
在 MQL5 中构建自定义市场状态检测系统(第二部分):智能交易系统(EA)
引言
在本系列文章的第一部分中,我们为应对瞬息万变的市场动态这一挑战奠定了必要的基础。我们建立了坚实的统计学根基,构建了能够客观分类市场行为的 CMarketRegimeDetector 类,并开发了自定义指标(MarketRegimeIndicator),以便在图表上直观地展示这些市场状态。我们从识别问题——即静态策略在动态市场中表现衰退——迈向了开发能够识别当前主导市场状态的系统:趋势(上涨/下跌)、震荡或高波动 (链接至第一部分以供参考)。
然而,仅仅识别当前的市场状态只完成了任务的一半。真正的力量在于基于这些认知来调整我们的交易方法。无论检测器多么精密,如果其洞察力不能转化为可执行的交易决策,它终究只是一个分析工具。如果我们的交易系统能够自动换挡:在趋势强劲时部署趋势跟踪逻辑,在横盘市场中切换至均值回归策略,并在波动率飙升时调整风险参数,那会怎样?
这正是我们要在第二部分中填补的空白。在之前奠定的基础上,我们现在将专注于实际应用与优化。在本文中,我们将深入探讨以下内容:
- 构建自适应智能交易系统(EA): 我们将构建一个完整的 MarketRegimeEA,它将集成我们的 CMarketRegimeDetector,以便根据检测到的市场状态,自动选择并执行不同的交易策略(趋势跟踪、均值回归、突破)。
- 实施特定状态的风险管理:该 EA 将演示如何根据当前市场状态调整手数、止损和止盈等参数。
- 实践考量:我们将探讨现实世界实施中的关键方面,包括针对不同品种和时间周期的参数优化。
- 处理状态过渡:管理市场从一种状态转换到另一种状态的关键时刻的策略,以确保策略调整更加平滑。
- 集成技术:讨论如何将市场状态检测系统纳入您现有的交易框架,以增强其适应性。
通过阅读这第二部分,您不仅将了解如何检测市场状态,还将学会构建一个能够智能调整自身行为的自动化交易系统,旨在在各种金融市况下实现更稳定的绩效表现。让我们将检测系统转变为真正的自适应交易解决方案。
创建一个EA
在本节中,我们将创建一个利用我们的市场状态检测器,根据当前市场状况调整其交易策略的智能交易系统(EA)。这将演示如何将状态检测集成到一个完整的交易系统中。
MarketRegimeEA
我们的 EA 将针对不同的市场状态采用不同的交易方法:- 在趋势市场中,它将使用趋势跟踪策略
- 在震荡市场中,它将使用均值回归策略
- 在高波动市场中,它将使用缩小仓位的突破策略
以下是其实现代码:
// Include the Market Regime Detector #include <MarketRegimeEnum.mqh> #include <MarketRegimeDetector.mqh> // EA input parameters input int LookbackPeriod = 100; // Lookback period for calculations input int SmoothingPeriod = 10; // Smoothing period for regime transitions input double TrendThreshold = 0.2; // Threshold for trend detection (0.1-0.5) input double VolatilityThreshold = 1.5; // Threshold for volatility detection (1.0-3.0) // Trading parameters input double TrendingLotSize = 0.1; // Lot size for trending regimes input double RangingLotSize = 0.05; // Lot size for ranging regimes input double VolatileLotSize = 0.02; // Lot size for volatile regimes input int TrendingStopLoss = 100; // Stop loss in points for trending regimes input int RangingStopLoss = 50; // Stop loss in points for ranging regimes input int VolatileStopLoss = 150; // Stop loss in points for volatile regimes input int TrendingTakeProfit = 200; // Take profit in points for trending regimes input int RangingTakeProfit = 80; // Take profit in points for ranging regimes input int VolatileTakeProfit = 300; // Take profit in points for volatile regimes // Global variables CMarketRegimeDetector *Detector = NULL; int OnBarCount = 0; datetime LastBarTime = 0;
该EA包含用于检测市场状态和交易策略的参数。请注意,我们如何针对不同的市场状态设置不同的手数、止损和止盈。这使得 EA 能够根据当前的市场状况调整其风险管理方法。
EA初始化
OnInit() 函数负责创建并配置市场状态检测器:
int OnInit() { // Create and initialize the Market Regime Detector Detector = new CMarketRegimeDetector(LookbackPeriod, SmoothingPeriod); if(Detector == NULL) { Print("Failed to create Market Regime Detector"); return INIT_FAILED; } // Configure the detector Detector.SetTrendThreshold(TrendThreshold); Detector.SetVolatilityThreshold(VolatilityThreshold); Detector.Initialize(); // Initialize variables OnBarCount = 0; LastBarTime = 0; return INIT_SUCCEEDED; }
该函数根据用户指定的参数创建并配置市场状态检测器。同时,它还初始化了用于跟踪新 K 线的计数变量。
EA Tick 处理函数
OnTick() 函数处理新的价格数据并执行基于状态的交易策略:
void OnTick() { // Check for new bar datetime currentBarTime = iTime(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, 0); if(currentBarTime == LastBarTime) return; // No new bar LastBarTime = currentBarTime; OnBarCount++; // Wait for enough bars to accumulate if(OnBarCount < LookbackPeriod) { Comment("Accumulating data: ", OnBarCount, " of ", LookbackPeriod, " bars"); return; } // Get price data double close[]; ArraySetAsSeries(close, true); int copied = CopyClose(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, 0, LookbackPeriod, close); if(copied != LookbackPeriod) { Print("Failed to copy price data: copied = ", copied, " of ", LookbackPeriod); return; } // Process data with the detector if(!Detector.ProcessData(close, LookbackPeriod)) { Print("Failed to process data with Market Regime Detector"); return; } // Get current market regime ENUM_MARKET_REGIME currentRegime = Detector.GetCurrentRegime(); // Display current regime information string regimeText = "Current Market Regime: " + Detector.GetRegimeDescription(); string trendText = "Trend Strength: " + DoubleToString(Detector.GetTrendStrength(), 4); string volatilityText = "Volatility: " + DoubleToString(Detector.GetVolatility(), 4); Comment(regimeText + "\n" + trendText + "\n" + volatilityText); // Execute trading strategy based on market regime ExecuteRegimeBasedStrategy(currentRegime); }该函数执行以下操作:
- 检查是否有新 K 线,以避免重复计算
- 等待累积足够的 K 线,以确保状态检测的可靠性
- 获取最新的价格数据
- 使用市场状态检测器处理数据
- 获取当前的市场状态
- 显示状态信息
- 执行基于状态的交易策略
使用 ArraySetAsSeries(close, true) 至关重要,因为它确保价格数组按倒序索引,即最新的价格位于索引 0 处。这是 MQL5 中处理时间序列数据的标准索引约定。
基于状态的交易策略
ExecuteRegimeBasedStrategy() 函数针对不同的市场状态实现了不同的交易方法:
void ExecuteRegimeBasedStrategy(ENUM_MARKET_REGIME regime) { // Check if we already have open positions if(PositionsTotal() > 0) return; // Don't open new positions if we already have one // Get current market information double ask = SymbolInfoDouble(Symbol(), SYMBOL_ASK); double bid = SymbolInfoDouble(Symbol(), SYMBOL_BID); double point = SymbolInfoDouble(Symbol(), SYMBOL_POINT); // Determine trading parameters based on regime double lotSize = 0.0; int stopLoss = 0; int takeProfit = 0; ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType = ORDER_TYPE_BUY; switch(regime) { case REGIME_TRENDING_UP: { lotSize = TrendingLotSize; stopLoss = TrendingStopLoss; takeProfit = TrendingTakeProfit; orderType = ORDER_TYPE_BUY; // Buy in uptrend break; } case REGIME_TRENDING_DOWN: { lotSize = TrendingLotSize; stopLoss = TrendingStopLoss; takeProfit = TrendingTakeProfit; orderType = ORDER_TYPE_SELL; // Sell in downtrend break; } case REGIME_RANGING: { // In ranging markets, we can use mean-reversion strategies // For simplicity, we'll use RSI to determine overbought/oversold double rsi[]; ArraySetAsSeries(rsi, true); int rsiCopied = CopyBuffer(iRSI(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, 14, PRICE_CLOSE), 0, 0, 2, rsi); if(rsiCopied != 2) return; lotSize = RangingLotSize; stopLoss = RangingStopLoss; takeProfit = RangingTakeProfit; if(rsi[0] < 30) // Oversold orderType = ORDER_TYPE_BUY; else if(rsi[0] > 70) // Overbought orderType = ORDER_TYPE_SELL; else return; // No signal break; } case REGIME_VOLATILE: { // In volatile markets, we can use breakout strategies // For simplicity, we'll use Bollinger Bands double upper[], lower[]; ArraySetAsSeries(upper, true); ArraySetAsSeries(lower, true); int bbCopied1 = CopyBuffer(iBands(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, 20, 2, 0, PRICE_CLOSE), 1, 0, 2, upper); int bbCopied2 = CopyBuffer(iBands(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, 20, 2, 0, PRICE_CLOSE), 2, 0, 2, lower); if(bbCopied1 != 2 || bbCopied2 != 2) return; lotSize = VolatileLotSize; stopLoss = VolatileStopLoss; takeProfit = VolatileTakeProfit; double close[]; ArraySetAsSeries(close, true); int copied = CopyClose(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, 0, 2, close); if(copied != 2) return; if(close[1] < upper[1] && close[0] > upper[0]) // Breakout above upper band orderType = ORDER_TYPE_BUY; else if(close[1] > lower[1] && close[0] < lower[0]) // Breakout below lower band orderType = ORDER_TYPE_SELL; else return; // No signal break; } default: return; // No trading in undefined regime } // Calculate stop loss and take profit levels double slLevel = 0.0; double tpLevel = 0.0; if(orderType == ORDER_TYPE_BUY) { slLevel = ask - stopLoss * point; tpLevel = ask + takeProfit * point; } else if(orderType == ORDER_TYPE_SELL) { slLevel = bid + stopLoss * point; tpLevel = bid - takeProfit * point; } // Execute trade MqlTradeRequest request; MqlTradeResult result; ZeroMemory(request); ZeroMemory(result); request.action = TRADE_ACTION_DEAL; request.symbol = Symbol(); request.volume = lotSize; request.type = orderType; request.price = (orderType == ORDER_TYPE_BUY) ? ask : bid; request.sl = slLevel; request.tp = tpLevel; request.deviation = 10; request.magic = 123456; // Magic number for this EA request.comment = "Market Regime: " + Detector.GetRegimeDescription(); request.type_filling = ORDER_FILLING_FOK; bool success = OrderSend(request, result); if(success) { Print("Trade executed successfully: ", result.retcode, " ", result.comment); } else { Print("Trade execution failed: ", result.retcode, " ", result.comment); } }该函数实施了一套全面的基于市场状态的交易策略:
- 趋势状态:采用趋势跟踪策略,在上升趋势中买入,在下降趋势中卖出。
- 震荡状态:基于相对强弱指数(RSI)采用均值回归策略,在超卖时买入,在超买时卖出。
- 高波动状态:基于布林带采用突破策略,并减小仓位规模以管控风险。
针对不同状态采用不同策略,正是该 EA 的核心创新点。通过根据当前市场状况调整其方法,该 EA 能够在各种市场环境下实现更稳定的绩效表现。
EA 清理工作
OnDeinit() 函数确保在移除 EA 时进行妥善的清理:
void OnDeinit(const int reason) { // Clean up if(Detector != NULL) { delete Detector; Detector = NULL; } // Clear the comment Comment(""); }
该函数删除市场状态检测器对象以防止内存泄漏,并清除图表上的任何注释。
基于状态交易的优势
该智EA展示了基于状态交易的几个关键优势:- 适应性:EA 能够根据当前市场状况自动调整交易策略,针对不同状态采用不同的方法。
- 风险管理:EA 会根据市场波动率调整仓位规模,在波动较大的状态下使用较小的仓位来管控风险。
- 策略选择:EA 会为每种状态选择最合适的策略,例如在趋势市场采用趋势跟踪策略,在震荡市场采用均值回归策略。
- 透明度:EA 清晰地显示当前的市场状态及其关键特征,为交易者的交易决策提供有价值的背景信息。
通过将市场状态检测纳入您的交易系统,您可以获得类似的好处,创建出在各种市场条件下均表现出色的、更具鲁棒性和自适应性的策略。
在下一节中,我们将讨论在实际交易环境中实施和优化市场状态检测系统的实践考量。
实践考量与优化
在最后一节中,我们将讨论在实际交易环境中实施和优化市场状态检测系统的实践考量。我们将涵盖参数优化、状态过渡处理以及与现有交易系统的集成。
参数优化
市场状态检测系统的有效性在很大程度上取决于参数的选择。以下是交易者应针对其特定交易品种和时间周期进行优化的关键参数:
- 回看周期:回看周期决定了用于状态检测的历史数据量。较长的周期能提供更稳定的状态分类,但对近期市场变化的响应可能较慢。较短的周期响应更迅速,但可能会产生更多的错误信号。
// Example of testing different lookback periods for(int lookback = 50; lookback <= 200; lookback += 25) { CMarketRegimeDetector detector(lookback, SmoothingPeriod); detector.SetTrendThreshold(TrendThreshold); detector.SetVolatilityThreshold(VolatilityThreshold); // Process historical data and evaluate performance // ... }
通常,50 到 200 根 K 线之间的回看周期适用于大多数品种和时间周期。最佳值取决于所交易特定品种的典型市场状态持续时间。 - 趋势阈值: 趋势阈值决定了趋势必须多强才能将市场归类为趋势状态。较高的阈值会导致趋势分类较少,但置信度更高。较低的阈值能识别更多的趋势,但可能包含较弱的趋势。
// Example of testing different trend thresholds for(double threshold = 0.1; threshold <= 0.5; threshold += 0.05) { CMarketRegimeDetector detector(LookbackPeriod, SmoothingPeriod); detector.SetTrendThreshold(threshold); detector.SetVolatilityThreshold(VolatilityThreshold); // Process historical data and evaluate performance // ... }
介于 0.1 和 0.3 之间的趋势阈值是常见的起始点。最佳值取决于品种的典型趋势行为特征。 - 波动率阈值:波动率阈值决定了需要多大的波动率才能将市场归类为高波动状态。较高的阈值会导致高波动分类较少,而较低的阈值能识别更多的高波动时期。
// Example of testing different volatility thresholds for(double threshold = 1.0; threshold <= 3.0; threshold += 0.25) { CMarketRegimeDetector detector(LookbackPeriod, SmoothingPeriod); detector.SetTrendThreshold(TrendThreshold); detector.SetVolatilityThreshold(threshold); // Process historical data and evaluate performance // ... }
介于 1.5 和 2.5 之间的波动率阈值是常见的起始点。最佳值取决于品种的典型波动率特征。
处理状态过渡
注意:以下 5 个代码块并非该想法的最终实现,而仅仅是关于实现可能样子的思路和伪代码。
状态过渡是关键时刻,需要特别关注。在过渡期间突然改变交易策略可能导致执行不佳和滑点增加。以下是更有效处理过渡的策略:
- 平滑过渡:平滑周期参数有助于减少状态分类噪音,它要求一个状态必须持续最少数量的 K 线才能被识别:
// Example of implementing smoothed regime transitions ENUM_MARKET_REGIME SmoothRegimeTransition(ENUM_MARKET_REGIME newRegime) { static ENUM_MARKET_REGIME regimeHistory[20]; static int historyCount = 0; // Add new regime to history for(int i = 19; i > 0; i--) regimeHistory[i] = regimeHistory[i-1]; regimeHistory[0] = newRegime; if(historyCount < 20) historyCount++; // Count occurrences of each regime int regimeCounts[5] = {0}; for(int i = 0; i < historyCount; i++) regimeCounts[regimeHistory[i]]++; // Find most common regime int maxCount = 0; ENUM_MARKET_REGIME dominantRegime = REGIME_UNDEFINED; for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { if(regimeCounts[i] > maxCount) { maxCount = regimeCounts[i]; dominantRegime = (ENUM_MARKET_REGIME)i; } } return dominantRegime; }
该函数维护了近期状态分类的历史记录,并返回最常见的状态,从而减少了暂时性波动的影响。 - 渐进式仓位调整:在状态过渡期间,调整仓位规模时采取渐进的方式而非突然改变,通常是更审慎的做法:
// Example of gradual position sizing during transitions double CalculateTransitionLotSize(ENUM_MARKET_REGIME previousRegime, ENUM_MARKET_REGIME currentRegime, int transitionBars, int maxTransitionBars) { // Base lot sizes for each regime double regimeLotSizes[5] = { TrendingLotSize, // REGIME_TRENDING_UP TrendingLotSize, // REGIME_TRENDING_DOWN RangingLotSize, // REGIME_RANGING VolatileLotSize, // REGIME_VOLATILE 0.0 // REGIME_UNDEFINED }; // If not in transition, use current regime's lot size if(previousRegime == currentRegime || transitionBars >= maxTransitionBars) return regimeLotSizes[currentRegime]; // Calculate weighted average during transition double previousWeight = (double)(maxTransitionBars - transitionBars) / maxTransitionBars; double currentWeight = (double)transitionBars / maxTransitionBars; return regimeLotSizes[previousRegime] * previousWeight + regimeLotSizes[currentRegime] * currentWeight; }
该函数在状态过渡期间计算仓位的加权平均值,从而在市场变化时提供更平滑的调整。
与现有交易系统的集成
市场状态检测系统可以与现有的交易系统集成,以增强其性能。以下是有效集成的策略:
- 策略选择:利用检测到的状态来选择最合适的交易策略:
// Example of strategy selection based on market regime bool ExecuteTradeSignal(ENUM_MARKET_REGIME regime, int strategySignal) { // Strategy signal: 1 = buy, -1 = sell, 0 = no signal switch(regime) { case REGIME_TRENDING_UP: case REGIME_TRENDING_DOWN: // In trending regimes, only take signals in the direction of the trend if((regime == REGIME_TRENDING_UP && strategySignal == 1) || (regime == REGIME_TRENDING_DOWN && strategySignal == -1)) return true; break; case REGIME_RANGING: // In ranging regimes, take all signals if(strategySignal != 0) return true; break; case REGIME_VOLATILE: // In volatile regimes, be more selective // Only take strong signals (implementation depends on strategy) if(IsStrongSignal(strategySignal)) return true; break; default: // In undefined regimes, don't trade break; } return false; }
该函数根据当前的市场状态过滤交易信号,仅执行与该状态特征相符的交易。 - 参数调整:根据检测到的状态调整策略参数:
// Example of parameter adaptation based on market regime void AdaptStrategyParameters(ENUM_MARKET_REGIME regime) { switch(regime) { case REGIME_TRENDING_UP: case REGIME_TRENDING_DOWN: // In trending regimes, use longer moving averages FastPeriod = 20; SlowPeriod = 50; // Use wider stop losses StopLoss = TrendingStopLoss; // Use larger take profits TakeProfit = TrendingTakeProfit; break; case REGIME_RANGING: // In ranging regimes, use shorter moving averages FastPeriod = 10; SlowPeriod = 25; // Use tighter stop losses StopLoss = RangingStopLoss; // Use smaller take profits TakeProfit = RangingTakeProfit; break; case REGIME_VOLATILE: // In volatile regimes, use very short moving averages FastPeriod = 5; SlowPeriod = 15; // Use wider stop losses StopLoss = VolatileStopLoss; // Use larger take profits TakeProfit = VolatileTakeProfit; break; default: // In undefined regimes, use default parameters FastPeriod = 14; SlowPeriod = 28; StopLoss = 100; TakeProfit = 200; break; } }
该函数根据当前的市场状态调整策略参数,针对特定的市场条件优化策略表现。
性能监控
定期监控市场状态检测系统的性能,以确保其准确分类市场状态:
// Example of performance monitoring for regime detection void MonitorRegimeDetectionPerformance() { static int regimeTransitions = 0; static int correctPredictions = 0; static ENUM_MARKET_REGIME lastRegime = REGIME_UNDEFINED; // Get current regime ENUM_MARKET_REGIME currentRegime = Detector.GetCurrentRegime(); // If regime has changed, evaluate the previous regime's prediction if(currentRegime != lastRegime && lastRegime != REGIME_UNDEFINED) { regimeTransitions++; // Evaluate if the previous regime's prediction was correct // Implementation depends on your specific evaluation criteria if(EvaluateRegimePrediction(lastRegime)) correctPredictions++; // Log performance metrics double accuracy = (double)correctPredictions / regimeTransitions * 100.0; Print("Regime Detection Accuracy: ", DoubleToString(accuracy, 2), "% (", correctPredictions, "/", regimeTransitions, ")"); } lastRegime = currentRegime; }
该函数跟踪状态转换并评估状态预测的准确性,为系统优化提供有价值的反馈。
指标:多时间周期市场状态
完整代码:
#property indicator_chart_window #property indicator_buffers 0 #property indicator_plots 0 // Include the Market Regime Detector #include <MarketRegimeEnum.mqh> #include <MarketRegimeDetector.mqh> // Input parameters input int LookbackPeriod = 100; // Lookback period for calculations input double TrendThreshold = 0.2; // Threshold for trend detection (0.1-0.5) input double VolatilityThreshold = 1.5; // Threshold for volatility detection (1.0-3.0) // Timeframes to analyze input bool UseM1 = false; // Use 1-minute timeframe input bool UseM5 = false; // Use 5-minute timeframe input bool UseM15 = true; // Use 15-minute timeframe input bool UseM30 = true; // Use 30-minute timeframe input bool UseH1 = true; // Use 1-hour timeframe input bool UseH4 = true; // Use 4-hour timeframe input bool UseD1 = true; // Use Daily timeframe input bool UseW1 = false; // Use Weekly timeframe input bool UseMN1 = false; // Use Monthly timeframe // Global variables CMarketRegimeDetector *Detectors[]; ENUM_TIMEFRAMES Timeframes[]; int TimeframeCount = 0; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { // Initialize timeframes array InitializeTimeframes(); // Create detectors for each timeframe ArrayResize(Detectors, TimeframeCount); for(int i = 0; i < TimeframeCount; i++) { Detectors[i] = new CMarketRegimeDetector(LookbackPeriod); if(Detectors[i] == NULL) { Print("Failed to create Market Regime Detector for timeframe ", EnumToString(Timeframes[i])); return INIT_FAILED; } // Configure the detector Detectors[i].SetTrendThreshold(TrendThreshold); Detectors[i].SetVolatilityThreshold(VolatilityThreshold); Detectors[i].Initialize(); } // Set indicator name IndicatorSetString(INDICATOR_SHORTNAME, "Multi-Timeframe Regime Analysis"); return INIT_SUCCEEDED; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Initialize timeframes array based on user inputs | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void InitializeTimeframes() { // Count selected timeframes TimeframeCount = 0; if(UseM1) TimeframeCount++; if(UseM5) TimeframeCount++; if(UseM15) TimeframeCount++; if(UseM30) TimeframeCount++; if(UseH1) TimeframeCount++; if(UseH4) TimeframeCount++; if(UseD1) TimeframeCount++; if(UseW1) TimeframeCount++; if(UseMN1) TimeframeCount++; // Resize and fill timeframes array ArrayResize(Timeframes, TimeframeCount); int index = 0; if(UseM1) Timeframes[index++] = PERIOD_M1; if(UseM5) Timeframes[index++] = PERIOD_M5; if(UseM15) Timeframes[index++] = PERIOD_M15; if(UseM30) Timeframes[index++] = PERIOD_M30; if(UseH1) Timeframes[index++] = PERIOD_H1; if(UseH4) Timeframes[index++] = PERIOD_H4; if(UseD1) Timeframes[index++] = PERIOD_D1; if(UseW1) Timeframes[index++] = PERIOD_W1; if(UseMN1) Timeframes[index++] = PERIOD_MN1; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator iteration function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnCalculate(const int rates_total, const int prev_calculated, const datetime &time[], const double &open[], const double &high[], const double &low[], const double &close[], const long &tick_volume[], const long &volume[], const int &spread[]) { // Check if there's enough data if(rates_total < LookbackPeriod) return 0; // Process data for each timeframe string commentText = "Multi-Timeframe Regime Analysis\n\n"; for(int i = 0; i < TimeframeCount; i++) { // Get price data for this timeframe double tfClose[]; ArraySetAsSeries(tfClose, true); int copied = CopyClose(Symbol(), Timeframes[i], 0, LookbackPeriod, tfClose); if(copied != LookbackPeriod) { Print("Failed to copy price data for timeframe ", EnumToString(Timeframes[i])); continue; } // Process data with the detector if(!Detectors[i].ProcessData(tfClose, LookbackPeriod)) { Print("Failed to process data for timeframe ", EnumToString(Timeframes[i])); continue; } // Add timeframe information to comment commentText += TimeframeToString(Timeframes[i]) + ": "; commentText += Detectors[i].GetRegimeDescription(); commentText += " (Trend: " + DoubleToString(Detectors[i].GetTrendStrength(), 2); commentText += ", Vol: " + DoubleToString(Detectors[i].GetVolatility(), 2) + ")"; commentText += "\n"; } // Display the multi-timeframe analysis Comment(commentText); // Return the number of calculated bars return rates_total; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Convert timeframe enum to readable string | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string TimeframeToString(ENUM_TIMEFRAMES timeframe) { switch(timeframe) { case PERIOD_M1: return "M1"; case PERIOD_M5: return "M5"; case PERIOD_M15: return "M15"; case PERIOD_M30: return "M30"; case PERIOD_H1: return "H1"; case PERIOD_H4: return "H4"; case PERIOD_D1: return "D1"; case PERIOD_W1: return "W1"; case PERIOD_MN1: return "MN1"; default: return "Unknown"; } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom indicator deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { // Clean up for(int i = 0; i < TimeframeCount; i++) { if(Detectors[i] != NULL) { delete Detectors[i]; Detectors[i] = NULL; } } // Clear the comment Comment(""); }
该指标不会在图标上绘制线条。相反,它利用 CMarketRegimeDetector 类(在第一部分中开发)分析多个用户选择时间周期上的市场状态(上涨趋势/下跌趋势、震荡、高波动),并将结果以文本形式显示在图表的左上角。
代码解释:
-
属性与包含文件:
- #property indicator_chart_window :使指标在主图表窗口中运行。
- #property indicator_buffers 0 , #property indicator_plots 0 :指定该指标本身不使用任何数据缓冲区或绘制线条/直方图。
- #include <MarketRegimeEnum.mqh> , #include <MarketRegimeDetector.mqh> :包含我们先前工作中所需的定义和核心检测器类。
-
输入参数:
- LookbackPeriod 、 TrendThreshold 、 VolatilityThreshold :这些是状态检测逻辑的核心设置,统一应用于所有分析的时间周期。
- UseM1 至 UseMN1 :一系列布尔输入,允许用户切换( true / false )哪些标准时间周期(从 1 分钟到月图)应包含在分析中。
-
全局变量:
- Detectors[] :一个用于存储 CMarketRegimeDetector 独立实例的数组。每个选定的时间周期都会在此存储其专用的检测器对象。
- Timeframes[] :一个用于存储 MQL5 时间周期标识符(如 PERIOD_H1 、 PERIOD_D1 )的数组,对应于用户通过输入选择的时间周期。
- TimeframeCount :一个整数,用于跟踪实际选择了多少个时间周期。
-
OnInit()(初始化函数):
- 在指标启动时运行一次。
- 调用 InitializeTimeframes() 来确定用户选择了哪些时间周期,并填充 Timeframes 数组。
- 调整 Detectors 数组的大小以匹配 TimeframeCount 。
- 循环 TimeframeCount 次:
- 对于每个选定的时间周期,它使用共享的 LookbackPeriod 创建一个新的 CMarketRegimeDetector 对象。
- 它使用共享的 TrendThreshold 和 VolatilityThreshold 配置该特定的检测器实例。
- 关键的是,每个检测器实例根据其指定时间周期的数据维护自己的内部状态。
- 设置指标的显示名称。
-
InitializeTimeframes()(辅助函数):
- 统计有多少个 Use… 输入被设置为 true 。
- 相应地调整全局 Timeframes 数组的大小。
- 将所选时间周期的实际 PERIOD_… 常量填充到 Timeframes 数组中。
-
OnCalculate()(主计算函数):
- 在每个新的 tick 或 K 线上运行。
- 检查图表当前时间周期上是否有足够的历史 K 线( rates_total )以满足 LookbackPeriod 的要求。
- 初始化一个空字符串 commentText 。
- 循环遍历每个选定的时间周期(由 i 跟踪):
- 使用 CopyClose() 获取 Symbol() 和 Timeframes[i] 的最后 LookbackPeriod 根收盘价(例如,即使指标在 M15 图表上,也会获取 H4 的收盘价)。
- 如果数据获取成功,则使用获取的价格数据( tfClose )调用对应检测器对象( Detectors[i] )的 ProcessData() 方法。
- 将 Detectors[i] 的结果(时间周期名称、状态描述、趋势强度、波动率)附加到 commentText 字符串中。
- 最后,使用 Comment(commentText) 将所有选定时间周期的汇总分析显示在图表的角落。
-
TimeframeToString()(辅助函数):
- 一个简单的工具函数,用于将 MQL5 PERIOD_… 常量转换为可读的字符串,如 “M1”、“H4”、“D1”。
- 一个简单的工具函数,用于将 MQL5 PERIOD_… 常量转换为可读的字符串,如 “M1”、“H4”、“D1”。
-
OnDeinit()(反初始化函数):
- 在指标从图表上移除或终端关闭时运行一次。
- 循环遍历 Detectors 数组,并使用 delete 释放为 OnInit() 中创建的每个 CMarketRegimeDetector 对象分配的内存,防止内存泄漏。
- 清除图表角落的文本注释。
从本质上讲,这段代码高效地为多个时间周期设置了独立的状态检测器,为每个时间周期获取必要的数据,执行分析,并直接在用户的图表上呈现统一的多时间周期状态概览。
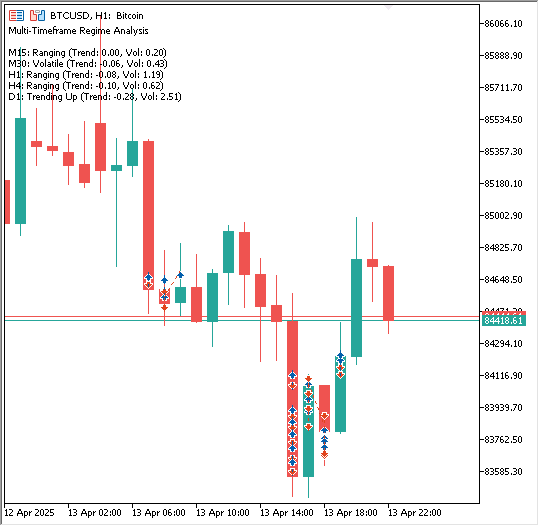
利用上述多时间周期指标,可以创建另一个在交易前分析多个时间周期的 EA。不过,为简洁起见,我们不会创建另一个EA,而应该先测试这个。
评估EA:回测结果
构建好 MarketRegimeEA 之后,合乎逻辑的下一步是通过回测来评估其性能。这使我们可以观察状态自适应逻辑在历史数据上的表现,并评估其参数设置的影响。
初始测试配置
在本演示中,我们选择黄金(XAUUSD)作为测试品种,使用 M1 时间周期的数据。应用于 EA 的初始参数是任意选择的:
- LookbackPeriod: 100
- SmoothingPeriod: 10
- TrendThreshold: 0.2
- VolatilityThreshold: 1.5
- Lot Sizes: Trending=0.1, Ranging=0.1, Volatile=0.1
- SL: Trending=1000, Ranging=1600, Volatile=2000
- TP: Trending=1400, Ranging=1000, Volatile=1800
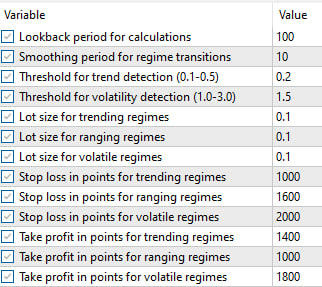
使用这些默认参数运行 EA 得到以下结果:
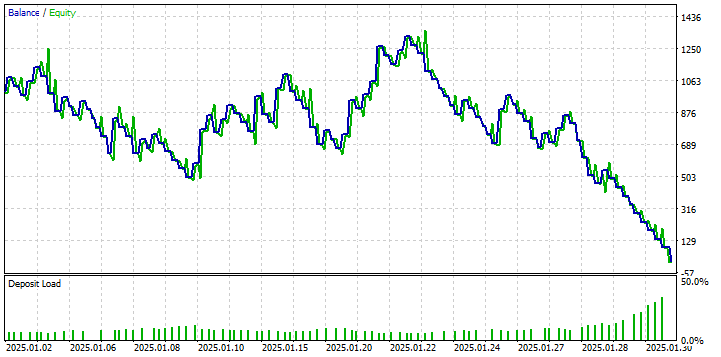
从资金曲线和绩效指标中我们可以观察到,使用这些设置的初始回测结果并不理想。虽然策略在有些时段产生了利润(一度达到约 20% 的权益增长),但整体绩效显示缺乏持续的盈利能力,且回撤显著。这一结果强调了针对所交易的特定品种和时间周期进行参数调整的重要性。这些参数仅作为起点,并不代表最佳配置。
为了探索提升性能的潜力,我们利用了 MetaTrader 5 策略测试器中的参数优化功能,并使用其遗传算法。目标是在测试范围内识别出一组参数,使状态检测和交易逻辑与回测期间黄金的历史价格行为更加一致。针对优化的参数包括状态特定的止损和止盈值,其他参数保持默认。
完成优化过程后,策略测试器识别出以下参数集可显著改善历史表现:
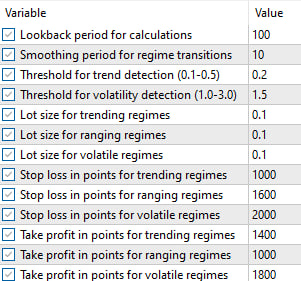
使用这些优化后的参数再次运行回测,绩效表现呈现出显著的不同:
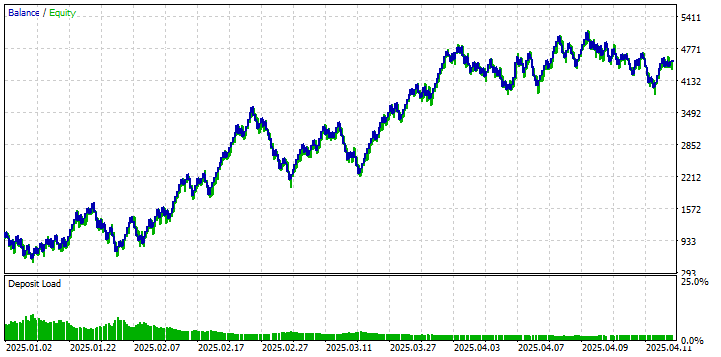
利用优化参数的回测展示了显著的改善,与初始运行相比,实现了正净收益和更有利的资金曲线。
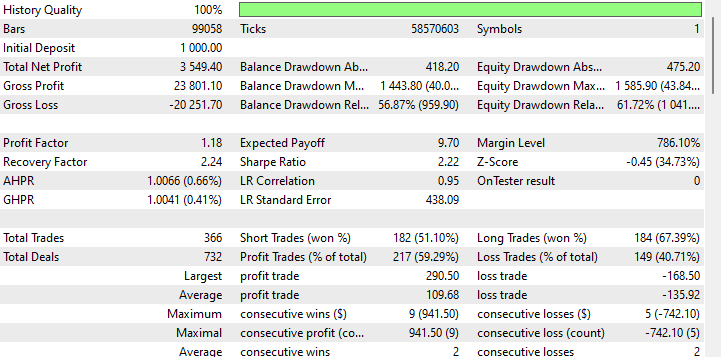
然而,对这些结果的解读必须保持谨慎。参数优化,特别是利用遗传算法在历史数据上进行优化,并在同一时期运行回测,本质上会引入过拟合的风险。这意味着这些参数可能对所使用的特定历史数据异常适用,但未必能很好地推广到未来未见的市场数据。
因此,虽然优化后的结果展示了当参数经过调整后自适应策略框架的潜力,但它们不应被视为未来盈利能力的确定证明。此示例的主要目的在于演示:
- 状态自适应 EA 的功能。
- 参数对效果的重大影响。
- 当配置恰当时,将策略适应状态这一基本概念可以在历史数据上产生积极结果。
即使未经优化的版本也显示出盈利的时段,这一事实表明核心逻辑本身并非存在根本性缺陷。不过,要将其发展为稳健的、可用于实盘的策略,还需要在简单优化之外采取进一步措施,包括:
- 严格的样本外测试,以验证参数的鲁棒性。
- 纳入更精细的风险管理机制。
- 可能实现之前讨论的技术,例如平滑过渡和渐进式仓位调整,以更有效地处理状态变化。
结论
在这篇两部分的系列文章中,我们从识别算法交易中的一个基本挑战——市场条件变化对静态策略的不利影响——到架构和实施一个完整的、自适应的解决方案,完成了一段旅程。在第一部分中,我们开发了基于统计的市场状态检测系统并将其输出可视化,从而构建了理解市场状态的引擎。
在这第二部分也是最终部分,我们迈出了从检测到行动的关键一步。我们通过构建 MarketRegimeEA 展示了如何利用 CMarketRegimeDetector 的强大功能,该 EA 能够根据识别的市场状态自动在趋势跟踪、均值回归和突破策略之间切换。我们看到,不仅调整入场逻辑,还调整手数和止损位等风险参数,可以创造更具韧性的交易方法。
此外,我们解决了部署此类系统的现实问题。我们探讨了参数优化(回看周期、趋势阈值、波动率阈值)的重要性,以将检测器调整到特定的市场特征,并讨论了平滑处理状态过渡、最大限度减少潜在震荡或突然策略切换的技术。最后,我们提及了如何将此状态检测框架集成到现有交易系统中,作为智能过滤器或参数调整器。
我们的目标很宏大:创建能够识别并适应市场固有非平稳性的交易系统。通过结合第一部分开发的检测能力与第二部分讨论的自适应执行框架和实践考量,您现在拥有了构建策略的蓝图,这些策略在面对金融市场的动态特性时将更加稳健和敏锐。从静态方法到状态自适应方法的转变已经完成,赋予您以更高的智慧和灵活性驾驭市场复杂性。
文件概览
以下是本文中创建的所有文件的摘要: | 文件名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| MarketRegimeEnum.mqh | 定义整个系统中使用的市场状态枚举类型 |
| CStatistics.mqh | 用于市场状态检测的统计计算类 |
| MarketRegimeDetector.mqh | 核心市场状态检测实现 |
| MarketRegimeEA.mq5 | 适应不同市场状态的EA |
| MultiTimeframeRegimes.mq5 | 分析多个时间周期状态的示例 |
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/17781
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 开发多币种 EA 交易(第 24 部分):添加新策略(一)
开发多币种 EA 交易(第 24 部分):添加新策略(一)
 在MQL5中构建自定义市场状态检测系统(第一部分):指标
在MQL5中构建自定义市场状态检测系统(第一部分):指标
 用于MetaTrader 5的WebSocket:借助Windows API实现异步客户端连接
用于MetaTrader 5的WebSocket:借助Windows API实现异步客户端连接
 基于MQL5中表模型的表类和表头类:应用MVC概念
基于MQL5中表模型的表类和表头类:应用MVC概念