
迷你行情模拟器或手动策略测试器
引言
外汇交易始于理论基础的研究: 收益策略, 数据分析方法, 成功的交易模型。所有新入行交易者都有相同的想法 — 每个人都想赚钱。但是每个人都定义了自己的优先级, 条件, 机会, 目标等。
新入行交易者的行为有若干种情况。
- "一次全部" 选项" 大多数初学者都想快速赚取很多钱。他们迷信于一个诱惑广告: 用很少的钱, 甚至免费即可得到神奇而无暇的策略。所有这一切看起来即快捷又容易, 但是, 损失本钱也同样迅速和轻易。
- "教育, 教育再教育" 选项: 负责任的新手培训, 是要他们不能相信童话故事。他们需要深入研究行情和交易系统的规律。那就是当在真实账户里开始交易后 — 事实证明利润会低于依据教科书的预期。这是如何发生的, 接下来应如何做?
一旦出现第一种状况, 大多数新人会对金融市场永远失望。而新人从第二种情景中继续研究理论及其实际策略。
本文主要针对那些迫不及待地想要在模拟账户上进行交易并测试其策略的初学者。这里也有两个选项:
- 一组想要尝试研究一个短线策略。但如果其成员为全职工作, 他们只能在夜间休息, 因为市场在周末才会闭市。
- 第二类交易者使用中线或长线策略。他们绝对不想花一整年时间在模拟账户上完善自己的策略。
自然而然地, 您也许会想: 如果有一个历史图表能够快速而有效地测试任何策略, 那这些还会如此困难吗?然而, 在实践中, 它并不能总是奏效: 出于某种原因, 经常会发生在回测时有出色表现的策略却在 "真实" 行情中效果很差。无论如何, 最好在更接近现实的系统中学习交易。举例来说, 行情模拟器恰好足够 (这样的程序可以在互联网上购得)。
在这篇文章中, 我想讨论一下我自己在 MetaTrader 5 中实现的这样一个系统。与完整的终端版本相比, 我所编写的 "迷你行情模拟器" 指标功能有限。它设计用于策略的理论验证。
应用程序功能
应用程序有自己的控制面板, 以及 "父系统" 的按钮, 即 MetaTrader 5 终端本身。
这是模拟器可以执行的 主要动作。
- 只能放置两个不同方向的订单: 买入和卖出。在设置订单和交易量之前, 还支持止损和止盈的设置。一旦订单被放置, 它可以被修改, 并且可以拖动其停止价位。
- 只有七种建模速度, 它们可以划分为三组。第一个是 "珠宝", 它所涉及的建模基于来自分钟时间帧的分笔报价, 就像在策略测试器中一样。第二个考虑分钟数据, 构建时无需生成 (这种模式更快, 但不太精准)。第三种模式是最快的: 每秒一根蜡烛, 无论时间帧如何。
- 所提供的当前交易信息: 利润, 点数和交易量。给出的数据针对当前和过去的订单, 以及自仿真开始时的正常交易。
- 终端中的所有标准图形对象都可用。
- 支持所有的标准时间帧 (通过终端面板的按钮切换)。
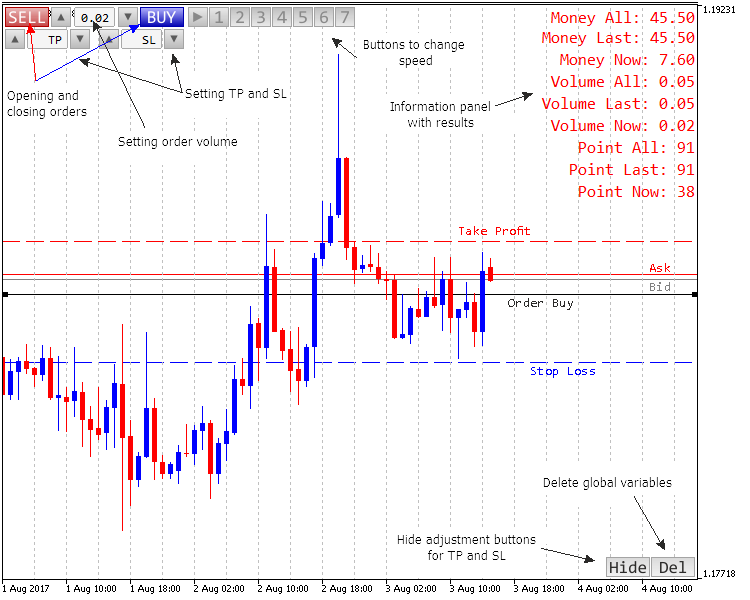
图例. 1. 应用程序的控件和外观
分笔报价生成系统
分笔报价的生成原理来自文章 "MetaTrader 5 终端策略测试器中的分笔报价生成算法"。它已被创造性地修改并作为替代版本呈现。
两个函数负责生成分笔报价 — 主要和辅助。
主函数是Tick Generation。它传递了两个参数: 蜡烛本身和响应数据 (ticks) 的数组。之后, 如果输入蜡烛的所有四个价位彼此相等, 则 ticks 的交易量设置为等于一个分笔报价。这样做是为了消除所传递数据不正确的情况下可能发生的除零错误。
随后会形成一根新的蜡烛。如果蜡烛内有 1 至 3 个分笔报价, 则按上文所述的分笔报价生成过程继续。
如果有 3 个以上的分笔报价, 则操作变得更加复杂。所传递的蜡烛被分成三个不等份 (在下面的代码中提供了划分的原则, 分别为 看跌 和 看涨 蜡烛。然后, 如果顶部和底部不再有分笔报价, 则进行调整。接下来, 根据蜡烛的性质将控制权转交给辅助函数。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Tick Generation 函数 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_tick_generation( MqlRates &rates, // 蜡烛数据 double &tick[] // 分笔报价数组 ) { if(rates.open==rates.close && rates.high==rates.low && rates.open==rates.high){rates.tick_volume=1;} if(rates.tick_volume<4)// 少于四个分笔报价 { ArrayResize(tick,int(rates.tick_volume)); // 调整分笔报价数组大小 if(rates.tick_volume==1)tick[0]=rates.close; // 一个分笔报价 if(rates.tick_volume==2) // 两个分笔报价 { tick[0]=rates.open; tick[1]=rates.close; } if(rates.tick_volume==3) // 三个分笔报价 { tick[0]=rates.open; tick[2]=rates.close; if(rates.open==rates.close) // 朝着一个方向前进, 并回到了开盘价 { if(rates.high==rates.open)tick[1]=rates.low; if(rates.low==rates.open)tick[1]=rates.high; } if(rates.close==rates.low && rates.open!=rates.high)tick[1]=rates.high; // 朝着一个方向前进, 回滚并突破开盘价 if(rates.close==rates.high && rates.open!=rates.low)tick[1]=rates.low; if(rates.open==rates.high && rates.close!=rates.low)tick[1]=rates.low; // 朝着一个方向前进, 回滚但未突破开盘价 if(rates.open==rates.low && rates.close!=rates.high)tick[1]=rates.high; if((rates.open==rates.low && rates.close==rates.high) || (rates.open==rates.high && rates.close==rates.low)) { tick[1]=NormalizeDouble((((rates.high-rates.low)/2)+rates.low),_Digits); // 在一个方向的若干点数 } } } if(rates.tick_volume>3) // 超过三个分笔报价 { // 按照点数计算蜡烛的大小 int candle_up=0; int candle_down=0; int candle_centre=0; if(rates.open>rates.close) { candle_up=int(MathRound((rates.high-rates.open)/_Point)); candle_down=int(MathRound((rates.close-rates.low)/_Point)); } if(rates.open<=rates.close) { candle_up=int(MathRound((rates.high-rates.close)/_Point)); candle_down=int(MathRound((rates.open-rates.low)/_Point)); } candle_centre=int(MathRound((rates.high-rates.low)/_Point)); int candle_all=candle_up+candle_down+candle_centre; // 走势的总长度 int point_max=int(MathRound(double(candle_all)/2)); // 分笔报价的最大可能数量 double share_up=double(candle_up)/double(candle_all); double share_down=double(candle_down)/double(candle_all); double share_centre=double(candle_centre)/double(candle_all); // 计算每个部分的参考点数量 char point=0; if(rates.tick_volume<10)point=char(rates.tick_volume); else point=10; if(point>point_max)point=char(point_max); char point_up=char(MathRound(point*share_up)); char point_down=char(MathRound(point*share_down)); char point_centre=char(MathRound(point*share_centre)); // 检查所选范围的参考点 if(candle_up>0 && point_up==0) {point_up=1;point_centre=point_centre-1;} if(candle_down>0 && point_down==0) {point_down=1;point_centre=point_centre-1;} // 调整输出数组的大小 ArrayResize(tick,11); char p=0; // 分笔报价数组的索引 (tick[]) tick[p]=rates.open; // 第一个分笔报价等于开盘价 if(rates.open>rates.close) // 下行趋势 { func_tick_small(rates.high,1,candle_up,point_up,tick,p); func_tick_small(rates.low,-1,candle_centre,point_centre,tick,p); func_tick_small(rates.close,1,candle_down,point_down,tick,p); ArrayResize(tick,p+1); } if(rates.open<=rates.close) // 上行或十字星 { func_tick_small(rates.low,-1,candle_down,point_down,tick,p); func_tick_small(rates.high,1,candle_centre,point_centre,tick,p); func_tick_small(rates.close,-1,candle_up,point_up,tick,p); ArrayResize(tick,p+1); } } }
顾名思义, Tick Small 函数执行次级分笔报价。它接收有关上次处理的订单信息, 走势 (上或下) 的方向, 所需的步数, 最后价格, 并将计算的步数传递给上述的分笔报价数组。结果数组包含的分笔报价不超过 11 个。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Tick Small 函数 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_tick_small( double end, // 走势结束 char route, // 走势方向 int candle, // 走势距离 char point, // 点数 double &tick[], // 分笔报价数组 char&i // 数组的当前索引 ) { if(point==1) { i++; if(i>10)i=10; // 调整 tick[i]=end; } if(point>1) { double wave_v=(point+1)/2; double step_v=(candle-1)/MathFloor(wave_v)+1; step_v=MathFloor(step_v); for(char p_v=i+1,i_v=i; p_v<i_v+point;) { i++; if(route==1)tick[i]=tick[i-1]+(step_v*_Point); if(route==-1)tick[i]=tick[i-1]-(step_v*_Point); p_v++; if(p_v<i_v+point) { i++; if(route==1)tick[i]=tick[i-1]-_Point; if(route==-1) tick[i]=tick[i-1]+_Point; } p_v++; } if(NormalizeDouble(tick[i],_Digits)!=NormalizeDouble(end,_Digits)) { i++; if(i>10)i=10; // 调整 tick[i]=end; } } }
这就是说, 整个 "珠宝" 建模的核心 (结论解释了为什么它被称为 "珠宝")。现在我们来继续讨论系统交互的本质。
交互和数据交换
系统的代码乍一看似乎令人困惑。函数并非完全一致, 它们可能来自程序的不同部分。事实证明, 这是因为系统不仅要与用户交互, 还要与终端交互。以下是这些互动的近似方案 (图例. 2):
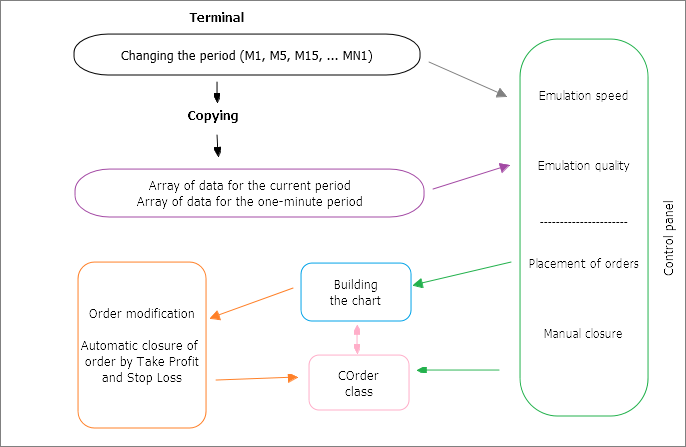
图例. 2. 应用程序中的交互方案
为了减少指标窗口中控件对象的数量, 切换周期的机制是从终端外壳借用的。但由于应用程序在切换周期时被重新初始化, 且本地和全局范围的所有变量均被覆盖, 所以每次切换时都会复制数据数组。特别要复制两个周期的数据 — M1和选定的那个。这些数据的后续处理参数在面板上进行选择: 模拟的速度和质量("珠宝" 或简单的快速方法)。一切准备就绪后, 图表的模型就开始了。
控制面板便于下订单和删除。为此, 程序引用了 "COrder" 类。这个类也用于在图表构建时管理订单。
如上所述, 如果图表周期发生变化, 指标将重新启动。相应地, 客户终端的全局变量 在应用程序的整体结构中用来提供通信。与传统的全局变量不同, 它们存储的时间更长 (4 周), 并可容忍重启。唯一的缺点是它们的数据类型是双精度。总之, 比创建一个新文件, 每次写/读都更方便。
我们直接进入交互元素的代码。
在代码中实现
代码的开始
首先是声明变量的标准流程。然后 OnInit() 函数初始化缓冲区, 绘制控制面板的界面, 计算从仿真开始的偏移量。需要偏移量来确保模拟不会从图表空白处开始, 且在确定的历史记录处立即开始检验策略。
数据数组被复制, 并且主连接变量也被读取 (命名为 time_end)。它指示模拟停止的时间:
//--- 设置指标绘制的时间 if(GlobalVariableCheck(time_end))end_time_indicator=datetime(GlobalVariableGet(time_end));
这样指标总是 "知晓" 它停在哪里。OnInit() 函数以一个定时器调用结束, 实际上, 该命令会输出一个新的分笔报价或者形成一根完整的蜡烛 (取决于速度)。
定时器函数
在函数开始时检查控制面板上 "播放" 按钮的状态。如果已按下, 则执行进一步的代码。
首先, 它检测模拟停止的指标柱线 (相对于当前时间)。最后模拟时间 'end_time_indicator' 和当前时间被视为端点。数据每秒钟都会重新计算, 因为图表正在不断移动 (周六和周日除外), 且不能及时同步。因此, 该图表由 ChartNavigate() 函数进行动态跟踪和移动。
之后, 计算变量 "number_now_rates", "bars_now_rates", "all_bars_indicator"。之后检查时间。如果所输入参数没有耗尽, 则使用 func_merger() 函数进行建模。接下来, 检查当前持仓及其获利能力, 记录在全局变量中并输出到指标的信息块中。
这里也称为 "COrder" 类, 即由用户操作 (position.Delete) 或激活的停止级别 (position.Check) 导致自动删除订单的部分。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Timer 函数 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTimer() { //--- if(button_play) { end_bar_indicator=Bars(_Symbol,_Period,end_time_indicator,TimeCurrent()); // 从最早到现在的柱线数量 ChartNavigate(0,CHART_END,-end_bar_indicator); // 移动图表 (指标) 到当前建模的柱线 number_now_rates=(Bars(_Symbol,_Period,real_start,end_time_indicator)-1); // 当前用于建模的柱线 bars_now_rates=(Bars(_Symbol,_Period,real_start,stop)-1); // 从来自历史记录的当前周期使用的柱线数 all_bars_indicator=(Bars(_Symbol,_Period,real_start,TimeCurrent()))-1; // 从模拟开始到当前时间的柱线数 if(end_time_indicator<stop) // 检查模拟时间 { func_merger(); ObjectSetDouble(0,line_bid,OBJPROP_PRICE,price_bid_now); if(ObjectFind(0,line_ask)>=0) {ObjectSetDouble(0,line_ask,OBJPROP_PRICE,price_ask_now);} //--- 订单的当前值 int point_now=0; double vol_now=0; double money_now=0; if(ObjectFind(0,order_buy)>=0 && GlobalVariableGet(order_buy)>0) // 存在买入订单 { int p_now=int((price_bid_now-GlobalVariableGet(order_buy))*dig_pow); double v_now=GlobalVariableGet(vol_buy); double m_now=p_now*v_now*10; point_now+=p_now; vol_now+=v_now; money_now+=m_now; } if(ObjectFind(0,order_sell)>=0 && GlobalVariableGet(order_sell)>0) // 存在卖出订单 { int p_now=int((GlobalVariableGet(order_sell)-price_ask_now)*dig_pow); double v_now=GlobalVariableGet(vol_sell); double m_now=p_now*v_now*10; point_now+=p_now; vol_now+=v_now; money_now+=m_now; } GlobalVariableSet(info_point_now,point_now); GlobalVariableSet(info_vol_now,vol_now); GlobalVariableSet(info_money_now,money_now); } COrder position; //"COrder" 类的对象 position.Delete(price_bid_now,price_ask_now,(-1)); position.Check(end_time_indicator,GlobalVariableGet(order_buy),GlobalVariableGet(tp_buy),GlobalVariableGet(sl_buy), GlobalVariableGet(order_sell),GlobalVariableGet(tp_sell),GlobalVariableGet(sl_sell)); func_info_print("Money All: ",info_money_all,2); func_info_print("Money Last: ",info_money_last,2); func_info_print("Money Now: ",info_money_now,2); func_info_print("Volume All: ",info_vol_all,2); func_info_print("Volume Last: ",info_vol_last,2); func_info_print("Volume Now: ",info_vol_now,2); func_info_print("Point All: ",info_point_all,0); func_info_print("Point Last: ",info_point_last,0); func_info_print("Point Now: ",info_point_now,0); position.Modify(); } //--- 管理隐藏按钮 char x=char(GlobalVariableGet("hide")); if(x==1) { ObjectSetInteger(0,"20",OBJPROP_STATE,false); ObjectSetInteger(0,"14",OBJPROP_YDISTANCE,24); ObjectSetInteger(0,"15",OBJPROP_YDISTANCE,24); ObjectSetInteger(0,"16",OBJPROP_YDISTANCE,24); ObjectSetInteger(0,"17",OBJPROP_YDISTANCE,24); ObjectSetInteger(0,"18",OBJPROP_YDISTANCE,24); ObjectSetInteger(0,"19",OBJPROP_YDISTANCE,24); } if(x==2) { ObjectSetInteger(0,"20",OBJPROP_STATE,true); ObjectSetInteger(0,"14",OBJPROP_YDISTANCE,-24); ObjectSetInteger(0,"15",OBJPROP_YDISTANCE,-24); ObjectSetInteger(0,"16",OBJPROP_YDISTANCE,-24); ObjectSetInteger(0,"17",OBJPROP_YDISTANCE,-24); ObjectSetInteger(0,"18",OBJPROP_YDISTANCE,-24); ObjectSetInteger(0,"19",OBJPROP_YDISTANCE,-24); } }
COrder 类
这个类包含开仓和平仓, 修改和检查订单当前状态 (管理它们的止盈和止损价) 的函数。
我们从使用 Placed 放置订单开始。通过 switch 操作符选择订单类型 (买入或卖出), 数据存储在全局变量 (order_buy或order_sell) 中。如果之前已经定义了 m_take_profit和m_stop_loss, 则将它们存储在相应的全局变量中, 并在图表上绘制它们的指示线。指示线由这个类的 Line 函数设置。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| COrder 类 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class COrder { public: void Placed( char m_type,// 订单类型 (1-买入, 2-卖出) double m_price_bid, // 竞买价 double m_price_ask, // 竞卖价 int m_take_profit,// 止盈点数 int m_stop_loss // 止损点数 ) { switch(m_type) { case 1: { GlobalVariableSet(order_buy,m_price_ask); Line(GlobalVariableGet(order_buy),order_buy,col_buy,STYLE_SOLID,1,true); if(m_take_profit>0) { GlobalVariableSet(tp_buy,(m_price_ask+(_Point*m_take_profit))); Line(GlobalVariableGet(tp_buy),tp_buy,col_tp,STYLE_DASH,1,true); } if(m_stop_loss>0) { GlobalVariableSet(sl_buy,(m_price_ask-(_Point*m_stop_loss))); Line(GlobalVariableGet(sl_buy),sl_buy,col_sl,STYLE_DASH,1,true); } } break; case 2: { GlobalVariableSet(order_sell,m_price_bid); Line(GlobalVariableGet(order_sell),order_sell,col_sell,STYLE_SOLID,1,true); if(m_take_profit>0) { GlobalVariableSet(tp_sell,(m_price_bid-(_Point*m_take_profit))); Line(GlobalVariableGet(tp_sell),tp_sell,col_tp,STYLE_DASH,1,true); } if(m_stop_loss>0) { GlobalVariableSet(sl_sell,(m_price_bid+(_Point*m_stop_loss))); Line(GlobalVariableGet(sl_sell),sl_sell,col_sl,STYLE_DASH,1,true); } } break; } }
接下来是用于删除订单的 Delete 函数。再次, switch 操作符选择三个选项之一 — 自动删除, 买入或卖出。在这种情况下, 自动删除是指通过从图表中删除其指示线来删除订单的情况。
这是由类的 Small_del_buy 和 Small_del_sell 辅助函数完成的。
void Delete( double m_price_bid, // 竞买价 double m_price_ask, // 竞卖价 char m_del_manual // 删除类型 (-1 - 自动, 1 - 买入, 2 - 卖出) ) { switch(m_del_manual) { case(-1): if(ObjectFind(0,order_buy)<0 && GlobalVariableGet(order_buy)>0) {Small_del_buy(m_price_bid);} if(ObjectFind(0,order_sell)<0 && GlobalVariableGet(order_sell)>0) {Small_del_sell(m_price_ask);} break; case 1: if(ObjectFind(0,order_buy)>=0) { ObjectDelete(0,order_buy); Small_del_buy(m_price_bid); } break; case 2: if(ObjectFind(0,order_sell)>=0) { ObjectDelete(0,order_sell); Small_del_sell(m_price_ask); } break; } }
我们研究其中之一 — Small_del_sell。
检查止盈和止损指示线。如果它们存在, 请将其删除。然后将 order_sell 全局变量清零。使用全局变量来检查订单是否存在, 将在稍后需要。
有关订单利润的信息也存储在全局变量 (info_point_last, info_vol_last, info_money_last) 中。这是由 small_concatenation 完成的 (类似于 += 运算符, 但配合全局变量)。汇总利润 (成交量), 并将其存储在全局变量 (info_point_all, info_vol_all, info_money_all) 中。
void Small_del_sell(double m_price_ask) { if(ObjectFind(0,tp_sell)>=0)ObjectDelete(0,tp_sell); // 删除止盈指示线 if(ObjectFind(0,sl_sell)>=0)ObjectDelete(0,sl_sell); // 删除止损指示线 int point_plus=int(MathRound((GlobalVariableGet(order_sell)-m_price_ask)/_Point)); // 计算交易的利润 GlobalVariableSet(order_sell,0); // 将所下订单的价格变量清零 GlobalVariableSet(info_vol_last,GlobalVariableGet(vol_sell)); GlobalVariableSet(vol_sell,0); GlobalVariableSet(info_point_last,point_plus); GlobalVariableSet(info_money_last,(GlobalVariableGet(info_point_last)*GlobalVariableGet(info_vol_last)*10)); Small_concatenation(info_point_all,info_point_last); Small_concatenation(info_vol_all,info_vol_last); Small_concatenation(info_money_all,info_money_last); }
订单的修改是通过用鼠标改变其位置来完成的。有两种方法可以做到这一点。第一个是尝试拖动订单开单价。在这种情况下, 根据移动方向和订单类型绘制新的止盈和止损线。Small_mod 函数也在 COrder 类中实现。其输入参数是对象名称、移动对象的权限和订单类型。
在 Small_mod 函数的开始处, 检查对象的存在。然后, 如果允许移动止盈/止损线, 则价格的变化被存储在全局变量中。如果移动 (买入和卖出线) 被禁止, 则根据订单类型, 在线的新位置出现新的止盈线或止损线, 且订单线返回到其位置。
void Small_mod(string m_name, // 对象的名称和全局变量 bool m_mode, // 改变位置的许可 char m_type // 1 — 买入, 2 — 卖出 ) { if(ObjectFind(0,m_name)>=0) { double price_obj_double=ObjectGetDouble(0,m_name,OBJPROP_PRICE); int price_obj=int(price_obj_double*dig_pow); double price_glo_double=GlobalVariableGet(m_name); int price_glo=int(price_glo_double*dig_pow); if(price_obj!=price_glo && m_mode==true) { GlobalVariableSet(m_name,(double(price_obj)/double(dig_pow))); } if(price_obj!=price_glo && m_mode==false) { switch(m_type) { case 1: // 买入订单 if(price_obj>price_glo) // 止盈 { GlobalVariableSet(tp_buy,(double(price_obj)/double(dig_pow))); Line(GlobalVariableGet(tp_buy),tp_buy,col_tp,STYLE_DASH,1,true); } if(price_obj<price_glo) // 止损 { GlobalVariableSet(sl_buy,(double(price_obj)/double(dig_pow))); Line(GlobalVariableGet(sl_buy),sl_buy,col_sl,STYLE_DASH,1,true); } break; case 2: // 卖出订单 if(price_obj>price_glo) // 止损 { GlobalVariableSet(sl_sell,(double(price_obj)/double(dig_pow))); Line(GlobalVariableGet(sl_sell),sl_sell,col_sl,STYLE_DASH,1,true); } if(price_obj<price_glo) // 止盈 { GlobalVariableSet(tp_sell,(double(price_obj)/double(dig_pow))); Line(GlobalVariableGet(tp_sell),tp_sell,col_tp,STYLE_DASH,1,true); } break; } ObjectSetDouble(0,m_name,OBJPROP_PRICE,(double(price_glo)/double(dig_pow))); } } }
在图表建模过程中, 订单通过 COrder 类的 Check 函数进行检查。该函数传递所有存储订单信息的全局变量。还有一个单独的全局变量, 其中包含有关最后一次调用的时间信息。这允许在最后一次调用函数和当前图表绘制时间之间每次调用检查整个价格范围 (一分钟时间帧)。
如果价格到达停止线之一, 或在此期间突破, 控制权被传递给删除订单的函数 (COrder 类中的 Delete 函数)。
void Check( datetime m_time, double m_price_buy, double m_price_tp_buy, double m_price_sl_buy, double m_price_sell, double m_price_tp_sell, double m_price_sl_sell ) { int start_of_z=0; int end_of_z=0; datetime time_end_check=datetime(GlobalVariableGet(time_end_order_check)); if(time_end_check<=0){time_end_check=m_time;} GlobalVariableSet(time_end_order_check,m_time); start_of_z=Bars(_Symbol,PERIOD_M1,real_start,time_end_check); end_of_z=Bars(_Symbol,PERIOD_M1,real_start,m_time); for(int z=start_of_z; z<end_of_z; z++) { COrder del; double p_bid_high=period_m1[z].high; double p_bid_low=period_m1[z].low; double p_ask_high=p_bid_high+(spread*_Point); double p_ask_low=p_bid_low+(spread*_Point); if(m_price_buy>0) // 这是一笔买入订单 { if(ObjectFind(0,tp_buy)>=0) { if(m_price_tp_buy<=p_bid_high && m_price_tp_buy>=p_bid_low) // 止盈触发 {del.Delete(m_price_tp_buy,0,1);} // 在止盈价平仓 } if(ObjectFind(0,sl_buy)>=0) { if(m_price_sl_buy>=p_bid_low && m_price_sl_buy<=p_bid_high) // 止损触发 {del.Delete(m_price_sl_buy,0,1);} // 在止损价平仓 } } if(m_price_sell>0) // 这是一笔卖出订单 { if(ObjectFind(0,tp_sell)>=0) { if(m_price_sl_sell<=p_ask_high && m_price_sl_sell>=p_ask_low) // 止损触发 {del.Delete(0,m_price_sl_sell,2);} // 在止损价平仓 } if(ObjectFind(0,sl_sell)>=0) { if(m_price_tp_sell>=p_ask_low && m_price_tp_sell<=p_ask_high) // 止盈触发 {del.Delete(0,m_price_tp_sell,2);} // 在止盈价平仓 } } } }
这总结了该类的主要函数。我们来看看直接负责在图表上绘制蜡烛的函数。
func_filling() 函数
由于切换周期会重新初始化指标, 所以必需重新填充图表, 并放置从过去到当前时间的蜡烛 (所谓的 "尾巴")。这个函数也是在新蜡烛生成之前使用的, 它允许常规化图表的 "尾部" 并提高显示精度。
该函数传递当前周期的数据数组, 当前显示时间, 所有的蜡烛数量和当前绘制的蜡烛。一旦执行, 该函数返回最后显示的蜡烛开盘时间以及随后的蜡烛开盘时间。指标数组也被填充, 函数返回完成标志 "work_status"。
函数使用 "for 循环来填充先前显示在绘制蜡烛上的整个指标缓冲区, 以及当前绘制的蜡烛的价格值 (通常等于开盘价)。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Filling 函数 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_filling(MqlRates &input_rates[], // 输入 (当前周期) 数据来填充 datetime input_end_time_indicator, // 指标的当前时间 int input_all_bars_indicator, // 指标的所有柱线数量 datetime &output_time_end_filling, // 最后一根柱线的开盘时间 datetime &output_time_next_filling, // 下一根柱线的开盘时间 int input_end_bar_indicator, // 指标的当前 (绘制) 柱线 double &output_o[], double &output_h[], double &output_l[], double &output_c[], double &output_col[], char &work_status) // 操作状态 { if(work_status==1) { int stopped_rates_bar; for(int x=input_all_bars_indicator,y=0;x>0;x--,y++) { if(input_rates[y].time<input_end_time_indicator) { output_o[x]=input_rates[y].open; output_h[x]=input_rates[y].high; output_l[x]=input_rates[y].low; output_c[x]=input_rates[y].close; if(output_o[x]>output_c[x])output_col[x]=0; else output_col[x]=1; output_time_end_filling=input_rates[y].time; output_time_next_filling=input_rates[y+1].time; input_end_bar_indicator=x; stopped_rates_bar=y; } else break; } output_o[input_end_bar_indicator]=input_rates[stopped_rates_bar].open; output_h[input_end_bar_indicator]=output_o[input_end_bar_indicator]; output_l[input_end_bar_indicator]=output_o[input_end_bar_indicator]; output_c[input_end_bar_indicator]=output_o[input_end_bar_indicator]; work_status=-1; } }
一旦执行, 控制权转移到三个函数之一来绘制当前的蜡烛。我们从最快的一个开始研究它们。
func_candle_per_seconds() 函数每秒钟绘制蜡烛
与其它两个函数不同的是, 在重载指标或更改图表绘制速度之前, 控制权不会转移到其它函数。通过计时器每秒发生一次调用, 在此期间, 当前的蜡烛被绘制 (填充数据)。首先, 将数据从传递的数组复制到当前的蜡烛, 然后将初始数据传递到下一根蜡烛。在最后, 函数传递最后的蜡烛形成时间。
上述函数负责蜡烛发生的 "第七速度" (参见控制面板)。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| 每秒蜡烛函数 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_candle_per_seconds(MqlRates &input_rates[], datetime &input_end_time_indicator, int input_bars_now_rates, int input_number_now_rates, int &input_end_bar_indicator, double &output_o[], double &output_h[], double &output_l[], double &output_c[], double &output_col[], char &work_status) { if(work_status==-1) { if(input_number_now_rates<input_bars_now_rates) { if(input_number_now_rates!=0) { output_o[input_end_bar_indicator]=input_rates[input_number_now_rates-1].open; output_h[input_end_bar_indicator]=input_rates[input_number_now_rates-1].high; output_l[input_end_bar_indicator]=input_rates[input_number_now_rates-1].low; output_c[input_end_bar_indicator]=input_rates[input_number_now_rates-1].close; if(output_o[input_end_bar_indicator]>output_c[input_end_bar_indicator])output_col[input_end_bar_indicator]=0; else output_col[input_end_bar_indicator]=1; } input_end_bar_indicator--; output_o[input_end_bar_indicator]=input_rates[input_number_now_rates].open; output_h[input_end_bar_indicator]=input_rates[input_number_now_rates].high; output_l[input_end_bar_indicator]=input_rates[input_number_now_rates].low; output_c[input_end_bar_indicator]=input_rates[input_number_now_rates].close; if(output_o[input_end_bar_indicator]>output_c[input_end_bar_indicator])output_col[input_end_bar_indicator]=0; else output_col[input_end_bar_indicator]=1; input_end_time_indicator=input_rates[input_number_now_rates+1].time; } } }
以下两个函数彼此非常相似。其中一个按时间构建蜡烛, 尽管有分笔报价。第二个 ("珠宝") 使用文章开头描述的分笔报价发生器来更加完整地模拟行情。
func_of_form_candle() 用于构建蜡烛
输入参数与之前的一样 (OHLC)。至于功能, 一切都很简单。在从 func_filling() 函数接收到的时间开始, 价格从 M1 时间帧数据复制到当前蜡烛周期。事实证明, 通过改变时间, 蜡烛逐渐形成。从第二到第六的速度是这样构建的 (参见控制面板)。在时间到达当前时间帧的蜡烛完成时刻之后, "work_status" 标志被改变, 以便计时器下一次执行时再次调用 func_filling() 函数。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| 形成蜡烛的函数 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_of_form_candle(MqlRates &input_rates[], int input_bars, datetime &input_time_end_filling, datetime &input_end_time_indicator, datetime &input_time_next_filling, int input_end_bar_indicator, double &output_o[], double &output_h[], double &output_l[], double &output_c[], double &output_col[], char &work_status) { if(work_status==-1) { int start_of_z=0; int end_of_z=0; start_of_z=Bars(_Symbol,PERIOD_M1,real_start,input_time_end_filling); end_of_z=Bars(_Symbol,PERIOD_M1,real_start,input_end_time_indicator); for(int z=start_of_z; z<end_of_z; z++) { output_c[input_end_bar_indicator]=input_rates[z].close; if(output_h[input_end_bar_indicator]<input_rates[z].high)output_h[input_end_bar_indicator]=input_rates[z].high; if(output_l[input_end_bar_indicator]>input_rates[z].low)output_l[input_end_bar_indicator]=input_rates[z].low; if(output_o[input_end_bar_indicator]>output_c[input_end_bar_indicator])output_col[input_end_bar_indicator]=0; else output_col[input_end_bar_indicator]=1; } if(input_end_time_indicator>=input_time_next_filling)work_status=1; } }
现在我们来看看这个函数, 它可以形成一个尽可能接近行情的蜡烛。
func_of_form_jeweler_candle() 函数用于蜡烛的 "珠宝" 模拟
在函数的开始, 一切都像以前的版本一样。除了最后一分钟, 分钟时间帧的数据完全填满了当前的蜡烛。它的数据被传递到 func_tick_generation() 函数来生成分笔报价, 这已在文章的开头部分描述过。每次调用该函数时, 接收到的分笔报价数组将逐渐作为当前蜡烛的收盘价传递, 同时考虑到对 "阴影" 的调整。当数组的 "分笔报价" 结束时, 重复该过程。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| 形成珠宝蜡烛的函数 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_of_form_jeweler_candle(MqlRates &input_rates[], // 用于生成分笔报价的信息 int input_bars, // 信息数组的大小 datetime &input_time_end_filling, // 快速填充的结束时间 datetime &input_end_time_indicator, // 指标的最后模拟时间 datetime &input_time_next_filling, // 距当前时间帧的柱线完全形成的剩余时间 int input_end_bar_indicator, // 指标的当前绘制柱线 double &output_o[], double &output_h[], double &output_l[], double &output_c[], double &output_col[], char &work_status // 操作结束类型 (用于快速填充函数的命令0 ) { if(work_status==-1) { int start_of_z=0; int current_of_z=0; start_of_z=Bars(_Symbol,PERIOD_M1,real_start,input_time_end_filling)-1; current_of_z=Bars(_Symbol,PERIOD_M1,real_start,input_end_time_indicator)-1; if(start_of_z<current_of_z-1) { for(int z=start_of_z; z<current_of_z-1; z++) { output_c[input_end_bar_indicator]=input_rates[z].close; if(output_h[input_end_bar_indicator]<input_rates[z].high)output_h[input_end_bar_indicator]=input_rates[z].high; if(output_l[input_end_bar_indicator]>input_rates[z].low)output_l[input_end_bar_indicator]=input_rates[z].low; if(output_o[input_end_bar_indicator]>output_c[input_end_bar_indicator])output_col[input_end_bar_indicator]=0; else output_col[input_end_bar_indicator]=1; } input_end_time_indicator=input_rates[current_of_z].time; } // 得到数组中的分笔报价 static int x=0; // 数组计数器和开始标志 static double tick_current[]; static int tick_current_size=0; if(x==0) { func_tick_generation(input_rates[current_of_z-1],tick_current); tick_current_size=ArraySize(tick_current); if(output_h[input_end_bar_indicator]==0) {output_h[input_end_bar_indicator]=tick_current[x];} if(output_l[input_end_bar_indicator]==0) {output_l[input_end_bar_indicator]=tick_current[x];} output_c[input_end_bar_indicator]=tick_current[x]; } if(x<tick_current_size) { output_c[input_end_bar_indicator]=tick_current[x]; if(tick_current[x]>output_h[input_end_bar_indicator]) {output_h[input_end_bar_indicator]=tick_current[x];} if(tick_current[x]<output_l[input_end_bar_indicator]) {output_l[input_end_bar_indicator]=tick_current[x];} if(output_o[input_end_bar_indicator]>output_c[input_end_bar_indicator])output_col[input_end_bar_indicator]=0; else output_col[input_end_bar_indicator]=1; x++; } else { input_end_time_indicator=input_rates[current_of_z+1].time; x=0; tick_current_size=0; ArrayFree(tick_current); } if(input_end_time_indicator>input_time_next_filling) {work_status=1;} } }
所有这三种生成蜡烛的函数都被合并在 Merger 函数中。
用于组合模拟的 func_merger() 函数
操作中使用的函数取决于 switch 操作符选择的速度。该函数有三种类型。任何情况都以 func_filling() 函数开始, 然后控制权传递给三个蜡烛生成函数之一: func_of_form_jeweler_candle(), func_of_form_candle() 或 func_candle_per_seconds()。传递第二到第六 (含) 速度时, 每次均要重新计算时间。func_calc_time() 函数计算当前时间帧所需部分, 并将其添加到当前时间。竞买价取自当前蜡烛的收盘价格, 竞卖价依据从服务器收到的点差数据计算。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Merger 函数 | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void func_merger() { switch(button_speed) { case 1: { func_filling(period_array,end_time_indicator,all_bars_indicator,time_open_end_rates,time_open_next_rates,end_bar_indicator,TST_C_O,TST_C_H,TST_C_L,TST_C_C,TST_C_Col,status); func_of_form_jeweler_candle(period_m1,bars_m1,time_open_end_rates,end_time_indicator,time_open_next_rates,end_bar_indicator,TST_C_O,TST_C_H,TST_C_L,TST_C_C,TST_C_Col,status); price_bid_now=TST_C_C[end_bar_indicator]; price_ask_now=price_bid_now+(spread*_Point); } break; case 2: { func_filling(period_array,end_time_indicator,all_bars_indicator,time_open_end_rates,time_open_next_rates,end_bar_indicator,TST_C_O,TST_C_H,TST_C_L,TST_C_C,TST_C_Col,status); func_of_form_candle(period_m1,bars_m1,time_open_end_rates,end_time_indicator,time_open_next_rates,end_bar_indicator,TST_C_O,TST_C_H,TST_C_L,TST_C_C,TST_C_Col,status); price_bid_now=TST_C_C[end_bar_indicator]; price_ask_now=price_bid_now+(spread*_Point); end_time_indicator+=func_calc_time(time_open_end_rates,time_open_next_rates,13); } break; case 3: { ... end_time_indicator+=func_calc_time(time_open_end_rates,time_open_next_rates,11); } break; case 4: { ... end_time_indicator+=func_calc_time(time_open_end_rates,time_open_next_rates,9); } break; case 5: { ... end_time_indicator+=func_calc_time(time_open_end_rates,time_open_next_rates,7); } break; case 6: { ... end_time_indicator+=func_calc_time(time_open_end_rates,time_open_next_rates,5); } break; case 7: { func_filling(period_array,end_time_indicator,all_bars_indicator,time_open_end_rates,time_open_next_rates,end_bar_indicator,TST_C_O,TST_C_H,TST_C_L,TST_C_C,TST_C_Col,status); func_candle_per_seconds(period_array,end_time_indicator,bars_now_rates,number_now_rates,end_bar_indicator,TST_C_O,TST_C_H,TST_C_L,TST_C_C,TST_C_Col,status); price_bid_now=TST_C_C[end_bar_indicator]; price_ask_now=price_bid_now+(spread*_Point); } break; } }
可能的用途
我建议使用这个指标来测试新思路和交易策略, 模拟新入行交易者在特定情况下的行为, 实行入场和离场。主要涉及的技术工具: 例如, 这个指标可以用来绘制 埃洛特波浪, 通道或测试支撑/阻力线的操作。
指标操作示例:
结束语
现在我将揭示这个秘密: 究竟为什么这个生成类型之一被称为 "珠宝"?
它很简单。在开发这个应用程序的时候, 我得出这样的结论: 这种平滑和准确的建模对于测试大多数策略并不是必须的。所以, 这是一种奢侈, 一件瑰宝。这些分笔报价模拟的波动几乎可以与点差媲美, 对策略的流动仅有微弱的影响, 更不用说考虑测试速度了。当有可能倒退回下一个方便的点位, 任何人都不可能浪费好几天的时间来捕捉一个入场点。
至于代码, 不排除各种失败的可能性。不过, 这不应该影响整个策略的分析。毕竟, 所有的基本操作都存储在全局变量中, 并且可以简单地重新加载时间帧或终端 (不关闭指标窗口), 然后继续进一步仿真。
在所描述的代码中已省略了许多辅助函数。它们很简单, 或已在文档中进行了解释。无论如何, 如果您有任何不明白的地方, 请随时提问。一如既往, 高度感谢任何品评。
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自俄文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/3965
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 交易中不同类型移动平均线的比较
交易中不同类型移动平均线的比较

有办法获得 MT4 版本吗?
我没有写 MT4。但也许有人会写。
晚上好,如何安装这个迷你模拟器? 我在这里试过了,但没有成功。
晚上好,如何安装这个迷你模拟器? 我在这里试过了,但没有成功。
打开 MetaEditor。
如下图所示,在打开的文件夹中选择 "STSv1.1.mq5 "文件。打开已放置的文件 (STSv1.1.mq5)。
然后选择如图(下图)所示,在打开的文件夹中放入包含图像的解压缩文件夹 "for_STS.zip"。
然后编译。
在 MT5 中作为指标使用。
Help, I get an error.
2021.11.08 00:04:32.398 STSv1.1(EURUSD,M1) 'STSv1.1.mq5' 中的数组超出范围 (734,54)
构建 2875。
这行代码发出警告。我能修复它吗?
output_o[input_end_bar_indicator]=input_rates[stopped_rates_bar].open;