
MQL5とPythonで自己最適化EAを構築する
概要
アルゴリズム取引の開発者にとって、予測が困難な市場の変動に適応することは大きな課題です。市場環境が変化するたびに、使用する戦略も変える必要があります。例えば、市場がレンジ相場のときは平均回帰戦略が最適かもしれませんが、強いトレンドが発生した際にはトレンドフォロー戦略がより適しています。
通常、私たちは単一の取引戦略を実装し、それをすべての市場環境で適用しようとしますが、これは安定した成果を保証するものではありません。また、複数の戦略を1つのプログラムに組み込み、ユーザーが手動で最適な戦略を選べるようにすることも可能ですが、これは完全な解決策とはいえません。
そこで、変化する市況に応じて自律的に最適な戦略を選び、切り替えるEAを設計することが重要となります。このためには、市場のトレンドや平均回帰の強度を定量的に測定する方法が必要です。EAがこれらの動きを的確に評価できれば、適切な戦略を自動的に選択することが可能になります。
この記事では、遷移行列を用いて市場の動向をモデル化し、トレンドフォロー戦略と平均回帰戦略のどちらを選択すべきかを判断する方法について説明します。まず、遷移行列の基本的な概念を理解し、これらの数学的ツールを活用して、より賢明な意思決定をおこなうインテリジェントな取引アルゴリズムを構築する手法を探ります。
はじめに:アンドレイ・マルコフとは誰か?

図1:若き日のアンドレイ・マルコフの写真
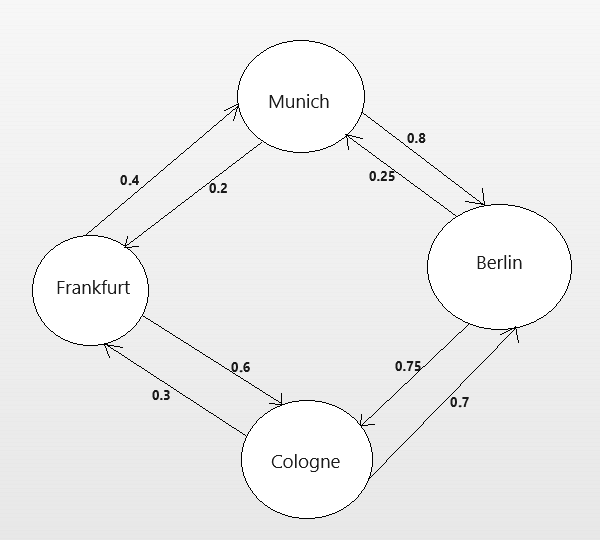
図2:ある運送会社の架空のマルコフモデルと、顧客によってランダムに使用されるルート
上のマルコフ連鎖を解釈してみましょう。このマルコフ連鎖モデルを解釈してみましょう。例えば、フランクフルトで搭乗した乗客のうち、40%がミュンヘンで下車し、残りの60%はケルンへ向かうことがわかります。さらに、ケルンに到着した乗客の30%はフランクフルトに戻り、70%はベルリンに移動します。このようにして、顧客が最も頻繁に利用するルートが視覚的に示されます。
また、このモデルからは、直行便のない目的地も明らかになります。つまり、過去70年の間に、ある2つの都市間を直接移動するニーズがほとんどなかったことを示しています。経営者として、フランクフルトからベルリンへの直行バスを追加するよりも、フランクフルトからケルンのような人気路線を強化する方が利益を見込めるという判断ができるのです。
ここでの重要なポイントは、遷移行列がある状態(都市)から別の状態へ移行する確率を示していることです。マルコフの理論によれば、次にどの状態に遷移するかは、現在の状態だけに依存します。これは、システムの変化を予測し、次に発生する可能性の高い状態を理解するのに役立ちます。金融市場にこの遷移行列を適用するには、まず市場が取り得るすべての状態を定義します。
戦略の構築 市場状態の定義
市場状態を定義する効果的な方法の1つは、テクニカル指標を使用することです。ここでは、MetaTrader 5端末で銘柄に移動平均を適用する例を挙げます。この方法により、以下のように市場の状態を分類することができます。ローソク足が移動平均線より上で終値をつけた場合、その状態を「UP」と定義します(図の「1」)。一方で、ローソク足が移動平均線より下で終値をつけた場合、その状態を「DOWN」と定義します(図の「2」)。
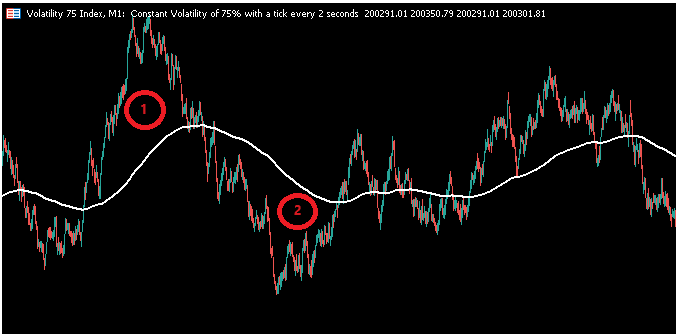
図3:市場状態を1か2のいずれかで表した模式図
マルコフ連鎖を用いて、市場が移動平均線の上で取引を終え、その後移動平均線の下で取引を終えるまでの推移をモデル化することができます。言い換えれば、移動平均線と終値の関係をマルコフ連鎖で表現することで、「あるローソク足が移動平均を上回って引けた場合、次のローソク足も移動平均を上回って引ける確率はどれくらいか?」という問いに答えることが可能になります。例えば、この確率が0.5を超える場合、次のローソク足も移動平均線の上で終わる可能性が高く、市場はトレンドフォロー戦略に適していると考えられます。逆に、この確率が0.5未満であれば、市場は平均回帰戦略に適している可能性が高いと推測できます。
はじめに:最初の遷移行列の構築
#Import packages
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import MetaTrader5 as mt5
from datetime import datetime
import pandas_ta as ta
import time
次に、ログイン認証情報を定義し、取引したい銘柄や使用したい時間枠など、関心のある他のグローバル変数を指定します。
#Account login details login = 123456789 password = "Enter Your Password" server = "Enter Your Server" symbol = "EURUSD" #What timeframe are we working on? timeframe = mt5.TIMEFRAME_M1 #This data frame will store the most recent price update last_close = pd.DataFrame() #We may not always enter at the price we want, how much deviation can we tolerate? deviation = 100 #The size of our positions volume = 0 #How many times the minimum volume should our positions be lot_multiple = 1
これでログインできます。
#Login if(mt5.initialize(login=login,password=password,server=server)): print("Logged in successfully") else: print("Failed to login")
次に、取引量を定義します。
#Setup trading volume symbols = mt5.symbols_get() for index,symbol in enumerate(symbols): if symbol.name == "EURUSD": print(f"{symbol.name} has minimum volume: {symbol.volume_min}") volume = symbol.volume_min * lot_multiple
#Specify date range of data to be collected date_start = datetime(2020,1,1) date_end = datetime.now()
データを取得したら、次に遷移行列を計算し、EUR USD市場がどのように推移するかを確認します。
#Fetch market data market_data = pd.DataFrame(mt5.copy_rates_range("EURUSD",timeframe,date_start,date_end)) market_data["time"] = pd.to_datetime(market_data["time"],unit='s') #Add simple moving average technical indicator market_data.ta.sma(length=20,append=True) #Delete missing rows market_data.dropna(inplace=True) #Inspect the data frame market_data
図4:現在の形式でのデータフレーム
次に、2本のローソク足の間にどれだけのスペースが必要かを定義します。この例では、「現在のローソク足が移動平均線の上で終値をつけた場合、次のローソク足も移動平均線の上で終値をつける確率は?」という質問に答えることに焦点を当てています。より長期的な移行確率に関心がある場合、このパラメータを大きく調整し、特定の戦略の要件に合わせることが重要です。
#Define how far ahead we are looking look_ahead = 1
遷移行列の計算は簡単です。
- まず、可能なすべての状態を定義します(ここでは単純な2つの状態であるUPとDOWN)。
- それぞれの状態に当てはまるローソク足の数を数えます。
- UP状態のローソク足全体の中で、次もUP状態になったローソク足の割合を計算します。
- DOWN状態のローソク足全体の中で、次もDOWN状態になったローソク足の割合を計算します。
#Count the number of times price was above the moving average up = market_data.loc[market_data["close"] > market_data["SMA_20"]].shape[0] #Count the number of times price was below the moving average down = market_data.loc[market_data["close"] < market_data["SMA_20"]].shape[0] #Count the number of times price was above the moving average and remained above it up_and_up = (market_data.loc[( (market_data["close"] > market_data["SMA_20"]) & (market_data["close"].shift(-look_ahead) > market_data["SMA_20"].shift(-look_ahead)) )].shape[0]) / up #Count the number of times price was below the moving average and remained below it down_and_down = (market_data.loc[( (market_data["close"] < market_data["SMA_20"]) & (market_data["close"].shift(-look_ahead) < market_data["SMA_20"].shift(-look_ahead)) )].shape[0]) / downそして、データをデータフレームにまとめます。
transition_matrix = pd.DataFrame({
"UP":[up_and_up,(1-down_and_down)],
"DOWN":[(1-up_and_up),down_and_down]
},index=['UP','DOWN'])
遷移行列を見てみましょう。
transition_matrix
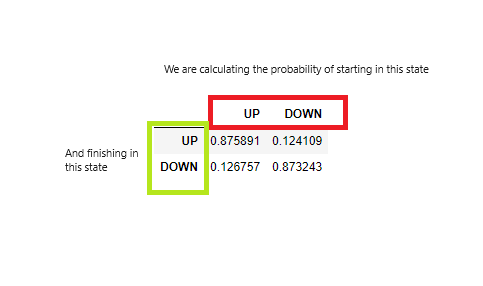
図5:遷移行列
現在のローソク足が移動平均線より上で引けた場合、次のローソク足が移動平均線より上で引ける確率は88%、次のローソク足が移動平均線より下で引ける確率は12%です。これは、この市場では価格が頻繁に反転しないことを示しており、トレンドフォロー戦略が適している可能性を示しています。したがって、市場はトレンドフォロー戦略に適合する可能性があります。
遷移行列ができたので、次はこの遷移行列を用いて、特定の証券を買うべきか売るべきかを判断するアルゴリズムの残りの部分を構築していきます。
def get_prices():
start = datetime(2024,6,1)
end = datetime.now()
data = pd.DataFrame(mt5.copy_rates_range("EURUSD",timeframe,start,end))
#Add simple moving average technical indicator
data.ta.sma(length=20,append=True)
#Delete missing rows
data.dropna(inplace=True)
data['time'] = pd.to_datetime(data['time'],unit='s')
data.set_index('time',inplace=True)
return(data.iloc[-1,:])
次に、現在の市場の状態を取得する関数を定義します。
def get_state(current_data): #Price is above the moving average, UP state if(current_data["close"] > current_data["SMA_20"]): return(1) #Price is below the moving average, DOWN state elif(current_data["close"] < current_data["SMA_20"]): return(2)
最後に、現在の市場の状態と移行確率が与えられたときに、アクションを選択する関数を定義します。
def get_action(current_state): if(current_state == 1): if(transition_matrix.iloc[0,0] > transition_matrix.iloc[0,1]): print("The market is above the moving average and has strong trends, buy") print("Opening a BUY position") mt5.Buy("EURUSD",volume) elif(transition_matrix.iloc[0,0] < transition_matrix.iloc[0,1]): print("The market is above the moving average and has strong mean reverting moves, sell") print("Opening a sell position") mt5.Sell("EURUSD",volume) elif(current_state == 2): if(transition_matrix.iloc[1,0] > transition_matrix.iloc[1,1]): print("The market is below the moving average and has strong mean reverting moves, buy") print("Opening a BUY position") mt5.Buy("EURUSD",volume) elif(transition_matrix.iloc[1,0] < transition_matrix.iloc[1,1]): print("The market is below the moving average and has strong trends, sell") print("Opening a sell position") mt5.Sell("EURUSD",volume)
これで、アルゴリズムが実際に動いているのを見ることができます。
while True: #Get data on the current state of our terminal and our portfolio positions = mt5.positions_total() #If we have no open positions then we can open one if(positions == 0): get_action(get_state(get_prices())) #If we have finished all checks then we can wait for one day before checking our positions again time.sleep(60)
市場が移動平均線を下回り、強いトレンドがある場合は売ります。
売りポジションを建てます。
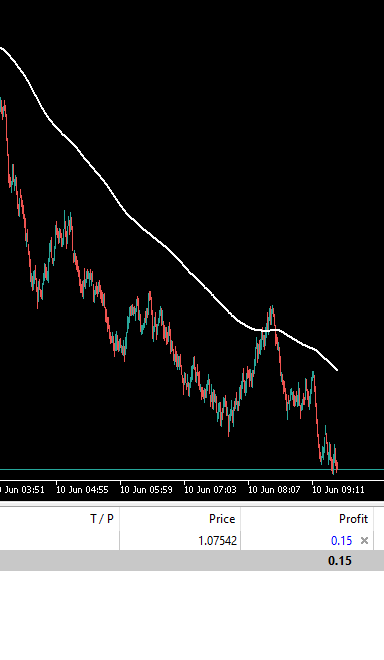
図6:取引アルゴリズムによって選択された取引
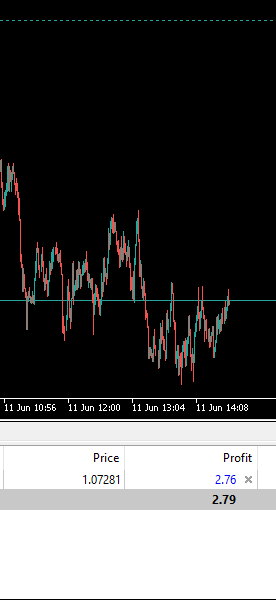
図7:翌日の取引アルゴリズムによって選択された取引
遷移行列については、まだ言えることがたくさんあります。しかし、これはこのトピックを紹介するための良い入門書です。議論を終える前に、遷移行列に影響を与える変数や、必要に応じて遷移行列をどのように操作できるかについても触れることが重要です。
| UP | DOWN | |
|---|---|---|
| UP | 0.926 | 0.074 |
| DOWN | 0.043 | 0.957 |
ご覧のように、EURUSDを銘柄として選択したとき、移動平均線の上に2本のローソク足が連続する確率は88%でしたが、今回選択した新しい銘柄「Boom 1000 Index」では、移動平均線の上に2本のローソク足が連続する確率は93%に上昇しました。したがって、選択の銘柄が遷移行列に与える影響は否定できません。
テクニカル指標のパラメータテクニカル指標は、市場状態を簡単に定義するのに役立ちます。移動平均の期間を変えることで、遷移行列に大きな影響を与えることができます。ポイントを簡単に説明するために、EURUSDのモデルに戻りましょう。最初の例では20期間の移動平均を使用しましたが、今回は2期間の移動平均を使用します。他の変数はすべて同じに保たれています。
| UP | DOWN | |
|---|---|---|
| UP | 0.456 | 0.544 |
| DOWN | 0.547 | 0.453 |
遷移確率が、どちらの方向にも50/50に収束していることに注目してください。これは、移動平均の期間が長くなるにつれて、遷移確率が50/50の可能性から離れていくことを示唆しています。
ローソク足の隙間これまでの議論では、連続する2本のローソク足の関係にのみ焦点を当てていました。しかし、ローソク足の間隔を広げると、遷移行列も変わります。再びEURUSDのモデルに戻り、今回は2本のローソク足の間隔を100に広げます。つまり、2本のローソク足の間隔を除けば、他の変数はすべて同じになります。
| UP | DOWN | |
|---|---|---|
| UP | 0.503 | 0.497 |
| DOWN | 0.507 | 0.493 |
推奨
マルコフ連鎖の設計に絶対的な「正しい」方法や「間違っている」方法はありませんが、アプリケーションを議論と一致させるためには、マルコフ連鎖を構築する際に以下に概説する設計パターンに従うことが必須です。transition_matrix = pd.DataFrame({
"UP":["UP AND UP","UP AND DOWN"],
"DOWN":["DOWN AND UP","DOWN AND DOWN"]
},index=['UP','DOWN']) 私たちの遷移行列は、トレンドに従うべきか、トレンドに逆らうべきかを素早く示すように設計されています。
トレンドフォロー戦略は、主対角線が最大の確率を含んでいるときに最もうまく機能する可能性があります。これは、市場がトレンドを拾い、そのトレンドを維持する傾向があることを意味します。

図8:トレンドに従う推移行列
逆に、平均回帰戦略は、非対角線に最大の確率が含まれる場合に最も効果的に機能する可能性があります。これは、市場が均衡レベルに戻る傾向があることを意味します。

図9:平均回帰する遷移行列
さらに、最も大きな確率が最下段にある場合、これは市場が弱気であることを意味します。
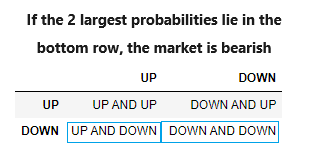
図10:弱気遷移行列
最後に、最大の確率が最上段にある場合、これは市場が強気であることを意味します。

図11:強気の遷移行列
MQL5の実装
MQL5を使ってストラテジーを実装し、実際の市場データを使って戦略を徹底的にテストします。
まず、必要なライブラリを読み込みます。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Transition Matrices.mq5 | //| Gamuchirai Zororo Ndawana. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Gamuchirai Zororo Ndawana." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|Overview | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ /* This expert advisor will demonstrate how we can use transition matrices to build self optimizing expert advisors. We will use the transition matrix to decide whether we should employ trend following, or mean reverting trading strategies. Gamuchirai Zororo Ndawana Friday 19 July 2024, 10:09 Selebi Phikwe Botswana */ //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Libraries | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #include <Trade/Trade.mqh>//Trade class CTrade Trade;
次に、エンドユーザーが編集できる入力パラメータを定義します。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Inputs | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ input int fetch = 5; //How much historical data should we fetch? input int look_ahead = 1; //Our forecast horizon input int ma_period = 20; //The MA Period input int rsi_period = 20; //The RSI Period input int wpr_period = 20; //The Williams Percent Range Period input int lot_multiple = 20; //How big should the lot sizes be input double sl_width = 0.4; //Stop loss size
次に、アプリケーション全体で必要となるグローバル変数があります。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|Global variables | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double minimum_volume;//Smallest lot size double ask_price;//Ask double bid_price;//Bid int ma_handler,rsi_handler,wpr_handler;//The handlers for our technical indicators vector ma_readings(fetch);//MA indicator values vector rsi_readings(fetch);//RSI indicator values vector wpr_readings(fetch);//WPR indicator values vector price_readings(fetch);//The vector we will use to store our historical price values matrix transition_matrix = matrix::Zeros(2,2);//The matrix to store our observations on price's transition behavior bool transition_matrix_initialized = false;//This flag will instruct the application to initialize the transition matrix double up_and_up = 0;//These variables will keep count of the price transitions double up_and_down = 0; double down_and_up = 0; double down_and_down = 0; double total_count = (double) fetch - look_ahead;//This variable will store the total number of observations used to calculate the transition matrix double trading_volume;//This is our desired trading size vector market_behavior = vector::Zeros(4);//Transition matrix interpretations
EAの初期化関数を定義します。この関数は、ユーザーが有効な入力を渡したことを確認し、テクニカル指標を設定します。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Initialization Function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- Initialize the technical indicator ma_handler = iMA(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,ma_period,0,MODE_EMA,PRICE_CLOSE); rsi_handler = iRSI(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,rsi_period,PRICE_CLOSE); wpr_handler = iWPR(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,wpr_period); minimum_volume = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol,SYMBOL_VOLUME_MIN); trading_volume = minimum_volume * lot_multiple; //--- Look ahead cannot be greater than fetch if(look_ahead > fetch) { Comment("We cannot forecast further into the future than thr to total amount of data fetched.\nEither fetch more data or forecast nearer to the present."); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- End of initialization return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
初期化が解除されるたびに従うプロシージャも必要です。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert de-initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { //--- Remove technical indicators IndicatorRelease(rsi_handler); IndicatorRelease(wpr_handler); IndicatorRelease(ma_handler); //--- Remove Expert Advisor ExpertRemove(); }
また、テクニカル指標を更新し、現在の市場価格を取得する機能も作ります。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|This function will update our technical indicator values | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void update_technical_indicators(void) { //--- Update bid and ask price ask_price = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol,SYMBOL_ASK); bid_price = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol,SYMBOL_BID); //--- Update each indicator value, we only need the most recent reading rsi_readings.CopyIndicatorBuffer(rsi_handler,0,0,1); wpr_readings.CopyIndicatorBuffer(wpr_handler,0,0,1); ma_readings.CopyIndicatorBuffer(ma_handler,0,0,1); }
テクニカル指標の数値の解釈は、常に推移行列によって測定される市場の動きに左右されることを忘れないでください。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|This function will find an entry opportunity based on our signals | | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void find_entry(void) { //--- Store the index of our largest entry ulong max_arg = market_behavior.ArgMax(); //--- First we have to know the behavior of the market before we decide to buy or sell if(max_arg == 0) { //--- This means that the market is bullish and we should probably only take buy oppurtunities Comment("The observed transition matrix can only be generated by a bullish market"); bullish_sentiment(0); } else if(max_arg == 1) { //--- This means that the market is bearish and we should probably only take sell oppurtunities Comment("The observed transition matrix can only be generated by a bearish market"); bearish_sentiment(0); } else if(max_arg == 2) { //--- This means that the market trends and we should probably join either side of the trend Comment("The observed transition matrix can only be generated by a trending market"); bearish_sentiment(0); bullish_sentiment(0); } else if(max_arg == 3) { //--- This means that the market is mean reverting and we should probably play against the trends on either side Comment("The observed transition matrix can only be generated by a mean reverting market"); bearish_sentiment(-1); bullish_sentiment(-1); } }
買い注文を実行する関数が必要です。
//+----------------------------------------------------------------+ //|This function will look for oppurtunities to buy | //+----------------------------------------------------------------+ void bullish_sentiment(int f_flag) { //--- This function analyses the market for bullish sentiment using our technical indicator //--- It has only 1 parameter, a flag denoting whether we should interpret the indicators in a trend following fashion //--- or a mean reverting fashion. For example 0 means interpret the indicators in a trend following fashion. //--- Therefore if we call the function and pass 0, RSI readings above 50 will trigger buy orders. //--- However if -1 was passed then RSI readings below 50 will trigger buy orders. //--- First make sure we have no open positions if(PositionsTotal() > 0) { return; } //--- Interpret the flag if(f_flag == 0) { //--- The flag is telling us to follow the trend if((rsi_readings[0] > 50) && (wpr_readings[0] > -50)) { Trade.Buy(trading_volume,_Symbol,ask_price,(ask_price - sl_width),(ask_price + sl_width),"Transition Matrix Order"); } } else if(f_flag == -1) { //--- The flag is telling us to bet against the trend if((rsi_readings[0] < 50) && (wpr_readings[0] < -50)) { Trade.Buy(trading_volume,_Symbol,ask_price,(ask_price - sl_width),(ask_price + sl_width),"Transition Matrix Order"); } } }
この関数は、売り注文を実行してくれます。市場が平均回帰的であれば、指標を「逆」に解釈することを思い出してください。
//+-------------------------------------------------------------+ //|This function will help us find oppurtunities to sell | //+-------------------------------------------------------------+ void bearish_sentiment(int f_flag) { //--- This function analysises the market for bearish sentiment using our technical indicator //--- It has only 1 parameter, a flag denoting whether we should interpret the indicators in a trend following fashion //--- or a mean reverting fashion. For example 0 means interpret the indicators in a trend following fashion. //--- Therefore if we call the function and pass 0, RSI readings below 50 will trigger sell orders. //--- However if -1 was passed then RSI readings above 50 will trigger sell orders. //--- First make sure we have no open positions if(PositionsTotal() > 0) { return; } //--- Interpret the flag if(f_flag == 0) { //--- Now we know how to interpret our technical indicators if((rsi_readings[0] < 50) && (wpr_readings[0] < -50)) { Trade.Sell(trading_volume,_Symbol,bid_price,(bid_price + sl_width),(bid_price - sl_width),"Transition Matrix Order"); } } else if(f_flag == -1) { //--- Now we know how to interpret our technical indicators if((rsi_readings[0] > 50) && (wpr_readings[0] > -50)) { Trade.Sell(trading_volume,_Symbol,bid_price,(bid_price + sl_width),(bid_price - sl_width),"Transition Matrix Order"); } } }
また、遷移行列が準備され、上で説明した手順に従って計算されるようにする関数も定義しておきましょう。
//+---------------------------------------------------------------+ //|This function will initialize our transition matrix | //+---------------------------------------------------------------+ void initialize_transition_matrix(void) { //--- We need to update our historical price readings and our MA readings ma_readings.CopyIndicatorBuffer(ma_handler,0,1,fetch); price_readings.CopyRates(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,1,fetch); //--- Now let us update our transition matrix for(int i = 0; i < fetch - look_ahead; i++) { //--- Did price go from being above the MA but end up beneath the MA? if((price_readings[i] > ma_readings[i]) && (price_readings[i + look_ahead] < ma_readings[i + look_ahead])) { up_and_down += 1; } //--- Did price go from being above the MA and remain above it? else if((price_readings[i] > ma_readings[i]) && (price_readings[i + look_ahead] > ma_readings[i + look_ahead])) { up_and_up += 1; } //--- Did price go from being below the MA but end up above it? else if((price_readings[i] < ma_readings[i]) && (price_readings[i + look_ahead] > ma_readings[i + look_ahead])) { down_and_up += 1; } //--- Did price go from being below the MA and remain below it? else if((price_readings[i] < ma_readings[i]) && (price_readings[i + look_ahead] < ma_readings[i + look_ahead])) { down_and_down += 1; } } //--- Let us see our counts so far Print("Up and up: ",up_and_up,"\nUp and down: ",up_and_down,"\nDown and up: ",down_and_up,"\nDown and down: ",down_and_down); double sum_of_counts = up_and_up + up_and_down + down_and_up + down_and_down; Print("Sum of counts: ",(sum_of_counts),"\nObservations made: ",total_count,"\nDifference:[the difference should always be 0] ",(total_count - sum_of_counts)); //--- Now we will calculate the transition matrix //--- The matrix position (0,0) stores the probaility that after making a move up, the market will continue rising //--- The matrix position (0,1) stores the probability that after making a move down, price will reverse and start rising //--- The matrix position (1,0) stores the probability that after making a move up, price will reverse and start falling //--- The matrix position (1,1) stores the probabilty that after making a move down, price will continue falling transition_matrix[0][0] = up_and_up / (up_and_up + up_and_down); transition_matrix[0][1] = down_and_up / (up_and_up + up_and_down); transition_matrix[1][0] = up_and_down / (down_and_up + down_and_down); transition_matrix[1][1] = down_and_down / (down_and_up + down_and_down); //--- Show the transition matrix Print("Our transition Matrix"); Print(transition_matrix); //--- Now we need to make sense of the transition matrix analyse_transition_matrix(); //--- Now we need to update the flag transition_matrix_initialized = true; }
遷移行列を解釈するヘルパー関数も必要です。
//+-------------------------------------------------------------+ //|This function will analyse our transition matrix | //+-------------------------------------------------------------+ void analyse_transition_matrix(void) { //--- Check if the market is bullish if((transition_matrix[0][0] > transition_matrix[1][0])&&(transition_matrix[0][1] > transition_matrix[1][1])) { market_behavior[0] = 1; } //--- Check if the market is bearish else if((transition_matrix[0][1] > transition_matrix[1][0])&&(transition_matrix[1][1] > transition_matrix[1][0])) { market_behavior[1] = 1; } //--- Check if the market trends else if(transition_matrix.Trace() > 1) { market_behavior[2] = 1; } //--- Check if the market is mean reverting else if(transition_matrix.Trace() < 1) { market_behavior[3] = 1; } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
OnTickハンドラは、上で説明したすべての関数が適切なタイミングで呼び出されるようにします。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { //--- First we must check if our transition matrix has been initialized if(!transition_matrix_initialized) { initialize_transition_matrix(); } //--- Otherwise our transition matrix has been initialized else { //--- Update technical indicator values update_technical_indicators(); //--- If we have no open positions we will use our tranistion matrix to help us interpret our technical indicators if(PositionsTotal() == 0) { find_entry(); } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
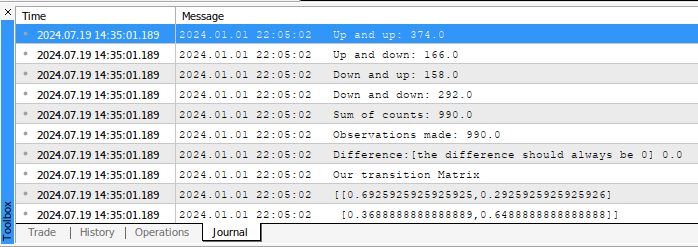
図12:MQL5で計算された遷移行列
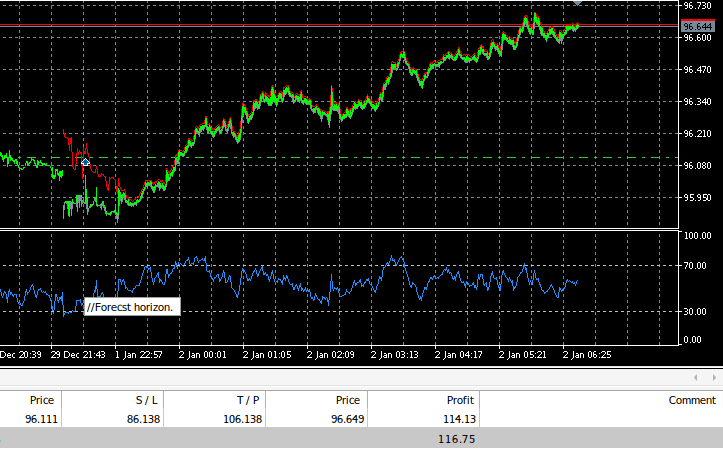
図13:EAがAUDJPYペアを取引している
結論
の記事では、変化する市況に適応するためのアルゴリズム取引におけるマルコフ連鎖の応用について考察しました。まず、マルコフ連鎖の基本概念を紹介し、それが市場のダイナミクスといったランダム過程のモデル化においていかに有用であるかを説明しました。次に、移動平均線などのテクニカル指標を用いて市場の状態を定義し、マルコフ連鎖を活用して市場の推移を分析する具体的な方法を示しました。この手法により、将来の市場動向の確率を予測し、トレンドフォロー戦略と平均回帰戦略のどちらを採用すべきかを判断できるようになります。このアプローチを通じて、意思決定能力を強化したインテリジェントな取引アルゴリズムを構築し、ダイナミックに変化する市場での取引パフォーマンスの向上を目指しています。
MetaQuotes Ltdにより英語から翻訳されました。
元の記事: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/15040
警告: これらの資料についてのすべての権利はMetaQuotes Ltd.が保有しています。これらの資料の全部または一部の複製や再プリントは禁じられています。
この記事はサイトのユーザーによって執筆されたものであり、著者の個人的な見解を反映しています。MetaQuotes Ltdは、提示された情報の正確性や、記載されているソリューション、戦略、または推奨事項の使用によって生じたいかなる結果についても責任を負いません。
 Candlestick Trend Constraintモデルの構築(第7回):EA開発モデルの改良
Candlestick Trend Constraintモデルの構築(第7回):EA開発モデルの改良
 時系列の非定常性の指標としての2標本コルモゴロフ–スミルノフ検定
時系列の非定常性の指標としての2標本コルモゴロフ–スミルノフ検定
 データサイエンスと機械学習(第27回):MetaTrader 5取引ボットにおける畳み込みニューラルネットワーク(CNN)に価値はあるか?
データサイエンスと機械学習(第27回):MetaTrader 5取引ボットにおける畳み込みニューラルネットワーク(CNN)に価値はあるか?
 パラボリックSARを使ってトレーリングストップを追加する方法
パラボリックSARを使ってトレーリングストップを追加する方法
- 無料取引アプリ
- 8千を超えるシグナルをコピー
- 金融ニュースで金融マーケットを探索
まあ、何事にもいろいろなやり方があるのはご存知の通りだ。私がここで説明したアプローチは、確実な結果を早く得るためのものだ。しかし、何事にも代償はつきものです。あなたが観察する遷移行列は、どれだけ多くのデータを取得したかに大きく影響されます。しかし、より多くのデータを取得するにつれて、遷移行列は安定し、変化しなくなります(収束します)。
このように言っておきましょう。遷移行列とNNアプローチは、まったく別の問題を解決しています。彼らは別の質問に答えているのです。遷移行列は何かを予測するものではなく、過去に起こったことを単に要約して教えてくれるものであり、未来に起こりそうなことを教えてくれるものではない。
一方、NNは将来何が起こりそうかを教えてくれる。1つのEAでその両方を使うことは可能だ。