
使用 LSTM 神经网络创建时间序列预测:规范化价格和令牌化时间
概述
我想探索神经网络在制定交易策略中的应用,所以我最初通过观看一些 Youtube 视频来深入研究这个主题。大多数都相对令人困惑,因为它们从非常基本的层面开始,比如如何用 Python 编程:使用字符串、数组、OOP 和所有其他基础知识。当教育者深入到课程的核心 — 神经网络和机器学习时,你意识到他们只是在解释如何使用特定的库或预训练的模型,而没有实际解释它们是如何工作的。经过大量搜索,我终于看到了 Andrej Karpathy 的视频,这些视频相当有启发性。特别是他的视频 “让我们从头开始构建 GPT,用代码清楚地说明” 让我看到了如何用几百行代码将简单的数学概念与代码结合起来,并将类人智能变为现实。 这段视频以一种相对直观和实用的方式为我打开了神经网络的世界,让我亲身体验了它们的力量。结合他频道中的一些基本理解,在数百个 ChatGPT 查询的帮助下,了解它们是如何工作的,如何用 Python 编写它们等等。我能够提出一种使用神经网络进行预测和构建 EA 交易的方法。在本文中,我不仅想记录这一历程,还想展示我所学到的知识以及如何使用像 LSTM 这样的简单神经网络进行市场预测。
LSTM 概述
当我开始在互联网上搜索时,我偶然发现了一些描述 LSTM 用于时间序列预测的文章。具体来说,我在 colah 的博客 上看到了 Christopher Olah 的一篇博客文章 “了解 LSTM 网络”。Olah 在他的博客中解释了 LSTM 的结构和功能,将其与标准 RNN 进行了比较,并讨论了各种 LSTM 变体,例如具有窥视孔连接或门控循环单元(GRU)的 LSTM 变体。Olah 最后强调了 LSTM 对 RNN 应用的重大影响,并指出了注意力机制等未来的进步。
本质上,由于缺乏记忆,传统神经网络在处理需要以前输入的上下文的任务时会遇到困难。RNN 通过允许信息持续存在的循环来解决这个问题,但它们仍然面临长期依赖的困难。例如,对于标准 RNN 来说,预测句子中的下一个单词(相关上下文是许多单词)可能是一项挑战。 长短期记忆(LSTM)网络是一种循环神经网络(RNN),旨在更好地处理 RNN 中缺乏的长期依赖性。
LSTM 通过使用更复杂的架构来解决这个问题,该架构包括一个单元状态和三种类型的门(输入、遗忘和输出)来调节信息流。这种设计允许 LSTM 长时间记住信息,使其在语言建模、语音识别和图像字幕等任务中非常有效。我感兴趣的是,LSTM 是否可以根据之前价格走势预测今天的价格走势,因为它们天生具有更长时间记忆信息的能力。我偶然发现了 Adrian Tam 撰写的另一篇很有帮助的文章,其标题很精明,为 “ LSTM for PyTorch 中的时间序列预测”,它通过一个实际的例子为我揭开了数学和编程方面的神秘面纱。我有足够的信心接受挑战,将它们应用于预测任何给定货币对的未来价格走势。
标记化和归一化过程
我设计了一种方法来标记一天内的时间,并对一天内特定时间段的价格进行归一化,以训练神经网络;然后,我找到了一种使用训练好的神经网络进行预测的方法;最后,对预测进行非规范化,得到未来价格的预测。这种方法的灵感来自我在介绍中提到的 ChatGPT 视频。LLM 使用类似的策略将文本字符串转换为数值和向量表示,以训练神经网络进行语言处理和响应生成。在我的例子中,对于价格,我希望输入到我的神经网络中的数据与给定日期的滚动基准上的当天高点或低点相关。我使用的归一化和标记化策略在下面的脚本中给出,并总结如下:
时间标记化
-
转换为秒:该脚本获取时间列(采用日期时间格式),并将其转换为自一天开始以来经过的总秒数。此计算包括小时、分钟和秒。
-
归一化为天数分数:然后将得到的秒数除以一天的总秒数(86400)。这将创建一个 time_token,以一天的一部分来表示时间。例如:中午占一天时间的 0.5,即 50%。
每日滚动价格归一化
-
按日期分组:数据按日期列分组,以确保每个交易日的归一化都独立发生。
-
滚动最高价/最低价计算:
- 对于每个组(天),脚本分别计算最高价和最低价的扩展最大值(rolling_high)和扩展最小值(rolling_low)。这意味着滚动最高价/最低价仅随着全天新数据的输入而增大/减小。
-
归一化:
- 开盘价、最高价、最低价和收盘价使用以下公式进行归一化:normalized_price = (price - rolling_low) / (rolling_high - rolling_low)
- 这会将每个价格相对于当天迄今为止的最高价和最低价缩放到 0 到 1 之间的范围。
- 归一化是在每日滚动的基础上进行的,确保捕获每天内的价格关系,同时防止归一化受到多天价格变动的影响。
-
处理 NaN:NaN 值可能在一天开始时在滚动最高价/最低价确定之前出现。我考虑了三种不同的方法来处理它们。第一种方法是删除它们,第二种方法是前向填充它们,第三种方法是用零来替换它们。经过多次测试和努力之后,我决定用零替换它们,因为我的最终目标是将此过程转换为 ONNX 数据处理流水线,可直接与 MQL5 一起使用来进行预测而无需复制代码。我意识到 ONNX 在输入和输出形状方面相对严格,并且删除 NaN 值会改变输出向量的形状,这会在 MQL 中使用 ONNX 时导致意外错误。我也尝试使用正向填充方法来替换 NaN,但这是 Pandas/NumPy 方法,不能方便地转换为 torch,torch 是我主要用来将神经网络模型转换为 ONNX 的库。最后,我决定简单地用零替换 NaN,这似乎是最有效的,让我可以绕过可变形状问题,为整个数据处理创建一个流水线,并通过 ONNX 在 MQL 中实现,从而简化在 MQL 内获取预测的整个过程。
总之,归一化是按日滚动进行的,确保捕捉到每天的价格关系,同时防止归一化受到多日价格变动的影响。这样做可以使价格处于相似的范围内,防止模型偏向具有较大量级的特征。它也有助于适应每天变化的波动性。
下面的代码有助于可视化上述过程。如果您下载了本文附带的zip文件,您可以在标题如下的文件夹中找到此代码:"Visualizing the Normalization and Tokenization Process"。文件名为:“visualizing.py”
import torch import torch.nn as nn import numpy as np import pandas as pd from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler import MetaTrader5 as mt5 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import joblib # Connect to MetaTrader 5 if not mt5.initialize(): print("Initialize failed") mt5.shutdown() # Load market data symbol = "EURUSD" timeframe = mt5.TIMEFRAME_M15 rates = mt5.copy_rates_from_pos(symbol, timeframe, 0, 96) # Note: 96 represents 1 day or 15*96= 1440 minutes of data (there are 1440 minutes in a day) mt5.shutdown() # Convert to DataFrame data = pd.DataFrame(rates) data['time'] = pd.to_datetime(data['time'], unit='s') data.set_index('time', inplace=True) # Tokenize time data['time_token'] = (data.index.hour * 3600 + data.index.minute * 60 + data.index.second) / 86400 # Normalize prices on a rolling basis resetting at the start of each day def normalize_daily_rolling(data): data['date'] = data.index.date data['rolling_high'] = data.groupby('date')['high'].transform(lambda x: x.expanding(min_periods=1).max()) data['rolling_low'] = data.groupby('date')['low'].transform(lambda x: x.expanding(min_periods=1).min()) data['norm_open'] = (data['open'] - data['rolling_low']) / (data['rolling_high'] - data['rolling_low']) data['norm_high'] = (data['high'] - data['rolling_low']) / (data['rolling_high'] - data['rolling_low']) data['norm_low'] = (data['low'] - data['rolling_low']) / (data['rolling_high'] - data['rolling_low']) data['norm_close'] = (data['close'] - data['rolling_low']) / (data['rolling_high'] - data['rolling_low']) # Replace NaNs with zeros data.fillna(0, inplace=True) return data # Visualize the price before normalization plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10)) plt.subplot(3, 1, 1) data['close'].plot() plt.title('Close Prices') plt.xlabel('Time') plt.ylabel('Price') data = normalize_daily_rolling(data) # Check for NaNs in the data if data.isnull().values.any(): print("Data contains NaNs") print(data.isnull().sum()) # Drop unnecessary columns data = data[['time_token', 'norm_open', 'norm_high', 'norm_low', 'norm_close']] # Visualize the normalized price plt.subplot(3, 1, 2) data['norm_close'].plot() plt.title('Normalized Close Prices') plt.xlabel('Time') plt.ylabel('Normalized Price') # Visualize Time After Tokenization plt.subplot(3, 1, 3) data['time_token'].plot() plt.title('Time Token') plt.xlabel('Time') plt.ylabel('Time Token') plt.tight_layout() plt.show()
如果您运行上面的代码,您将看到我所提出的方法的实际效果。下图中,2024 年 6 月 12 日整个交易日的价格与 2024 年 6 月 13 日重叠。这一天也是 CPI 和美联储会议日,两大红色新闻事件同一天出现,比较少见。您可以看到,时间标记在每天结束时重置,并在一天中线性增加。价格也会重置,但这在图中更难看到。每当形成新的高点时,归一化收盘价的值就会变为 1。当形成新的低点时,归一化收盘价的值变为 0。

训练和验证步骤摘要
下面的代码训练了一个 LSTM(长短期记忆)模型来预测价格,特别关注 EURUSD 货币对。用户可以将 “EURUSD” 更改为他们想要的任何其他货币对。
数据准备
- 获取数据:连接到 MetaTrader 5 平台,以 15 分钟为间隔获取 EURUSD 的历史价格数据(最高价、最低价、开盘价、收盘价)。同样,您可以根据个人风格选择您喜欢的时间范围,1 分钟、5 分钟、15 分钟等。
- 预处理数据:
- 将数据转换为 Pandas DataFrame,并将时间戳设置为索引。
- 创建一个“time_token”特征,将时间表示为一天的一小部分。
- 根据连续滚动的最高价/最低价来规范每天的价格,以解释每日的波动。
- 通过将缺失值(NAN)替换为零来处理缺失值(NAN)。
- 删除不必要的列,例如,分时报价量、实际交易量和价差。
- 创建序列:将数据结构化为 60 个时间步长的序列,其中每个序列成为一个输入 (X),而接下来的收盘价是目标 (y)。
- 分割数据:将序列分为训练集(80%)和测试集(20%)。
- 转换为张量:将数据转换为 PyTorch 张量以实现模型兼容性。
模型定义和训练
- 定义LSTM模型:按以下结构为 LSTM 模型创建一个类:
- 处理序列数据的 LSTM 层。
- 产生最终预测的线性层。
- 用于 LSTM 的内部状态变量。
- 设置训练:
- 将均方误差 (MSE) 定义为要最小化的损失函数。
- 使用 Adam 优化器调整模型权重。
- 设置随机种子以实现可重复性。
- 训练模型:
- 迭代超过 100 个世代(完整遍历训练数据)。
- 对于训练集中的每个序列:
- 重置 LSTM 的隐藏状态。
- 将序列传递给模型以获得预测。
- 计算预测值和真实值之间的 MSE 损失。
- 执行反向传播来更新模型权重。
- 每 10 个世代打印一次损失。
- 保存模型:保存训练模型的参数。文件保存为 “lstm_model.pth”,位于与用于运行 LSTM_model_training.py 文件相同的文件夹中。还将模型转换为 ONNX 格式以便直接与 MQL5 一起使用。ONNX 文件名为 “lstm_model.onnx”。注意:预测所需的向量形式为 seq_length、1、input_size,即 60、1、5,表示需要 60 个 15 分钟的前期数据作为 1 个批次,有 5 个值(time_token、norm_open、norm_high、norm_low 和 norm_close),均介于 0 和 1 之间。我们将在本文后面使用它在 ONNX 中创建数据处理流水线以供我们的模型使用。
评估
- 生成预测:
- 将模型切换至评估模式。
- 迭代测试集中的序列并生成预测。
- 可视化结果:
- 绘制真实的归一化价格和预测的归一化价格。
- 计算并绘制真实值和预测值的价格变化百分比。
模型参数选择:
- 编写此代码的大部分目的是为了专注于发现日内趋势。但是,它可以轻松适应其他时段,例如每周、每月等。对我来说唯一的问题是数据的可用性。否则,我可以扩展代码以包含其中一些其他时段。
- 我选择以 15 分钟为时间范围,因为我可以获得大约 80,000 个柱的数据输入到我的神经网络中。这是大约 3 年的交易数据(不包括周末),足以构建一个不错的 LSTM 神经网络来预测日内价格走势。
- 模型的总体基础是以下 5 个参数:time_token、norm_open、norm_high、norm_low、norm_close。因此 input_size = 5。我选择忽略另外三个参数:分时报价交易量、实际交易量和价差。我排除了分时报价量,因为我找不到足够可靠的数据源来确保它们足够可靠和值得信赖。我排除了实际交易量,因为我的经纪商没有这些交易量,所以它们总是被报告为零。最后,我排除了价差,因为我从模拟账户中获取了数据,所以它们与真实账户经纪商的价差不匹配。
- 隐藏层数设为 100。这是我随意选择的值,似乎效果很好。
- output_size 的值为 1,因为根据该模型的设计方式,我们只关心接下来 15 分钟的预测。
- 我选择将训练分配 80%,而 20% 用于测试。这也是一个随意的选择。有些人喜欢 50:50 分割,其他人则喜欢 70:30 分割。我不太确定,所以我决定以 80:20 的比例分割。
- 我选择的种子值为 42。我的主要目标是使试验结果具有一定的可重复性。因此,我指定了种子值,这样我就可以在均匀的基础上比较结果,以防将来决定使用任何参数。
- 我选择的学习率为 0.001,这又是一个随意的选择。用户可以自由地根据自己的需要设定学习率。
- 我选择的序列长度(seq_length)为 60。基本上,这就是 LSTM 模型对下一节进行预测所需的“上下文”柱数。这也是一个随意的选择。60 * 15 分钟 = 900 分钟或 15 小时。为了预测一个 15 分钟的柱形,需要花费大量的时间来获取背景信息,这可能有点过长。我没有充分的理由选择这个值;然而,该模型是灵活的,用户可以根据需要自由更改这些值。
- 训练时间:之所以选择 100 个世代,是因为包含 80,000 个柱形的模型在我的计算机上运行大约需要 8 个小时。我使用 CPU 进行训练。在撰写这篇文章时,我对代码进行了多次改进,并且不得不多次重新运行该模型。所以8个小时的训练时间是我可以接受的。
import torch import torch.nn as nn import numpy as np import pandas as pd import MetaTrader5 as mt5 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import torch.onnx import torch.nn.functional as F # Connect to MetaTrader 5 if not mt5.initialize(): print("Initialize failed") mt5.shutdown() # Load market data symbol = "EURUSD" timeframe = mt5.TIMEFRAME_M15 rates = mt5.copy_rates_from_pos(symbol, timeframe, 0, 80000) mt5.shutdown() # Convert to DataFrame data = pd.DataFrame(rates) data['time'] = pd.to_datetime(data['time'], unit='s') data.set_index('time', inplace=True) # Tokenize time data['time_token'] = (data.index.hour * 3600 + data.index.minute * 60 + data.index.second) / 86400 # Normalize prices on a rolling basis resetting at the start of each day def normalize_daily_rolling(data): data['date'] = data.index.date data['rolling_high'] = data.groupby('date')['high'].transform(lambda x: x.expanding(min_periods=1).max()) data['rolling_low'] = data.groupby('date')['low'].transform(lambda x: x.expanding(min_periods=1).min()) data['norm_open'] = (data['open'] - data['rolling_low']) / (data['rolling_high'] - data['rolling_low']) data['norm_high'] = (data['high'] - data['rolling_low']) / (data['rolling_high'] - data['rolling_low']) data['norm_low'] = (data['low'] - data['rolling_low']) / (data['rolling_high'] - data['rolling_low']) data['norm_close'] = (data['close'] - data['rolling_low']) / (data['rolling_high'] - data['rolling_low']) # Replace NaNs with zeros data.fillna(0, inplace=True) return data data = normalize_daily_rolling(data) # Check for NaNs in the data if data.isnull().values.any(): print("Data contains NaNs") print(data.isnull().sum()) # Drop unnecessary columns data = data[['time_token', 'norm_open', 'norm_high', 'norm_low', 'norm_close']] # Create sequences def create_sequences(data, seq_length): xs, ys = [], [] for i in range(len(data) - seq_length): x = data.iloc[i:(i + seq_length)].values y = data.iloc[i + seq_length]['norm_close'] xs.append(x) ys.append(y) return np.array(xs), np.array(ys) seq_length = 60 X, y = create_sequences(data, seq_length) # Split data split = int(len(X) * 0.8) X_train, X_test = X[:split], X[split:] y_train, y_test = y[:split], y[split:] # Convert to tensors X_train = torch.tensor(X_train, dtype=torch.float32) y_train = torch.tensor(y_train, dtype=torch.float32) X_test = torch.tensor(X_test, dtype=torch.float32) y_test = torch.tensor(y_test, dtype=torch.float32) # Set the seed for reproducibility seed_value = 42 torch.manual_seed(seed_value) # Define LSTM model class class LSTMModel(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_layer_size, output_size): super(LSTMModel, self).__init__() self.hidden_layer_size = hidden_layer_size self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_layer_size) self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_layer_size, output_size) def forward(self, input_seq): h0 = torch.zeros(1, input_seq.size(1), self.hidden_layer_size).to(input_seq.device) c0 = torch.zeros(1, input_seq.size(1), self.hidden_layer_size).to(input_seq.device) lstm_out, _ = self.lstm(input_seq, (h0, c0)) predictions = self.linear(lstm_out.view(input_seq.size(0), -1)) return predictions[-1] print(f"Seed value used: {seed_value}") input_size = 5 # time_token, norm_open, norm_high, norm_low, norm_close hidden_layer_size = 100 output_size = 1 model = LSTMModel(input_size, hidden_layer_size, output_size) #model = torch.compile(model) loss_function = nn.MSELoss() optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001) # Training epochs = 100 for epoch in range(epochs + 1): for seq, labels in zip(X_train, y_train): optimizer.zero_grad() y_pred = model(seq.unsqueeze(1)) # Ensure both are tensors of shape [1] y_pred = y_pred.view(-1) labels = labels.view(-1) single_loss = loss_function(y_pred, labels) # Print intermediate values to debug NaN loss if torch.isnan(single_loss): print(f'Epoch {epoch} NaN loss detected') print('Sequence:', seq) print('Prediction:', y_pred) print('Label:', labels) single_loss.backward() optimizer.step() if epoch % 10 == 0 or epoch == epochs: # Include the final epoch print(f'Epoch {epoch} loss: {single_loss.item()}') # Save the model's state dictionary torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'lstm_model.pth') # Convert the model to ONNX format model.eval() dummy_input = torch.randn(seq_length, 1, input_size, dtype=torch.float32) onnx_model_path = "lstm_model.onnx" torch.onnx.export(model, dummy_input, onnx_model_path, input_names=['input'], output_names=['output'], dynamic_axes={'input': {0: 'sequence'}, 'output': {0: 'sequence'}}, opset_version=11) print(f"Model has been converted to ONNX format and saved to {onnx_model_path}") # Predictions model.eval() predictions = [] for seq in X_test: with torch.no_grad(): predictions.append(model(seq.unsqueeze(1)).item()) # Evaluate the model plt.plot(y_test.numpy(), label='True Prices (Normalized)') plt.plot(predictions, label='Predicted Prices (Normalized)') plt.legend() plt.show() # Calculate percent changes with a small value added to the denominator to prevent divide by zero error true_prices = y_test.numpy() predicted_prices = np.array(predictions) true_pct_change = np.diff(true_prices) / (true_prices[:-1] + 1e-10) predicted_pct_change = np.diff(predicted_prices) / (predicted_prices[:-1] + 1e-10) # Plot the true and predicted prices plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6)) plt.subplot(2, 1, 1) plt.plot(true_prices, label='True Prices (Normalized)') plt.plot(predicted_prices, label='Predicted Prices (Normalized)') plt.legend() plt.title('True vs Predicted Prices (Normalized)') # Plot the percent change plt.subplot(2, 1, 2) plt.plot(true_pct_change, label='True Percent Change') plt.plot(predicted_pct_change, label='Predicted Percent Change') plt.legend() plt.title('True vs Predicted Percent Change') plt.tight_layout() plt.show()
模型评估结果
训练时间约为 8 小时,共 100 个世代。该模型未使用 GPU 进行训练。我使用了我自己的 PC,这是一台已有 4 年历史的游戏机,其规格如下:AMD Ryzen 5 4600H,配备 Radeon Graphics 3.00 GHz 和 64 GB 安装的 RAM。
每 10 个 世代的种子值和均方差损失都会打印在控制台上
- 使用的种子值:42
- 世代 0 损失:0.01435865368694067
- 世代 10 损失:0.014593781903386116
- 世代 20 损失:0.02026239037513733
- 世代 30 损失:0.017134636640548706
- 世代 40 损失:0.017405137419700623
- 世代 50 损失:0.004391830414533615
- 世代 60 损失:0.0210900716483593
- 世代 70 损失:0.008576949127018452
- 世代 80 损失:0.019675739109516144
- 世代 90 损失:0.008747504092752934
- 世代 100 损失:0.033280737698078156
在训练结束时,我还收到了如下所示的警告。警告建议以不同的方式指定模型,我四处摸索试图修复它。但由于训练时间很长,我决定忽略警告,因为我们批次中的序列不会有不同的长度。

另外还生成了以下图表:


模型结果分析
种子值为 42 的世代损失似乎不稳定地减少。由于它们不是单调的,也许模型可以从进一步的训练中受益。或者,用户可以考虑提供不同的种子值或使用 Python 中的 Torch 库自动生成的随机种子值,并使用 torch.seed() 命令打印出该值。此外,如果可用数据量增加,模型性能也可能提高;然而,通过这样做,用户可能会经历与更长的训练时间和更大的硬件内存要求相关的额外计算成本。
生成的图表试图总结超过 16000 个 15 分钟柱的数据。因此,我使用的图形系统不是很有效,因为大多数数据变得拥挤且难以评估。这些图表是对所进行的整体训练的更“全局”的表示,因为它们没有增加任何价值。我将它们作为参考,因为我也使用较小的数据集训练了模型,它们很有帮助;然而对于 80,000 个柱形来说,它们并不是很有用。我们将在下一节中解决这个问题,届时我们将尝试根据我们生成的模型进行预测,数据将是“本地”表示,即每日价格行为。在下一节中,我们将基于我们的模型创建一个连续预测,利用我们的序列长度 60 并添加 100 个柱形(15 分钟数据总共 160 个柱形),并连续从第 100 个柱形到第 0 个柱形进行预测,并将其表示在图表上,这也许会更有启发性。
使用训练好的模型进行预测(使用 Python)
为了创建预测脚本,我们理想情况下会使用 15 分钟时段内 EURUSD 数据的最后 60 个值,使用保存的 LSTM 模型进行预测。然而,我觉得最好在 python 中获得滚动预测和图形,这样我就可以在使用之前快速验证模型。以下是 Python 用例预测脚本的主要特性,脚本摘要如下:
-
LSTM 模型定义:该脚本定义了 LSTM 模型的结构。该模型由一个 LSTM 层和一个线性层组成。这与我们在上面的训练脚本中用于训练模型相同。
-
数据准备:
- 它连接到 MetaTrader 5 以获取最新的 160 个柱(15 分钟间隔)的 EURUSD 数据。请注意,尽管我们只需要 60 个 15 分钟数据来进行预测,但我们会提取 160 个柱的数据来进行预测,并与最后 100 个预测进行比较。这将让我们对预测与实际的潜在趋势有所了解。
- 数据被转换为 pandas DataFrame 并使用训练期间使用的相同滚动归一化技术进行归一化。
- 时间标记化用于将时间转换为数字表示。
-
模型加载:
- 已训练的 LSTM 模型(来自“lstm_model.pth”)已加载。这是我们在训练阶段训练过的模型。
-
评估:
- 该脚本迭代数据的最后 100 步。
- 对于每一步,它以前 60 个柱形作为输入,并使用模型来预测标准化的收盘价。
- 存储真实价格和预测价格以供比较。
-
下一个预测:
- 它使用最近的 60 个柱形对下一步做出预测。
- 计算此预测的百分比变化。
- 在图表上将预测显示为红点。
-
可视化:
- 生成了两个图:
- 真实与预测价格(已归一化),并突出显示下一个预测。
- 真实与预测价格百分比变化,并突出显示下一个预测。
- 为了获得更好的可视化效果,Y 轴上限为 100%。
- 生成了两个图:
下面的代码可以在文件“LSTM_model_prediction.py”中找到,该文件位于本文附带的 LSTM_Files.zip 的根目录中。
import torch import torch.nn as nn import numpy as np import pandas as pd import MetaTrader5 as mt5 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Define LSTM model class (same as during training) class LSTMModel(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_layer_size, output_size): super(LSTMModel, self).__init__() self.hidden_layer_size = hidden_layer_size self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_layer_size) self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_layer_size, output_size) self.hidden_cell = (torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_layer_size), torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_layer_size)) def forward(self, input_seq): lstm_out, self.hidden_cell = self.lstm(input_seq.view(len(input_seq), 1, -1), self.hidden_cell) predictions = self.linear(lstm_out.view(len(input_seq), -1)) return predictions[-1] # Normalize prices on a rolling basis resetting at the start of each day def normalize_daily_rolling(data): data['date'] = data.index.date data['rolling_high'] = data.groupby('date')['high'].transform(lambda x: x.expanding(min_periods=1).max()) data['rolling_low'] = data.groupby('date')['low'].transform(lambda x: x.expanding(min_periods=1).min()) data['norm_open'] = (data['open'] - data['rolling_low']) / (data['rolling_high'] - data['rolling_low']) data['norm_high'] = (data['high'] - data['rolling_low']) / (data['rolling_high'] - data['rolling_low']) data['norm_low'] = (data['low'] - data['rolling_low']) / (data['rolling_high'] - data['rolling_low']) data['norm_close'] = (data['close'] - data['rolling_low']) / (data['rolling_high'] - data['rolling_low']) # Replace NaNs with zeros data.fillna(0, inplace=True) return data[['norm_open', 'norm_high', 'norm_low', 'norm_close']] # Load the saved model input_size = 5 # time_token, norm_open, norm_high, norm_low, norm_close hidden_layer_size = 100 output_size = 1 model = LSTMModel(input_size, hidden_layer_size, output_size) model.load_state_dict(torch.load('lstm_model.pth')) model.eval() # Connect to MetaTrader 5 if not mt5.initialize(): print("Initialize failed") mt5.shutdown() # Load the latest 160 bars of market data symbol = "EURUSD" timeframe = mt5.TIMEFRAME_M15 bars = 160 # 60 for sequence length + 100 for evaluation steps rates = mt5.copy_rates_from_pos(symbol, timeframe, 0, bars) mt5.shutdown() # Convert to DataFrame data = pd.DataFrame(rates) data['time'] = pd.to_datetime(data['time'], unit='s') data.set_index('time', inplace=True) # Normalize the new data data[['norm_open', 'norm_high', 'norm_low', 'norm_close']] = normalize_daily_rolling(data) # Tokenize time data['time_token'] = (data.index.hour * 3600 + data.index.minute * 60 + data.index.second) / 86400 # Drop unnecessary columns data = data[['time_token', 'norm_open', 'norm_high', 'norm_low', 'norm_close']] # Fetch the last 100 sequences for evaluation seq_length = 60 evaluation_steps = 100 # Initialize lists for storing evaluation results all_true_prices = [] all_predicted_prices = [] model.eval() for step in range(evaluation_steps, 0, -1): # Get the sequence ending at 'step' seq = data.values[-step-seq_length:-step] seq = torch.tensor(seq, dtype=torch.float32) # Make prediction with torch.no_grad(): model.hidden_cell = (torch.zeros(1, 1, model.hidden_layer_size), torch.zeros(1, 1, model.hidden_layer_size)) prediction = model(seq).item() all_true_prices.append(data['norm_close'].values[-step]) all_predicted_prices.append(prediction) # Calculate percent changes and convert to percentages true_pct_change = (np.diff(all_true_prices) / np.array(all_true_prices[:-1])) * 100 predicted_pct_change = (np.diff(all_predicted_prices) / np.array(all_predicted_prices[:-1])) * 100 # Make next prediction next_seq = data.values[-seq_length:] next_seq = torch.tensor(next_seq, dtype=torch.float32) with torch.no_grad(): model.hidden_cell = (torch.zeros(1, 1, model.hidden_layer_size), torch.zeros(1, 1, model.hidden_layer_size)) next_prediction = model(next_seq).item() # Calculate percent change for the next prediction next_true_price = data['norm_close'].values[-1] next_price_pct_change = ((next_prediction - all_predicted_prices[-1]) / all_predicted_prices[-1]) * 100 print(f"Next predicted close price (normalized): {next_prediction}") print(f"Percent change for the next prediction based on normalized price: {next_price_pct_change:.5f}%") print("All Predicted Prices: ", all_predicted_prices) # Plot the evaluation results with capped y-axis plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8)) plt.subplot(2, 1, 1) plt.plot(all_true_prices, label='True Prices (Normalized)') plt.plot(all_predicted_prices, label='Predicted Prices (Normalized)') plt.scatter(len(all_true_prices), next_prediction, color='red', label='Next Prediction') plt.legend() plt.title('True vs Predicted Prices (Normalized, Last 100 Steps)') plt.ylim(min(min(all_true_prices), min(all_predicted_prices))-0.1, max(max(all_true_prices), max(all_predicted_prices))+0.1) plt.subplot(2, 1, 2) plt.plot(true_pct_change, label='True Percent Change') plt.plot(predicted_pct_change, label='Predicted Percent Change') plt.scatter(len(true_pct_change), next_price_pct_change, color='red', label='Next Prediction') plt.legend() plt.title('True vs Predicted Price Percent Change (Last 100 Steps)') plt.ylabel('Percent Change (%)') plt.ylim(-100, 100) # Cap the y-axis at -100% to 100% plt.tight_layout() plt.show()
下面是我们在控制台上得到的输出和获得的图表。此预测是在 2024 年 6 月 14 日当天开始时生成的(大约是经纪商时间 00:45 UTC + 3)
控制台输出:
预计下一收盘价(已归一化):0.9003118872642517
根据归一化价格进行的下一次预测的百分比变化:73.64274%
所有预测价格:[0.6229779124259949, 0.6659790277481079, 0.6223553419113159, 0.5994003415107727, 0.565409243106842, 0.5767043232917786, 0.5080181360244751, 0.5245669484138489, 0.6399291753768921, 0.5184902548789978, 0.6269711256027222, 0.6532717943191528, 0.7470211386680603、0.6783792972564697、0.6942530870437622、0.6399927139282227、0.5649009943008423、 0.6392825841903687、0.6454082727432251、0.4829435348510742、0.5231367349624634、0.17141318321228027、 0.3651347756385803, 0.2568517327308655, 0.41483253240585327、0.43905267119407654、0.40459558367729187、0.25486069917678833、0.3488359749317169、 0.41225481033325195、0.13895493745803833、0.21675345301628113、0.04991495609283447、0.28392884135246277、 0.17570143938064575, 0.34913408756256104、0.17591500282287598、0.33855849504470825、0.43142321705818176、0.5618296265602112、 0.0774659514427185、0.13539350032806396、0.4843936562538147、0.5048894882202148、0.8364744186401367、 0.782444417476654, 0.7968958616256714, 0.7907949686050415、0.5655181407928467、0.6196668744087219、0.7133172750473022、0.5095566511154175、 0.3565239906311035、0.2686333656311035、0.3386841118335724、0.5644893646240234、0.23622554540634155、 0.3433009088039398, 0.3493557274341583, 0.2939424216747284、0.08992069959640503、0.33946871757507324、0.20876094698905945、0.4227801263332367、 0.4044940173625946、0.654332160949707、0.49300187826156616、0.6266812086105347、0.807404637336731、 0.5183461904525757、0.46170246601104736、 0.24424996972084045、0.3224128782749176、0.5156376957893372、0.06813174486160278、0.1865384578704834、 0.15443122386932373、0.300825834274292、0.28375834226608276、0.4036571979522705、0.015333771705627441、 0.09899216890335083, 0.16346102952957153、0.27330827713012695、0.2869266867637634、0.21237093210220337、0.35913240909576416、 0.4736405313014984、0.3459511995315552、0.47014304995536804、0.3305799663066864、0.47306257486343384、 0.4134630858898163, 0.4199170768260956, 0.5666837692260742、0.46681761741638184、0.35662856698036194、0.3547590374946594、0.5447400808334351、 0.5184851884841919]

预测结果分析
控制台输出为 0.9003118872642517,这表明下一个价格变动可能是当前每日范围的 0.9,大约在 1.07402 和 1.07336 之间或 ~8 点。这可能不足以引起价格变化,这是可以理解的,因为在撰写本文时,我们在 2024 年 6 月 14 日仅进行了约 45 分钟的交易。然而,该模型确实预测,价格将接近当前每日区间的上限。
下一行是: 根据归一化价格进行的下一次预测的百分比变化:73.64274%。这表明下一个价格变动可能比之前的价格高出约 74%,如果以每日 8 个点的范围来计算,可能无法提供足够的点数来进行交易。
用户可以不处理数字和分数,而是考虑添加一行,将每日(最高 - 最低)数据乘以标准化的预测收盘价,以获得他们可以预期的实际点数值。当我们将脚本转换为 MQL 时,我们不仅会这样做,而且还会得到准确的价格预测。
正如您在上面的输出中看到的,100 个预测的列表也被打印到控制台。我们可以使用这些值进行验证,特别是当我们过渡到 MQL5 并开始使用那里的脚本时。
最后,我们还从 Python 中的 Matplotlib 库中获得了一张图,它为我们提供了一组最后 100 个预测,绘制了它们的图示,并在归一化基础上(0 到 1 的比例)将它们与收盘价的实际变化进行比较。红点显示了下一个最可能的价格(以归一化为基础),为我们提供下一个可能的价格走向的指示。根据当天的特定数据,我们的预测似乎落后于市场,这表明预测结果可能与当天的实际价格走势不太一致。在这样的日子里,自主交易者或用户应该考虑保持观望,不进行交易,因为模型不能准确做出预测。请注意,这并不一定意味着模型预测在整个数据集中都是不正确的,因此可能也不需要重新训练。
从 Python 过渡到 ONNX 并通过 MQL5 直接使用经过训练的模型
创建数据处理流水线
对于我来说,创建数据处理流水线的想法是不复制我在 Python 中创建的归一化和标记化代码。我不想用 MQL 重写该代码。所以我决定将脚本转换成数据流水线,将其转换为 ONNX,并直接使用 ONNX 在 MQL 中进行数据处理。由于我缺乏创建数据处理流水线的经验,所以我花了好几天的时间才弄清楚执行此操作的代码。我之所以苦苦挣扎是因为 Python 在数据类型方面相对灵活。但是当转换到 ONNX 时,您必须更加严格和具体。一路上我遇到了很多错误。最后,当我弄明白了的时候,我很高兴,并且很高兴在下面分享这个脚本。以下是脚本工作原理的快速总结:
正如我们在前面的讨论中所指出的,预处理包括两个关键步骤:
-
时间标记:它将一天的原始时间(例如下午 3:45)转换为 0 到 1 之间的分数值,表示一天中 24 小时已经过去的部分。
-
每日滚动归一化:此过程每日标准化价格数据(开盘价、最高价、最低价、收盘价)。它计算每天的滚动最低价格和最高价格,并根据这些值对价格进行归一化。这种归一化有助于模型训练,确保价格数据具有一致的规模。
组件:
-
TimeTokenizer(自定义转换器):此类处理时间标记。它从输入张量中提取时间列,将其转换为当天的分数表示,然后将其与其他价格数据组合回来。
-
DailyRollingNormalizer(自定义转换器):此类执行每日滚动归一化。它迭代价格数据,跟踪每天的滚动最高价和最低价。然后使用这些动态值对价格进行归一化。它还包括替换计算过程中可能出现的任何潜在 NaN 值的步骤。
-
ReplaceNaNs(自定义转换器):将计算中的所有 NaN 值替换为零。
-
Pipeline (nn.Sequential):这将上述三个自定义转换器组合成一个顺序的工作流程。输入数据按顺序经过 TimeTokenizer、DailyRollingNormalizer,最后经过 ReplaceNaNs。
-
MetaTrader5 Connection:该脚本建立与 MetaTrader 5 的连接以获取历史 EUR/USD 价格数据。
执行:
-
数据加载:脚本从 MetaTrader 5 获取 15 分钟时间范围内 EURUSD 对的 160 个柱形(价格数据点)。
-
数据转换:原始数据被转换为 PyTorch 张量以供进一步处理。
-
流水线处理:张量通过定义的流水线,应用时间标记化和每日滚动归一化步骤。
-
ONNX 导出:最终预处理的数据被打印到控制台以显示前后结果。此外,整个预处理流水线被导出到 ONNX 文件。ONNX 是一种开放格式,允许机器学习模型在不同的框架和环境之间轻松转移,确保模型部署和使用的更广泛的兼容性。
要点:
- 模块化:自定义转换器的使用使得代码模块化且可重复使用。每个转换器都封装了一个特定的预处理步骤。
- PyTorch:该脚本依赖于流行的深度学习框架 PyTorch 进行张量运算和模型管理。
- ONNX 导出:导出到 ONNX 可确保预处理步骤可以与部署训练模型的不同平台或工具无缝集成。
import torch import torch.nn as nn import pandas as pd import MetaTrader5 as mt5 # Custom Transformer for tokenizing time class TimeTokenizer(nn.Module): def forward(self, X): time_column = X[:, 0] # Assuming 'time' is the first column time_token = (time_column % 86400) / 86400 time_token = time_token.unsqueeze(1) # Add a dimension to match the input shape return torch.cat((time_token, X[:, 1:]), dim=1) # Concatenate the time token with the rest of the input # Custom Transformer for daily rolling normalization class DailyRollingNormalizer(nn.Module): def forward(self, X): time_tokens = X[:, 0] # Assuming 'time_token' is the first column price_columns = X[:, 1:] # Assuming 'open', 'high', 'low', 'close' are the remaining columns normalized_price_columns = torch.zeros_like(price_columns) rolling_max = price_columns.clone() rolling_min = price_columns.clone() for i in range(1, price_columns.shape[0]): reset_mask = (time_tokens[i] < time_tokens[i-1]).float() rolling_max[i] = reset_mask * price_columns[i] + (1 - reset_mask) * torch.maximum(rolling_max[i-1], price_columns[i]) rolling_min[i] = reset_mask * price_columns[i] + (1 - reset_mask) * torch.minimum(rolling_min[i-1], price_columns[i]) denominator = rolling_max[i] - rolling_min[i] normalized_price_columns[i] = (price_columns[i] - rolling_min[i]) / denominator time_tokens = time_tokens.unsqueeze(1) # Assuming 'time_token' is the first column return torch.cat((time_tokens, normalized_price_columns), dim=1) class ReplaceNaNs(nn.Module): def forward(self, X): X[torch.isnan(X)] = 0 X[X != X] = 0 # replace negative NaNs with 0 return X # Connect to MetaTrader 5 if not mt5.initialize(): print("Initialize failed") mt5.shutdown() # Load market data (reduced sample size for demonstration) symbol = "EURUSD" timeframe = mt5.TIMEFRAME_M15 rates = mt5.copy_rates_from_pos(symbol, timeframe, 0, 160) #intialize with maximum number of bars allowed by your broker mt5.shutdown() # Convert to DataFrame and keep only 'time', 'open', 'high', 'low', 'close' columns data = pd.DataFrame(rates)[['time', 'open', 'high', 'low', 'close']] # Convert the DataFrame to a PyTorch tensor data_tensor = torch.tensor(data.values, dtype=torch.float32) # Create the updated pipeline pipeline = nn.Sequential( TimeTokenizer(), DailyRollingNormalizer(), ReplaceNaNs() ) # Print the data before processing print('Data Before Processing\n', data[:100]) # Process the data processed_data = pipeline(data_tensor) print('Data After Processing\n', processed_data[:100]) # Export the pipeline to ONNX format dummy_input = torch.randn(len(data), len(data.columns)) torch.onnx.export(pipeline, dummy_input, "data_processing_pipeline.onnx", input_names=["input"], output_names=["output"])
代码的输出给出了控制台上打印的处理前和处理后的数据。我不会重现该输出,因为它并不重要,但用户可以考虑运行脚本来自己查看输出。此外,输出还会创建一个文件:data_processing_pipeline.onnx。为了验证此 ONNX 模型使用的形式,我创建了一个如下脚本:
该脚本可以在 ONNX Data Pipeline 文件夹中找到,名为“shape_check.py”。这些文件位于本文附带的 LSTM_Files.zip 中。
import onnx
model = onnx.load("data_processing_pipeline.onnx")
onnx.checker.check_model(model)
for input in model.graph.input:
print(f'Input name: {input.name}')
print(f'Input type: {input.type}')
for dim in input.type.tensor_type.shape.dim:
print(dim.dim_value) 得出以下结果:
- 160
- 5
因此,我们的模型所需的形式是 160 – 15 分钟柱和 5 个值(时间值为 UNIX 整数、开盘价、最高价、最低价、收盘价)。处理数据后,结果将是归一化的数据,即 time_token、norm_open、norm_high、norm_low 和 norm_close。
为了测试 MQL 中的数据处理,我还想出了一个特定的脚本,称为“LSTM Data Pipeline.mq5”,位于附加 zip 文件的根文件夹中,用于验证数据是否按照我最初预期的方式进行转换。该脚本可以在下面找到。主要特点概括如下:
-
初始化(OnInit):
- 从嵌入为资源的二进制数据(“data_processing_pipeline.onnx”)中加载 ONNX 模型。请注意,ONNX 模型存储在名为“LSTM”的文件夹中,该文件夹是“Experts”文件夹内的子文件夹,如下所示。
- 然后我们根据 ONNX 代码配置模型输入和输出形式。因此,“LSTM Data Pipeline Test.ex5”应该存储在 Experts 文件夹中,因为我们使用以下路径。如果您决定以其他方式存储文件,请更新此行以确保代码正常工作。
-
#resource "\\LSTM\\data_processing_pipeline.onnx" as uchar ExtModel[]

-
分时报价数据处理 (OnTick):
- 每次价格变动更新时都会触发此函数。
- 它等待下一个柱形的 (在本例中为 15 分钟蜡烛图) 形成。
- 调用 ProcessData 函数进行数据处理和预测。
-
数据处理(ProcessData):
- 获取 EURUSD M15 数据的最新 SAMPLE_SIZE(在本例中为 160)个柱。
- 从获取的数据中提取时间、开盘价、最高价、最低价和收盘价。
- 将时间部分归一化以表示一天的一小部分(0 到 1 之间)。
- 将 ONNX 模型的输入数据准备为一维向量。
- 使用准备好的输入向量执行 ONNX 模型 ( OnnxRun )。
- 接收来自模型的处理后的输出。
- 打印处理后的数据,其中包括时间标记和归一化价格。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ONNX Test | //| Copyright 2023 | //| Your Name Here | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, Your Name Here" #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" static vectorf ExtOutputData(1); vectorf output_data(1); #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> CTrade trade; #resource "\\LSTM\\data_processing_pipeline.onnx" as uchar ExtModel[] #define SAMPLE_SIZE 160 // Adjusted to match the model's expected input size long ExtHandle=INVALID_HANDLE; datetime ExtNextBar=0; // Expert Advisor initialization int OnInit() { // Load the ONNX model ExtHandle = OnnxCreateFromBuffer(ExtModel, ONNX_DEFAULT); if (ExtHandle == INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("Error creating model OnnxCreateFromBuffer ", GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } // Set input shape const long input_shape[] = {SAMPLE_SIZE, 5}; // Adjust based on your model's input dimensions if (!OnnxSetInputShape(ExtHandle, ONNX_DEFAULT, input_shape)) { Print("Error setting the input shape OnnxSetInputShape ", GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } // Set output shape const long output_shape[] = {SAMPLE_SIZE, 5}; // Adjust based on your model's output dimensions if (!OnnxSetOutputShape(ExtHandle, 0, output_shape)) { Print("Error setting the output shape OnnxSetOutputShape ", GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } // Expert Advisor deinitialization void OnDeinit(const int reason) { if (ExtHandle != INVALID_HANDLE) { OnnxRelease(ExtHandle); ExtHandle = INVALID_HANDLE; } } // Process the tick function void OnTick() { if (TimeCurrent() < ExtNextBar) return; ExtNextBar = TimeCurrent(); ExtNextBar -= ExtNextBar % PeriodSeconds(); ExtNextBar += PeriodSeconds(); // Fetch new data and run the ONNX model if (!ProcessData()) { Print("Error processing data"); return; } } // Function to process data using the ONNX model bool ProcessData() { MqlRates rates[SAMPLE_SIZE]; int copied = CopyRates(_Symbol, PERIOD_M15, 1, SAMPLE_SIZE, rates); if (copied != SAMPLE_SIZE) { Print("Failed to copy the expected number of rates. Expected: ", SAMPLE_SIZE, ", Copied: ", copied); return false; } else if(copied == SAMPLE_SIZE) { Print("Successfully copied the expected number of rates. Expected: ", SAMPLE_SIZE, ", Copied: ", copied); } double min_time = rates[0].time; double max_time = rates[0].time; for (int i = 1; i < copied; i++) { if (rates[i].time < min_time) min_time = rates[i].time; if (rates[i].time > max_time) max_time = rates[i].time; } float input_data[SAMPLE_SIZE * 5]; int count; for (int i = 0; i < copied; i++) { count++; // Normalize time to be between 0 and 1 within a day input_data[i * 5 + 0] = (float)((rates[i].time)); // normalized time input_data[i * 5 + 1] = (float)rates[i].open; // open input_data[i * 5 + 2] = (float)rates[i].high; // high input_data[i * 5 + 3] = (float)rates[i].low; // low input_data[i * 5 + 4] = (float)rates[i].close; // close } Print("Count of copied after for loop: ", count); // Resize input vector to match the copied data size vectorf input_vector; input_vector.Resize(copied * 5); for (int i = 0; i < copied * 5; i++) { input_vector[i] = input_data[i]; } vectorf output_vector; output_vector.Resize(copied * 5); if (!OnnxRun(ExtHandle, ONNX_NO_CONVERSION, input_vector, output_vector)) { Print("Error running the ONNX model: ", GetLastError()); return false; } // Process the output data as needed for (int i = 0; i < copied; i++) { float time_token = output_vector[i * 5 + 0]; float norm_open = output_vector[i * 5 + 1]; float norm_high = output_vector[i * 5 + 2]; float norm_low = output_vector[i * 5 + 3]; float norm_close = output_vector[i * 5 + 4]; // Print the processed data PrintFormat("Time Token: %f, Norm Open: %f, Norm High: %f, Norm Low: %f, Norm Close: %f", time_token, norm_open, norm_high, norm_low, norm_close); } return true; }
该脚本的输出如下:验证数据流水线是否按预期工作。

为了仔细检查上面的输出,我用 Python 创建了一个额外的脚本,名为“LSTM Data Pipeline Test.py”,它基本上给出相同的输出。该脚本也包含在本文末尾附加的 zip 文件中(位于 “ONNX Data Pipeline” 文件夹中),下面提供以供快速检查。
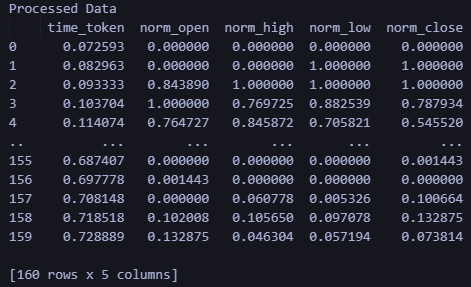
import torch import onnx import onnxruntime as ort import MetaTrader5 as mt5 import pandas as pd import numpy as np # Load the ONNX model onnx_model = onnx.load("data_processing_pipeline.onnx") onnx.checker.check_model(onnx_model) # Initialize MT5 and fetch new data if not mt5.initialize(): print("Initialize failed") mt5.shutdown() symbol = "EURUSD" timeframe = mt5.TIMEFRAME_M15 rates = mt5.copy_rates_from_pos(symbol, timeframe, 0, 160) mt5.shutdown() # Convert the new data to a DataFrame data = pd.DataFrame(rates)[['time', 'open', 'high', 'low', 'close']] data_tensor = torch.tensor(data.values, dtype=torch.float32) # Prepare the input for ONNX input_data = data_tensor.numpy() # Run the ONNX model ort_session = ort.InferenceSession("data_processing_pipeline.onnx") input_name = ort_session.get_inputs()[0].name output_name = ort_session.get_outputs()[0].name processed_data = ort_session.run([output_name], {input_name: input_data})[0] # Convert the output back to DataFrame for easy viewing processed_df = pd.DataFrame(processed_data, columns=['time_token', 'norm_open', 'norm_high', 'norm_low', 'norm_close']) print('Processed Data') print(processed_df)
运行上述脚本的输出如下。输出格式和形式与我们在上面的 MQL 输出中看到的一致。
使用训练好的模型在 MQL 中进行预测
在本节中,我最终想将本文的不同部分 — 数据处理和预测 — 连接到一个脚本中,允许用户在训练模型后获得预测。让我们简要回顾一下在 MQL 中获得预测和创建 EA 交易所需的条件:
- 运行 LSTM_model_training.py 训练模型。请随意调整参数以满足您的需要。运行此文件将创建 lstm_model.onnx。
- 将运行 LSTM_model_training.py 输出的 lstm_model.onnx 文件复制到 MQL Experts 文件夹中名为 “LSTM” 的子文件夹中
- 通过运行 LSTM Data Pipeline.py 创建数据处理流水线。该文件位于附加 zip 文件中的 “ONNX Data Pipeline Folder” 内。
- 运行该文件将生成一个 ONNX 文件用于数据处理。将 data_processing_pipeline.onnx 复制到 MQL Experts 文件夹下的 LSTM 子文件夹中
- 将下面给出的脚本存储在主“Experts”文件夹中,并将其附加到 EURUSD 15 分钟图表以获得预测:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ONNX Test | //| Copyright 2023 | //| Your Name Here | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, Your Name Here" #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" static vectorf ExtOutputData(1); vectorf output_data(1); #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> //#include <Chart\Chart.mqh> CTrade trade; #resource "\\LSTM\\data_processing_pipeline.onnx" as uchar DataProcessingModel[] #resource "\\LSTM\\lstm_model.onnx" as uchar PredictionModel[] #define SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA 160 // Adjusted to match the model's expected input size #define SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED 60 long DataProcessingHandle = INVALID_HANDLE; long PredictionHandle = INVALID_HANDLE; datetime ExtNextBar = 0; // Expert Advisor initialization int OnInit() { // Load the data processing ONNX model DataProcessingHandle = OnnxCreateFromBuffer(DataProcessingModel, ONNX_DEFAULT); if (DataProcessingHandle == INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("Error creating data processing model OnnxCreateFromBuffer ", GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } // Set input shape for data processing model const long input_shape[] = {SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA, 5}; // Adjust based on your model's input dimensions if (!OnnxSetInputShape(DataProcessingHandle, ONNX_DEFAULT, input_shape)) { Print("Error setting the input shape OnnxSetInputShape for data processing model ", GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } // Set output shape for data processing model const long output_shape[] = {SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA, 5}; // Adjust based on your model's output dimensions if (!OnnxSetOutputShape(DataProcessingHandle, 0, output_shape)) { Print("Error setting the output shape OnnxSetOutputShape for data processing model ", GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } // Load the prediction ONNX model PredictionHandle = OnnxCreateFromBuffer(PredictionModel, ONNX_DEFAULT); if (PredictionHandle == INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("Error creating prediction model OnnxCreateFromBuffer ", GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } // Set input shape for prediction model const long prediction_input_shape[] = {SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED, 1, 5}; // Adjust based on your model's input dimensions if (!OnnxSetInputShape(PredictionHandle, ONNX_DEFAULT, prediction_input_shape)) { Print("Error setting the input shape OnnxSetInputShape for prediction model ", GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } // Set output shape for prediction model const long prediction_output_shape[] = {1}; // Adjust based on your model's output dimensions if (!OnnxSetOutputShape(PredictionHandle, 0, prediction_output_shape)) { Print("Error setting the output shape OnnxSetOutputShape for prediction model ", GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } // Expert Advisor deinitialization void OnDeinit(const int reason) { if (DataProcessingHandle != INVALID_HANDLE) { OnnxRelease(DataProcessingHandle); DataProcessingHandle = INVALID_HANDLE; } if (PredictionHandle != INVALID_HANDLE) { OnnxRelease(PredictionHandle); PredictionHandle = INVALID_HANDLE; } } // Process the tick function void OnTick() { if (TimeCurrent() < ExtNextBar) return; ExtNextBar = TimeCurrent(); ExtNextBar -= ExtNextBar % PeriodSeconds(); ExtNextBar += PeriodSeconds(); // Fetch new data and run the data processing ONNX model vectorf input_data = ProcessData(DataProcessingHandle); if (input_data.Size() == 0) { Print("Error processing data"); return; } // Make predictions using the prediction ONNX model double predictions[SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA - SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA - SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED + 1; i++) { double prediction = MakePrediction(input_data, PredictionHandle, i, SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED); //if (prediction < 0) //{ // Print("Error making prediction"); // return; //} // Print the prediction //PrintFormat("Predicted close price (index %d): %f", i, prediction); double min_price = iLow(Symbol(), PERIOD_D1, 0); //price is relative to the day's price therefore we use low of day for min price double max_price = iHigh(Symbol(), PERIOD_D1, 0); //high of day for max price double price = prediction * (max_price - min_price) + min_price; predictions[i] = price; PrintFormat("Predicted close price (index %d): %f", i, predictions[i]); } // Get the actual prices for the last 60 bars double actual_prices[SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED]; for (int i = 0; i < SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED; i++) { actual_prices[i] = iClose(Symbol(), PERIOD_M15, SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED - i); Print(actual_prices[i]); } // Create a label object to display the predicted and actual prices string label_text = "Predicted | Actual\n"; for (int i = 0; i < SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED; i++) { label_text += StringFormat("%.5f | %.5f\n", predictions[i], actual_prices[i]); } label_text += StringFormat("Next prediction: %.5f", predictions[SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA - SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED]); Print(label_text); //int label_handle = ObjectCreate(OBJ_LABEL, 0, 0, 0); //ObjectSetText(label_handle, label_text, 12, clrWhite, clrBlack, ALIGN_LEFT); //ObjectMove(label_handle, 0, ChartHeight() - 20, ChartWidth(), 20); } // Function to process data using the data processing ONNX model vectorf ProcessData(long data_processing_handle) { MqlRates rates[SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA]; vectorf blank_vector; int copied = CopyRates(_Symbol, PERIOD_M15, 1, SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA, rates); if (copied != SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA) { Print("Failed to copy the expected number of rates. Expected: ", SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA, ", Copied: ", copied); return blank_vector; } float input_data[SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA * 5]; for (int i = 0; i < copied; i++) { // Normalize time to be between 0 and 1 within a day input_data[i * 5 + 0] = (float)((rates[i].time)); // normalized time input_data[i * 5 + 1] = (float)rates[i].open; // open input_data[i * 5 + 2] = (float)rates[i].high; // high input_data[i * 5 + 3] = (float)rates[i].low; // low input_data[i * 5 + 4] = (float)rates[i].close; // close } vectorf input_vector; input_vector.Resize(copied * 5); for (int i = 0; i < copied * 5; i++) { input_vector[i] = input_data[i]; } vectorf output_vector; output_vector.Resize(copied * 5); if (!OnnxRun(data_processing_handle, ONNX_NO_CONVERSION, input_vector, output_vector)) { Print("Error running the data processing ONNX model: ", GetLastError()); return blank_vector; } return output_vector; } // Function to make predictions using the prediction ONNX model double MakePrediction(const vectorf& input_data, long prediction_handle, int start_index, int size) { vectorf input_subset; input_subset.Resize(size * 5); for (int i = 0; i < size * 5; i++) { input_subset[i] = input_data[start_index * 5 + i]; } vectorf output_vector; output_vector.Resize(1); if (!OnnxRun(prediction_handle, ONNX_NO_CONVERSION, input_subset, output_vector)) { Print("Error running the prediction ONNX model: ", GetLastError()); return -1.0; } // Extract the normalized close price from the output data double norm_close = output_vector[0]; return norm_close; }
如果您使用的文件夹结构与我在本文中概述的不同,请考虑更改以下代码行以匹配您自己的文件夹所需的文件路径。
#resource "\\LSTM\\data_processing_pipeline.onnx" as uchar DataProcessingModel[] #resource "\\LSTM\\lstm_model.onnx" as uchar PredictionModel[]
回顾一下,脚本的工作原理如下。它运行于 EURUSD,时间框架为 15 分钟。
-
数据预处理模型:该模型(“data_processing_pipeline.onnx”)处理时间标记化(将时间转换为数值表示)和价格数据归一化等任务,以备与我们训练过的 LSTM 模型一起使用。
-
预测模型:该模型(“lstm_model.onnx”)是 LSTM 模型(长短期记忆)网络,经过训练可以分析前 60 个 15 分钟柱形价格走势图,从而预测下一个可能的收盘价。
功能:
-
初始化(OnInit):
- 从嵌入式资源加载两个 ONNX 模型(数据预处理和预测)。
- 根据两个模型的需求配置其输入和输出形式。
-
分时报价数据处理 (OnTick):
- 该函数在每次新的价格变动时触发。
- 它等待下一个 15 分钟的柱形(蜡烛)形成。
- 调用 ProcessData 函数对数据进行预处理。
- 遍历预处理的数据,使用 MakePrediction 函数生成价格预测。
- 将归一化的预测转换回实际价格值。请注意:在 MQL 中进行预测时,我们现在使用以下代码行。这几行代码将我们得到的预测(相对于每日最高价和最低价在 0 到 1 之间进行归一化)转换回实际价格目标。
-
double min_price = iLow(Symbol(), PERIOD_D1, 0); //price is relative to the day's price therefore we use low of day for min price double max_price = iHigh(Symbol(), PERIOD_D1, 0); //high of day for max price double price = prediction * (max_price - min_price) + min_price;
- 打印预测价格和实际收盘价格以供比较。您可在“日志”选项卡中查看这些值。
- 使用预测价格与实际价格信息来格式化字符串。
- 请注意:注释的代码部分旨在在图表上创建标签以显示预测值和实际值。这将成为实时评估模型性能的良好可视化辅助工具。但是,我还不能完成代码,因为我仍在思考如何最好地使用这些预测 —— 作为指标还是 EA。
-
数据处理(ProcessData):
- 获取最新的 160 个柱的 EURUSD M15 数据。
- 为数据处理模型准备输入数据(时间、开盘价、最高价、最低价、收盘价)。
- 执行数据处理模型来归一化和标记化输入数据。
-
预测(MakePrediction):
- 将预处理数据的子集(60 个数据点的序列)作为输入。
- 执行预测模型,连续获取归一化的预测收盘价。
- 打印出预测 -> 可以在“专家”选项卡中查看。
请注意下面给出的输出格式:

正如我们所见,我们得到了一些不同的输出。首先是“"Next Prediction”上方列中的预测值和实际值。按照上面代码中的格式,预测|实际。
for (int i = 0; i < SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED; i++) { label_text += StringFormat("%.5f | %.5f\n", predictions[i], actual_prices[i]); }
“Next prediction:1.07333” 行来自上面代码中的以下几行:
label_text += StringFormat("Next prediction: %.5f", predictions[SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA - SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED]); Print(label_text);
训练模型的应用:创建 EA 交易
创建 EA 交易
我采用的将预测转化为 EA 交易的方法受到了 Yevgeniy Koshtenko 的一篇文章的启发,该文章的标题为 “ Python、ONNX 和 MetaTrader 5:使用 RobustScaler 和 PolynomialFeatures 数据预处理创建 RandomForest 模型“。它是一个相对简单的 EA,为 EA 创建奠定了基础。当然,用户可以扩展我下面概述的方法,以包括附加参数,例如追踪止损,或者将 LSTM 神经网络预测与他们在 EA 交易开发中已经使用的其他工具结合起来。
我们使用整体框架来处理数据并做出预测,就像我们上面所做的那样。然而,在 EA 脚本中,我们使用了以下额外的修改:
-
信号确定(DetermineSignal):
- 将最后预测的收盘价与当前收盘价和价差进行比较,以确定交易信号。
- 考虑使用较小的扩展阈值来滤除噪声信号。
-
交易管理(CheckForOpen、CheckForClose):
- CheckForOpen:如果没有开仓且收到有效信号(买入或卖出),则以配置的手数、止损和止盈开立新仓位。
- CheckForClose :如果持仓未平仓且收到相反方向的信号,则平仓。仅当 InpUseStops 为“False”时才会发生这种情况,因为代码中有以下几行:
// Check position closing conditions void CheckForClose(void) { if (InpUseStops) return; //...rest of code }否则,如果将 InpUseStops 设置为 true,则仅当触发止损或止盈时才会平仓。 包含所有实现内容的 EA 完整代码可在本文附带的 LSTM_Files.zip 内的根文件夹中找到。文件名为 LSTM_Simple_EA.mq5
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ONNX Test | //| Copyright 2023 | //| Your Name Here | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, Your Name Here" #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" static vectorf ExtOutputData(1); vectorf output_data(1); #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> CTrade trade; input double InpLots = 1.0; // Lot volume to open a position input bool InpUseStops = true; // Trade with stop orders input int InpTakeProfit = 500; // Take Profit level input int InpStopLoss = 500; // Stop Loss level #resource "\\LSTM\\data_processing_pipeline.onnx" as uchar DataProcessingModel[] #resource "\\LSTM\\lstm_model.onnx" as uchar PredictionModel[] #define SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA 160 // Adjusted to match the model's expected input size #define SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED 60 long DataProcessingHandle = INVALID_HANDLE; long PredictionHandle = INVALID_HANDLE; datetime ExtNextBar = 0; int ExtPredictedClass = -1; #define PRICE_UP 1 #define PRICE_SAME 2 #define PRICE_DOWN 0 // Expert Advisor initialization int OnInit() { // Load the data processing ONNX model DataProcessingHandle = OnnxCreateFromBuffer(DataProcessingModel, ONNX_DEFAULT); if (DataProcessingHandle == INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("Error creating data processing model OnnxCreateFromBuffer ", GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } // Set input shape for data processing model const long input_shape[] = {SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA, 5}; // Adjust based on your model's input dimensions if (!OnnxSetInputShape(DataProcessingHandle, ONNX_DEFAULT, input_shape)) { Print("Error setting the input shape OnnxSetInputShape for data processing model ", GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } // Set output shape for data processing model const long output_shape[] = {SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA, 5}; // Adjust based on your model's output dimensions if (!OnnxSetOutputShape(DataProcessingHandle, 0, output_shape)) { Print("Error setting the output shape OnnxSetOutputShape for data processing model ", GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } // Load the prediction ONNX model PredictionHandle = OnnxCreateFromBuffer(PredictionModel, ONNX_DEFAULT); if (PredictionHandle == INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("Error creating prediction model OnnxCreateFromBuffer ", GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } // Set input shape for prediction model const long prediction_input_shape[] = {SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED, 1, 5}; // Adjust based on your model's input dimensions if (!OnnxSetInputShape(PredictionHandle, ONNX_DEFAULT, prediction_input_shape)) { Print("Error setting the input shape OnnxSetInputShape for prediction model ", GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } // Set output shape for prediction model const long prediction_output_shape[] = {1}; // Adjust based on your model's output dimensions if (!OnnxSetOutputShape(PredictionHandle, 0, prediction_output_shape)) { Print("Error setting the output shape OnnxSetOutputShape for prediction model ", GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } // Expert Advisor deinitialization void OnDeinit(const int reason) { if (DataProcessingHandle != INVALID_HANDLE) { OnnxRelease(DataProcessingHandle); DataProcessingHandle = INVALID_HANDLE; } if (PredictionHandle != INVALID_HANDLE) { OnnxRelease(PredictionHandle); PredictionHandle = INVALID_HANDLE; } } // Process the tick function void OnTick() { if (TimeCurrent() < ExtNextBar) return; ExtNextBar = TimeCurrent(); ExtNextBar -= ExtNextBar % PeriodSeconds(); ExtNextBar += PeriodSeconds(); // Fetch new data and run the data processing ONNX model vectorf input_data = ProcessData(DataProcessingHandle); if (input_data.Size() == 0) { Print("Error processing data"); return; } // Make predictions using the prediction ONNX model double predictions[SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA - SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA - SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED + 1; i++) { double prediction = MakePrediction(input_data, PredictionHandle, i, SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED); double min_price = iLow(Symbol(), PERIOD_D1, 0); // price is relative to the day's price therefore we use low of day for min price double max_price = iHigh(Symbol(), PERIOD_D1, 0); // high of day for max price double price = prediction * (max_price - min_price) + min_price; predictions[i] = price; PrintFormat("Predicted close price (index %d): %f", i, predictions[i]); } // Determine the trading signal DetermineSignal(predictions); // Execute trades based on the signal if (ExtPredictedClass >= 0) if (PositionSelect(_Symbol)) CheckForClose(); else CheckForOpen(); } // Function to determine the trading signal void DetermineSignal(double &predictions[]) { double spread = GetSpreadInPips(_Symbol); double predicted = predictions[SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA - SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED]; // Use the last prediction for decision making if (spread < 0.000005 && predicted > iClose(Symbol(), PERIOD_M15, 1)) { ExtPredictedClass = PRICE_UP; } else if (spread < 0.000005 && predicted < iClose(Symbol(), PERIOD_M15, 1)) { ExtPredictedClass = PRICE_DOWN; } else { ExtPredictedClass = PRICE_SAME; } } // Check position opening conditions void CheckForOpen(void) { ENUM_ORDER_TYPE signal = WRONG_VALUE; if (ExtPredictedClass == PRICE_DOWN) signal = ORDER_TYPE_SELL; else if (ExtPredictedClass == PRICE_UP) signal = ORDER_TYPE_BUY; if (signal != WRONG_VALUE && TerminalInfoInteger(TERMINAL_TRADE_ALLOWED)) { double price, sl = 0, tp = 0; double bid = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_BID); double ask = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_ASK); if (signal == ORDER_TYPE_SELL) { price = bid; if (InpUseStops) { sl = NormalizeDouble(bid + InpStopLoss * _Point, _Digits); tp = NormalizeDouble(ask - InpTakeProfit * _Point, _Digits); } } else { price = ask; if (InpUseStops) { sl = NormalizeDouble(ask - InpStopLoss * _Point, _Digits); tp = NormalizeDouble(bid + InpTakeProfit * _Point, _Digits); } } trade.PositionOpen(_Symbol, signal, InpLots, price, sl, tp); } } // Check position closing conditions void CheckForClose(void) { if (InpUseStops) return; bool tsignal = false; long type = PositionGetInteger(POSITION_TYPE); if (type == POSITION_TYPE_BUY && ExtPredictedClass == PRICE_DOWN) tsignal = true; if (type == POSITION_TYPE_SELL && ExtPredictedClass == PRICE_UP) tsignal = true; if (tsignal && TerminalInfoInteger(TERMINAL_TRADE_ALLOWED)) { trade.PositionClose(_Symbol, 3); CheckForOpen(); } } // Function to get the current spread double GetSpreadInPips(string symbol) { double spreadPoints = SymbolInfoInteger(symbol, SYMBOL_SPREAD); double spreadPips = spreadPoints * _Point / _Digits; return spreadPips; } // Function to process data using the data processing ONNX model vectorf ProcessData(long data_processing_handle) { MqlRates rates[SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA]; vectorf blank_vector; int copied = CopyRates(_Symbol, PERIOD_M15, 1, SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA, rates); if (copied != SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA) { Print("Failed to copy the expected number of rates. Expected: ", SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA, ", Copied: ", copied); return blank_vector; } float input_data[SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA * 5]; for (int i = 0; i < copied; i++) { // Normalize time to be between 0 and 1 within a day input_data[i * 5 + 0] = (float)((rates[i].time)); // normalized time input_data[i * 5 + 1] = (float)rates[i].open; // open input_data[i * 5 + 2] = (float)rates[i].high; // high input_data[i * 5 + 3] = (float)rates[i].low; // low input_data[i * 5 + 4] = (float)rates[i].close; // close } vectorf input_vector; input_vector.Resize(copied * 5); for (int i = 0; i < copied * 5; i++) { input_vector[i] = input_data[i]; } vectorf output_vector; output_vector.Resize(copied * 5); if (!OnnxRun(data_processing_handle, ONNX_NO_CONVERSION, input_vector, output_vector)) { Print("Error running the data processing ONNX model: ", GetLastError()); return blank_vector; } return output_vector; } // Function to make predictions using the prediction ONNX model double MakePrediction(const vectorf& input_data, long prediction_handle, int start_index, int size) { vectorf input_subset; input_subset.Resize(size * 5); for (int i = 0; i < size * 5; i++) { input_subset[i] = input_data[start_index * 5 + i]; } vectorf output_vector; output_vector.Resize(1); if (!OnnxRun(prediction_handle, ONNX_NO_CONVERSION, input_subset, output_vector)) { Print("Error running the prediction ONNX model: ", GetLastError()); return -1.0; } // Extract the normalized close price from the output data double norm_close = output_vector[0]; return norm_close; }
EA 交易测试
创建 EA 交易后,我使用以下设置运行了优化器:

我在不到1个小时的时间内就得出了以下优化参数。为了演示目的,我仅显示出现的第一个结果。我没有完成完整的优化周期,因为我只是想说明即使在很少的优化和我们上面制作的相对简单的 EA 的情况下,预测效果仍然很好:

使用指定设置的测试期间的结果如下所示。完整的回溯测试报告也以 zip 文件形式附加,以供进一步查阅。

结论
在本文中,我分享了从将数据从 Metatrader 拉入 Python 到使用可在 MQL 中使用的经过训练的 LSTM 神经网络创建 EA 交易的整个过程。在此过程中,我记录了如何使用 Python 和 MQL 来标记时间、归一化价格、验证数据和获取预测。当我了解到新事物并决定将它们纳入文章中时,我不得不对这篇文章进行超过 200 次修改。我唯一的希望是读者可以使用我的工作并快速掌握使用 Python 中强大的神经网络的方法,并使用 ONNX 将它们实现到 MQL 中。我还希望允许用户利用数据处理管道以他们认为合适的方式转换数据,并使用 ONNX 将该功能实现到他们的 MQL 脚本中。我希望读者会喜欢这篇文章,我期待着他们可能对我提出的任何问题和建议。
补充说明:
- LSTM_Files.zip 包含一个带有所需 python 包的 requirements.txt 文件。只需在终端中使用命令 pip install -r requirements.txt 即可。这将安装 requirements.txt 文件中列出的所有包。
- 如果你仔细检查这段代码,你会注意到缩放是基于当天的最高价和最低价,而预测数组也可能包含前一天的数据,因为它使用了 60 个连续的预测,这可能会与前一天重叠,尤其是在亚洲时段。
for (int i = 0; i < SAMPLE_SIZE_DATA - SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED + 1; i++) { double prediction = MakePrediction(input_data, PredictionHandle, i, SAMPLE_SIZE_PRED); double min_price = iLow(Symbol(), PERIOD_D1, 0); // price is relative to the day's price therefore we use low of day for min price double max_price = iHigh(Symbol(), PERIOD_D1, 0); // high of day for max price double price = prediction * (max_price - min_price) + min_price; predictions[i] = price; PrintFormat("Predicted close price (index %d): %f", i, predictions[i]); }
因此,使用前一天价格的一部分进行预测以获得实际预测价格会更准确。
double min_price = iLow(Symbol(), PERIOD_D1, 1 ); // previous day's low double max_price = iHigh(Symbol(), PERIOD_D1, 1 ); // previous day's high
- 即使上面的代码也不是很准确,因为您需要考虑当天的滚动最高价和最低价才能获得准确的预测。
- 我保持原样,因为我的目标是将我的代码转换为 EA,它将主要根据最近的当前标记值进行未来预测,这就是 data_processing_pipeline.onnx 所做的。但对于那些开发指标的人来说,他们应该考虑使用前一天最高价/最低价的滚动范围来扩展与前一天重叠的过去预测。也许创建一个 data_processing_pipeline.onnx 的逆函数来反向执行此操作是一个合乎逻辑的选择。
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/15063
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 分歧问题:深入探讨人工智能的复杂性可解释性
分歧问题:深入探讨人工智能的复杂性可解释性
 数据科学和机器学习(第 19 部分):利用 AdaBoost 为您的 AI 模型增压
数据科学和机器学习(第 19 部分):利用 AdaBoost 为您的 AI 模型增压

