
基于通用 MLP 逼近器的EA
内容
引言
当提到神经网络时,许多人会联想到复杂的算法和繁琐的技术细节。其核心在于,神经网络是函数的复合体,其中每一层都由一个线性变换和一个非线性激活函数的组合构成。如果我们将其写成一个方程,它看起来会是这样的:
F(x) = f2(f1(x))
其中,f1 是第一层的函数,f2 是第二层的函数。
许多人认为神经网络是极其复杂且难以理解的东西,但我想用简单的术语来解释它,以便每个人都能从一个全新的视角来看待它。神经网络有许多不同的架构,每种架构都为执行特定任务而设计。在本文中,我们将聚焦于最简单的多层感知机,它通过非线性函数对输入信息进行变换。只要知道了网络架构,我们就可以用解析形式将其写出来,其中神经元中的每个激活函数都充当一个非线性变换器。
网络的每一层都包含一组神经元,它们处理经过多次非线性变换传递而来的信息。多层感知机能够执行近似、分类和推断等任务。描述感知机工作的通用方程通过权重进行调整,这使得它能适应于不同的任务。
有趣的是,我们可以将这个逼近器集成到任何交易系统中。如果我们不提及 SGD 或 ADAM 这类优化器,只谈神经网络本身,那么 MLP 就可以作为一个信息变换器来使用。例如,它可以分析市场状况——无论是盘整、趋势还是过渡状态——并基于此应用不同的交易策略。我们也可以使用神经网络将指标数据转换为交易信号。
在本文中,我们的目标是破除关于神经网络使用复杂性的迷思,并展示如何在抛开权重和优化的复杂细节后,即使没有深厚的机器学习知识,也能创建一个基于神经网络的交易 EA。我们将逐步介绍创建 EA 的全过程,从数据的收集与准备,到模型的训练,再到将其集成到交易策略中。
深入探究训练中的问题
主要有三种训练类型。我们感兴趣的是这些类型在应用于市场数据分析时的细微差别。本文提出的方法旨在考虑到这些训练类型的缺点。
有监督学习。模型在带标签的数据上进行训练,基于样例进行预测。目标函数:最小化预测值与目标值之间的误差(例如均方误差 MSE)。然而,这种方法存在一些缺点。它需要大量高质量的带标签数据,这在时间序列的背景下是一个巨大的挑战。如果我们有清晰可靠的样例来进行训练,比如在手写数字识别或图像内容识别任务中,那么训练过程就会很顺利。神经网络学会识别的,正是它被训练去识别的东西。
在时间序列的情况下,情况则有所不同:为数据打标签,使其可靠性和相关性都值得信赖,是极其困难的。在实践中,结果往往是网络学到了我们假设”的东西,而不是与研究过程真正相关的东西。许多作者强调,成功的监督训练需要使用好的”标签,但在时间序列背景下,其质量程度往往难以预先确定。
因此,便产生了其他对训练质量的主观评估,例如“过拟合”。还引入了“噪声”这一人为概念,意味着一个过度“过拟合”的网络可能记住了噪声数据,而不是主要模式。你不可能在任何地方找到关于“噪声”和“过拟合”的明确定义和量化标准,正因为它们在时间序列分析中是主观的。因此,必须承认,将监督学习应用于时间序列需要考虑许多难以算法化的细微差别,这会显著影响模型在新数据上的稳定性。
无监督学习。模型本身在无标签的数据中寻找隐藏结构。目标函数可能因方法不同而异。由于没有明确的验证标记,评估所得结果的质量非常困难。如果数据没有清晰的结构,模型可能找不到有用的模式,而且我们也不知道数据中是否真的找到了与载体过程”直接相关的结构。
传统上被归类为无监督学习的方法包括:K-均值、自组织映射等。所有这些方法都使用其特定的目标函数进行训练。
让我们看几个例子:
- K-均值(K-means)。最小化簇内方差,该方差定义为每个点与其簇中心之间距离的平方和。
- 主成分分析(PCA)。最大化数据在新轴(主成分)上投影的方差。
- 决策树(DT)。最小化熵、基尼指数、方差等。
强化学习。目标函数:总奖励。这是一种机器学习技术,智能体(如程序或机器人)通过与环境交互来学习做出决策。智能体根据其行为获得奖励或惩罚。智能体的目标是通过从经验中学习来最大化总奖励。
由于训练的随机性,结果可能不稳定,这使得预测模型的行为变得困难,并且对于没有明确奖惩系统的问题,它并不总是适用,因为这会降低学习效果。强化学习通常与许多实际问题相关联:当使用 ADAM 等神经网络学习算法时,难以表示目标强化函数,因为需要将目标函数的值归一化到接近 [-1;1] 的范围内。这涉及到计算神经元中激活函数的导数,并将误差通过网络反向传递以调整权重,从而避免“权重爆炸”和导致神经网络停滞的类似效应。
我们上面看了训练类型的传统分类。如你所见,它们都基于对某个目标函数的最小化/最大化。于是很明显,它们之间的主要区别只有一点——“监督者”的存在与否。如果不存在,训练类型的划分就归结为需要优化的目标函数的具体特性。
因此,在我看来,训练类型的分类可以表示为:当存在目标值时(最小化预测相对于目标的误差)为监督学习;当不存在目标值时为无监督学习。无监督学习的子类型取决于基于数据属性(距离、密度等)、系统性能(综合指标,如利润、生产力等)、分布(用于生成模型)和其他评估标准的目标函数类型。
通用逼近器
我提出的方法属于第二种类型——无监督学习。在这种方法中,我们不试图“教会”神经网络如何正确交易,也不告诉它在哪里开仓或平仓,因为我们自己也不知道这些问题的答案。相反,让网络自己做出交易决策,而我们的工作是评估其整体的交易结果。
在这种情况下,我们不需要对评估函数进行归一化,也无需担心“权重爆炸”和“网络停滞”等问题,因为在这种方法中它们根本不存在。我们从代码逻辑上将神经网络与优化算法分离开来,只赋予它一项任务:将输入数据转换为一种反映交易员技能的新型信息。本质上,我们只是将一种信息转换为另一种信息,而无需理解时间序列中的模式,也无需知道如何交易才能盈利。
MLP(多层感知机)这类神经网络非常适合扮演这个角色,通用逼近定理也证实了这一点。该定理指出,神经网络可以逼近任何连续函数。在我们的案例中,“连续函数”指的是在被分析的时间序列中发生的过程。这种方法使我们无需诉诸于“噪声”和“过拟合”这类人为且主观的概念,因为它们没有量化价值。
要想了解其工作原理,只需看图 1 即可。我们向 MLP 输入一些与当前市场数据相关的信息(可以是 OHLC K线价格、指标值等),在输出端就能获得可直接使用的交易信号。在遍历完一个交易品种的历史数据后,我们就可以计算出目标函数,它是对交易结果的一项综合性评估(或评估组合),然后通过一个外部优化算法来调整网络权重,以最大化这个描述神经网络交易结果质量的目标函数。
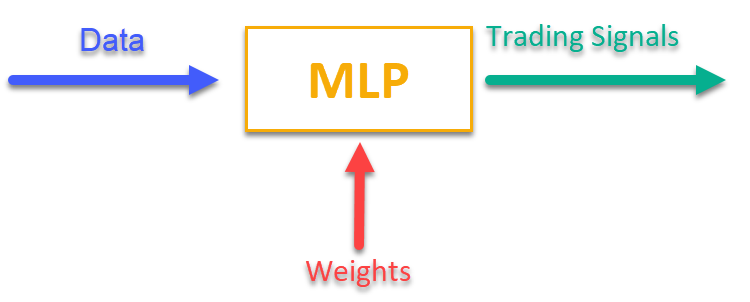
图例 1. 将一种类型的信息转换位另一种类型
将MLP集成至交易EA中
首先,我们将编写 MLP 类,然后我们将该类嵌入到 EA 中。这篇文章中包含了许多不同架构网络的不同实现,但我会展示我自己的 MLP 版本,它是一个纯粹的神经网络,不包含优化器。
让我们声明一个实现多层感知机的 C_MLP 类。主要功能:
1. Init () — 初始化:根据所需的层数和每层的神经元数量来配置网络,并返回权重的总数。
2. ANN () — 前向传播:从第一个输入层计算到最后一个输出层。该方法接收输入数据和权重,计算出网络的输出值(见图 1)。
3. GetWcount () — 获取网络中权重的总数。
4. LayerCalc () — 计算网络的单个层。
内部元素:
- layers — 存储神经元的值
- weightsCNT — 权重总数
- layersCNT — 层的总数
该类允许我们创建一个具有任意数量隐藏层以及任意数量神经元的 MLP 神经网络。
//+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) class | //| Implement a forward pass through a fully connected neural network | //| Architecture: Lin -> L1 -> L2 -> ... Ln -> Lout | //+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ class C_MLP { public: //-------------------------------------------------------------------- // Initialize the network with the given configuration // Return the total number of weights in the network, or 0 in case of an error int Init (int &layerConfig []); // Calculate the values of all layers sequentially from input to output void ANN (double &inLayer [], // input values double &weights [], // network weights (including biases) double &outLayer []); // output layer values // Get the total number of weights in the network int GetWcount () { return weightsCNT; } int layerConf []; // Network configuration - number of neurons in each layer private: //------------------------------------------------------------------- // Structure for storing the neural network layer struct S_Layer { double l []; // Neuron values }; S_Layer layers []; // Array of all network layers int weightsCNT; // Total number of weights in the network (including biases) int layersCNT; // Total number of layers (including input and output ones) int cnt_W; // Current index in the weights array when traversing the network double temp; // Temporary variable to store the sum of the weighted inputs // Calculate values of one layer of the network void LayerCalc (double &inLayer [], // values of neurons of the previous layer double &weights [], // array of weights and biases of the entire network double &outLayer [], // array for writing values of the current layer const int inSize, // number of neurons in the input layer const int outSize); // outSize - number of neurons in the output layer };
多层感知机(MLP) 根据给定的层配置进行初始化。主要步骤:
1. 检查配置:
- 检查网络是否至少有 2 层(输入层和输出层)。
- 检查每一层是否至少有 1 个神经元。如果条件不满足,则显示一条错误信息,并且函数返回 0。
2. 将每一层的配置保存到 layerconf 数组中,以便快速访问。
3. 创建层相关的数组:分配内存以存储每一层的神经元。
4. 权重计数:计算网络中的权重总数,包括每个神经元的偏置项。
该函数返回权重的总数,若发生错误则返回 0。
//+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Initialize the network | //| layerConfig - array with the number of neurons in each layer | //| Returns the total number of weights needed, or 0 in case of an error | //+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ int C_MLP::Init (int &layerConfig []) { // Check that the network has at least 2 layers (input and output) layersCNT = ArraySize (layerConfig); if (layersCNT < 2) { Print ("Error Net config! Layers less than 2!"); return 0; } // Check that each layer has at least 1 neuron for (int i = 0; i < layersCNT; i++) { if (layerConfig [i] <= 0) { Print ("Error Net config! Layer No." + string (i + 1) + " contains 0 neurons!"); return 0; } } // Save network configuration ArrayCopy (layerConf, layerConfig, 0, 0, WHOLE_ARRAY); // Create an array of layers ArrayResize (layers, layersCNT); // Allocate memory for neurons of each layer for (int i = 0; i < layersCNT; i++) { ArrayResize (layers [i].l, layerConfig [i]); } // Calculate the total number of weights in the network weightsCNT = 0; for (int i = 0; i < layersCNT - 1; i++) { // For each neuron of the next layer we need: // - one bias value // - weights for connections with all neurons of the current layer weightsCNT += layerConf [i] * layerConf [i + 1] + layerConf [i + 1]; } return weightsCNT; }
LayerCalc 方法使用双曲正切函数作为激活函数,对神经网络的单个层执行计算。主要步骤:
1. 输入与输出参数:
- inLayer [] — 来自前一层的输入值数组
- weights [] — 权重数组,包含偏置项和连接的权重
- outLayer [] — 用于存储当前层输出值的数组
- inSize — 输入层的神经元数量
- outSize — 输出层的神经元数量
2. 遍历输出层的神经元。对于输出层中的每一个神经元:
- 从一个偏置值开始
- 累加加权后的输入值(每个输入值乘以其对应的权重)
- 计算该神经元的激活函数值
3. 应用激活函数:
- 使用双曲正切函数,将数值非线性地转换到 -1 到 1 的区间内
- 将结果写入 outLayer [] 输出数组
//+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Calculate values of one layer of the network | //| Implement the equation: y = tanh(bias + w1*x1 + w2*x2 + ... + wn*xn) | //+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ void C_MLP::LayerCalc (double &inLayer [], double &weights [], double &outLayer [], const int inSize, const int outSize) { // Calculate the value for each neuron in the output layer for (int i = 0; i < outSize; i++) { // Start with the bias value for the current neuron temp = weights [cnt_W]; cnt_W++; // Add weighted inputs from each neuron in the previous layer for (int u = 0; u < inSize; u++) { temp += inLayer [u] * weights [cnt_W]; cnt_W++; } // Apply the "hyperbolic tangent" activation function // f(x) = 2/(1 + e^(-x)) - 1 // Range of values f(x): [-1, 1] outLayer [i] = 2.0 / (1.0 + exp (-temp)) - 1.0; } }
我们通过顺序计算所有层的数值——从输入层到输出层——来实现人工神经网络。
1. 输入与输出参数:
- inLayer [] — 输入到神经网络的输入值数组
- weights [] — 权重数组,既包含神经元之间的连接权重,也包含偏置项
- outLayer [] — 用于存放神经网络最后一层输出值的数组
2. 重置权重计数器:在计算开始前,用于追踪权重数组中当前位置的 cnt_W 变量被重置为 0。
3. 复制输入数据:使用 ArrayCopy 函数,将来自 inLayer 的输入数据复制到网络的第一层。
4. 遍历各层:
- 循环遍历神经网络的所有层。
- 对于每一层,都会调用 LayerCalc 函数,该函数基于前一层的输出值、权重以及各层的大小,来计算当前层的数值。
5. 在所有层都完成计算后,使用 ArrayCopy 函数将最后一层的输出值复制到 outLayer 中。
//+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Calculate the values of all layers sequentially from input to output | //+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ void C_MLP::ANN (double &inLayer [], // input values double &weights [], // network weights (including biases) double &outLayer []) // output layer values { // Reset the weight counter before starting the pass cnt_W = 0; // Copy the input data to the first layer of the network ArrayCopy (layers [0].l, inLayer, 0, 0, WHOLE_ARRAY); // Calculate the values of each layer sequentially for (int i = 0; i < layersCNT - 1; i++) { LayerCalc (layers [i].l, // output of the previous layer weights, // network weights (including bias) layers [i + 1].l, // next layer layerConf [i], // size of current layer layerConf [i + 1]); // size of the next layer } // Copy the values of the last layer to the output array ArrayCopy (outLayer, layers [layersCNT - 1].l, 0, 0, WHOLE_ARRAY); }
是时候编写一个基于MLP神经网络的机器学习自动化交易策略EA了。
1. 我们将引入用于交易操作、处理交易品种信息、数学函数、多层感知机以及优化算法的库。
2. 交易参数 - 持仓量、交易开始和结束时间。训练参数 - 选择优化器、神经网络结构、要分析的K线数量、用于训练的历史深度、模型有效期以及信号阈值。
3. 声明类和变量 - 用于工具类、神经网络的类对象,以及用于存储输入数据、权重和上次训练时间的变量。
#include "#Symbol.mqh" #include <Math\AOs\Utilities.mqh> #include <Math\AOs\NeuroNets\MLP.mqh> #include <Math\AOs\PopulationAO\#C_AO_enum.mqh> //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ input group "---Trade parameters-------------------"; input double Lot_P = 0.01; // Position volume input int StartTradeH_P = 3; // Trading start time input int EndTradeH_P = 12; // Trading end time input group "---Training parameters----------------"; input E_AO OptimizerSelect_P = AO_CLA; // Select optimizer input int NumbTestFuncRuns_P = 5000; // Total number of function runs input string MLPstructure_P = "1|1"; // Hidden layers, <4|6|2> - three hidden layers input int BarsAnalysis_P = 3; // Number of bars to analyze input int DepthHistoryBars_P = 10000; // History depth for training in bars input int RetrainingPeriod_P = 12; // Duration in hours of the model's relevance input double SigThr_P = 0.5; // Signal threshold //------------------------------------------------------------------------------ C_AO_Utilities U; C_MLP NN; int InpSigNumber; int WeightsNumber; double Inputs []; double Weights []; double Outs [1]; datetime LastTrainingTime = 0; C_Symbol S; C_NewBar B; int HandleS; int HandleR;
我选择了最先想到的、传递给神经网络进行处理的数据:OHLC - K线价格(在设置中默认为当前K线之前的3根K线)以及这些K线上的RSI和随机指标值。OnInit () 函数用于初始化一个使用神经网络的交易策略。
1. 初始化指标 - 创建RSI和随机指标的对象。
2. 根据 BarsAnalysis_P 输入参数计算网络的输入信号数量。
3. 设置神经网络结构 - 将包含网络配置的输入参数字符串进行拆分,检查层数和神经元数量的有效性。输入字符串参数指定了网络的隐藏层数及每层的神经元数,默认参数为 “1|1”,表示网络中有2个隐藏层,每层各有1个神经元。
4. 初始化神经网络 - 调用方法来初始化网络,并创建用于权重和输入数据的数组。
5. 信息输出 - 打印出关于层数和网络参数的数据。
6. 返回成功的初始化状态。
该函数确保了交易策略运行所需的所有必要组件都已准备就绪。
//—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— int OnInit () { //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Initializing indicators: Stochastic and RSI HandleS = iStochastic (_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 5, 3, 3, MODE_EMA, STO_LOWHIGH); HandleR = iRSI (_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 14, PRICE_TYPICAL); // Calculate the number of inputs to the neural network based on the number of bars to analyze InpSigNumber = BarsAnalysis_P * 2 + BarsAnalysis_P * 4; // Display information about the number of inputs Print ("Number of network logins : ", InpSigNumber); //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Initialize the structure of the multilayer MLP string sepResult []; int layersNumb = StringSplit (MLPstructure_P, StringGetCharacter ("|", 0), sepResult); // Check if the number of hidden layers is greater than 0 if (layersNumb < 1) { Print ("Network configuration error, hidden layers < 1..."); return INIT_FAILED; // Return initialization error } // Increase the number of layers by 2 (input and output) layersNumb += 2; // Initialize array for neural network configuration int nnConf []; ArrayResize (nnConf, layersNumb); // Set the number of inputs and outputs in the network configuration nnConf [0] = InpSigNumber; // Input layer nnConf [layersNumb - 1] = 1; // Output layer // Filling the hidden layers configuration for (int i = 1; i < layersNumb - 1; i++) { nnConf [i] = (int)StringToInteger (sepResult [i - 1]); // Convert a string value to an integer // Check that the number of neurons in a layer is greater than 0 if (nnConf [i] < 1) { Print ("Network configuration error, in layer ", i, " <= 0 neurons..."); return INIT_FAILED; // Return initialization error } } // Initialize the neural network and get the number of weights WeightsNumber = NN.Init (nnConf); if (WeightsNumber <= 0) { Print ("Error initializing MLP network..."); return INIT_FAILED; // Return initialization error } // Resize the input array and weights ArrayResize (Inputs, InpSigNumber); ArrayResize (Weights, WeightsNumber); // Initialize weights with random values in the range [-1, 1] (for debugging) for (int i = 0; i < WeightsNumber; i++) Weights [i] = 2 * (rand () / 32767.0) - 1; // Output network configuration information Print ("Number of all layers : ", layersNumb); Print ("Number of network parameters: ", WeightsNumber); //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Initialize the trade and bar classes S.Init (_Symbol); B.Init (_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT); return (INIT_SUCCEEDED); // Return successful initialization result } //——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
交易策略的主要逻辑在 OnTick () 函数中实现。该策略很简单:如果输出层神经元的信号超过了参数中设定的阈值,那么该信号就被解读为对应买入/卖出方向,并且如果没有未平仓的持仓且当前时间允许交易,我们就开仓。如果神经网络收到相反的信号,持仓就会被平仓;或者,如果允许交易的时间结束,持仓也会被强制平仓。让我们来列举策略的主要步骤:
1. 检查是否需要重新训练。如果距离上次训练已经过去了足够长的时间,则启动神经网络训练。如果发生错误,会显示一条消息。
2. 检测新K线。如果当前的价格变动不是新K线的开始,则终止函数的执行。
3. 获取数据。代码请求价格数据(开盘价、收盘价、最高价、最低价)和指标值(RSI 和随机指标)。
4. 数据归一化。在获取到的品种价格数据中找到最大值和最小值,之后所有数据都在 -1 到 1 的范围内进行归一化。
5. 预测。将归一化后的数据输入神经网络,以产生输出信号。
6. 生成交易信号。根据输出数据,生成买入(1)或卖出(-1)的信号。
7. 仓位管理。如果当前持仓与信号相悖,则将其平仓。如果开新仓的信号与允许交易的时间相符,则开仓。否则,如果存在未平仓的持仓,则将其平仓。
因此,OnTick() 中的逻辑实现了自动化交易的完整周期,包括训练、数据获取、归一化、预测和持仓管理。
//—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— void OnTick () { // Check if the neural network needs to be retrained if (TimeCurrent () - LastTrainingTime >= RetrainingPeriod_P * 3600) { // Start the neural network training if (Training ()) LastTrainingTime = TimeCurrent (); // Update last training time else Print ("Training error..."); // Display an error message return; // Complete function execution } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Check if the current tick is the start of a new bar if (!B.IsNewBar ()) return; //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Declare arrays to store price and indicator data MqlRates rates []; double rsi []; double sto []; // Get price data if (CopyRates (_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 1, BarsAnalysis_P, rates) != BarsAnalysis_P) return; // Get Stochastic values if (CopyBuffer (HandleS, 0, 1, BarsAnalysis_P, sto) != BarsAnalysis_P) return; // Get RSI values if (CopyBuffer (HandleR, 0, 1, BarsAnalysis_P, rsi) != BarsAnalysis_P) return; // Initialize variables to normalize data int wCNT = 0; double max = -DBL_MAX; // Initial value for maximum double min = DBL_MAX; // Initial value for minimum // Find the maximum and minimum among high and low for (int b = 0; b < BarsAnalysis_P; b++) { if (rates [b].high > max) max = rates [b].high; // Update the maximum if (rates [b].low < min) min = rates [b].low; // Update the minimum } // Normalization of input data for neural network for (int b = 0; b < BarsAnalysis_P; b++) { Inputs [wCNT] = U.Scale (rates [b].high, min, max, -1, 1); wCNT++; // Normalizing high Inputs [wCNT] = U.Scale (rates [b].low, min, max, -1, 1); wCNT++; // Normalizing low Inputs [wCNT] = U.Scale (rates [b].open, min, max, -1, 1); wCNT++; // Normalizing open Inputs [wCNT] = U.Scale (rates [b].close, min, max, -1, 1); wCNT++; // Normalizing close Inputs [wCNT] = U.Scale (sto [b], 0, 100, -1, 1); wCNT++; // Normalizing Stochastic Inputs [wCNT] = U.Scale (rsi [b], 0, 100, -1, 1); wCNT++; // Normalizing RSI } // Convert data from Inputs to Outs NN.ANN (Inputs, Weights, Outs); //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Generate a trading signal based on the output of a neural network int signal = 0; if (Outs [0] > SigThr_P) signal = 1; // Buy signal if (Outs [0] < -SigThr_P) signal = -1; // Sell signal // Get the type of open position int posType = S.GetPosType (); S.GetTick (); if ((posType == 1 && signal == -1) || (posType == -1 && signal == 1)) { if (!S.PosClose ("", ORDER_FILLING_FOK) != 0) posType = 0; else return; } MqlDateTime time; TimeToStruct (TimeCurrent (), time); // Check the allowed time for trading if (time.hour >= StartTradeH_P && time.hour < EndTradeH_P) { // Open a new position depending on the signal if (posType == 0 && signal != 0) S.PosOpen (signal, Lot_P, "", ORDER_FILLING_FOK, 0, 0.0, 0.0, 1); } else { if (posType != 0) S.PosClose ("", ORDER_FILLING_FOK); } } //——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
接下来,让我们来看看在历史数据上训练一个神经网络:
1. 获取数据。历史价格数据与RSI和随机指标值一同被加载。
2. 定义交易时间。创建一个数组,用于标记哪些K线柱落在允许的交易时间范围内。
3. 设置优化参数。初始化用于优化的参数边界和步长。
4. 选择优化算法。定义一个优化算法并指定种群大小。
5. 神经网络权重优化的主循环:
- 对于种群中的每一个解,都会计算其目标函数值,以评估其质量。
- 根据结果更新解的种群。
6. 输出结果。打印算法名称、最佳结果,并将最佳参数复制到权重数组中。
7. 释放优化算法对象所占用的内存。
该函数执行神经网络的训练,以基于历史数据寻找最佳参数。
//—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— bool Training () { MqlRates rates []; double rsi []; double sto []; int bars = CopyRates (_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 1, DepthHistoryBars_P, rates); Print ("Training on history of ", bars, " bars"); if (CopyBuffer (HandleS, 0, 1, DepthHistoryBars_P, sto) != bars) return false; if (CopyBuffer (HandleR, 0, 1, DepthHistoryBars_P, rsi) != bars) return false; MqlDateTime time; bool truTradeTime []; ArrayResize (truTradeTime, bars); ArrayInitialize (truTradeTime, false); for (int i = 0; i < bars; i++) { TimeToStruct (rates [i].time, time); if (time.hour >= StartTradeH_P && time.hour < EndTradeH_P) truTradeTime [i] = true; } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- int popSize = 50; // Population size for optimization algorithm int epochCount = NumbTestFuncRuns_P / popSize; // Total number of epochs (iterations) for optimization double rangeMin [], rangeMax [], rangeStep []; // Arrays for storing the parameters' boundaries and steps ArrayResize (rangeMin, WeightsNumber); // Resize 'min' borders array ArrayResize (rangeMax, WeightsNumber); // Resize 'max' borders array ArrayResize (rangeStep, WeightsNumber); // Resize the steps array for (int i = 0; i < WeightsNumber; i++) { rangeMax [i] = 5.0; rangeMin [i] = -5.0; rangeStep [i] = 0.01; } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- C_AO *ao = SelectAO (OptimizerSelect_P); // Select an optimization algorithm ao.params [0].val = popSize; // Assigning population size.... ao.SetParams (); //... (optional, then default population size will be used) ao.Init (rangeMin, rangeMax, rangeStep, epochCount); // Initialize the algorithm with given boundaries and number of epochs // Main loop by number of epochs for (int epochCNT = 1; epochCNT <= epochCount; epochCNT++) { ao.Moving (); // Execute one epoch of the optimization algorithm // Calculate the value of the objective function for each solution in the population for (int set = 0; set < ArraySize (ao.a); set++) { ao.a [set].f = TargetFunction (ao.a [set].c, rates, rsi, sto, truTradeTime); //FF.CalcFunc (ao.a [set].c); //ObjectiveFunction (ao.a [set].c); // Apply the objective function to each solution } ao.Revision (); // Update the population based on the results of the objective function } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Output the algorithm name, best result and number of function runs Print (ao.GetName (), ", best result: ", ao.fB); ArrayCopy (Weights, ao.cB); delete ao; // Release the memory occupied by the algorithm object return true; } //——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
我们实现一个目标函数,用以评估使用神经网络的交易策略的效率。
1. 初始化变量。设置用于追踪盈利、亏损、交易次数及其他参数的变量。
2. 处理历史数据。循环遍历历史数据,并检查当前K线柱上是否允许开仓。
3. 数据归一化。对于每一根K线,其价格值(最高价、最低价、开盘价、收盘价)和指标值(RSI和随机指标)都会被归一化,以便后续输入神经网络。
4. 信号预测。将归一化后的数据输入神经网络,由其生成交易信号(买入或卖出)。
5. 根据 OnTick () 中的交易策略管理虚拟仓位。
6. 计算结果。在函数末尾,计算总的盈亏比,乘以交易次数,并考虑一个用于平衡买卖次数不均衡的缩减因子。
该函数通过分析由神经网络生成的信号所产生的盈亏情况来评估交易策略的效率,并返回一个反映其质量的数值(本质上,该函数执行了一次从当前EA所处时间点开始的历史回测)。
//—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— double TargetFunction (double &weights [], MqlRates &rates [], double &rsi [], double &sto [], bool &truTradeTime []) { int bars = ArraySize (rates); // Initialize variables to normalize data int wCNT = 0; double max = 0.0; double min = 0.0; int signal = 0; double profit = 0.0; double allProfit = 0.0; double allLoss = 0.0; int dealsNumb = 0; int sells = 0; int buys = 0; int posType = 0; double posOpPrice = 0.0; double posClPrice = 0.0; // Run through history for (int h = BarsAnalysis_P; h < bars - 1; h++) { if (!truTradeTime [h]) { if (posType != 0) { posClPrice = rates [h].open; profit = (posClPrice - posOpPrice) * signal - 0.00003; if (profit > 0.0) allProfit += profit; else allLoss += -profit; if (posType == 1) buys++; else sells++; allProfit += profit; posType = 0; } continue; } max = -DBL_MAX; // Initial value for maximum min = DBL_MAX; // Initial value for minimum // Find the maximum and minimum among high and low for (int b = 1; b <= BarsAnalysis_P; b++) { if (rates [h - b].high > max) max = rates [h - b].high; // Update maximum if (rates [h - b].low < min) min = rates [h - b].low; // Update minimum } // Normalization of input data for neural network wCNT = 0; for (int b = BarsAnalysis_P; b >= 1; b--) { Inputs [wCNT] = U.Scale (rates [h - b].high, min, max, -1, 1); wCNT++; // Normalizing high Inputs [wCNT] = U.Scale (rates [h - b].low, min, max, -1, 1); wCNT++; // Normalizing low Inputs [wCNT] = U.Scale (rates [h - b].open, min, max, -1, 1); wCNT++; // Normalizing open Inputs [wCNT] = U.Scale (rates [h - b].close, min, max, -1, 1); wCNT++; // Normalizing close Inputs [wCNT] = U.Scale (sto [h - b], 0, 100, -1, 1); wCNT++; // Normalizing Stochastic Inputs [wCNT] = U.Scale (rsi [h - b], 0, 100, -1, 1); wCNT++; // Normalizing RSI } // Convert data from Inputs to Outs NN.ANN (Inputs, weights, Outs); //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- // Generate a trading signal based on the output of a neural network signal = 0; if (Outs [0] > SigThr_P) signal = 1; // Buy signal if (Outs [0] < -SigThr_P) signal = -1; // Sell signal if ((posType == 1 && signal == -1) || (posType == -1 && signal == 1)) { posClPrice = rates [h].open; profit = (posClPrice - posOpPrice) * signal - 0.00003; if (profit > 0.0) allProfit += profit; else allLoss += -profit; if (posType == 1) buys++; else sells++; allProfit += profit; posType = 0; } if (posType == 0 && signal != 0) { posType = signal; posOpPrice = rates [h].open; } } dealsNumb = buys + sells; double ko = 1.0; if (sells == 0 || buys == 0) return -DBL_MAX; if (sells / buys > 1.5 || buys / sells > 1.5) ko = 0.001; return (allProfit / (allLoss + DBL_EPSILON)) * dealsNumb; } //——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
图2展示了一个基于MLP的EA在神经网络未曾见过的新数据上所获得的交易结果资金余额图。其输入是经过归一化处理的OHLC价格值,以及基于指定K线柱数量计算出的RSI和随机指标。只要神经网络保持时效性,该EA就会持续交易;否则,它会先对网络进行训练,然后再继续交易。因此,图2中所示的结果反映了其在OOS(样本外)数据上的表现。
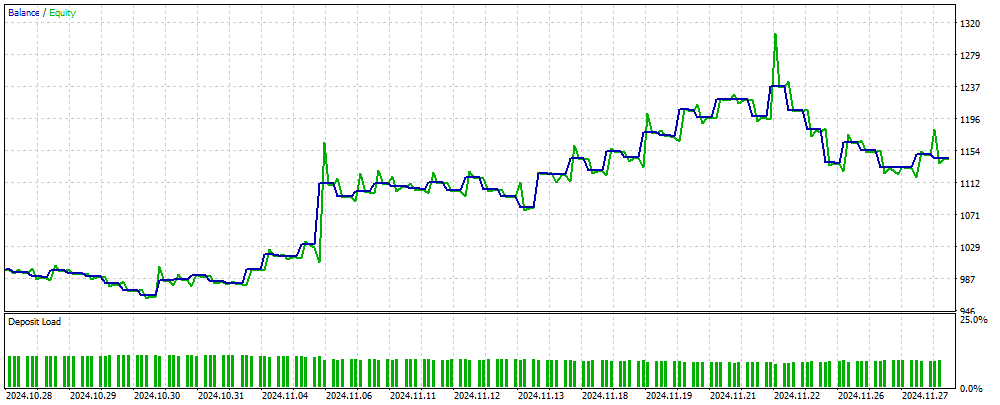
图例 2. EA在MLP未接触过的数据上的运行结果
总结
本文介绍了一种在交易EA中使用神经网络的简单且易于实现的方法,该方法适用于广大交易者,并不要求其在机器学习领域具备深厚的知识。这种方法免去了将目标函数值归一化后作为误差输入神经网络的步骤,也无需采用防止“权重爆炸”的方法。此外,它还解决了“网络停滞”的问题,并提供了带有结果可视化控制的直观训练方式。
需要注意的是,该EA在执行交易操作时并未包含必要的检查机制,其目的仅在于提供信息参考。
文中所用程序
| # | 名称 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | #C_AO.mqh | 包含 | 种群优化算法的父类 |
| 2 | #C_AO_enum.mqh | 包含 | 群体优化算法枚举 |
| 3 | Utilities.mqh | 包含 | 辅助函数库 |
| 4 | #Symbol.mqh | 包含 | 交易及辅助函数库 |
| 5 | ANN EA.mq5 | EA | 基于MLP神经网络的EA |
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自俄文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/16515
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 数据科学和机器学习(第 32 部分):保持您的 AI 模型更新,在线学习
数据科学和机器学习(第 32 部分):保持您的 AI 模型更新,在线学习
 开发回放系统(第 71 部分):取得正确的时间(四)
开发回放系统(第 71 部分):取得正确的时间(四)
 使用凯利准则与蒙特卡洛模拟的投资组合风险模型
使用凯利准则与蒙特卡洛模拟的投资组合风险模型

你好,安德烈、
知道了,谢谢您的快速回复。
科达角
在净值型账户上试试。这篇文章只是提供了一个思路,你必须根据你的经纪商的交易条件来调整 EA。
非常感谢你分享这篇文章和你的见解。好主意。我实施了一些独立的头寸处理,并在对冲账户(我的经纪商)上运行起来了。
你是最棒的。
非常感谢你分享这篇文章和你的见解。好主意。我实施了一些独立的头寸处理,并在对冲账户(我的经纪商)上运行起来了
你是最棒的。
超级棒
亲爱的作者,我重读了 TargetFunction() 代码好几遍,你似乎犯了一些错误。
1.在计算仓位利润时,您对利润进行了双重求和。
2.计算适应性指数时不使用 Ko 系数。亲爱的作者,我重读了 TargetFunction() 代码好几遍,你似乎犯了一些错误。
1.在计算仓位利润时,您对利润进行了双重求和。
2.计算适应性指数时不使用 Ko 系数。