
MQL5における高度な注文執行アルゴリズム:TWAP、VWAP、アイスバーグ注文
はじめに
想像してみてください。あなたは取引フロアのk片隅に立ち、心臓が高鳴る中で価格がリアルタイムに動くのを見ています。一度の誤った判断、あるいは過大な注文で、その優位性は一瞬にして消えてしまいます。ここでは、執行の質は単なる「便利な機能」ではなく、勝者とその他のトレーダーを分ける秘密兵器なのです。
何十年もの間、機関投資家は高度なアルゴリズムを駆使して、注文を巧みに分割・管理し、市場への影響やスリッページを最小限に抑えてきました。そして今、MQL5の柔軟性のおかげで、その強力な手法が、意欲的な個人トレーダーの手元でも利用可能になっています。
何が重要なのか
たとえば、絶好のチャンスを見つけて大きく攻めるとします。フルサイズの成行注文を投入した途端、自分の取引の重みで価格が滑り、理想のエントリーが不安定な妥協に変わってしまう。これが市場影響の厄介な作用です。流動性の高い市場でも、この現象は起こります。
そこで登場するのが執行アルゴリズムです。大きな注文を小さな戦略的スライスに分割して順次発注することで、オーダーブック上での自分の足跡を滑らかにできます。その結果、スリッページの低減、約定の改善、平均執行価格の向上が実現します。
個人トレーダーでも恩恵を受けられる理由
「でも自分は機関投資家のような大口を動かしているわけではない」と思うかもしれません。肝心なのは、そうする必要がないということです。0.5ロットや数ミニロットの取引でも、ボラティリティ次第で執行に影響が出ます。これらのツールは次のような利点を提供します。
- スリッページを抑える:小さな注文でも乱高下する市場で価格のブレを抑制
- 優位性を強化:分割発注により、単発の一括注文より有利な平均価格を実現
- 冷静さを維持:自動化によりパニック的な売買の誘惑を排除
- スムーズなスケーリング:口座規模が拡大しても執行精度は維持
-
存在を隠す:特にアイスバーグ注文は、真の注文サイズを隠して他アルゴリズムからの追跡を回避
今日では、かつて数百万ドル規模の予算が必要だった執行テクノロジーが、個人の取引環境でも利用可能です。TWAP、VWAP、アイスバーグ戦略用の洗練されたMQL5コードをプラットフォームに組み込むことで、個人トレーダーでも機関投資家レベルの執行力を手に入れられます。
執行プロセスを刷新する準備をしましょう。市場は変化しています。これらのアルゴリズムをツールキットに加えることで、勝つための取引を仕掛けられるようになります。
執行アルゴリズムの理解
実装の詳細に入る前に、各執行アルゴリズムの理論と、異なる市場環境でなぜ効果的なのかを理解しておくことが重要です。
- 時間加重平均価格(TWAP:Time Weighted Average Price)TWAPはシンプルな執行アルゴリズムで、大口注文を等分して、設定された期間にわたり一定の時間間隔で発注します。目的は、その期間の平均価格に近い価格で執行することです。
-
仕組み
- 開始から終了までの一定時間間隔で注文を送信
- 通常は同じサイズの注文(必要に応じてランダムサイズも可能)
- 価格変動に関係なく、あらかじめ決められたタイムテーブルに従う
-
市場への影響を時間的に分散させ、スリッページを抑える
-
使用する場合
- 特定の時間軸で平均執行価格を求めたい
- 取引期間中の流動性が安定している
- 注文を完了する固定されたウィンドウがある
-
シンプルで予測可能な方法を好む
-
- 出来高加重平均価格(VWAP: Volume-Weighted Average Price)VWAPはTWAPを改良したもので、注文サイズを予想出来高に応じて加重します。等分ではなく、出来高が高い時間帯に大きな注文を出すことで、市場への影響を抑えます。
-
仕組み
- 過去の出来高パターンに応じて注文サイズを割り当て
- 過去の取引量を分析して、将来の出来高分布を予測
- 実装によってはリアルタイムの出来高変化に適応可能
-
出来高が多い時間帯に注文を集中させることで市場への影響を軽減
-
使用する場合
- パフォーマンスの評価基準がVWAPである
- 出来高が日中のパターンに従う市場
- セッション中に流動性が変動する市場で取引する
-
市場の自然なフローに沿った執行を目指す
-
- アイスバーグ注文アイスバーグ注文は、大口注文の実際のサイズを隠すことに特化しています。常に少量だけが見えるように表示され、執行されると次の一部が現れます。
-
仕組み
- 注文全体の一部だけを表示
- 各ティップが約定した後に次の可視部分を公開
- 表示される数量を固定またはランダムにすることで、他の市場参加者に察知されるのを防ぐ
-
価格制御のためにリミット注文として配置されることが多い
-
使用する場合
- 注文の全サイズを隠したい
- 流動性が低く、大口取引で価格が動きやすい市場
- 特定の価格水準で執行を維持したい
-
他のトレーダーに注文を察知され、先回りされることを避けたい
-
MQL5での実装
これらの執行アルゴリズムの理論を理解した上で、実際にMQL5で実装していきます。モジュール化され、オブジェクト指向のフレームワークを作成し、各アルゴリズムを個別に使用したり、統合された執行システムとして組み合わせたりできるようにします。
基盤クラス:CExecutionAlgorithm
まず、すべての実行アルゴリズムに共通の機能を提供する基盤クラスを定義します。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Base class for all execution algorithms | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CExecutionAlgorithm { protected: string m_symbol; // Symbol to trade double m_totalVolume; // Total volume to execute double m_executedVolume; // Volume already executed double m_remainingVolume; // Volume remaining to execute datetime m_startTime; // Start time for execution datetime m_endTime; // End time for execution bool m_isActive; // Flag indicating if the algorithm is active int m_totalOrders; // Total number of orders placed int m_filledOrders; // Number of filled orders double m_avgExecutionPrice; // Average execution price double m_executionValue; // Total value of executed orders int m_slippage; // Allowed slippage in points public: // Constructor CExecutionAlgorithm(string symbol, double volume, datetime startTime, datetime endTime, int slippage = 3); // Destructor virtual ~CExecutionAlgorithm(); // Common methods virtual bool Initialize(); virtual bool Execute() = 0; virtual bool Update() = 0; virtual bool Terminate(); // Utility methods bool PlaceOrder(ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, double volume, double price); bool CancelOrder(ulong ticket); void UpdateAverageExecutionPrice(double price, double volume); // Getters string GetSymbol() const { return m_symbol; } double GetTotalVolume() const { return m_totalVolume; } double GetExecutedVolume() const { return m_executedVolume; } double GetRemainingVolume() const { return m_remainingVolume; } datetime GetStartTime() const { return m_startTime; } datetime GetEndTime() const { return m_endTime; } bool IsActive() const { return m_isActive; } int GetTotalOrders() const { return m_totalOrders; } int GetFilledOrders() const { return m_filledOrders; } double GetAverageExecutionPrice() const { return m_avgExecutionPrice; } };
PlaceOrderメソッドは特に重要で、実際の注文執行をおこない、注文量の追跡を更新する役割を担います。
bool CExecutionAlgorithm::PlaceOrder(ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, double volume, double price) { // Prepare the trade request MqlTradeRequest request; MqlTradeResult result; ZeroMemory(request); ZeroMemory(result); request.action = TRADE_ACTION_DEAL; request.symbol = m_symbol; request.volume = volume; request.type = orderType; request.price = price; request.deviation = m_slippage; request.magic = 123456; // Magic number for identification // Send the order bool success = OrderSend(request, result); if(!success) { Print("OrderSend error: ", GetLastError()); return false; } // Check the result if(result.retcode != TRADE_RETCODE_DONE) { Print("OrderSend failed with code: ", result.retcode); return false; } // Update statistics m_totalOrders++; m_filledOrders++; m_executedVolume += volume; m_remainingVolume -= volume; UpdateAverageExecutionPrice(price, volume); // Store the order ticket for future reference ulong ticket = result.order; return true; }
この関数は、MqlTradeRequestとMqlTradeResultをゼロ初期化した上で、銘柄、注文数量、注文種類、価格、スリッページ、マジックナンバーなどを設定し、OrderSendを呼び出して成行注文を作成・送信します。もし送信に失敗した場合や、ブローカーからの返却コードがTRADE_RETCODE_DONEでない場合は、エラーをログに記録してfalseを返します。成功した場合は、内部カウンタ(総注文数や約定済み/残り数量)を更新し、平均価格を再計算し、チケットIDを記録した上でtrueを返します。
TWAPの実装
TWAPアルゴリズムは、執行期間を等しい時間間隔に分割し、各間隔で同じサイズ(またはランダム化されたサイズ)の注文を発注します。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) Algorithm | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CTWAP : public CExecutionAlgorithm { private: int m_intervals; // Number of time intervals int m_currentInterval; // Current interval datetime m_nextExecutionTime; // Next execution time double m_intervalVolume; // Volume per interval bool m_useRandomization; // Whether to randomize order sizes double m_randomizationFactor; // Factor for randomization (0-1) ENUM_ORDER_TYPE m_orderType; // Order type (buy or sell) bool m_firstOrderPlaced; // Flag to track if first order has been placed int m_initialDelay; // Initial delay in seconds before first execution datetime m_lastCheckTime; // Last time order status was checked int m_checkInterval; // How often to check order status (seconds) public: // Constructor CTWAP(string symbol, double volume, datetime startTime, datetime endTime, int intervals, ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, bool useRandomization = false, double randomizationFactor = 0.2, int slippage = 3, int initialDelay = 10); // Implementation of virtual methods virtual bool Initialize() override; virtual bool Execute() override; virtual bool Update() override; virtual bool Terminate() override; // TWAP specific methods void CalculateIntervalVolume(); datetime CalculateNextExecutionTime(); double GetRandomizedVolume(double baseVolume); bool IsTimeToExecute(); };
主要メソッド:CalculateNextExecutionTime
このメソッドは、注文が時間的に適切に分散されるようにし、最初の注文には初期遅延を設けます。datetime CTWAP::CalculateNextExecutionTime() { // Calculate the duration of each interval int totalSeconds = (int)(m_endTime - m_startTime); int intervalSeconds = totalSeconds / m_intervals; // Calculate the next execution time datetime nextTime; if(m_currentInterval == 0) { // First interval - start at the defined start time plus initial delay nextTime = m_startTime + m_initialDelay; Print("TWAP: First execution time calculated with ", m_initialDelay, " seconds delay: ", TimeToString(nextTime)); } else { // For subsequent intervals, ensure proper spacing from current time datetime currentTime = TimeCurrent(); nextTime = currentTime + intervalSeconds; // Make sure we don't exceed the end time if(nextTime > m_endTime) nextTime = m_endTime; Print("TWAP: Next execution time calculated: ", TimeToString(nextTime), " (interval: ", intervalSeconds, " seconds)"); } return nextTime; }
このメソッドは、m_startTimeからm_endTimeまでの期間をm_intervals個の等しいセグメントに分割し、次の取引を実行すべき時刻を返します。最初の呼び出しでは単純にm_startTime + m_initialDelayを返し、それ以降の呼び出しでは TimeCurrent() + 1セグメント分の秒数を返しますが、m_endTimeを超えることはありません。
Executeメソッド:注文を発注するタイミングかどうかをチェックし、実際の注文発注処理を担当します。
bool CTWAP::Execute() { if(!m_isActive) return false; // Check if it's time to execute the next order if(!IsTimeToExecute()) return true; // Not time yet // Calculate the volume for this execution double volumeToExecute = m_useRandomization ? GetRandomizedVolume(m_intervalVolume) : m_intervalVolume; // Ensure we don't exceed the remaining volume if(volumeToExecute > m_remainingVolume) volumeToExecute = m_remainingVolume; // Get current market price double price = 0.0; if(m_orderType == ORDER_TYPE_BUY) price = SymbolInfoDouble(m_symbol, SYMBOL_ASK); else price = SymbolInfoDouble(m_symbol, SYMBOL_BID); Print("TWAP: Placing order for interval ", m_currentInterval, ", Volume: ", DoubleToString(volumeToExecute, 2), ", Price: ", DoubleToString(price, _Digits)); // Place the order using OrderSend directly for more control MqlTradeRequest request; MqlTradeResult result; ZeroMemory(request); ZeroMemory(result); request.action = TRADE_ACTION_DEAL; request.symbol = m_symbol; request.volume = volumeToExecute; request.type = m_orderType; request.price = price; request.deviation = m_slippage; request.magic = 123456; // Magic number for identification // Send the order bool success = OrderSend(request, result); if(!success) { Print("TWAP: OrderSend error: ", GetLastError()); return false; } // Check the result if(result.retcode != TRADE_RETCODE_DONE) { Print("TWAP: OrderSend failed with code: ", result.retcode); return false; } // Update statistics m_totalOrders++; m_filledOrders++; m_executedVolume += volumeToExecute; m_remainingVolume -= volumeToExecute; // Update interval counter m_currentInterval++; m_firstOrderPlaced = true; // Calculate the time for the next execution if(m_currentInterval < m_intervals && m_remainingVolume > 0) m_nextExecutionTime = CalculateNextExecutionTime(); else m_isActive = false; // All intervals completed or no volume left Print("TWAP: Executed ", DoubleToString(volumeToExecute, 2), " at price ", DoubleToString(price, _Digits), ". Remaining: ", DoubleToString(m_remainingVolume, 2), ", Next execution: ", TimeToString(m_nextExecutionTime)); return true; }
このExecuteメソッドは、TWAPの1スライス分の処理を管理します。まず、戦略がアクティブでない場合や、まだ取引のタイミングでない場合は処理を中断します。取引可能な場合には、残りの注文量の中から固定またはランダム化されたスライス量を選択し(残量を超えない範囲で)、現在の買値(Buyの場合)または売値(Sellの場合)を取得します。次に、間隔、注文量、価格をログに記録し、シンボル、数量、注文種類、価格、スリッページ、マジックナンバーを設定したMqlTradeRequestを構築してOrderSendを呼び出します。送信に失敗した場合や、ブローカーの返却コードがTRADE_RETCODE_DONEでない場合は、エラーを出力してfalseを返します。
注文が成功した場合は、注文カウンタを増加させ、実行済みおよび残りの注文量を調整し、間隔カウントを更新、初回注文送信フラグを立てます。その後、次の実行時刻をスケジュールするか、間隔や残量が尽きた場合は戦略を非アクティブ化します。最後に、処理結果をログに記録し、trueを返します。
VWAPの実装
VWAPアルゴリズムはTWAPに似ていますが、注文サイズを過去の出来高パターンに基づいて分配する点が異なります。//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP) Algorithm | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CVWAP : public CExecutionAlgorithm { private: int m_intervals; // Number of time intervals int m_currentInterval; // Current interval datetime m_nextExecutionTime; // Next execution time double m_volumeProfile[]; // Historical volume profile double m_intervalVolumes[]; // Volume per interval based on profile bool m_adaptiveMode; // Whether to adapt to real-time volume ENUM_ORDER_TYPE m_orderType; // Order type (buy or sell) int m_historyDays; // Number of days to analyze for volume profile bool m_profileLoaded; // Flag indicating if profile was loaded bool m_firstOrderPlaced; // Flag to track if first order has been placed int m_initialDelay; // Initial delay in seconds before first execution datetime m_lastCheckTime; // Last time order status was checked int m_checkInterval; // How often to check order status (seconds) public: // Constructor CVWAP(string symbol, double volume, datetime startTime, datetime endTime, int intervals, ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, int historyDays = 5, bool adaptiveMode = true, int slippage = 3, int initialDelay = 10); // Implementation of virtual methods virtual bool Initialize() override; virtual bool Execute() override; virtual bool Update() override; virtual bool Terminate() override; // VWAP specific methods bool LoadVolumeProfile(); void CalculateIntervalVolumes(); void AdjustToRealTimeVolume(); datetime CalculateNextExecutionTime(); double GetCurrentVWAP(); bool IsTimeToExecute(); };TWAPと同様に、VWAPもCalculateNextExecutionTimeメソッドを実装しており、注文が適切な間隔で発注されるようにしています。
datetime CVWAP::CalculateNextExecutionTime() { // Calculate the duration of each interval int totalSeconds = (int)(m_endTime - m_startTime); int intervalSeconds = totalSeconds / m_intervals; // Calculate the next execution time datetime nextTime; if(m_currentInterval == 0) { // First interval - start at the defined start time plus initial delay nextTime = m_startTime + m_initialDelay; Print("VWAP: First execution time calculated with ", m_initialDelay, " seconds delay: ", TimeToString(nextTime)); } else { // For subsequent intervals, ensure proper spacing from current time datetime currentTime = TimeCurrent(); nextTime = currentTime + intervalSeconds; // Make sure we don't exceed the end time if(nextTime > m_endTime) nextTime = m_endTime; Print("VWAP: Next execution time calculated: ", TimeToString(nextTime), " (interval: ", intervalSeconds, " seconds)"); } return nextTime; }
アイスバーグ注文の実装
アイスバーグ注文は、大口注文の実際のサイズを隠し、常に市場に一部の注文のみを表示することで実現されます。//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Iceberg Order Implementation | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CIcebergOrder : public CExecutionAlgorithm { private: double m_visibleVolume; // Visible portion of the order double m_minVisibleVolume; // Minimum visible volume double m_maxVisibleVolume; // Maximum visible volume bool m_useRandomVisibleVolume; // Whether to randomize visible volume int m_orderPlacementDelay; // Delay between order placements (ms) bool m_avoidRoundNumbers; // Whether to avoid round numbers in price double m_limitPrice; // Limit price for the orders ulong m_currentOrderTicket; // Current active order ticket ENUM_ORDER_TYPE m_orderType; // Order type (buy or sell) bool m_orderActive; // Flag indicating if an order is currently active int m_priceDeviation; // Price deviation to avoid round numbers (in points) datetime m_lastCheckTime; // Last time order status was checked int m_checkInterval; // How often to check order status (seconds) int m_maxOrderLifetime; // Maximum lifetime for an order in seconds datetime m_orderPlacementTime; // When the current order was placed public: // Constructor CIcebergOrder(string symbol, double volume, double limitPrice, ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, double visibleVolume, double minVisibleVolume = 0.0, double maxVisibleVolume = 0.0, bool useRandomVisibleVolume = true, int orderPlacementDelay = 1000, bool avoidRoundNumbers = true, int priceDeviation = 2, int slippage = 3); // Implementation of virtual methods virtual bool Initialize() override; virtual bool Execute() override; virtual bool Update() override; virtual bool Terminate() override; // Iceberg specific methods double GetRandomVisibleVolume(); double AdjustPriceToAvoidRoundNumbers(double price); bool CheckAndReplaceOrder(); bool IsOrderFilled(ulong ticket); bool IsOrderPartiallyFilled(ulong ticket, double &filledVolume); bool IsOrderCancelled(ulong ticket); bool IsOrderExpired(ulong ticket); bool IsOrderTimeout(); ulong GetCurrentOrderTicket() { return m_currentOrderTicket; } bool IsOrderActive() { return m_orderActive; } };Executeメソッドは、注文の新しい可視部分を市場に発注します。
bool CIcebergOrder::Execute() { if(!m_isActive) { Print("Iceberg: Execute called but algorithm is not active"); return false; } // If an order is already active, check its status if(m_orderActive) { Print("Iceberg: Execute called with active order ", m_currentOrderTicket); return CheckAndReplaceOrder(); } // Calculate the volume for this execution double volumeToExecute = m_useRandomVisibleVolume ? GetRandomVisibleVolume() : m_visibleVolume; // Ensure we don't exceed the remaining volume if(volumeToExecute > m_remainingVolume) volumeToExecute = m_remainingVolume; Print("Iceberg: Placing order for ", DoubleToString(volumeToExecute, 2), " at price ", DoubleToString(m_limitPrice, _Digits)); // Place the order using OrderSend directly for more control MqlTradeRequest request; MqlTradeResult result; ZeroMemory(request); ZeroMemory(result); request.action = TRADE_ACTION_PENDING; request.symbol = m_symbol; request.volume = volumeToExecute; request.type = m_orderType; request.price = m_limitPrice; request.deviation = m_slippage; request.magic = 123456; // Magic number for identification // Send the order bool success = OrderSend(request, result); if(!success) { Print("Iceberg: OrderSend error: ", GetLastError()); return false; } // Check the result if(result.retcode != TRADE_RETCODE_DONE) { Print("Iceberg: OrderSend failed with code: ", result.retcode); return false; } // Store the order ticket m_currentOrderTicket = result.order; m_orderActive = true; m_orderPlacementTime = TimeCurrent(); Print("Iceberg: Order placed successfully. Ticket: ", m_currentOrderTicket, ", Volume: ", DoubleToString(volumeToExecute, 2), ", Remaining: ", DoubleToString(m_remainingVolume, 2)); return true; }
Executeが実行されると、まずアルゴリズムがアクティブであることを確認します。すでに生きているアイスバーグの子注文がある場合は、CheckAndReplaceOrderを呼び出して、キャンセルや再発注が必要かどうかを確認します。そうでなければ、可視スライス(固定またはランダム)を選び、残りの総量で上限を設定し、サイズと価格をログに記録します。
その後、銘柄、数量、リミット価格、スリッページ、マジックナンバーを指定した予約注文リクエスト(TRADE_ACTION_PENDING)を構築し、OrderSendを呼び出します。送信エラーやTRADE_RETCODE_DONE以外の返却コードが返された場合はログに記録してfalseを返します。成功した場合は、新しいチケット番号を保存し、注文をアクティブとしてマーク、発注時刻を記録し、詳細をログに残してtrueを返します。
Updateメソッドでは、注文が無期限にアクティブな状態にならないよう、タイムアウト検出機能が組み込まれています。
bool CIcebergOrder::Update() { if(!m_isActive) { Print("Iceberg: Update called but algorithm is not active"); return false; } // Check if all volume has been executed if(m_remainingVolume <= 0) { Print("Iceberg: All volume executed. Terminating algorithm."); return Terminate(); } // Check if it's time to check order status datetime currentTime = TimeCurrent(); if(currentTime >= m_lastCheckTime + m_checkInterval) { m_lastCheckTime = currentTime; // Log current market conditions double currentBid = SymbolInfoDouble(m_symbol, SYMBOL_BID); double currentAsk = SymbolInfoDouble(m_symbol, SYMBOL_ASK); Print("Iceberg: Market update - Bid: ", DoubleToString(currentBid, _Digits), ", Ask: ", DoubleToString(currentAsk, _Digits), ", Limit Price: ", DoubleToString(m_limitPrice, _Digits)); // If an order is active, check its status if(m_orderActive) { // Check if the order has been active too long if(IsOrderTimeout()) { Print("Iceberg: Order ", m_currentOrderTicket, " has timed out. Replacing it."); // Cancel the current order if(!CancelOrder(m_currentOrderTicket)) { Print("Iceberg: Failed to cancel timed out order ", m_currentOrderTicket); } // Reset order tracking m_orderActive = false; m_currentOrderTicket = 0; // Place a new order after a delay Sleep(m_orderPlacementDelay); return Execute(); } return CheckAndReplaceOrder(); } else { // If no order is active, execute a new one Print("Iceberg: No active order, executing new order"); return Execute(); } } return true; }
Updateメソッドは、m_checkIntervalで定義された間隔で市場および注文の状態を定期的に監視します。すべての注文量が完了していれば処理を終了します。そうでない場合、チェック時刻になると、現在の買値/売値とリミット価格をログに記録します。注文がアクティブな場合はタイムアウトを確認し、期限切れであれば注文をキャンセルして状態をリセットし、m_orderPlacementDelay秒待機してから新しいスライスを発注するために再実行します。期限切れでない場合は CheckAndReplaceOrderに処理を委ねます。アクティブな注文がない場合は、単純にExecuteを呼び出して次の可視スライスを発注します。
パフォーマンスアナライザーの実装
パフォーマンスアナライザークラスは、各種指標を追跡し、アルゴリズムのパフォーマンスを分析・比較するためのメソッドを提供します。//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Performance Analyzer for Execution Algorithms | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CPerformanceAnalyzer { private: string m_symbol; // Symbol being analyzed datetime m_startTime; // Analysis start time datetime m_endTime; // Analysis end time double m_decisionPrice; // Price at decision time double m_avgExecutionPrice; // Average execution price double m_totalVolume; // Total volume executed double m_implementationShortfall; // Implementation shortfall double m_marketImpact; // Estimated market impact double m_slippage; // Average slippage int m_executionTime; // Total execution time in seconds double m_priceImprovement; // Total price improvement public: // Constructor CPerformanceAnalyzer(string symbol, double decisionPrice); // Analysis methods void RecordExecution(datetime time, double price, double volume); void CalculateMetrics(); void CompareAlgorithms(CPerformanceAnalyzer &other); // Reporting methods void PrintReport(); void SaveReportToFile(string filename); // Getters double GetImplementationShortfall() const { return m_implementationShortfall; } double GetMarketImpact() const { return m_marketImpact; } double GetSlippage() const { return m_slippage; } int GetExecutionTime() const { return m_executionTime; } double GetPriceImprovement() const { return m_priceImprovement; } };
CPerformanceAnalyzerは、すべての取引後指標を一箇所にまとめて管理するクラスです。インスタンス生成時に銘柄と意思決定時の基準価格を渡すと、現在時刻を開始時刻として記録します。各子注文が約定するたびに RecordExecution(time, price, volume)を呼び出すことで、累積出来高、加重平均約定価格、タイムスタンプなどの集計が更新されます。戦略の終了時(または定期的に) CalculateMetrics() を呼ぶと、以下の指標が計算されます。
- 実装ショートフォール(意思決定価格と実際の約定価格の損益差)
- 公開価格に対する平均スリッページ
- 自身の市場フットプリントによる推定市場影響
- 総執行時間(終了時刻−開始時刻)
- ベンチマークに対する価格改善の有無
さらに、CompareAlgorithms(otherAnalyzer)を使えば、2回の実行を比較してどちらの戦略が有利だったかを確認できます。PrintReport()は主要統計をログに出力し、SaveReportToFile(filename)を使えば外部ファイルにフルレポートを保存できます。また、各指標を取得する軽量なゲッターも用意されており、カスタムダッシュボードや追加分析に活用可能です。
アルゴリズムのパフォーマンスの比較
市場環境によって最適な実行アルゴリズムは異なります。以下は一般的な目安(経験則)です。- TWAP
- 最適な市場環境:流動性が安定している市場
- 長所:単純で予測可能な執行パターン
- 短所:市場状況の変化に適応できない
- VWAP
- 最適な市場環境:出来高パターンが予測可能な市場
- 長所:市場の自然なリズムに合わせられるため、より良い価格で約定することが多い
- 短所:過去の出来高データが必要であり、実装がより複雑
- アイスバーグ注文
- 最適な市場環境:流動性が低い市場、または価格への影響を最小化したい場合
- 長所:市場インパクトを抑えつつ価格コントロールを維持できる
- 短所:執行時間が予測しにくく、部分的な約定のリスクがある
執行アルゴリズムと取引戦略の統合
実行アルゴリズムの本当の強みは、それらを取引戦略に統合したときに発揮されます。このセクションでは、作成した実行アルゴリズムを完全な売買システムへ組み込む方法を示します。
実行マネージャー
統合をシンプルにするために、すべての実行アルゴリズムを一括管理する実行マネージャークラス(CExecutionManager)を用意します。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Execution Manager - Facade for all execution algorithms | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CExecutionManager { private: CExecutionAlgorithm* m_algorithm; // Current execution algorithm CPerformanceAnalyzer* m_analyzer; // Performance analyzer public: // Constructor CExecutionManager(); // Destructor ~CExecutionManager(); // Algorithm creation methods bool CreateTWAP(string symbol, double volume, datetime startTime, datetime endTime, int intervals, ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, bool useRandomization = false, double randomizationFactor = 0.2, int slippage = 3); bool CreateVWAP(string symbol, double volume, datetime startTime, datetime endTime, int intervals, ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, int historyDays = 5, bool adaptiveMode = true, int slippage = 3); bool CreateIcebergOrder(string symbol, double volume, double limitPrice, ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, double visibleVolume, double minVisibleVolume = 0.0, double maxVisibleVolume = 0.0, bool useRandomVisibleVolume = true, int orderPlacementDelay = 1000, bool avoidRoundNumbers = true, int priceDeviation = 2, int slippage = 3); // Execution methods bool Initialize(); bool Execute(); bool Update(); bool Terminate(); // Performance analysis void EnablePerformanceAnalysis(double decisionPrice); void PrintPerformanceReport(); // Getters CExecutionAlgorithm* GetAlgorithm() { return m_algorithm; } };
このクラスはファサードとして機能し、戦略コードから直接アルゴリズムの詳細を扱わずに済むようにします。内部的には、現在選択されている CExecutionAlgorithm(TWAP、VWAP、または Iceberg)のポインタと、発注のパフォーマンスを追跡するためのCPerformanceAnalyzerを保持しています。
ユーザーは、Create...メソッドのいずれかを呼び出して戦略を選択します。その際には、銘柄、総発注量、開始・終了時間(TWAP/VWAP 用)、インターバル数またはスライスサイズ、注文タイプ、そしてアルゴリズム固有のパラメータ(ランダム化、出来高履歴ウィンドウ、指値価格など)を渡します。アルゴリズムが生成された後は、通常のライフサイクルに従って実行を進めていきます。
- Initialize()は必要な状態やデータを準備します。
- Execute()は次のスライスや子注文を発注します。
- Update()は約定状況、市場データ、あるいはタイムアウトを監視します。
-
Terminate()はすべての発注が完了した、または手動で停止したいときにクリーンアップをおこないます。
パフォーマンス分析を有効化するにはEnablePerformanceAnalysis()を呼び出します。するとマネージャーは意思決定時の基準価格に対して実際の執行価格を記録し、PrintPerformanceReport()によって簡潔な損益およびスリッページのレポートを出力できます。さらに必要であれば、GetAlgorithm()を用いて生のアルゴリズムオブジェクトを取得し、独自の検証やメトリクス抽出に利用することも可能です。
統合例
以下は、異なるタイプの取引戦略に本稿の執行アルゴリズムを統合する方法の例です。
-
トレンドフォロー戦略 × TWAP執行
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Trend-Following Strategy with TWAP Execution | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { // Strategy parameters int maPeriodFast = 20; int maPeriodSlow = 50; double volume = 1.0; int executionIntervals = 5; // Calculate indicators double maFast = iMA(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, maPeriodFast, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE, 0); double maSlow = iMA(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, maPeriodSlow, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE, 0); // Check for entry conditions static bool inPosition = false; static CExecutionManager executionManager; if(!inPosition) { // Buy signal: Fast MA crosses above Slow MA if(maFast > maSlow) { // Create TWAP execution algorithm datetime startTime = TimeCurrent(); datetime endTime = startTime + 3600; // 1 hour execution window if(executionManager.CreateTWAP(Symbol(), volume, startTime, endTime, executionIntervals, ORDER_TYPE_BUY)) { executionManager.Initialize(); inPosition = true; Print("Buy signal detected. Starting TWAP execution."); } } } else { // Update the execution algorithm if(executionManager.Update()) { // Check if execution is complete if(!executionManager.GetAlgorithm().IsActive()) { inPosition = false; Print("TWAP execution completed."); } } } }
-
平均回帰戦略 × VWAP執行
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Mean-Reversion Strategy with VWAP Execution | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { // Strategy parameters int rsiPeriod = 14; int rsiOversold = 30; int rsiOverbought = 70; double volume = 1.0; int executionIntervals = 5; // Calculate indicators double rsi = iRSI(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, rsiPeriod, PRICE_CLOSE, 0); // Check for entry conditions static bool inPosition = false; static bool isLong = false; static CExecutionManager executionManager; if(!inPosition) { // Buy signal: RSI oversold if(rsi < rsiOversold) { // Create VWAP execution algorithm datetime startTime = TimeCurrent(); datetime endTime = startTime + 3600; // 1 hour execution window if(executionManager.CreateVWAP(Symbol(), volume, startTime, endTime, executionIntervals, ORDER_TYPE_BUY)) { executionManager.Initialize(); inPosition = true; isLong = true; Print("Buy signal detected. Starting VWAP execution."); } } // Sell signal: RSI overbought else if(rsi > rsiOverbought) { // Create VWAP execution algorithm datetime startTime = TimeCurrent(); datetime endTime = startTime + 3600; // 1 hour execution window if(executionManager.CreateVWAP(Symbol(), volume, startTime, endTime, executionIntervals, ORDER_TYPE_SELL)) { executionManager.Initialize(); inPosition = true; isLong = false; Print("Sell signal detected. Starting VWAP execution."); } } } else { // Update the execution algorithm if(executionManager.Update()) { // Check if execution is complete if(!executionManager.GetAlgorithm().IsActive()) { inPosition = false; Print("VWAP execution completed."); } } // Check for exit conditions if(isLong && rsi > rsiOverbought) { executionManager.Terminate(); inPosition = false; Print("Exit signal detected. Terminating VWAP execution."); } else if(!isLong && rsi < rsiOversold) { executionManager.Terminate(); inPosition = false; Print("Exit signal detected. Terminating VWAP execution."); } } }
- ブレイクアウト戦略 x アイスバーグ注文
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Breakout Strategy with Iceberg Orders | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { // Strategy parameters int channelPeriod = 20; double volume = 1.0; double visibleVolume = 0.1; // Calculate indicators double upperChannel = iHigh(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, iHighest(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, MODE_HIGH, channelPeriod, 1)); double lowerChannel = iLow(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, iLowest(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, MODE_LOW, channelPeriod, 1)); double currentPrice = SymbolInfoDouble(Symbol(), SYMBOL_BID); // Check for entry conditions static bool inPosition = false; static CExecutionManager executionManager; if(!inPosition) { // Buy signal: Price breaks above upper channel if(currentPrice > upperChannel) { // Create Iceberg Order double limitPrice = upperChannel; // Place limit order at breakout level if(executionManager.CreateIcebergOrder(Symbol(), volume, limitPrice, ORDER_TYPE_BUY, visibleVolume, visibleVolume * 0.8, visibleVolume * 1.2, true, 1000, true, 2, 3)) { executionManager.Initialize(); inPosition = true; Print("Buy breakout detected. Starting Iceberg Order execution."); } } // Sell signal: Price breaks below lower channel else if(currentPrice < lowerChannel) { // Create Iceberg Order double limitPrice = lowerChannel; // Place limit order at breakout level if(executionManager.CreateIcebergOrder(Symbol(), volume, limitPrice, ORDER_TYPE_SELL, visibleVolume, visibleVolume * 0.8, visibleVolume * 1.2, true, 1000, true, 2, 3)) { executionManager.Initialize(); inPosition = true; Print("Sell breakout detected. Starting Iceberg Order execution."); } } } else { // Update the execution algorithm if(executionManager.Update()) { // Check if execution is complete if(!executionManager.GetAlgorithm().IsActive()) { inPosition = false; Print("Iceberg Order execution completed."); } } } }
すべての例に共通して、統合は次のような高レベルのパターンに従います。
-
状態管理
- ブール値inPositionで現在注文を執行中かどうかを管理します。
-
CExecutionManager executionManagerは静的に保持され、ティックをまたいで選択したアルゴリズムのライフサイクルを管理します。
-
エントリーロジック
- エントリーシグナル(MAクロスオーバー、RSI閾値、チャネルブレイク)が発生したら、executionManagerの適切な生成メソッド(TWAP, VWAP, Iceberg)を呼び出し、銘柄シン、合計注文量、時間ウィンドウまたは指値価格、スライスのパラメータ、注文種別を渡します。
-
生成に成功したら、すぐに executionManager.Initialize()を呼び、inPosition=true に設定し、開始をログに残します。
-
実行の継続
- inPositionがtrueの間は、毎回OnTick()内で executionManager.Update()を呼びます。
-
Update()の内部では、必要に応じてExecute()を呼び、約定状況をチェックし、タイムアウトやマーケット更新を処理し、次のスライスをスケジューリングします(Icebergの場合は子注文のキャンセル・差し替えもおこないます)。
-
完了と終了
- 各アップデート後にexecutionManager.GetAlgorithm()->IsActive()を確認します。これがfalseを返したら(すべてのインターバルが終了したか、残量が尽きた状態)、inPosition=falseにして実行完了をログに残します。
-
VWAPを用いた平均回帰(逆張り)の例では、追加の退出条件があります。もし実行途中で価格がRSIの閾値を超えて反転した場合、executionManager.Terminate()を呼び、残りのスライスを中止します。
- トレンドフォロー + TWAP
エントリ:短期MAが長期MAを上抜けたら発動
実行:1ロットの買い注文を1時間で5つの等分スライスに分割 - 平均回帰 + VWAP
エントリ:RSI < 30 で買い、RSI > 70 で売り
実行:過去の出来高に基づき、1時間にわたって5スライスに分配して1ロットを執行
早期終了:シグナルが反転(例:買い途中で RSI > 70)したら executionManager.Terminate() で残りを中止 - ブレイクアウト + アイスバーグ
エントリ:価格がチャネル高値を上抜け(買い)、安値を下抜け(売り)したとき
実行:ブレイクアウト価格に指値を置き、常に約0.1ロットだけを板に見せ、全1ロットが完了するまで補充を繰り返す
CreateTWAP、CreateVWAP、CreateIcebergOrderを入れ替えるだけで、注文管理ロジックを重複させることなく、任意の執行アルゴリズムをシグナルロジックに組み込むことができます。
統合戦略
以下が完全なコードです。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| IntegratedStrategy.mq5 | //| Copyright 2025, MetaQuotes Software Corp. | //| https://www.metaquotes.net | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2025, MetaQuotes Software Corp." #property link "https://www.metaquotes.net" #property version "1.00" #include "ExecutionAlgorithm.mqh" #include "TWAP.mqh" #include "VWAP.mqh" #include "IcebergOrder.mqh" #include "PerformanceAnalyzer.mqh" #include "ExecutionManager.mqh" // Input parameters input int FastMA = 20; // Fast moving average period input int SlowMA = 50; // Slow moving average period input double TradingVolume = 0.1; // Trading volume input bool UseAdaptiveExecution = true; // Use adaptive execution based on market conditions // Global variables CExecutionManager *g_executionManager = NULL; int g_maHandle1 = INVALID_HANDLE; int g_maHandle2 = INVALID_HANDLE; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { // Initialize execution manager g_executionManager = new CExecutionManager(Symbol(), 3, UseAdaptiveExecution); // Initialize indicators g_maHandle1 = iMA(Symbol(), Period(), FastMA, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE); g_maHandle2 = iMA(Symbol(), Period(), SlowMA, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE); if(g_maHandle1 == INVALID_HANDLE || g_maHandle2 == INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("Failed to create indicator handles"); return INIT_FAILED; } return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { // Clean up if(g_executionManager != NULL) { delete g_executionManager; g_executionManager = NULL; } // Release indicator handles IndicatorRelease(g_maHandle1); IndicatorRelease(g_maHandle2); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { // Update execution algorithms if(g_executionManager != NULL) g_executionManager.UpdateAlgorithms(); // Only process at bar open if(iVolume(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 0) > 1) return; // Get indicator values double fastMA[2], slowMA[2]; if(CopyBuffer(g_maHandle1, 0, 0, 2, fastMA) <= 0 || CopyBuffer(g_maHandle2, 0, 0, 2, slowMA) <= 0) { Print("Failed to copy indicator buffers"); return; } // Check for trend signals bool buySignal = (fastMA[0] > slowMA[0]) && (fastMA[1] <= slowMA[1]); bool sellSignal = (fastMA[0] < slowMA[0]) && (fastMA[1] >= slowMA[1]); // Execute signals using the execution manager if(buySignal) { Print("Buy signal detected"); if(UseAdaptiveExecution) { // Let the execution manager select the best algorithm g_executionManager.ExecuteSignal(SIGNAL_TYPE_BUY, TradingVolume); } else { // Manually create a TWAP algorithm datetime currentTime = TimeCurrent(); CTWAP *twap = g_executionManager.CreateTWAP(TradingVolume, currentTime, currentTime + 3600, 6, ORDER_TYPE_BUY, true); } } else if(sellSignal) { Print("Sell signal detected"); if(UseAdaptiveExecution) { // Let the execution manager select the best algorithm g_executionManager.ExecuteSignal(SIGNAL_TYPE_SELL, TradingVolume); } else { // Manually create a TWAP algorithm datetime currentTime = TimeCurrent(); CTWAP *twap = g_executionManager.CreateTWAP(TradingVolume, currentTime, currentTime + 3600, 6, ORDER_TYPE_SELL, true); } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
IntegratedStrategy.mq5 EAは、まずメタデータ(著作権、リンク、バージョン)を宣言し、すべての執行アルゴリズムクラスおよびパフォーマンスアナライザーのヘッダをインクルードするところから始まります。次に、ユーザーが調整可能な4つの入力を定義します。すなわち、短期・長期のSMA期間、シグナルごとの総取引量、そして「アダプティブ」執行をオン/オフするブールフラグです(アダプティブモードでは、マネージャが内部的にTWAP, VWAP, Icebergのどれを使うかを自動選択します)。さらに、CExecutionManager へのグローバルポインタと、ティックをまたいで保持される2つのインジケーターハンドルも宣言されます。
OnInit()では、現在の銘柄、同時最大3アルゴリズム、そしてアダプティブフラグを渡して執行マネージャをインスタンス化し、2つのSMAインジケーターハンドルを作成します。もしどちらかのハンドル作成に失敗した場合は初期化を中断します。OnDeinit()は単にマネージャを削除し、インジケータハンドルを解放して、EAを削除したりプラットフォームを終了したときにメモリやハンドルがリークしないようにします。
コアロジックは OnTick()内にあります。最初に、執行マネージャのUpdateAlgorithms()を呼び出し、既存の子注文(TWAPスライス、VWAPバケット、Icebergレッグ)が必要に応じて処理・キャンセル・補充されるようにします。次に、新しいバーを待つために、ティックボリュームがまだ積み上がっている場合はスキップします。バーが開始すると、短期・長期それぞれのSMA値を直近2本取得します。短期が長期を下から上へクロスすれば買いシグナル、逆なら売りシグナルが発生します。
アダプティブ執行が有効な場合は、シグナルと取引量を g_executionManager.ExecuteSignal() に渡し、適切なアルゴリズムの選択を任せます。そうでなければ、1時間のウィンドウと6スライスでTWAPインスタンスを手動で起動します。このパターンにより、エントリーロジック(トレンド検出)と注文管理ロジックを明確に分離でき、同じファサードから複数の執行スタイルを重複なく扱えるようになります。
ここにテイクプロフィットを組み込むと、コードは次のように変更されます。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| IntegratedStrategy.mq5 | //| Copyright 2025, MetaQuotes Software Corp. | //| https://www.metaquotes.net | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2025, MetaQuotes Software Corp." #property link "https://www.metaquotes.net" #property version "1.00" #include "ExecutionAlgorithm.mqh" #include "TWAP.mqh" #include "VWAP.mqh" #include "IcebergOrder.mqh" #include "PerformanceAnalyzer.mqh" #include "ExecutionManager.mqh" #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> // Input parameters input int FastMA = 20; // Fast moving average period input int SlowMA = 50; // Slow moving average period input double TradingVolume = 0.1; // Trading volume input bool UseAdaptiveExecution = true; // Use adaptive execution based on market conditions input double EquityTPPercent = 10.0; // Equity Take Profit in percent input double EquitySLPercent = 5.0; // Equity Stop Loss in percent // Global variables CExecutionManager *g_executionManager = NULL; int g_maHandle1 = INVALID_HANDLE; int g_maHandle2 = INVALID_HANDLE; double g_initialEquity = 0.0; CTrade trade; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { // Record initial equity g_initialEquity = AccountInfoDouble(ACCOUNT_EQUITY); // Initialize execution manager g_executionManager = new CExecutionManager(Symbol(), 3, UseAdaptiveExecution); // Initialize indicators g_maHandle1 = iMA(Symbol(), Period(), FastMA, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE); g_maHandle2 = iMA(Symbol(), Period(), SlowMA, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE); if(g_maHandle1 == INVALID_HANDLE || g_maHandle2 == INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("Failed to create indicator handles"); return INIT_FAILED; } return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { // Clean up if(g_executionManager != NULL) { delete g_executionManager; g_executionManager = NULL; } // Release indicator handles IndicatorRelease(g_maHandle1); IndicatorRelease(g_maHandle2); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Check equity-based TP and SL, then reset baseline | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CheckEquityTPandSL() { double currentEquity = AccountInfoDouble(ACCOUNT_EQUITY); double tpEquity = g_initialEquity * (1.0 + EquityTPPercent / 100.0); double slEquity = g_initialEquity * (1.0 - EquitySLPercent / 100.0); if(currentEquity >= tpEquity) { Print("Equity Take Profit reached: ", currentEquity); CloseAllPositions(); g_initialEquity = currentEquity; Print("Equity baseline reset to: ", g_initialEquity); } else if(currentEquity <= slEquity) { Print("Equity Stop Loss reached: ", currentEquity); CloseAllPositions(); g_initialEquity = currentEquity; Print("Equity baseline reset to: ", g_initialEquity); } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Close all open positions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CloseAllPositions() { CPositionInfo m_position; CTrade m_trade; for(int i = PositionsTotal() - 1; i >= 0; i--) // loop all Open Positions if(m_position.SelectByIndex(i)) { // select a position m_trade.PositionClose(m_position.Ticket()); // then delete it --period } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { // Check and reset equity thresholds CheckEquityTPandSL(); // Update execution algorithms if(g_executionManager != NULL) g_executionManager.UpdateAlgorithms(); // Only process at bar open if(iVolume(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 0) > 1) return; // Get indicator values double fastMA[2], slowMA[2]; if(CopyBuffer(g_maHandle1, 0, 0, 2, fastMA) <= 0 || CopyBuffer(g_maHandle2, 0, 0, 2, slowMA) <= 0) { Print("Failed to copy indicator buffers"); return; } // Check for trend signals bool buySignal = (fastMA[0] > slowMA[0]) && (fastMA[1] <= slowMA[1]); bool sellSignal = (fastMA[0] < slowMA[0]) && (fastMA[1] >= slowMA[1]); // Execute signals using the execution manager if(buySignal) { Print("Buy signal detected"); if(UseAdaptiveExecution) { // Let the execution manager select the best algorithm g_executionManager.ExecuteSignal(SIGNAL_TYPE_BUY, TradingVolume); } else { datetime currentTime = TimeCurrent(); CTWAP *twap = g_executionManager.CreateTWAP(TradingVolume, currentTime, currentTime + 3600, 6, ORDER_TYPE_BUY, true); } } else if(sellSignal) { Print("Sell signal detected"); if(UseAdaptiveExecution) { // Let the execution manager select the best algorithm g_executionManager.ExecuteSignal(SIGNAL_TYPE_SELL, TradingVolume); } else { datetime currentTime = TimeCurrent(); CTWAP *twap = g_executionManager.CreateTWAP(TradingVolume, currentTime, currentTime + 3600, 6, ORDER_TYPE_SELL, true); } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
バックテスト結果
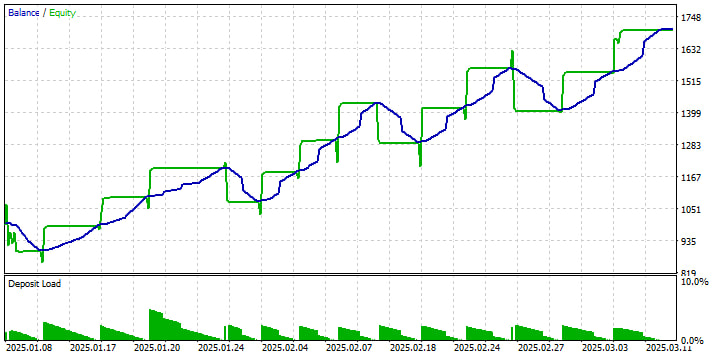
1. 資産曲線と残高曲線
緑の「Balance(残高)」はポジションをクローズしたタイミングでの口座資産を階段状に描き、青の「Equity」(資産)」は未実現損益を含んだ推移を滑らかに示しています。1月から3月初旬にかけて明確な上昇トレンドが見られ、いくつかの押し目が確認できます。各ドローダウンは約10〜16%で止まり、その後の勝ちトレードの連続で利益を回復しています。このパターンから、このシステムはトレンド相場で優位性を発揮する一方で、許容範囲内のドローダウンを抱えることがわかります。
2. ボリュームとリスクの活用
下部の「Deposit Load(三角形)」は時間の経過とともに徐々に縮小しています。これは、エクイティに対するポジションサイズの割合を示しています。開始時は残高の約10%でしたが、固定ロット運用のためエクイティが増えるにつれて割合が低下していきます。そのため、口座残高が増えても取引ごとのリスクは減少し、ドローダウンがドルベースでは大きくなっても割合としては同程度に収まります。
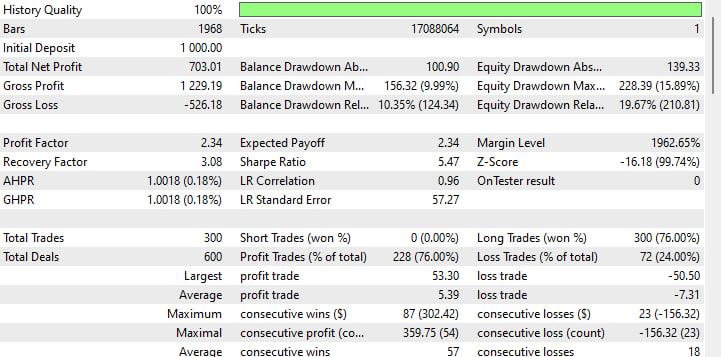
3. 主要な収益性指標
-
初回入金額:1,000ドル
-
純利益: +$703(約2か月で70%のリターン)
-
プロフィットファクター:2.34(1ドルの損失に対して2.34ドルの利益)
-
期待利益:平均1取引あたり2.34ドル
-
シャープレシオ:5.47(非常に高く、リスク調整後のリターンが優秀)
これらの数値は、この戦略が単に利益を出すだけでなく、ボラティリティを上回る健全な収益性を確保していることを示しています。
4. ドローダウンと回復
-
最大残高ドローダウン:156ポイント(9.99%)
-
最大エクイティドローダウン:228ポイント(15.89%)
-
リカバリーファクター:3.08(純利益 ÷ 最大ドローダウン)
リカバリーファクターは2以上で良好とされますが、この場合3.08で、最悪の損失に対して3倍以上の利益を生み出しています。
5. 取引分布
-
総取引数:300(600ディール、エントリー+エグジットを1セットとしてカウント)
-
勝率:76%(228勝、72敗)
-
平均利益:$5.39
-
平均損失:–$7.31
勝率とプロフィットファクターは優秀ですが、平均損失が平均利益を上回っている点には注意が必要です。相場環境が逆転した際にリスクになる可能性があります。
6. 連勝・連敗と一貫性
-
最大連勝:87取引、+$302
-
最大連敗:23取引、–$156
-
平均連勝:57取引
-
平均連敗:18取引
長期の連勝が右肩上がりの成績を支えていますが、最大の連敗でも口座の約15%に留まっています。
結論
混雑した市場アリーナで孤独なトレーダーを想像してください。すべてのティックが重要であり、すべての約定価格が利益か損失をささやきます。TWAP、VWAP、そしてアイスバーグ注文をツールキットに組み込めば、単に値動きに反応するだけではなく、それを演奏する側に回れるのです。かつては機関投資家専用の高度なアルゴリズムが、今やあなたの指先ひとつで使え、流動性をレーザーのように切り裂き、混沌とした板情報を機会へと変えていきます。
TWAPはあなたの安定したメトロノームとなり、設定した時間間隔で均等にサイズを刻んでいきます。これは、相場が落ち着いていて、ただ滑らかに約定させたいときに最適です。VWAPは市場のリズムを読み取り、出来高が最も集中する瞬間を狙って仕掛け、マーケットの鼓動に合わせて売買します。そして、自分の意図を隠したいときには、アイスバーグ注文が本当のサイズを水面下に隠し、約定に必要な分だけを見せ、大口プレイヤーを警戒させることなく取引を成立させます。
しかし、これらは単なる個別のテクニックではありません。私たちのモジュール型MQL5フレームワークによって、どんな戦略(トレンドフォロー、逆張り、ブレイクアウト狙い)にも簡単に組み込むことができます。統合されたExecutionManagerによってアルゴリズムをスワップ、組み合わせ、さらには取引中にレイヤーとして重ねることも可能です。同時に、PerformanceAnalyzerが隙なく監視し、スリッページやショートフォール、市場インパクトをピップ単位で計測します。
次のステップは、執行を生き物のように進化させることです。TWAP にボラティリティの急変から学習させ、VWAPをより深い流動性プールへとルーティングし、アイスバーグには捕食者が潜む場を感知させ、さらに奥深く身を隠す力を持たせるのです。そして、それで終わりではありません。機械学習を注入して最適な発注タイミングを予測させたり、複数の注文タイプを組み合わせて自分だけのハイブリッド執行を創り出すこともできます。
取引の世界は決して止まりません。あなたの注文執行も同じです。果敢に試し、積極的に実験し、あらゆるスライス、あらゆる約定を計算された優位性へと変えてください。あなたのアドバンテージは、コードの中に眠っています。
便宜上、この記事に含まれるファイルの概要を以下に示します。
| ファイル名 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| ExecutionAlgorithm.mqh | すべての実行アルゴリズムの基盤クラス |
| TWAP.mqh | 時間加重平均価格の実装 |
| VWAP.mqh | 出来高加重平均価格の導入 |
| IcebergOrder.mqh | アイスバーグ注文の実装 |
| PerformanceAnalyzer.mqh | 実行パフォーマンスを分析するためのツール |
| ExecutionManager.mqh | 取引戦略との簡単な統合のためのファサード |
| IntegratedStrategy.mq5 | 取引戦略との統合を示すEAの例 |
| IntegratedStrategy - Take Profit.mq5 | 口座残高のパーセンテージで利益確定と損切りを設定する取引戦略との統合を示すEAの例 |
MetaQuotes Ltdにより英語から翻訳されました。
元の記事: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/17934
警告: これらの資料についてのすべての権利はMetaQuotes Ltd.が保有しています。これらの資料の全部または一部の複製や再プリントは禁じられています。
この記事はサイトのユーザーによって執筆されたものであり、著者の個人的な見解を反映しています。MetaQuotes Ltdは、提示された情報の正確性や、記載されているソリューション、戦略、または推奨事項の使用によって生じたいかなる結果についても責任を負いません。
 MQL5経済指標カレンダーを使った取引(第9回):動的スクロールバーと洗練表示によるニュースインタラクション強化
MQL5経済指標カレンダーを使った取引(第9回):動的スクロールバーと洗練表示によるニュースインタラクション強化
 データサイエンスとML(第40回):機械学習データにおけるフィボナッチリトレースメントの利用
データサイエンスとML(第40回):機械学習データにおけるフィボナッチリトレースメントの利用
 機械学習の限界を克服する(第2回):再現性の欠如
機械学習の限界を克服する(第2回):再現性の欠如
 データサイエンスとML(第39回):ニュース × 人工知能、それに賭ける価値はあるか
データサイエンスとML(第39回):ニュース × 人工知能、それに賭ける価値はあるか
- 無料取引アプリ
- 8千を超えるシグナルをコピー
- 金融ニュースで金融マーケットを探索
ファイル、ExecutionAlgorithm.mqh に、注文を出す際に request.type_filling = ORDER_FILLING_IOC; という行を追加し、注文を出す際の問題を修正しました。
H1 でテストしたところ、SL も TP も適用されず、すべての取引が損失で終了しました。
また、コンパイル中に警告が発生しました。
アルゴのテスト方法、
時間枠、その他推奨事項があれば教えてください。
また、コンパイル中に警告が発生する
コード行
m_volumeProfile[intervalIndex] += rates[i].tick_volu
を
に変更した。
それは警告を修正しました
今、私の他のクエリに関する指導が必要です。
時間枠
また、
バックテスト中のすべての取引が損失となる理由
あなたのこの偉大な仕事をテストする方法。
アルゴのテスト方法、
時間枠、その他推奨事項があれば教えてください。
警告は問題ではないが、すぐに修正できるだろう。しかし、作者がバックテストに使用した設定と入力をステップ・バイ・ステップで示すことができれば最高だ。
I_Virgoの結果は、おそらく彼が間違った時間枠と通貨ペアを使用したためです。 バックテストレポートを見る限り、約2000バーのうち、時間枠はM1かM5で、ペアは不明でした。
MQがバックテストレポートに時間枠と通貨ペアを追加し、さらにペアの結果をより詳細に分けてくれれば、著者のバックテスト結果を より忠実に再現でき、FXペアへの適用性も判断できるのにと思います。また、EAが実行中にチャートにテキストを投稿できれば非常に助かります。
私もこの記事はすばらしいと思いますし、彼のテクニックを他のEAに応用することを期待して、徹底的に研究するつもりです。
ケープコッダ