
MQL5 中的高级订单执行算法:TWAP、VWAP 和冰山订单
概述
想象一下,你站在交易大厅的边缘,随着价格实时变化,你的心跳也随之加速。一步走错,一次超量下单,你的优势就会瞬间消失殆尽。欢迎来到这个世界,在这里,执行质量不仅仅是一件好事,它是区分赢家和其他人的秘密武器。
几十年来,机构巨头们一直悄悄地运用复杂的算法来细分、分割和隐蔽地部署他们的订单,所有这些都是为了避免滑点和控制市场冲击。现在,得益于 MQL5 的灵活性,每个雄心勃勃的散户交易者都能轻松获得同样的强大交易策略。
有什么厉害的?
想象一下:你发现了一个绝佳的机会,决定放手一搏。你猛打市价单,买入全部交易量,却眼睁睁看着价格在你自己的交易压力下滑远。几秒钟之内,你理想的方案就变成了摇摇欲坠的妥协方案。这就是市场冲击带来的臭名昭著的拖累 —— 即使在流动性最强的市场,它也会产生影响。
执行算法是你的解药,通过将大订单拆分成一系列较小的、经过策略性时间安排的订单,他们可以平滑订单簿上的信息。结果如何?滑点减少,成交更精准,平均成交价格有整体提高。
从象牙塔到你的桌面
“当然,”你可能会耸耸肩,“但我经手的又不是机构资金。”关键是:你完全不必这么做。无论你投入半手还是少量迷你手,波动性仍然会影响你的执行。这些工具可以帮助您:
- 驯服滑点:即使是数额不大的订单,在震荡的市场中也可能出现波动。
- 磨砺你的锋芒:分层执行往往会让你获得比一次性赌博更有利的平均价格。
- 保持禅意:自动化的工作流消除了恐慌性买入或恐慌性卖出的诱惑。
- 无缝扩展:随着账户的增长,无论订单金额有多大,您的执行都能保持高效。
-
低调行事:特别是冰山订单,可以隐藏您的真实订单规模,让窥探的算法难以猜测。
如今的民主化环境意味着,曾经需要数百万美元预算的执行技术现在可以在你的个人交易站上运行。通过将完善的 MQL5 代码(用于 TWAP、VWAP 和 Iceberg 策略)添加到您的平台中,您将拥有机构级的强大火力 —— 而无需离开散户领域。
准备好彻底改变你的执行流程吧。游戏正在改变,有了这些算法在你的工具箱里,你就会玩得赢。
理解执行算法
在深入研究实现细节之前,有必要了解每种执行算法背后的理论,以及它们为什么在不同的市场场景中有效。
- 时间加权平均价格(TWAP):TWAP 是一种简单的执行算法,它将大订单分成相等的部分,并在设定的时间段内以固定的时间间隔发送它们。其目的是匹配该工具在那段时间内的平均价格。
-
工作原理:
- 在开始和结束之间按固定时间间隔发送订单。
- 通常使用相等交易量的订单(尽管你可以增加订单大小的随机性)。
- 遵循预定的时间表,不受价格波动的影响。
-
将市场冲击均匀分散到一段时间内,以保持较低的滑点。
-
何时使用:
- 你需要特定时间周期内的平均成交价格。
- 交易期间流动性保持稳定。
- 您需要在确定的时间内完成订单。
-
你更喜欢简单、可预测的方法。
-
- 成交量加权平均价格(VWAP):VWAP 通过根据预期交易量对订单规模进行加权,从而改进了 TWAP。它不会进行等量交易,而是在交易量较高时进行较大量的交易。
-
工作原理:
- 根据历史交易量模式按比例分配订单规模。
- 分析历史交易量以预测未来交易量分布。
- 在某些实现方式中,可以适应实时交易量变化。
-
在高峰期执行更多操作以减少影响。
-
何时使用:
- 您的表现将以 VWAP 为衡量标准。
- 成交量遵循可预测的每日模式。
- 你正在交易的市场流动性会随着交易时段的变化而波动。
-
你想与市场的自然流动性保持一致。
-
- 冰山订单:冰山订单专注于隐藏大订单的真实规模。每次只能看到一小部分“尖端”;一旦尖端完成,下一部分就会出现。
-
工作原理:
- 仅显示订单总量的一部分。
- 每次执行完成后,都会释放新的可见数据块。
- 你可以固定或随机改变可见量的大小,以降低被检测到的概率。
-
通常以限价单的形式下单,以便更好地控制价格。
-
何时使用:
- 你需要隐藏你的订单的完整规模。
- 市场流动性不高,大量交易可能会影响价格。
- 您希望将执行价格维持在特定水平。
-
你担心其他交易者会发现并抢先下单。
-
MQL5 中的实现
现在我们已经理解了这些执行算法背后的理论,让我们在 MQL5 中实现它们。我们将创建一个模块化的、面向对象的框架,允许这些算法单独使用或组合成一个统一的执行系统。
基类:CExecutionAlgorithm
我们将首先定义一个基类,为所有执行算法提供通用功能:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Base class for all execution algorithms | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CExecutionAlgorithm { protected: string m_symbol; // Symbol to trade double m_totalVolume; // Total volume to execute double m_executedVolume; // Volume already executed double m_remainingVolume; // Volume remaining to execute datetime m_startTime; // Start time for execution datetime m_endTime; // End time for execution bool m_isActive; // Flag indicating if the algorithm is active int m_totalOrders; // Total number of orders placed int m_filledOrders; // Number of filled orders double m_avgExecutionPrice; // Average execution price double m_executionValue; // Total value of executed orders int m_slippage; // Allowed slippage in points public: // Constructor CExecutionAlgorithm(string symbol, double volume, datetime startTime, datetime endTime, int slippage = 3); // Destructor virtual ~CExecutionAlgorithm(); // Common methods virtual bool Initialize(); virtual bool Execute() = 0; virtual bool Update() = 0; virtual bool Terminate(); // Utility methods bool PlaceOrder(ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, double volume, double price); bool CancelOrder(ulong ticket); void UpdateAverageExecutionPrice(double price, double volume); // Getters string GetSymbol() const { return m_symbol; } double GetTotalVolume() const { return m_totalVolume; } double GetExecutedVolume() const { return m_executedVolume; } double GetRemainingVolume() const { return m_remainingVolume; } datetime GetStartTime() const { return m_startTime; } datetime GetEndTime() const { return m_endTime; } bool IsActive() const { return m_isActive; } int GetTotalOrders() const { return m_totalOrders; } int GetFilledOrders() const { return m_filledOrders; } double GetAverageExecutionPrice() const { return m_avgExecutionPrice; } };
PlaceOrder 方法尤为重要,因为它负责处理实际的订单执行并更新交易量跟踪:
bool CExecutionAlgorithm::PlaceOrder(ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, double volume, double price) { // Prepare the trade request MqlTradeRequest request; MqlTradeResult result; ZeroMemory(request); ZeroMemory(result); request.action = TRADE_ACTION_DEAL; request.symbol = m_symbol; request.volume = volume; request.type = orderType; request.price = price; request.deviation = m_slippage; request.magic = 123456; // Magic number for identification // Send the order bool success = OrderSend(request, result); if(!success) { Print("OrderSend error: ", GetLastError()); return false; } // Check the result if(result.retcode != TRADE_RETCODE_DONE) { Print("OrderSend failed with code: ", result.retcode); return false; } // Update statistics m_totalOrders++; m_filledOrders++; m_executedVolume += volume; m_remainingVolume -= volume; UpdateAverageExecutionPrice(price, volume); // Store the order ticket for future reference ulong ticket = result.order; return true; }
该函数通过对 MqlTradeRequest 和 MqlTradeResult 进行零初始化,填充交易品种、成交量、订单类型、价格、滑点和幻数,然后调用 OrderSend 来构建和发送市价单。如果发送失败或经纪商的返回代码不是 TRADE_RETCODE_DONE,则会记录错误并返回 false。成功后,它会更新内部计数器(总计数/完成计数、已执行和剩余量),重新计算平均价格,获取单号 ID,并返回 true。
TWAP 的实现
TWAP 算法将执行周期划分为相等的时间间隔,并在每个时间间隔内下达大小相等(或随机)的订单:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) Algorithm | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CTWAP : public CExecutionAlgorithm { private: int m_intervals; // Number of time intervals int m_currentInterval; // Current interval datetime m_nextExecutionTime; // Next execution time double m_intervalVolume; // Volume per interval bool m_useRandomization; // Whether to randomize order sizes double m_randomizationFactor; // Factor for randomization (0-1) ENUM_ORDER_TYPE m_orderType; // Order type (buy or sell) bool m_firstOrderPlaced; // Flag to track if first order has been placed int m_initialDelay; // Initial delay in seconds before first execution datetime m_lastCheckTime; // Last time order status was checked int m_checkInterval; // How often to check order status (seconds) public: // Constructor CTWAP(string symbol, double volume, datetime startTime, datetime endTime, int intervals, ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, bool useRandomization = false, double randomizationFactor = 0.2, int slippage = 3, int initialDelay = 10); // Implementation of virtual methods virtual bool Initialize() override; virtual bool Execute() override; virtual bool Update() override; virtual bool Terminate() override; // TWAP specific methods void CalculateIntervalVolume(); datetime CalculateNextExecutionTime(); double GetRandomizedVolume(double baseVolume); bool IsTimeToExecute(); };
关键方法:CalculateNextExecutionTime
这个方法确保订单在时间上合理间隔,首单会有初始延迟:datetime CTWAP::CalculateNextExecutionTime() { // Calculate the duration of each interval int totalSeconds = (int)(m_endTime - m_startTime); int intervalSeconds = totalSeconds / m_intervals; // Calculate the next execution time datetime nextTime; if(m_currentInterval == 0) { // First interval - start at the defined start time plus initial delay nextTime = m_startTime + m_initialDelay; Print("TWAP: First execution time calculated with ", m_initialDelay, " seconds delay: ", TimeToString(nextTime)); } else { // For subsequent intervals, ensure proper spacing from current time datetime currentTime = TimeCurrent(); nextTime = currentTime + intervalSeconds; // Make sure we don't exceed the end time if(nextTime > m_endTime) nextTime = m_endTime; Print("TWAP: Next execution time calculated: ", TimeToString(nextTime), " (interval: ", intervalSeconds, " seconds)"); } return nextTime; }
此方法将从 m_startTime 到 m_endTime 的窗口分割成 m_intervals 个相等的段,并返回何时触发下一次交易:第一次调用时,它只是 m_startTime + m_initialDelay,而每次后续调用时,它都是 TimeCurrent() + 一个间隔的秒数(但一定不会超过 m_endTime)。
Execute 方法:Execute 方法检查是否到了下单的时间,并处理实际的下单操作:
bool CTWAP::Execute() { if(!m_isActive) return false; // Check if it's time to execute the next order if(!IsTimeToExecute()) return true; // Not time yet // Calculate the volume for this execution double volumeToExecute = m_useRandomization ? GetRandomizedVolume(m_intervalVolume) : m_intervalVolume; // Ensure we don't exceed the remaining volume if(volumeToExecute > m_remainingVolume) volumeToExecute = m_remainingVolume; // Get current market price double price = 0.0; if(m_orderType == ORDER_TYPE_BUY) price = SymbolInfoDouble(m_symbol, SYMBOL_ASK); else price = SymbolInfoDouble(m_symbol, SYMBOL_BID); Print("TWAP: Placing order for interval ", m_currentInterval, ", Volume: ", DoubleToString(volumeToExecute, 2), ", Price: ", DoubleToString(price, _Digits)); // Place the order using OrderSend directly for more control MqlTradeRequest request; MqlTradeResult result; ZeroMemory(request); ZeroMemory(result); request.action = TRADE_ACTION_DEAL; request.symbol = m_symbol; request.volume = volumeToExecute; request.type = m_orderType; request.price = price; request.deviation = m_slippage; request.magic = 123456; // Magic number for identification // Send the order bool success = OrderSend(request, result); if(!success) { Print("TWAP: OrderSend error: ", GetLastError()); return false; } // Check the result if(result.retcode != TRADE_RETCODE_DONE) { Print("TWAP: OrderSend failed with code: ", result.retcode); return false; } // Update statistics m_totalOrders++; m_filledOrders++; m_executedVolume += volumeToExecute; m_remainingVolume -= volumeToExecute; // Update interval counter m_currentInterval++; m_firstOrderPlaced = true; // Calculate the time for the next execution if(m_currentInterval < m_intervals && m_remainingVolume > 0) m_nextExecutionTime = CalculateNextExecutionTime(); else m_isActive = false; // All intervals completed or no volume left Print("TWAP: Executed ", DoubleToString(volumeToExecute, 2), " at price ", DoubleToString(price, _Digits), ". Remaining: ", DoubleToString(m_remainingVolume, 2), ", Next execution: ", TimeToString(m_nextExecutionTime)); return true; }
此 Execute 方法管理 TWAP 运行的一个片段。首先,如果策略未激活或尚未到交易时间,则会中止交易。届时,它会从剩余的交易量中选取一个固定或随机的部分(永远不会超过剩余的交易量),然后查找当前的卖价(买入)或买价(卖出)。它会记录间隔、成交量和价格,构建一个包含你的交易品种、成交量、类型、价格、滑点和幻数的 MqlTradeRequest,并调用 OrderSend。如果发送失败或经纪商返回除 TRADE_RETCODE_DONE 以外的任何内容,则会打印错误并返回 false。
成功后,它会增加订单计数器,调整已执行和剩余的交易量,增加间隔计数,标记第一个订单已发出,然后安排下一次执行时间,或者如果间隔或交易量用完,则停止该策略。最后,它会记录发生的事情并返回 true。
VWAP 的实现
VWAP 算法与 TWAP 算法类似,但它根据历史交易量模式来分配订单规模://+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Volume-Weighted Average Price (VWAP) Algorithm | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CVWAP : public CExecutionAlgorithm { private: int m_intervals; // Number of time intervals int m_currentInterval; // Current interval datetime m_nextExecutionTime; // Next execution time double m_volumeProfile[]; // Historical volume profile double m_intervalVolumes[]; // Volume per interval based on profile bool m_adaptiveMode; // Whether to adapt to real-time volume ENUM_ORDER_TYPE m_orderType; // Order type (buy or sell) int m_historyDays; // Number of days to analyze for volume profile bool m_profileLoaded; // Flag indicating if profile was loaded bool m_firstOrderPlaced; // Flag to track if first order has been placed int m_initialDelay; // Initial delay in seconds before first execution datetime m_lastCheckTime; // Last time order status was checked int m_checkInterval; // How often to check order status (seconds) public: // Constructor CVWAP(string symbol, double volume, datetime startTime, datetime endTime, int intervals, ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, int historyDays = 5, bool adaptiveMode = true, int slippage = 3, int initialDelay = 10); // Implementation of virtual methods virtual bool Initialize() override; virtual bool Execute() override; virtual bool Update() override; virtual bool Terminate() override; // VWAP specific methods bool LoadVolumeProfile(); void CalculateIntervalVolumes(); void AdjustToRealTimeVolume(); datetime CalculateNextExecutionTime(); double GetCurrentVWAP(); bool IsTimeToExecute(); };与 TWAP 类似,VWAP 也实现了 CalculateNextExecutionTime 方法,以确保订单之间的适当间隔:
datetime CVWAP::CalculateNextExecutionTime() { // Calculate the duration of each interval int totalSeconds = (int)(m_endTime - m_startTime); int intervalSeconds = totalSeconds / m_intervals; // Calculate the next execution time datetime nextTime; if(m_currentInterval == 0) { // First interval - start at the defined start time plus initial delay nextTime = m_startTime + m_initialDelay; Print("VWAP: First execution time calculated with ", m_initialDelay, " seconds delay: ", TimeToString(nextTime)); } else { // For subsequent intervals, ensure proper spacing from current time datetime currentTime = TimeCurrent(); nextTime = currentTime + intervalSeconds; // Make sure we don't exceed the end time if(nextTime > m_endTime) nextTime = m_endTime; Print("VWAP: Next execution time calculated: ", TimeToString(nextTime), " (interval: ", intervalSeconds, " seconds)"); } return nextTime; }
冰山订单的实现
冰山订单通过每次只向市场展示一小部分订单来隐藏订单的真实规模://+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Iceberg Order Implementation | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CIcebergOrder : public CExecutionAlgorithm { private: double m_visibleVolume; // Visible portion of the order double m_minVisibleVolume; // Minimum visible volume double m_maxVisibleVolume; // Maximum visible volume bool m_useRandomVisibleVolume; // Whether to randomize visible volume int m_orderPlacementDelay; // Delay between order placements (ms) bool m_avoidRoundNumbers; // Whether to avoid round numbers in price double m_limitPrice; // Limit price for the orders ulong m_currentOrderTicket; // Current active order ticket ENUM_ORDER_TYPE m_orderType; // Order type (buy or sell) bool m_orderActive; // Flag indicating if an order is currently active int m_priceDeviation; // Price deviation to avoid round numbers (in points) datetime m_lastCheckTime; // Last time order status was checked int m_checkInterval; // How often to check order status (seconds) int m_maxOrderLifetime; // Maximum lifetime for an order in seconds datetime m_orderPlacementTime; // When the current order was placed public: // Constructor CIcebergOrder(string symbol, double volume, double limitPrice, ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, double visibleVolume, double minVisibleVolume = 0.0, double maxVisibleVolume = 0.0, bool useRandomVisibleVolume = true, int orderPlacementDelay = 1000, bool avoidRoundNumbers = true, int priceDeviation = 2, int slippage = 3); // Implementation of virtual methods virtual bool Initialize() override; virtual bool Execute() override; virtual bool Update() override; virtual bool Terminate() override; // Iceberg specific methods double GetRandomVisibleVolume(); double AdjustPriceToAvoidRoundNumbers(double price); bool CheckAndReplaceOrder(); bool IsOrderFilled(ulong ticket); bool IsOrderPartiallyFilled(ulong ticket, double &filledVolume); bool IsOrderCancelled(ulong ticket); bool IsOrderExpired(ulong ticket); bool IsOrderTimeout(); ulong GetCurrentOrderTicket() { return m_currentOrderTicket; } bool IsOrderActive() { return m_orderActive; } };Execute 方法会在订单中添加一个新的可见部分:
bool CIcebergOrder::Execute() { if(!m_isActive) { Print("Iceberg: Execute called but algorithm is not active"); return false; } // If an order is already active, check its status if(m_orderActive) { Print("Iceberg: Execute called with active order ", m_currentOrderTicket); return CheckAndReplaceOrder(); } // Calculate the volume for this execution double volumeToExecute = m_useRandomVisibleVolume ? GetRandomVisibleVolume() : m_visibleVolume; // Ensure we don't exceed the remaining volume if(volumeToExecute > m_remainingVolume) volumeToExecute = m_remainingVolume; Print("Iceberg: Placing order for ", DoubleToString(volumeToExecute, 2), " at price ", DoubleToString(m_limitPrice, _Digits)); // Place the order using OrderSend directly for more control MqlTradeRequest request; MqlTradeResult result; ZeroMemory(request); ZeroMemory(result); request.action = TRADE_ACTION_PENDING; request.symbol = m_symbol; request.volume = volumeToExecute; request.type = m_orderType; request.price = m_limitPrice; request.deviation = m_slippage; request.magic = 123456; // Magic number for identification // Send the order bool success = OrderSend(request, result); if(!success) { Print("Iceberg: OrderSend error: ", GetLastError()); return false; } // Check the result if(result.retcode != TRADE_RETCODE_DONE) { Print("Iceberg: OrderSend failed with code: ", result.retcode); return false; } // Store the order ticket m_currentOrderTicket = result.order; m_orderActive = true; m_orderPlacementTime = TimeCurrent(); Print("Iceberg: Order placed successfully. Ticket: ", m_currentOrderTicket, ", Volume: ", DoubleToString(volumeToExecute, 2), ", Remaining: ", DoubleToString(m_remainingVolume, 2)); return true; }
Execute 运行时,首先会验证算法是否处于活动状态。如果已经存在一个有效的冰山子订单,它会调用 CheckAndReplaceOrder() 来查看是否需要取消或重新填充。否则,它会选择一个可见的切片(固定或随机),将其限制在剩余总量的范围内,并记录大小和价格。
然后,它构建一个包含交易品种、成交量、限价、滑点和幻数的挂单请求(TRADE_ACTION_PENDING),并调用 OrderSend。如果出现错误或未完成的返回代码,则记录并返回 false;如果成功,则保存新单号,将订单标记为活动状态,记录下单时间,记录详细信息,并返回 true。
Update 方法包含订单超时检测,以确保订单不会无限期地保持有效状态:
bool CIcebergOrder::Update() { if(!m_isActive) { Print("Iceberg: Update called but algorithm is not active"); return false; } // Check if all volume has been executed if(m_remainingVolume <= 0) { Print("Iceberg: All volume executed. Terminating algorithm."); return Terminate(); } // Check if it's time to check order status datetime currentTime = TimeCurrent(); if(currentTime >= m_lastCheckTime + m_checkInterval) { m_lastCheckTime = currentTime; // Log current market conditions double currentBid = SymbolInfoDouble(m_symbol, SYMBOL_BID); double currentAsk = SymbolInfoDouble(m_symbol, SYMBOL_ASK); Print("Iceberg: Market update - Bid: ", DoubleToString(currentBid, _Digits), ", Ask: ", DoubleToString(currentAsk, _Digits), ", Limit Price: ", DoubleToString(m_limitPrice, _Digits)); // If an order is active, check its status if(m_orderActive) { // Check if the order has been active too long if(IsOrderTimeout()) { Print("Iceberg: Order ", m_currentOrderTicket, " has timed out. Replacing it."); // Cancel the current order if(!CancelOrder(m_currentOrderTicket)) { Print("Iceberg: Failed to cancel timed out order ", m_currentOrderTicket); } // Reset order tracking m_orderActive = false; m_currentOrderTicket = 0; // Place a new order after a delay Sleep(m_orderPlacementDelay); return Execute(); } return CheckAndReplaceOrder(); } else { // If no order is active, execute a new one Print("Iceberg: No active order, executing new order"); return Execute(); } } return true; }
定期更新,轮询市场和订单状态,轮询间隔由 m_checkInterval 定义。如果所有交易量都已处理完毕,则程序终止。否则,一旦检查时间到达,它将记录当前的买价/卖价和限价。如果订单处于活动状态,它会测试超时:如果超时,则取消订单,重置状态,休眠 m_orderPlacementDelay,然后重新执行以设置新的切片;如果未超时,则将其交给 CheckAndReplaceOrder() 处理。如果没有活动订单,它就调用 Execute 来发送下一个可见部分。
性能分析器实现
我们的性能分析器类会跟踪这些指标,并提供分析和比较算法性能的方法://+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Performance Analyzer for Execution Algorithms | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CPerformanceAnalyzer { private: string m_symbol; // Symbol being analyzed datetime m_startTime; // Analysis start time datetime m_endTime; // Analysis end time double m_decisionPrice; // Price at decision time double m_avgExecutionPrice; // Average execution price double m_totalVolume; // Total volume executed double m_implementationShortfall; // Implementation shortfall double m_marketImpact; // Estimated market impact double m_slippage; // Average slippage int m_executionTime; // Total execution time in seconds double m_priceImprovement; // Total price improvement public: // Constructor CPerformanceAnalyzer(string symbol, double decisionPrice); // Analysis methods void RecordExecution(datetime time, double price, double volume); void CalculateMetrics(); void CompareAlgorithms(CPerformanceAnalyzer &other); // Reporting methods void PrintReport(); void SaveReportToFile(string filename); // Getters double GetImplementationShortfall() const { return m_implementationShortfall; } double GetMarketImpact() const { return m_marketImpact; } double GetSlippage() const { return m_slippage; } int GetExecutionTime() const { return m_executionTime; } double GetPriceImprovement() const { return m_priceImprovement; } };
CPerformanceAnalyzer 将所有交易后指标集中在一个地方。构建它时,给它一个交易品种和决策时的基准价格;它将当前时间标记为开始时间。当每个子订单成交时,你会调用 RecordExecution(time, price, volume),它会更新运行总计 —— 累计成交量、加权平均成交价格和时间戳。策略执行完毕(或定期执行)后,调用 CalculateMetrics() 函数,该函数会计算:
- 执行成本缺口(决策价格与实际执行成本之间的损益差)
- 平均滑点与报价的比较
- 您的操作预计带来的市场影响
- 总执行时间(结束时间减去开始时间),
- 与基准相比,价格是否有所改善?
您甚至可以通过 CompareAlgorithms(otherAnalyzer) 比较两次运行,看看哪种策略表现更好。最后,PrintReport() 会将关键统计信息输出到日志中以便快速查看,而 SaveReportToFile(filename) 则允许您将完整的报告保存到外部。轻量级读取器可将每个指标公开,以便进行自定义仪表板或进一步分析。
算法性能比较
不同的市场条件适合采用不同的执行算法。以下是一个大致的比较,也就是经验法则:- TWAP:
- 最适合:市场稳定,有持续流动性。
- 优点:简单、可预测的执行模式
- 缺点:无法适应不断变化的市场环境
- VWAP:
- 最适合:成交量模式可预测的市场
- 优点:顺应自然市场节奏,通常能获得更佳价格。
- 缺点:需要历史交易量数据,实现起来也更复杂。
- 冰山订单:
- 最适合:市场流动性较差或价格敏感度较高时
- 优点:最大限度减少市场冲击,维持价格控制
- 缺点:执行时间可能难以预测,存在部分执行的风险。
集成执行算法和交易策略
当这些执行算法与交易策略相结合时,它们真正的力量就会显现出来。本节演示如何将我们的执行算法整合到完整的交易系统中。
执行管理器
为了简化集成,我们将创建一个执行管理器类,作为所有执行算法的接口:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Execution Manager - Facade for all execution algorithms | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CExecutionManager { private: CExecutionAlgorithm* m_algorithm; // Current execution algorithm CPerformanceAnalyzer* m_analyzer; // Performance analyzer public: // Constructor CExecutionManager(); // Destructor ~CExecutionManager(); // Algorithm creation methods bool CreateTWAP(string symbol, double volume, datetime startTime, datetime endTime, int intervals, ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, bool useRandomization = false, double randomizationFactor = 0.2, int slippage = 3); bool CreateVWAP(string symbol, double volume, datetime startTime, datetime endTime, int intervals, ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, int historyDays = 5, bool adaptiveMode = true, int slippage = 3); bool CreateIcebergOrder(string symbol, double volume, double limitPrice, ENUM_ORDER_TYPE orderType, double visibleVolume, double minVisibleVolume = 0.0, double maxVisibleVolume = 0.0, bool useRandomVisibleVolume = true, int orderPlacementDelay = 1000, bool avoidRoundNumbers = true, int priceDeviation = 2, int slippage = 3); // Execution methods bool Initialize(); bool Execute(); bool Update(); bool Terminate(); // Performance analysis void EnablePerformanceAnalysis(double decisionPrice); void PrintPerformanceReport(); // Getters CExecutionAlgorithm* GetAlgorithm() { return m_algorithm; } };
CExecutionManager 充当任何执行算法的简单外界面,并将它们连接成一个统一的交易工作流程。内部包含指向当前选定的 CExecutionAlgorithm(TWAP、VWAP 或冰山订单)的指针,以及一个 CPerformanceAnalyzer,用于跟踪订单的执行情况。
您可以通过调用 Create… 方法之一来选择您的策略 —— 传入交易品种、总成交量、开始/结束时间(对于 TWAP/VWAP)、间隔计数或切片大小、订单类型以及任何算法特定的参数(随机化、历史窗口、限价等)。创建完成后,即可按照常规生命周期进行操作:
- Initialize() 函数用于设置所需的任何状态或数据。
- Execute() 会触发下一个切片或子订单。
- Update() 更新订单填充、市场数据或超时。
-
Terminate() 会在所有工作完成或您想要停止时进行清理。
如果使用 EnablePerformanceAnalysis() 启用性能分析,则管理器将根据决策基准记录执行价格,并且您可以通过 PrintPerformanceReport() 导出简洁的损益和滑点报告。您始终可以使用 GetAlgorithm() 获取原始算法对象,以便进行自定义探测或指标分析。
集成示例
以下是一些将我们的执行算法与不同类型的交易策略相结合的示例:
-
采用 TWAP 执行的趋势跟踪策略。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Trend-Following Strategy with TWAP Execution | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { // Strategy parameters int maPeriodFast = 20; int maPeriodSlow = 50; double volume = 1.0; int executionIntervals = 5; // Calculate indicators double maFast = iMA(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, maPeriodFast, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE, 0); double maSlow = iMA(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, maPeriodSlow, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE, 0); // Check for entry conditions static bool inPosition = false; static CExecutionManager executionManager; if(!inPosition) { // Buy signal: Fast MA crosses above Slow MA if(maFast > maSlow) { // Create TWAP execution algorithm datetime startTime = TimeCurrent(); datetime endTime = startTime + 3600; // 1 hour execution window if(executionManager.CreateTWAP(Symbol(), volume, startTime, endTime, executionIntervals, ORDER_TYPE_BUY)) { executionManager.Initialize(); inPosition = true; Print("Buy signal detected. Starting TWAP execution."); } } } else { // Update the execution algorithm if(executionManager.Update()) { // Check if execution is complete if(!executionManager.GetAlgorithm().IsActive()) { inPosition = false; Print("TWAP execution completed."); } } } }
-
采用成交量加权平均价格 (VWAP) 执行的均值回归策略。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Mean-Reversion Strategy with VWAP Execution | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { // Strategy parameters int rsiPeriod = 14; int rsiOversold = 30; int rsiOverbought = 70; double volume = 1.0; int executionIntervals = 5; // Calculate indicators double rsi = iRSI(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, rsiPeriod, PRICE_CLOSE, 0); // Check for entry conditions static bool inPosition = false; static bool isLong = false; static CExecutionManager executionManager; if(!inPosition) { // Buy signal: RSI oversold if(rsi < rsiOversold) { // Create VWAP execution algorithm datetime startTime = TimeCurrent(); datetime endTime = startTime + 3600; // 1 hour execution window if(executionManager.CreateVWAP(Symbol(), volume, startTime, endTime, executionIntervals, ORDER_TYPE_BUY)) { executionManager.Initialize(); inPosition = true; isLong = true; Print("Buy signal detected. Starting VWAP execution."); } } // Sell signal: RSI overbought else if(rsi > rsiOverbought) { // Create VWAP execution algorithm datetime startTime = TimeCurrent(); datetime endTime = startTime + 3600; // 1 hour execution window if(executionManager.CreateVWAP(Symbol(), volume, startTime, endTime, executionIntervals, ORDER_TYPE_SELL)) { executionManager.Initialize(); inPosition = true; isLong = false; Print("Sell signal detected. Starting VWAP execution."); } } } else { // Update the execution algorithm if(executionManager.Update()) { // Check if execution is complete if(!executionManager.GetAlgorithm().IsActive()) { inPosition = false; Print("VWAP execution completed."); } } // Check for exit conditions if(isLong && rsi > rsiOverbought) { executionManager.Terminate(); inPosition = false; Print("Exit signal detected. Terminating VWAP execution."); } else if(!isLong && rsi < rsiOversold) { executionManager.Terminate(); inPosition = false; Print("Exit signal detected. Terminating VWAP execution."); } } }
- 冰山订单突破策略。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Breakout Strategy with Iceberg Orders | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { // Strategy parameters int channelPeriod = 20; double volume = 1.0; double visibleVolume = 0.1; // Calculate indicators double upperChannel = iHigh(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, iHighest(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, MODE_HIGH, channelPeriod, 1)); double lowerChannel = iLow(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, iLowest(Symbol(), PERIOD_CURRENT, MODE_LOW, channelPeriod, 1)); double currentPrice = SymbolInfoDouble(Symbol(), SYMBOL_BID); // Check for entry conditions static bool inPosition = false; static CExecutionManager executionManager; if(!inPosition) { // Buy signal: Price breaks above upper channel if(currentPrice > upperChannel) { // Create Iceberg Order double limitPrice = upperChannel; // Place limit order at breakout level if(executionManager.CreateIcebergOrder(Symbol(), volume, limitPrice, ORDER_TYPE_BUY, visibleVolume, visibleVolume * 0.8, visibleVolume * 1.2, true, 1000, true, 2, 3)) { executionManager.Initialize(); inPosition = true; Print("Buy breakout detected. Starting Iceberg Order execution."); } } // Sell signal: Price breaks below lower channel else if(currentPrice < lowerChannel) { // Create Iceberg Order double limitPrice = lowerChannel; // Place limit order at breakout level if(executionManager.CreateIcebergOrder(Symbol(), volume, limitPrice, ORDER_TYPE_SELL, visibleVolume, visibleVolume * 0.8, visibleVolume * 1.2, true, 1000, true, 2, 3)) { executionManager.Initialize(); inPosition = true; Print("Sell breakout detected. Starting Iceberg Order execution."); } } } else { // Update the execution algorithm if(executionManager.Update()) { // Check if execution is complete if(!executionManager.GetAlgorithm().IsActive()) { inPosition = false; Print("Iceberg Order execution completed."); } } } }
在所有三个例子中,整合遵循相同的高层模式:
-
保持状态
- 布尔值 inPosition 用于跟踪您当前是否正在处理订单。
-
静态 CExecutionManager executionManager 会跨越分时报价运行,以管理您选择的算法的生命周期。
-
入场逻辑
- 收到入场信号(MA 交叉、RSI 阈值、通道突破)后,调用 executionManager 的相应创建方法(TWAP、VWAP 或 冰山),并传递交易品种、总成交量、时间窗口或限价、切片参数和订单类型。
-
如果创建成功,立即调用 executionManager.Initialize(),设置 inPosition=true,并记录您的开始。
-
持续执行
- 当 inPosition 为 true 时,每次 OnTick() 都会调用 executionManager.Update()。
-
在 Update() 函数内部,管理器会根据需要内部调用 Execute() 函数,轮询成交情况,处理超时或市场更新,并安排下一个切片(或取消/替换冰山订单的子订单)。
-
完成与退出
- 每次更新后,检查 executionManager.GetAlgorithm()->IsActive() 的结果。如果返回 false(所有间隔完成或交易量耗尽),则设置 inPosition=false 并记录执行已完成。
-
在 VWAP 均值回归示例中,还有一个额外的退出检查:如果在执行过程中价格反转超过 RSI 阈值,则调用 executionManager.Terminate() 提前停止。
- 趋势跟踪 + TWAP
入场:快速移动平均线向上穿越慢速移动平均线触发信号。
执行:在接下来的一个小时内,将您的 1 手买入订单分成 5 等份。 - 均值回归 + VWAP
入场:RSI < 30 为买入信号,> 70 为卖出信号。
执行:1 小时内将 1 手按历史成交量分成 5 份进行分配
提前离场:如果信号反转(例如买入期间 RSI > 70),executionManager.Terminate() 将中止剩余的切片。 - 突破 + 冰山
入场:价格突破通道高点(买入)或低点(卖出)
执行:在突破价位设置待定限价单,每次仅显示约 0.1 手,并不断补充直至显示完整的 1 手。
通过替换 CreateTWAP、CreateVWAP 或 CreateIcebergOrder,您可以将任何执行算法插入到信号逻辑中,而无需重复订单管理样板。
集成策略
完整代码:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| IntegratedStrategy.mq5 | //| Copyright 2025, MetaQuotes Software Corp. | //| https://www.metaquotes.net | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2025, MetaQuotes Software Corp." #property link "https://www.metaquotes.net" #property version "1.00" #include "ExecutionAlgorithm.mqh" #include "TWAP.mqh" #include "VWAP.mqh" #include "IcebergOrder.mqh" #include "PerformanceAnalyzer.mqh" #include "ExecutionManager.mqh" // Input parameters input int FastMA = 20; // Fast moving average period input int SlowMA = 50; // Slow moving average period input double TradingVolume = 0.1; // Trading volume input bool UseAdaptiveExecution = true; // Use adaptive execution based on market conditions // Global variables CExecutionManager *g_executionManager = NULL; int g_maHandle1 = INVALID_HANDLE; int g_maHandle2 = INVALID_HANDLE; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { // Initialize execution manager g_executionManager = new CExecutionManager(Symbol(), 3, UseAdaptiveExecution); // Initialize indicators g_maHandle1 = iMA(Symbol(), Period(), FastMA, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE); g_maHandle2 = iMA(Symbol(), Period(), SlowMA, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE); if(g_maHandle1 == INVALID_HANDLE || g_maHandle2 == INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("Failed to create indicator handles"); return INIT_FAILED; } return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { // Clean up if(g_executionManager != NULL) { delete g_executionManager; g_executionManager = NULL; } // Release indicator handles IndicatorRelease(g_maHandle1); IndicatorRelease(g_maHandle2); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { // Update execution algorithms if(g_executionManager != NULL) g_executionManager.UpdateAlgorithms(); // Only process at bar open if(iVolume(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 0) > 1) return; // Get indicator values double fastMA[2], slowMA[2]; if(CopyBuffer(g_maHandle1, 0, 0, 2, fastMA) <= 0 || CopyBuffer(g_maHandle2, 0, 0, 2, slowMA) <= 0) { Print("Failed to copy indicator buffers"); return; } // Check for trend signals bool buySignal = (fastMA[0] > slowMA[0]) && (fastMA[1] <= slowMA[1]); bool sellSignal = (fastMA[0] < slowMA[0]) && (fastMA[1] >= slowMA[1]); // Execute signals using the execution manager if(buySignal) { Print("Buy signal detected"); if(UseAdaptiveExecution) { // Let the execution manager select the best algorithm g_executionManager.ExecuteSignal(SIGNAL_TYPE_BUY, TradingVolume); } else { // Manually create a TWAP algorithm datetime currentTime = TimeCurrent(); CTWAP *twap = g_executionManager.CreateTWAP(TradingVolume, currentTime, currentTime + 3600, 6, ORDER_TYPE_BUY, true); } } else if(sellSignal) { Print("Sell signal detected"); if(UseAdaptiveExecution) { // Let the execution manager select the best algorithm g_executionManager.ExecuteSignal(SIGNAL_TYPE_SELL, TradingVolume); } else { // Manually create a TWAP algorithm datetime currentTime = TimeCurrent(); CTWAP *twap = g_executionManager.CreateTWAP(TradingVolume, currentTime, currentTime + 3600, 6, ORDER_TYPE_SELL, true); } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
IntegratedStrategy.mq5 EA 交易首先声明其元数据(版权、链接、版本),并包含我们所有执行算法类和性能分析器的头文件。然后,它定义了四个用户可调整的输入参数:快慢 SMA 周期、每个信号的总交易量,以及一个布尔标志,用于切换“自适应”执行(其中管理器决定在底层使用 TWAP、VWAP 还是冰山)。同时声明了指向 CExecutionManager 的全局指针和两个指示器句柄,以便它们在时钟周期之间保持不变。
在 OnInit() 中,我们实例化执行管理器 —— 向其传递当前交易品种、最多三个并发算法和我们的自适应标志 —— 然后创建两个 SMA 指标句柄。如果任一句柄失败,初始化将中止。OnDeinit() 函数通过删除管理器和释放指标句柄来进行清理,从而确保在移除 EA 或平台关闭时不会发生内存或句柄泄漏。
核心逻辑位于 OnTick() 函数中。首先,我们在执行管理器上调用 UpdateAlgorithms(),以便根据需要处理、取消或重新填充任何现有的子订单(TWAP 切片、VWAP 块或冰山可见订单)。然后我们等待新的柱形出现(如果成交量仍在累积,则跳过)。开盘后,我们提取快慢两个周期的最后两个 SMA 值。价格由下向上交叉触发买入信号;反之则触发卖出信号。
如果启用自适应执行,我们将信号和交易量交给 g_executionManager.ExecuteSignal(),让它选择合适的算法。否则,我们将手动启动一个 TWAP 实例,运行一小时,并划分六个切片。这种模式将你的入场逻辑(趋势检测)与你的订单管理逻辑清晰地分开,让同一个外界面驱动多种执行方式,而无需重复编写样板代码。
加入止盈后,代码变为:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| IntegratedStrategy.mq5 | //| Copyright 2025, MetaQuotes Software Corp. | //| https://www.metaquotes.net | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2025, MetaQuotes Software Corp." #property link "https://www.metaquotes.net" #property version "1.00" #include "ExecutionAlgorithm.mqh" #include "TWAP.mqh" #include "VWAP.mqh" #include "IcebergOrder.mqh" #include "PerformanceAnalyzer.mqh" #include "ExecutionManager.mqh" #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> // Input parameters input int FastMA = 20; // Fast moving average period input int SlowMA = 50; // Slow moving average period input double TradingVolume = 0.1; // Trading volume input bool UseAdaptiveExecution = true; // Use adaptive execution based on market conditions input double EquityTPPercent = 10.0; // Equity Take Profit in percent input double EquitySLPercent = 5.0; // Equity Stop Loss in percent // Global variables CExecutionManager *g_executionManager = NULL; int g_maHandle1 = INVALID_HANDLE; int g_maHandle2 = INVALID_HANDLE; double g_initialEquity = 0.0; CTrade trade; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { // Record initial equity g_initialEquity = AccountInfoDouble(ACCOUNT_EQUITY); // Initialize execution manager g_executionManager = new CExecutionManager(Symbol(), 3, UseAdaptiveExecution); // Initialize indicators g_maHandle1 = iMA(Symbol(), Period(), FastMA, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE); g_maHandle2 = iMA(Symbol(), Period(), SlowMA, 0, MODE_SMA, PRICE_CLOSE); if(g_maHandle1 == INVALID_HANDLE || g_maHandle2 == INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("Failed to create indicator handles"); return INIT_FAILED; } return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { // Clean up if(g_executionManager != NULL) { delete g_executionManager; g_executionManager = NULL; } // Release indicator handles IndicatorRelease(g_maHandle1); IndicatorRelease(g_maHandle2); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Check equity-based TP and SL, then reset baseline | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CheckEquityTPandSL() { double currentEquity = AccountInfoDouble(ACCOUNT_EQUITY); double tpEquity = g_initialEquity * (1.0 + EquityTPPercent / 100.0); double slEquity = g_initialEquity * (1.0 - EquitySLPercent / 100.0); if(currentEquity >= tpEquity) { Print("Equity Take Profit reached: ", currentEquity); CloseAllPositions(); g_initialEquity = currentEquity; Print("Equity baseline reset to: ", g_initialEquity); } else if(currentEquity <= slEquity) { Print("Equity Stop Loss reached: ", currentEquity); CloseAllPositions(); g_initialEquity = currentEquity; Print("Equity baseline reset to: ", g_initialEquity); } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Close all open positions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CloseAllPositions() { CPositionInfo m_position; CTrade m_trade; for(int i = PositionsTotal() - 1; i >= 0; i--) // loop all Open Positions if(m_position.SelectByIndex(i)) { // select a position m_trade.PositionClose(m_position.Ticket()); // then delete it --period } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { // Check and reset equity thresholds CheckEquityTPandSL(); // Update execution algorithms if(g_executionManager != NULL) g_executionManager.UpdateAlgorithms(); // Only process at bar open if(iVolume(_Symbol, PERIOD_CURRENT, 0) > 1) return; // Get indicator values double fastMA[2], slowMA[2]; if(CopyBuffer(g_maHandle1, 0, 0, 2, fastMA) <= 0 || CopyBuffer(g_maHandle2, 0, 0, 2, slowMA) <= 0) { Print("Failed to copy indicator buffers"); return; } // Check for trend signals bool buySignal = (fastMA[0] > slowMA[0]) && (fastMA[1] <= slowMA[1]); bool sellSignal = (fastMA[0] < slowMA[0]) && (fastMA[1] >= slowMA[1]); // Execute signals using the execution manager if(buySignal) { Print("Buy signal detected"); if(UseAdaptiveExecution) { // Let the execution manager select the best algorithm g_executionManager.ExecuteSignal(SIGNAL_TYPE_BUY, TradingVolume); } else { datetime currentTime = TimeCurrent(); CTWAP *twap = g_executionManager.CreateTWAP(TradingVolume, currentTime, currentTime + 3600, 6, ORDER_TYPE_BUY, true); } } else if(sellSignal) { Print("Sell signal detected"); if(UseAdaptiveExecution) { // Let the execution manager select the best algorithm g_executionManager.ExecuteSignal(SIGNAL_TYPE_SELL, TradingVolume); } else { datetime currentTime = TimeCurrent(); CTWAP *twap = g_executionManager.CreateTWAP(TradingVolume, currentTime, currentTime + 3600, 6, ORDER_TYPE_SELL, true); } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
回测结果
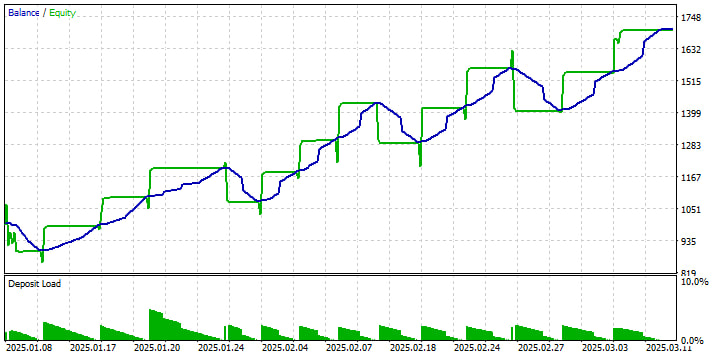
1.净值与余额曲线
绿色的“余额”阶梯显示 EA 平仓时您账户的账面权益;蓝色的“净值”线平滑了交易之间未实现的损益。我们可以看到从 1 月到 3 月初的明显上升趋势,期间出现了一些回调 —— 每次回调的幅度都在 10% 到 16% 左右,之后下一轮的盈利就能恢复之前的涨幅。这种模式表明,该系统在趋势行情中表现良好,但也能承受可承受的净值下跌。
2.交易量与风险利用率
底部的“存款负荷”三角形会随着时间的推移逐渐缩小 —— 这是您的持仓规模占净值的百分比。它从您账户余额的 10% 左右开始,随着您的权益增长而逐渐减少(采用固定交易量),这意味着随着账户余额的增加,我们每笔交易的风险实际上会降低。这就是为什么即使你的美元净值增加,回撤幅度也基本保持不变的原因。
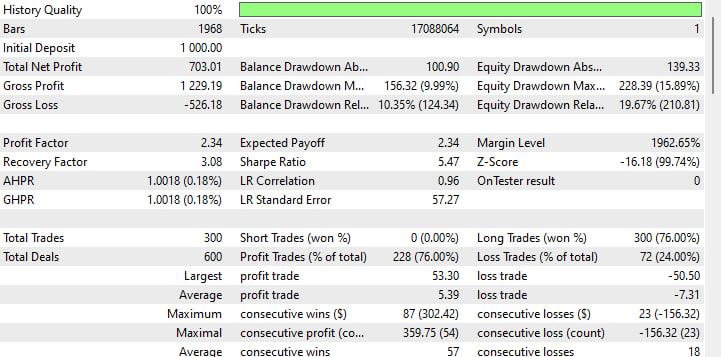
3.关键盈利指标
-
初始入金:1000 美元
-
净利润:+703 美元(约 2 个月内收益率为 70%)
-
利润因子:2.34(每损失 1 美元,您就能赚回 2.34 美元)
-
预期收益:平均每次交易 2.34 美元
-
夏普比率:5.47(非常高 —— 风险调整后收益强劲)
这些数据表明,该策略不仅可以获利,而且还能获得远超其自身波动性的健康缓冲。
4.回撤与恢复
-
最大余额回撤:156 个点或 9.99%
-
最大净值回撤:228 个点或 15.89%
-
恢复因子:3.08(净利润÷最大回撤)
恢复因子高于 2 通常被认为是好的,因此 3.08 的恢复因子意味着你的收益是最大损失的三倍多。
5.交易分布
-
交易总数:300(共 600 笔交易,因此每次进出场都算作两笔)
-
胜率:76%(228 次盈利 vs.72 次亏损)
-
平均盈利:5.39 美元
-
平均亏损:-7.31 美元
虽然你的胜率和利润因子都很高,但要注意的是,你的亏损额平均比盈利额要大 —— 如果市场情况发生变化,这一点需要注意。
6.连胜与稳定性
-
最大连胜纪录:87 笔交易,+302美元
-
最大连败次数:23 笔交易,-156美元
-
平均连胜场数:57笔交易
-
平均连败次数:18笔交易
长期的连胜推动价格上涨,而最长的连败也只会损失大约 15% 的净值。
结论
想象一下,你是一名在拥挤的市场中独自交易的交易者 —— 每一笔交易都至关重要,每一次成交价都影响着盈亏。通过将 TWAP、VWAP 和冰山订单融入你的工具箱,你不再只是对价格波动做出反应;你是在掌控价格波动。这些曾经只有精英机构才能使用的算法现在触手可及,它们像激光一样精准地切割流动性,将混乱的订单簿转化为机遇。
TWAP 成为你稳定的节拍器,在设定的时间间隔内均匀地控制你的体型 —— 非常适合在潮水平静、你只想一帆风顺的时候。VWAP 能让你成为一名精明的成交量追踪者,把握一天中最强劲的交易节奏,并跟随市场的脉搏。当你需要掩盖你的意图时,“冰山订单”会将你的真实规模隐藏在水面之下,只透露出足够多的信息来满足需求,而不会惊动大玩家。
但这并非只是孤立的技巧,借助我们模块化的 MQL5 框架,您可以像扣上新镜头一样轻松地将它们插入任何策略 —— 趋势跟踪者、均值回归者、突破猎手。一个 ExecutionManager 外界面即可让您在交易过程中交换、组合甚至叠加算法,而 PerformanceAnalyzer 则像鹰一样精准地记录分数,精确测量滑点、亏损和市场影响,直至最后一个点。
接下来是什么?把执行看作是一个会适应环境的生物。让你的 TWAP 从剧烈的波动中学习。将您的 VWAP 切片送到最深的池子。教你的冰山意识到捕食者潜伏在哪里,藏得更深。为什么要到此为止?运用机器学习技术预测最佳触发时间(以微秒为单位),或将订单类型混合成定制的混合订单,以匹配您独特的优势。
交易世界永不停歇 —— 你的订单执行也应该如此。大胆尝试,勇于创新,将每一片蛋糕、每一次成交都转化为精心计算的优势。你的优势就蕴藏在代码之中。
为了方便起见,以下是本文所包含文件的概要:
| 文件名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ExecutionAlgorithm.mqh | 所有执行算法的基类 |
| TWAP.mqh | 时间加权平均价格实现 |
| VWAP.mqh | 成交量加权平均价格实现 |
| IcebergOrder.mqh | 冰山订单实现 |
| PerformanceAnalyzer.mqh | 用于分析执行性能的工具 |
| ExecutionManager.mqh | 便于与交易策略集成的外界面设计 |
| IntegratedStrategy.mq5 | 示例 EA 展示了与交易策略的集成 |
| IntegratedStrategy - Take Profit.mq5 | 示例 EA 展示了如何将交易策略与账户余额百分比挂钩,并设置止盈和止损。 |
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/17934
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 您应当知道的 MQL5 向导技术(第 56 部分):比尔·威廉姆斯(Bill Williams)分形
您应当知道的 MQL5 向导技术(第 56 部分):比尔·威廉姆斯(Bill Williams)分形
 突破机器学习的局限(第一部分):缺乏可互操作的度量指标
突破机器学习的局限(第一部分):缺乏可互操作的度量指标
 MQL5 简介(第 16 部分):利用技术图表形态构建 EA 交易
MQL5 简介(第 16 部分):利用技术图表形态构建 EA 交易
 MQL5交易工具(第一部分):构建交互式可视化挂单交易助手工具
MQL5交易工具(第一部分):构建交互式可视化挂单交易助手工具
建议如何测试算法、
时间框架以及任何其他建议。
在编译时也会产生警告
我更改了代码行
m_volumeProfile[intervalIndex] += rates[i].tick_volu
至
它修复了警告
现在需要您就我的其他疑问提供指导,如
时间框架
还有
为什么在回溯测试期间所有交易都导致亏损
如何测试您的这项伟大工作。
建议如何测试算法、
时间框架以及任何其他建议。
警告不是问题所在,但可以很快解决。不过,如果作者能逐步说明他在回溯测试中使用了哪些设置和输入,那就再好不过了。
我同意 Dominic 的观点,因为警告只是警告。 I_Virgo 的结果可能是因为他使用了错误的时间框架和货币对。 从回溯测试报告来看,在近 2000 个条形图中,时间框架一定是 M1 或 M5,货币对不明。
如果 MQ 能在回溯测试报告中添加时间框架和货币对,并将货币对结果更详细地分开,那就更好了,这样我们就能更接近地复制作者的回溯测试结果,并确定其对外汇货币对的适用性。 此外,如果 EA 能在运行时将文本发布到图表上,那将非常有帮助。
我也认为这是一篇很好的文章,并计划深入研究,以便将他的技术应用到其他 EA 中。
科达角