使用格兹尔算法的循环分析
概述
格兹尔算法(Goertzel algorithm)是一种数字信号处理技术,以其在检测特定频率分量方面的效率而闻名。其精度、实时性和计算效率使其适用于金融时间序列分析。在这篇文章中,我们将研究并演示该方法可用于分析主导周期,从而可能以此开发策略。我们将研究MQL5中算法的实现,并提供一个如何使用代码来识别价格报价中的周期的示例。
格兹尔算法
Goertzel算法的名字来源于Gerald Goertzel,它被用来以有效的方式计算离散傅立叶变换(Discrete Fourier Transform,DFT)的各个项。这项技术最初于1958年引入,后来被应用于各个领域,包括工程、数学和物理。Goertzel算法的主要应用是识别数字信号中的特定频率分量,这使得它在只有少数频率分量很重要的情况下非常有价值。与快速傅立叶变换(Fast Fourier Transform,FFT)相比,当检测有限数量的频率分量时,它需要更少的计算,使其在计算上高效。
它由以下公式表示:
其中:- X是频率k时的累积幅度
- cos()是余弦函数
- π是数学常数pi(约3.14159)
- k是您感兴趣的频率仓的索引(范围从0到N-1,其中N是样本总数)
- N 是输入信号的长度- X[k-1]和X[k-2]是在k时频率的X的先前计算值
- x[n]是输入信号的第n个样本
要使用Goertzel算法计算实部和虚部,我们需要迭代输入信号样本,并执行以下计算:
- N:输入信号中的采样数。
- k:感兴趣的频率仓的索引(0<=k<N)。
- omega:与期望频率 bin(2*pi*k/N)相对应的频率。
- coeff:计算中使用的系数(2*cos(omega))。
- s_prev:“state”变量的上一个值。
- s_prev2:“state”变量的上一个值之前的值。
- s:“state”变量的当前值。
-
使用以下公式更新“state”变量的当前值:
其中x[n]是当前输入样本。
更新“state”变量以前的值:
在迭代所有样本之后,“state”变量(S,Sprev,Sprev2)的最终值表示在所需频率bin(k)处DFT的实部和虚部。
实部由以下公式给出:
虚部由下式给出:
DFT可以检测到的频率范围从1/N到(N/2)/N,其中N表示序列中数据点的数量,或者在我们的情况下表示正在分析的价格柱的数量。在分析报价时,它可能被限制为只能观察到限制在1/N间距内的频带。这就是J.Ehlers等人提出最大熵谱分析(MESA)技术来克服这一限制的原因。
Goertzel算法可以作为Ehler的MESA的替代方案,根据D.Meyers撰写的一篇研究论文,该算法能够在某些条件下获得更好的结果(就光谱分辨率而言)。这些条件中的一个恰好与信号中包含的噪声量有关。根据Meyers的说法,goertzel算法能够优于MESA技术,尤其是在处理噪声信号时,这是金融时间序列的一个常见问题。感兴趣的读者可以阅读pdf格式的白皮书。
CGoertzel 类
CGoertzel类是goertzel算法的一个简单实现,该算法能够在数据集上对一系列频率进行采样。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| CGoertze class implementing Goertzel algorithm | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CGoertzel { private: uint m_minPeriod; uint m_maxPeriod; public: //constructor CGoertzel(void) { m_minPeriod=m_maxPeriod=0; } //destructor ~CGoertzel(void) { } //get methods uint GetMinPeriodLength(void) { return m_minPeriod;} uint GetMaxPerodLength(void) { return m_maxPeriod;} //set methods bool SetMinMaxPeriodLength(const uint min_wavePeriod, const uint max_wavePeriod); // goertzel dft transform methods bool Dft(const double &in_data[],complex &out[]); bool Dft(const double &in_data[], double &out_real[], double &out_imaginary[]); bool Dft(const uint min_wavePeriod,const uint max_wavePeriod,const double &in_data[],complex &out[]); bool Dft(const uint min_wavePeriod,const uint max_wavePeriod,const double &in_data[], double &out_real[], double &out_imaginary[]); };
由于goertzel一次只采样有限的频率,我们必须设置我们感兴趣的频带。在该类中,频带是根据频率的最小和最大周期来设置的。
有两种方法可以设置这些值:使用SetMinMaxPeriodLength(),可以指定最小周期和最大周期。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Set the Minimum and maximum periods of selected frequency band | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CGoertzel::SetMinMaxPeriodLength(const uint min_wavePeriod,const uint max_wavePeriod) { if(min_wavePeriod<2 || min_wavePeriod>=max_wavePeriod) { Print("Critical error min_wavePeriod cannot be less than max_wavePeriod or less than 2"); return false; } m_minPeriod=min_wavePeriod; m_maxPeriod=max_wavePeriod; return true; }
此外,当调用Dft方法的两个重载方法之一时,可以设置频带。
//+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Calculate the frequency domain representation of input array as complex array | //+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CGoertzel::Dft(const uint min_wavePeriod,const uint max_wavePeriod,const double &in_data[],complex &out[]) { if(!SetMinMaxPeriodLength(min_wavePeriod,max_wavePeriod)) return(false); return Dft(in_data,out); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Calculate the frequency domain representation of input array as two separate arrays| //+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CGoertzel::Dft(const uint min_wavePeriod,const uint max_wavePeriod,const double &in_data[], double &out_real[], double &out_imaginary[]) { if(!SetMinMaxPeriodLength(min_wavePeriod,max_wavePeriod)) return(false); return Dft(in_data,out_real,out_imaginary); }
根据所使用的Dft方法的版本,Dft的实部和虚部以单独的阵列或典型复数的单个阵列输出。
//+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Calculate the frequency domain representation of input array as complex array | //+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CGoertzel::Dft(const double &in_data[],complex &out[]) { uint minsize=(3*m_maxPeriod); uint fullsize=in_data.Size(); if(fullsize<minsize) { Print("Sample size too small in relation to the largest period cycle parameter"); return false; } if(m_minPeriod>=m_maxPeriod || m_minPeriod<2) { Print("Critical error: Invalid input parameters :- max_period should be larger than min_period and min_period cannot be less than 2"); return false; } if(out.Size()!=m_maxPeriod) ArrayResize(out,m_maxPeriod); double v0,v1,v2,freq,coeff,real,imag; for(uint i=0; i<m_maxPeriod; i++) { if(i<m_minPeriod) { out[i].imag=out[i].real=0.0; continue; } v0=v1=v2=0.0; freq=MathPow(i,-1); coeff=2.0*MathCos(2.0*M_PI*freq); for(uint k=minsize-1; k>0; k--) { v0=coeff*v1-v2+in_data[k]; v2=v1; v1=v0; } real=v1-v2*0.5*coeff; imag=v2*MathSin(2*M_PI*freq); out[i].real=real; out[i].imag=imag; } return true; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Calculate the frequency domain representation of input array as two separate arrays| //+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CGoertzel::Dft(const double &in_data[],double &out_real[],double &out_imaginary[]) { uint minsize=(3*m_maxPeriod); uint fullsize=in_data.Size(); if(fullsize<minsize) { Print("Sample size too small in relation to the largest period cycle parameter"); return false; } if(m_minPeriod>=m_maxPeriod || m_minPeriod<2) { Print("Critical error: Invalid input parameters :- max_period should be larger than min_period and min_period cannot be less than 2"); return false; } if(out_real.Size()!=m_maxPeriod) ArrayResize(out_real,m_maxPeriod); if(out_imaginary.Size()!=m_maxPeriod) ArrayResize(out_imaginary,m_maxPeriod); double v0,v1,v2,freq,coeff,real,imag; for(uint i=0; i<m_maxPeriod; i++) { if(i<m_minPeriod) { out_real[i]=out_imaginary[i]=0.0; continue; } v0=v1=v2=0.0; freq=MathPow(i,-1); coeff=2.0*MathCos(2.0*M_PI*freq); for(uint k=minsize-1; k>0; k--) { v0=coeff*v1-v2+in_data[k]; v2=v1; v1=v0; } real=v1-v2*0.5*coeff; imag=v2*MathSin(2*M_PI*freq); out_real[i]=real; out_imaginary[i]=imag; } return true; }
预处理
数据不能总是简单地插入goertzel算法并转换到频域中。根据数据样本的性质,可能需要执行一些预处理步骤。Goertzel算法是dft的子集,因此在执行快速傅立叶变换之前所需的变换也适用于此。对于非周期性数据尤其如此。这样的系列需要用适当的窗口函数来处理。这将使该系列的末端充分变细,从而将频谱泄漏的可能性降至最低。Goertzel在文献中的大多数应用通常采用端点平坦化算法。该技术的实现由以下公式给出:
其中a是要分析的序列中的第一个价格值,b是最后一个,flat(i)是将传递给goertzel算法的序列。
在窗口化数据之前,最好去除任何明显的趋势和异常值。应该对原始数据进行解压缩,但仅在必要时进行解压缩。未排列的去趋势会导致失真,失真将被带到样本的频域表示上。去趋势是一个广泛的话题,可以采用多种类型的去趋势方法。每一种都有自己的优点和缺点。从业者应该努力彻底调查最合适的应用方法。为了本文的目的,我们将使用一个简单的最小二乘拟合来给报价去趋势。代码如下所示。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| helper method for detrending data | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CGoertzelCycle::detrend(const double &in_data[], double &out_data[]) { uint i ; double xmean, ymean, x, y, xy, xx ; xmean=ymean=x=y=xx=xy=0.0; xmean=0.5*double(in_data.Size()-1); if(out_data.Size()!=in_data.Size()) ArrayResize(out_data,in_data.Size()); for(i=0; i<out_data.Size(); i++) { x = double(i) - xmean ; y = in_data[i] - ymean ; xx += x * x ; xy += x * y ; } m_slope=xy/xx; m_pivot=xmean; for(i=0; i<out_data.Size(); i++) out_data[i]=in_data[i]-(double(i)-xmean)*m_slope; }
CGoertzelCycle 类
包含文件GoertzelCycle.mqh将包含CGoertzelCycle类,该类用于使用goertzel算法对数据集进行循环分析。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| CGoertzelCycle class for cycle using the Goertzel Algorithm | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CGoertzelCycle { private: CGoertzel*m_ga; double m_pivot; double m_slope; bool m_detrend; bool m_squaredamp; bool m_flatten; uint m_cycles; uint m_maxper,m_minper; double m_amplitude[]; double m_peaks[]; double m_cycle[]; double m_phase[]; uint m_peaks_index[]; double m_detrended[]; double m_flattened[]; double m_raw[]; void detrend(const double &in_data[], double &out_data[]); double wavepoint(bool use_cycle_strength,uint max_cycles); bool spectrum(const double &in_data[],int shift=-1); uint cyclepeaks(bool use_cycle_strength); public : CGoertzelCycle(void); CGoertzelCycle(bool detrend,bool squared_amp,bool apply_window, uint min_period,uint max_period); ~CGoertzelCycle(void); bool GetSpectrum(const double &in_data[],double &out_amplitude[]); bool GetSpectrum(bool detrend,bool squared_amp,bool apply_window, uint min_period,uint max_period,const double &in_data[],double &out_amplitude[]); uint GetDominantCycles(bool use_cycle_strength,const double &in_data[],double &out_cycles[]); uint GetDominantCycles(bool use_cycle_strenght,bool detrend,bool squared_amp,bool apply_window, uint min_period,uint max_period,const double &in_data[],double &out_cycles[]); void CalculateDominantCycles(uint prev,uint total,bool use_cycle_strength,const double &in_data[], double &out_signal[]); void CalculateWave(uint prev,uint total,uint max_cycles, bool use_cycle_strength,const double &in_data[], double &out_signal[]); };
它有两个构造函数。参数化构造函数允许使用自定义设置初始化实例。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Default Constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CGoertzelCycle::CGoertzelCycle(void) { m_pivot=m_slope=0.0; m_maxper=m_minper=m_cycles=0; m_detrend=m_squaredamp=m_flatten=false; m_ga=new CGoertzel(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Parametric Constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CGoertzelCycle::CGoertzelCycle(bool detrend,bool squared_amp,bool apply_window, uint min_period,uint max_period) { m_pivot=m_slope=0.0; m_cycles=0; m_maxper=max_period; m_minper=min_period; m_detrend=detrend; m_squaredamp=squared_amp; m_flatten=apply_window; m_ga=new CGoertzel(); if(m_maxper) { ArrayResize(m_amplitude,m_maxper); ArrayResize(m_phase,m_maxper); ArrayResize(m_cycle,m_maxper); ArrayResize(m_peaks,m_maxper); ArrayResize(m_peaks_index,m_maxper); } }
输入参数如下所示:
- detrend - 一个布尔型输入参数,指示需要删除趋势。
- apply_window -另一个布尔参数,指定是否应应用窗口函数。
- min_period -此参数定义goertzel算法将解析的最短周期或最高频率。请注意,此值不能设置为低于2。
- max_period -分析过程中考虑的最长周期。此值表示周期最长的频率,不能小于或等于min_period。
- squared_amp -指示振幅值应该如何呈现。选择false会将振幅计算为平方根。
该类有6个用户应该感兴趣的可访问方法。
//+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| public method to access the amplitude values | //+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CGoertzelCycle::GetSpectrum(const double &in_data[],double &out_amplitude[]) { if(spectrum(in_data)) { ArrayCopy(out_amplitude,m_amplitude); return true; } return false; }
GetSpectrum()需要2个输入数组,其中第一个in_data是要分析的原始序列。第二个数组是输出振幅值的地方。应该通过使用参数化构造函数初始化实例来指定用于执行转换的参数。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| public method to access the amplitude values | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CGoertzelCycle::GetSpectrum(bool detrend,bool squared_amp,bool apply_window,uint min_period,uint max_period,const double &in_data[],double &out_amplitude[]) { m_pivot=m_slope=0.0; m_cycles=0; m_maxper=max_period; m_minper=min_period; m_detrend=detrend; m_squaredamp=squared_amp; m_flatten=apply_window; if(m_maxper) { ArrayResize(m_amplitude,m_maxper); ArrayResize(m_phase,m_maxper); ArrayResize(m_cycle,m_maxper); ArrayResize(m_peaks,m_maxper); ArrayResize(m_peaks_index,m_maxper); } if(spectrum(in_data)) { ArrayCopy(out_amplitude,m_amplitude); return true; } return false; }
另一个重载的GetSpectrum()方法采用与参数化构造函数相同的附加参数。两者都在成功时返回 true,在失败时返回 false。任何错误数据都将写入终端的日志。
//+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|public method to get the dominant cycle periods arranged in descending order| //+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ uint CGoertzelCycle::GetDominantCycles(bool use_cycle_strength,const double &in_data[],double &out_cycles[]) { if(!spectrum(in_data)) { ArrayInitialize(out_cycles,0.0); return(0); } cyclepeaks(use_cycle_strength); if(out_cycles.Size()!=m_cycles) ArrayResize(out_cycles,m_cycles); for(uint i=0; i<m_cycles; i++) out_cycles[i]=m_cycle[m_peaks_index[i]]; return m_cycles; } //+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|public method to get the dominant cycle periods arranged in descending order| //+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ uint CGoertzelCycle::GetDominantCycles(bool use_cycle_strength,bool detrend,bool squared_amp,bool apply_window,uint min_period,uint max_period,const double &in_data[],double &out_cycles[]) { m_pivot=m_slope=0.0; m_cycles=0; m_maxper=max_period; m_minper=min_period; m_detrend=detrend; m_squaredamp=squared_amp; m_flatten=apply_window; if(m_maxper) { ArrayResize(m_amplitude,m_maxper); ArrayResize(m_phase,m_maxper); ArrayResize(m_cycle,m_maxper); ArrayResize(m_peaks,m_maxper); ArrayResize(m_peaks_index,m_maxper); } return(GetDominantCycles(use_cycle_strength,in_data,out_cycles)); }
GetDominantCycle() 方法也会被重载,与GetSpectrum() 类似。除了这两个数组之外,还需要指定一个布尔参数use_cycle_stngth,它指出了确定优势周期的标准。设置为false意味着使用振幅最大的频率,而备选方案通过计算公式给出的循环强度来确定主循环:
主循环以降序排列的值输出到输入阵列的最后一个。
//+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|method used to access calculated dominant cycles , for use in indcators| //+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CGoertzelCycle::CalculateDominantCycles(uint prev,uint total,bool use_cycle_strength,const double &in_data[], double &out_signal[]) { uint limit =0; bool indexOut=ArrayGetAsSeries(out_signal); bool indexIn=ArrayGetAsSeries(in_data); if(prev<=0) { uint firstindex=0; if(indexOut) { limit=total-(m_maxper*3); firstindex=limit+1; } else { limit=m_maxper*3; firstindex=limit-1; } out_signal[firstindex]=0; } else { limit=(indexOut)?total-prev:prev; } uint found_cycles=0; if(indexOut) { for(int ibar=(int)limit; ibar>=0; ibar--) { spectrum(in_data,(indexIn)?ibar:total-ibar-1); out_signal[ibar]=(cyclepeaks(use_cycle_strength))?m_cycle[m_peaks_index[0]]:0.0; } } else { for(int ibar=(int)limit; ibar<(int)total; ibar++) { spectrum(in_data,(indexIn)?total-ibar-1:ibar); out_signal[ibar]=(cyclepeaks(use_cycle_strength))?m_cycle[m_peaks_index[0]]:0.0; } } }
前缀为Calculate的方法最好用于指标。CalculateDominantCycles()输出对应条形图的主循环。prev应当被设置为先前计算的指示符值的数目。Total应该是图表上可用条形图的数量。in_data是传入报价的地方,out_signal应该是指标缓冲区之一。
//+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|method used to access newly formed wave form, for use in indcators | //+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CGoertzelCycle::CalculateWave(uint prev,uint total,uint max_cycles,bool use_cycle_strength,const double &in_data[], double &out_signal[]) { uint limit =0; bool indexOut=ArrayGetAsSeries(out_signal); bool indexIn=ArrayGetAsSeries(in_data); if(prev<=0) { uint firstindex=0; if(indexOut) { limit=total-(m_maxper*3); firstindex=limit+1; } else { limit=m_maxper*3; firstindex=limit-1; } out_signal[firstindex]=0; } else { limit=(indexOut)?total-prev:prev; } uint found_cycles=0; if(indexOut) { for(int ibar=(int)limit; ibar>=0; ibar--) { spectrum(in_data,(indexIn)?ibar:total-ibar-1); out_signal[ibar]=out_signal[ibar+1]+wavepoint(use_cycle_strength,max_cycles); } } else { for(int ibar=(int)limit; ibar<(int)total; ibar++) { spectrum(in_data,(indexIn)?total-ibar-1:ibar); out_signal[ibar]=out_signal[ibar-1]+wavepoint(use_cycle_strength,max_cycles); } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
CalculateWave()的大部分参数与CalculateDominantCycles()不相关。它输出根据goertzel算法揭示的主频分量计算的滤波值。频率分量的最大数量由max_cycles参数设置。
波形构造
为了演示类的使用以及goertzel在策略开发中的可能应用,我们将提出两个指标。第一个是Dennis Meyers撰写的白皮书中提出的策略的实现。他将这种策略称为自适应10周期Goertzel DFT系统。有关该策略的确切细节可在该文件中查阅。简而言之,该策略使用goertzel从价格数据的移动窗口中提取前十个主导周期,然后使用这些周期构建新的价格曲线。据推测,这代表了噪音被过滤掉后的价格行为。该策略的关键参数是要采样的频率的最小周期和最大周期,连同要用于构造滤波信号的最大数量的频率分量。
//--- input parameters input bool Detrend=true; input bool EndFlatten=true; input bool SquaredAmp=true; input bool UseCycleStrength=false; input uint Maxper=72; input uint Minper=5; input uint MaxCycles=10; input double pntup=0.5;//Percent increase threshold input double pntdn=0.5;//Percent decrease threshold //--- indicator buffers
该指标使用两个阈值来触发长信号和短信号,这取决于相对于最近峰值或波谷的移动幅度。在代码中,输入变量pntup和pntdn表示百分比。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| NCycleGoertzelDft.mq5 | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #include<GoertzelCycle.mqh> #property indicator_separate_window #property indicator_buffers 5 #property indicator_plots 5 //--- plot Wave #property indicator_label1 "Wave" #property indicator_type1 DRAW_LINE #property indicator_color1 clrBlack #property indicator_style1 STYLE_SOLID #property indicator_width1 1 //--- plot Up #property indicator_label2 "Peak" #property indicator_type2 DRAW_NONE //--- plot Dwn #property indicator_label3 "Trough" #property indicator_type3 DRAW_NONE //--- plot Up #property indicator_label4 "Long" #property indicator_type4 DRAW_LINE #property indicator_color4 clrBlue #property indicator_style4 STYLE_SOLID #property indicator_width4 2 //--- plot Dwn #property indicator_label5 "Short" #property indicator_type5 DRAW_LINE #property indicator_color5 clrRed #property indicator_style5 STYLE_SOLID #property indicator_width5 2 //--- input parameters input bool Detrend=true; input bool EndFlatten=true; input bool SquaredAmp=true; input bool UseCycleStrength=false; input uint Maxper=72; input uint Minper=5; input uint MaxCycles=10; input double pntup=0.5;//Percent increase threshold input double pntdn=0.5;//Percent decrease threshold //--- indicator buffers double Wave[],Peak[],Trough[],Long[],Short[]; CGoertzelCycle *Gc; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- indicator buffers mapping SetIndexBuffer(0,Wave,INDICATOR_DATA); SetIndexBuffer(1,Peak,INDICATOR_DATA); SetIndexBuffer(2,Trough,INDICATOR_DATA); SetIndexBuffer(3,Long,INDICATOR_DATA); SetIndexBuffer(4,Short,INDICATOR_DATA); //--- IndicatorSetInteger(INDICATOR_DIGITS,5); //--- PlotIndexSetDouble(0,PLOT_EMPTY_VALUE,0.0); PlotIndexSetDouble(1,PLOT_EMPTY_VALUE,0.0); PlotIndexSetDouble(2,PLOT_EMPTY_VALUE,0.0); PlotIndexSetDouble(3,PLOT_EMPTY_VALUE,0.0); PlotIndexSetDouble(4,PLOT_EMPTY_VALUE,0.0); //--- Gc=new CGoertzelCycle(Detrend,SquaredAmp,EndFlatten,Minper,Maxper); if(Gc==NULL) { Print("Invalid Goertzel object"); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Indicator DeInitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit (const int reason) { if(CheckPointer(Gc)==POINTER_DYNAMIC) delete Gc; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator iteration function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnCalculate(const int rates_total, const int prev_calculated, const int begin, const double &price[]) { int lim=0; if(prev_calculated<=0) lim=(int)(Maxper*3)+2; else lim=prev_calculated; //--- Gc.CalculateWave(prev_calculated,rates_total,MaxCycles,UseCycleStrength,price,Wave); //--- for(int i=lim;i<rates_total-1;i++) { Peak[i]=Trough[i]=0.0; if(Wave[i]>Wave[i+1] && Wave[i]>Wave[i-1]) Peak[i]=Wave[i]; else if(Wave[i]<Wave[i+1] && Wave[i]<Wave[i-1]) Trough[i]=Wave[i]; if(i<int(Maxper*3*2)) { continue; } double lp,lt; lp=lt=0; if(i==int(Maxper*3*2)) { lp=getlastPeakTrough(i,Peak); lt=getlastPeakTrough(i,Trough); if(Wave[i]>Wave[i-1] && lt) { Long[i]=Wave[i]; Short[i]=0.0; } else if(Wave[i]<Wave[i-1] && lp) { Short[i]=Wave[i]; Long[i]=0.0; } } else { Long[i]=(Long[i-1]!=0)?Wave[i]:Long[i-1]; Short[i]=(Short[i-1]!=0)?Wave[i]:Short[i-1]; if(Short[i-1]!=0 && Wave[i]>Wave[i-1]) { lt=getlastPeakTrough(i,Trough); if(lt && (Wave[i]-lt)/lt > pntup/100 ) { Long[i]=Wave[i]; Short[i]=0.0; } else { Short[i]=Wave[i]; Long[i]=0.0; } } else if(Long[i-1]!=0 && Wave[i]<Wave[i-1]) { lp=getlastPeakTrough(i,Peak); if(lp && (lp-Wave[i])/lp > pntdn/100 ) { Short[i]=Wave[i]; Long[i]=0.0; } else { Long[i]=Wave[i]; Short[i]=0.0; } } } } //--- return value of prev_calculated for next call return(rates_total); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| helper function that returns either last peak or trough | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double getlastPeakTrough(int shift, double &buffer[]) { uint j; double value=0.0; for(j=shift-1;j>(Maxper*3)+2;j--) { if(buffer[j]==0.0) continue; else return(buffer[j]); } return(value); } //+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------++
使用以下公式计算信号:
其中:-a是振幅-phi是相位-f是频率-B是过去采样的条数,表示从中提取频率分量的数据,相当于移动窗口大小。该值等于所考虑的最大周期周期的三倍。指标的代码如上所示。波点是曲线在相应索引处的值。
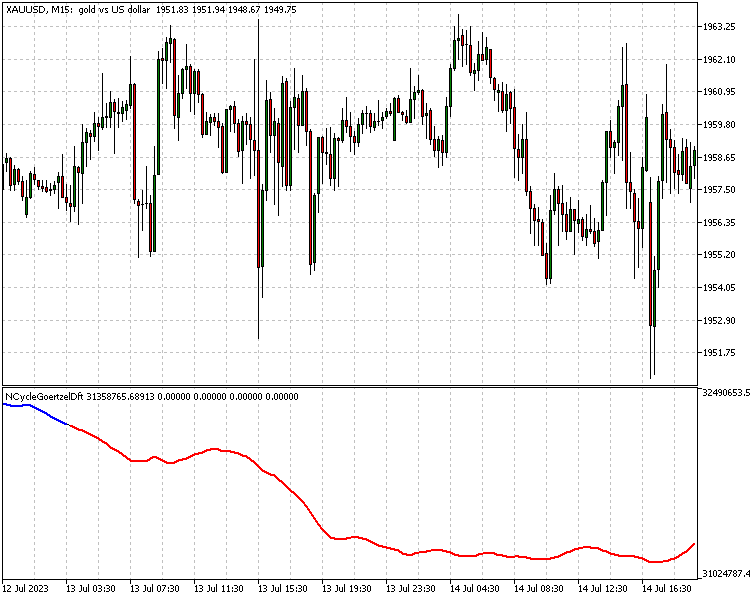
如果感兴趣,白皮书中会提供更多交易规则的详细信息
自适应指标
将goertzel应用于策略开发的另一种方法是使用它使指标具有自适应性。文章Mql5中的高级自适应理论和实现,详细介绍了使用J.Ehlers的著名技术的这种方法。我们可以用goertzel做同样的事情。以下是相对强度指标的自适应版本的实现。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| AdaptiveGARSI.mq5 | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #property indicator_separate_window #include<GoertzelCycle.mqh> #property indicator_buffers 2 #property indicator_plots 1 //--- plot RSi #property indicator_label1 "RSi" #property indicator_type1 DRAW_LINE #property indicator_color1 clrRed #property indicator_style1 STYLE_SOLID #property indicator_width1 1 //--- #property indicator_level1 70 #property indicator_level2 50 #property indicator_level3 30 //--- input bool Detrend=true; input bool EndFlatten=true; input bool SquaredAmp=true; input bool UseCycleStrength=false; input uint Maxper=72; input uint Minper=5; //--- indicator buffers double RSiBuffer[]; double DomPeriodBuffer[]; CGoertzelCycle *Gc; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- indicator buffers mapping SetIndexBuffer(0,RSiBuffer,INDICATOR_DATA); SetIndexBuffer(1,DomPeriodBuffer,INDICATOR_CALCULATIONS); //--- Gc=new CGoertzelCycle(Detrend,SquaredAmp,EndFlatten,Minper,Maxper); //--- if(Gc==NULL) { Print("Invalid Goertzel object"); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Indicator DeInitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit (const int reason) { if(CheckPointer(Gc)==POINTER_DYNAMIC) delete Gc; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator iteration function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnCalculate(const int rates_total, const int prev_calculated, const datetime &time[], const double &open[], const double &high[], const double &low[], const double &close[], const long &tick_volume[], const long &volume[], const int &spread[]) { //--- uint lim=0; //--- Gc.CalculateDominantCycles(prev_calculated,rates_total,UseCycleStrength,close,DomPeriodBuffer); //--- if(prev_calculated<=0) lim=int(Maxper*3)+int(DomPeriodBuffer[(Maxper*3)-1]) - 1; else lim=prev_calculated; //--- double cu,cd; for(int i =int(lim);i<rates_total;i++) { cd=0.0; cu=0.0; double p=DomPeriodBuffer[i]; int j=0; for(j=0;j<int(p);j++) { if(close[i-j]-close[i-j-1]>0)cu=cu+(close[i-j]-close[i-j-1]); if(close[i-j]-close[i-j-1]<0)cd=cd+(close[i-j-1]-close[i-j]); } if(cu+cd!=0) RSiBuffer[i]=100*cu/(cu+cd); else RSiBuffer[i]=0.0; } //--- return value of prev_calculated for next call return(rates_total); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
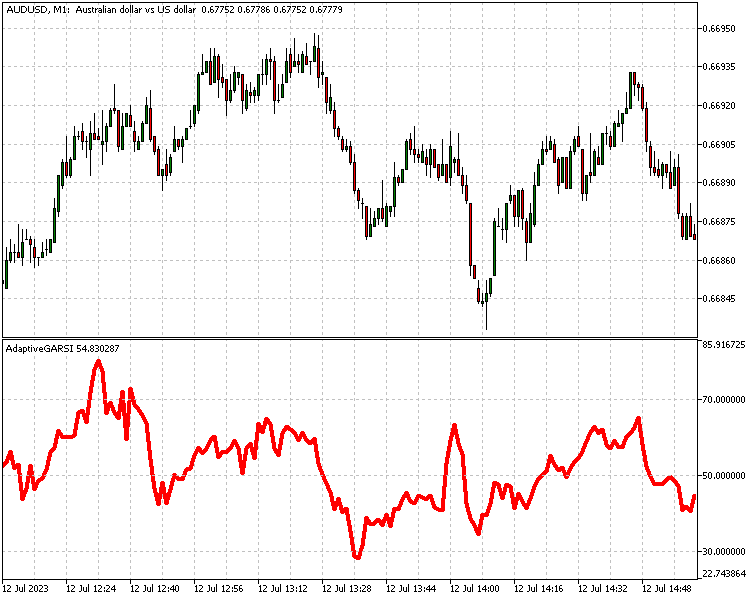
结论
Goertzel算法的功能及其应用程序的有用代码实用程序已经得到了明确的演示。挑战在于如何将这项技术有效地应用于金融数据并提取有意义的信号。与MESA技术相比,GA显然处于劣势,因为它一次只能解析一个频率。它的实际应用也突显了金融市场周期检测的弱点,因为很难测量一个主要周期并准确确定它何时结束。解决这些困难需要结合领域知识、稳健的数据预处理技术、风险管理策略以及持续监测和适应不断变化的市场动态。
所附的zip文件包含文章中描述的所有源代码。
| 文件名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Mql5/include/Goertzel.mqh | 实现goertzel算法的CGoertzel类的include文件 |
| Mql5/include/ GoertzelCycle.mqh | 使用goertzel算法进行循环分析的CGoertzelCycle类的include文件 |
| Mql5/indicators/ NCycleGoertzelDft.mq5 | 部分实现D.Meyers开发的使用goertzel算法的策略的指标 |
| Mql5/indicators/ AdaptiveGARSI.mq5 | 通过goertzel算法计算动态回溯的相对强度指标的自适应版本的实现 |
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/975
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
我们发表了一篇 文章:使用 Goertzel 算法分析循环:
作者:Francis Dube
在归档文件夹结构中用 "指标 "代替 "指示器"
我们发表了一篇 文章:使用 Goertzel 算法分析循环:
作者:Francis Dube
感谢您的文章 !
很久很久以来,这篇文章一直是第一个值得添加到 "书签 "中的文章。