在 MQL5 中利用 ARIMA 模型进行预测
概述
在 MQL5 中实现 ARIMA 训练算法 一文,讲述了构建 ARIMA 模型的 CArima 类。 尽管从技术上讲,可把该类应用于模型,并进行预测,但它并不太直观。 在本文中,我们将客服这一缺陷,并扩展该类,从而更易于利用模型的方法进行预测。 我们将讨论实现预测时会遇到的相关复杂性,以及添加到该类中的一些新功能。 总而言之,我们将用完整的类来构建一个模型,将其应用在智能系统和指标之中,来预测外汇价格。
输入序列
众所周知,ARIMA 模型依赖于数据集中的时间依赖性。 因此,为了进行一次或更多的预测,我们需要向模型提供一序列输入数据。 模型的规格确定了输入序列的最小尺度。 知道了这一点,很明显,如果输入序列不充分,就不可能做出任何预测,或者说至少预测不能反映所应用的模型。 不同类型的 ARIMA 模型对输入序列的尺度提出了不同的要求,而不仅仅是模型的顺序。
实现纯自回归模型的预测是微不足道的,因为其所需只是输入与模型的最大滞后相等。 使用移动平均项的混合模型在进行预测时会产生问题。 我们还没有实际的误差或创新序列。 为了克服这一点,我们必须首先决定如何计算误差的初始值。
该过程事关首先采用任意可用的模型参数来获取模型的初始状态,其中不包括任何移动平均项,在此阶段假定它们为 0。 然后,依据已知的序列值,循环遍历批量冗余预测来计算初始误差值。这些初始预测是冗余的,因为它们与我们最终感兴趣的最终预测无关。 这显然对预测所需的输入数量提出了更高的要求。 与此对应的关键是,为了做出有效的预测,应该执行多少次冗余预测循环,才能得出合适的误差序列值。
在模型输入的数量方面仍需更多的考量。 CArima 类能够指定具有非连续滞后的模型。 这对所需的输入数量提出了更高的要求。 在这种实例中,任一类型(AR/MA)的最大滞后将增加到所需的输入尺度。 研究由函数定义的模型
price(t) = constant_term + AR*price(t-4)
该函数指定具有单个 AR 项的模型,滞后为 4。 这意味着当前价格会部分地由前 4 个时序槽位的数值判定。 即使我们只需要一个这样的数值,我们也必须意识到要维持输入的时间关系。 因此,除了其它模型需求之外,我们实际上还需要四个输入,取代仅需一个输入的需求。 输入序列尺度的最终判定因素取决于是否任何差异所需。
考虑差异
差异的需求增加了所需的输入数量,不是因为与预测值的计算有关,而是因为差异会导致信息丢失。 创建差异序列时,相对于原始序列,它的长度总是少一个。 这个较短的序列最终将作为输入传递给模型。 因此,通常需要额外的输入来补偿,对应的差异顺序由模型指定。
除了差异对输入尺度的影响外,由于它们将处于差异域中,故它也会影响最终预测。 必须对预测以及提供的输入序列进行并合和整合,以便将合并值返回到原始域。
预测遥远的未来
有时,用户也许对基于单一输入集预测未来的若干时序槽位感兴趣。 尽管不建议这样做,但这是一条值得探索和解封的道路。 在对遥远的未来做出预测时,我们必须重视某些真理。 首先,我们走得越远,我们最终必须采用来自先前时间槽位的预测作为任意自回归项的输入。一旦我们超越已知的初始输入序列的数值,我们不再拥有计算误差值的手段。 鉴于未来的真实值是未知的。 因此,这些时间槽位对应的移动平均线项只能假定为零。 而这导致预测的序列退化为纯自回归过程(如果指定),或仅由常数项定义的过程。 在对遥远的未来进行多次预测时,应该意识到固有的局限性。
CArima 类的新增功能
针对该类所做的第一处修改与其父级 CPowellsMethod 相关。 Optimize() 方法现在的访问权修饰符是受保护,故无法从类的外部访问。 当然,这种变化也延申至 CArima。 由于此修改,含有 CPowellsMethod 类的包含文件名被更名为 Powells.mqh。
//----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Minimization of Functions. // Unconstrained Powell’s Method. // References: // 1. Numerical Recipes in C. The Art of Scientific Computing. //----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- class PowellsMethod:public CObject { protected: double P[],Xi[]; double Pcom[],Xicom[],Xt[]; double Pt[],Ptt[],Xit[]; int N; double Fret; int Iter; int ItMaxPowell; double FtolPowell; int ItMaxBrent; double FtolBrent; int MaxIterFlag; int Optimize(double &p[],int n=0); public: void PowellsMethod(void); void SetItMaxPowell(int n) { ItMaxPowell=n; } void SetFtolPowell(double er) { FtolPowell=er; } void SetItMaxBrent(int n) { ItMaxBrent=n; } void SetFtolBrent(double er) { FtolBrent=er; } double GetFret(void) { return(Fret); } int GetIter(void) { return(Iter); } private: void powell(void); void linmin(void); void mnbrak(double &ax,double &bx,double &cx,double &fa,double &fb,double &fc); double brent(double ax,double bx,double cx,double &xmin); double f1dim(double x); virtual double func(const double &p[]) { return(0); } };
加入该类的一个重要功能是能够保存和加载模型。 这样能训练和保存一个模型,以供将来使用,或包含在任何其它的 Mql5 程序之中。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CArima::SaveModel(const string model_name) { uint model_order[]= {m_const,m_ar_order,m_diff_order,m_ma_order}; CFileBin file; ResetLastError(); if(!file.Open("models\\"+model_name+".model",FILE_WRITE|FILE_COMMON)) { Print("Failed to save model.Error: ",GetLastError()); return false; } m_modelname=(m_modelname=="")?model_name:m_modelname; long written=0; written = file.WriteIntegerArray(model_order); if(!written) { Print("Failed write operation, ",__LINE__,".Error: ",GetLastError()); return false; } if(m_ar_order) { written = file.WriteIntegerArray(m_arlags); if(!written) { Print("Failed write operation, ",__LINE__,".Error: ",GetLastError()); return false; } } if(m_ma_order) { written = file.WriteIntegerArray(m_malags); if(!written) { Print("Failed write operation, ",__LINE__,".Error: ",GetLastError()); return false; } } written = file.WriteDoubleArray(m_model); if(!written) { Print("Failed write operation, ",__LINE__,".Error: ",GetLastError()); return false; } written = file.WriteDouble(m_sse); if(!written) { Print("Failed write operation, ",__LINE__,".Error: ",GetLastError()); return false; } file.Close(); return true; }
SaveModel 方法启动模型保存,它需要一个字符串输入,即模型的新名称。该方法本身在共用文件文件夹( 终端\Common\Files\models)的 models 目录中写入二进制 .model 文件。 保存的文件包含模型顺序及其参数(如果已训练),还包括平方误差总和(sse)值。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CArima::LoadModel(const string model_name) { int found=StringFind(model_name,".model"); if(found>=0) m_modelname=StringSubstr(model_name,0,found); else m_modelname=model_name; if(StringFind(m_modelname,"\\")>=0) return false; string filename="models\\"+m_modelname+".model"; if(!FileIsExist(filename,FILE_COMMON)) { Print("Failed to find model, ",__LINE__,".Error: ",GetLastError()); return false; } CFileBin file; ResetLastError(); if(file.Open(filename,FILE_READ|FILE_COMMON)<0) { Print("Failed open operation, ",__LINE__,".Error: ",GetLastError()); return false; } uint model_order[]; file.Seek(0,SEEK_SET); if(!file.ReadIntegerArray(model_order,0,4)) { Print("Failed read operation, ",__LINE__,".Error: ",GetLastError()); return false; } m_const=bool(model_order[0]); m_ar_order=model_order[1]; m_diff_order=model_order[2]; m_ma_order=model_order[3]; file.Seek(sizeof(uint)*4,SEEK_SET); if(m_ar_order && !file.ReadIntegerArray(m_arlags,0,m_ar_order)) { Print("Failed read operation, ",__LINE__,".Error: ",GetLastError()); return false; } if(!m_ar_order) ArrayFree(m_arlags); if(m_ar_order) file.Seek(sizeof(uint)*(4+m_ar_order),SEEK_SET); if(m_ma_order && !file.ReadIntegerArray(m_malags,0,m_ma_order)) { Print("Failed read operation, ",__LINE__,".Error: ",GetLastError()); return false; } ArrayPrint(m_malags); if(!m_ma_order) ArrayFree(m_malags); if(m_ar_order || m_ma_order) file.Seek(sizeof(uint)*(4+m_ar_order+m_ma_order),SEEK_SET); if(!file.ReadDoubleArray(m_model,0,m_ma_order+m_ar_order+1)) { Print("Failed read operation, ",__LINE__,".Error: ",GetLastError()); return false; } file.Seek(sizeof(uint)*(4+m_ar_order+m_ma_order) + sizeof(double)*ArraySize(m_model),SEEK_SET); if(!file.ReadDouble(m_sse)) { Print("Failed read operation, ",__LINE__,".Error: ",GetLastError()); return false; } if(m_model[1]) m_istrained=true; else m_istrained=false; ZeroMemory(m_differenced); ZeroMemory(m_leads); ZeroMemory(m_innovation); m_insize=0; return true; }
LoadModel 方法需要模型名称,并读取以前保存的模型的所有属性。 这两个方法都返回 true 或 false,并将有用的错误消息写入终端的日志之中。
string GetModelName(void) { return m_modelname;}
GetModelName() 方法返回模型的名称,如果模型未曾保存,那它返回一个空字符串,否则它将返回保存模型时设置的名称。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| calculate the bayesian information criterion | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CArima::BIC(void) { if(!m_istrained||!m_sse) { Print(m_modelname," Model not trained. Train the model first to calculate the BIC."); return 0; } if(!m_differenced.Size()) { Print("To calculate the BIC, supply a training data set"); return 0; } uint n = m_differenced.Size(); uint k = m_ar_order+m_ma_order+m_diff_order+uint(m_const); return((n*MathLog(m_sse/n)) + (k*MathLog(n))); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CArima::AIC(void) { if(!m_istrained||!m_sse) { Print(m_modelname," Model not trained. Train the model first to calculate the AIC."); return 0; } if(!m_differenced.Size()) { Print("To calculate the AIC, supply a training data set"); return 0; } uint n = m_differenced.Size(); uint k = m_ar_order+m_ma_order+m_diff_order+uint(m_const); return((2.0*k)+(double(n)*MathLog(m_sse/double(n)))); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
BIC 和 AIC 方法也是全新的。 BIC 方法基于模型的 sse 值返回贝叶斯(Bayesian)信息准则。AIC 方法计算 Akiake 信息准则,其工作方式类似于 BIC 函数。贝叶斯信息(Bayesian)准则(BIC)和 Akaike 信息准则(AIC)是进行模型选择的统计度量。 这两个准则都旨在平衡模型的拟合优度与其复杂性,如此这般,若较简单模型的数据拟合能力与更复杂的模型近乎一样的话,则首选简单模型。
BIC 和 AIC 的不同之处在于它们如何平衡拟合优度和复杂性。 与 AIC 相比,BIC 更偏重模型的简单性,这意味着它比 AIC 更偏好较简单的模型。 另一方面,AIC 比 BIC 更喜欢选择较复杂的模型。 简单来说,BIC 和 AIC 允许我们比较不同的模型,并在参考模型复杂性的同时,选择最拟合我们数据的模型。 通过选择较简单的模型,我们可以避免过度拟合,当模型过于复杂,并且与数据拟合得太紧密时,就会发生过度拟合,从而降低其对预测新观测值的实用性。
它们都返回 0 误差,并且应该在训练模型后立即调用,同时仍加载训练数据。 当已训练模型初始化时,用于训练的数据将不可用,因此无法计算 BIC 和 AIC。
uint GetMinModelInputs(void) { return(m_diff_order + GetMaxArLag() + (GetMaxMaLag()*m_infactor));}
现在还可以查询模型所需的最小输入数量。 这是由 GetMinModelInputs() 方法完成的。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CArima::Summary(void) { string print = m_modelname+" Arima("+IntegerToString(m_ar_order)+","+IntegerToString(m_diff_order)+","+IntegerToString(m_ma_order)+")\n"; print+= "SSE : "+string(m_sse); int k=0; if(m_const) print+="\nConstant: "+string(m_model[k++]); else k++; for(uint i=0; i<m_ar_order; i++) print+="\nAR coefficient at lag "+IntegerToString(m_arlags[i])+": "+string(m_model[k++]); for(uint j=0; j<m_ma_order; j++) print+="\nMA coefficient at lag "+IntegerToString(m_malags[j])+": "+string(m_model[k++]); Print(print); return; }
最后,调用 Summary() 将模型的属性写入终端,它不再返回字符串。
实现预测
bool Predict(const uint num_pred,double &predictions[]); bool Predict(const uint num_pred,double &in_raw[], double &predictions[]); bool SaveModel(const string model_name); bool LoadModel(const string model_name); double BIC(void); double AIC(void);
应用模型进行预测是通过重载两个名为 Predict() 的方法实现的。 两者都采用两个相似的输入作为输入:
- num_pred - 此整数值定义所需的预测数。
- predictions - 输出预测值的双精度类型数组。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CArima::Predict(const uint num_pred,double &predictions[]) { if(!num_pred) { Print("Invalid number of predictions"); return false; } if(!m_istrained || !m_insize) { ZeroMemory(predictions); if(m_istrained) Print("Model not trained"); else Print("No input data available to make predictions"); return false; } ArrayResize(m_differenced,ArraySize(m_differenced)+num_pred,num_pred); ArrayResize(m_innovation,ArraySize(m_differenced)); evaluate(num_pred); if(m_diff_order) { double raw[]; integrate(m_differenced,m_leads,raw); ArrayPrint(raw,_Digits,NULL,m_insize-5); ArrayCopy(predictions,raw,0,m_insize+m_diff_order); ArrayFree(raw); } else ArrayCopy(predictions,m_differenced,0,m_insize); return true; }
Predict 方法的区别在于函数参数的数量。第一种方法需要两个参数,基于用于推导模型最优系数的训练数据进行预测。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CArima::Predict(const uint num_pred,double &in_raw[],double &predictions[]) { if(!num_pred) { Print("Invalid number of predictions"); return false; } if(!m_istrained) { ZeroMemory(predictions); Print("Model not trained"); return false; } int numofinputs=0; if(m_ar_order) numofinputs+=(int)GetMaxArLag(); if(m_ma_order) numofinputs+=int(GetMaxMaLag()*m_infactor); if(m_diff_order) numofinputs+=(int)m_diff_order; if(in_raw.Size()<(uint)numofinputs) { ZeroMemory(predictions); Print("Input dataset size inadequate. Size required: ",numofinputs); return false; } ZeroMemory(m_differenced); if(m_diff_order) { difference(m_diff_order,in_raw,m_differenced,m_leads); m_insize=m_differenced.Size(); } else { m_insize=in_raw.Size(); ArrayCopy(m_differenced,in_raw); } if(m_differenced.Size()!=(m_insize+num_pred)) ArrayResize(m_differenced,m_insize+num_pred,num_pred); ArrayFill(m_differenced,m_insize,num_pred,0.0); if(m_innovation.Size()!=m_insize+num_pred) ArrayResize(m_innovation,ArraySize(m_differenced)); ArrayInitialize(m_innovation,0.0); evaluate(num_pred); if(m_diff_order) { double raw[]; integrate(m_differenced,m_leads,raw); ArrayCopy(predictions,raw,0,m_insize+m_diff_order); ArrayFree(raw); } else ArrayCopy(predictions,m_differenced,0,m_insize); return true; }
第二种 Predict 方法需要第三个输入参数数组,该数组应包含用于计算预测的一个输入序列。 这两种方法都返回一个布尔值,并且还调用了私密 evaluate 函数。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CArima::evaluate(const uint num_p) { double pred=0; uint start_shift=(m_ma_order)?((!m_innovation[m_insize-1])?m_insize-(GetMaxMaLag()*m_infactor):m_insize):m_insize; uint d_size=(uint)ArraySize(m_differenced); int p_shift; for(uint i=start_shift; i<d_size; i++) { p_shift=0; pred=0; if(i>=m_insize) m_innovation[i]=0.0; if(m_const) pred+=m_model[p_shift++]; for(uint j=0; j<m_ar_order; j++) pred+=m_model[p_shift++]*m_differenced[i-m_arlags[j]]; for(uint k=0; i>=GetMaxMaLag() && k<m_ma_order; k++) pred+=m_model[p_shift++]*m_innovation[i-m_malags[k]]; if(i>=m_insize) m_differenced[i]=pred; if(i<m_insize) m_innovation[i]=pred-m_differenced[i]; } return; }
evaluate() 方法类似于 func() 方法,但略有不同。 它取所需的预测数量作为其唯一参数,并根据模型规格扫过多达五个数组。 它计算新的预测,并根据需要往误差(创新)序列添加新值。 一旦完成,将提取预测值,并复制到目标数组,提供给 Predict() 方法。 Predict 方法在成功时返回 true,如果遇到任何错误,则返回 false。
使用类
为了向用户演示修改后的 CArima 类,我们将构建一个脚本来训练一些模型,并执行一次暴力搜索,保存最佳模型。 然后,我们将展示如何在指标中使用这个保存的模型,利用它来提前一步进行预测。 最后,我们将使用相同的模型来创建一个简单的智能交易系统。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TrainARModel.mq5 | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #property script_show_inputs #include<Arima.mqh> enum ENUM_QUOTES { closeprices,//Close price medianprices//Mid price }; input uint MaximumSearchLag=5; input bool DifferenceQuotes=true; input datetime TrainingDataStartDate=D'2020.01.01 00:01'; input datetime TrainingDataStopDate=D'2021.01.01 23:59'; input string Sy="AUDUSD";//Set The Symbol input ENUM_TIMEFRAMES SetTimeFrame=PERIOD_M1; input ENUM_QUOTES quotestypes = closeprices; input string SetModelName = "ModelName"; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- CArima *arima[]; uint max_it=MaximumSearchLag; double sse[],quotes[],mid_prices[]; if(!max_it) ++max_it; MqlRates prices[]; int a_size=CopyRates(Sy,SetTimeFrame,TrainingDataStartDate,TrainingDataStopDate,prices); if(a_size<=0) { Print("downloaded size is ", a_size," error ",GetLastError()); return; } ArrayResize(arima,max_it); ArrayResize(sse,max_it); ArrayResize(quotes,a_size); for(uint i=0; i<prices.Size(); i++) { switch(quotestypes) { case medianprices: quotes[i]=(prices[i].high+prices[i].low)/2; break; case closeprices: quotes[i]=prices[i].close; break; } } uint u=0; for(uint i=0; i<max_it; i++) { u=uint(DifferenceQuotes); arima[i]=new CArima(i+1,u,0,true); if(arima[i].Fit(quotes)) { sse[i]=arima[i].GetSSE()*1.e14; Print("Fitting model ",i+1," completed successfully."); } else { sse[i]=DBL_MAX; Print("Fitting model ",i+1, " failed."); } } int index = ArrayMinimum(sse); Print("**** Saved model *****"); arima[index].Summary(); //save the best model for later use. arima[index].SaveModel(SetModelName); for(int i=0; i<(int)arima.Size(); i++) if(CheckPointer(arima[i])==POINTER_DYNAMIC) delete arima[i]; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
该脚本有助于暴力搜索拟合收盘价样本的最佳纯自回归模型。 应当强调的是,这只是一个简单的演示。 其可实现更复杂的模型,配合数量及类型各异的(AR/MA)项,不要忘记为这些项指定非连续滞后的能力。 如此这般,可能性是巨大的。 现在,我们只限于拟合一个纯自回归模型。
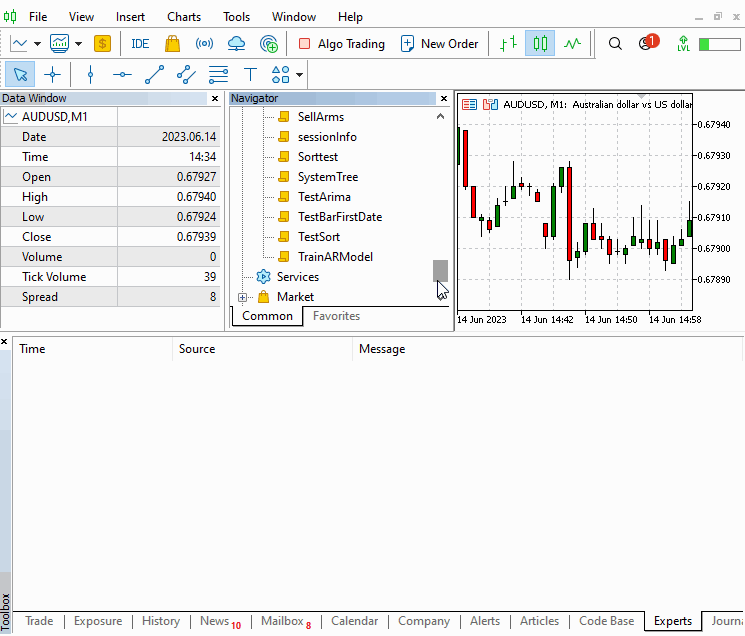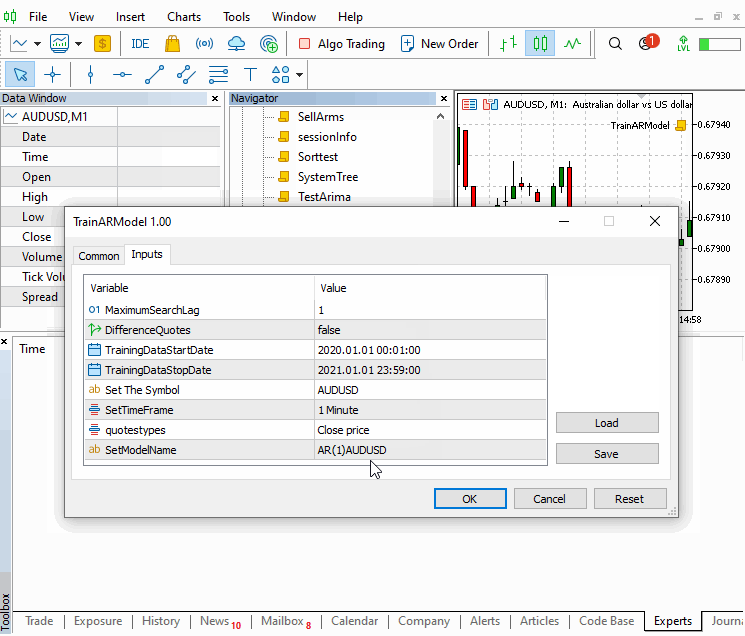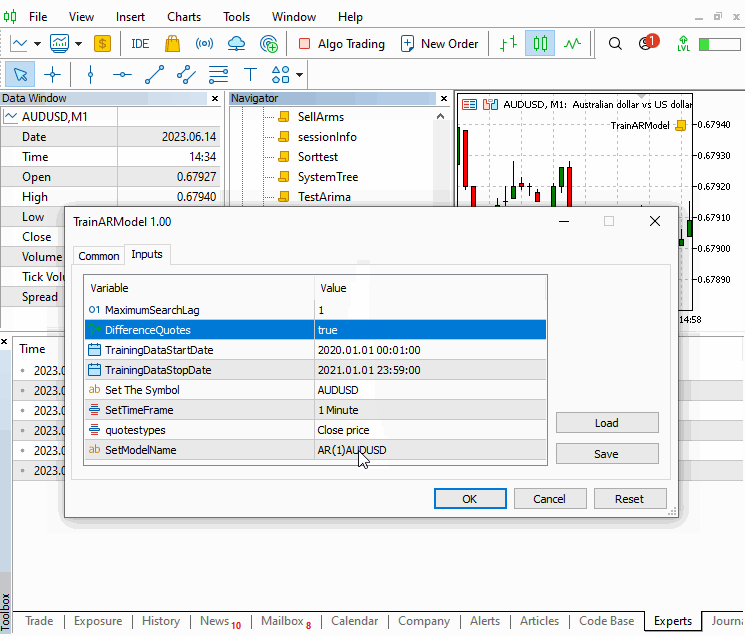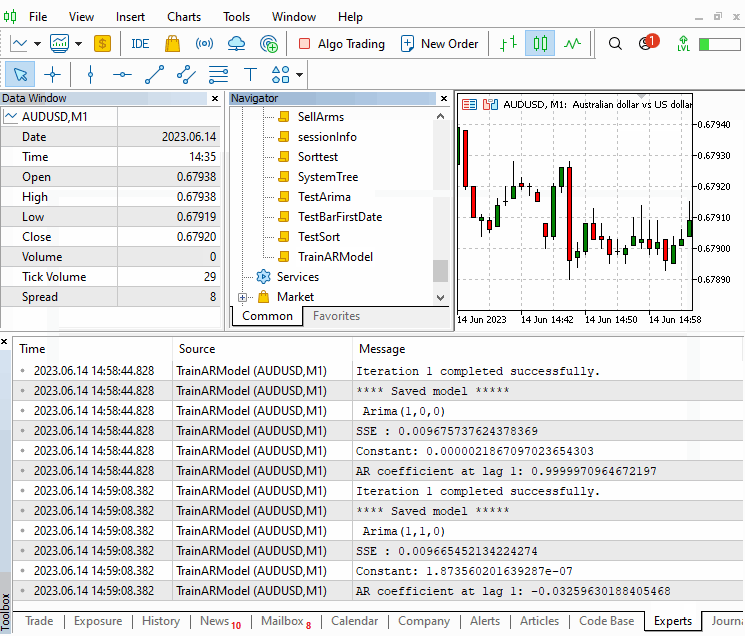
该脚本允许设置终止搜索的最大 AR 订单,以及价格样本数据的交易品种、时间帧和日期周期。 重要的是所用样本价格应充当运用模型进行预测时可能遇到的条件代表。
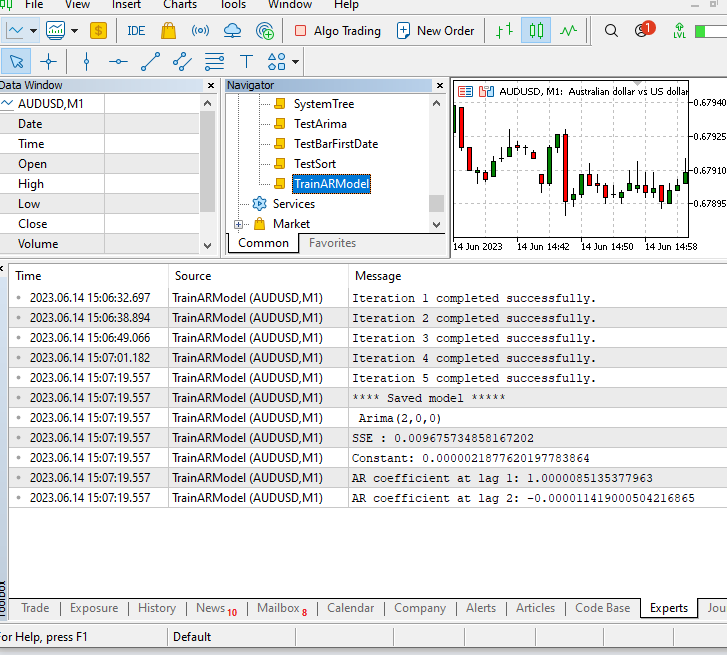
该脚本从已训练模型集中选择最小 sse 值的模型来判定最佳模型。然后保存所选模型,并将其属性打印到终端。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ArimaOneStepForecast.mq5 | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #property indicator_chart_window #property indicator_buffers 1 #property indicator_plots 1 #include<Arima.mqh> //--- plot PredictedPrice #property indicator_label1 "PredictedPrice" #property indicator_type1 DRAW_LINE #property indicator_color1 clrRed #property indicator_style1 STYLE_SOLID #property indicator_width1 1 //--- input parameters input string ModelName = "Model name"; //--- indicator buffers uint NumberOfPredictions=1; double PredictedPriceBuffer[]; double forecast[]; double pricebuffer[]; uint modelinputs; CArima arima; double mj[]; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- indicator buffers mapping SetIndexBuffer(0,PredictedPriceBuffer,INDICATOR_DATA); ArraySetAsSeries(PredictedPriceBuffer,true); if(!arima.LoadModel(ModelName)) return(INIT_FAILED); //--- modelinputs=arima.GetMinModelInputs(); ArrayResize(pricebuffer,modelinputs); ArrayResize(forecast,NumberOfPredictions); if(modelinputs<=0) return(INIT_FAILED); arima.Summary(); arima.GetModelParameters(mj); return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator iteration function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnCalculate(const int rates_total, const int prev_calculated, const datetime &time[], const double &open[], const double &high[], const double &low[], const double &close[], const long &tick_volume[], const long &volume[], const int &spread[]) { //--- ArraySetAsSeries(time,true); int limit = (prev_calculated<=0)?1000-(int)modelinputs-1:rates_total-prev_calculated+1; if(NewBar(time[0])) { for(int i = limit; i>=0; i--) { if(CopyClose(_Symbol,_Period,i+1,modelinputs,pricebuffer)==modelinputs) if(arima.Predict(NumberOfPredictions,pricebuffer,forecast)) PredictedPriceBuffer[i]=forecast[NumberOfPredictions-1]; } } //--- return value of prev_calculated for next call return(rates_total); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool NewBar(datetime c_time) { static datetime prev_time; if(c_time>prev_time) { prev_time=c_time; return true; } return false; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
该指标使用选定的模型提前一步进行预测。
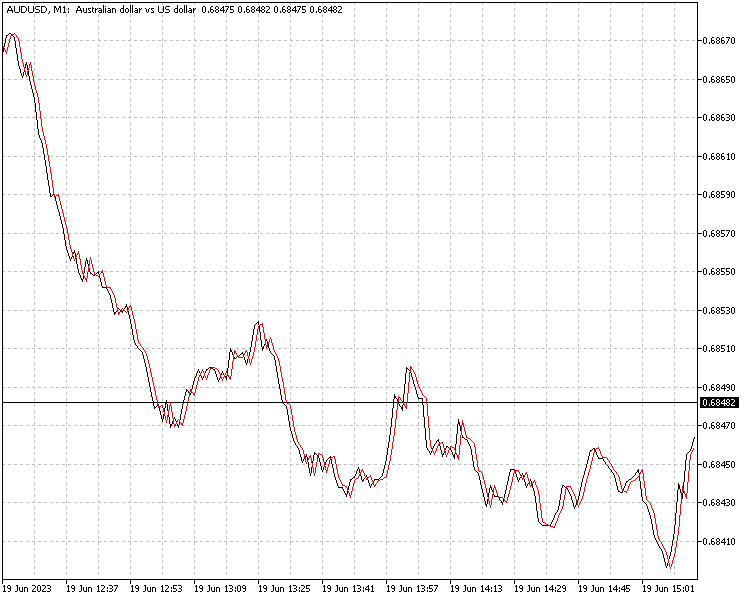
指定的模型在指标初始化期间加载。 然后,在主指标循环中调用 Predict 方法,基于提供的收盘价输入序列进行远期预测。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ArForecasterEA.mq5 | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> #include <Trade\SymbolInfo.mqh> #include <Trade\PositionInfo.mqh> #include <Trade\AccountInfo.mqh> #include <Arima.mqh> //--- input string ModelName ="model name"; // Saved Arima model name input long InpMagicNumber = 87383; input double InpLots =0.1; // Lots input int InpTakeProfit =40; // Take Profit (in pips) input int InpTrailingStop =30; // Trailing Stop Level (in pips) //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int InpOpenThreshold =1; // Differential to trigger trade (in points) int InpStopLoss = 0;// Stoploss (in pips) //--- //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ARIMA Sample expert class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CArExpert { protected: double m_adjusted_point; // point value adjusted for 3 or 5 points CTrade m_trade; // trading object CSymbolInfo m_symbol; // symbol info object CPositionInfo m_position; // trade position object CAccountInfo m_account; // account info wrapper CArima *m_arima; // Arma object pointer uint m_inputs; // Minimum number of inputs for Arma model //--- indicator buffers double m_buffer[]; // close prices buffer double m_pbuffer[1]; // predicted close prices go here //--- double m_open_level; double m_traling_stop; double m_take_profit; double m_stop_loss; public: CArExpert(void); ~CArExpert(void); bool Init(void); void Deinit(void); void OnTick(void); protected: bool InitCheckParameters(const int digits_adjust); bool InitModel(void); bool CheckForOpen(void); bool LongModified(void); bool ShortModified(void); bool LongOpened(void); bool ShortOpened(void); };
智能交易系统再次应用所保存模型来实现简单的策略。 基于下一根柱线上的预测,如果预测收盘价大于上一个已知收盘价,我们买入。 如果预测值较低,则卖出。
这只是一个简单的演示,不应该把它用在实盘账户里进行交易。
完整的 CArima 类及其依赖项的代码,以及本文中描述的脚本、指标和 EA,均包含在本文末尾附带的 zip 文件当中。
结束语
自回归模型可以使用 MT5 终端轻松训练,并应用在各种程序之中。 难点在于模型规格和选择。 为了克服这些挑战,并在外汇分析中建立有效的自回归模型,交易者应遵循一些最佳实践。 这些包括:- 从一个明确的研究问题开始:在构建自回归模型之前,交易者应该定义一个明确的研究问题,以及他们想要测试的假设。 这有助于确保建模过程保持重点,并与交易者的目标相关。
- 收集高品质数据:模型的准确性很大程度上取决于所用数据的质量。 交易者应使用可靠的数据来源,并确保其干净、完整、且与他们的研究问题相关。
- 测试多个模型:交易者应测试具有不同滞后长度和参数的多个模型,从而判定数据最准确、最有效的模型。
- 验证模型:一旦模型构建后,交易者应运用统计技术验证其准确性。
- 监控和调整模型:由于市场条件会随时间变化,模型的有效性也许发生变化。 交易者应随着时间的推移监控其模型的业绩,并根据需要进行调整,从而确保它继续提供对未来价格走势的准确见解。
| 文件 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Mql5/include/Powells.mqh | 包含 CPowellsMethod 类声明和定义的文件 |
| Mql5/include/Arima.mqh | CArima 类的包含文件 |
| Mql5/indicator/ArimaOneStepForecast.mql5 | 指标源代码,显示如何在指标中加载和应用模型 |
| Mql5/scripts/TrainARModel.mql5 | 演示如何训练模型并将其保存以备后用的脚本 |
| Mql5/experts/ArForecasterEA.mql5 | 专家顾问显示 EA 中保存模型的使用。 |
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/12798
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
@ndnz2018: habe vor kurzem folgende Klasse für ARIMA-Modell heruntergeladen: https://www.mql5.com/zh/articles/12798
当我看到机器人在几个时间框架内对简单的 AR 模型(20,1,0)显示出超过 90% 的命中率时,我真的很恼火。我还在网上找到其他文章,其中 ARIMA 模型的准确率超过 90%。然而,你可以在任何一本金融数学书中读到,增长(回报)并没有显示出明显的自相关性。我自己也计算了不同滞后期的自相关性 Corr(r(t),r(t-d)),确实没有相关性。怎么会这样呢?自相关在 ARIMA 模型中的定义是否有所不同?事实上,我一直认为自回归是对前值的简单回归。我是不是看得太简单了?
希望有人能帮我理清思路。
非常感谢
ndnz
文章中有一个 EA。为什么不在模拟账户上运行一下,看看数值是否得到确认。
你好,弗朗西斯
FileBin.mqh 是 MQL5 标准库的一部分,是任何 MT5 版本的一部分,您应该已经拥有它。