
以 MQL5 实现强化分类任务的融汇方法
概述
在上一篇文章中,我们探讨了用于数值预测的模型组合方法。本文聚焦专为分类任务量身定制的融汇技术来扩展这一探索。沿途我们还验证了利用组件分类器,依据序数尺度生成类排位的策略。尽管数字组合技术有时能够应用于分类任务,其模型依赖数字输出,但许多分类器采用更严格的方式,仅产生离散的类决策。此外,基于数字的分类器往往表现出预测不稳定性,这凸显了对专门组合方法的必要性。
本文中讨论的分类融汇,运作在关于其组件模型的特定假设下。首先,假设这些模型据互斥、且详尽的类目标数据上训练过,确保每个实例只属于一个类。当需要“以上都不是”选项时,应将其视为单独的类,或由数字组合方法配合所定义隶属阈值加以管理。甚至,当给定一个预测因子的输入向量时,组件模型期望产生 N 个输出,其中 N 表示类的数量。这些输出或许是概率、或置信度分数,针对每个类指示其隶属似然性。它们也可以是二元决策,其中一个输出为 1.0(true),其它输出为 0.0(false),或者模型输出为从 1 到 N 的整数排位,反映相对类隶属似然性。
我们将考察的一些融汇方法极大地受益于生成排位输出的组件分类器。能够准确估测类隶属概率的模型通常具有很高价值,只不过若输出并非概率,却将其当作概率,则存在很大的风险。当怀疑模型输出代表什么时,将它们转换为排位或能提供些许益处。排位信息的功用随着类的数量增加而增加。对于二元分类,排位不提供额外见解,并且它们的数值对三类问题仍无大用。然而,在涉及众多类别的场景中,解释模型次要选择的能力变得高度有益,特别是当单个预测伴随不确定性时。例如,可以强化支持向量机(SVM),不仅可以生成二元分类,还有每个类的决策边界距离,从而更深入地洞察预测置信度。
排位还解决了融汇方法中的一项关键挑战:归一化来自不同分类模型的输出。考虑两个分析市场走势的模型:一个专门研究高流动性市场的短期价格波动,而另一个则关注数周、或数月的长期趋势。第二个模型的焦点更广泛,或许会在短期预测中引入噪声。将类决策置信度转换为排位可以缓解这个问题,确保有价值的短期见解不会被更广泛的趋势信号所掩盖。该方式导致更加平衡、和有效的融汇预测。
分类器组合的替代意向
应用融汇分类器的主要目标通常是提升分类准确性。情况并非总需如此,因为在某些分类问题中,超越该特定目标可能更得益。除了基本的分类准确性外,在最初的决策或许出错的场景下,还能实现更复杂的成功量值。考虑到这一点,分类可经由两个不同、但互补的意向来逼近,其中任何一个都可以作为类组合策略的性能量值:
- 类集合缩减:该方式旨在识别原始类,保留大概率包含真实类的最小子集。此处,子集中的内部排位是次要的,这是确保子集既紧凑、且尽可能包含正确的分类。
- 类排序:该方法专注对类隶属似然性排位,从而把真实类尽可能定位到靠近顶部。取代使用固定排位阈值,而是通过测量真实类与排位靠前位置之间的平均距离来评估绩效。
在某些应用中,赋予其中一个规程高于其它的优先级,能够提供显著的优势。即使没有明确要求这样的优先级。选择最相关的目标并实现相应的误差度量,比仅依赖分类准确性,往往产生更可靠的性能量值。此外,这两个意向不必相互排斥。混合方式可能特别有效:首先,应用向心化类集合缩减组合方法来识别一个小型、高概率的类子集。然后,使用次要方法对该精细子集内的类排位。自这两步过程后排位最高的类成为最终决策,并从集合缩减的效率、和秩序排序的精度中受益。这种双管齐下的策略能提供比传统单类预测方法更健壮的分类框架,特别是在分类确定性变化较大的复杂场景中。据此思绪,我们开始融汇分类器的探索。
基于多数规则的融汇
多数规则是一种简单、且直观的融汇分类方式,衍生自熟悉的投票概念。该方法涉及从组件模型中选择获得最多选票的类。该方法直截了当,在模型只能提供离散类选择的场景中具有特殊价值,对于模型复杂性有限的系统,令其成为绝佳选择。多数规则的数学形式表示如下。
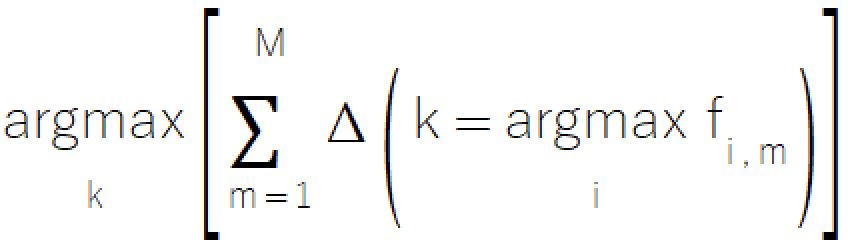
多数规则的实现驻留在 ensemble.mqh 文件中,其中 CMajority 类通过 classify() 方法管控其核心功能。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Compute the winner via simple majority | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CMajority { private: ulong m_outputs; ulong m_inputs; vector m_output; matrix m_out; public: CMajority(void); ~CMajority(void); ulong classify(vector &inputs, IClassify* &models[]); };
该方法取预测因子向量、及 IClassify 类型的组件模型指针数组作为输入。IClassify 接口标准化操纵模型,其方式与上一篇文章中讲述的 IModel 接口大致相同。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| IClassify interface defining methods for manipulation of | //|classification algorithms | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ interface IClassify { //train a model bool train(matrix &predictors,matrix&targets); //make a prediction with a trained model vector classify(vector &predictors); //get number of inputs for a model ulong getNumInputs(void); //get number of class outputs for a model ulong getNumOutputs(void); };
classify() 函数返回一个表示所选类的整数,范围从零至比可能类的总数少一。返回的类对应于从组件模型中获得最多“投票”的类。多数规则的实现初看似乎很简单,但其实际应用存在一个重大问题。当两个或多个类获得相同数量的选票时会发生什么?在民主设定中,这样的情形会导致另一轮投票,但在该境况下是行不通的。为了公平地解决平局,该方法在比较期间针对每个类的计票引入了小型随机扰动。该技术可确保平局的类能得到相等的选择概率,从而维持方法的完整性,并避免偏差。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ensemble classification | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ulong CMajority::classify(vector &inputs,IClassify *&models[]) { double best, sum, temp; ulong ibest; best =0; ibest = 0; CHighQualityRandStateShell state; CHighQualityRand::HQRndRandomize(state.GetInnerObj()); m_output = vector::Zeros(models[0].getNumOutputs()); for(uint i = 0; i<models.Size(); i++) { vector classification = models[i].classify(inputs); m_output[classification.ArgMax()] += 1.0; } sum = 0.0; for(ulong i=0 ; i<m_output.Size() ; i++) { temp = m_output[i] + 0.999 * CAlglib::HQRndUniformR(state); if((i == 0) || (temp > best)) { best = temp ; ibest = i ; } sum += m_output[i] ; } if(sum>0.0) m_output/=sum; return ibest; }
尽管多数规则有其功效,但它存在若干值得考虑的限制:
- 该方法仅参考来自每个模型的顶层选择,潜在地会舍弃较低排位中包含的有价值信息。而使用类输出的简单算术平均值似乎是一种解决方案,但该方式可能会引入与噪声和缩放相关的其它复杂性。
- 在涉及多个类的场景中,简单的投票机制可能无法捕捉到不同类选项之间的细微关系。
- 该方式平等对待所有组件模型,无关它们在不同境况下的单独性能特征、或可靠性。
下一个我们要讨论的方法是另一种基于“投票”的系统,其靠采用更复杂一点的技术来克服多数规则的一些缺点。
Borda 计数方法
Borda 方法跨所有模型,聚合排位低于每个模型估值的类数量,以此计算每个类的得分。该方法在利用和中和较低排位选择的影响之间达成了最优平衡,为更简单的投票机制提供了更精细的替代品。在具有 “m” 个模型和 “k” 个类的系统中,评分范围已明确定义:在所有模型中始终排位最后的类的 Borda 计数为零,而在所有模型中排位第一的类最高得分为 m(k-1)。

相比简单的投票方法,该方法呈现出重大成就,保持计算效率的同时,提供了捕获和利用全方位模型预测的强化能力。尽管该方法有效地处理单个模型排位内的平局,但跨模型之间,最终 Borda 计数的平局仍需仔细考虑。对于二元分类任务,Borda 计数方法在功能上等同于多数规则。因此,其明显优势主要体现在涉及三个、或更多类的场景中。该方法的效率源于其基于排序的方法,其可简化类输出的处理,同时维持准确的索引关联。
实现的 Borda 计数,其结构相似于多数规则方法,但需额外计算效率通力合作。该过程经由 ensemble.mqh 中的 CBorda 类管控,无需初步训练阶段即可运作。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Compute the winner via Borda count | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CBorda { private: ulong m_outputs; ulong m_inputs; vector m_output; matrix m_out; long m_indices[]; public: CBorda(void); ~CBorda(void); ulong classify(vector& inputs, IClassify* &models[]); };
分类过程从初始化输出向量开始,设计用于存储累积 Borda 计数。随后评估所有组件模型给定输入向量。建立索引数组,以便跟踪类隶属。每个模型的分类输出按升序排序。最后,基于排序的排位系统性累积 Borda 计数。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ensemble classification | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ulong CBorda::classify(vector &inputs,IClassify *&models[]) { double best=0, sum, temp; ulong ibest=0; CHighQualityRandStateShell state; CHighQualityRand::HQRndRandomize(state.GetInnerObj()); if(m_indices.Size()) ArrayFree(m_indices); m_output = vector::Zeros(models[0].getNumOutputs()); if(ArrayResize(m_indices, int(m_output.Size()))<0) { Print(__FUNCTION__, " ", __LINE__, " array resize error ", GetLastError()); return ULONG_MAX; } for(uint i = 0; i<models.Size(); i++) { vector classification = models[i].classify(inputs); for(long j = 0; j<long(classification.Size()); j++) m_indices[j] = j; if(!classification.Size()) { Print(__FUNCTION__," ", __LINE__," empty vector "); return ULONG_MAX; } qsortdsi(0,classification.Size()-1,classification,m_indices); for(ulong k =0; k<classification.Size(); k++) m_output[m_indices[k]] += double(k); } sum = 0.0; for(ulong i=0 ; i<m_output.Size() ; i++) { temp = m_output[i] + 0.999 * CAlglib::HQRndUniformR(state); if((i == 0) || (temp > best)) { best = temp ; ibest = i ; } sum += m_output[i] ; } if(sum>0.0) m_output/=sum; return ibest; }
在接下来的章节中,我们将研究融汇,其中包括组件模型在做出最终类决策时生成的大部分(如果不是全部)信息。
均化组件模型输出
当组件模型生成的输出,都具有意义、以及可跨模型比较的相对值时,合并这些数字量值可显著强化融汇性能。而多数规则和 Borda 计数方法忽略了大部分可用信息,但均化组件输出提供了一种更全面的数据利用方式。该方法计算所有组件模型中每个类的中位输出。鉴于给定的模型数量维持常数,该方式在数学上等同于输出求和。该技术有效地将每个分类模型视为数字预测因子,经由简单的均化方法将它们组合起来。最终的判定分类决策是识别具有最高聚合输出的类。
均化数值预测任务对比分类任务之间存在显著区别。在数值预测中,组件模型典型情况下分享共同的训练目标,确保输出一致性。而分类任务,对于单个模型仅有输出排位才有意义,故可能会无意中产生不可比较的输出。有时,这种不连贯性会导致组合实际上成为隐式加权均值,而非真正的算术平均值。不然的话,单个模型可能会对最终总和产生不成比例的影响,从而损害融汇的有效性。因此,为了维持元模型的完整性,验证所有组件模型输出的一致性至关重要。
假设组件模型输出实际上是概率,会导致替代组合方法的扩展,在概念上类似于均化。其中之一是乘积规则。它将模型输出加法换成乘法。问题在于,该方式即使对于最轻微的概率假设违反也表现出极度敏感。单个模型严重低估类概率的可能性,会不可逆转地惩罚该类,在于无关其它因素,乘以接近零的值都会产生可忽略不计的结果。这样高的灵敏度令乘积规则对于大多数应用来说是不切实际的,尽管它在理论上很优雅。它主要作为一个警示性示例,证明数学上听着合理的方式在实际实现中或许会出现问题。
进化规则实现驻留在 CAvgClass 类中,结构上则镜像 CMajority 类框架。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| full resolution' version of majority rule. | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CAvgClass { private: ulong m_outputs; ulong m_inputs; vector m_output; public: CAvgClass(void); ~CAvgClass(void); ulong classify(vector &inputs, IClassify* &models[]); };
在分类期间,classify() 方法自所有组件模型收集预测,并累积它们各自的输出。最终类基于最高累积得分。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| make classification with consensus model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ulong CAvgClass::classify(vector &inputs, IClassify* &models[]) { m_output=vector::Zeros(models[0].getNumOutputs()); vector model_classification; for(uint i =0 ; i<models.Size(); i++) { model_classification = models[i].classify(inputs); m_output+=model_classification; } double sum = m_output.Sum(); ulong min = m_output.ArgMax(); m_output/=sum; return min; }
中位数
中位值聚合拥有综合数据利用率的优势,但代价是对异常值的敏感性,这可能会影响融汇性能。中位数表现出一个健壮的替代方案,尽管信息利用率略有降低,但仍提供可靠的集中趋势化量值,同时维持对极端值的抵抗力。在 ensemble.mqh 中的 CMedian 类实现的中位数融汇方法,提供了一种直截了当、且有效的融汇分类方式。该实现解决了管理异常值预测、与保留类之间有意义的相对排序的挑战。通过实现基于排位的转换来处置异常值。每个组件模型的输出都独立排位,然后计算每个类的排位的中值。该方式有效地降低了极端预测的影响,同时保留了类预测之间的本质层次化关系。
中值方式强化了偶尔存在极端预测时的稳定性。即使在处置不对称、或偏斜的预测分布时,它仍有效,并在利用完整信息、及管控异常值健壮性之间取得了平衡折衷。当应用中位规则时,从业者应评估其具体用例要求。在可能偶尔出现极端预测、或预测稳定性至关重要的情况下,中位方法往往能在可靠性和性能之间提供最优平衡。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| median of predications | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CMedian { private: ulong m_outputs; ulong m_inputs; vector m_output; matrix m_out; public: CMedian(void); ~CMedian(void); ulong classify(vector &inputs, IClassify* &models[]); }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CMedian::CMedian(void) { } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| destructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CMedian::~CMedian(void) { } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| consensus classification | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ulong CMedian::classify(vector &inputs,IClassify *&models[]) { m_out = matrix::Zeros(models[0].getNumOutputs(),models.Size()); vector model_classification; for(uint i = 0; i<models.Size(); i++) { model_classification = models[i].classify(inputs); if(!m_out.Col(model_classification,i)) { Print(__FUNCTION__, " ", __LINE__, " failed row insertion ", GetLastError()); return ULONG_MAX; } } m_output = vector::Zeros(models[0].getNumOutputs()); for(ulong i = 0; i<m_output.Size(); i++) { vector row = m_out.Row(i); if(!row.Size()) { Print(__FUNCTION__," ", __LINE__," empty vector "); return ULONG_MAX; } qsortd(0,row.Size()-1,row); m_output[i] = row.Median(); } double sum = m_output.Sum(); ulong mx = m_output.ArgMax(); if(sum>0.0) m_output/=sum; return mx; }
MaxMax 和 MaxMin 融汇分类器
有时,在组件模型融汇中,单个模型或许被设计成拥有类集合特定子集的专业技能。当在其专业领域内运作时,这些模型会生成高置信度的输出,同时针对专业之外的类产生无甚意义的中等值。MaxMax 规则解决该场景时,则是基于所有模型中的最大输出来评估每个类。该方式优先考虑高置信度预测,同时忽略可能信息量较少的中等输出。然而,从业者应当注意,该方法被证明不适合二次输出含有重大分析价值的场景。
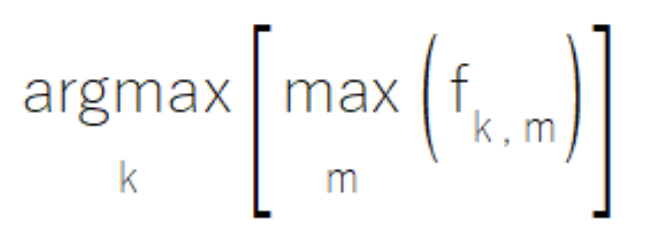
MaxMax 规则的实现驻留在 ensemble.mqh 中的 CMaxmax 类,为利用模型专门形态提供了一个结构化框架。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|Compute the maximum of the predictions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CMaxMax { private: ulong m_outputs; ulong m_inputs; vector m_output; matrix m_out; public: CMaxMax(void); ~CMaxMax(void); ulong classify(vector &inputs, IClassify* &models[]); }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CMaxMax::CMaxMax(void) { } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| destructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CMaxMax::~CMaxMax(void) { } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ensemble classification | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ulong CMaxMax::classify(vector &inputs,IClassify *&models[]) { double sum; ulong ibest; m_output = vector::Zeros(models[0].getNumOutputs()); for(uint i = 0; i<models.Size(); i++) { vector classification = models[i].classify(inputs); for(ulong j = 0; j<classification.Size(); j++) { if(classification[j] > m_output[j]) m_output[j] = classification[j]; } } ibest = m_output.ArgMax(); sum = m_output.Sum(); if(sum>0.0) m_output/=sum; return ibest; }
相较之,一些融汇系统的模型,擅长排除特定类,而非识别它们。在这些情况下,当一个实例属于特定类时,融汇中至少有一个模型会为每个不正确的类生成明显较低的输出,从而有效将它们排除在考虑之外。
MaxMin 规则利用了这一特性,基于每个类的所有模型的最小输出来评估类隶属。
该方式在 ensemble.mqh 中的 CMaxmin 类实现,提供了一种机制,来利用某些模型容易出现异常的能力。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Compute the minimum of the predictions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CMaxMin { private: ulong m_outputs; ulong m_inputs; vector m_output; matrix m_out; public: CMaxMin(void); ~CMaxMin(void); ulong classify(vector &inputs, IClassify* &models[]); }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CMaxMin::CMaxMin(void) { } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| destructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CMaxMin::~CMaxMin(void) { } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ensemble classification | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ulong CMaxMin::classify(vector &inputs,IClassify *&models[]) { double sum; ulong ibest; for(uint i = 0; i<models.Size(); i++) { vector classification = models[i].classify(inputs); if(i == 0) m_output = classification; else { for(ulong j = 0; j<classification.Size(); j++) if(classification[j] < m_output[j]) m_output[j] = classification[j]; } } ibest = m_output.ArgMax(); sum = m_output.Sum(); if(sum>0.0) m_output/=sum; return ibest; }
在实现 MaxMax 或 MaxMin 方式时,从业者应仔细评估其模型融汇的特征。对于MaxMax方式,必须确认模型表现出明显的专业化形态。确保中度输出代表噪音,而非有价值的次要信息尤为重要,最后,确保融汇提供所有相关类别的全面覆盖。在应用 MaxMin 方式时,应确保融汇能集体解决所有潜在的错误分类场景,并找出异常覆盖率中的任何间隙。
交集方法
交集方法代表一种专门的分类器组合方式,主要设计用于类集合缩减,而非普通分类目的。诚然,直接应用它或许受限,它已包含在本文中,作为基础先驱,提供更健壮的方法,特别是联合方法。该方式要求组件模型为每个输入案例生成整体类排位,从最有可能到最不可能。许多分类器可以满足这一需求,对实值输出排位的过程往往可通过有效过滤噪声、同时保留有价值的信息来强化性能。该方法的训练阶段辨别必须保留的每个组件模型最小排位靠前的输出数量,从而确保在整个训练数据集中可持续地启用真实类。对于新样本,组合决策是包含真实类的最小子集,这是通过与所有组件模型中的最小子集相交来判定。
研究一个拥有多个类、及四个模型的实际示例。验证训练集中的五个样本,发现跨模型的真实类排位形态不同。
| 样本 | 模型 1 | 模型 2 | 模型 3 | 模型 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 21 | 4 | 5 |
| 2 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 9 |
| 3 | 1 | 17 | 12 | 3 |
| 4 | 7 | 16 | 2 | 8 |
| 5 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 1 |
| 最大 | 8 | 21 | 12 | 9 |
表格显示,第二个样本的真实类在第一个模型中排位第八,在第二个模型中排位第四,在第四个模型中排位第九。表中的最后一行显示了按列的最大排位,分别是 8、21、12 和 9。当评估未知案例时,融汇根据这些阈值从每个模型中选择并相交排位靠前的类,产生所有集合共有类的最终子集。
CIntersection 类管控交集方法的实现,经由其 fit() 函数提供独特的训练过程。该函数分析训练数据,判定每个模型的最坏情况排位,跟踪始终包含正确分类所需的排位靠前的最小类数量。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Use intersection rule to compute minimal class set | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CIntersection { private: ulong m_nout; long m_indices[]; vector m_ranks; vector m_output; public: CIntersection(void); ~CIntersection(void); ulong classify(vector &inputs, IClassify* &models[]); bool fit(matrix &inputs, matrix &targets, IClassify* &models[]); vector proba(void) { return m_output;} };
调用 CIntersection 类的 classify() 方法会顺序计算输入数据上的所有组件模型。对于每个模型,对其输出向量排序,并用已排序向量的索引来计算属于每个模型最高排位子集的类交集。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| fit an ensemble model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CIntersection::fit(matrix &inputs,matrix &targets,IClassify *&models[]) { m_nout = targets.Cols(); m_output = vector::Ones(m_nout); m_ranks = vector::Zeros(models.Size()); double best = 0.0; ulong nbad; if(ArrayResize(m_indices,int(m_nout))<0) { Print(__FUNCTION__, " ", __LINE__, " array resize error ", GetLastError()); return false; } ulong k; for(ulong i = 0; i<inputs.Rows(); i++) { vector trow = targets.Row(i); vector inrow = inputs.Row(i); k = trow.ArgMax(); best = trow[k]; for(uint j = 0; j<models.Size(); j++) { vector classification = models[j].classify(inrow); best = classification[k]; nbad = 1; for(ulong ii = 0; ii<m_nout; ii++) { if(ii == k) continue; if(classification[ii] >= best) ++nbad; } if(nbad > ulong(m_ranks[j])) m_ranks[j] = double(nbad); } } return true; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ensemble classification | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ulong CIntersection::classify(vector &inputs,IClassify *&models[]) { for(long j =0; j<long(m_nout); j++) m_indices[j] = j; for(uint i =0; i<models.Size(); i++) { vector classification = models[i].classify(inputs); ArraySort(m_indices); qsortdsi(0,classification.Size()-1,classification,m_indices); for(ulong j = 0; j<m_nout-ulong(m_ranks[i]); j++) { m_output[m_indices[j]] = 0.0; } } ulong n=0; double cut = 0.5; for(ulong i = 0; i<m_nout; i++) { if(m_output[i] > cut) ++n; } return n; }
尽管理论上很优雅,但交集方法有几个显著的局限性。虽然它保证了训练集中包含真实类,但这种优势会受其固有约束而减弱。该方法或可为训练集之外的案例生成空的类子集,特别是当排位靠前的子集缺乏跨模型的共用元素时。最要紧的是,该方法对最坏情况性能的依赖通常会导致类子集过大,从而降低其有效性和效率。
交集方法在某些境况中或许很有价值,其中所有组件模型跨整个类集合都表现一致。然而,它对非专业领域的较差模型性能的敏感性,往往限制了其实际功效,特别是依赖不同类子集的专业模型的应用中。最终,该方法的主要价值在于更健壮方式这一概念的贡献,譬如联合方法,而非直接在大多数分类任务中应用。
联合规则
联合规则体现了对交集方法的策略强化,解决其过度依赖最坏情况性能的主要局限性。当结合具有不同专业领域的专业模型时,这种修改证明特有价值,将重点从最坏情况转移到最佳情况性能状况。初始过程是交集方法的镜像:分析训练集案例,从而判定组件模型之间的真实类排位。然而,联合规则的分歧在于识别和跟踪每个案例的最佳性能模型,而非监控最差情况的性能。然后,该方法评估整个训练数据集中这些最佳情况性能中最不利的。对于未知案例的分类,系统通过统一来自每个组件模型中的最优子集,构造一个组合的类子集。考虑我们之前的数据集示例,现在按 “Perf” 为前缀的性能跟踪列加以强化。
| 样本 | 模型 1 | 模型 2 | 模型 3 | 模型 4 | Perf_Model 1 | Perf_Model 2 | Perf_Model 3 | Perf_Model 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 21 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 8 | 4 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 1 | 17 | 12 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 7 | 16 | 2 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 5 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 最大 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
额外列跟踪表现出卓越性能的每个模型实例,底部行指示这些最佳情况的最大值。
联合规则提供了若干超越交集方法的显见优势。它剔除了空子集的可能性,在任何给定情况下至少有一个模型能始终如一地发挥最优性能。该方法还在训练期间忽略其专业领域之外的不良表现,有效地管理专门模型,允许相应的专家进行控制。最后,它提供了一种自然机制来识别、及可能排除持续表现不佳的模型,如跟踪矩阵中的零列所示。
联合方法的实现维持与交集方法的结构相似性,利用 m_ranks 容器来监控性能跟踪列的最大值。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Use union rule to compute minimal class set | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CUnion { private: ulong m_nout; long m_indices[]; vector m_ranks; vector m_output; public: CUnion(void); ~CUnion(void); ulong classify(vector &inputs, IClassify* &models[]); bool fit(matrix &inputs, matrix &targets, IClassify* &models[]); vector proba(void) { return m_output;} };
然而,在处理类排位和标志初始化方面出现了关键区别。在训练期间,系统跟踪每个案例的模型之间的最小排位,并在必要时更新 m_ranks 的最大值。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| fit an ensemble model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CUnion::fit(matrix &inputs,matrix &targets,IClassify *&models[]) { m_nout = targets.Cols(); m_output = vector::Zeros(m_nout); m_ranks = vector::Zeros(models.Size()); double best = 0.0; ulong nbad; if(ArrayResize(m_indices,int(m_nout))<0) { Print(__FUNCTION__, " ", __LINE__, " array resize error ", GetLastError()); return false; } ulong k, ibestrank=0, bestrank=0; for(ulong i = 0; i<inputs.Rows(); i++) { vector trow = targets.Row(i); vector inrow = inputs.Row(i); k = trow.ArgMax(); for(uint j = 0; j<models.Size(); j++) { vector classification = models[j].classify(inrow); best = classification[k]; nbad = 1; for(ulong ii = 0; ii<m_nout; ii++) { if(ii == k) continue; if(classification[ii] >= best) ++nbad; } if(j == 0 || nbad < bestrank) { bestrank = nbad; ibestrank = j; } } if(bestrank > ulong(m_ranks[ibestrank])) m_ranks[ibestrank] = double(bestrank); } return true; }
分类阶段逐步包括满足特定性能准则的类。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ensemble classification | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ulong CUnion::classify(vector &inputs,IClassify *&models[]) { for(long j =0; j<long(m_nout); j++) m_indices[j] = j; for(uint i =0; i<models.Size(); i++) { vector classification = models[i].classify(inputs); ArraySort(m_indices); qsortdsi(0,classification.Size()-1,classification,m_indices); for(ulong j =(m_nout-ulong(m_ranks[i])); j<m_nout; j++) { m_output[m_indices[j]] = 1.0; } } ulong n=0; double cut = 0.5; for(ulong i = 0; i<m_nout; i++) { if(m_output[i] > cut) ++n; } return n; }
尽管联合规则能够有效解决交集方法的诸多局限性,但它在遇到所有组件模型产生较差排位异常值时仍很脆弱。这种状况尽管颇具挑战性,但在设计良好的应用程序中应当很罕见,并且往往能经由正确的系统设计、及模型选择来缓解。该方法的有效性在配以专业模型的环境中尤其出色,其中每个组件在特定领域胜任,而在另外领域可能表现糟糕。这一特性令其对于需要不同专业知识的复杂分类任务特别有价值。
基于逻辑回归的分类器组合
在迄今为止讨论的所有融汇分类器中,Borda 计数方法是组合具有相似性能分类器的通用有效的解决方案,它假设所有模型的预测能力一致。当模型之间的性能差异很大时,或许要基于单个模型性能实现差异权重。逻辑回归为这种加权组合方式提供了一个周全的框架。
针对分类器组合的逻辑回归实现建立在普通线性回归原理的基础之上,但解决了分类的特定挑战。取代直接预测连续值,逻辑回归计算类隶属概率,为分类任务提供了一种精细方式。该过程首先将原始训练数据转换为回归兼容的格式。研究一个含有三个类和四个模型的系统,生成以下输出。
| 模型 1 | 模型 2 | 模型 3 | 模型 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| 2 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 0.3 |
| 3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 0.2 |
改数据为每个原始案例生成三个新的回归训练案例,对于正确的类,目标变量设置为 1.0,对于不正确的类,则为 0.0。预测因子利用比例排位,而非生料输出,从而提升了数值稳定性。
在 ensemble.mqh 中的 CLogitReg 类管控分类器融汇的加权组合方法的实现。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Use logistic regression to find best class | //| This uses one common weight vector for all classes. | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class ClogitReg { private: ulong m_nout; long m_indices[]; matrix m_ranks; vector m_output; vector m_targs; matrix m_input; logistic::Clogit *m_logit; public: ClogitReg(void); ~ClogitReg(void); ulong classify(vector &inputs, IClassify* &models[]); bool fit(matrix &inputs, matrix &targets, IClassify* &models[]); vector proba(void) { return m_output;} };
fit() 方法系统地处理单个案例来构造回归训练集。首先,判定每个训练样本的真实类隶属。然后,来自每个组件模型的评估结果会被归组到矩阵 m_ranks 之中。处理该矩阵,生成回归问题的因变量和自变量,随后使用 m_logit 对象顺序求解。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| fit an ensemble model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool ClogitReg::fit(matrix &inputs,matrix &targets,IClassify *&models[]) { m_nout = targets.Cols(); m_input = matrix::Zeros(inputs.Rows(),models.Size()); m_targs = vector::Zeros(inputs.Rows()); m_output = vector::Zeros(m_nout); m_ranks = matrix::Zeros(models.Size(),m_nout); double best = 0.0; ulong nbelow; if(ArrayResize(m_indices,int(m_nout))<0) { Print(__FUNCTION__, " ", __LINE__, " array resize error ", GetLastError()); return false; } ulong k; if(CheckPointer(m_logit) == POINTER_DYNAMIC) delete m_logit; m_logit = new logistic::Clogit(); for(ulong i = 0; i<inputs.Rows(); i++) { vector trow = targets.Row(i); vector inrow = inputs.Row(i); k = trow.ArgMax(); best = trow[k]; for(uint j = 0; j<models.Size(); j++) { vector classification = models[j].classify(inrow); if(!m_ranks.Row(classification,j)) { Print(__FUNCTION__, " ", __LINE__, " failed row insertion ", GetLastError()); return false; } } for(ulong j = 0; j<m_nout; j++) { for(uint jj =0; jj<models.Size(); jj++) { nbelow = 0; best = m_ranks[jj][j]; for(ulong ii =0; ii<m_nout; ii++) { if(m_ranks[jj][ii]<best) ++nbelow; } m_input[i][jj] = double(nbelow)/double(m_nout); } m_targs[i] = (j == k)? 1.0:0.0; } } return m_logit.fit(m_input,m_targs); }
这种实现体现了一种复杂的分类器组合方式,其中组件模型跨不同分类任务,表现出动态有效性水平,为该场景提供特殊值。
加权分类过程建立在 Borda 计数方法的基础上,整合特定于模型的权重。该算法首先初始化累积向量,并遍历每个组件模型处理未知案例。由 m_logit 对象计算出的最优权重,用来调整来自组件分类器的贡献。所判定最终类,作为 m_output 中最大值的对应索引。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| classify with ensemble model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ulong ClogitReg::classify(vector &inputs,IClassify *&models[]) { double temp; for(uint i =0; i<models.Size(); i++) { vector classification = models[i].classify(inputs); for(long j =0; j<long(classification.Size()); j++) m_indices[j] = j; if(!classification.Size()) { Print(__FUNCTION__," ", __LINE__," empty vector "); return ULONG_MAX; } qsortdsi(0,classification.Size()-1,classification,m_indices); temp = m_logit.coeffAt(i); for(ulong j = 0 ; j<m_nout; j++) { m_output[m_indices[j]] += j * temp; } } double sum = m_output.Sum(); ulong ibest = m_output.ArgMax(); double best = m_output[ibest]; if(sum>0.0) m_output/=sum; return ibest; }
该实现强调通用权重,因为它们具有更高的稳定性、及更低的过度拟合风险。然而,对于依据大型训练数据的应用来说,特定类的权重仍是一个可行的选项。下一章节将讨论采用特定类权重的一种方法。至于现在,我们将注意力转移到如何推导最优权重上,特别是逻辑回归模型。
逻辑回归的核心是如下所示的逻辑或 Logit 变换。
该函数将无限域映射到区间 [0, 1]。当上式中的 x 为极值负数时,结果接近于零。相较之,随着 x 变大,函数的值接近完数一。如果 x=0,则该函数返回一个恰好是两个极值之间半程的数值。允许 x 表示回归模型中的预测变量,意味着当 x 为零时,样本有 50% 的机率会属于特定类。随着 x 的值从 0 递增,机率百分比相应递增。另一方面,随着 x 的值从 0 递减,百分亦会递减。
另一种替代概率传达方式是几率。它的正式称呼为率比,即事件发生的概率除以不发生的概率。在 logit 变换中的表达式 e^x,按 f(x) 导出 得到以下方程。
等式两边应用对数,并让 x 作为回归问题的预测变量,可消除该方程中的指数,方程结果如下所示。
该表达式在分类器融汇的境况下所述,规定对于训练集中的每个样本,来自组件分类器的预测因子的线性组合提供了相应类标签的几率对数。最优权重 w,能用最大似然估算、或由最小化意向函数来获得。其详细信息超出了本文的范畴。
起初,全面实现 MQL5 版本的逻辑回归被证实很难。Alglib 函数库的 MQL5 港端有专门的逻辑回归工具,但作者从未能够成功编译它们。即便 Alglib 工具的演示程序中,也没有任何使用它们的示例。哎,在实现 logistic.mqh 文件中定义的 Clogit 类时,Alglib 函数库才派上用场。该文件包括实现 CNDimensional_Grad 接口的 CFg 类的定义。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| function and gradient calculation object | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CFg:public CNDimensional_Grad { private: matrix m_preds; vector m_targs; ulong m_nclasses,m_samples,m_features; double loss_gradient(matrix &coef,double &gradients[]); void weight_intercept_raw(matrix &coef,matrix &x, matrix &wghts,vector &intcept,matrix &rpreds); void weight_intercept(matrix &coef,matrix &wghts,vector &intcept); double l2_penalty(matrix &wghts,double strenth); void sum_exp_minus_max(ulong index,matrix &rp,vector &pr); void closs_grad_halfbinmial(double y_true,double raw, double &inout_1,double &intout_2); public: //--- constructor, destructor CFg(matrix &predictors,vector &targets, ulong num_classes) { m_preds = predictors; vector classes = np::unique(targets); np::sort(classes); vector checkclasses = np::arange(classes.Size()); if(checkclasses.Compare(classes,1.e-1)) { double classv[]; np::vecAsArray(classes,classv); m_targs = targets; for(ulong i = 0; i<targets.Size(); i++) m_targs[i] = double(ArrayBsearch(classv,m_targs[i])); } else m_targs = targets; m_nclasses = num_classes; m_features = m_preds.Cols(); m_samples = m_preds.Rows(); } ~CFg(void) {} virtual void Grad(double &x[],double &func,double &grad[],CObject &obj); virtual void Grad(CRowDouble &x,double &func,CRowDouble &grad,CObject &obj); }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| this function is not used | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CFg::Grad(double &x[],double &func,double &grad[],CObject &obj) { matrix coefficients; arrayToMatrix(x,coefficients,m_nclasses>2?m_nclasses:m_nclasses-1,m_features+1); func=loss_gradient(coefficients,grad); return; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| get function value and gradients | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CFg::Grad(CRowDouble &x,double &func,CRowDouble &grad,CObject &obj) { double xarray[],garray[]; x.ToArray(xarray); Grad(xarray,func,garray,obj); grad = garray; return; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| loss gradient | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CFg::loss_gradient(matrix &coef,double &gradients[]) { matrix weights; vector intercept; vector losses; matrix gradpointwise; matrix rawpredictions; matrix gradient; double loss; double l2reg; //calculate weights intercept and raw predictions weight_intercept_raw(coef,m_preds,weights,intercept,rawpredictions); gradpointwise = matrix::Zeros(m_samples,rawpredictions.Cols()); losses = vector::Zeros(m_samples); double sw_sum = double(m_samples); //loss gradient calculations if(m_nclasses>2) { double max_value, sum_exps; vector p(rawpredictions.Cols()+2); //--- for(ulong i = 0; i< m_samples; i++) { sum_exp_minus_max(i,rawpredictions,p); max_value = p[rawpredictions.Cols()]; sum_exps = p[rawpredictions.Cols()+1]; losses[i] = log(sum_exps) + max_value; //--- for(ulong k = 0; k<rawpredictions.Cols(); k++) { if(ulong(m_targs[i]) == k) losses[i] -= rawpredictions[i][k]; p[k]/=sum_exps; gradpointwise[i][k] = p[k] - double(int(ulong(m_targs[i])==k)); } } } else { for(ulong i = 0; i<m_samples; i++) { closs_grad_halfbinmial(m_targs[i],rawpredictions[i][0],losses[i],gradpointwise[i][0]); } } //--- loss = losses.Sum()/sw_sum; l2reg = 1.0 / (1.0 * sw_sum); loss += l2_penalty(weights,l2reg); gradpointwise/=sw_sum; //--- if(m_nclasses>2) { gradient = gradpointwise.Transpose().MatMul(m_preds) + l2reg*weights; gradient.Resize(gradient.Rows(),gradient.Cols()+1); vector gpsum = gradpointwise.Sum(0); gradient.Col(gpsum,m_features); } else { gradient = m_preds.Transpose().MatMul(gradpointwise) + l2reg*weights.Transpose(); gradient.Resize(gradient.Rows()+1,gradient.Cols()); vector gpsum = gradpointwise.Sum(0); gradient.Row(gpsum,m_features); } //--- matrixToArray(gradient,gradients); //--- return loss; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| weight intercept raw preds | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CFg::weight_intercept_raw(matrix &coef,matrix &x,matrix &wghts,vector &intcept,matrix &rpreds) { weight_intercept(coef,wghts,intcept); matrix intceptmat = np::vectorAsRowMatrix(intcept,x.Rows()); rpreds = (x.MatMul(wghts.Transpose()))+intceptmat; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| weight intercept | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CFg::weight_intercept(matrix &coef,matrix &wghts,vector &intcept) { intcept = coef.Col(m_features); wghts = np::sliceMatrixCols(coef,0,m_features); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| sum exp minus max | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CFg::sum_exp_minus_max(ulong index,matrix &rp,vector &pr) { double mv = rp[index][0]; double s_exps = 0.0; for(ulong k = 1; k<rp.Cols(); k++) { if(mv<rp[index][k]) mv=rp[index][k]; } for(ulong k = 0; k<rp.Cols(); k++) { pr[k] = exp(rp[index][k] - mv); s_exps += pr[k]; } pr[rp.Cols()] = mv; pr[rp.Cols()+1] = s_exps; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| l2 penalty | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CFg::l2_penalty(matrix &wghts,double strenth) { double norm2_v; if(wghts.Rows()==1) { matrix nmat = (wghts).MatMul(wghts.Transpose()); norm2_v = nmat[0][0]; } else norm2_v = wghts.Norm(MATRIX_NORM_FROBENIUS); return 0.5*strenth*norm2_v; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| closs_grad_half_binomial | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CFg::closs_grad_halfbinmial(double y_true,double raw, double &inout_1,double &inout_2) { if(raw <= -37.0) { inout_2 = exp(raw); inout_1 = inout_2 - y_true * raw; inout_2 -= y_true; } else if(raw <= -2.0) { inout_2 = exp(raw); inout_1 = log1p(inout_2) - y_true * raw; inout_2 = ((1.0 - y_true) * inout_2 - y_true) / (1.0 + inout_2); } else if(raw <= 18.0) { inout_2 = exp(-raw); // log1p(exp(x)) = log(1 + exp(x)) = x + log1p(exp(-x)) inout_1 = log1p(inout_2) + (1.0 - y_true) * raw; inout_2 = ((1.0 - y_true) - y_true * inout_2) / (1.0 + inout_2); } else { inout_2 = exp(-raw); inout_1 = inout_2 + (1.0 - y_true) * raw; inout_2 = ((1.0 - y_true) - y_true * inout_2) / (1.0 + inout_2); } }
这是 LBFGS 函数最小化过程所需要的。Clogit 拥有熟悉的训练和推理方法。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| logistic regression implementation | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class Clogit { public: Clogit(void); ~Clogit(void); bool fit(matrix &predictors, vector &targets); double predict(vector &preds); vector proba(vector &preds); matrix probas(matrix &preds); double coeffAt(ulong index); private: ulong m_nsamples; ulong m_nfeatures; bool m_trained; matrix m_train_preds; vector m_train_targs; matrix m_coefs; vector m_bias; vector m_classes; double m_xin[]; CFg *m_gradfunc; CObject m_dummy; vector predictProba(double &in); }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ Clogit::Clogit(void) { } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| destructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ Clogit::~Clogit(void) { if(CheckPointer(m_gradfunc) == POINTER_DYNAMIC) delete m_gradfunc; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| fit a model to a dataset | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool Clogit::fit(matrix &predictors, vector &targets) { m_trained = false; m_classes = np::unique(targets); np::sort(m_classes); if(predictors.Rows()!=targets.Size() || m_classes.Size()<2) { Print(__FUNCTION__," ",__LINE__," invalid inputs "); return m_trained; } m_train_preds = predictors; m_train_targs = targets; m_nfeatures = m_train_preds.Cols(); m_nsamples = m_train_preds.Rows(); m_coefs = matrix::Zeros(m_classes.Size()>2?m_classes.Size():m_classes.Size()-1,m_nfeatures+1); matrixToArray(m_coefs,m_xin); m_gradfunc = new CFg(m_train_preds,m_train_targs,m_classes.Size()); //--- CMinLBFGSStateShell state; CMinLBFGSReportShell rep; CNDimensional_Rep frep; //--- CAlglib::MinLBFGSCreate(m_xin.Size(),m_xin.Size()>=5?5:m_xin.Size(),m_xin,state); //--- CAlglib::MinLBFGSOptimize(state,m_gradfunc,frep,true,m_dummy); //--- CAlglib::MinLBFGSResults(state,m_xin,rep); //--- if(rep.GetTerminationType()>0) { m_trained = true; arrayToMatrix(m_xin,m_coefs,m_classes.Size()>2?m_classes.Size():m_classes.Size()-1,m_nfeatures+1); m_bias = m_coefs.Col(m_nfeatures); m_coefs = np::sliceMatrixCols(m_coefs,0,m_nfeatures); } else Print(__FUNCTION__," ", __LINE__, " failed to train the model ", rep.GetTerminationType()); delete m_gradfunc; return m_trained; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| get probability for single sample | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ vector Clogit::proba(vector &preds) { vector predicted; if(!m_trained) { Print(__FUNCTION__," ", __LINE__," no trained model available "); predicted.Fill(EMPTY_VALUE); return predicted; } predicted = ((preds.MatMul(m_coefs.Transpose()))); predicted += m_bias; if(predicted.Size()>1) { if(!predicted.Activation(predicted,AF_SOFTMAX)) { Print(__FUNCTION__," ", __LINE__," errror ", GetLastError()); predicted.Fill(EMPTY_VALUE); return predicted; } } else { predicted = predictProba(predicted[0]); } return predicted; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| get probability for binary classification | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ vector Clogit::predictProba(double &in) { vector out(2); double n = 1.0/(1.0+exp(-1.0*in)); out[0] = 1.0 - n; out[1] = n; return out; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| get probabilities for multiple samples | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ matrix Clogit::probas(matrix &preds) { matrix output(preds.Rows(),m_classes.Size()); vector rowin,rowout; for(ulong i = 0; i<preds.Rows(); i++) { rowin = preds.Row(i); rowout = proba(rowin); if(rowout.Max() == EMPTY_VALUE || !output.Row(rowout,i)) { Print(__LINE__," probas error ", GetLastError()); output.Fill(EMPTY_VALUE); break; } } return output; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| get probability for single sample | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double Clogit::predict(vector &preds) { vector prob = proba(preds); if(prob.Max() == EMPTY_VALUE) { Print(__LINE__," predict error "); return EMPTY_VALUE; } return m_classes[prob.ArgMax()]; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| get model coefficient at specific index | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double Clogit::coeffAt(ulong index) { if(index<(m_coefs.Rows())) { return (m_coefs.Row(index)).Sum(); } else { return 0.0; } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
基于逻辑回归的融汇组合,配以类特定权重
上一章节中讲述的单一权重集合方式,提供了稳定性和有效性,但它的局限性在于它或许无法充分利用模型专业性。如果单个模型在特定类中表现出卓越的性能,无论是通过设计、亦或自然发展,那么为每个类实现单独权重集合能够更有效地利用这些专用能力。向特定类权重集合的过渡,给优化过程引入了显著的复杂性。融汇必须管理 K 集合(每类一个),每个集合包含 M 个参数,从而产生总共 K*M 个参数,而非优化单个权重集合。参数的增加需要仔细考虑数据需求、及实现风险。
单独权重集合的稳健应用,需要大量的训练数据来维持统计有效性。作为一般指导,每个类的训练用例应至少是模型的十倍。即使有足够的数据,也应谨慎实现这种方式,且须有明确证据表明跨类模型的专业性。
CLogitRegSep 类管控单独权重集合的实现,与 CLogitReg 的不同之处在于,它为每个类分配单独的 Clogit 对象。训练过程将回归案例分布在特定于类的训练集合当中,取代将它们合并到单一训练集当中。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Use logistic regression to find best class. | //| This uses separate weight vectors for each class. | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class ClogitRegSep { private: ulong m_nout; long m_indices[]; matrix m_ranks; vector m_output; vector m_targs[]; matrix m_input[]; logistic::Clogit *m_logit[]; public: ClogitRegSep(void); ~ClogitRegSep(void); ulong classify(vector &inputs, IClassify* &models[]); bool fit(matrix &inputs, matrix &targets, IClassify* &models[]); vector proba(void) { return m_output;} };
未知案例的分类遵循与单权重方式类似的过程,但有一个关键区别:在计算 Borda 计数期间应用特定类的权重。这种专业性令系统能够更有效地利用特定类模型的专业技能。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| classify with ensemble model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ulong ClogitRegSep::classify(vector &inputs,IClassify *&models[]) { double temp; for(uint i =0; i<models.Size(); i++) { vector classification = models[i].classify(inputs); for(long j =0; j<long(classification.Size()); j++) m_indices[j] = j; if(!classification.Size()) { Print(__FUNCTION__," ", __LINE__," empty vector "); return ULONG_MAX; } qsortdsi(0,classification.Size()-1,classification,m_indices); for(ulong j = 0 ; j<m_nout; j++) { temp = m_logit[j].coeffAt(i); m_output[m_indices[j]] += j * temp; } } double sum = m_output.Sum(); ulong ibest = m_output.ArgMax(); double best = m_output[ibest]; if(sum>0.0) m_output/=sum; return ibest; }
单独权重集合的实现需要严格的验证过程。从业者应监测权重分布中无法解释的极值,确保权重差异与已知模型特征一致。必须实现保护措施,以防止回归过程不稳定。所有这些都可通过维护综合测试协议来有效应用。
特定类权重集合的成功实现依赖于仔细关注几个关键因素:确保每个类都有足够的训练数据,验证专业形态是否证明单独权重是合理的,监控权重稳定性,以及确认与单一权重方法相比分类准确性有所提高。虽然逻辑回归的这种高级实现提供了强化的分类能力,但它需要仔细管控,以便解决增加的复杂性、及潜在风险。
利用局部精度的融汇
为了进一步利用各个模型的优势,我们能够参考它们在预测因子空间内的局部准确性。有时,组件分类器在预测因子空间的特定区域内表现出卓越的性能。当模型在特定的预测因子条件下表现出色时,这种专业性就会显现出来 — 例如,一个模型或许在较低的变量值下表现最优,而另一个模型在较高的数值下表现出色。这种专业性形态,无论是有意设计的、亦或自然出现的,如果使用得当,都可以显著强化分类准确性。
实现遵循一种简单而有效的方式。在评估未知案例时,系统会从所有组件模型中收集分类,并选择对于该特定案例最可靠的模型。该融汇采用由 Woods、Kegelmeyer 和 Bowyer 撰写的论文《使用局部精度评估多个分类器的组合》中所提议方法来评估模型的可靠性。该方式经由若干个定义步骤进行操作:
- 计算未知案例与所有正训练案例之间的欧几里得距离。
- 确定预定数量的最接近训练样本,以便进行比较分析。
- 据这些最接近案例专门评估每个模型的性能,重点关注分配相同分类的模型,如同未知案例所做。
- 当模型预测未知案例、及其相邻的同类时,基于案例中正确分类的比例计算性能准则。
研究场景分析 10 个最近邻。按欧几里得距离计算识别这些近邻后,融汇向模型呈现一个未知情况,为其分配到类 3。然后,系统评估该模型在附近十个训练案例上的性能。如果模型将其中六个案例分类到类 3,其中四个分类正确,则模型达成 0.67(4/6)的性能准则。该评估过程在所有组件模型中持续,得分最高的模型最终判定出最终分类。该方式可确保针对每个特定案例上下文的分类决策,都能利用最可靠的模型。
为了解决平局问题,我们选择确定性最高的模型,计算为其最大输出与所有输出总和的比率。判定这个局部子集的大小是必要的,因为较小的子集对局部变化更敏感,而较大的子集更健壮,但或许会降低评估的“局部”性质。交叉验证可有助于判定最优子集大小,在出现平局的情况下,典型情况下较小大小优先。通过应用该方式,该融汇有效地利用了特定领域的模型专业知识,同时维持了计算效率。该方法允许融汇动态适应预测因子空间的不同区域,并且可靠性衡量能为模型选择提供一个透明的量值。
在 ensemble.mqh 中的 ClocalAcc 类设计用于基于局部准确性从分类器融汇中判定最有可能的类。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Use local accuracy to choose the best model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class ClocalAcc { private: ulong m_knn; ulong m_nout; long m_indices[]; matrix m_ranks; vector m_output; vector m_targs; matrix m_input; vector m_dist; matrix m_trnx; matrix m_trncls; vector m_trntrue; ulong m_classprep; bool m_crossvalidate; public: ClocalAcc(void); ~ClocalAcc(void); ulong classify(vector &inputs, IClassify* &models[]); bool fit(matrix &inputs, matrix &targets, IClassify* &models[], bool crossvalidate = false); vector proba(void) { return m_output;} };
fit() 方法训练 ClocalAcc 对象。它取输入数据(inputs)、目标值(targets)、分类器模型数组(models)、和用于交叉验证的可选标志(crossvalidate)。在训练过程中,fit() 计算每个输入数据点与所有其它数据点之间的距离。然后,它判定每个点的 k 个最近邻,如果 crossvalidate 设置为 true,则经由交叉验证判定 k。对于每个邻居,该方法评估融汇中每个分类器的性能。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| fit an ensemble model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool ClocalAcc::fit(matrix &inputs,matrix &targets,IClassify *&models[], bool crossvalidate = false) { m_crossvalidate = crossvalidate; m_nout = targets.Cols(); m_input = matrix::Zeros(inputs.Rows(),models.Size()); m_targs = vector::Zeros(inputs.Rows()); m_output = vector::Zeros(m_nout); m_ranks = matrix::Zeros(models.Size(),m_nout); m_dist = vector::Zeros(inputs.Rows()); m_trnx = matrix::Zeros(inputs.Rows(),inputs.Cols()); m_trncls = matrix::Zeros(inputs.Rows(),models.Size()); m_trntrue = vector::Zeros(inputs.Rows()); double best = 0.0; if(ArrayResize(m_indices,int(inputs.Rows()))<0) { Print(__FUNCTION__, " ", __LINE__, " array resize error ", GetLastError()); return false; } ulong k, knn_min,knn_max,knn_best=0,true_class, ibest=0; for(ulong i = 0; i<inputs.Rows(); i++) { np::matrixCopyRows(m_trnx,inputs,i,i+1,1); vector trow = targets.Row(i); vector inrow = inputs.Row(i); k = trow.ArgMax(); best = trow[k]; m_trntrue[i] = double(k); for(uint j=0; j<models.Size(); j++) { vector classification = models[j].classify(inrow); ibest = classification.ArgMax(); best = classification[ibest]; m_trncls[i][j] = double(ibest); } } m_classprep = 1; if(!m_crossvalidate) { m_knn=3; return true; } else { ulong ncases = inputs.Rows(); if(inputs.Rows()<20) { m_knn=3; return true; } knn_min = 3; knn_max = 10; vector testcase(inputs.Cols()) ; vector clswork(m_nout) ; vector knn_counts(knn_max - knn_min + 1) ; for(ulong i = knn_min; i<=knn_max; i++) knn_counts[i-knn_min] = 0; --ncases; for(ulong i = 0; i<=ncases; i++) { testcase = m_trnx.Row(i); true_class = ulong(m_trntrue[i]); if(i<ncases) { if(!m_trnx.SwapRows(ncases,i)) { Print(__FUNCTION__, " ", __LINE__, " failed row swap ", GetLastError()); return false; } m_trntrue[i] = m_trntrue[ncases]; double temp; for(uint j = 0; j<models.Size(); j++) { temp = m_trncls[i][j]; m_trncls[i][j] = m_trncls[ncases][j]; m_trncls[ncases][j] = temp; } } m_classprep = 1; for(ulong knn = knn_min; knn<knn_max; knn++) { ulong iclass = classify(testcase,models); if(iclass == true_class) { ++knn_counts[knn-knn_min]; } m_classprep=0; } if(i<ncases) { if(!m_trnx.SwapRows(i,ncases) || !m_trnx.Row(testcase,i)) { Print(__FUNCTION__, " ", __LINE__, " error ", GetLastError()); return false; } m_trntrue[ncases] = m_trntrue[i]; m_trntrue[i] = double(true_class); double temp; for(uint j = 0; j<models.Size(); j++) { temp = m_trncls[i][j]; m_trncls[i][j] = m_trncls[ncases][j]; m_trncls[ncases][j] = temp; } } } ++ncases; for(ulong knn = knn_min; knn<=knn_max; knn++) { if((knn==knn_min) || (ulong(knn_counts[knn-knn_min])>ibest)) { ibest = ulong(knn_counts[knn-knn_min]); knn_best = knn; } } m_knn = knn_best; m_classprep = 1; } return true; }
classify() 方法预测给定输入向量的类标签。它计算输入向量和所有训练数据点之间的距离,并识别 k 个最近邻。对于融汇中的每个分类器,它判定分类器对于这些邻居的准确性。选择最近邻精度最高的分类器,并返回其预测的类标签。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| classify with an ensemble model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ulong ClocalAcc::classify(vector &inputs,IClassify *&models[]) { double dist=0, diff=0, best=0, crit=0, bestcrit=0, conf=0, bestconf=0, sum ; ulong k, ibest, numer, denom, bestmodel=0, bestchoice=0 ; if(m_classprep) { for(ulong i = 0; i<m_input.Rows(); i++) { m_indices[i] = long(i); dist = 0.0; for(ulong j = 0; j<m_trnx.Cols(); j++) { diff = inputs[j] - m_trnx[i][j]; dist+= diff*diff; } m_dist[i] = dist; } if(!m_dist.Size()) { Print(__FUNCTION__," ", __LINE__," empty vector "); return ULONG_MAX; } qsortdsi(0, m_dist.Size()-1, m_dist,m_indices); } for(uint i = 0; i<models.Size(); i++) { vector vec = models[i].classify(inputs); sum = vec.Sum(); ibest = vec.ArgMax(); best = vec[ibest]; conf = best/sum; denom = numer = 0; for(ulong ii = 0; ii<m_knn; ii++) { k = m_indices[ii]; if(ulong(m_trncls[k][i]) == ibest) { ++denom; if(ibest == ulong(m_trntrue[k])) ++numer; } } if(denom > 0) crit = double(numer)/double(denom); else crit = 0.0; if((i == 0) || (crit > bestcrit)) { bestcrit = crit; bestmodel = ulong(i); bestchoice = ibest; bestconf = conf; m_output = vec; } else if(fabs(crit-bestcrit)<1.e-10) { if(conf > bestconf) { bestcrit= crit; bestmodel = ulong(i); bestchoice = ibest; bestconf = conf; m_output = vec; } } } sum = m_output.Sum(); if(sum>0) m_output/=sum; return bestchoice; }
融汇组合用到模糊积分
模糊逻辑是一种数学框架,它是与真实程度打交道,而非绝对真值或假值。在分类器组合的境况下,模糊逻辑可用于对多个模型的输出进行积分,同时参考每个模型的可靠性。模糊积分最初由 Sugeno(1977)提出,涉及将数值分配给通用子集的模糊量级。该量级满足某些属性,包括边界条件、单调性和连续性。Sugeno 用 λ 模糊量级扩展了这一概念,它协同一个额外的因子来组合不相交集合的量级。
模糊积分本身用到特定公式计算,涉及隶属函数和模糊量级。虽然暴力计算也是可能的,但对于有限集合存在一种更有效的方法,涉及递归计算。λ 值的判定,是确保最终量级等于 1。在分类器组合的境况中,应用模糊积分时,可把每个分类器视为一个通用元素,并将其可靠性作为其隶属值。然后计算每个类的模糊积分,并选择积分最高的类。该方法有效地结合了多个分类器的输出,同时参考了它们各自的可靠性。
CFuzzyInt 类实现了组合分类器的模糊积分方法。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Use fuzzy integral to combine decisions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CFuzzyInt { private: ulong m_nout; vector m_output; long m_indices[]; matrix m_sort; vector m_g; double m_lambda; double recurse(double x); public: CFuzzyInt(void); ~CFuzzyInt(void); bool fit(matrix &predictors, matrix &targets, IClassify* &models[]); ulong classify(vector &inputs, IClassify* &models[]); vector proba(void) { return m_output;} };
该方法的核心在于 recurse() 函数,其迭代计算模糊量级。关键参数 λ 的判定,是找到确保所有模型的模糊量级收敛到数值一。我们从一个初始值开始,递次调整它,直到所有模型的模糊量级收敛到一。典型情况下涉及将正确的 λ 值括起来,然后使用平分法细化搜索。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| recurse | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CFuzzyInt::recurse(double x) { double val ; val = m_g[0] ; for(ulong i=1 ; i<m_g.Size() ; i++) val += m_g[i] + x * m_g[i] * val ; return val - 1.0 ; }
为了估算每个模型的可靠性,我们评估了其在训练集上的准确性。然后,我们从随机猜测中减去预期准确性,并将结果值重新缩放到零到一之间,来调整准确性。有更复杂的途径来估算模型可靠性,但该方式因其简单性而成为首选。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| fit ensemble model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CFuzzyInt::fit(matrix &predictors,matrix &targets,IClassify *&models[]) { m_nout = targets.Cols(); m_output = vector::Zeros(m_nout); m_sort = matrix::Zeros(models.Size(), m_nout); m_g = vector::Zeros(models.Size()); if(ArrayResize(m_indices,int(models.Size()))<0) { Print(__FUNCTION__, " ", __LINE__, " array resize error ", GetLastError()); return false; } ulong k=0, iclass =0 ; double best=0, xlo=0, xhi=0, y=0, ylo=0, yhi=0, step=0 ; for(ulong i = 0; i<predictors.Rows(); i++) { vector trow = targets.Row(i); vector inrow = predictors.Row(i); k = trow.ArgMax(); best = trow[k]; for(uint ii = 0; ii< models.Size(); ii++) { vector vec = models[ii].classify(inrow); iclass = vec.ArgMax(); best = vec[iclass]; if(iclass == k) m_g[ii] += 1.0; } } for(uint i = 0; i<models.Size(); i++) { m_g[i] /= double(predictors.Rows()) ; m_g[i] = (m_g[i] - 1.0 / m_nout) / (1.0 - 1.0 / m_nout) ; if(m_g[i] > 1.0) m_g[i] = 1.0 ; if(m_g[i] < 0.0) m_g[i] = 0.0 ; } xlo = m_lambda = -1.0 ; ylo = recurse(xlo) ; if(ylo >= 0.0) // Theoretically should never exceed zero return true; // But allow for pathological numerical problems step = 1.0 ; for(;;) { xhi = xlo + step ; yhi = recurse(xhi) ; if(yhi >= 0.0) // If we have just bracketed the root break ; // We can quit the search if(xhi > 1.e5) // In the unlikely case of extremely poor models { m_lambda = xhi ; // Fudge a value return true ; // And quit } step *= 2.0 ; // Keep increasing the step size to avoid many tries xlo = xhi ; // Move onward ylo = yhi ; } for(;;) { m_lambda = 0.5 * (xlo + xhi) ; y = recurse(m_lambda) ; // Evaluate the function here if(fabs(y) < 1.e-8) // Primary convergence criterion break ; if(xhi - xlo < 1.e-10 * (m_lambda + 1.1)) // Backup criterion break ; if(y > 0.0) { xhi = m_lambda ; yhi = y ; } else { xlo = m_lambda ; ylo = y ; } } return true; }
在分类期间,选择模糊积分最高的类。每个类的模糊积分是通过迭代将模型的输出与递归计算的模糊量级进行比较,并在每一步选择最小值来计算的。类的最终模糊积分表示该类中模型的组合置信度。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| classify with ensemble | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ulong CFuzzyInt::classify(vector &inputs,IClassify *&models[]) { ulong k, iclass; double sum, gsum, minval, maxmin, best ; for(uint i = 0; i<models.Size(); i++) { vector vec = models[i].classify(inputs); sum = vec.Sum(); vec/=sum; if(!m_sort.Row(vec,i)) { Print(__FUNCTION__, " ", __LINE__, " row insertion error ", GetLastError()); return false; } } for(ulong i = 0; i<m_nout; i++) { for(uint ii =0; ii<models.Size(); ii++) m_indices[ii] = long(ii); vector vec = m_sort.Col(i); if(!vec.Size()) { Print(__FUNCTION__," ", __LINE__," empty vector "); return ULONG_MAX; } qsortdsi(0,long(vec.Size()-1), vec, m_indices); maxmin = gsum = 0.0; for(int j = int(models.Size()-1); j>=0; j--) { k = m_indices[j]; if(k>=vec.Size()) { Print(__FUNCTION__," ",__LINE__, " out of range ", k); } gsum += m_g[k] + m_lambda * m_g[k] * gsum; if(gsum<vec[k]) minval = gsum; else minval = vec[k]; if(minval > maxmin) maxmin = minval; } m_output[i] = maxmin; } iclass = m_output.ArgMax(); best = m_output[iclass]; return iclass; }
配对耦合
配对耦合是一种独特的多类分类方式,即利用专门的二元分类器的强大。它结合了一组 K(K−1)/2 二元分类器(其中 K 是类数量),每个分类器都设计用于区分一对特定类。想象我们有一个数据集,由具有 3 个类的目标组成。为了比较它们,我们创建了一组 3*(3-1)/2 = 3 个模型。每个模型都设计用来仅在两个类之间做出决定。如果指派了类,则标识符(A、B 和 C)。这 3 个模型应当配置如下:
- 模型 1:在类 A 和类 B 之间做出决定。
- 模型 2:在类 A 和类 C 之间做出决定。
- 模型 3:在类 B 和类 C 之间做出决定。
必须对训练数据进行分区,以便包含与每个模型的分类任务相关的样本。对这些模型的评估将产生一组可以排列在 K x K 矩阵中的概率。下面是这种矩阵的推测示例。
| A | B | C | |
| A | ---- | 0.2 | 0.7 |
| B | 0.8 | ---- | 0.4 |
| C | 0.3 | 0.6 | ---- |
在该矩阵中,区分类 A 和类 B 的模型为属于类 A 的样本分配概率 0.2。由于矩阵是对称的,矩阵右上角对角元素描述了计算出的完整概率集合,以便在成对类之间做出决定。给定了模型输出,目标是计算样本外案例属于特定类的概率估值。这意味着我们需要找到一组概率,其分布与观察到的配对概率的分布相匹配,或至少尽可能接近它们。采用迭代方法来细化这些初始概率估值,无需调用函数最小化过程。
该迭代过程逐渐精细初始类概率估值,确保它们与来自各个分类器的配对预测更好地保持一致。本质上,这就像逐渐精细地图,直至它准确反映现实世界。我们从粗略的草图开始,然后基于新信息进行小调整,直至我们得到一个高度准确的地图。该迭代方式非常有效,通常可以快速收敛到一个解。
CPairWise 类实现配对耦合算法。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Use pairwise coupling to combine decisions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CPairWise { private: ulong m_nout; ulong m_npairs; vector m_output; vector m_rij; vector m_uij; public: CPairWise(void); ~CPairWise(void); ulong classify(ulong numclasses,vector &inputs,IClassify *&models[],ulong &samplesPerModel[]); vector proba(void) { return m_output;} };
核心计算是在 classify() 方法中完成的,其遵循结构化过程,依据配对分类器的输出计算类概率。该方法首先评估给定测试用例的所有配对模型。每个模型对应于一对特定类,并生成一个输出,该输出表示测试用例属于该对中两个类之一的似然性。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| classify using ensemble model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ulong CPairWise::classify(ulong numclasses,vector &inputs,IClassify *&models[],ulong &samplesPerModel[]) { m_nout=numclasses; m_npairs = m_nout*(m_nout-1)/2; m_output = vector::Zeros(m_nout); m_rij = vector::Zeros(m_npairs); m_uij = vector::Zeros(m_npairs); long k; ulong iclass=0 ; double rr, best=0, numer, denom, sum, delta, oldval ; for(ulong i = 0; i<m_npairs; i++) { vector vec = models[i].classify(inputs); rr = vec[0]; if(vec[0]> 0.999999) vec[0] = 0.999999 ; if(vec[0] < 0.000001) vec[0] = 0.000001 ; m_rij[i] = vec[0] ; } k = 0 ; for(ulong i=0 ; i<m_nout-1 ; i++) { for(ulong j=i+1 ; j<m_nout ; j++) { rr = m_rij[k++] ; m_output[i] += rr ; m_output[j] += 1.0 - rr ; } } for(ulong i=0 ; i<m_nout ; i++) m_output[i] /= double(m_npairs) ; k = 0 ; for(ulong i=0 ; i<m_nout-1 ; i++) { for(ulong j=i+1 ; j<m_nout ; j++) m_uij[k++] = m_output[i] / (m_output[i] + m_output[j]) ; } for(int iter=0 ; iter<10000 ; iter++) { delta = 0.0 ; for(ulong i=0 ; i<m_nout ; i++) { numer = denom = 0.0 ; for(ulong j=0 ; j<m_nout ; j++) { if(i < j) { k = (long(i) * (2 * long(m_nout) - long(i) - 3) - 2) / 2 + long(j) ; numer += samplesPerModel[k] * m_rij[k] ; denom += samplesPerModel[k] * m_uij[k] ; } else if(i > j) { k = (long(j) * (2 * long(m_nout) - long(j) - 3) - 2) / 2 + long(i) ; //Print(__FUNCTION__," ",__LINE__," k ", k); numer += samplesPerModel[k] * (1.0 - m_rij[k]) ; denom += samplesPerModel[k] * (1.0 - m_uij[k]) ; } } oldval = m_output[i] ; m_output[i] *= numer / denom ; sum = 0.0 ; for(ulong j=0 ; j<m_nout ; j++) sum += m_output[j] ; for(ulong j=0 ; j<m_nout ; j++) m_output[j] /= sum ; if(fabs(m_output[i]-oldval) > delta) delta = fabs(m_output[i]-oldval) ; k = 0 ; for(ulong i=0 ; i<m_nout-1 ; i++) { for(ulong j=i+1 ; j<m_nout ; j++) m_uij[k++] = m_output[i] / (m_output[i] + m_output[j]) ; } } if(delta < 1.e-6) break ; } return m_output.ArgMax() ; }
一旦获得初始输出(概率),它们就会被用作类概率的起始估值。然后,该方法迭代精细这些估值,从而提高准确性。精细类概率后,最后一步是识别概率最大的类。对于给定测试用例,概率最高的类被认为是最有可能的类,其索引作为 classify() 方法的输出返回。
结论:比较组合方法
ClassificationEnsemble_Demo.mq5 脚本设计用来比较本文中所讨论融汇算法在各种场景中的性能。通过运行多个蒙特卡洛复制,该脚本可以评估每个融汇方法在不同条件下的性能。该脚本允许用户指定每次运行中采用的训练样本数量,从而能够跨不同大小(从小到大)的数据集进行测试。随着问题复杂性的增加,可以调整类数量,以便测试融汇方法的可扩展性。融汇中所用的基础分类器(模型)的数量可以变化,以便评估算法在不同复杂度下的性能。
用户可为每个场景指定蒙特卡罗复制的次数,以便评估融汇算法的稳定性、和一致性。错误分类的样本外概率用作性能量值,确保在未见数据上评估模型,从而模拟现实世界的分类任务。如果使用四个或更多模型,则故意令一个模型变得无用(例如,令其进行随机预测、或产生恒定的输出)。这可测试融汇算法的健壮性,评估它们处理包含不相关、或非信息富有模型的能力。
如果用五个或更多模型,则第五个模型将设置为偶尔产生极值、或不稳定的预测,模拟现实世界中模型或许不稳定、或嘈杂的场景。该功能评估融汇方法如何处理不可靠的模型,以及它们是否能够通过正确加权、或降低有问题的模型加权,来保持良好的分类性能。分类难度因子定义了类之间的散布,其控制组件模型的问题难度。散布越大越容易分类,散布越小则难度增加。这允许测试融汇方法在不同难度级别下的性能,评估它们在具有挑战性的场景中维持准确性的能力。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ClassificationEnsemble_Demo.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #property script_show_inputs #include<ensemble.mqh> #include<multilayerperceptron.mqh> //--- input parameters input int NumSamples=10; input int NumClasses=3; input int NumModels=3; input int NumReplications=1000; input double ClassificationDifficultyFactor=0.0; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| normal(rngstate) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double normal(CHighQualityRandStateShell &state) { return CAlglib::HQRndNormal(state); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| unifrand(rngstate) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double unifrand(CHighQualityRandStateShell &state) { return CAlglib::HQRndUniformR(state); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|Multilayer perceptron | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CMLPC:public ensemble::IClassify { private: CMlp *m_mlfn; double m_learningrate; double m_tolerance; double m_alfa; double m_beyta; uint m_epochs; ulong m_in,m_out; ulong m_hl1,m_hl2; public: CMLPC(ulong ins, ulong outs,ulong numhl1,ulong numhl2); ~CMLPC(void); void setParams(double alpha_, double beta_,double learning_rate, double tolerance, uint num_epochs); bool train(matrix &predictors,matrix&targets); vector classify(vector &predictors); ulong getNumInputs(void) { return m_in;} ulong getNumOutputs(void) { return m_out;} }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CMLPC::CMLPC(ulong ins, ulong outs,ulong numhl1,ulong numhl2) { m_in = ins; m_out = outs; m_alfa = 0.3; m_beyta = 0.01; m_learningrate=0.001; m_tolerance=1.e-8; m_epochs= 1000; m_hl1 = numhl1; m_hl2 = numhl2; m_mlfn = new CMlp(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| destructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CMLPC::~CMLPC(void) { if(CheckPointer(m_mlfn) == POINTER_DYNAMIC) delete m_mlfn; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| set other hyperparameters of the i_model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CMLPC::setParams(double alpha_, double beta_,double learning_rate, double tolerance, uint num_epochs) { m_alfa = alpha_; m_beyta = beta_; m_learningrate=learning_rate; m_tolerance=tolerance; m_epochs= num_epochs; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| fit a i_model to the data | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CMLPC::train(matrix &predictors,matrix &targets) { if(m_in != predictors.Cols() || m_out != targets.Cols()) { Print(__FUNCTION__, " failed training due to invalid training data"); return false; } return m_mlfn.fit(predictors,targets,m_alfa,m_beyta,m_hl1,m_hl2,m_epochs,m_learningrate,m_tolerance); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| make a prediction with the trained i_model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ vector CMLPC::classify(vector &predictors) { return m_mlfn.predict(predictors); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| clean up dynamic array pointers | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void cleanup(ensemble::IClassify* &array[]) { for(uint i = 0; i<array.Size(); i++) if(CheckPointer(array[i])==POINTER_DYNAMIC) delete array[i]; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| global variables | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int nreplications, nsamps,nmodels, divisor, nreps_done ; int n_classes, nnn, n_pairs, nh_g ; ulong ntrain_pair[]; matrix xdata, xbad_data, xtainted_data, test[],x_targ,xbad_targ,xwild_targ; vector inputdata; double cd_factor, err_score, err_score_1, err_score_2, err_score_3 ; vector classification_err_raw, output_vector; double classification_err_average ; double classification_err_median ; double classification_err_maxmax ; double classification_err_maxmin ; double classification_err_intersection_1 ; double classification_err_intersection_2 ; double classification_err_intersection_3 ; double classification_err_union_1 ; double classification_err_union_2 ; double classification_err_union_3 ; double classification_err_majority ; double classification_err_borda ; double classification_err_logit ; double classification_err_logitsep ; double classification_err_localacc ; double classification_err_fuzzyint ; double classification_err_pairwise ; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ensemble i_model objects | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ensemble::CAvgClass average_ensemble ; ensemble::CMedian median_ensemble ; ensemble::CMaxMax maxmax_ensemble ; ensemble::CMaxMin maxmin_ensemble ; ensemble::CIntersection intersection_ensemble ; ensemble::CUnion union_rule ; ensemble::CMajority majority_ensemble ; ensemble::CBorda borda_ensemble ; ensemble::ClogitReg logit_ensemble ; ensemble::ClogitRegSep logitsep_ensemble ; ensemble::ClocalAcc localacc_ensemble ; ensemble::CFuzzyInt fuzzyint_ensemble ; ensemble::CPairWise pairwise_ensemble ; int n_hid = 4 ; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { CHighQualityRandStateShell rngstate; CHighQualityRand::HQRndRandomize(rngstate.GetInnerObj()); //--- nsamps = NumSamples ; n_classes = NumClasses ; nmodels = NumModels ; nreplications = NumReplications ; cd_factor = ClassificationDifficultyFactor ; if((nsamps <= 3) || (n_classes <= 1) || (nmodels <= 0) || (nreplications <= 0) || (cd_factor < 0.0)) { Alert(" Invalid inputs "); return; } divisor = 1 ; ensemble::IClassify* models[]; ensemble::IClassify* model_pairs[]; /* Allocate memory and initialize */ n_pairs = n_classes * (n_classes-1) / 2 ; if(ArrayResize(models,nmodels)<0 || ArrayResize(model_pairs,n_pairs)<0 || ArrayResize(test,10)<0 || ArrayResize(ntrain_pair,n_pairs)<0) { Print(" Array resize errors ", GetLastError()); cleanup(models); cleanup(model_pairs); return; } ArrayInitialize(ntrain_pair,0); for(int i=0 ; i<nmodels ; i++) models[i] = new CMLPC(2,ulong(n_classes),4,0) ; xdata = matrix::Zeros(nsamps,(2+n_classes)); xbad_data = matrix::Zeros(nsamps,(2+n_classes)); xtainted_data = matrix::Zeros(nsamps,(2+n_classes)); inputdata = vector::Zeros(3); for(uint i = 0; i<test.Size(); i++) test[i] = matrix::Zeros(nsamps,(2+n_classes)); classification_err_raw = vector::Zeros(nmodels); classification_err_average = 0.0 ; classification_err_median = 0.0 ; classification_err_maxmax = 0.0 ; classification_err_maxmin = 0.0 ; classification_err_intersection_1 = 0.0 ; classification_err_intersection_2 = 0.0 ; classification_err_intersection_3 = 0.0 ; classification_err_union_1 = 0.0 ; classification_err_union_2 = 0.0 ; classification_err_union_3 = 0.0 ; classification_err_majority = 0.0 ; classification_err_borda = 0.0 ; classification_err_logit = 0.0 ; classification_err_logitsep = 0.0 ; classification_err_localacc = 0.0 ; classification_err_fuzzyint = 0.0 ; classification_err_pairwise = 0.0 ; for(int i_rep=0 ; i_rep<nreplications ; i_rep++) { nreps_done = i_rep + 1 ; if(i_rep>0) xdata.Fill(0.0); //--- for(int i=0, z=0; i<nsamps ; i++) { xdata[i][0] = normal(rngstate) ; xdata[i][1] = normal(rngstate) ; if(i < n_classes) z = i ; else z = (int)(unifrand(rngstate) * n_classes) ; if(z >= n_classes) z = n_classes - 1 ; xdata[i][2+z] = 1.0 ; xdata[i][0] += double(z) * cd_factor ; xdata[i][1] -= double(z) * cd_factor ; } if(nmodels >= 4) { xbad_data = xdata; matrix arm = np::sliceMatrixCols(xbad_data,2); for(int i = 0; i<nsamps; i++) for(int z = 0; z<n_classes; z++) arm[i][z] = (unifrand(rngstate)<(1.0/double(n_classes)))?1.0:0.0; np::matrixCopy(xbad_data,arm,0,xbad_data.Rows(),1,2); } if(nmodels >= 5) { xtainted_data = xdata; matrix arm = np::sliceMatrixCols(xtainted_data,2); for(int i = 0; i<nsamps; i++) for(int z = 0; z<n_classes; z++) if(unifrand(rngstate)<0.1) arm[i][z] = xdata[i][2+z] * 1000.0 - 500.0 ; np::matrixCopy(xtainted_data,arm,0,xtainted_data.Rows(),1,2); } for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) // Build a test dataset { if(i_rep>0) test[i].Fill(0.0); for(int j=0,z=0; j<nsamps; j++) { test[i][j][0] = normal(rngstate) ; test[i][j][1] = normal(rngstate) ; z = (int)(unifrand(rngstate) * n_classes) ; if(z >= n_classes) z = n_classes - 1 ; test[i][j][2+z] = 1.0 ; test[i][j][0] += double(z) * cd_factor ; test[i][j][1] -= double(z) * cd_factor ; } } for(int i_model=0 ; i_model<nmodels ; i_model++) { matrix preds,targs; if(i_model == 3) { targs = np::sliceMatrixCols(xbad_data,2); preds = np::sliceMatrixCols(xbad_data,0,2); } else if(i_model == 4) { targs = np::sliceMatrixCols(xtainted_data,2); preds = np::sliceMatrixCols(xtainted_data,0,2); } else { targs = np::sliceMatrixCols(xdata,2); preds = np::sliceMatrixCols(xdata,0,2); } if(!models[i_model].train(preds,targs)) { Print(" failed to train i_model at shift ", i_model); cleanup(model_pairs); cleanup(models); return; } err_score = 0.0 ; for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) { vector testvec,testin,testtarg; for(int j=0; j<nsamps; j++) { testvec = test[i].Row(j); testtarg = np::sliceVector(testvec,2); testin = np::sliceVector(testvec,0,2); output_vector = models[i_model].classify(testin) ; if(output_vector.ArgMax() != testtarg.ArgMax()) err_score += 1.0 ; } } classification_err_raw[i_model] += err_score / (10 * nsamps) ; } int i_model = 0; for(int i=0 ; i<n_classes-1 ; i++) { for(int j=i+1 ; j<n_classes ; j++) { ntrain_pair[i_model] = 0 ; for(int z=0 ; z<nsamps ; z++) { if((xdata[z][2+i]> 0.5) || (xdata[z][2+j] > 0.5)) ++ntrain_pair[i_model] ; } nh_g = (n_hid < int(ntrain_pair[i_model]) - 1) ? n_hid : int(ntrain_pair[i_model]) - 1; model_pairs[i_model] = new CMLPC(2, 1, ulong(nh_g+1),0) ; matrix training; matrix preds,targs; ulong msize=0; for(int z=0 ; z<nsamps ; z++) { inputdata[0] = xdata[z][0] ; inputdata[1] = xdata[z][1] ; if(xdata[z][2+i]> 0.5) inputdata[2] = 1.0 ; else if(xdata[z][2+j] > 0.5) inputdata[2] = 0.0 ; else continue ; training.Resize(msize+1,inputdata.Size()); training.Row(inputdata,msize++); } preds = np::sliceMatrixCols(training,0,2); targs = np::sliceMatrixCols(training,2); model_pairs[i_model].train(preds,targs); ++i_model ; } } err_score = 0.0 ; for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) { for(int z=0;z<nsamps;z++) { vector row = test[i].Row(z); vector rowtest = np::sliceVector(row,0,2); vector rowtarg = np::sliceVector(row,2); if(average_ensemble.classify(rowtest,models) != rowtarg.ArgMax()) err_score += 1.0 ; } } classification_err_average += err_score / (10 * nsamps) ; /* median_ensemble */ err_score = 0.0 ; for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) { for(int z=0;z<nsamps;z++) { vector row = test[i].Row(z); vector rowtest = np::sliceVector(row,0,2); vector rowtarg = np::sliceVector(row,2); if(median_ensemble.classify(rowtest,models) != rowtarg.ArgMax()) err_score += 1.0 ; } } classification_err_median += err_score / (10 * nsamps) ; /* maxmax_ensemble */ err_score = 0.0 ; for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) { for(int z=0;z<nsamps;z++) { vector row = test[i].Row(z); vector rowtest = np::sliceVector(row,0,2); vector rowtarg = np::sliceVector(row,2); if(maxmax_ensemble.classify(rowtest,models) != rowtarg.ArgMax()) err_score += 1.0 ; } } classification_err_maxmax += err_score / (10 * nsamps) ; err_score = 0.0 ; for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) { for(int z=0;z<nsamps;z++) { vector row = test[i].Row(z); vector rowtest = np::sliceVector(row,0,2); vector rowtarg = np::sliceVector(row,2); if(maxmin_ensemble.classify(rowtest,models) != rowtarg.ArgMax()) // If predicted class not true class err_score += 1.0 ; // Count this misclassification } } classification_err_maxmin += err_score / (10 * nsamps) ; matrix preds,targs; err_score_1 = err_score_2 = err_score_3 = 0.0 ; preds = np::sliceMatrixCols(xdata,0,2); targs = np::sliceMatrixCols(xdata,2); intersection_ensemble.fit(preds,targs,models); for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) { for(int z=0;z<nsamps;z++) { vector row = test[i].Row(z); vector rowtest = np::sliceVector(row,0,2); vector rowtarg = np::sliceVector(row,2); ulong class_ = intersection_ensemble.classify(rowtest,models) ; output_vector = intersection_ensemble.proba(); if(output_vector[rowtarg.ArgMax()] < 0.5) { err_score_1 += 1.0 ; err_score_2 += 1.0 ; err_score_3 += 1.0 ; } else { if(class_ > 3) err_score_3 += 1.0 ; if(class_ > 2) err_score_2 += 1.0 ; if(class_ > 1) err_score_1 += 1.0 ; } } } classification_err_intersection_1 += err_score_1 / (10 * nsamps) ; classification_err_intersection_2 += err_score_2 / (10 * nsamps) ; classification_err_intersection_3 += err_score_3 / (10 * nsamps) ; union_rule.fit(preds,targs,models); err_score_1 = err_score_2 = err_score_3 = 0.0 ; for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) { for(int z=0;z<nsamps;z++) { vector row = test[i].Row(z); vector rowtest = np::sliceVector(row,0,2); vector rowtarg = np::sliceVector(row,2); ulong clss = union_rule.classify(rowtest,models) ; output_vector = union_rule.proba(); if(output_vector[rowtarg.ArgMax()] < 0.5) { err_score_1 += 1.0 ; err_score_2 += 1.0 ; err_score_3 += 1.0 ; } else { if(clss > 3) err_score_3 += 1.0 ; if(clss > 2) err_score_2 += 1.0 ; if(clss > 1) err_score_1 += 1.0 ; } } } classification_err_union_1 += err_score_1 / (10 * nsamps) ; classification_err_union_2 += err_score_2 / (10 * nsamps) ; classification_err_union_3 += err_score_3 / (10 * nsamps) ; err_score = 0.0 ; for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) { for(int z=0;z<nsamps;z++) { vector row = test[i].Row(z); vector rowtest = np::sliceVector(row,0,2); vector rowtarg = np::sliceVector(row,2); if(majority_ensemble.classify(rowtest,models) != rowtarg.ArgMax()) err_score += 1.0 ; } } classification_err_majority += err_score / (10 * nsamps) ; err_score = 0.0 ; for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) { for(int z=0;z<nsamps;z++) { vector row = test[i].Row(z); vector rowtest = np::sliceVector(row,0,2); vector rowtarg = np::sliceVector(row,2); if(borda_ensemble.classify(rowtest,models) != rowtarg.ArgMax()) err_score += 1.0 ; } } classification_err_borda += err_score / (10 * nsamps) ; err_score = 0.0 ; logit_ensemble.fit(preds,targs,models); for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) { for(int z=0;z<nsamps;z++) { vector row = test[i].Row(z); vector rowtest = np::sliceVector(row,0,2); vector rowtarg = np::sliceVector(row,2); if(logit_ensemble.classify(rowtest,models) != rowtarg.ArgMax()) err_score += 1.0 ; } } classification_err_logit += err_score / (10 * nsamps) ; err_score = 0.0 ; logitsep_ensemble.fit(preds,targs,models); for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) { for(int z=0;z<nsamps;z++) { vector row = test[i].Row(z); vector rowtest = np::sliceVector(row,0,2); vector rowtarg = np::sliceVector(row,2); if(logitsep_ensemble.classify(rowtest,models) != rowtarg.ArgMax()) err_score += 1.0 ; } } classification_err_logitsep += err_score / (10 * nsamps) ; err_score = 0.0 ; localacc_ensemble.fit(preds,targs,models); for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) { for(int z=0;z<nsamps;z++) { vector row = test[i].Row(z); vector rowtest = np::sliceVector(row,0,2); vector rowtarg = np::sliceVector(row,2); if(localacc_ensemble.classify(rowtest,models) != rowtarg.ArgMax()) err_score += 1.0 ; } } classification_err_localacc += err_score / (10 * nsamps) ; err_score = 0.0 ; fuzzyint_ensemble.fit(preds,targs,models); for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) { for(int z=0;z<nsamps;z++) { vector row = test[i].Row(z); vector rowtest = np::sliceVector(row,0,2); vector rowtarg = np::sliceVector(row,2); if(fuzzyint_ensemble.classify(rowtest,models) != rowtarg.ArgMax()) err_score += 1.0 ; } } classification_err_fuzzyint += err_score / (10 * nsamps) ; err_score = 0.0 ; for(int i=0 ; i<10 ; i++) { for(int z=0;z<nsamps;z++) { vector row = test[i].Row(z); vector rowtest = np::sliceVector(row,0,2); vector rowtarg = np::sliceVector(row,2); if(pairwise_ensemble.classify(ulong(n_classes),rowtest,model_pairs,ntrain_pair) != rowtarg.ArgMax()) err_score += 1.0 ; } } classification_err_pairwise += err_score / (10 * nsamps) ; cleanup(model_pairs); } err_score = 0.0 ; PrintFormat("Test Config: Classification Difficulty - %8.8lf\nNumber of classes - %5d\nNumber of component models - %5d\n Sample Size - %5d", ClassificationDifficultyFactor,NumClasses,NumModels,NumSamples); PrintFormat("%5d Replications:", nreps_done) ; for(int i_model=0 ; i_model<nmodels ; i_model++) { PrintFormat(" %.8lf", classification_err_raw[i_model] / nreps_done) ; err_score += classification_err_raw[i_model] / nreps_done ; } PrintFormat(" Mean raw error = %8.8lf", err_score / nmodels) ; PrintFormat(" average_ensemble error = %8.8lf", classification_err_average / nreps_done) ; PrintFormat(" median_ensemble error = %8.8lf", classification_err_median / nreps_done) ; PrintFormat(" maxmax_ensemble error = %8.8lf", classification_err_maxmax / nreps_done) ; PrintFormat(" maxmin_ensemble error = %8.8lf", classification_err_maxmin / nreps_done) ; PrintFormat(" majority_ensemble error = %8.8lf", classification_err_majority / nreps_done) ; PrintFormat(" borda_ensemble error = %8.8lf", classification_err_borda / nreps_done) ; PrintFormat(" logit_ensemble error = %8.8lf", classification_err_logit / nreps_done) ; PrintFormat(" logitsep_ensemble error = %8.8lf", classification_err_logitsep / nreps_done) ; PrintFormat(" localacc_ensemble error = %8.8lf", classification_err_localacc / nreps_done) ; PrintFormat(" fuzzyint_ensemble error = %8.8lf", classification_err_fuzzyint / nreps_done) ; PrintFormat(" pairwise_ensemble error = %8.8lf", classification_err_pairwise / nreps_done) ; PrintFormat(" intersection_ensemble error 1 = %8.8lf", classification_err_intersection_1 / nreps_done) ; PrintFormat(" intersection_ensemble error 2 = %8.8lf", classification_err_intersection_2 / nreps_done) ; PrintFormat(" intersection_ensemble error 3 = %8.8lf", classification_err_intersection_3 / nreps_done) ; PrintFormat(" Union error 1 = %8.8lf", classification_err_union_1 / nreps_done) ; PrintFormat(" Union error 2 = %8.8lf", classification_err_union_2 / nreps_done) ; PrintFormat(" Union error 3 = %8.8lf", classification_err_union_3 / nreps_done) ; cleanup(models); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
运行脚本获得的结果示例如下所示。这些是将分类任务设置为最高难度的结果。
ClassificationDifficultyFactor=0.0 DM 0 05:40:06.441 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Test Config: Classification Difficulty - 0.00000000 RP 0 05:40:06.441 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Number of classes - 3 QI 0 05:40:06.441 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Number of component models - 3 EK 0 05:40:06.441 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Sample Size - 10 MN 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) 1000 Replications: CF 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) 0.66554000 HI 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) 0.66706000 DP 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) 0.66849000 II 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Mean raw error = 0.66703000 JS 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) average_ensemble error = 0.66612000 HR 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) median_ensemble error = 0.66837000 QF 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) maxmax_ensemble error = 0.66704000 MD 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) maxmin_ensemble error = 0.66586000 GI 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) majority_ensemble error = 0.66772000 HR 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) borda_ensemble error = 0.66747000 MO 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) logit_ensemble error = 0.66556000 MP 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) logitsep_ensemble error = 0.66570000 JD 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) localacc_ensemble error = 0.66578000 OJ 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) fuzzyint_ensemble error = 0.66503000 KO 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) pairwise_ensemble error = 0.66799000 GS 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) intersection_ensemble error 1 = 0.96686000 DP 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) intersection_ensemble error 2 = 0.95847000 QE 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) intersection_ensemble error 3 = 0.95447000 OI 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Union error 1 = 0.99852000 DM 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Union error 2 = 0.97931000 JR 0 05:40:06.442 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Union error 3 = 0.01186000
接下来是分类难度为中等的测试结果。
LF 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Test Config: Classification Difficulty - 1.00000000 IG 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Number of classes - 3 JP 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Number of component models - 3 FQ 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Sample Size - 10 KH 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) 1000 Replications: NO 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) 0.46236000 QF 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) 0.45818000 II 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) 0.45779000 FR 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Mean raw error = 0.45944333 DI 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) average_ensemble error = 0.44881000 PH 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) median_ensemble error = 0.45564000 JO 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) maxmax_ensemble error = 0.46763000 GS 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) maxmin_ensemble error = 0.44935000 GP 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) majority_ensemble error = 0.45573000 PI 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) borda_ensemble error = 0.45593000 DF 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) logit_ensemble error = 0.46353000 FO 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) logitsep_ensemble error = 0.46726000 ER 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) localacc_ensemble error = 0.46096000 KP 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) fuzzyint_ensemble error = 0.45098000 OD 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) pairwise_ensemble error = 0.66485000 IJ 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) intersection_ensemble error 1 = 0.93533000 RO 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) intersection_ensemble error 2 = 0.92527000 OL 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) intersection_ensemble error 3 = 0.92527000 OR 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Union error 1 = 0.99674000 KG 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Union error 2 = 0.97231000 NK 0 05:42:00.329 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Union error 3 = 0.00877000
最后一组结果说明了将分类难度配置为相对容易时的测试结果。
PL 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Test Config: Classification Difficulty - 10.00000000 CN 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Number of classes - 3 PK 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Number of component models - 3 LH 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Sample Size - 10 EQ 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) 1000 Replications: MD 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) 0.02905000 LO 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) 0.02861000 CF 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) 0.02879000 IK 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Mean raw error = 0.02881667 RN 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) average_ensemble error = 0.02263000 PQ 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) median_ensemble error = 0.02956000 QD 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) maxmax_ensemble error = 0.03426000 KJ 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) maxmin_ensemble error = 0.02263000 IO 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) majority_ensemble error = 0.02956000 HP 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) borda_ensemble error = 0.02956000 KM 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) logit_ensemble error = 0.03171000 OE 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) logitsep_ensemble error = 0.04840000 GK 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) localacc_ensemble error = 0.03398000 FO 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) fuzzyint_ensemble error = 0.02263000 QM 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) pairwise_ensemble error = 0.65277000 CQ 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) intersection_ensemble error 1 = 0.96303000 DF 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) intersection_ensemble error 2 = 0.96167000 IK 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) intersection_ensemble error 3 = 0.96167000 IK 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Union error 1 = 0.98620000 CP 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Union error 2 = 0.95624000 LD 0 05:45:11.711 ClassificationEnsemble_Demo (BTCUSD,D1) Union error 3 = 0.00000000
文章中的所有代码均附于文后。下表给出了每个源文件的说明。
| 文件名 | 文件描述 |
|---|---|
| MQL5/include/np.mqh | 这是操控向量和矩阵的实用函数集合 |
| MQL5/include/nom2ord.mqh | 该文件包含类别数据的编码类 |
| MQL5/include/multilayerperceptron.mqh | 提供表示前馈神经网络的 CMlp 类定义 |
| MQL5/include/logistic.mqh | 包含实现逻辑回归的 Clogit 类定义 |
| MQL5/include/ensemble.mqh | 包含元模型的各种实现的定义 |
| MQL5/scripts/ClassificationEnsemble_Demo.mq5 | 这是一个比较 ensemble.mqh 中定义的融汇分类器性能的脚本 |
| MQL5/scripts/PairWise_Ensemble_Demo.mq5 | 这是一个演示脚本,展示了如何应用 CPairWise 类进行配对耦合 |
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/16838
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 在MQL5中自动化交易策略(第5部分):开发自适应交叉RSI交易套件策略
在MQL5中自动化交易策略(第5部分):开发自适应交叉RSI交易套件策略
 MQL5自动化交易策略(第四部分):构建多层级区域恢复系统
MQL5自动化交易策略(第四部分):构建多层级区域恢复系统
 MQL5 简介(第 10 部分):MQL5 中使用内置指标的初学者指南
MQL5 简介(第 10 部分):MQL5 中使用内置指标的初学者指南
 开发回放系统(第 77 部分):新 Chart Trade(四)
开发回放系统(第 77 部分):新 Chart Trade(四)