
ONNXモデルをクラスでラップする
はじめに
前回の記事では、投票分類器をアレンジするために2つのONNXモデルを使用しました。ソーステキスト全体は、1つのMQ5ファイルとして整理されました。コード全体が関数に分割されました。ただし、モデルを入れ替えたり、別のモデルを追加する場合、原文がさらに大きくなります。オブジェクト指向のアプローチを試してみましょう。
1.どんなモデルを使うのか
前回の投票分類器では、1つの分類モデルと1つの回帰モデルを使用しました。回帰モデルでは、予測された価格の動き(下降、上昇、変化なし)の代わりに、クラスを計算するために使用される予測価格が得られます。しかしこの場合、クラス別の確率分布がないため、いわゆる「ソフト投票」ができません。
は3つの分類モデルを用意しました。MQL5でONNXモデルをアンサンブルする方法の例」稿では、すでに2つのモデルが使用されています。最初のモデル(回帰)は分類モデルに変換されました。トレーニングはOHLCの10価格シリーズでおこなわれました。l2番目のモデルは分類モデルです。トレーニングは63の終値でおこなわれました。
最後に、もうひとつモデルがあります。分類モデルは、30の終値と、平均期間が21と34の単純移動平均のシリーズで訓練されました。移動平均線と終値チャートの交点や、移動平均線同士の交点については一切想定していません。すべてのパターンは、レイヤー間の係数行列の形で計算され、ネットワークに記憶されます。
すべてのモデルは、2010.01.01から2023.01.01までのMetaQuotes-Demoサーバーのデータ、EURUSD D1で学習されました。3つのモデルすべてのトレーニングスクリプトはPythonで書かれており、この記事に添付されています。本稿の本題から読者の注意を逸らさないために、ここではそれらのソースコードは提供しません。
2.すべてのモデルに1つの基本クラスが必要
3つのモデルがあります。それぞれの違いは、入力データのサイズと準備にあります。どのモデルもインターフェイスは同じです。すべてのモデルのクラスは、同じ基本クラスから継承されなければなりません。
基本クラスを表現してみましょう。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ModelSymbolPeriod.mqh | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- price movement prediction #define PRICE_UP 0 #define PRICE_SAME 1 #define PRICE_DOWN 2 //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Base class for models based on trained symbol and period | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CModelSymbolPeriod { protected: long m_handle; // created model session handle string m_symbol; // symbol of trained data ENUM_TIMEFRAMES m_period; // timeframe of trained data datetime m_next_bar; // time of next bar (we work at bar begin only) double m_class_delta; // delta to recognize "price the same" in regression models public: //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CModelSymbolPeriod(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES period,const double class_delta=0.0001) { m_handle=INVALID_HANDLE; m_symbol=symbol; m_period=period; m_next_bar=0; m_class_delta=class_delta; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Destructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ~CModelSymbolPeriod(void) { Shutdown(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| virtual stub for Init | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ virtual bool Init(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES period) { return(false); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Check for initialization, create model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CheckInit(const string symbol,const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES period,const uchar& model[]) { //--- check symbol, period if(symbol!=m_symbol || period!=m_period) { PrintFormat("Model must work with %s,%s",m_symbol,EnumToString(m_period)); return(false); } //--- create a model from static buffer m_handle=OnnxCreateFromBuffer(model,ONNX_DEFAULT); if(m_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("OnnxCreateFromBuffer error ",GetLastError()); return(false); } //--- ok return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Release ONNX session | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void Shutdown(void) { if(m_handle!=INVALID_HANDLE) { OnnxRelease(m_handle); m_handle=INVALID_HANDLE; } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Check for continue OnTick | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ virtual bool CheckOnTick(void) { //--- check new bar if(TimeCurrent()<m_next_bar) return(false); //--- set next bar time m_next_bar=TimeCurrent(); m_next_bar-=m_next_bar%PeriodSeconds(m_period); m_next_bar+=PeriodSeconds(m_period); //--- work on new day bar return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| virtual stub for PredictPrice (regression model) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ virtual double PredictPrice(void) { return(DBL_MAX); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Predict class (regression -> classification) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ virtual int PredictClass(void) { double predicted_price=PredictPrice(); if(predicted_price==DBL_MAX) return(-1); int predicted_class=-1; double last_close=iClose(m_symbol,m_period,1); //--- classify predicted price movement double delta=last_close-predicted_price; if(fabs(delta)<=m_class_delta) predicted_class=PRICE_SAME; else { if(delta<0) predicted_class=PRICE_UP; else predicted_class=PRICE_DOWN; } //--- return predicted class return(predicted_class); } }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
基本クラスは回帰モデルにも分類モデルにも使えます。子孫クラス(PredictPriceまたはPredictClass)に適切なメソッドを実装するだけです。
基本クラスは、モデルが扱う銘柄と期間(モデルが訓練されたデータ)を設定します。基本クラスはまた、モデルを使用するEAが必要な銘柄と期間で動作することを確認し、モデルを実行するためのONNXセッションを作成します。基本クラスは、新しいバーの始まりにのみ仕事を提供します。
3.最初のモデルクラス
最初のモデルは、model.eurusd.D1.10.class.onnxと呼ばれるもので、EURUSD D1の10のOHLC価格シリーズで訓練した分類モデルです。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ModelEurusdD1_10Class.mqh | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #include "ModelSymbolPeriod.mqh" #resource "Python/model.eurusd.D1.10.class.onnx" as uchar model_eurusd_D1_10_class[] //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ONNX-model wrapper class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CModelEurusdD1_10Class : public CModelSymbolPeriod { private: int m_sample_size; public: //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CModelEurusdD1_10Class(void) : CModelSymbolPeriod("EURUSD",PERIOD_D1) { m_sample_size=10; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ONNX-model initialization | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ virtual bool Init(const string symbol, const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES period) { //--- check symbol, period, create model if(!CModelSymbolPeriod::CheckInit(symbol,period,model_eurusd_D1_10_class)) { Print("model_eurusd_D1_10_class : initialization error"); return(false); } //--- since not all sizes defined in the input tensor we must set them explicitly //--- first index - batch size, second index - series size, third index - number of series (OHLC) const long input_shape[] = {1,m_sample_size,4}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(m_handle,0,input_shape)) { Print("model_eurusd_D1_10_class : OnnxSetInputShape error ",GetLastError()); return(false); } //--- since not all sizes defined in the output tensor we must set them explicitly //--- first index - batch size, must match the batch size of the input tensor //--- second index - number of classes (up, same or down) const long output_shape[] = {1,3}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(m_handle,0,output_shape)) { Print("model_eurusd_D1_10_class : OnnxSetOutputShape error ",GetLastError()); return(false); } //--- ok return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Predict class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ virtual int PredictClass(void) { static matrixf input_data(m_sample_size,4); // matrix for prepared input data static vectorf output_data(3); // vector to get result static matrix mm(m_sample_size,4); // matrix of horizontal vectors Mean static matrix ms(m_sample_size,4); // matrix of horizontal vectors Std static matrix x_norm(m_sample_size,4); // matrix for prices normalize //--- prepare input data matrix rates; //--- request last bars if(!rates.CopyRates(m_symbol,m_period,COPY_RATES_OHLC,1,m_sample_size)) return(-1); //--- get series Mean vector m=rates.Mean(1); //--- get series Std vector s=rates.Std(1); //--- prepare matrices for prices normalization for(int i=0; i<m_sample_size; i++) { mm.Row(m,i); ms.Row(s,i); } //--- the input of the model must be a set of vertical OHLC vectors x_norm=rates.Transpose(); //--- normalize prices x_norm-=mm; x_norm/=ms; //--- run the inference input_data.Assign(x_norm); if(!OnnxRun(m_handle,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,input_data,output_data)) return(-1); //--- evaluate prediction return(int(output_data.ArgMax())); } }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
すでに述べたとおり、モデルは3つあり、それぞれの違いは、入力データのサイズと準備にあります。InitとPredictClassの2つのメソッドだけを再定義しました。同じメソッドが、他の2つのモデルのために他の2つのクラスで再定義されます。
Initメソッドは、ONNXモデルのセッションが作成され、入力テンソルと出力テンソルのサイズが明示的に設定されるCheckInit基底クラスメソッドを呼び出します。ここではコードよりもコメントの方が多くなります。
PredictClassメソッドは、モデルをトレーニングするときとまったく同じ入力データを準備します。入力は正規化されたOHLC価格の行列です。
4.どのように機能するのか確認してみましょう。
このクラスのパフォーマンスをテストするために、非常にコンパクトなエキスパートアドバイザー(EA)が作成されました。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ONNX.eurusd.D1.Prediction.mq5 | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #include "ModelEurusdD1_10Class.mqh" #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> input double InpLots = 1.0; // Lots amount to open position CModelEurusdD1_10Class ExtModel; CTrade ExtTrade; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { if(!ExtModel.Init(_Symbol,_Period)) return(INIT_FAILED); //--- return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { ExtModel.Shutdown(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { if(!ExtModel.CheckOnTick()) return; //--- predict next price movement int predicted_class=ExtModel.PredictClass(); //--- check trading according to prediction if(predicted_class>=0) if(PositionSelect(_Symbol)) CheckForClose(predicted_class); else CheckForOpen(predicted_class); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Check for open position conditions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CheckForOpen(const int predicted_class) { ENUM_ORDER_TYPE signal=WRONG_VALUE; //--- check signals if(predicted_class==PRICE_DOWN) signal=ORDER_TYPE_SELL; // sell condition else { if(predicted_class==PRICE_UP) signal=ORDER_TYPE_BUY; // buy condition } //--- open position if possible according to signal if(signal!=WRONG_VALUE && TerminalInfoInteger(TERMINAL_TRADE_ALLOWED)) { double price=SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol,(signal==ORDER_TYPE_SELL) ? SYMBOL_BID : SYMBOL_ASK); ExtTrade.PositionOpen(_Symbol,signal,InpLots,price,0,0); } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Check for close position conditions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CheckForClose(const int predicted_class) { bool bsignal=false; //--- position already selected before long type=PositionGetInteger(POSITION_TYPE); //--- check signals if(type==POSITION_TYPE_BUY && predicted_class==PRICE_DOWN) bsignal=true; if(type==POSITION_TYPE_SELL && predicted_class==PRICE_UP) bsignal=true; //--- close position if possible if(bsignal && TerminalInfoInteger(TERMINAL_TRADE_ALLOWED)) { ExtTrade.PositionClose(_Symbol,3); //--- open opposite CheckForOpen(predicted_class); } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
モデルは2023年までの価格データで学習されたので、2023年1月1日からテストを開始しましょう。
結果は以下のように表示されます。
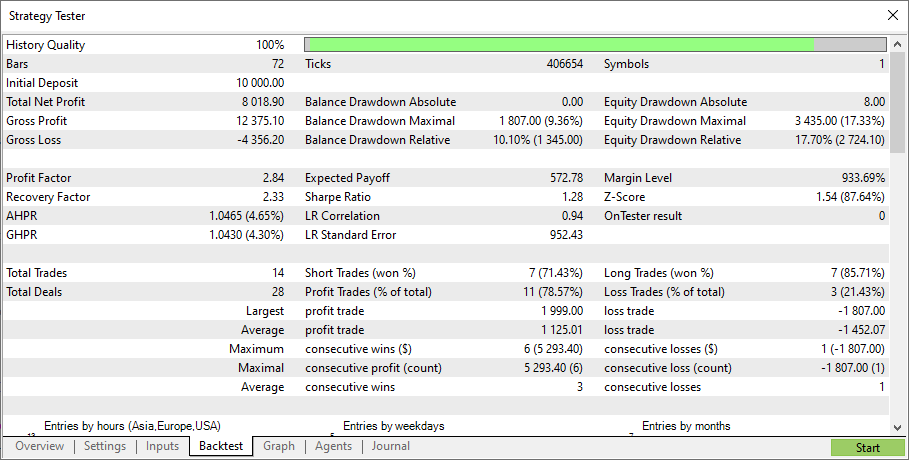
見ての通り、このモデルは完全に機能します。
5.2つ目のモデルクラス
2つ目のモデルはmodel.eurusd.D1.30.class.onnxと呼ばれます。EURUSDのD1で訓練された分類モデルは、30の終値と、平均期間が21と34の2つの単純移動平均のシリーズで訓練されました。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ModelEurusdD1_30Class.mqh | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #include "ModelSymbolPeriod.mqh" #resource "Python/model.eurusd.D1.30.class.onnx" as uchar model_eurusd_D1_30_class[] //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ONNX-model wrapper class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CModelEurusdD1_30Class : public CModelSymbolPeriod { private: int m_sample_size; int m_fast_period; int m_slow_period; int m_sma_fast; int m_sma_slow; public: //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CModelEurusdD1_30Class(void) : CModelSymbolPeriod("EURUSD",PERIOD_D1) { m_sample_size=30; m_fast_period=21; m_slow_period=34; m_sma_fast=INVALID_HANDLE; m_sma_slow=INVALID_HANDLE; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ONNX-model initialization | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ virtual bool Init(const string symbol, const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES period) { //--- check symbol, period, create model if(!CModelSymbolPeriod::CheckInit(symbol,period,model_eurusd_D1_30_class)) { Print("model_eurusd_D1_30_class : initialization error"); return(false); } //--- since not all sizes defined in the input tensor we must set them explicitly //--- first index - batch size, second index - series size, third index - number of series (Close, MA fast, MA slow) const long input_shape[] = {1,m_sample_size,3}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(m_handle,0,input_shape)) { Print("model_eurusd_D1_30_class : OnnxSetInputShape error ",GetLastError()); return(false); } //--- since not all sizes defined in the output tensor we must set them explicitly //--- first index - batch size, must match the batch size of the input tensor //--- second index - number of classes (up, same or down) const long output_shape[] = {1,3}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(m_handle,0,output_shape)) { Print("model_eurusd_D1_30_class : OnnxSetOutputShape error ",GetLastError()); return(false); } //--- indicators m_sma_fast=iMA(m_symbol,m_period,m_fast_period,0,MODE_SMA,PRICE_CLOSE); m_sma_slow=iMA(m_symbol,m_period,m_slow_period,0,MODE_SMA,PRICE_CLOSE); if(m_sma_fast==INVALID_HANDLE || m_sma_slow==INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("model_eurusd_D1_30_class : cannot create indicator"); return(false); } //--- ok return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Predict class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ virtual int PredictClass(void) { static matrixf input_data(m_sample_size,3); // matrix for prepared input data static vectorf output_data(3); // vector to get result static matrix x_norm(m_sample_size,3); // matrix for prices normalize static vector vtemp(m_sample_size); static double ma_buffer[]; //--- request last bars if(!vtemp.CopyRates(m_symbol,m_period,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,1,m_sample_size)) return(-1); //--- get series Mean double m=vtemp.Mean(); //--- get series Std double s=vtemp.Std(); //--- normalize vtemp-=m; vtemp/=s; x_norm.Col(vtemp,0); //--- fast sma if(CopyBuffer(m_sma_fast,0,1,m_sample_size,ma_buffer)!=m_sample_size) return(-1); vtemp.Assign(ma_buffer); m=vtemp.Mean(); s=vtemp.Std(); vtemp-=m; vtemp/=s; x_norm.Col(vtemp,1); //--- slow sma if(CopyBuffer(m_sma_slow,0,1,m_sample_size,ma_buffer)!=m_sample_size) return(-1); vtemp.Assign(ma_buffer); m=vtemp.Mean(); s=vtemp.Std(); vtemp-=m; vtemp/=s; x_norm.Col(vtemp,2); //--- run the inference input_data.Assign(x_norm); if(!OnnxRun(m_handle,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,input_data,output_data)) return(-1); //--- evaluate prediction return(int(output_data.ArgMax())); } }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
前のクラスと同様に、CheckInit基本クラスメソッドはInitメソッドの中で呼び出されます。基本クラスのメソッドでは、ONNXモデルのセッションが作成され、入力テンソルと出力テンソルのサイズが明示的に設定されます。
PredictClassメソッドは、過去30回の終値と算出された移動平均を提供します。データはトレーニングと同じ方法で正規化されます。
このモデルがどのように機能するか見てみましょう。そのために、テストEAの2つの文字列だけを変更します。
#include "ModelEurusdD1_30Class.mqh" #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> input double InpLots = 1.0; // Lots amount to open position CModelEurusdD1_30Class ExtModel; CTrade ExtTrade;
テストパラメータは同じです。
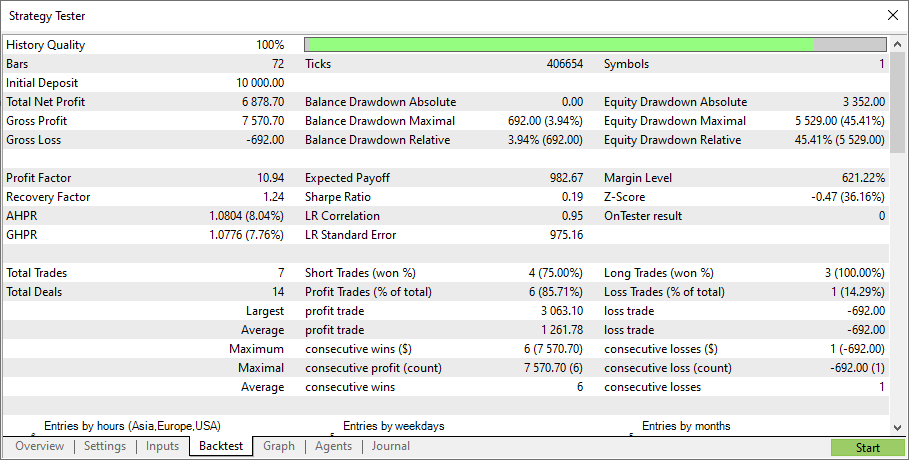
このモデルは機能していることがわかります。
6.3番目のモデルクラス
最後のモデルはmodel.eurusd.D1.63.class.onnxと呼ばれます。EURUSDのD1で訓練された分類モデルは、63の終値のシリーズを対象としました。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ModelEurusdD1_63.mqh | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #include "ModelSymbolPeriod.mqh" #resource "Python/model.eurusd.D1.63.class.onnx" as uchar model_eurusd_D1_63_class[] //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ONNX-model wrapper class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CModelEurusdD1_63Class : public CModelSymbolPeriod { private: int m_sample_size; public: //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CModelEurusdD1_63Class(void) : CModelSymbolPeriod("EURUSD",PERIOD_D1,0.0001) { m_sample_size=63; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ONNX-model initialization | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ virtual bool Init(const string symbol, const ENUM_TIMEFRAMES period) { //--- check symbol, period, create model if(!CModelSymbolPeriod::CheckInit(symbol,period,model_eurusd_D1_63_class)) { Print("model_eurusd_D1_63_class : initialization error"); return(false); } //--- since not all sizes defined in the input tensor we must set them explicitly //--- first index - batch size, second index - series size const long input_shape[] = {1,m_sample_size}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(m_handle,0,input_shape)) { Print("model_eurusd_D1_63_class : OnnxSetInputShape error ",GetLastError()); return(false); } //--- since not all sizes defined in the output tensor we must set them explicitly //--- first index - batch size, must match the batch size of the input tensor //--- second index - number of classes (up, same or down) const long output_shape[] = {1,3}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(m_handle,0,output_shape)) { Print("model_eurusd_D1_63_class : OnnxSetOutputShape error ",GetLastError()); return(false); } //--- ok return(true); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Predict class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ virtual int PredictClass(void) { static vectorf input_data(m_sample_size); // vector for prepared input data static vectorf output_data(3); // vector to get result //--- request last bars if(!input_data.CopyRates(m_symbol,m_period,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,1,m_sample_size)) return(-1); //--- get series Mean float m=input_data.Mean(); //--- get series Std float s=input_data.Std(); //--- normalize prices input_data-=m; input_data/=s; //--- run the inference if(!OnnxRun(m_handle,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,input_data,output_data)) return(-1); //--- evaluate prediction return(int(output_data.ArgMax())); } }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
これは3つの中で最もシンプルなモデルです。これが、PredictClassメソッドのコードが非常にコンパクトな理由です。
EAの2つの文字列をもう一度変更してみましょう。
#include "ModelEurusdD1_63Class.mqh" #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> input double InpLots = 1.0; // Lots amount to open position CModelEurusdD1_63Class ExtModel; CTrade ExtTrade;
同じ設定でテストを開始します。
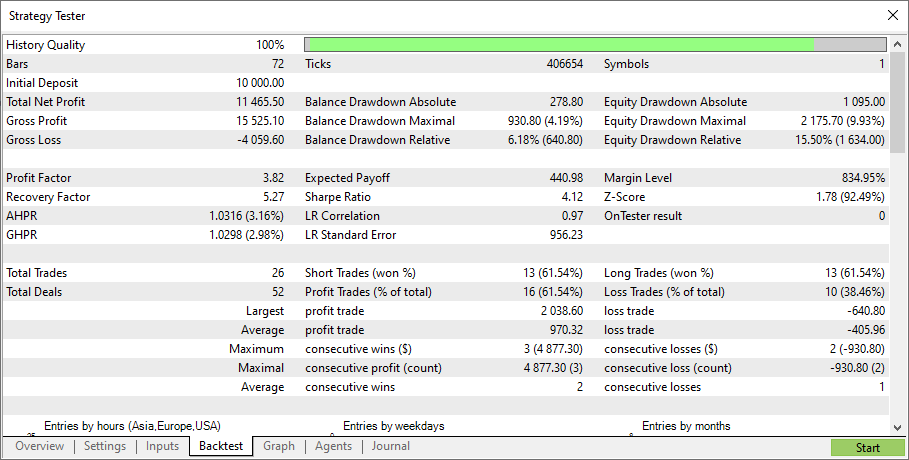
このモデルは機能します。
7.すべてのモデルを1つのEAに集める - ハード投票
3モデルともその能力を発揮しているので、次に、それらの努力を結集してみましょう。モデルの投票を手配しましょう。
前方宣言と定義
#include "ModelEurusdD1_10Class.mqh" #include "ModelEurusdD1_30Class.mqh" #include "ModelEurusdD1_63Class.mqh" #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> input double InpLots = 1.0; // Lots amount to open position CModelSymbolPeriod *ExtModels[3]; CTrade ExtTrade;
OnInit関数
int OnInit() { ExtModels[0]=new CModelEurusdD1_10Class; ExtModels[1]=new CModelEurusdD1_30Class; ExtModels[2]=new CModelEurusdD1_63Class; for(long i=0; i<ExtModels.Size(); i++) if(!ExtModels[i].Init(_Symbol,_Period)) return(INIT_FAILED); //--- return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
OnTick関数
void OnTick() { for(long i=0; i<ExtModels.Size(); i++) if(!ExtModels[i].CheckOnTick()) return; //--- predict next price movement int returned[3]={0,0,0}; //--- collect returned classes for(long i=0; i<ExtModels.Size(); i++) { int pred=ExtModels[i].PredictClass(); if(pred>=0) returned[pred]++; } //--- get one prediction for all models int predicted_class=-1; //--- count votes for predictions for(int n=0; n<3; n++) { if(returned[n]>=2) { predicted_class=n; break; } } //--- check trading according to prediction if(predicted_class>=0) if(PositionSelect(_Symbol)) CheckForClose(predicted_class); else CheckForOpen(predicted_class); }
過半数の得票は、<総得票数>/2+1という式に従って計算されます。合計3票で、過半数は2票です。いわゆる「ハード投票」です。
テスト結果は同じ設定のままです。
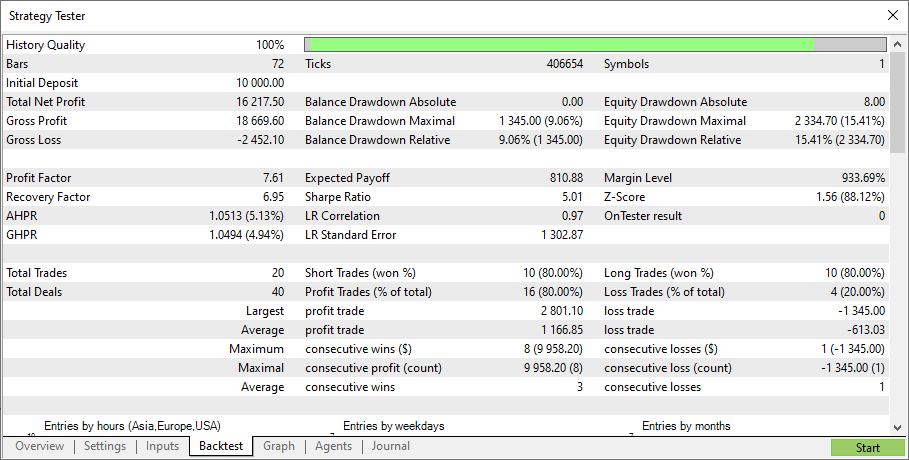
3つのモデルの仕事、すなわち、利益の出る取引と利益の出ない取引の数を別々に見てみましょう。モデル1 - 11:3、モデル2 - 6:1、モデル3 - 16:10です。
ハード投票で結果は改善されたようです(16:4)が、もちろん、フルレポートやテストチャートを見る必要があります。
8.ソフト投票
ソフト投票がハード投票と異なるのは、考慮されるのが投票数ではなく、3つのモデルから得られる3つのクラスすべての確率の合計であるという点です。クラスは最も高い確率で選ばれます。
ソフト投票を保証するためには、いくつかの変更を加える必要があります。
基本クラス
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Predict class (regression -> classification) | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ virtual int PredictClass(vector& probabilities) { ... //--- set predicted probability as 1.0 probabilities.Fill(0); if(predicted_class<(int)probabilities.Size()) probabilities[predicted_class]=1; //--- and return predicted class return(predicted_class); }
子孫のクラス
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Predict class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ virtual int PredictClass(vector& probabilities) { ... //--- evaluate prediction probabilities.Assign(output_data); return(int(output_data.ArgMax())); }
EA
#include "ModelEurusdD1_10Class.mqh" #include "ModelEurusdD1_30Class.mqh" #include "ModelEurusdD1_63Class.mqh" #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> enum EnVotes { Two=2, // Two votes Three=3, // Three votes Soft=4 // Soft voting }; input double InpLots = 1.0; // Lots amount to open position input EnVotes InpVotes = Two; // Votes to make trade decision CModelSymbolPeriod *ExtModels[3]; CTrade ExtTrade;
void OnTick() { for(long i=0; i<ExtModels.Size(); i++) if(!ExtModels[i].CheckOnTick()) return; //--- predict next price movement int returned[3]={0,0,0}; vector soft=vector::Zeros(3); //--- collect returned classes for(long i=0; i<ExtModels.Size(); i++) { vector prob(3); int pred=ExtModels[i].PredictClass(prob); if(pred>=0) { returned[pred]++; soft+=prob; } } //--- get one prediction for all models int predicted_class=-1; //--- soft or hard voting if(InpVotes==Soft) predicted_class=(int)soft.ArgMax(); else { //--- count votes for predictions for(int n=0; n<3; n++) { if(returned[n]>=InpVotes) { predicted_class=n; break; } } } //--- check trading according to prediction if(predicted_class>=0) if(PositionSelect(_Symbol)) CheckForClose(predicted_class); else CheckForOpen(predicted_class); }
テストの設定は同じです。入力で、[ソフト]を選択します。
結果は以下のとおりです。
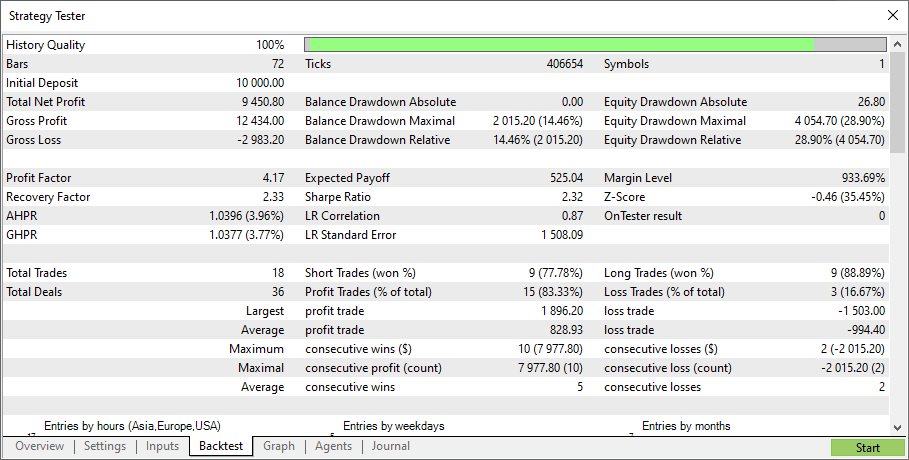
有益な取引 - 15件、有益でない取引 - 3件。金銭的な面でも、ハード投票の方がソフト投票よりも優れていることが判明しました。
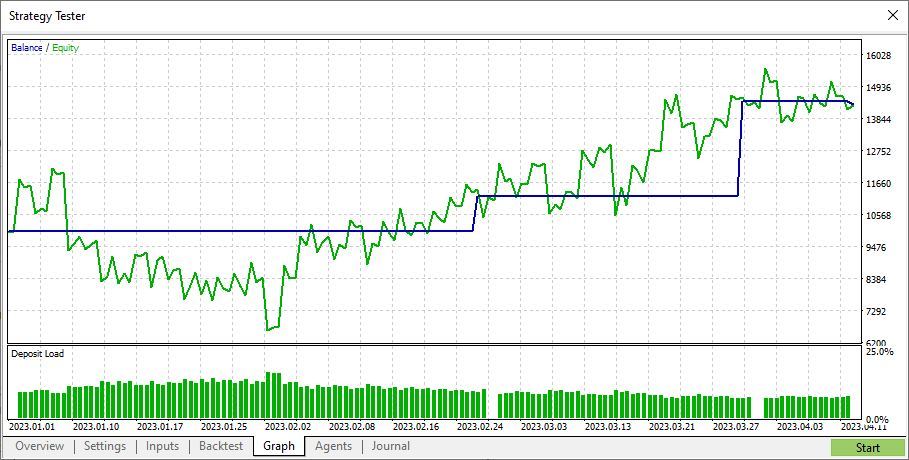
全会一致、つまり投票数3の結果を見てみましょう。
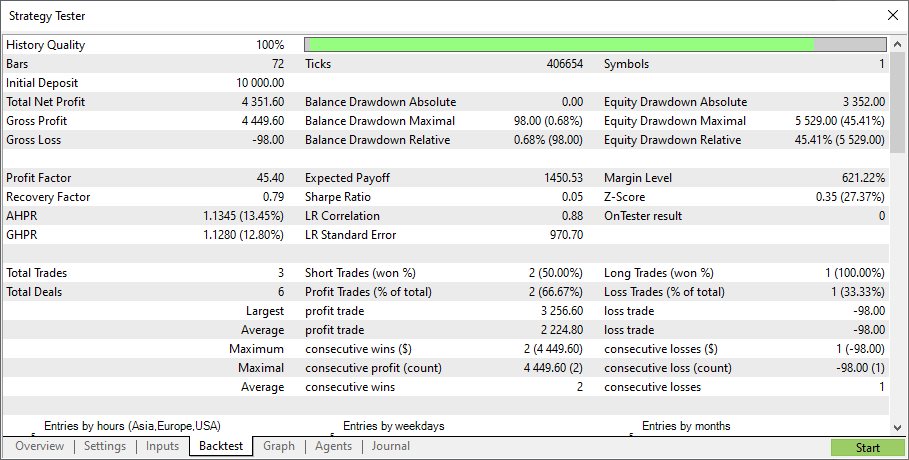
非常に保守的な取引だ。唯一の不採算取引はテスト終了時に決済された(おそらく、不採算ではない)。
重要な注意点:この記事で使用されているモデルは、MQL5言語を使用してONNXモデルを操作する方法を示すためにのみ提示されています。EAは、実際の口座での取引を意図したものではありません。
結論
この記事では、オブジェクト指向プログラミングがいかにプログラムを書きやすくするかを紹介しました。モデルの複雑さはすべて、そのクラスに隠されています(モデルは、例として紹介したものよりもはるかに複雑になることができます)。残りの「複雑さ」は、OnTick関数の45個の文字列に収まっています。
MetaQuotes Ltdによってロシア語から翻訳されました。
元の記事: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/12484
警告: これらの資料についてのすべての権利はMetaQuotes Ltd.が保有しています。これらの資料の全部または一部の複製や再プリントは禁じられています。
- 無料取引アプリ
- 8千を超えるシグナルをコピー
- 金融ニュースで金融マーケットを探索
これは本当に興味深い。
記事に添付したMLファイルONNX.eurusd.D1.30.class.Training.pyの def collect_dataset() に以下の行があります(48行目~59行目):
for i in tqdm(range(n - sample_size)): w = df.iloc[i: i + sample_size + 1] x = w[['close', 'ma_fast', 'ma_slow']].iloc[:-1].values delta = x[0][-1] - w.iloc[-1]['close'] if np.abs(delta)<=0.0001: y = 0, 1, 0 else: if delta>0: y = 1, 0, 0 else: y = 0, 0, 1上記のハイライトされた行の背後にあるロジックを教えてください。
分類は最初のサンプルの'ma_slow'(x[0][-1])と新しいターゲットの'close'(w.iloc[-1]['close'])の差に基づいています。さらに'sample_size-1'の時間差がある。
さらに
if delta>0: y = 1, 0, 0これはy = 0,0,1 ではないのか?つまり売りシグナル だ。
同様に、ONNX.eurusd.D1.10.class.Training.py のdef collect_dataset(), line45-47:
x = w[['open', 'high', 'low', 'close']].iloc[:-1].values delta = x[3][-1] - w.iloc[-1]['close']どのように?分類は、4つ目のサンプルの「終値」(x[3][-1])と新しいターゲットの「終値」(w.iloc[-1]['close'])の差に基づいています。