
种群优化算法:人工多社区搜索对象(MSO)
内容
1. 概述
在上一篇文章中,我们研究了社群的演变,它们在搜索空间中可自由移动。然而,在此,我提议我们改变一下概念,并假设群在地区间移动,从一个地区跳到另一个地区。所有群都有自己的中枢,这些中枢在算法的每次迭代中都会更新。此外,我们还为整个群和其中的每个份子引入了记忆的概念。依据这些变化,我们的算法现在允许群基于有关最佳解的信息从一个地区移动到另一个地区。
这种新的修改为研究社群的演变开辟了新的可能性。路过的地区可与当地群分享信息和经验,从而导致更有效的搜索和适应。记忆引入令群能够保留有关之前迁徙的信息,并据其来决定未来的迁徙。
在本文中,我们将进行一连串实验,以便探讨这些新概念如何影响算法的搜索性能。我们将分析群间的互动、它们的合作和协调能力、以及它们的学习和适应能力。我们的研究成果可能会阐明社区系统的演变,并有助于更好地了解群体如何形成、进化、及适应变化中的环境。
最后,我们讨论了改进算法的可能性,及其在各个领域的应用。这项工作中引入的修改,令我们能够更有效地探索解空间,并找到最优值。这对于在优化和求解搜索领域工作的研究人员和从业者也许很实用。
2. 算法
整合社群原则的算法的最终目标是在群体成员之间创建一个有效的协调合作系统。此处是能被集成到该类算法中的普适原则:
- 迁徙算法允许团体在不同地区或区域之间移动。这将令该群能够探索各种资源和经验,不仅交流有关个体坐标的信息,且还能与其它群按地区形式交流元数据。
- 角色分离和专业化允许群成员选择、并专注于某些区域。这将令该群能够有效地利用其资源和技能来达成共同目标。这在求解多维空间问题时特别实用,因为多维空间同时存在具有不同属性(平滑和离散)的函数表面。
- 合作和互动允许群成员相互协作和互动。这也许涉及分享信息、讨论思路、以及插值和外推到未知区域。
- 冲突和冲突解决 — 群内冲突的解决机制。这也许包括制定规则和流程、调解和对话,从而解决分歧和争议。例如,防止份子竞争相同的区域,并使之节省算法的宝贵迭代。
- 领导和组织 — 在群中拥立提供组织、协调和决策的领导者的可能性。领导者应能激励和带领群达成目标。
- 知识和经验的交流令群能够积极地在份子间交流知识和经验。这将有助于群体从别处学习,适应新情况,并制定更明智的决策。能够在坐标之间建立复杂的逻辑连接,而不仅仅只会随机探索空间。
- 群记忆审计允许群保留有关先前迁徙、角色、专业化、合作、和解决冲突的信息。这将令该群能够据其经验,对未来的行动和互动制定更明智的决策。
将这些普遍原则整合到算法中,将创建一个更高效的社区系统,能够合作、协调、信息交流、及适应变化中的环境。
我们解释一下地区的含义,以便在算法的上下文中更好地理解。地区是优化参数的定义域(多维空间的坐标轴)的一部分。轴划分的地区对于所有群都是相同的。两个群 G0 和 G1 可以位于相应坐标的地区上,例如,如下所示:
G0 (X) |---V---|-------|-------|-------|-------|
G0 (Y) |-------|---V---|-------|-------|-------|
G0 (Z) |-------|-------|-------|-------|---V---|
-----------------------------------------------------
G1 (X) |-------|-------|---V---|-------|-------|
G1 (Y) |---V---|-------|-------|-------|-------|
G1 (Z) |-------|-------|-------|---V---|-------|
该算法的主要思路之一是启动群间交流有关繁荣地区的知识,同时在自由选择地区中保持一定的随机度。
现在我们转到讲述算法的第一个概念。首先,我们研究一种算法,其中群跨地区随机迁徙,无需考虑最佳解的记忆。
该算法的伪代码如下:
1. 随机为群选择地区
2. 均匀创建跨遍地区的点
3. 计算适应度函数
4. 更新全局解(最佳种群份子)
5. 获取当前迭代时群中最佳份子的数值
6. 更新每个群的地区最佳解记忆
7. 更新每个份子在地区的最佳解记忆
8. 按群更新最佳解
9. 对于一个群,询问另一个群是否其解好于每个坐标:
9. a)如果是:则取其地区
9. b)如果不是:选择另一个具有某个概率的地区
10. 按概率创建份子:
10. a)如果是:均匀跨遍地区
10. b)如果不是:澄清群的决定
11. 从流程第 4 项重复
群内部架构,及按地区标记坐标可以表示如下:
Group [groups]|
|-----------------------------------------
|fB
|-----------------------------------------
|fBLast
|-----------------------------------------
|cB [coords]
|-----------------------------------------
|cLast [coords]
|-----------------------------------------
|centre [coords]
|-----------------------------------------
|secInd [coords]
|-----------------------------------------
|secIndLast [coords]
|-----------------------------------------
|p [groupSize]|
| |-------------------
| |c [coords]
| |f
m [coords]|
|--------------
|min [sectNumb]
|max [sectNumb]
我们转到代码讲述。
为了把搜索空间标记为多个地区,我们需要指定地区的边界。为达此目的,我们将编写 S_Min_Max 结构。我们把其逐片分解:
S_Min_Max 结构有两个数据字段:“min” 和 “max”,它们表示地区的左侧边界,“max” — 地区的右侧边界。两个数组的大小均等于地区数量,由 “sectNumb” 参数指定。
该结构还定义了 Init 函数,其初始化 “min” 和 “max” 数组。它接受一个参数 “sectNumb”,其指定地区数量。在 Init 函数中,“min” 和 “max” 数组的大小依据传递的 “sectNumb” 参数进行更改。因此,该结构提供了一种存储地区边界,并调用 Init 函数初始化它们的方法。
//—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— struct S_Min_Max { void Init (int sectNumb) { ArrayResize (min, sectNumb); ArrayResize (max, sectNumb); } double min []; //sector border on the left, size - number of sectors double max []; //sector border on the right, size - number of sectors }; //——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
为了讲述作为群成员的份子,我们将编写 S_Particle 结构,其中包含两个字段:“c” 和 “f”。
- “c” - 存储份子坐标的数组。数组的大小由传递给 Init 函数的 “coords” 参数决定。
- “f” 是在 Init 函数中以 “-DBL_MAX” 值初始化的份子适应度函数的值。
因此,该结构提供了一个容器,用于存储份子的坐标,和关联的函数值。
//—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— struct S_Particle { void Init (int coords, int sectNumb) { ArrayResize (c, coords); f = -DBL_MAX; } double c []; double f; }; //——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
将一个群的份子合并到 S_Group 数据结构之中。S_Group 结构包含多个数据字段:
- “p” 表示存储群份子的 S_Particle 结构数组。“p” 数组的大小由传递给 Init 函数的 “groupSize” 参数决定。在 “for” 循环中,每个份子都调用 S_Particle 结构体中的 Init 函数进行初始化。
- “secInd” 和 “secIndLast” - 数组在每个坐标处存储地区索引。“secInd” 和 “secIndLast” 数组的大小由 “coords” 参数确定。
- “cB” 和 “cBLast” - 数组分别存储群中的最佳坐标,和前一个最佳坐标。“cB” 和 “cBLast” 数组的大小也由 “coords” 参数决定。
- “fB” 和 “fBLast” - 变量分别存储群中的最佳结果,和前一个最佳结果。
- “centre” - 数组存储中枢。“centre” 数组的大小也由 “coords” 参数决定,用于判定整个群的最佳地区坐标。
Init 函数初始化 S_Group 结构中的所有数组和变量。它需要三个参数:“coords” - 坐标的数量,“groupSize” - 群的大小,“sectNumb” - 地区的数量。
因此,该结构提供了一个容器,存储有关一群份子的信息。份子遵循群规则,不与其它群份子互动。互动是在群层面通过地区间接传递信息来实现的。
//—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— struct S_Group { void Init (int coords, int groupSize, int sectNumb) { ArrayResize (p, groupSize); ArrayResize (secInd, coords); ArrayResize (cB, coords); ArrayResize (cBLast, coords); ArrayResize (secIndLast, coords); ArrayResize (centre, coords); for (int i = 0; i < groupSize; i++) p [i].Init (coords, sectNumb); fB = -DBL_MAX; fBLast = -DBL_MAX; } S_Particle p []; int secInd []; //sector index on the coordinate, size is the number of coordinates int secIndLast []; //previous index of the sector on the coordinate, the size is the number of coordinates double cB []; //the best coord's in the group double cBLast []; //the previous best coord's in the group double fB; //the best result in the group double fBLast; //the previous best result in the group double centre []; }; //——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
我们来讲述具有 S_Agent 结构的优化个体,通过该结构,信息将从群份子传输到适应度函数计算。S_Agent 结构包含两个字段:
- “c” - 数组存储个体坐标。
- “f” - 存储个体适应度函数。
Init 函数初始化 S_Agent 结构体中的 “c” 数组和 “f” 变量。它需要一个参数 “coords”,由其指定了 “c” 数组的大小。
//—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— struct S_Agent { void Init (const int coords) { ArrayResize (c, coords); f = -DBL_MAX; } double c []; //coordinates double f; //fitness }; //——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
我们使用 C_AO_MSO 类来描述多社区算法。该类包含多个数据字段和方法:
- “cB” - 存储最佳坐标的数组。
- “fB” - 存储最佳坐标适应度的变量。
- “a” - 存储个体的 S_Agent 结构的数组。
- “rangeMax”、“rangeMin” 和 “rangeStep” - 数组分别存储最大和最小搜索范围和步长。
该类还包含多个方法:
- Init 初始化类的所有数据成员。它接受以下参数:coordinatesNumberP - 坐标数量,populationSizeP - 种群大小,groupsP - 群数量,sectorsNumberP - 每个坐标的地区数量,probRNSectorP - 随机地区概率,probUniformSectorP - 均匀地区分布概率,probClgroupP - 群的优调结果概率,和 powerP - 幂律分布函数的幂。
- Moving 和 Revision - 对群和群内份子执行基本操作的方法。
通常,C_AO_MSO 类是依据个体最优分布进行多重搜索的优化算法的实现。它包含管理个体、群、地区、以及执行搜索操作和优化结果的数据和方法。
//—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— class C_AO_MSO { //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- public: double cB []; //best coordinates public: double fB; //FF of the best coordinates public: S_Agent a []; //agents public: double rangeMax []; //maximum search range public: double rangeMin []; //manimum search range public: double rangeStep []; //step search public: void Init (const int coordinatesNumberP, //coordinates number const int populationSizeP, //population size const int groupsP, //number of groups const int sectorsNumberP, //sectors number const double probRNSsectorP, //probability random sector const double probUniformSectorP, //probability uniform distribution const double probClgroupP, //probability of clarifying the group's result const double powerP); //power public: void Moving (); public: void Revision (); //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- private: int coords; //coordinates number private: int popSize; //population size private: int sectNumb; //sectors number private: double sectorSpace []; //sector space private: S_Group gr []; //groups private: S_Min_Max min_max_Sector []; //sector boundary by coordinates private: int groups; //number of groups private: int sectorsNumber; //sectors number private: double probRNSsector; //probability random sector private: double probUniformSector; //probability uniform distribution private: double probClgroup; //probability of clarifying the group's result private: double power; //power private: bool revision; private: double SeInDiSp (double In, double InMin, double InMax, double Step); private: double RNDfromCI (double min, double max); private: double Scale (double In, double InMIN, double InMAX, double OutMIN, double OutMAX, bool revers); private: double PowerDistribution (const double In, const double outMin, const double outMax, const double power); }; //——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
Init 方法按给定的参数初始化 C_AO_MSO 类的对象。我们将该段代码分解为片段:
在函数伊始,初始化类的变量和数据成员。随机数生成器按当前时间(以微秒为单位)进行重置。然后,将 “fB” 变量设置为最小可能的双精度值 “-DBL_MAX”,并将 “revision” 变量设置为 “false”。
然后,传递给函数的参数被分配给类的相应字段。
为了将种群份子分配到群中,创建了 “partInSwarms” 数组。它将存储每个群中的份子数量。数组大小设置为等于群数量。然后,“particles” 变量通过将 “popSize” 总种群大小除以 “group” 的数量来计算每个群中的份子数量。
如果存在 “丢失” 的超额,则按群分配。循环一直运行,直到超额为 0。
接下来,更改数组大小,并初始化对象。
//—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— void C_AO_MSO::Init (const int coordinatesNumberP, //coordinates number const int populationSizeP, //population size const int groupsP, //number of groups const int sectorsNumberP, //sectors number const double probRNSsectorP, //probability random sector const double probUniformSectorP, //probability uniform distribution const double probClgroupP, //probability of clarifying the group's result const double powerP) //power { MathSrand ((int)GetMicrosecondCount ()); // reset of the generator fB = -DBL_MAX; revision = false; coords = coordinatesNumberP; popSize = populationSizeP; groups = groupsP; sectNumb = sectorsNumberP; probRNSsector = probRNSsectorP; probUniformSector = probUniformSectorP; probUniformSector = probClgroupP; power = powerP; //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- int partInSwarms []; ArrayResize (partInSwarms, groups); int particles = popSize / groups; ArrayInitialize (partInSwarms, particles); int lost = popSize - particles * groups; if (lost > 0) { int pos = 0; while (true) { partInSwarms [pos]++; lost--; pos++; if (pos >= groups) pos = 0; if (lost == 0) break; } } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- ArrayResize (rangeMax, coords); ArrayResize (rangeMin, coords); ArrayResize (rangeStep, coords); ArrayResize (cB, coords); ArrayResize (gr, groups); for (int s = 0; s < groups; s++) gr [s].Init (coords, partInSwarms [s], sectNumb); ArrayResize (sectorSpace, coords); ArrayResize (a, popSize); for (int i = 0; i < popSize; i++) a [i].Init (coords); } //——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
Moving 方法负责在第一次迭代时移动份子,并执行初始化群、及其份子位置的初始化函数。
在函数开始时,检查 “revision” 变量的值,以确保它只会执行一次,即它是否为 “false”。
代码的第一部分负责将空间划分为多个地区,并初始化 “min_max_Sector” 数组。对于每个 “c” 坐标,“sectorSpace[c]” 地区大小的计算方式为 “rangeMax[c]” 和 “rangeMin[c]” 之间的差值除以地区 “sectNumb” 的数量。然后在 “min_max_Sector” 数组中为每个坐标和地区初始化 “min” 和 “max” 值。
接下来,在搜索空间中排列份子。对于每个 “s” 群,为每个坐标选择随机地区。地区索引值存储在每个群的 “secInd” 数组之中。然后,该群的份子将随机分布在选定的地区内。对于每个 “p” 份子和 “c” 坐标,在地区的最小值和最大值内选择一个随机值 “cd”,该值存储在份子坐标中。
最后一个代码模块负责将份子发送到个体。将创建 “cnt” 计数器,该计数器将是列举个体。然后,对于每个 “s” 群和每个 “p” 份子,份子坐标值被复制到 “a[cnt].c” 数组当中,其中 “cnt” 在每次复制后递增。
如此,该方法负责优化算法中份子的随机初始放置,将空间划分为地区,为每个群随机选择地区,并在选定的地区内分布份子。然后将份子发送至个进一步处理。
//—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— void C_AO_MSO::Moving () { if (!revision) { //marking up sectors-------------------------------------------------------- ArrayResize (min_max_Sector, coords); for (int c = 0; c < coords; c++) { sectorSpace [c] = (rangeMax [c] - rangeMin [c]) / sectNumb; min_max_Sector [c].Init (sectNumb); for (int sec = 0; sec < sectNumb; sec++) { min_max_Sector [c].min [sec] = rangeMin [c] + sectorSpace [c] * sec; min_max_Sector [c].max [sec] = min_max_Sector [c].min [sec] + sectorSpace [c]; } } //-------------------------------------------------------------------------- int sect = 0; //sector double sectMin = 0.0; //sector's min double sectMax = 0.0; //sector's max int ind = 0; //index double cd = 0.0; //coordinate for (int s = 0; s < groups; s++) { //select random sectors for the group------------------------------------- for (int c = 0; c < coords; c++) { ind = (int)(RNDfromCI (0, sectNumb)); if (ind >= sectNumb) ind = sectNumb - 1; gr [s].secInd [c] = ind; gr [s].secIndLast [c] = ind; } //random distribute the particles of the group within the sectors--------- for (int p = 0; p < ArraySize (gr [s].p); p++) { for (int c = 0; c < coords; c++) { sect = gr [s].secInd [c]; cd = RNDfromCI (min_max_Sector [c].min [sect], min_max_Sector [c].max [sect]); gr [s].p [p].c [c] = SeInDiSp (cd, rangeMin [c], rangeMax [c], rangeStep [c]); } } } //-------------------------------------------------------------------------- //send particles to agents int cnt = 0; for (int s = 0; s < groups; s++) { for (int p = 0; p < ArraySize (gr [s].p); p++) { ArrayCopy (a [cnt].c, gr [s].p [p].c, 0, 0, WHOLE_ARRAY); cnt++; } } revision = true; } } //——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
在搜索空间中移动群及其份子的主要操作由 Revision 方法执行:
- 将每个份子的适应度函数值,与当前最佳值进行比较来更新全局最佳解。如果当前份子的目标函数值大于当前最佳值,则它将成为新的最佳值,且把其坐标复制到 “cB” 变量当中。
- 来自个体的结果移动到份子,并判定每个群中的最佳份子。每个份子的适应度函数的值设置为等于对应于该份子的个体的目标函数的值。如果份子适应度函数值大于群中的当前最佳值,则它将成为新的最佳值,且把其坐标复制到群 “cB” 变量当中。
- 为每个群更新最佳解。如果群中新的最佳值大于前值,则它将变为当前最佳值,且把其坐标复制到群的 “cBLast” 和 “secIndLast” 变量当中。
- 对于每个群的每个坐标,检查是否有具有更好解的其它群。如果存在这样的群,则当前群的地区和中枢将被更新为具有最佳解的群的地区和中枢值。否则,地区和中枢保持不变。
- 基于概率创建新份子。对于每个群和群中的每个份子,将基于概率生成新的坐标值。选择均匀分布,或调用 PowerDistribution 函数得到的分布,其概率由 “probUniformSector” 和 “power” 参数判定。
- 将所创建份子移至个体,以便在优化算法的下一次迭代中进一步使用。
该方法在每次迭代时更新解,并依据有关群中最佳解和概率的信息来创建新份子。
//—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— void C_AO_MSO::Revision () { //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- //Update the best global solution for (int i = 0; i < popSize; i++) { if (a [i].f > fB) { fB = a [i].f; ArrayCopy (cB, a [i].c, 0, 0, WHOLE_ARRAY); } } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- //Transfer the results from the agents to the particles //and get the value of the best particle in the group at the current iteration int cnt = 0; for (int s = 0; s < groups; s++) { gr [s].fB = -DBL_MAX; for (int p = 0; p < ArraySize (gr [s].p); p++) { gr [s].p [p].f = a [cnt].f; if (a [cnt].f > gr [s].fB) { gr [s].fB = a [cnt].f; ArrayCopy (gr [s].cB, a [cnt].c, 0, 0, WHOLE_ARRAY); } cnt++; } } int sector = 0; //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- //Update the best solution for the group for (int s = 0; s < groups; s++) { if (gr [s].fB > gr [s].fBLast) { gr [s].fBLast = gr [s].fB; ArrayCopy (gr [s].cBLast, gr [s].cB, 0, 0, WHOLE_ARRAY); ArrayCopy (gr [s].secIndLast, gr [s].secInd, 0, 0, WHOLE_ARRAY); } ArrayCopy (gr [s].centre, gr [s].cBLast); } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- int sect = 0; //sector double sectMin = 0.0; //sector's min double sectMax = 0.0; //sector's max int ind = 0; //index double cd = 0.0; //coordinate for (int s = 0; s < groups; s++) { for (int c = 0; c < coords; c++) { if (RNDfromCI (0.0, 1.0) < 0.6) { ind = (int)(RNDfromCI (0, groups)); if (ind >= groups) ind = groups - 1; if (ind == s) ind++; if (ind > groups - 1) ind = 0; if (gr [ind].fBLast > gr [s].fBLast) { gr [s].secInd [c] = gr [ind].secIndLast [c]; gr [s].centre [c] = gr [ind].cBLast [c]; } } else { if (RNDfromCI (0.0, 1.0) < probRNSsector) { ind = (int)(RNDfromCI (0, sectNumb)); if (ind >= sectNumb) ind = sectNumb - 1; gr [s].secInd [c] = ind; sect = gr [s].secInd [c]; cd = RNDfromCI (min_max_Sector [c].min [sect], min_max_Sector [c].max [sect]); gr [s].centre [c] = SeInDiSp (cd, rangeMin [c], rangeMax [c], rangeStep [c]); } else gr [s].secInd [c] = gr [s].secIndLast [c]; } } } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- for (int s = 0; s < groups; s++) { for (int p = 0; p < ArraySize (gr [s].p); p++) { for (int c = 0; c < coords; c++) { sect = gr [s].secInd [c]; if (RNDfromCI (0.0, 1.0) < probUniformSector) { cd = RNDfromCI (min_max_Sector [c].min [sect], min_max_Sector [c].max [sect]); } else { cd = PowerDistribution (gr [s].centre [c], min_max_Sector [c].min [sect], min_max_Sector [c].max [sect], power); } gr [s].p [p].c [c] = SeInDiSp (cd, rangeMin [c], rangeMax [c], rangeStep [c]); } } } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- cnt = 0; for (int s = 0; s < groups; s++) { for (int p = 0; p < ArraySize (gr [s].p); p++) { ArrayCopy (a [cnt].c, gr [s].p [p].c, 0, 0, WHOLE_ARRAY); cnt++; } } } //——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
接下来,我们将研究相同的算法,但增加了群及其份子的记忆,以及在搜索策略逻辑中的一些其它变化。
我们将更改算法的伪代码,同时参考群和份子的记忆可用性:
- 1. 随机为群选择地区
- 2. 创建跨地区的均匀点
- 4. 计算 FF
- 5. 更新全局解(最佳种群份子)
- 6. 获取当前迭代时群中最佳份子的数值。
- 7. 更新每个群的地区最佳解的记忆
- 8. 更新每个份子所在地区最佳解的记忆
- 9. 按群更新最佳解。
- 10. 对于一个群,询问另一个群的每个坐标是否有更好的解:
- 10. a)如果是:则取其地区
- 10. b)如果不是:按某个概率选择其它地区。
- 11. 按概率创建份子:
- 11. a)如果是:均匀跨越地区
- 11. b)如果不是:(概率 ? (澄清群的决定) : (澄清您的决定))
- 12. 从流程第 4 项重复
从理论上讲,添加记忆将允许群保留有关以前迁徙的信息,并用它来决定未来的动作。这可以帮助群体更好地适应不断变化的环境,并更有效地探索解空间。
我们对群的内部架构进行如下修改:
|-----------------------------------------
|fB
|-----------------------------------------
|fBLast
|-----------------------------------------
|cB [coords]
|-----------------------------------------
|cBLast [coords]
|-----------------------------------------
|secInd [coords]
|-----------------------------------------
|secIndLast [coords]
|-----------------------------------------
|sMemory [coords]|
| |---------------
| |cB [sectNumb]
| |fB [sectNumb]
|-----------------------------------------
|p [groupSize] |
| |-------------------
| |c [coords]
| |f
| |pMemory [coords]|
| |--------
| |cB [sectNumb]
| |fB [sectNumb]
添加描述记忆的 S_Memory 结构。对于群和份子,记忆看起来相同,并包含两个 “cB” 和 “fB” 数组,用于存储有关最佳坐标的信息,以及这些坐标的适应度函数。
//—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— struct S_Memory { void Init (int sectNumb) { ArrayResize (cB, sectNumb); ArrayResize (fB, sectNumb); ArrayInitialize (fB, -DBL_MAX); } double cB []; //the best sector coordinate, size is the number of sectors double fB []; //FF is the best coordinate on a sector, size is the number of sectors }; //——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
因此,将记忆声明添加到份子和群的结构之中:
//—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— struct S_Particle { <..............code is hidden.................> S_Memory pMemory []; //particle memory, size - the number of coordinates }; //—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— //—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— struct S_Group { <..............code is hidden.................> S_Memory sMemory []; //group memory, size - number of coordinates }; //——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
这些修改还影响到 Revision 方法:
- 更新集体记忆的最佳地区坐标。为每个群和每个坐标列举所有地区。如果地区上某个群的 “fB” 值大于地区记忆的 “fB” 值,则记忆的 “fB” 和 “cB” 会更新。
- 更新份子记忆的最佳位置。如果份子适应度函数值大于份子记忆的值,则记忆的 “fB” 和 “cB” 将更新。
//—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————— void C_AO_MSO::Revision () { //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- //Update the best global solution for (int i = 0; i < popSize; i++) { if (a [i].f > fB) { fB = a [i].f; ArrayCopy (cB, a [i].c, 0, 0, WHOLE_ARRAY); } } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- //Transfer the results from the agents to the particles //and get the value of the best particle in the group at the current iteration int cnt = 0; for (int s = 0; s < groups; s++) { gr [s].fB = -DBL_MAX; for (int p = 0; p < ArraySize (gr [s].p); p++) { gr [s].p [p].f = a [cnt].f; if (a [cnt].f > gr [s].fB) { gr [s].fB = a [cnt].f; ArrayCopy (gr [s].cB, a [cnt].c, 0, 0, WHOLE_ARRAY); } cnt++; } } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- //Update the best sector coordinates in the swarm's memory int sector = 0; for (int s = 0; s < groups; s++) { for (int c = 0; c < coords; c++) { sector = gr [s].secInd [c]; if (gr [s].fB > gr [s].sMemory [c].fB [sector]) { gr [s].sMemory [c].fB [sector] = gr [s].fB; gr [s].sMemory [c].cB [sector] = gr [s].cB [c]; } } } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- //Update in the memory of the particles their best positions by sector sector = 0; for (int s = 0; s < groups; s++) { for (int p = 0; p < ArraySize (gr [s].p); p++) { for (int c = 0; c < coords; c++) { sector = gr [s].secInd [c]; if (gr [s].p [p].f > gr [s].p [p].pMemory [c].fB [sector]) { gr [s].p [p].pMemory [c].fB [sector] = gr [s].p [p].f; gr [s].p [p].pMemory [c].cB [sector] = gr [s].p [p].c [c]; } } } } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- //Update the best solution for the group for (int s = 0; s < groups; s++) { if (gr [s].fB > gr [s].fBLast) { gr [s].fBLast = gr [s].fB; ArrayCopy (gr [s].cBLast, gr [s].cB, 0, 0, WHOLE_ARRAY); ArrayCopy (gr [s].secIndLast, gr [s].secInd, 0, 0, WHOLE_ARRAY); } } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- int sect = 0; //sector double sectMin = 0.0; //sector's min double sectMax = 0.0; //sector's max int ind = 0; //index double cd = 0.0; //coordinate for (int s = 0; s < groups; s++) { for (int c = 0; c < coords; c++) { ind = (int)(RNDfromCI (0, groups)); if (ind >= groups) ind = groups - 1; if (ind == s) ind++; if (ind > groups - 1) ind = 0; if (RNDfromCI (0.0, 1.0) < 0.6) { if (gr [ind].fBLast > gr [s].fBLast) { gr [s].secInd [c] = gr [ind].secIndLast [c]; } } else { if (RNDfromCI (0.0, 1.0) < probRNSsector) { ind = (int)(RNDfromCI (0, sectNumb)); if (ind >= sectNumb) ind = sectNumb - 1; gr [s].secInd [c] = ind; sect = gr [s].secInd [c]; if (gr [s].sMemory [c].fB [sect] == -DBL_MAX) { cd = RNDfromCI (min_max_Sector [c].min [sect], min_max_Sector [c].max [sect]); gr [s].sMemory [c].cB [sect] = SeInDiSp (cd, rangeMin [c], rangeMax [c], rangeStep [c]); } } else gr [s].secInd [c] = gr [s].secIndLast [c]; } } } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- for (int s = 0; s < groups; s++) { for (int p = 0; p < ArraySize (gr [s].p); p++) { for (int c = 0; c < coords; c++) { sect = gr [s].secInd [c]; if (RNDfromCI (0.0, 1.0) < probUniformSector) { cd = RNDfromCI (min_max_Sector [c].min [sect], min_max_Sector [c].max [sect]); } else { if (RNDfromCI (0.0, 1.0) < probClgroup) { cd = PowerDistribution (gr [s].sMemory [c].cB [sect], min_max_Sector [c].min [sect], min_max_Sector [c].max [sect], power); } else { cd = PowerDistribution (gr [s].p [p].pMemory [c].cB [sect], min_max_Sector [c].min [sect], min_max_Sector [c].max [sect], power); } } gr [s].p [p].c [c] = SeInDiSp (cd, rangeMin [c], rangeMax [c], rangeStep [c]); } } } //---------------------------------------------------------------------------- //send the particles to the agents cnt = 0; for (int s = 0; s < groups; s++) { for (int p = 0; p < ArraySize (gr [s].p); p++) { ArrayCopy (a [cnt].c, gr [s].p [p].c, 0, 0, WHOLE_ARRAY); cnt++; } } } //——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
3. 测试结果
该算法在不考虑份子记忆的情况下进行测试,产生了相当好的结果。该算法在排位表中排名前十。重点要注意的是,该算法只是一个逻辑示例,如果它展现了出色的结果,我会将其包含在表格中。该算法的进一步实现和修改也有很多机会。
虽然结果并不突出,但该算法在探索搜索空间的各个领域方面表现出了良好的搜索能力。
C_AO_MSO|60|30|9|0.05|0.05|10.0
=============================
5 Hilly's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.9313358190790157
25 Hilly's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.6649184286250989
500 Hilly's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.3282041522365852
=============================
5 Forest's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.9522099605531393
25 Forest's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.5542256622730999
500 Forest's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.08984352753493675
=============================
5 Megacity's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.7899999999999998
25 Megacity's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.33533333333333326
500 Megacity's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.042983333333333325
=============================
All score: 4.68905 (52.1%)
这些结果适用于拥有记忆的社群。我们可以看到整体算法结果略有恶化。无论如何,该算法在排位表的顶部占据了应有的位置。这表明算法的潜力,及其获得令人满意结果的能力。考虑不仅在群之间分享记忆,而且还延伸到份子之间,是改进算法的合乎逻辑的步骤。引入这种额外的互动可以带来新的思路和策略。正如本文前面提到的,描述了社群之间互动的各种场景,我只包括了其中的一部分。这意味着修改和改进算法的空间很大。
C_AO_MSOm|60|30|9|0.1|0.9|0.1|10.0
=============================
5 Hilly's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.9468984351872132
25 Hilly's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.5865441453580522
500 Hilly's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.3186653673403949
=============================
5 Forest's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.9064162754293653
25 Forest's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.43175851113448455
500 Forest's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.06865408175918558
=============================
5 Megacity's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.6783333333333333
25 Megacity's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.213
500 Megacity's; Func runs: 10000; result: 0.03310000000000002
=============================
All score: 4.18337 (46.4%)
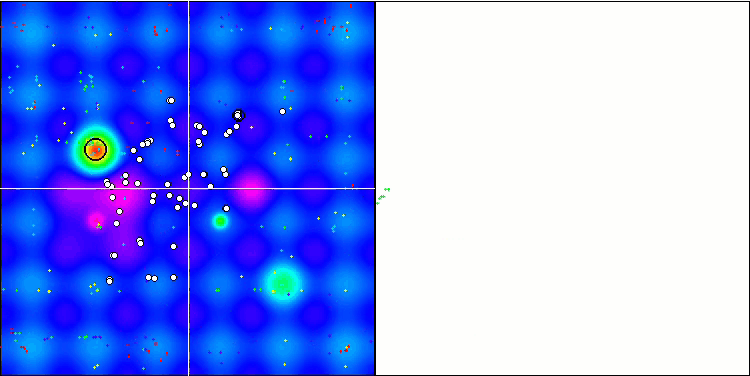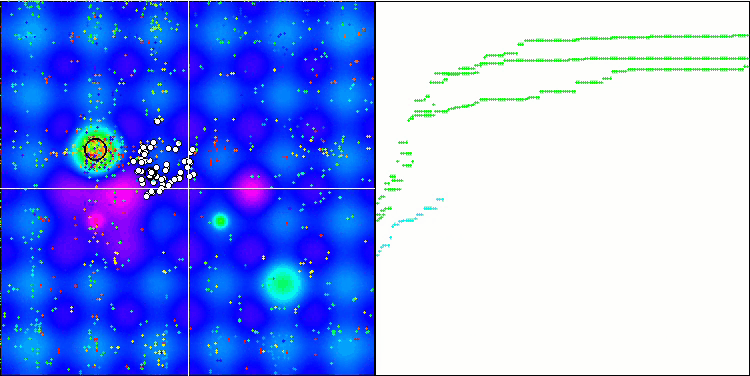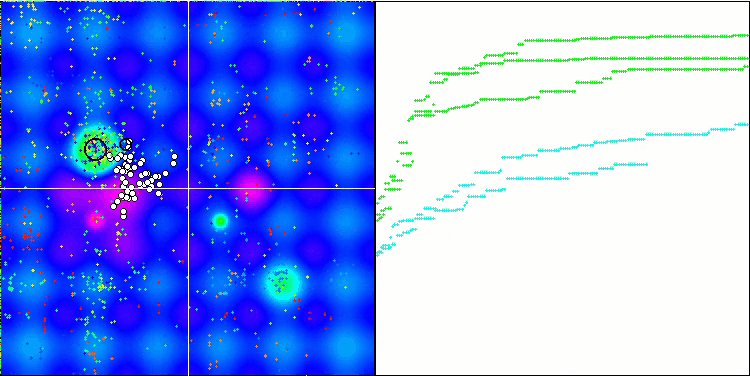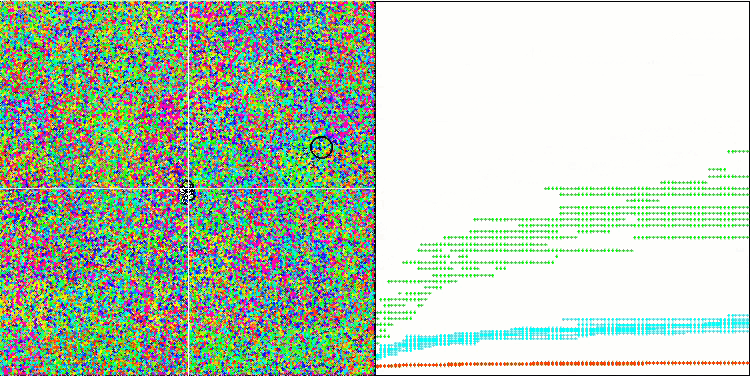
MSO 依据 Hilly 测试函数
MSO 依据 Forest 测试函数
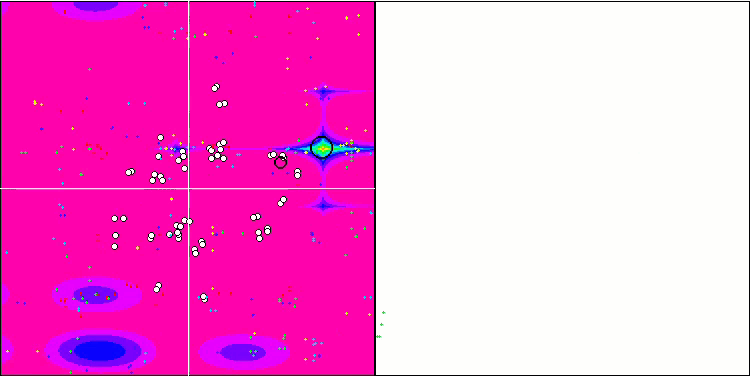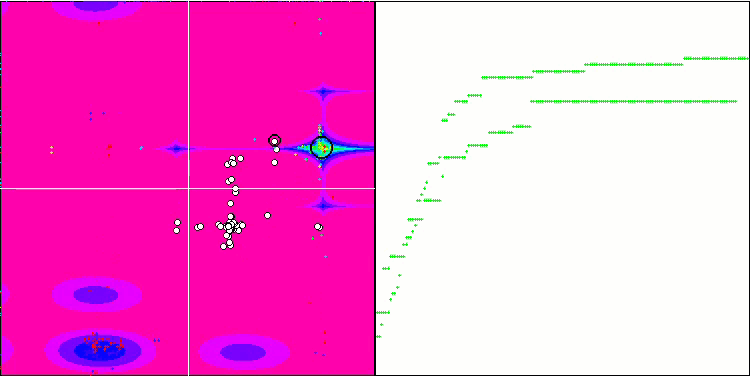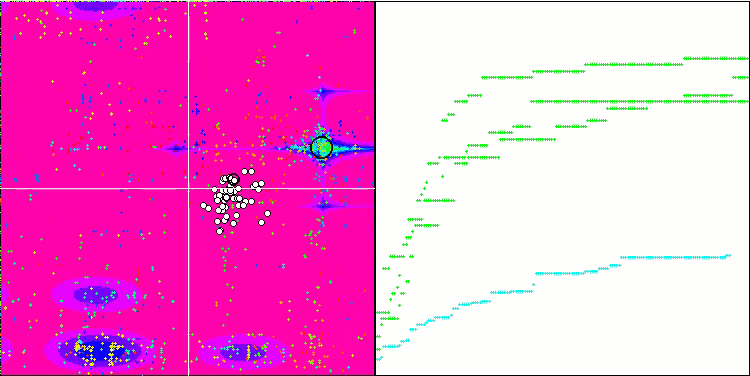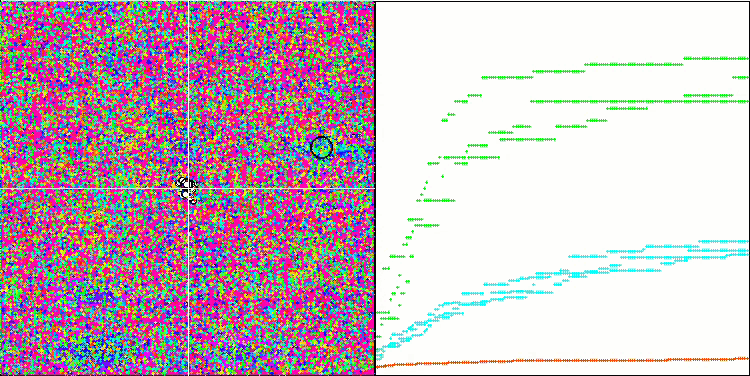
MSO 依据 Megacity 测试函数
总结
考虑到前面的推理和结果,我可以补充以下内容:在实验期间,发现与没有记忆的算法相比,有记忆的算法展现出的结果略差。不过,这并不意味着基于记忆的算法前景渺茫。最有可能的是,有必要修改群和份子之间的记忆交流概念,以便改善其结果。
此外,值得注意的是,结合社群之间互动的其它原则,可以显著提高记忆算法的效率。引入群之间的合作、协调和学习机制可以显著提高性能,并令该算法在我们的排位表中占据领先地位。
总而言之,该研究提出了一个基于地区间移动、及利用记忆,令社群进化的新概念。这些概念为研究社会系统及其合作、协调和适应能力开辟了新的可能性。我希望这些结果将有助于更好地了解社群在复杂的社会环境中如何运作和进化,并为该领域的进一步研究提供机会。
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自俄文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/14162
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 利用Python进行季节性过滤并为EA的ONNX深度学习模型选择时间周期
利用Python进行季节性过滤并为EA的ONNX深度学习模型选择时间周期
 构建K线图趋势约束模型(第一部分):针对EA和技术指标
构建K线图趋势约束模型(第一部分):针对EA和技术指标
 种群优化算法:鲸鱼优化算法(WOA)
种群优化算法:鲸鱼优化算法(WOA)

关于 FF 作为 TC 的复杂性。
工作人员的 GA 已在绿色框中完成优化。
先摸索着重新启动 GA,结果要好得多(红框)。
对于标准 GA 来说,多次发射是推荐的技术(我不知道这样做是好是坏--有支持也有反对)。
理论问题(可在实践中检验)。
如果我们在集合中添加一个假参数(不参与 FF 计算),其取值范围例如为 5 个值,算法结果会改善/恶化吗?
毫无疑问是恶化。为了找到 "好的 "假参数,FF 运算将被白白浪费掉。
假参数的可能变体占可能参数变体总数的百分比越大,影响就越大--在以随机结果为目标的限度内。
。
对于标准 GA 来说,多次启动是推荐的技术(我不知道这样做是好是坏--有支持也有反对)。
谢谢,这是内置的。
恶化,毫不含糊。为了找到 "好的 "假参数,Ff 运行将被白白浪费。
假参数的可能变体占可能参数变体总数的百分比越大,影响就越大--在以随机结果为目标的限度内。
。
我得去看看。
我得去看看。
我觉得更正确的说法是,假参数会增加查找难度。但在同等条件下,结果会更糟。比方说,如果你运行 100 万次 ff,结果是一样的,但如果你运行 1k 次,差别就会很明显。