FP16-Format
Die Formate FLOAT16 und BFLOAT16 sind Datentypen, die zur Darstellung von Gleitkommazahlen verwendet werden.
FLOAT16, auch bekannt als Format half-precision floating point, das 16 Bits zur Darstellung einer Gleitkommazahl verwendet. Dieses Format bietet ein ausgewogenes Verhältnis zwischen Präzision und Rechenleistung. FLOAT16 wird häufig bei Deep Learning und neuronalen Netzen eingesetzt, wo eine hohe Leistung bei der Verarbeitung großer Datenmengen erforderlich ist. Dieses Format ermöglicht beschleunigte Berechnungen, indem es die Größe der Zahlen reduziert, was besonders wichtig ist, wenn tiefe neuronale Netze auf Grafikprozessoren (GPUs) trainiert werden.
BFLOAT16 (Brain Floating Point 16) verwendet ebenfalls 16 Bits, unterscheidet sich aber von FLOAT16 durch die Art der Zahlendarstellung. In diesem Format sind 8 Bits für die Darstellung des Exponenten vorgesehen, die restlichen 7 Bits werden für die Darstellung der Mantisse verwendet. Dieses Format wurde für den Einsatz im Bereich des Deep Learning und der künstlichen Intelligenz entwickelt, insbesondere für die Tensor Processing Unit (TPU)-Prozessoren von Google. BFLOAT16 bietet eine gute Leistung beim Training neuronaler Netze und kann effektiv zur Beschleunigung von Berechnungen eingesetzt werden.
Beide Formate haben ihre Vorteile und Grenzen. FLOAT16 bietet eine höhere Genauigkeit, erfordert aber mehr Ressourcen für Speicherung und Berechnungen. BFLOAT16 hingegen bietet eine höhere Leistung und Effizienz bei der Datenverarbeitung, ist aber möglicherweise weniger präzise.
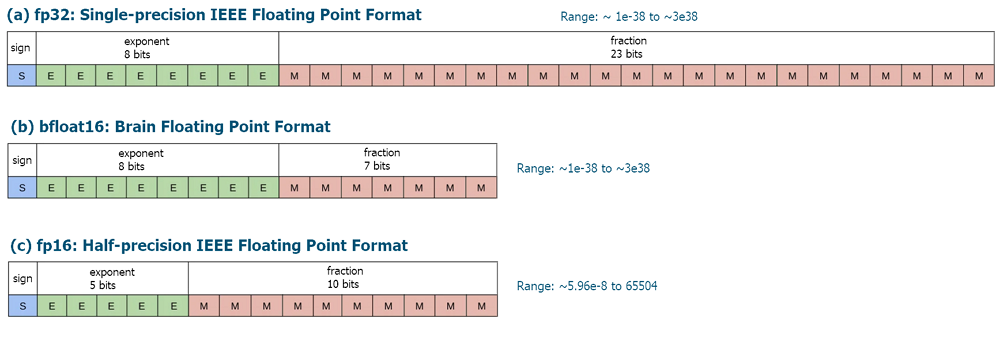
Fig.1. Formate der Bit-Darstellung von Gleitkommazahlen FLOAT16 und BFLOAT16
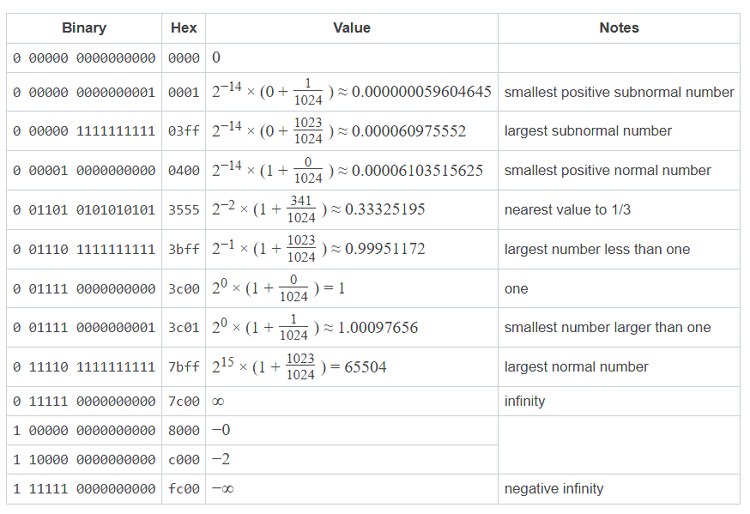
Tabelle 1. Fließkommazahlen im FLOAT16-Format
1.1.1. Ausführungstests des ONNX-Cast-Operators für FLOAT16
Zur Veranschaulichung betrachten wir die Aufgabe, Daten vom Typ FLOAT16 in die Typen float und double zu konvertieren.
ONNX-Modelle mit dem Cast-Verfahren:
- https://github.com/onnx/onnx/tree/main/onnx/backend/test/data/node/test_cast_FLOAT16_to_FLOAT
- https://github.com/onnx/onnx/tree/main/onnx/backend/test/data/node/test_cast_FLOAT16_to_DOUBLE
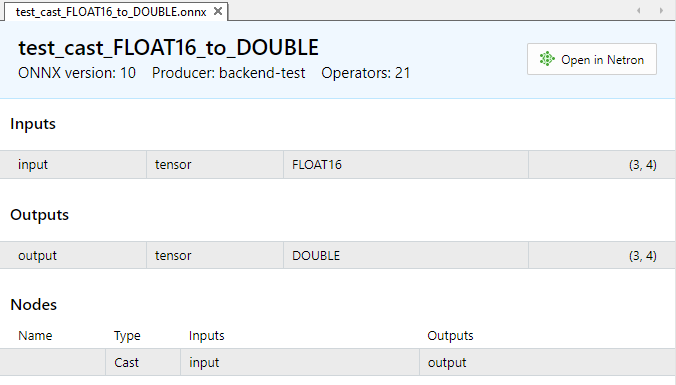
Abb.2. Eingabe- und Ausgabeparameter des Modells test_cast_FLOAT16_to_DOUBLE.onnx
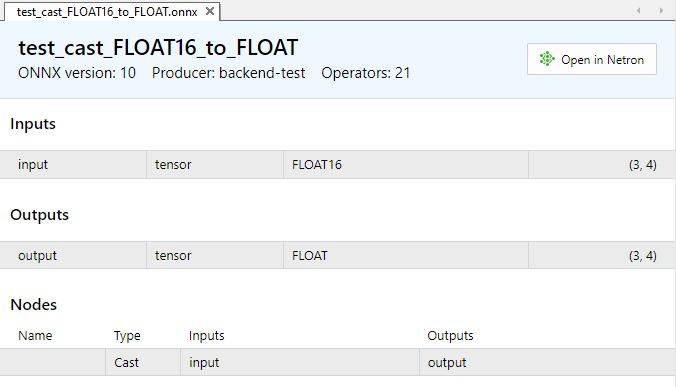
Abb.3. Eingabe- und Ausgabeparameter des Modells test_cast_FLOAT16_to_FLOAT.onnx
Wie aus der Beschreibung der Eigenschaften von ONNX-Modellen hervorgeht, erfordert die Eingabe Daten des Typs ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT16, und das Modell liefert Ausgabedaten im Format ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT.
Um die Werte umzuwandeln, verwenden wir die Funktionen ArrayToFP16() und ArrayFromFP16() mit dem Parameter FLOAT_FP16.
Beispiel:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TestCastFloat16.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #resource "models\\test_cast_FLOAT16_to_DOUBLE.onnx" as const uchar ExtModel1[]; #resource "models\\test_cast_FLOAT16_to_FLOAT.onnx" as const uchar ExtModel2[]; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| union for data conversion | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> union U { uchar uc[sizeof(T)]; T value; }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ArrayToString | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> string ArrayToString(const T &data[],uint length=16) { string res; for(uint n=0; n<MathMin(length,data.Size()); n++) res+="," + StringFormat("%.2x",data[n]); StringSetCharacter(res,0,'['); return res+"]"; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PatchONNXModel | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void PatchONNXModel(const uchar &original_model[],uchar &patched_model[]) { ArrayCopy(patched_model,original_model,0,0,WHOLE_ARRAY); //--- special ONNX model patch(IR=9,Opset=20) patched_model[1]=0x09; patched_model[ArraySize(patched_model)-1]=0x14; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| CreateModel | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CreateModel(long &model_handle,const uchar &model[]) { model_handle=INVALID_HANDLE; ulong flags=ONNX_DEFAULT; //ulong flags=ONNX_DEBUG_LOGS; //--- model_handle=OnnxCreateFromBuffer(model,flags); if(model_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) return(false); //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PrepareShapes | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool PrepareShapes(long model_handle) { ulong input_shape1[]= {3,4}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(model_handle,0,input_shape1)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetInputShape for input1. error code=%d",GetLastError()); //-- OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } //--- ulong output_shape[]= {3,4}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(model_handle,0,output_shape)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetOutputShape for output. error code=%d",GetLastError()); //-- OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| RunCastFloat16ToDouble | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool RunCastFloat16ToDouble(long model_handle) { PrintFormat("test=%s",__FUNCTION__); double test_data[12]= {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12}; ushort data_uint16[12]; if(!ArrayToFP16(data_uint16,test_data,FLOAT_FP16)) { Print("error in ArrayToFP16. error code=",GetLastError()); return(false); } Print("test array:"); ArrayPrint(test_data); Print("ArrayToFP16:"); ArrayPrint(data_uint16); U<ushort> input_float16_values[3*4]; U<double> output_double_values[3*4]; float test_data_float[]; if(!ArrayFromFP16(test_data_float,data_uint16,FLOAT_FP16)) { Print("error in ArrayFromFP16. error code=",GetLastError()); return(false); } for(int i=0; i<12; i++) { input_float16_values[i].value=data_uint16[i]; PrintFormat("%d input value =%f Hex float16 = %s ushort value=%d",i,test_data_float[i],ArrayToString(input_float16_values[i].uc),input_float16_values[i].value); } Print("ONNX input array:"); ArrayPrint(input_float16_values); bool res=OnnxRun(model_handle,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,input_float16_values,output_double_values); if(!res) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxRun. error code=%d",GetLastError()); return(false); } Print("ONNX output array:"); ArrayPrint(output_double_values); //--- double sum_error=0.0; for(int i=0; i<12; i++) { double delta=test_data[i]-output_double_values[i].value; sum_error+=MathAbs(delta); PrintFormat("%d output double %f = %s difference=%f",i,output_double_values[i].value,ArrayToString(output_double_values[i].uc),delta); } //--- PrintFormat("test=%s sum_error=%f",__FUNCTION__,sum_error); //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| RunCastFloat16ToFloat | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool RunCastFloat16ToFloat(long model_handle) { PrintFormat("test=%s",__FUNCTION__); double test_data[12]= {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12}; ushort data_uint16[12]; if(!ArrayToFP16(data_uint16,test_data,FLOAT_FP16)) { Print("error in ArrayToFP16. error code=",GetLastError()); return(false); } Print("test array:"); ArrayPrint(test_data); Print("ArrayToFP16:"); ArrayPrint(data_uint16); U<ushort> input_float16_values[3*4]; U<float> output_float_values[3*4]; float test_data_float[]; if(!ArrayFromFP16(test_data_float,data_uint16,FLOAT_FP16)) { Print("error in ArrayFromFP16. error code=",GetLastError()); return(false); } for(int i=0; i<12; i++) { input_float16_values[i].value=data_uint16[i]; PrintFormat("%d input value =%f Hex float16 = %s ushort value=%d",i,test_data_float[i],ArrayToString(input_float16_values[i].uc),input_float16_values[i].value); } Print("ONNX input array:"); ArrayPrint(input_float16_values); bool res=OnnxRun(model_handle,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,input_float16_values,output_float_values); if(!res) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxRun. error code=%d",GetLastError()); return(false); } Print("ONNX output array:"); ArrayPrint(output_float_values); //--- double sum_error=0.0; for(int i=0; i<12; i++) { double delta=test_data[i]-(double)output_float_values[i].value; sum_error+=MathAbs(delta); PrintFormat("%d output float %f = %s difference=%f",i,output_float_values[i].value,ArrayToString(output_float_values[i].uc),delta); } //--- PrintFormat("test=%s sum_error=%f",__FUNCTION__,sum_error); //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TestCastFloat16ToFloat | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool TestCastFloat16ToFloat(const uchar &res_model[]) { uchar model[]; PatchONNXModel(res_model,model); //--- get model handle long model_handle=INVALID_HANDLE; //--- get model handle if(!CreateModel(model_handle,model)) return(false); //--- prepare input and output shapes if(!PrepareShapes(model_handle)) return(false); //--- run ONNX model if(!RunCastFloat16ToFloat(model_handle)) return(false); //--- release model handle OnnxRelease(model_handle); //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TestCastFloat16ToDouble | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool TestCastFloat16ToDouble(const uchar &res_model[]) { uchar model[]; PatchONNXModel(res_model,model); //--- long model_handle=INVALID_HANDLE; //--- get model handle if(!CreateModel(model_handle,model)) return(false); //--- prepare input and output shapes if(!PrepareShapes(model_handle)) return(false); //--- run ONNX model if(!RunCastFloat16ToDouble(model_handle)) return(false); //--- release model handle OnnxRelease(model_handle); //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnStart(void) { if(!TestCastFloat16ToDouble(ExtModel1)) return 1; if(!TestCastFloat16ToFloat(ExtModel2)) return 1; //--- return 0; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Ausgabe:
TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test=RunCastFloat16ToDouble TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test array: TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1.00000 2.00000 3.00000 4.00000 5.00000 6.00000 7.00000 8.00000 9.00000 10.00000 11.00000 12.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ArrayToFP16: TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 15360 16384 16896 17408 17664 17920 18176 18432 18560 18688 18816 18944 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 0 input value =1.000000 Hex float16 = [00,3c] ushort value=15360 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1 input value =2.000000 Hex float16 = [00,40] ushort value=16384 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 2 input value =3.000000 Hex float16 = [00,42] ushort value=16896 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 3 input value =4.000000 Hex float16 = [00,44] ushort value=17408 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 4 input value =5.000000 Hex float16 = [00,45] ushort value=17664 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 5 input value =6.000000 Hex float16 = [00,46] ushort value=17920 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 6 input value =7.000000 Hex float16 = [00,47] ushort value=18176 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 7 input value =8.000000 Hex float16 = [00,48] ushort value=18432 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 8 input value =9.000000 Hex float16 = [80,48] ushort value=18560 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 9 input value =10.000000 Hex float16 = [00,49] ushort value=18688 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 10 input value =11.000000 Hex float16 = [80,49] ushort value=18816 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 11 input value =12.000000 Hex float16 = [00,4a] ushort value=18944 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX input array: TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [uc] [value] TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 0] ... 15360 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 1] ... 16384 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 2] ... 16896 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 3] ... 17408 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 4] ... 17664 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 5] ... 17920 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 6] ... 18176 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 7] ... 18432 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 8] ... 18560 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 9] ... 18688 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [10] ... 18816 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [11] ... 18944 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX output array: TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [uc] [value] TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 0] ... 1.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 1] ... 2.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 2] ... 3.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 3] ... 4.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 4] ... 5.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 5] ... 6.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 6] ... 7.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 7] ... 8.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 8] ... 9.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 9] ... 10.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [10] ... 11.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [11] ... 12.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 0 output double 1.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,f0,3f] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1 output double 2.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,00,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 2 output double 3.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,08,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 3 output double 4.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,10,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 4 output double 5.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,14,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 5 output double 6.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,18,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 6 output double 7.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,1c,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 7 output double 8.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,20,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 8 output double 9.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,22,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 9 output double 10.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,24,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 10 output double 11.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,26,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 11 output double 12.000000 = [00,00,00,00,00,00,28,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test=RunCastFloat16ToDouble sum_error=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test=RunCastFloat16ToFloat TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test array: TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1.00000 2.00000 3.00000 4.00000 5.00000 6.00000 7.00000 8.00000 9.00000 10.00000 11.00000 12.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ArrayToFP16: TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 15360 16384 16896 17408 17664 17920 18176 18432 18560 18688 18816 18944 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 0 input value =1.000000 Hex float16 = [00,3c] ushort value=15360 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1 input value =2.000000 Hex float16 = [00,40] ushort value=16384 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 2 input value =3.000000 Hex float16 = [00,42] ushort value=16896 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 3 input value =4.000000 Hex float16 = [00,44] ushort value=17408 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 4 input value =5.000000 Hex float16 = [00,45] ushort value=17664 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 5 input value =6.000000 Hex float16 = [00,46] ushort value=17920 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 6 input value =7.000000 Hex float16 = [00,47] ushort value=18176 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 7 input value =8.000000 Hex float16 = [00,48] ushort value=18432 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 8 input value =9.000000 Hex float16 = [80,48] ushort value=18560 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 9 input value =10.000000 Hex float16 = [00,49] ushort value=18688 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 10 input value =11.000000 Hex float16 = [80,49] ushort value=18816 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 11 input value =12.000000 Hex float16 = [00,4a] ushort value=18944 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX input array: TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [uc] [value] TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 0] ... 15360 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 1] ... 16384 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 2] ... 16896 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 3] ... 17408 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 4] ... 17664 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 5] ... 17920 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 6] ... 18176 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 7] ... 18432 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 8] ... 18560 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 9] ... 18688 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [10] ... 18816 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [11] ... 18944 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX output array: TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [uc] [value] TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 0] ... 1.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 1] ... 2.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 2] ... 3.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 3] ... 4.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 4] ... 5.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 5] ... 6.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 6] ... 7.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 7] ... 8.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 8] ... 9.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 9] ... 10.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [10] ... 11.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [11] ... 12.00000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 0 output float 1.000000 = [00,00,80,3f] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1 output float 2.000000 = [00,00,00,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 2 output float 3.000000 = [00,00,40,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 3 output float 4.000000 = [00,00,80,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 4 output float 5.000000 = [00,00,a0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 5 output float 6.000000 = [00,00,c0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 6 output float 7.000000 = [00,00,e0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 7 output float 8.000000 = [00,00,00,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 8 output float 9.000000 = [00,00,10,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 9 output float 10.000000 = [00,00,20,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 10 output float 11.000000 = [00,00,30,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 11 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test=RunCastFloat16ToFloat sum_error=0.000000
1.1.2. Ausführungstests des ONNX-Cast-Operators für BFLOAT16
In diesem Beispiel wird die Umwandlung von BFLOAT16 in Float untersucht.
ONNX-Modell mit der Operation Cast:
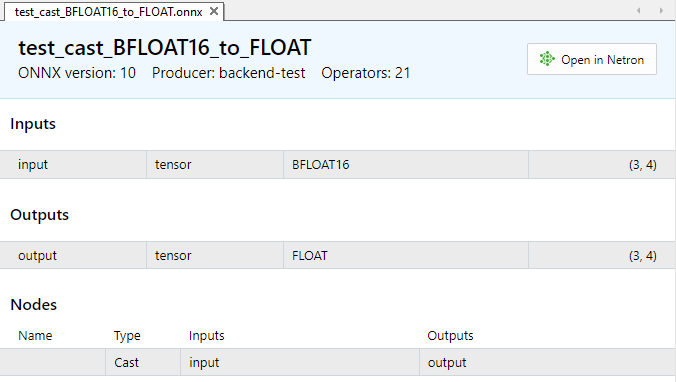
Abb.4. Eingabe- und Ausgabeparameter des Modells test_cast_BFLOAT16_to_FLOAT.onnx
Das Modell verlangt Eingabedaten vom Typ ONNX_DATA_TYPE_BFLOAT16 und gibt Ausgabedaten im Format ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT zurück.
Um die Werte umzuwandeln, verwenden wir die Funktionen ArrayToFP16() und ArrayFromFP16() mit dem Parameter BFLOAT_FP16.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TestCastBFloat16.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #resource "models\\test_cast_BFLOAT16_to_FLOAT.onnx" as const uchar ExtModel1[]; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| union for data conversion | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> union U { uchar uc[sizeof(T)]; T value; }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ArrayToString | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> string ArrayToString(const T &data[],uint length=16) { string res; for(uint n=0; n<MathMin(length,data.Size()); n++) res+="," + StringFormat("%.2x",data[n]); StringSetCharacter(res,0,'['); return res+"]"; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PatchONNXModel | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void PatchONNXModel(const uchar &original_model[],uchar &patched_model[]) { ArrayCopy(patched_model,original_model,0,0,WHOLE_ARRAY); //--- special ONNX model patch(IR=9,Opset=20) patched_model[1]=0x09; patched_model[ArraySize(patched_model)-1]=0x14; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| CreateModel | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CreateModel(long &model_handle,const uchar &model[]) { model_handle=INVALID_HANDLE; ulong flags=ONNX_DEFAULT; //ulong flags=ONNX_DEBUG_LOGS; //--- model_handle=OnnxCreateFromBuffer(model,flags); if(model_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) return(false); //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PrepareShapes | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool PrepareShapes(long model_handle) { ulong input_shape1[]= {3,4}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(model_handle,0,input_shape1)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetInputShape for input1. error code=%d",GetLastError()); //-- OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } //--- ulong output_shape[]= {3,4}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(model_handle,0,output_shape)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetOutputShape for output. error code=%d",GetLastError()); //-- OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| RunCastBFloat16ToFloat | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool RunCastBFloat16ToFloat(long model_handle) { PrintFormat("test=%s",__FUNCTION__); double test_data[12]= {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12}; ushort data_uint16[12]; if(!ArrayToFP16(data_uint16,test_data,FLOAT_BFP16)) { Print("error in ArrayToFP16. error code=",GetLastError()); return(false); } Print("test array:"); ArrayPrint(test_data); Print("ArrayToFP16:"); ArrayPrint(data_uint16); U<ushort> input_float16_values[3*4]; U<float> output_float_values[3*4]; float test_data_float[]; if(!ArrayFromFP16(test_data_float,data_uint16,FLOAT_BFP16)) { Print("error in ArrayFromFP16. error code=",GetLastError()); return(false); } for(int i=0; i<12; i++) { input_float16_values[i].value=data_uint16[i]; PrintFormat("%d input value =%f Hex float16 = %s ushort value=%d",i,test_data_float[i],ArrayToString(input_float16_values[i].uc),input_float16_values[i].value); } Print("ONNX input array:"); ArrayPrint(input_float16_values); bool res=OnnxRun(model_handle,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,input_float16_values,output_float_values); if(!res) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxRun. error code=%d",GetLastError()); return(false); } Print("ONNX output array:"); ArrayPrint(output_float_values); //--- double sum_error=0.0; for(int i=0; i<12; i++) { double delta=test_data[i]-(double)output_float_values[i].value; sum_error+=MathAbs(delta); PrintFormat("%d output float %f = %s difference=%f",i,output_float_values[i].value,ArrayToString(output_float_values[i].uc),delta); } //--- PrintFormat("test=%s sum_error=%f",__FUNCTION__,sum_error); //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnStart(void) { uchar model[]; PatchONNXModel(ExtModel1,model); //--- get model handle long model_handle=INVALID_HANDLE; //--- get model handle if(!CreateModel(model_handle,model)) return 1; //--- prepare input and output shapes if(!PrepareShapes(model_handle)) return 1; //--- run ONNX model if(!RunCastBFloat16ToFloat(model_handle)) return 1; //--- release model handle OnnxRelease(model_handle); //--- return 0; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+Ausgabe:
TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test=RunCastBFloat16ToFloat TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test array: TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1.00000 2.00000 3.00000 4.00000 5.00000 6.00000 7.00000 8.00000 9.00000 10.00000 11.00000 12.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ArrayToFP16: TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 16256 16384 16448 16512 16544 16576 16608 16640 16656 16672 16688 16704 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 0 input value =1.000000 Hex float16 = [80,3f] ushort value=16256 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1 input value =2.000000 Hex float16 = [00,40] ushort value=16384 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 2 input value =3.000000 Hex float16 = [40,40] ushort value=16448 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 3 input value =4.000000 Hex float16 = [80,40] ushort value=16512 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 4 input value =5.000000 Hex float16 = [a0,40] ushort value=16544 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 5 input value =6.000000 Hex float16 = [c0,40] ushort value=16576 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 6 input value =7.000000 Hex float16 = [e0,40] ushort value=16608 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 7 input value =8.000000 Hex float16 = [00,41] ushort value=16640 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 8 input value =9.000000 Hex float16 = [10,41] ushort value=16656 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 9 input value =10.000000 Hex float16 = [20,41] ushort value=16672 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 10 input value =11.000000 Hex float16 = [30,41] ushort value=16688 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 11 input value =12.000000 Hex float16 = [40,41] ushort value=16704 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX input array: TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [uc] [value] TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 0] ... 16256 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 1] ... 16384 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 2] ... 16448 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 3] ... 16512 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 4] ... 16544 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 5] ... 16576 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 6] ... 16608 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 7] ... 16640 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 8] ... 16656 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 9] ... 16672 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [10] ... 16688 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [11] ... 16704 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX output array: TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [uc] [value] TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 0] ... 1.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 1] ... 2.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 2] ... 3.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 3] ... 4.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 4] ... 5.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 5] ... 6.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 6] ... 7.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 7] ... 8.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 8] ... 9.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [ 9] ... 10.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [10] ... 11.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) [11] ... 12.00000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 0 output float 1.000000 = [00,00,80,3f] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 1 output float 2.000000 = [00,00,00,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 2 output float 3.000000 = [00,00,40,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 3 output float 4.000000 = [00,00,80,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 4 output float 5.000000 = [00,00,a0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 5 output float 6.000000 = [00,00,c0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 6 output float 7.000000 = [00,00,e0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 7 output float 8.000000 = [00,00,00,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 8 output float 9.000000 = [00,00,10,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 9 output float 10.000000 = [00,00,20,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 10 output float 11.000000 = [00,00,30,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) 11 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastBFloat16 (EURUSD,H1) test=RunCastBFloat16ToFloat sum_error=0.000000
1.2. FP8-Format
Moderne Sprachmodelle können Milliarden von Parametern enthalten. Das Training von Modellen mit FP16-Nummern hat sich bereits bewährt. Die Umstellung von 16-Bit-Gleitkommazahlen auf FP8 ermöglicht eine Halbierung des Speicherbedarfs und eine Beschleunigung des Trainings und der Modellausführung.
Das FP8-Format (8-Bit-Gleitkommazahl) ist einer der Datentypen, die zur Darstellung von Gleitkommazahlen verwendet werden. Im FP8 wird jede Zahl durch 8 Datenbits dargestellt, die in der Regel in drei Komponenten aufgeteilt sind: Vorzeichen, Exponent und Mantisse. Dieses Format bietet einen Kompromiss zwischen Genauigkeit und Speichereffizienz, was es für Anwendungen interessant macht, bei denen Speicher- und Rechenressourcen gespart werden müssen.
Einer der Hauptvorteile des RP8 ist seine Effizienz bei der Verarbeitung großer Datenmengen. Dank seiner kompakten Zahlendarstellung reduziert FP8 den Speicherbedarf und beschleunigt Berechnungen. Dies ist besonders wichtig bei Anwendungen des maschinellen Lernens und der künstlichen Intelligenz, wo die Verarbeitung großer Datensätze üblich ist.
Außerdem kann FP8 für die Implementierung von Low-Level-Operationen wie arithmetische Berechnungen und Signalverarbeitung nützlich sein. Durch sein kompaktes Format eignet es sich für den Einsatz in eingebetteten Systemen und Anwendungen, bei denen die Ressourcen begrenzt sind. Es ist jedoch darauf hinzuweisen, dass das RP8 aufgrund seiner begrenzten Präzision seine Grenzen hat. Bei einigen Anwendungen, die hochpräzise Berechnungen erfordern, wie z. B. bei wissenschaftlichen Berechnungen oder Finanzanalysen, kann die Verwendung des RP8 unzureichend sein.
1.2.1. FP8-Formate fp8_e5m2 und fp8_e4m3
Im Jahr 2022 wurden zwei Artikel veröffentlicht, in denen Gleitkommazahlen vorgestellt wurden, die in einem Byte gespeichert werden, im Gegensatz zu float32-Zahlen, die in 4 Byte gespeichert werden.
In dem Artikel „FP8 Formats for Deep Learning“ (2022) von NVIDIA, Intel und ARM werden zwei Typen vorgestellt, die den IEEE-Spezifikationen folgen. Der erste Typ ist E4M3, mit 1 Bit für das Vorzeichen, 4 Bit für den Exponenten und 3 Bit für die Mantisse. Der zweite Typ ist E5M2, mit 1 Bit für das Vorzeichen, 5 Bit für den Exponenten und 2 Bit für die Mantisse. Der erste Typ wird in der Regel für Gewichte verwendet, der zweite für Farbverläufe.
Der zweite Artikel, „8-bit Numerical Formats For Deep Neural Networks“, stellt ähnliche Typen vor. Der IEEE-Standard weist +0 (oder Ganzzahl 0) und -0 (oder Ganzzahl 128) denselben Wert zu. In dem Artikel wird vorgeschlagen, diesen beiden Zahlen unterschiedliche Float-Werte zuzuordnen. Außerdem werden verschiedene Teilungen zwischen Exponent und Mantisse untersucht, wobei sich E4M3 und E5M2 als die besten herausstellen.
Infolgedessen hat ONNX 4 neue Typen eingeführt (ab Version 1.15.0):
- E4M3FN: 1 Bit für das Vorzeichen, 4 Bit für den Exponenten, 3 Bit für die Mantisse, nur NaN-Werte und keine unendlichen Werte (FN).
- E4M3FNUZ: 1 Bit für das Vorzeichen, 4 Bit für den Exponenten, 3 Bit für die Mantisse, nur NaN-Werte und keine unendlichen Werte (FN), keine negative Null (UZ).
- E5M2: 1 Bit für das Vorzeichen, 5 Bit für den Exponenten, 2 Bit für die Mantisse.
- E5M2FNUZ: 1 Bit für das Vorzeichen, 5 Bit für den Exponenten, 2 Bit für die Mantisse, nur NaN-Werte und keine unendlichen Werte (FN), keine negative Null (UZ).
Die Implementierung hängt in der Regel von der Hardware ab. NVIDIA, Intel und Arm implementieren E4M3FN, während E5M2 in modernen Grafikprozessoren implementiert ist. GraphCore macht dasselbe, aber mit E4M3FNUZ und E5M2FNUZ.
Hier eine kurze Zusammenfassung der wichtigsten Informationen über den Typ FP8 gemäß dem Artikel NVIDIA Hopper: H100 und FP8 Unterstützung.
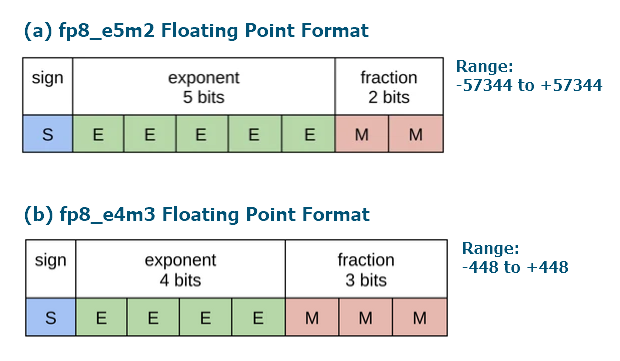
Abb. 5. Bit-Darstellung der FP8-Formate
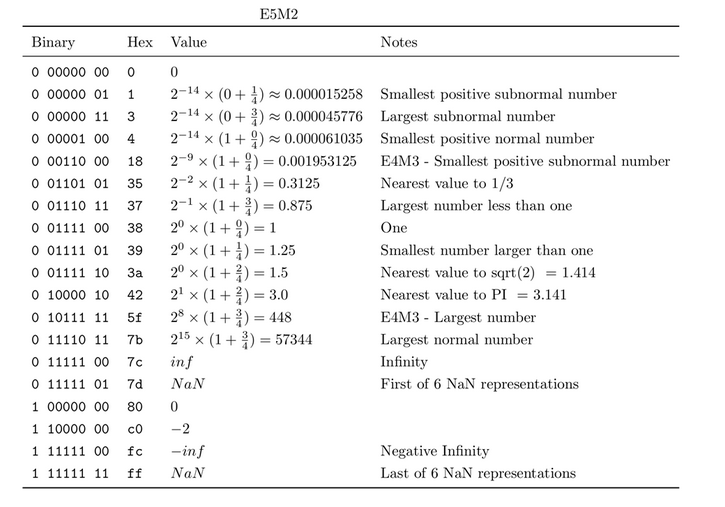
Tabelle 3. Fließkommazahlen im E5M2-Format
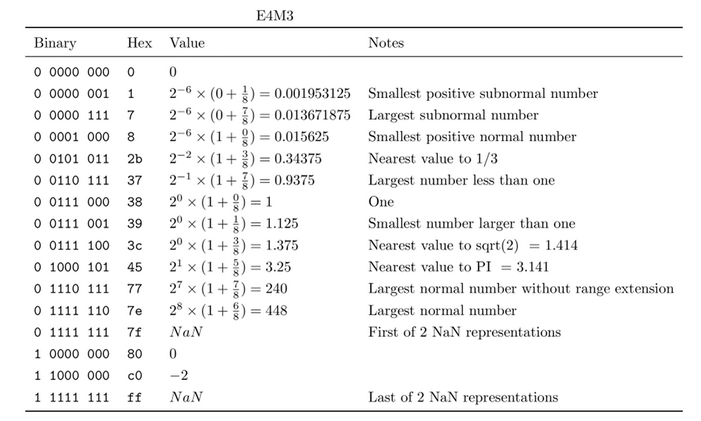
Tabelle 4. Fließkommazahlen im E4M3-Format
Ein Vergleich der Bereiche der positiven Werte von FP8_E4M3 und FP8_E5M2 ist in Abbildung 6 dargestellt.
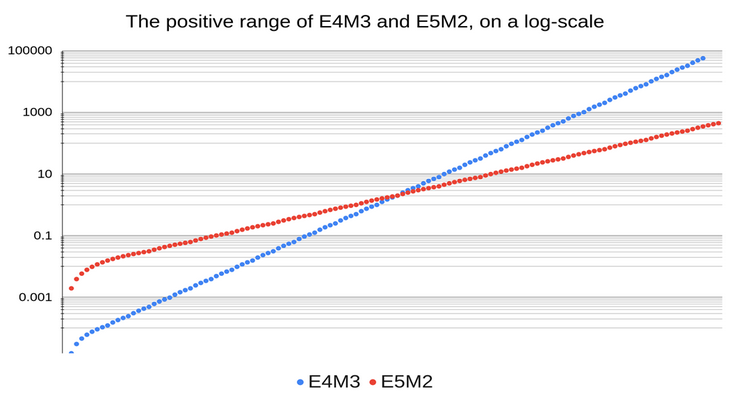
Abb. 6. Vergleich der Bereiche für positive FP8-Nummern (Referenz)
Ein Vergleich der Genauigkeit der arithmetischen Operationen (Add, Mul, Div) für Zahlen in den Formaten FP8_E5M2 und FP8_E4M3 ist in Abbildung 7 dargestellt.
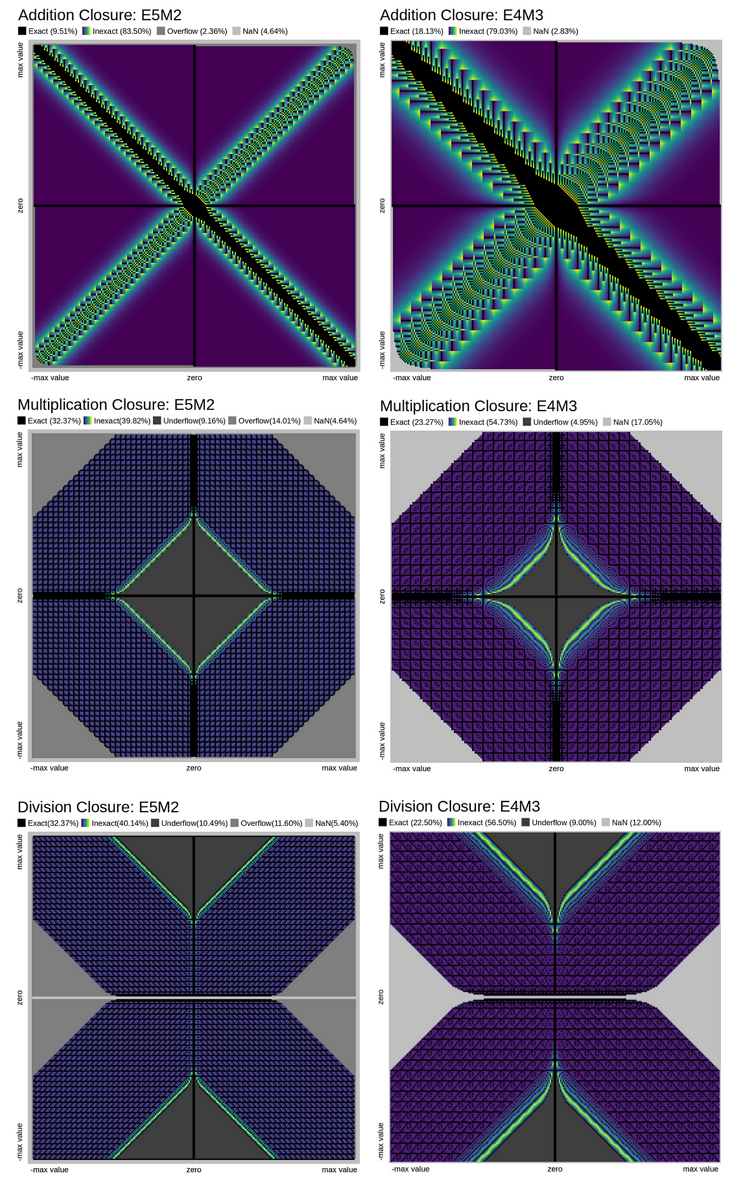
Abb. 7. Vergleich der Genauigkeit der arithmetischen Operationen für Zahlen in den Formaten float8_e5m2 und float8_e4m3 (Referenz)
Empfohlene Verwendung von Zahlen im FP8-Format:
- E4M3 für Gewichts- und Aktivierungstensoren;
- E5M2 für Gradiententensoren.
1.2.2. Ausführungstests des ONNX-Operators Cast für FLOAT8
In diesem Beispiel geht es um die Umwandlung von verschiedenen FLOAT8-Typen in Float.
ONNX-Modelle mit dem Cast-Verfahren:
- https://github.com/onnx/onnx/tree/main/onnx/backend/test/data/node/test_cast_FLOAT8E4M3FN_to_FLOAT.onnx
- https://github.com/onnx/onnx/tree/main/onnx/backend/test/data/node/test_cast_FLOAT8E4M3FNUZ_to_FLOAT.onnx
- https://github.com/onnx/onnx/tree/main/onnx/backend/test/data/node/test_cast_FLOAT8E5M2_to_FLOAT.onnx
- https://github.com/onnx/onnx/tree/main/onnx/backend/test/data/node/test_cast_FLOAT8E5M2FNUZ_to_FLOAT.onnx
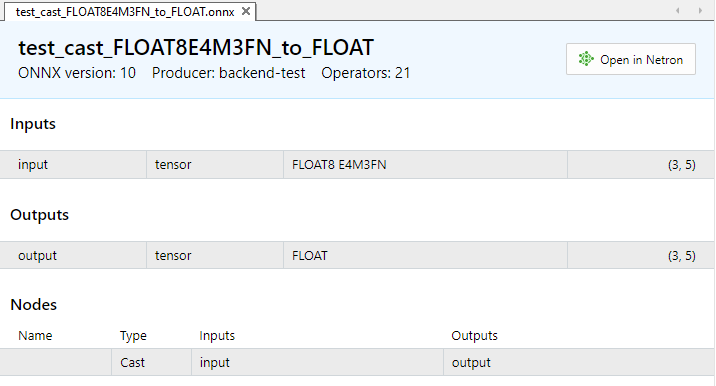
Abb. 8. Eingabe- und Ausgabeparameter des Modells test_cast_FLOAT8E4M3FN_to_FLOAT.onnx in MetaEditor
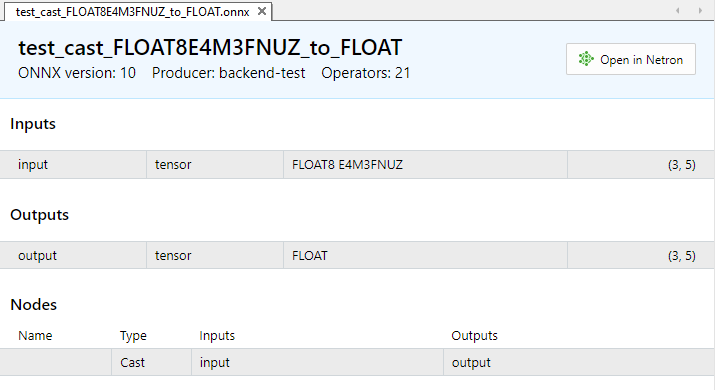
Abb. 9. Eingabe- und Ausgabeparameter des Modells test_cast_FLOAT8E4M3FNUZ_to_FLOAT.onnx in MetaEditor
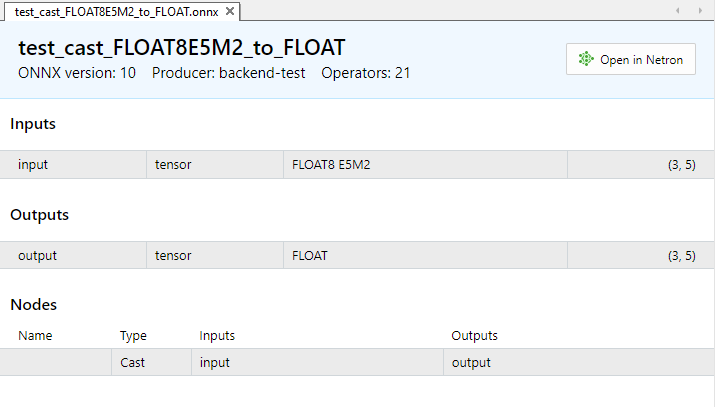
Abb.10. Eingabe- und Ausgabeparameter des Modells test_cast_FLOAT8E5M2_to_FLOAT.onnx in MetaEditor
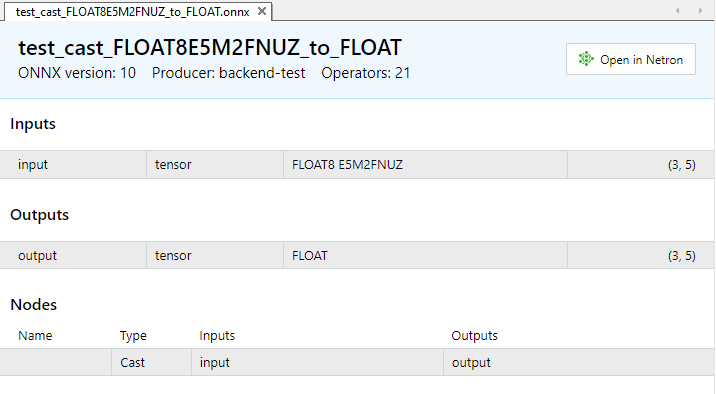
Abb.11. Eingabe- und Ausgabeparameter des Modells test_cast_FLOAT8E5M2FNUZ_to_FLOAT.onnx in MetaEditor
Beispiel:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TestCastBFloat8.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #resource "models\\test_cast_FLOAT8E4M3FN_to_FLOAT.onnx" as const uchar ExtModel_FLOAT8E4M3FN_to_FLOAT[]; #resource "models\\test_cast_FLOAT8E4M3FNUZ_to_FLOAT.onnx" as const uchar ExtModel_FLOAT8E4M3FNUZ_to_FLOAT[]; #resource "models\\test_cast_FLOAT8E5M2_to_FLOAT.onnx" as const uchar ExtModel_FLOAT8E5M2_to_FLOAT[]; #resource "models\\test_cast_FLOAT8E5M2FNUZ_to_FLOAT.onnx" as const uchar ExtModel_FLOAT8E5M2FNUZ_to_FLOAT[]; #define TEST_PASSED 0 #define TEST_FAILED 1 //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| union for data conversion | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> union U { uchar uc[sizeof(T)]; T value; }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ArrayToHexString | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> string ArrayToHexString(const T &data[],uint length=16) { string res; for(uint n=0; n<MathMin(length,data.Size()); n++) res+="," + StringFormat("%.2x",data[n]); StringSetCharacter(res,0,'['); return(res+"]"); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ArrayToString | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> string ArrayToString(const U<T> &data[],uint length=16) { string res; for(uint n=0; n<MathMin(length,data.Size()); n++) res+="," + (string)data[n].value; StringSetCharacter(res,0,'['); return(res+"]"); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PatchONNXModel | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ long CreatePatchedModel(const uchar &original_model[]) { uchar patched_model[]; ArrayCopy(patched_model,original_model); //--- special ONNX model patch(IR=9,Opset=20) patched_model[1]=0x09; patched_model[ArraySize(patched_model)-1]=0x14; return(OnnxCreateFromBuffer(patched_model,ONNX_DEFAULT)); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PrepareShapes | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool PrepareShapes(long model_handle) { //--- configure input shape ulong input_shape[]= {3,5}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(model_handle,0,input_shape)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetInputShape for input1. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } //--- configure output shape ulong output_shape[]= {3,5}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(model_handle,0,output_shape)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetOutputShape for output. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| RunCastFloat8Float | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool RunCastFloat8ToFloat(long model_handle,const ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT fmt) { PrintFormat("TEST: %s(%s)",__FUNCTION__,EnumToString(fmt)); //--- float test_data[15] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15}; uchar data_float8[15] = {}; if(!ArrayToFP8(data_float8,test_data,fmt)) { Print("error in ArrayToFP8. error code=",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } U<uchar> input_float8_values[3*5]; U<float> output_float_values[3*5]; float test_data_float[]; //--- convert float8 to float if(!ArrayFromFP8(test_data_float,data_float8,fmt)) { Print("error in ArrayFromFP8. error code=",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } for(uint i=0; i<data_float8.Size(); i++) { input_float8_values[i].value=data_float8[i]; PrintFormat("%d input value =%f Hex float8 = %s ushort value=%d",i,test_data_float[i],ArrayToHexString(input_float8_values[i].uc),input_float8_values[i].value); } Print("ONNX input array: ",ArrayToString(input_float8_values)); //--- execute model (convert float8 to float using ONNX) if(!OnnxRun(model_handle,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,input_float8_values,output_float_values)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxRun. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(false); } Print("ONNX output array: ",ArrayToString(output_float_values)); //--- calculate error (compare ONNX and ArrayFromFP8 results) double sum_error=0.0; for(uint i=0; i<test_data.Size(); i++) { double delta=test_data_float[i]-(double)output_float_values[i].value; sum_error+=MathAbs(delta); PrintFormat("%d output float %f = %s difference=%f",i,output_float_values[i].value,ArrayToHexString(output_float_values[i].uc),delta); } //--- PrintFormat("%s(%s): sum_error=%f\n",__FUNCTION__,EnumToString(fmt),sum_error); return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TestModel | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool TestModel(const uchar &model[],const ENUM_FLOAT8_FORMAT fmt) { //--- create patched model long model_handle=CreatePatchedModel(model); if(model_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) return(false); //--- prepare input and output shapes if(!PrepareShapes(model_handle)) return(false); //--- run ONNX model if(!RunCastFloat8ToFloat(model_handle,fmt)) return(false); //--- release model handle OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnStart(void) { //--- run ONNX model if(!TestModel(ExtModel_FLOAT8E4M3FN_to_FLOAT,FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FN)) return(TEST_FAILED); //--- run ONNX model if(!TestModel(ExtModel_FLOAT8E4M3FNUZ_to_FLOAT,FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FNUZ)) return(TEST_FAILED); //--- run ONNX model if(!TestModel(ExtModel_FLOAT8E5M2_to_FLOAT,FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FN)) return(TEST_FAILED); //--- run ONNX model if(!TestModel(ExtModel_FLOAT8E5M2FNUZ_to_FLOAT,FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FNUZ)) return(TEST_FAILED); return(TEST_PASSED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+Ausgabe:
TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) TEST: RunCastFloat8ToFloat(FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FN) TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 0 input value =1.000000 Hex float8 = [38] ushort value=56 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 1 input value =2.000000 Hex float8 = [40] ushort value=64 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 2 input value =3.000000 Hex float8 = [44] ushort value=68 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 3 input value =4.000000 Hex float8 = [48] ushort value=72 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 4 input value =5.000000 Hex float8 = [4a] ushort value=74 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 5 input value =6.000000 Hex float8 = [4c] ushort value=76 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 6 input value =7.000000 Hex float8 = [4e] ushort value=78 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 7 input value =8.000000 Hex float8 = [50] ushort value=80 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 8 input value =9.000000 Hex float8 = [51] ushort value=81 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 9 input value =10.000000 Hex float8 = [52] ushort value=82 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 10 input value =11.000000 Hex float8 = [53] ushort value=83 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 11 input value =12.000000 Hex float8 = [54] ushort value=84 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 12 input value =13.000000 Hex float8 = [55] ushort value=85 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 13 input value =14.000000 Hex float8 = [56] ushort value=86 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 14 input value =15.000000 Hex float8 = [57] ushort value=87 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX input array: [56,64,68,72,74,76,78,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87] TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX output array: [1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0,7.0,8.0,9.0,10.0,11.0,12.0,13.0,14.0,15.0] TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 0 output float 1.000000 = [00,00,80,3f] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 1 output float 2.000000 = [00,00,00,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 2 output float 3.000000 = [00,00,40,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 3 output float 4.000000 = [00,00,80,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 4 output float 5.000000 = [00,00,a0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 5 output float 6.000000 = [00,00,c0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 6 output float 7.000000 = [00,00,e0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 7 output float 8.000000 = [00,00,00,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 8 output float 9.000000 = [00,00,10,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 9 output float 10.000000 = [00,00,20,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 10 output float 11.000000 = [00,00,30,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 11 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 12 output float 13.000000 = [00,00,50,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 13 output float 14.000000 = [00,00,60,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 14 output float 15.000000 = [00,00,70,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) RunCastFloat8ToFloat(FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FN): sum_error=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) TEST: RunCastFloat8ToFloat(FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FNUZ) TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 0 input value =1.000000 Hex float8 = [40] ushort value=64 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 1 input value =2.000000 Hex float8 = [48] ushort value=72 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 2 input value =3.000000 Hex float8 = [4c] ushort value=76 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 3 input value =4.000000 Hex float8 = [50] ushort value=80 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 4 input value =5.000000 Hex float8 = [52] ushort value=82 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 5 input value =6.000000 Hex float8 = [54] ushort value=84 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 6 input value =7.000000 Hex float8 = [56] ushort value=86 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 7 input value =8.000000 Hex float8 = [58] ushort value=88 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 8 input value =9.000000 Hex float8 = [59] ushort value=89 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 9 input value =10.000000 Hex float8 = [5a] ushort value=90 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 10 input value =11.000000 Hex float8 = [5b] ushort value=91 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 11 input value =12.000000 Hex float8 = [5c] ushort value=92 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 12 input value =13.000000 Hex float8 = [5d] ushort value=93 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 13 input value =14.000000 Hex float8 = [5e] ushort value=94 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 14 input value =15.000000 Hex float8 = [5f] ushort value=95 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX input array: [64,72,76,80,82,84,86,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95] TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX output array: [1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0,7.0,8.0,9.0,10.0,11.0,12.0,13.0,14.0,15.0] TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 0 output float 1.000000 = [00,00,80,3f] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 1 output float 2.000000 = [00,00,00,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 2 output float 3.000000 = [00,00,40,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 3 output float 4.000000 = [00,00,80,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 4 output float 5.000000 = [00,00,a0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 5 output float 6.000000 = [00,00,c0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 6 output float 7.000000 = [00,00,e0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 7 output float 8.000000 = [00,00,00,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 8 output float 9.000000 = [00,00,10,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 9 output float 10.000000 = [00,00,20,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 10 output float 11.000000 = [00,00,30,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 11 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 12 output float 13.000000 = [00,00,50,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 13 output float 14.000000 = [00,00,60,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 14 output float 15.000000 = [00,00,70,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) RunCastFloat8ToFloat(FLOAT_FP8_E4M3FNUZ): sum_error=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) TEST: RunCastFloat8ToFloat(FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FN) TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 0 input value =1.000000 Hex float8 = [3c] ushort value=60 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 1 input value =2.000000 Hex float8 = [40] ushort value=64 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 2 input value =3.000000 Hex float8 = [42] ushort value=66 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 3 input value =4.000000 Hex float8 = [44] ushort value=68 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 4 input value =5.000000 Hex float8 = [45] ushort value=69 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 5 input value =6.000000 Hex float8 = [46] ushort value=70 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 6 input value =7.000000 Hex float8 = [47] ushort value=71 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 7 input value =8.000000 Hex float8 = [48] ushort value=72 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 8 input value =8.000000 Hex float8 = [48] ushort value=72 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 9 input value =10.000000 Hex float8 = [49] ushort value=73 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 10 input value =12.000000 Hex float8 = [4a] ushort value=74 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 11 input value =12.000000 Hex float8 = [4a] ushort value=74 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 12 input value =12.000000 Hex float8 = [4a] ushort value=74 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 13 input value =14.000000 Hex float8 = [4b] ushort value=75 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 14 input value =16.000000 Hex float8 = [4c] ushort value=76 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX input array: [60,64,66,68,69,70,71,72,72,73,74,74,74,75,76] TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX output array: [1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0,7.0,8.0,8.0,10.0,12.0,12.0,12.0,14.0,16.0] TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 0 output float 1.000000 = [00,00,80,3f] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 1 output float 2.000000 = [00,00,00,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 2 output float 3.000000 = [00,00,40,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 3 output float 4.000000 = [00,00,80,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 4 output float 5.000000 = [00,00,a0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 5 output float 6.000000 = [00,00,c0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 6 output float 7.000000 = [00,00,e0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 7 output float 8.000000 = [00,00,00,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 8 output float 8.000000 = [00,00,00,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 9 output float 10.000000 = [00,00,20,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 10 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 11 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 12 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 13 output float 14.000000 = [00,00,60,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 14 output float 16.000000 = [00,00,80,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) RunCastFloat8ToFloat(FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FN): sum_error=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) TEST: RunCastFloat8ToFloat(FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FNUZ) TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 0 input value =1.000000 Hex float8 = [40] ushort value=64 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 1 input value =2.000000 Hex float8 = [44] ushort value=68 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 2 input value =3.000000 Hex float8 = [46] ushort value=70 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 3 input value =4.000000 Hex float8 = [48] ushort value=72 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 4 input value =5.000000 Hex float8 = [49] ushort value=73 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 5 input value =6.000000 Hex float8 = [4a] ushort value=74 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 6 input value =7.000000 Hex float8 = [4b] ushort value=75 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 7 input value =8.000000 Hex float8 = [4c] ushort value=76 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 8 input value =8.000000 Hex float8 = [4c] ushort value=76 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 9 input value =10.000000 Hex float8 = [4d] ushort value=77 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 10 input value =12.000000 Hex float8 = [4e] ushort value=78 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 11 input value =12.000000 Hex float8 = [4e] ushort value=78 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 12 input value =12.000000 Hex float8 = [4e] ushort value=78 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 13 input value =14.000000 Hex float8 = [4f] ushort value=79 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 14 input value =16.000000 Hex float8 = [50] ushort value=80 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX input array: [64,68,70,72,73,74,75,76,76,77,78,78,78,79,80] TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) ONNX output array: [1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0,7.0,8.0,8.0,10.0,12.0,12.0,12.0,14.0,16.0] TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 0 output float 1.000000 = [00,00,80,3f] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 1 output float 2.000000 = [00,00,00,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 2 output float 3.000000 = [00,00,40,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 3 output float 4.000000 = [00,00,80,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 4 output float 5.000000 = [00,00,a0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 5 output float 6.000000 = [00,00,c0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 6 output float 7.000000 = [00,00,e0,40] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 7 output float 8.000000 = [00,00,00,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 8 output float 8.000000 = [00,00,00,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 9 output float 10.000000 = [00,00,20,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 10 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 11 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 12 output float 12.000000 = [00,00,40,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 13 output float 14.000000 = [00,00,60,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) 14 output float 16.000000 = [00,00,80,41] difference=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1) RunCastFloat8ToFloat(FLOAT_FP8_E5M2FNUZ): sum_error=0.000000 TestCastFloat8 (EURUSD,H1)
2. Verwendung von ONNX für die Super-Resolution von Bildern
In diesem Abschnitt werden wir ein Beispiel für die Verwendung von SRGAN-Modellen zur Verbesserung der Bildauflösung untersuchen.
ESRGAN (Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Networks) ist eine leistungsstarke neuronale Netzarchitektur, die für die Aufgabe der Super-Resolution von Bildern entwickelt wurde. ESRGAN wurde entwickelt, um die Bildqualität durch Erhöhung der Auflösung zu verbessern. Dies wird erreicht, indem ein tiefes neuronales Netz auf einem großen Datensatz von Bildern mit niedriger Auflösung und den entsprechenden Bildern mit hoher Qualität trainiert wird. ESRGAN verwendet die Architektur von Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), die aus zwei Hauptkomponenten besteht: einem Generator und einem Diskriminator. Der Generator ist für die Erzeugung hochauflösender Bilder zuständig, während der Diskriminator darauf trainiert ist, zwischen den erzeugten Bildern und den echten Bildern zu unterscheiden.
Das Herzstück der ESRGAN-Architektur sind Restblöcke, die dazu beitragen, wichtige Bildmerkmale auf verschiedenen Abstraktionsebenen zu extrahieren und zu erhalten. Dadurch kann das Netzwerk Details und Texturen in hochwertigen Bildern effizient wiederherstellen.
Um eine hohe Qualität und Universalität bei der Lösung der Super-Resolution-Aufgabe zu erreichen, benötigt ESRGAN umfangreiche Trainingsdatensätze. Auf diese Weise kann das Netz verschiedene Stile und Merkmale von Bildern erlernen, was es anpassungsfähiger für verschiedene Arten von Eingabedaten macht. ESRGAN kann zur Verbesserung der Bildqualität in vielen Bereichen eingesetzt werden, z. B. in der Fotografie, der medizinischen Diagnostik, der Film- und Videoproduktion, dem Grafikdesign und vielen mehr. Ihre Flexibilität und Effizienz machen sie zu einer der führenden Methoden auf dem Gebiet der Super-Resolution.
ESRGAN stellt einen bedeutenden Fortschritt auf dem Gebiet der Bildverarbeitung und der künstlichen Intelligenz dar und eröffnet neue Möglichkeiten für die Erstellung und Verbesserung von Bildern.
2.1. Ausführen eines ONNX-Modells mit float32
Um das Beispiel auszuführen, müssen Sie die Datei https://github.com/amannm/super-resolution-service/blob/main/models/esrgan.onnx herunterladen und sie in den Ordner \MQL5\Scripts\models kopieren.
Das Modell ESRGAN.onnx enthält ~1200 ONNX-Operationen, von denen die ersten in Abb.12 dargestellt sind.
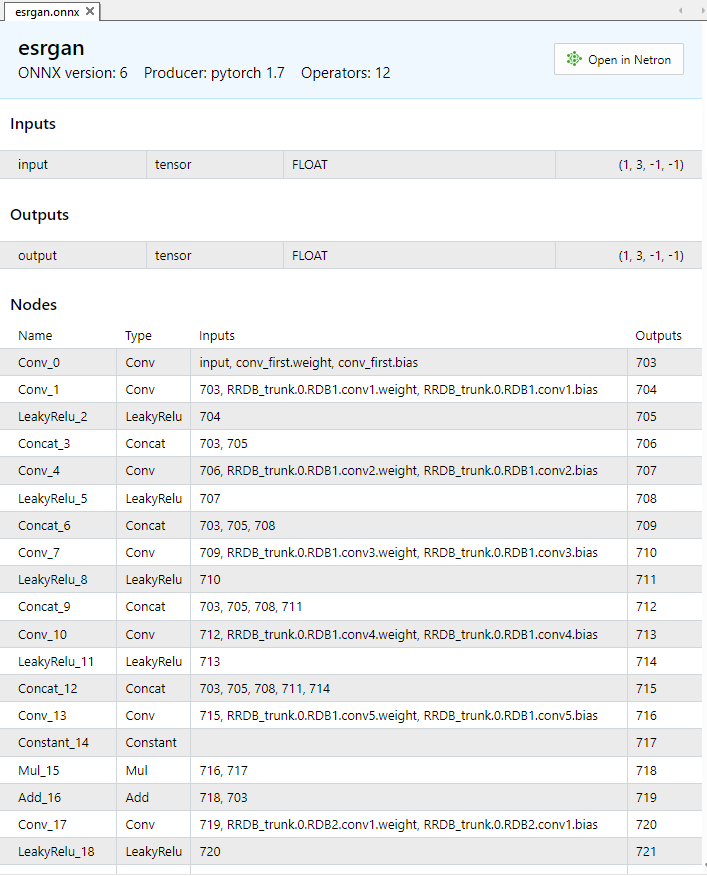
Abb.12. ESRGAN.onnx Modellbeschreibung in MetaEditor
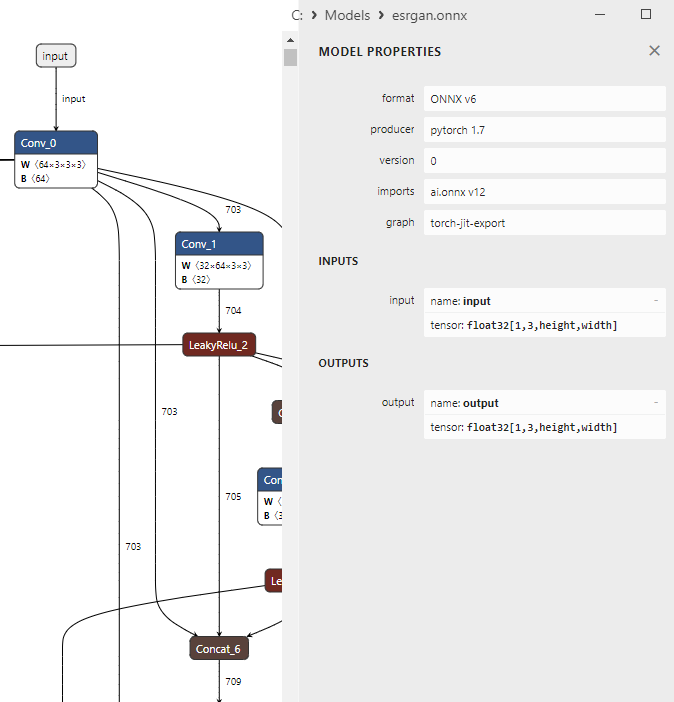
Abb.13. ESRGAN.ONNX-Modell in Netron
Zunächst wird das Modell esrgan.onnx geladen, dann wird das Originalbild im BMP-Format ausgewählt und geladen. Danach wird das Bild in einzelne RGB-Kanäle umgewandelt, die dann als Eingabe in das Modell eingespeist werden. Das Modell führt eine Hochskalierung des Bildes um den Faktor 4 durch, woraufhin das hochskalierte Bild einer inversen Transformation unterzogen und für die Anzeige vorbereitet wird.
Die Canvas-Bibliothek wird für die Anzeige und die ONNX Runtime-Bibliothek für die Modellausführung verwendet. Bei der Ausführung des Programms wird das hochskalierte Bild in einer Datei gespeichert, wobei an den ursprünglichen Dateinamen „_upscaled“ angehängt wird. Zu den Schlüsselfunktionen gehören die Bildvor- und -nachbearbeitung sowie die Modellausführung für die Hochskalierung von Bildern.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ESRGAN.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| 4x image upscaling demo using ESRGAN | //| esrgan.onnx model from | //| https://github.com/amannm/super-resolution-service/ | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Xintao Wang et al (2018) | //| ESRGAN: Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Networks| //| https://arxiv.org/abs/1809.00219 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #resource "models\\esrgan.onnx" as uchar ExtModel[]; #include <Canvas\Canvas.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| clamp | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ float clamp(float value, float minValue, float maxValue) { return MathMin(MathMax(value, minValue), maxValue); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Preprocessing | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool Preprocessing(float &data[],uint &image_data[],int &image_width,int &image_height) { //--- checkup if(image_height==0 || image_width==0) return(false); //--- prepare destination array with separated RGB channels for ONNX model int data_count=3*image_width*image_height; if(ArrayResize(data,data_count)!=data_count) { Print("ArrayResize failed"); return(false); } //--- converting for(int y=0; y<image_height; y++) for(int x=0; x<image_width; x++) { //--- load source RGB int offset=y*image_width+x; uint clr =image_data[offset]; uchar r =GETRGBR(clr); uchar g =GETRGBG(clr); uchar b =GETRGBB(clr); //--- store RGB components as separated channels int offset_ch1=0*image_width*image_height+offset; int offset_ch2=1*image_width*image_height+offset; int offset_ch3=2*image_width*image_height+offset; data[offset_ch1]=r/255.0f; data[offset_ch2]=g/255.0f; data[offset_ch3]=b/255.0f; } //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PostProcessing | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool PostProcessing(const float &data[], uint &image_data[], const int &image_width, const int &image_height) { //--- checks if(image_height == 0 || image_width == 0) return(false); int data_count=image_width*image_height; if(ArraySize(data)!=3*data_count) return(false); if(ArrayResize(image_data,data_count)!=data_count) return(false); //--- for(int y=0; y<image_height; y++) for(int x=0; x<image_width; x++) { int offset =y*image_width+x; int offset_ch1=0*image_width*image_height+offset; int offset_ch2=1*image_width*image_height+offset; int offset_ch3=2*image_width*image_height+offset; //--- rescale to [0..255] float r=clamp(data[offset_ch1]*255,0,255); float g=clamp(data[offset_ch2]*255,0,255); float b=clamp(data[offset_ch3]*255,0,255); //--- set color image_data image_data[offset]=XRGB(uchar(r),uchar(g),uchar(b)); } //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ShowImage | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool ShowImage(CCanvas &canvas,const string name,const int x0,const int y0,const int image_width,const int image_height, const uint &image_data[]) { if(ArraySize(image_data)==0 || name=="") return(false); //--- prepare canvas canvas.CreateBitmapLabel(name,x0,y0,image_width,image_height,COLOR_FORMAT_XRGB_NOALPHA); //--- copy image to canvas for(int y=0; y<image_height; y++) for(int x=0; x<image_width; x++) canvas.PixelSet(x,y,image_data[y*image_width+x]); //--- ready to draw canvas.Update(true); return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnStart(void) { //--- select BMP from <data folder>\MQL5\Files string image_path[1]; if(FileSelectDialog("Select BMP image",NULL,"Bitmap files (*.bmp)|*.bmp",FSD_FILE_MUST_EXIST,image_path,"lenna-original4.bmp")!=1) { Print("file not selected"); return(-1); } //--- load BMP into array uint image_data[]; int image_width; int image_height; if(!CCanvas::LoadBitmap(image_path[0],image_data,image_width,image_height)) { PrintFormat("CCanvas::LoadBitmap failed with error %d",GetLastError()); return(-1); } //--- convert RGB image to separated RGB channels float input_data[]; Preprocessing(input_data,image_data,image_width,image_height); PrintFormat("input array size=%d",ArraySize(input_data)); //--- load model long model_handle=OnnxCreateFromBuffer(ExtModel,ONNX_DEFAULT); if(model_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) { PrintFormat("OnnxCreate error %d",GetLastError()); return(-1); } PrintFormat("model loaded successfully"); PrintFormat("original: width=%d, height=%d Size=%d",image_width,image_height,ArraySize(image_data)); //--- set input shape ulong input_shape[]={1,3,image_height,image_width}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(model_handle,0,input_shape)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetInputShape. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(-1); } //--- upscaled image size int new_image_width =4*image_width; int new_image_height=4*image_height; ulong output_shape[]= {1,3,new_image_height,new_image_width}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(model_handle,0,output_shape)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetOutputShape. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(-1); } //--- run the model float output_data[]; int new_data_count=3*new_image_width*new_image_height; if(ArrayResize(output_data,new_data_count)!=new_data_count) { OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(-1); } if(!OnnxRun(model_handle,ONNX_DEBUG_LOGS,input_data,output_data)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxRun. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(-1); } Print("model successfully executed, output data size ",ArraySize(output_data)); OnnxRelease(model_handle); //--- postprocessing uint new_image[]; PostProcessing(output_data,new_image,new_image_width,new_image_height); //--- show images CCanvas canvas_original,canvas_scaled; ShowImage(canvas_original,"original_image",new_image_width,0,image_width,image_height,image_data); ShowImage(canvas_scaled,"upscaled_image",0,0,new_image_width,new_image_height,new_image); //--- save upscaled image StringReplace(image_path[0],".bmp","_upscaled.bmp"); Print(ResourceSave(canvas_scaled.ResourceName(),image_path[0])); //--- while(!IsStopped()) Sleep(100); return(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Ausgabe:
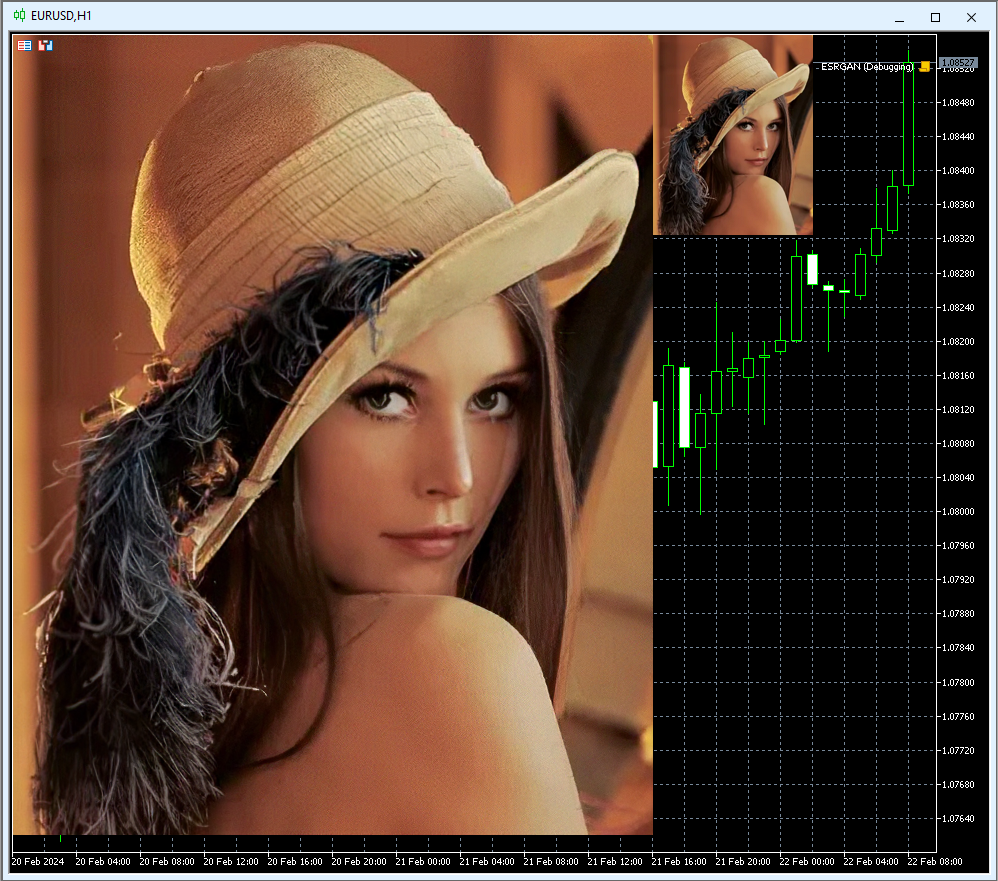
Abb.14. Das Ergebnis der Ausführung des Modells ESRGAN.onnx (160x200 -> 640x800)
In diesem Beispiel wurde das kleine Bild mit 160x200 durch das Modell ESRGAN.onnx auf das Vierfache vergrößert (auf 640x800).
2.2. Beispiel für die Ausführung eines ONNX-Modells mit float16
Um Modelle in float16 zu konvertieren, verwenden wir die in Create Float16 and Mixed Precision Models beschriebene Methode.
# Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. # https://www.mql5.com import onnx from onnxconverter_common import float16 from sys import argv # Define the path for saving the model data_path = argv[0] last_index = data_path.rfind("\\") + 1 data_path = data_path[0:last_index] # convert the model to float16 model_path = data_path+'\\models\\esrgan.onnx' modelfp16_path = data_path+'\\models\\esrgan_float16.onnx' model = onnx.load(model_path) model_fp16 = float16.convert_float_to_float16(model) onnx.save(model_fp16, modelfp16_path)
Nach der Konvertierung hat sich die Dateigröße halbiert (von 64 MB auf 32 MB).
Die Änderungen im Code sind minimal.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ESRGAN_float16.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| 4x image upscaling demo using ESRGAN | //| esrgan.onnx model from | //| https://github.com/amannm/super-resolution-service/ | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Xintao Wang et al (2018) | //| ESRGAN: Enhanced Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Networks| //| https://arxiv.org/abs/1809.00219 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #resource "models\\esrgan_float16.onnx" as uchar ExtModel[]; #include <Canvas\Canvas.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| clamp | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ float clamp(float value, float minValue, float maxValue) { return MathMin(MathMax(value, minValue), maxValue); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Preprocessing | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool Preprocessing(float &data[],uint &image_data[],int &image_width,int &image_height) { //--- checkup if(image_height==0 || image_width==0) return(false); //--- prepare destination array with separated RGB channels for ONNX model int data_count=3*image_width*image_height; if(ArrayResize(data,data_count)!=data_count) { Print("ArrayResize failed"); return(false); } //--- converting for(int y=0; y<image_height; y++) for(int x=0; x<image_width; x++) { //--- load source RGB int offset=y*image_width+x; uint clr =image_data[offset]; uchar r =GETRGBR(clr); uchar g =GETRGBG(clr); uchar b =GETRGBB(clr); //--- store RGB components as separated channels int offset_ch1=0*image_width*image_height+offset; int offset_ch2=1*image_width*image_height+offset; int offset_ch3=2*image_width*image_height+offset; data[offset_ch1]=r/255.0f; data[offset_ch2]=g/255.0f; data[offset_ch3]=b/255.0f; } //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| PostProcessing | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool PostProcessing(const float &data[], uint &image_data[], const int &image_width, const int &image_height) { //--- checks if(image_height == 0 || image_width == 0) return(false); int data_count=image_width*image_height; if(ArraySize(data)!=3*data_count) return(false); if(ArrayResize(image_data,data_count)!=data_count) return(false); //--- for(int y=0; y<image_height; y++) for(int x=0; x<image_width; x++) { int offset =y*image_width+x; int offset_ch1=0*image_width*image_height+offset; int offset_ch2=1*image_width*image_height+offset; int offset_ch3=2*image_width*image_height+offset; //--- rescale to [0..255] float r=clamp(data[offset_ch1]*255,0,255); float g=clamp(data[offset_ch2]*255,0,255); float b=clamp(data[offset_ch3]*255,0,255); //--- set color image_data image_data[offset]=XRGB(uchar(r),uchar(g),uchar(b)); } //--- return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ShowImage | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool ShowImage(CCanvas &canvas,const string name,const int x0,const int y0,const int image_width,const int image_height, const uint &image_data[]) { if(ArraySize(image_data)==0 || name=="") return(false); //--- prepare canvas canvas.CreateBitmapLabel(name,x0,y0,image_width,image_height,COLOR_FORMAT_XRGB_NOALPHA); //--- copy image to canvas for(int y=0; y<image_height; y++) for(int x=0; x<image_width; x++) canvas.PixelSet(x,y,image_data[y*image_width+x]); //--- ready to draw canvas.Update(true); return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnStart(void) { //--- select BMP from <data folder>\MQL5\Files string image_path[1]; if(FileSelectDialog("Select BMP image",NULL,"Bitmap files (*.bmp)|*.bmp",FSD_FILE_MUST_EXIST,image_path,"lenna.bmp")!=1) { Print("file not selected"); return(-1); } //--- load BMP into array uint image_data[]; int image_width; int image_height; if(!CCanvas::LoadBitmap(image_path[0],image_data,image_width,image_height)) { PrintFormat("CCanvas::LoadBitmap failed with error %d",GetLastError()); return(-1); } //--- convert RGB image to separated RGB channels float input_data[]; Preprocessing(input_data,image_data,image_width,image_height); PrintFormat("input array size=%d",ArraySize(input_data)); ushort input_data_float16[]; if(!ArrayToFP16(input_data_float16,input_data,FLOAT_FP16)) { Print("error in ArrayToFP16. error code=",GetLastError()); return(false); } //--- load model long model_handle=OnnxCreateFromBuffer(ExtModel,ONNX_DEFAULT); if(model_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) { PrintFormat("OnnxCreate error %d",GetLastError()); return(-1); } PrintFormat("model loaded successfully"); PrintFormat("original: width=%d, height=%d Size=%d",image_width,image_height,ArraySize(image_data)); //--- set input shape ulong input_shape[]={1,3,image_height,image_width}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(model_handle,0,input_shape)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetInputShape. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(-1); } //--- upscaled image size int new_image_width =4*image_width; int new_image_height=4*image_height; ulong output_shape[]= {1,3,new_image_height,new_image_width}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(model_handle,0,output_shape)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxSetOutputShape. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(-1); } //--- run the model float output_data[]; ushort output_data_float16[]; int new_data_count=3*new_image_width*new_image_height; if(ArrayResize(output_data_float16,new_data_count)!=new_data_count) { OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(-1); } if(!OnnxRun(model_handle,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,input_data_float16,output_data_float16)) { PrintFormat("error in OnnxRun. error code=%d",GetLastError()); OnnxRelease(model_handle); return(-1); } Print("model successfully executed, output data size ",ArraySize(output_data)); OnnxRelease(model_handle); if(!ArrayFromFP16(output_data,output_data_float16,FLOAT_FP16)) { Print("error in ArrayFromFP16. error code=",GetLastError()); return(false); } //--- postprocessing uint new_image[]; PostProcessing(output_data,new_image,new_image_width,new_image_height); //--- show images CCanvas canvas_original,canvas_scaled; ShowImage(canvas_original,"original_image",new_image_width,0,image_width,image_height,image_data); ShowImage(canvas_scaled,"upscaled_image",0,0,new_image_width,new_image_height,new_image); //--- save upscaled image StringReplace(image_path[0],".bmp","_upscaled.bmp"); Print(ResourceSave(canvas_scaled.ResourceName(),image_path[0])); //--- while(!IsStopped()) Sleep(100); return(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Die Änderungen im Code, die zur Ausführung des in das Float16-Format konvertierten Modells erforderlich sind, sind farblich hervorgehoben.
Ausgabe:
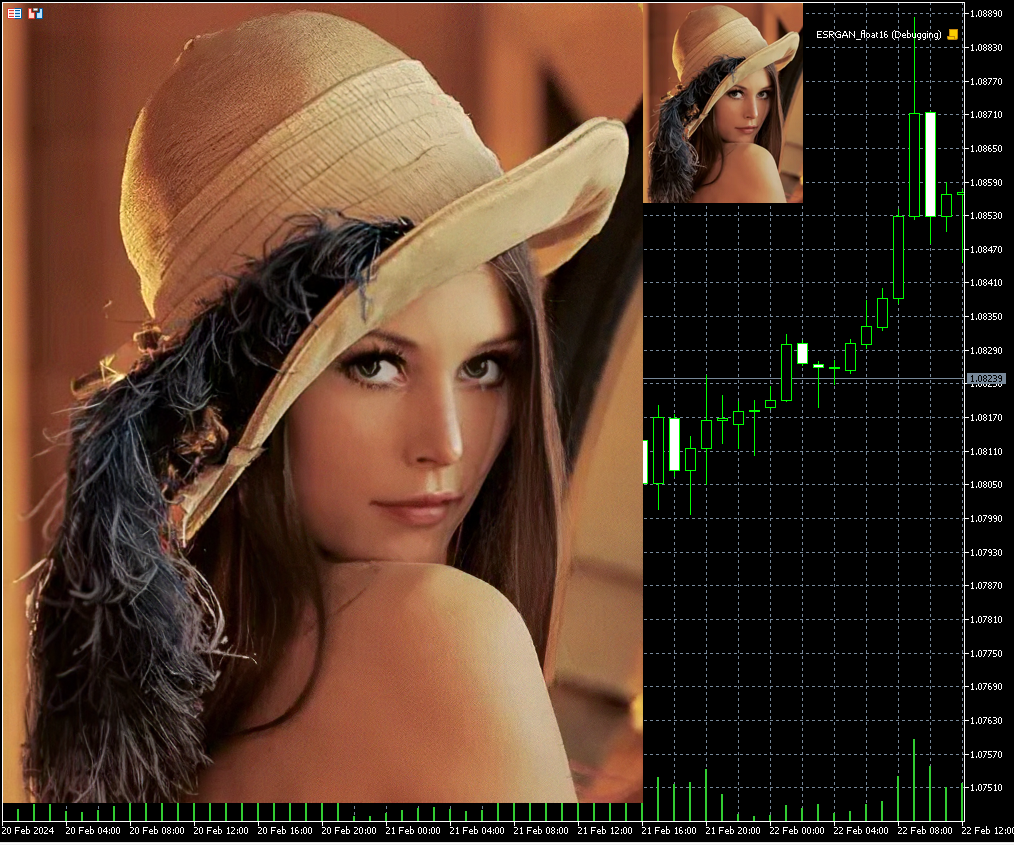
Abb.15. Das Ergebnis der Ausführung des Modells ESRGAN_float16.onnx (160x200 -> 640x800)
Durch die Verwendung von float16-Zahlen anstelle von float32 kann die Größe der ONNX-Modelldatei um die Hälfte reduziert werden (von 64 MB auf 32 MB).
Bei der Ausführung von Modellen mit Float16-Zahlen blieb die Bildqualität vergleichbar hoch, sodass es visuell schwierig ist, Unterschiede zu erkennen:
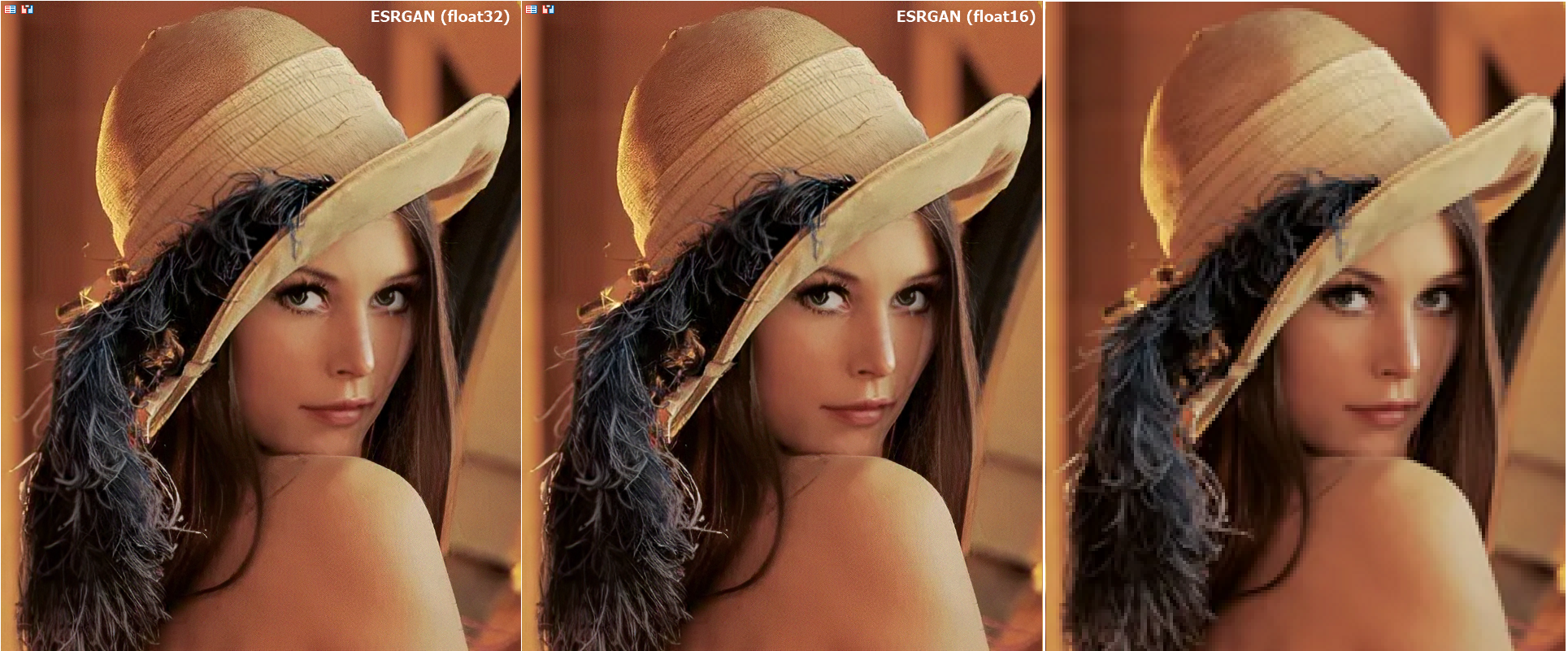

Abb.16. Vergleich der Ergebnisse des ESRGAN-Modellbetriebs für float und float16
Die Änderungen im Code sind minimal, es muss lediglich die Konvertierung der Eingangs- und Ausgangsdaten beachtet werden.
In diesem Fall hat sich die Qualität des Modells nach der Umstellung auf float16 nicht wesentlich verändert. Bei der Analyse von Finanzdaten ist es jedoch unerlässlich, Berechnungen mit der größtmöglichen Genauigkeit anzustreben.
Schlussfolgerungen
Die Verwendung neuer Datentypen für Fließkommazahlen ermöglicht die Verringerung der Größe von ONNX-Modellen ohne nennenswerte Qualitätsverluste.
Die Vor- und Nachbearbeitung der Daten wird durch die Konvertierungsfunktionen ArrayToFP16/ArrayFromFP16 und ArrayToFP8/ArrayFromFP8 erheblich vereinfacht.
Für die Arbeit mit konvertierten ONNX-Modellen sind nur minimale Änderungen im Code erforderlich.
Übersetzt aus dem Russischen von MetaQuotes Ltd.
Originalartikel: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/14330
Warnung: Alle Rechte sind von MetaQuotes Ltd. vorbehalten. Kopieren oder Vervielfältigen untersagt.
 Algorithmen zur Optimierung mit Populationen: Evolutionsstrategien, (μ,λ)-ES und (μ+λ)-ES
Algorithmen zur Optimierung mit Populationen: Evolutionsstrategien, (μ,λ)-ES und (μ+λ)-ES
 Datenwissenschaft und maschinelles Lernen (Teil 20): Algorithmische Handelseinblicke, eine Gegenüberstellung von LDA und PCA in MQL5
Datenwissenschaft und maschinelles Lernen (Teil 20): Algorithmische Handelseinblicke, eine Gegenüberstellung von LDA und PCA in MQL5
 Erstellen eines Market-Making-Algorithmus in MQL5
Erstellen eines Market-Making-Algorithmus in MQL5
 Einführung in MQL5 (Teil 4): Strukturen, Klassen und Zeitfunktionen beherrschen
Einführung in MQL5 (Teil 4): Strukturen, Klassen und Zeitfunktionen beherrschen
- Freie Handelsapplikationen
- Über 8.000 Signale zum Kopieren
- Wirtschaftsnachrichten für die Lage an den Finanzmärkte
Sie stimmen der Website-Richtlinie und den Nutzungsbedingungen zu.
Bitte fügen Sie rechts ein weiteres Bild in der gleichen Größe hinzu - ein vierfaches (statt eines Pixels - vier (2x2) der gleichen Farbe) Originalbild.
Sie können den Code ersetzen, um es anzuzeigen:
Sie können den Code ersetzen, um ihn auszugeben:
Danke! Verkleinert um einen Faktor von zwei an jeder Koordinate, um das richtige Bild wie das Original zu erhalten.
Ich dachte, dass float16/32 mit dieser Transformation nahe an das Original herankommen würde. Aber sie sind spürbar besser! D.h. UpScale+DownScale >> Original.
ZY Überrascht. Es scheint sinnvoll, alle alten Bilder/Videos durch ein solches onnx-Modell laufen zu lassen.
Wenn dem onnx-Modell dieselben Daten eingegeben werden, ist dann die Ausgabe immer dieselbe?
Gibt es ein Zufallselement im onnx-Modell?
Wenn das onnx-Modell mit den gleichen Daten als Eingabe gefüttert wird, aber die Ausgabe immer das gleiche Ergebnis hat?
Gibt es ein Zufallselement im onnx-Modell?
Im Allgemeinen hängt es davon ab, welche Operatoren innerhalb des ONNX-Modells verwendet werden.
Bei diesem Modell sollte das Ergebnis dasselbe sein, da es deterministische Operationen enthält (insgesamt 1195)
Описание float16
https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%A7%D0%B8%D1%81%D0%BB%D0%BE_%D0%BF%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%B2%D0%B8%D0%BD%D0%BD%D0%BE%D0%B9_%D1%82%D0%BE%D1%87%D0%BD%D0%BE%D1%81%D1%82%D0%B8
Примеры чисел половинной точности
In diesen Beispielen werden Fließkommazahlen in Binärform dargestellt. Sie enthalten das Vorzeichenbit, den Exponenten und die Mantisse.
0 01111 0000000000 = +1 *215-15 = 1
0 01111 0000000001 = +1.0000000001 2 *215-15=1+ 2-10 = 1.0009765625 (die nächsthöhere Zahl nach 1)
D.h. für Zahlen mit 5 Dezimalstellen (die meisten Währungen) kann nach 1,00000 nur noch 1,00098 verwendet werden.
Cool! Aber nicht für den Handel und die Arbeit mit Kursen.