
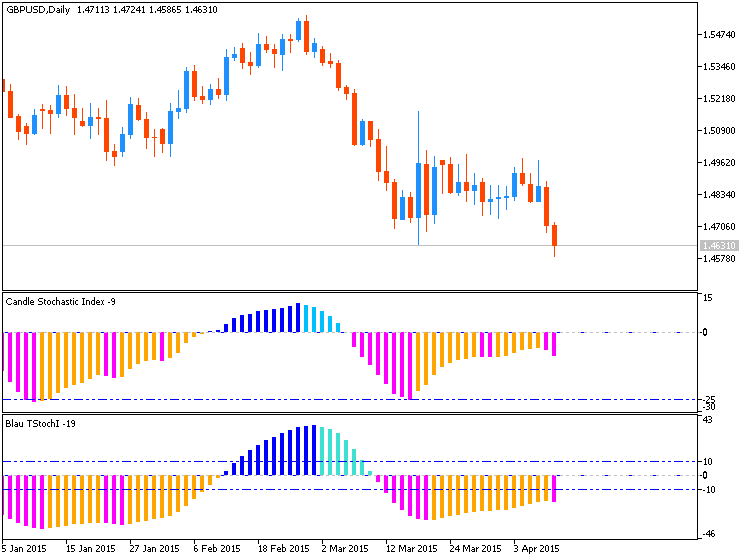
Video Manual: How to Trade - Key Points regarding the Stochastic Momentum Index, and Free to Downloads
Evaluates the Current Close relative to the midpoint of the Recent High/Low Range instead of simply the High and Low, and graphs this value along with a moving average (Stochastic %D)
Helps predict turning points and duration of current price move
Best used alongside a way to predict trendiness of market (like Chande Momentum Oscillator or R-Squared); like other oscillators, the indicator calculates the direction of an emerging trend, but does not generate reliable signals in a trending market
CALCULATING THE STOCHASTIC MOMENTUM INDEX
First select a period N; then, determine the center (C) of the range
during this period by adding the highest high and lowest low within the
period and dividing the sum by 2
C = (HMAX + LMIN)/2
Now subtract this C from the current close (CC) to get D, the "distance”:
D = CC–C
The indicator smooths the distance value twice (DS1 and DS2) with a 3-period EMA:
DS1 = EMA(3)(D)
DS2 = EMA(3)(DS1)
Now smooth the difference between HMAX and LMIN twice (DHL and DHL2),
using the earlier EMA, and dividing the second result by 2:
DHL = EMA(3)(HMAX – LMIN)
DHL2 = EMA(3)(DHL)/2
We can now calculate today's SMI value:
SMI = 100 * (DS2/DHL2)
READING THE STOCHASTIC MOMENTUM INDEX
An extreme position (approaching -100 or +100) implies the likelihood of a reversal
Common trading level: Overbought (bullish) above +40 / Oversold (bearish) below -40
Basic turning point signals:
- Buy when the indicator rises above -40 from below
- Sell when the indicator moves below +40 from above
- Cross-over 1: SMI passes moving average from below = Buy
- Cross-over 2: SMI falls below moving average from above = Sell (Cross-overs that occur between -15 and +15 are often unreliable)
Divergences are uncommon, but can be used to check signals or produce strong signals: Buy for bullish divergence, sell for bearish
FREE TO DOWNLOADS:
- Stochastic Momentum Index Blau_SMI - indicator for MetaTrader 5
- Stochastic Momentum Oscillator Blau_SM_Stochastic - indicator for MetaTrader 5
- Stochastic Index Blau_TStochI - indicator for MetaTrader 5
- Stochastic Oscillator Blau_TS_Stochastic - indicator for MetaTrader 5
- BlauCSI - indicator for MetaTrader 5
- BlauTStochI - indicator for MetaTrader 5


