
在MQL5中构建自适应的自动化交易系统(EA)
概述
在当今瞬息万变的金融市场中,创建自优化的交易系统至关重要。在数字时代,由于算法交易(尤其是高频次交易者所使用的算法交易)的广泛应用,市场波动性显著增加。根据美国证券交易委员会(SEC)的这份文件SEC高频次交易文件,显示,高频次交易者占据了欧洲和美国近一半的交易量。
与一些看法相反的是,MQL5非常适合这项任务。其应用程序接口(API)提供了丰富的矩阵和向量功能,使其能够创建紧凑的机器学习模型。本文重点强调使用MQL5来构建自优化的机器人。采用面向对象编程(OOP)方法可以减少重复编码,并且提升在不同时间框架和市场条件下的适应性。
选择MQL5的矩阵和向量功能,相较于ONNX和Python等替代方案,具有显著的优势。使用ONNX模型需要为每个交易标的创建单独的模型实例,并且对于任何微小的参数变化(如时间框架调整)都需要创建新的模型。然而,MQL5提供了适应性,无需为不同的条件管理众多的模型。
摘要:开发自优化的交易策略(EA)
我们需要一个框架来评估我们的交易策略的执行效率。一旦确定了明确的性能指标,我们就可以相应地最大化或最小化所选指标。在构建用于价格预测的监控机器学习模型时,我们的目标是最小化预测值与实际观测值之间的误差。另一方面,对于强化学习问题,目标是预期回报总折扣的最大化。
在本文中,我们将最小化交易策略预测的未来预期价格与实际观察到的未来价格之间的差异。可以通过计算这些价格之间的绝对差来实现。
本文探讨了构建自优化交易策略的基本方向。之后的文章将深入探讨使用MQL5 API中更高级功能创建自优化交易策略的更先进的方法。
阅读本文后,读者将了解到:
- 一系列实用的矩阵和向量函数
- MQL5中面向对象编程的基础概念
- 在MQL5中构建动态和自适应交易策略(Expert Advisors)的框架
使用梯度下降的自优化
我们的目标是设计一个能够持续与当前市场条件保持一致的交易策略。为了实现这一目标,我们将在MQL5中实现梯度下降算法。对于不熟悉梯度下降算法的读者来说,将其与DJ设置音响设备的过程进行比较可能会有助于理解。想象一下,你是一名DJ,正在准备表演一场。你打开设备,发现音量太大。那么接下来你会做什么?你很可能会降低音量。但是,现在音量又太轻了,你就会调高音量。这种在增加和减少之间的反复调整会一直进行,直到你找到一个平衡的音量水平。
梯度下降算法的工作原理与此相似。我们从所在市场的模型的随机系数开始。然后,我们测量当前系数所产生的误差。就像DJ所做的那样,我们迭代地调整模型系数的方向,使其与误差增加的方向相反。这种增加和减少之间的反复调整会一直进行,直到你找到一个平衡点。
此外,除了系数之外,梯度下降中的另一个关键参数是学习率。学习率类似于DJ每次调整音量时音量变化的幅度。学习率决定了我们每次调整模型参数时所要采取的步长大小。如果学习率太大或太小,我们的模型将无法达到最佳学习效果。
每个市场可能都有不同的最佳学习率。理想的方法是设计我们的交易策略,使其能够针对每个市场场景动态优化学习率和系数,即使在我们改变了时间框架和数据范围的情况下。这种适应性有望使我们有很大机会站在市场的正确一边,充分利用原生解决方案的潜力进行无限制的交易。
交易策略
我们的交易策略将采用技术分析和机器学习相结合的方法。我们将使用移动平均线来帮助我们确定市场的主导趋势。如果价格高于移动平均线,我们认为主导趋势是上涨的;否则,如果价格低于移动平均线,我们认为市场趋势是下跌的。一旦我们确定了市场趋势,我们就会寻求两个辅助指标来确认这一趋势。这两个辅助指标是相对强弱指数(RSI)和威廉百分比范围(WPR)。
RSI指标的读数范围在0到100之间。通常,当RSI读数高于70时,证券被认为超买,应该卖出;反之,如果RSI读数低于30,证券被认为超卖,应该买入。这一策略在交易数量有限的证券(如股票或相似商品)时效果很好,但在交易货币对时则效果一般。货币不能被超卖或超买,因为中央银行可以根据需要制造任意多或少的货币。因此,在我们的策略中,当RSI读数高于50时,我们将倾向于买入而不是卖出;同样,当RSI读数低于50时,我们将倾向于卖出而不是买入。
威廉指标(WPR)的取值范围在0到-100之间。与相对强弱指数(RSI)类似,威廉指标也能识别超买和超卖区域。然而,货币不能被超买或超卖,因为货币的供应量是无限的。因此,在我们的策略中,我们将对威廉指标作出少许不同的解释。在我们的策略中,当威廉指标高于-20时,我们将其视为买入信号;如果威廉指标低于-80,我们则将其视为卖出信号。
如果所有三个指标都在市场的同一侧,那么我们将最终调用我们的模型来预测未来的预期价格。如果我们的模型预测结果与通过分析指标得出的市场观点一致,我们将开立仓位;否则,如果我们的模型结果和指标数据相互矛盾,我们将等待它们达成一致后再行动。
我们的止盈和止损水平也将根据当前的市场波动水平动态设置,我们将取价格与移动平均线之间差异的绝对值。我们的止损和止盈点将是移动平均线与收盘价之间差值绝对值的两倍。我们的理由是,在市场低迷的情况下,我们的止损和止盈点会设置得较为紧密;而在市场波动较大的日子里,我们的止损和止盈点则会设置得足够宽泛。简言之,我们的整个系统将自动进行动态调整,而无需我们进行任何干预。
使用 MQL5 实现
首先,我们需要为我们的机器学习模型定义一个类。采用面向对象编程(OOP)的方法具有许多优势,特别是在数据相关项目中。想象一下,如果已经构建了一个机器学习模型,然后只要手动复制该代码并将其插入到你拥有的每个智能交易系统中。几天后,你发现代码中的一个函数存在错误。如果你没有使用OOP设计方法,那么你将不得不手动检查你复制的每一份代码实例,并逐一进行更正。但是,如果你采用了OOP设计方法,那么你只需要更正该类,然后重新编译其他程序即可。简而言之,OOP设计原则可以让你对成千上万个不同的代码实例进行明确且精确的控制。
我们首先在MetaTrader 5编辑器中构建一个新类。
Fig 1: 在MQL5中构建新类。
在那里我们设置了类的名称。确保已将构建的类保存在“Include”文件夹中,此外,我建议为每个类分配自己的文件夹,并为该文件夹命名,因为这样操作确保将来更容易找到这些类。
Fig 2: 构建我们的线性回归类。
如果您按照以上步骤操作,MQL5向导会帮助您生成类似下列代码。
class LinearRegegression { private: public: LinearRegegression(); ~LinearRegegression(); }; LinearRegegression::LinearRegegression() { } LinearRegegression::~LinearRegegression() { }
在MQL5中,如果你是第一次接触面向对象编程(OOP)方法,那么让我们一起来逐步分析上面的代码。在最顶部,我们定义一个类。class 关键字表示接下来的代码是一个类,class 关键字后面跟着的是类的名称。从这里开始,我们进入了类的主体。关键字 private 用来定义那些不能从类的外部访问的变量和函数,而 public 关键字则用来定义那些可以从类的外部访问的变量和函数。注意,在我们的类定义中已经有两个函数了。
第一个函数“LinearRegression()”被称为构造函数。每当我们构建一个类的新实例时,就会先调用这个函数。而最后一个函数“~LinearRegression()”则被称为析构函数。析构函数是在我们从图表中移除该类时最后调用的函数。
我们现在可以开始定义我们将用于计算线性回归模型的变量。
- 最大学习率定义了我们在搜索良好学习率时可以达到的高度(或范围)。
- 用fetch(获取)简要地表示我们想要分析市场中的多少根蜡烛图。
- start(开始)和predict(预测)定义了我们将何时开始获取数据以及我们从哪个点开始进行预测。
- look ahead(前瞻)定义了我们希望预测未来多少步(或时间段)。
- 使用mae_array 存储表示误差指标的数组。
- trained是一个标识,用来判断模型是否已经被训练并且已经准备好被使用。
- Epochs power定义了我们将用于训练模型的迭代次数(epoch数)。
- 我们有两个向量 mae_train 和 mae_validation,它们分别存储了我们在训练和验证过程中得到的误差指标。
- 我们还有四个向量 x_validation、y_validation、x_train 和 y_train。这些向量包含了我们的训练和验证数据。
- m和b向量包含了我们模型中相应m和b系数的估计值。
- “双重预测”(double forecast)实际上就是我们模型的预测结果。
- 学习率(Learning rate power)是我们将0.1提升到某个标准来定义学习效率的数值。
- 迭代次数(Epochs)是我们训练模型的次数。
- n是我们数据中的行数,它始终等于 fetch(获取的数据量)
- "output_end,output_start,input_end,input_start" 用于定义我们的测试阶段。
private: //This is the highest power that we will raise ten to, as we are searching for coefficients ulong max_learning_rate_power; //This is how many bars we should fetch int fetch; //This is where we will start collecting data, it is the end of our validation data set. datetime start,predict; //This is how many steps into the future we want to forecast int look_ahead; //This is the array that will contain our MAE readings from testing different learning rates on the validation data double mae_array[30]; //Trained flag to inform us if the model has been fit and optimised succesfuly and is ready for use bool trained; //The number to raise the power of 10 buy when calculating the number of epochs int epochs_power; //Our error metrics vector mae_train,mae_validation; //This vector contains our inputs validation and training set vector x_validation,x_train; //This vector contains our outputs validation and training set vector y_validation,y_train; //This vector contains our predictions on the validation set vector y_hat_validation,y_hat_train; //This vector contains our gradient coefficient vector m; //This vector contains our model bias vector b; //This is our model's forecast double forecast; //This is our current learning rate power ulong learning_rate_power; //This is the learning rate power we are currently evaluating int lr_error_index; //This is our current learning rate double learning_rate; //This is the number of rounds we will allow whilst training our model double epochs; //This is used in calculations, it is the number of rows in our data, or the fetch size. ulong n; //These are the times for our input and output data datetime output_end,output_start,input_end,input_start; //These are the index times for our input and output data int index_output_end,index_output_start,index_input_end,index_input_start; //This is the value we will use to scale our data double first_reading; bool allowed_to_evaluate; //Update the learning rate bool UpdateLearningRate(void); //Update the number of epochs bool UpdateEpochs(void); //Set the number of epochs bool SetEpochs(int _epochs_power); //Reset the number of epochs bool ResetEpochs(void); //Reset the learning rate bool ResetLearningRate(void); //This function will fit the coeffeicients bool Fit(void); //This function evaluates the current settings bool Evaluate(ulong _index,int _epochs_power); //This function will scale the input data bool ScaleInputs(void); //This function sets the learning rate bool SetLearningRate(ulong _learning_rate_power);
现在让我们继续讨论类中的公共定义。
public: //Constructor LinearRegression(); //Fetch Current Validation Data bool GetCurrentValidationData(void); //Initialise the LinearRegressor Model void Init(int _fetch,int _look_ahead); //Function to determine if the model has been trained and is ready for use. bool Trained(void); //A function to train the model using the best learning rate and the most recent prices bool Train(void); //A function to predict future price using the current price. double Predict(void); //Destructor ~LinearRegression();
上述代码定义了我们类中的函数和每个函数的名称,虽然我们还没有实现每个函数。现在让我们从实现构造函数开始。
请注意,我们的构造函数不接受任何输入,因此被认为是默认或非参数构造函数。此外,请注意,构造函数没有返回类型,甚至没有空值。
LinearRegression::LinearRegression()
{
Print("Current Symbol: ",_Symbol);
}
我们设计的构造函数(constructor)除了显示当前的交易符号外,不执行其他任何操作。这样设计选择使我们能够从EA的输入中检索信息,并基于这些输入信息来初始化我们的线性回归对象。值得注意的是,构造函数不会设置任何变量或默认值,这一任务需要通过在“Init()”函数中定义一个单独方法来实现。简而言之,将构造函数与Init()函数分离开来是非常有用的,因为它允许我们动态地从EA的设置中收集输入。如果构造函数负责变量初始化,那么这种动态输入收集行为将会受到限制。
现在,让我们定义用于初始化变量为默认值的Init()函数。在初始化变量之后,Init方法将自动尝试对我们的输入进行缩放并为我们训练模型。
void LinearRegression::Init(int _fetch,int _look_ahead) { //Clear The Chart ObjectsDeleteAll(0); //Allow evaluations allowed_to_evaluate = true; //Epochs power epochs_power =4; //Set the number of epochs epochs = 5 * MathPow(10,epochs_power); //Has the model been trained? trained = false; //Set the maximum learning rate power max_learning_rate_power = 30; //Set the end of our validation data start = iTime(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,1); //This is how much data we're going to fetch this.fetch = _fetch - 1; //This is how far into the future we want to forecast this.look_ahead = _look_ahead + 1; //Set the gradient coefficient to a random value m = vector::Zeros(1); //Set the bias to a random value b = vector::Zeros(1); //Set the forecast to 0 forecast = 0; //Our model's learning rate will start at 0 learning_rate_power = 0; //This is the learning rate we are evaluting lr_error_index = 0; mae_train = vector::Full(1,MathPow(10,100)); mae_validation = vector::Full(30,MathPow(10,10000)); //Set the initial learning rate learning_rate = MathPow(0.1,(learning_rate_power)); //Set the number of rows n = fetch; if(GetCurrentValidationData()) { //Scale the data ScaleInputs(); //Fit the model Fit(); } }
定义predict 函数为无需任何参数即可返回一个双精度数据类型(double),因此其输入参数为空。值得注意的是,若要将一个函数指定为类的成员,我们需要在函数名前加上类名,并在两者之间使用两个冒号进行分隔。
predict 函数首先会调用 Trained() 函数来检查模型是否已完成训练。一旦确认了模型的训练状态,我们将开始收集实时数据,具体包括当前价格、收盘价以及用于预测市场环境的时间戳数据。我们通过将当前价格乘以 m 并加上 b 来计算预测价格。如果模型未经过训练,则直接返回0。
double LinearRegression::Predict(void) { if(Trained()) { double _current_reading = iClose(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,0); predict = iTime(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,0); double prediction = (m[0]*_current_reading)+b[0]; if(prediction > _current_reading) { Comment("Buy, forecast: ",prediction); } else if(prediction < _current_reading) { Comment("Sell, forecast: ",prediction); } ObjectCreate(0,"prediction point",OBJ_VLINE,0,predict,0); ObjectCreate(0,"forecast",OBJ_HLINE,0,predict,prediction); return(prediction); } return(0); }
我们的下一个函数被用于收集训练和验证数据,并且始终获取可用的最新市场数据。这一过程是通过 copy_rates 向量函数来实现的,该函数专门用于将历史价格数据传输到向量中。
在获取数据后,我们需要确保这些向量的大小相同,这可以通过定义代表向量大小的函数来实现。
bool LinearRegression::GetCurrentValidationData(void) { //Indexes index_output_end = 1; index_output_start = index_output_end + fetch; index_input_end = index_output_end + look_ahead; index_input_start = index_output_start + look_ahead; //Assigning time stamps output_end = iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,index_output_end); output_start = iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,index_output_start); input_end = iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,index_input_end); input_start = iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,index_input_start); //Get the output data if(!y_validation.CopyRates(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,output_end,fetch)) { Print("Failed to get market data: ",GetLastError()); return(false); } //Get the input data if(!x_validation.CopyRates(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,input_end,fetch)) { Print("Failed to get market data: ",GetLastError()); return(false); } //Print the vectors we have if(x_validation.Size() != y_validation.Size()) { Print("Failed to get market data: Our vectors aren't the same length."); return(false); } //Print the vectors and plot the data points Print("X validation: ",x_validation); ObjectCreate(0,"X validation end",OBJ_VLINE,0,input_end,0); ObjectCreate(0,"X validation start",OBJ_VLINE,0,input_start,0); //Print the vectors and plot the data points Print("y validation: ",y_validation); ObjectCreate(0,"y validation end",OBJ_VLINE,0,output_end,0); ObjectCreate(0,"y validation start",OBJ_VLINE,0,output_start,0); //Set the training data index_output_end = index_input_start + (look_ahead * 2); index_output_start = index_output_end + fetch; index_input_end = index_output_end + look_ahead; index_input_start = index_output_start + look_ahead; //Assigning time stamps output_end = iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,index_output_end); output_start = iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,index_output_start); input_end = iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,index_input_end); input_start = iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,index_input_start); //Copy the training data if(!y_train.CopyRates(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,output_end,fetch)) { Print("Error fetching training data ",GetLastError()); } //Copy the training data if(!x_train.CopyRates(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,input_end,fetch)) { Print("Error fetching training data ",GetLastError()); } //Check if the data matches if(x_train.Size() != y_train.Size()) { Print("Error fetching training dataL: The x and y vectors are not the same size"); } //Print the vectors and plot the data points Print("X training: ",x_train); ObjectCreate(0,"X training end",OBJ_VLINE,0,input_end,0); ObjectCreate(0,"X training start",OBJ_VLINE,0,input_start,0); Print("y training: ",y_train); ObjectCreate(0,"y training end",OBJ_VLINE,0,output_end,0); ObjectCreate(0,"y training start",OBJ_VLINE,0,output_start,0); return(true); }
现在,我们来定义 fit 函数。该函数首先使用当前的 m 和 b 值对训练数据进行预测。随后,通过计算实际 Y 值与预测 Y 值之间的绝对差来评估训练数据中的误差。
一旦确定了误差,我们就利用另一个高效的向量函数 'Mean' 来计算误差向量的算术平均值,从而得到平均误差。
接下来,我们将通过近似计算 m 和 b 误差的导数来实现梯度下降算法。这些导数近似值将指导我们按照部分导数来更新系数。
在更新系数后,验证新系数的有效性至关重要,因为某些情况可能会产生无效系数,如 NaN(非数字)或无穷大。这一验证步骤对于确保更新后系数的完整性和可用性至关重要。
bool LinearRegression::Fit() { Print("Fitting a linear regression on the training set with learning rate ",learning_rate_power); Print("Evalutaions: ",allowed_to_evaluate); for(int i =0; i < epochs;i++) { //Measure error y_hat_train = (m[0]*x_train) + b[0]; vector y_minus_y_hat = (y_train - y_hat_train); vector y_minus_y_hat_sqaured = MathAbs((y_train - y_hat_train)); mae_train.Set(0,( y_minus_y_hat_sqaured.Mean())); vector x_times_y_minus_y_hat = (x_train*(y_train -y_hat_train)); //Aproximate the derivatives double derivative_m = (-2.0/n) * x_times_y_minus_y_hat.Sum(); double derivative_b = (-2.0/n) * y_minus_y_hat.Sum(); //Update the linear parameters m[0] = m[0] - (learning_rate * derivative_m); b[0] = b[0] - (learning_rate * derivative_b); } //Finished fitting the coefficients Print("Fit on training data complete.\nm: ",m[0]," b: ",b[0]," mae ",mae_train[0],"\nlearning rate: ",learning_rate); if(allowed_to_evaluate) { Evaluate(learning_rate_power,epochs_power); } //Return true return(true); }
让我们继续来定义评估函数。该函数负责为我们交易的每个标识选择最佳的学习率。我们首先验证系数的有效性。如果系数为零或包含NaN值(非数字),则将它们重置。
这一验证过程的背后逻辑,是精心选择在不同学习率下产生最低验证误差的系数。在系数选择阶段,被标记为高度无效的系数将不列入考虑范围。相反,有效的系数将被存储以供进一步分析。
接下来,我们使用这些存储的系数,基于验证数据生成预测,并评估误差。这个迭代过程包括更新学习率、拟合模型以及评估误差。我们设置的最大迭代次数限制值为30,这个值对应最大学习率。
在整个评估函数执行过程中,会不断检查以确保索引始终处在最大学习率的范围内。我们将绝对误差数据存储到一个向量中,以便高效处理,利用如vector.Min()和Argmin()这样的向量函数来确定与最低验证误差相关联的学习率。
//此功能用于评估当前系数设置和学习率 bool LinearRegression::Evaluate(ulong _index) { Print("Evaluating the coefficients m:",m[0]," b: ",b[0]," at learning rate: ",learning_rate); //First check if the coefficient and learning rate are valid if((m.HasNan() > 0 || b.HasNan() > 0 || m[0] == 0 || b[0] == 0 || _index > max_learning_rate_power) && (_index < max_learning_rate_power)) { Print("Coefficients are invalid"); m[0] = 0; b[0] = 0 ; mae_array[_index] = MathPow(10,100000); //Update the learning rate UpdateLearningRate(); //Fit the model again Fit(); } else { //Validation predictions if(_index < max_learning_rate_power) { Print("Coefficients are valid, solution at index ",_index); y_hat_validation = (m[0] * x_validation) + b[0]; vector y_minus_y_hat_squared = MathAbs(y_validation - y_hat_validation); //If everything is fine, let's assess the validation mae mae_array[_index] = (1.0/n) * y_minus_y_hat_squared.Sum(); //What was the validation error? Print("Validation error: ",(1.0/n) * y_minus_y_hat_squared.Sum()); //Update the learning rate UpdateLearningRate(); //Fit the model again Fit(); } } if(_index == max_learning_rate_power) { for(int i = 0; i < max_learning_rate_power;i++) { mae_validation[i] = mae_array[i]; } allowed_to_evaluate = false; trained = true; Print("Validation mae: \n",mae_validation); Print("Lowest validation mae: ",mae_validation.Min()); ulong chosen_learning_rate = mae_validation.ArgMin(); Print("Chosen learning rate ",MathPow(0.1,(chosen_learning_rate))); SetLearningRate(chosen_learning_rate); Fit(); } return(true); }
我们还将定义一个用于缩放输入的函数。这个函数很容易理解,它将我们的所有输入除以训练向量中的第一个元素。
//此函数用于缩放我们的输入 bool LinearRegression::ScaleInputs(void) { //Set the first reading first_reading = x_train[0]; x_train = x_train / first_reading; x_validation = x_validation / first_reading; return(true); }
这里我们定义了析构函数,它重置了我们刚刚优化的所有系数。
LinearRegression::~LinearRegression()
{
ResetLearningRate();
ResetLastError();
} 析构函数调用的功能定义如下:
bool LinearRegression::ResetLearningRate(void) { learning_rate_power = 0; learning_rate = MathPow(0.1,learning_rate_power); return(true); }
把它们放在一起时,就定义了我们的类:
#property copyright "Gamuchirai Ndawana" #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" class LinearRegression { private: //This is the highest power that we will raise ten to, as we are searching for coefficients ulong max_learning_rate_power; //This is how many bars we should fetch int fetch; //This is where we will start collecting data, it is the end of our validation data set. datetime start,predict; //This is how many steps into the future we want to forecast int look_ahead; //This is the array that will contain our MAE readings from testing different learning rates on the validation data double mae_array[30]; //Trained flag to inform us if the model has been fit and optimised succesfuly and is ready for use bool trained; //The number to raise the power of 10 buy when calculating the number of epochs int epochs_power; //Our error metrics vector mae_train,mae_validation; //This vector contains our inputs validation and training set vector x_validation,x_train; //This vector contains our outputs validation and training set vector y_validation,y_train; //This vector contains our predictions on the validation set vector y_hat_validation,y_hat_train; //This vector contains our gradient coefficient vector m; //This vector contains our model bias vector b; //This is our model's forecast double forecast; //This is our current learning rate power ulong learning_rate_power; //This is the learning rate power we are currently evaluating int lr_error_index; //This is our current learning rate double learning_rate; //This is the number of rounds we will allow whilst training our model double epochs; //This is used in calculations, it is the number of rows in our data, or the fetch size. ulong n; //These are the times for our input and output data datetime output_end,output_start,input_end,input_start; //These are the index times for our input and output data int index_output_end,index_output_start,index_input_end,index_input_start; //This is the value we will use to scale our data double first_reading; bool allowed_to_evaluate; //Update the learning rate bool UpdateLearningRate(void); //Update the number of epochs bool UpdateEpochs(void); //Set the number of epochs bool SetEpochs(int _epochs_power); //Reset the number of epochs bool ResetEpochs(void); //Reset the learning rate bool ResetLearningRate(void); //This function will fit the coeffeicients bool Fit(void); //This function evaluates the current settings bool Evaluate(ulong _index); //This function will scale the input data bool ScaleInputs(void); //This function sets the learning rate bool SetLearningRate(ulong _learning_rate_power); public: //Constructor LinearRegression(); //Fetch Current Validation Data bool GetCurrentValidationData(void); //Initialise the LinearRegressor Model void Init(int _fetch,int _look_ahead); //Function to determine if the model has been trained and is ready for use. bool Trained(void); //A function to train the model using the best learning rate and the most recent prices bool Train(void); //A function to predict future price using the current price. double Predict(void); //Destructor ~LinearRegression(); }; bool LinearRegression::UpdateEpochs(void) { epochs_power = epochs_power + 1; epochs = MathPow(10,epochs_power); return(true); } bool LinearRegression::ResetEpochs(void) { epochs_power = 0 ; epochs = MathPow(10,epochs_power); return(true); } bool LinearRegression::SetEpochs(int _epochs_power) { epochs_power = _epochs_power; epochs = MathPow(10,epochs_power); return(true); } double LinearRegression::Predict(void) { if(Trained()) { double _current_reading = iClose(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,0); predict = iTime(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,0); double prediction = (m[0]*_current_reading)+b[0]; if(prediction > _current_reading) { Comment("Buy, forecast: ",prediction); } else if(prediction < _current_reading) { Comment("Sell, forecast: ",prediction); } ObjectCreate(0,"prediction point",OBJ_VLINE,0,predict,0); ObjectCreate(0,"forecast",OBJ_HLINE,0,predict,prediction); return(prediction); } return(0); } bool LinearRegression::GetCurrentValidationData(void) { //Indexes index_output_end = 1; index_output_start = index_output_end + fetch; index_input_end = index_output_end + look_ahead; index_input_start = index_output_start + look_ahead; //Assigning time stamps output_end = iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,index_output_end); output_start = iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,index_output_start); input_end = iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,index_input_end); input_start = iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,index_input_start); //Get the output data if(!y_validation.CopyRates(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,output_end,fetch)) { Print("Failed to get market data: ",GetLastError()); return(false); } //Get the input data if(!x_validation.CopyRates(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,input_end,fetch)) { Print("Failed to get market data: ",GetLastError()); return(false); } //Print the vectors we have if(x_validation.Size() != y_validation.Size()) { Print("Failed to get market data: Our vectors aren't the same length."); return(false); } //Print the vectors and plot the data points Print("X validation: ",x_validation); ObjectCreate(0,"X validation end",OBJ_VLINE,0,input_end,0); ObjectCreate(0,"X validation start",OBJ_VLINE,0,input_start,0); //Print the vectors and plot the data points Print("y validation: ",y_validation); ObjectCreate(0,"y validation end",OBJ_VLINE,0,output_end,0); ObjectCreate(0,"y validation start",OBJ_VLINE,0,output_start,0); //Set the training data index_output_end = index_input_start + (look_ahead * 2); index_output_start = index_output_end + fetch; index_input_end = index_output_end + look_ahead; index_input_start = index_output_start + look_ahead; //Assigning time stamps output_end = iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,index_output_end); output_start = iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,index_output_start); input_end = iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,index_input_end); input_start = iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,index_input_start); //Copy the training data if(!y_train.CopyRates(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,output_end,fetch)) { Print("Error fetching training data ",GetLastError()); } //Copy the training data if(!x_train.CopyRates(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,input_end,fetch)) { Print("Error fetching training data ",GetLastError()); } //Check if the data matches if(x_train.Size() != y_train.Size()) { Print("Error fetching training dataL: The x and y vectors are not the same size"); } //Print the vectors and plot the data points Print("X training: ",x_train); ObjectCreate(0,"X training end",OBJ_VLINE,0,input_end,0); ObjectCreate(0,"X training start",OBJ_VLINE,0,input_start,0); Print("y training: ",y_train); ObjectCreate(0,"y training end",OBJ_VLINE,0,output_end,0); ObjectCreate(0,"y training start",OBJ_VLINE,0,output_start,0); return(true); } bool LinearRegression::Train(void) { m = vector::Zeros(1); //Set the bias to a random value b = vector::Zeros(1); forecast = 0; if(GetCurrentValidationData()) { if(Fit()) { Print("Model last updated: ",iTime(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,0)); return(true); } } return(false); } void LinearRegression::Init(int _fetch,int _look_ahead) { //Clear The Chart ObjectsDeleteAll(0); //Allow evaluations allowed_to_evaluate = true; //Epochs power epochs_power =4; //Set the number of epochs epochs = 5 * MathPow(10,epochs_power); //Has the model been trained? trained = false; //Set the maximum learning rate power max_learning_rate_power = 30; //Set the end of our validation data start = iTime(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,1); //This is how much data we're going to fetch this.fetch = _fetch - 1; //This is how far into the future we want to forecast this.look_ahead = _look_ahead + 1; //Set the gradient coefficient to a random value m = vector::Zeros(1); //Set the bias to a random value b = vector::Zeros(1); //Set the forecast to 0 forecast = 0; //Our model's learning rate will start at 0 learning_rate_power = 0; //This is the learning rate we are evaluting lr_error_index = 0; mae_train = vector::Full(1,MathPow(10,100)); mae_validation = vector::Full(30,MathPow(10,10000)); //Set the initial learning rate learning_rate = MathPow(0.1,(learning_rate_power)); //Set the number of rows n = fetch; if(GetCurrentValidationData()) { //Scale the data ScaleInputs(); //Fit the model Fit(); } } bool LinearRegression::Trained(void) { return(trained); } bool LinearRegression::SetLearningRate(ulong _learning_rate_power) { learning_rate_power = _learning_rate_power; learning_rate = MathPow(0.1,(learning_rate_power)); return(true); } bool LinearRegression::UpdateLearningRate(void) { learning_rate_power = learning_rate_power + 1; learning_rate = MathPow(0.1,(learning_rate_power)); Print("New learning rate: ",learning_rate," learning rate power: ",learning_rate_power); return(true); } bool LinearRegression::ResetLearningRate(void) { learning_rate_power = 0; learning_rate = MathPow(0.1,learning_rate_power); return(true); } LinearRegression::LinearRegression() { Print("Current Symbol: ",_Symbol); } bool LinearRegression::Fit() { Print("Fitting a linear regression on the training set with learning rate ",learning_rate_power); Print("Evalutaions: ",allowed_to_evaluate); for(int i =0; i < epochs;i++) { //Measure error y_hat_train = (m[0]*x_train) + b[0]; vector y_minus_y_hat = (y_train - y_hat_train); vector y_minus_y_hat_sqaured = MathAbs((y_train - y_hat_train)); mae_train.Set(0,( y_minus_y_hat_sqaured.Mean())); vector x_times_y_minus_y_hat = (x_train*(y_train -y_hat_train)); //Aproximate the derivatives double derivative_m = (-2.0/n) * x_times_y_minus_y_hat.Sum(); double derivative_b = (-2.0/n) * y_minus_y_hat.Sum(); //Update the linear parameters m[0] = m[0] - (learning_rate * derivative_m); b[0] = b[0] - (learning_rate * derivative_b); } //Finished fitting the coefficients Print("Fit on training data complete.\nm: ",m[0]," b: ",b[0]," mae ",mae_train[0],"\nlearning rate: ",learning_rate); if(allowed_to_evaluate) { Evaluate(learning_rate_power); } //Return true return(true); } //This function evaluates the current coefficient settings and learning rate bool LinearRegression::Evaluate(ulong _index) { Print("Evaluating the coefficients m:",m[0]," b: ",b[0]," at learning rate: ",learning_rate); //First check if the coefficient and learning rate are valid if((m.HasNan() > 0 || b.HasNan() > 0 || m[0] == 0 || b[0] == 0 || _index > max_learning_rate_power) && (_index < max_learning_rate_power)) { Print("Coefficients are invalid"); m[0] = 0; b[0] = 0 ; mae_array[_index] = MathPow(10,100000); //Update the learning rate UpdateLearningRate(); //Fit the model again Fit(); } else { //Validation predictions if(_index < max_learning_rate_power) { Print("Coefficients are valid, solution at index ",_index); y_hat_validation = (m[0] * x_validation) + b[0]; vector y_minus_y_hat_squared = MathAbs(y_validation - y_hat_validation); //If everything is fine, let's assess the validation mae mae_array[_index] = (1.0/n) * y_minus_y_hat_squared.Sum(); //What was the validation error? Print("Validation error: ",(1.0/n) * y_minus_y_hat_squared.Sum()); //Update the learning rate UpdateLearningRate(); //Fit the model again Fit(); } } if(_index == max_learning_rate_power) { for(int i = 0; i < max_learning_rate_power;i++) { mae_validation[i] = mae_array[i]; } allowed_to_evaluate = false; trained = true; Print("Validation mae: \n",mae_validation); Print("Lowest validation mae: ",mae_validation.Min()); ulong chosen_learning_rate = mae_validation.ArgMin(); Print("Chosen learning rate ",MathPow(0.1,(chosen_learning_rate))); SetLearningRate(chosen_learning_rate); Fit(); } return(true); } //This function will scale our inputs bool LinearRegression::ScaleInputs(void) { //Set the first reading first_reading = x_train[0]; x_train = x_train / first_reading; x_validation = x_validation / first_reading; return(true); } LinearRegression::~LinearRegression() { ResetLearningRate(); ResetEpochs(); ResetLastError(); }
既然我们已经定义好了LinearRegression类,之后就可以在我们的EA中使用它了。
我们首先创建一个包含该类的新EA。
#property copyright "Gamuchirai Zororo Ndawana" #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" //Include our linear regression class #include <LinearRegression/LinearRegression.mqh> LinearRegression ExtLinearRegression;
上述代码调用了LinearRegression类的默认构造函数。
此处还包括其他有用的类。
//Include the trade class #include <Trade/Trade.mqh> CTrade Trade;
我们定义了EA所需的输入。
//Inputs int input look_ahead = 10; //How many steps into the future should we forecast? int input fetch_data = 100; //How much data should we fetch? int input ma_period = 10; //Moving Average Period int input rsi_period = 10; //RSI Period int input wr_period = 10; //Williams Percent R Period
我们还将定义对技术分析有用的其他变量,例如允许的最小交易量和存储指标缓冲区的向量。
//Technical Analysis double min_volume =SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol,SYMBOL_VOLUME_MIN); //Indicator Handlers int ma_handler,rsi_handler,wr_handler,total_time; vector ma_vector,rsi_vector,wr_vector; double _price; ulong _ticket;
完成后,我们现在就可以定义EA的OnInit()处理程序了。该处理程序通过用户传递给EA的参数来初始化我们的线性回归对象,再设置技术指标。
int OnInit() { //Setup our model ExtLinearRegression.Init(fetch_data,look_ahead); //Keep Track Of Time total_time = 0; //Set up our technical indicators ma_handler = iMA(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,ma_period,0,MODE_EMA,PRICE_CLOSE); rsi_handler = iRSI(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,rsi_period,PRICE_CLOSE); wr_handler = iWPR(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,wr_period); return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
现在我们来到了onTick函数。使用onTick函数跟踪时间,允许我们在每个新蜡烛之后执行某些操作,并在每次价格变动(tick)之后执行一些操作。每当出现一个新的蜡烛时,如果之前的蜡烛总数超过了用户选择的预测周期,我们需要使用已经实现的Train函数再次训练我们的模型。此外,我们还希望使用另一个有用的向量函数CopyIndicatorBuffer来更新记录中的指标值。我们已经创建了一个用于该操作的函数。最后,如果我们有未平仓头寸,需要创建了一个负责管理未平仓头寸的函数。
void OnTick() { //--- static datetime time_stamp; datetime current_time = iTime(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,0); if(time_stamp != current_time) { //Update the values of the indicators update_vectors(); total_time += 1; if(total_time > look_ahead) { total_time = 0; //Let the model adapt to the market dynamically ExtLinearRegression.Train(); } //If our model is ready then let's start trading if(ExtLinearRegression.Trained()) { if(PositionsTotal() == 0) { analyse_indicators(); } } if(PositionsTotal() == 1) { //Get position ticket _ticket = PositionGetTicket(0); //Manage the position manage_position(_ticket); } time_stamp = current_time; } }
此函数负责从我们的智能体中获取最新可用的条形图。
void update_vectors(void) { //Get the current reading of our indicators ma_vector.CopyIndicatorBuffer(ma_handler,0,1,1); rsi_vector.CopyIndicatorBuffer(rsi_handler,0,1,1); wr_vector.CopyIndicatorBuffer(wr_handler,0,1,1); _price = iClose(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,1); }
该函数负责解释我们的指标和模型的预测。如果它们全部一致,那么我们可以开仓交易;否则,我们将等待它们达成一致。
void analyse_indicators(void) { double forecast = ExtLinearRegression.Predict(); Comment("Forecast: ",forecast," Price: ",_price); //If price is above the moving average, check if the other indicators also confirm the buy signal if(_price - ma_vector[0] > 0) { if(rsi_vector[0] > 50) { if(wr_vector[0] > -20) { if(forecast > _price) { Trade.Buy(min_volume,_Symbol,SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol,SYMBOL_ASK),0,0); } } } } //If price is below the moving average, check if the other indicators also confirm the sell signal if(_price - ma_vector[0] < 0) { if(rsi_vector[0] < 50) { if(wr_vector[0] < -80) { if( forecast < _price) { Trade.Sell(min_volume,_Symbol,SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol,SYMBOL_BID),0,0); } } } }
这个函数负责管理我们所有的未平仓头寸,并根据当前市场的波动水平动态地设置止损和止盈。请注意,它只有在头寸没有设置止损或止盈的情况下才会修改头寸。
void manage_position(ulong m_ticket) { if(PositionSelectByTicket(m_ticket)) { double volatility = 2 * MathAbs(ma_vector[0] - _price); double entry = PositionGetDouble(POSITION_PRICE_OPEN); double current_sl = PositionGetDouble(POSITION_SL); double current_tp = PositionGetDouble(POSITION_TP); if(PositionGetInteger(POSITION_TYPE) == POSITION_TYPE_BUY) { double new_sl = _price - volatility; double new_tp = _price + volatility; if(current_sl == 0 || current_tp == 0) { Trade.PositionModify(m_ticket,new_sl,new_tp); } } if(PositionGetInteger(POSITION_TYPE) == POSITION_TYPE_SELL) { double new_sl = _price + volatility; double new_tp = _price - volatility; if(current_sl == 0 || current_tp == 0) { Trade.PositionModify(m_ticket,new_sl,new_tp); } } } }
我们的EA现在是这样的
Fig 3: 可以自优化的EA。
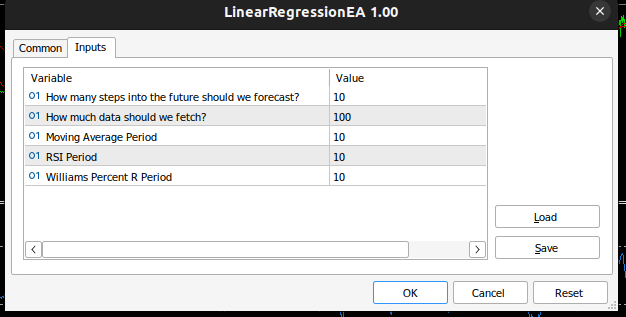
Fig 4: 自优化EA的输入。
当您在任何交易对象上应用EA时,都可以在EA的选项卡中看到EA的运算情况
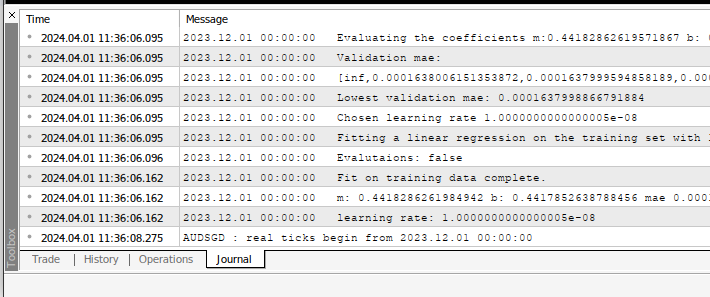
Fig 5: 我们的EA执行的计算。
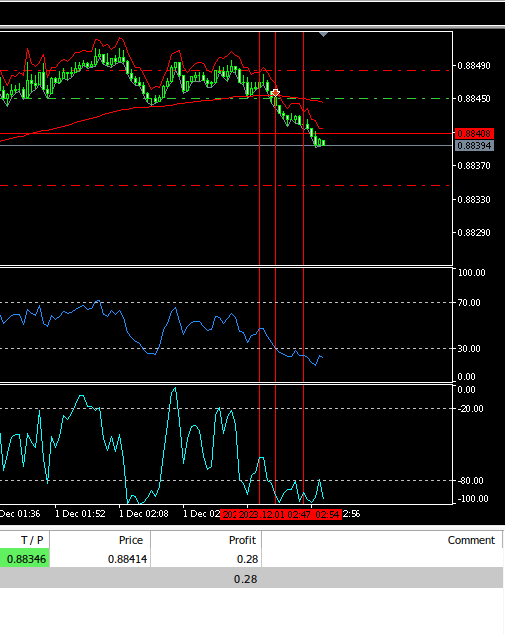
FIg 6: 回测我们的EA。
推荐配置
这篇文章介绍了构建自动化交易机器人(Expert Advisor,简称EA)的最简单方法。然而,这并不是最佳方法,因为它只能手动搜索最优系数。理想的解决方案是使用更高级的矩阵和向量通过计算自动获取最优系数。事实上,当我们使用矩阵和向量函数时,我们可以不使用任何for循环来构建线性回归模型。我们的代码会更加紧凑,系数也将具有更高的数值稳定性。但手动搜索并不总是能够保证找到解决方案。
结论
得益于MQL5 API中的强大矩阵和向量函数,在MQL5中构建自适应EA非常容易。事实上,我们能够在MQL5中构建的内容是基于我们对API的理解。
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/14630
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 神经网络实践:割线
神经网络实践:割线
 使用 LSTM 神经网络创建时间序列预测:规范化价格和令牌化时间
使用 LSTM 神经网络创建时间序列预测:规范化价格和令牌化时间


嗨,太棒了!谢谢!
我看到了这几行:
如何解决这个问题?
有谁也遇到过这个问题吗?
嘿,哈维尔,你能上传更多终端的输出结果吗?
因为你分享的结果看起来很正常,我也希望有这样的输出结果。
不过,我注意到你的输出结果有一个问题,那就是最后的 "0.0"。误差为 0.0 意味着模型是完美的,这在现实中是不可能的。
你好,加姆奇莱、
(我希望这是一种公认的打招呼方式)。
我一直在饶有兴趣地阅读您的文章,因为我非常渴望找到改进我非常幼稚的代码的机会。我刚刚从 MQL4 过渡到 MQL5,没有数学背景。
在回溯测试中运行您下载的代码时,我注意到唯一的交易都是卖出头寸--见附件。
显示预测价格的注释总是显示为 0.0000nnnnnn,这似乎是不正确的。
作为初学者,我无法确定明显的错误出在哪里,因此希望您能给出修正或更正,因为我希望在未来的 EA 中实施回归分析。
感谢您的考虑和可爱的言传身教。
亲切的问候,
Bryan
Thank you for your valuable commitment, especially for providing us with the opportunity to broaden our horizons - I think this is the most important thing.
I have some practical, if naive, questions.
Thanks
Have a nice day
Man I haven't thought of using the comments to track positions, but it such a simple algorithm that it can't fail, I like it, thank you for that suggestion. Otherwise, magic numbers are well covered in the MQL5 API, just hit F1 on your IDE and then search, or look it up online or in forums, it is well covered.
Money management, has now been covered in our series of articles. I'll find the link for you if you missed it.
Hi, that's great! Thanks!
I saw these lines:
How to solve this problem?
Has anyone encountered this problem as well?
Hello Javier, you know we're on a lifelong learning journey in our community, from what I have learned in the time that has passed since I wrote this article I would say that the implementation is not stable, I'll review this article and update it with more numerically stable solutions. Fortunately for us, there exist compact solutions that could easily solve in one line, what I did in this entire article, if only I knew back then, what I know now.
Hello, Gamchilai,
(I wish this was a recognized way of saying hello).
I have been reading your articles with interest, as I am very eager to find opportunities to improve my very naive code. I have just made the transition from MQL4 to MQL5 and have no mathematical background.
When running the code you downloaded in a backtest, I noticed that the only trades were all sell positions - see attached. The annotation showing the predicted price always shows 0.0000nnnnnn which does not seem to be correct.
As a beginner I can't figure out where the obvious mistake is so I hope you can give me a fix or correction as I hope to implement regression analysis in a future EA .
Thank you for your consideration and lovely words.
Kind regards, Bryan
Hello Bryan, your concerns are material. Rest assured it is not your fault, the algorithm I implemented in this article is a good start, however it is not stable. I will update this article with stable solutions, that are remarkably easier to implement.