Implementation of the Augmented Dickey Fuller test in MQL5
Introduction
The Augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF) test is a common procedure used to assess whether a time series is stationary or not. Although, it is well known that financial time series are inherently non-stationary. Many statistical methods that benefit from stationarity usually require that non-stationary datasets be transformed in some way before being analyzed. The ADF test can be used to evaluate the efficacy of these tranformations in inducing stationarity. Alternatively, evaluating the cointegration of series also makes use of tests for stationarity. Usefull in the development of trading strategies that exploit discrepancies in pricing of related financial instruments. In this article we will present the implementation of the ADF test in pure MQL5 and demonstrate its application by using it to identify cointegrated symbols in MetaTrader 5.
Understanding the ADF Test
Simply put an ADF test is a hypothesis test, that allows us to determine if a specific characteristic of the observed data is statistically significant. In this instance the characteristic being acertained is the stationarity of a series. A statistical hypothesis is an assumption made about a data set that is represented by a sample. We can only know the real truth by working with the entire data set. Which is usually not possible for one reason or another. So a sample of a data set is tested to posit an assumption of the entire data set. The important point to remember here is that the truth of a statistical hypothesis is never known with certainty when working with samples. What we get is whether an assumption is likely true or false.
In an ADF test we consider two scenarios:
- The Null hypothesis that a unit root is present in the time series.
- The Alternative hypothesis that the times series does not exhibit a unit root.
In time series analysis a unit root is a special characteristic of a sequential data set. Imagine a man walking down a street with their dog. The man will likely walk in a fairly straight line towards his destination. Whilst the dog will often wander off, to sniff at something or chase some critter that has caught its attention. But ultimately it will follow its owner. If the path of the dog is plotted we may observe some type of oscillation. Where the dog wanders off, but eventually reverts back to the expected general direction being followed by the man.
An arbitrary point on the dog's path represents the value of a variable at a specific time. If we evaluate these values, its likely they will stay with in a certain range around a central tendency. The statistical properties donot change significantly over time. Such a series will not have a unit root. Now imagine if the man was walking his untrained dog on the same street. The dog will likely run off and never come back to the owner. The values associated with the path taken by this dog wil vary unpredictably. Such a series will have a unit root.
The notion of a unit root comes from the characteristic equation of a stochastic process. A stochastic process is a sequence of variables indexed by time, describing a system that evolves randomly. The characterisitc equation of a stochastic process is an equation that captures the system's properties. The unit root is a solution of the characteristic equation that equals 1. If a process has a unit root, it means that the shocks or random effects have a persistent effect on the process. Such a system is modelled by random effects and lagged values. Meaning that it is autoregressive in nature.
Therefore, the ADF test uses a regression model to test for a unit root. The most common form of the model is given by the equation below.
Where:
- " Y " The first difference of the time series
- "a" A constant term
- "b" The coefficient of the lagged level of the time series
- "x" The coefficient of the time trend (t)
- "V" Coefficients of lagged first differences
- "E" The error term
The test focuses on the coefficient "b". If "b" = 0, there is a unit root otherwise if "b" < 0, the time series is stationary. The ADF statistic is calculated based on the estimated value of "b" and its standard error. It's compared to critical values from a Dickey-Fuller distribution. If the ADF statistic is more negative than the critical value at a specific significance level, the null hypothesis of a unit root is rejected. Meaning that the series is stationary.
Implementation
In order to ensure that our implementation is accurate we will use an existing implementation of the ADF test in Python as a reference. In the 'statsmodels' Python package, the `adfuller` function is used to perform an ADF test.
adfuller(x, maxlag: 'int | None' = None, regression='c', autolag='AIC', store=False, regresults=False)
The function first estimates the parameters of an autoregressive model of the input series using ordinary least squares. A test statistic is computed based on the estimated parameters. Which is used to calculate a p-value. Three critical values are drawn from a distribution table which represent confidence levels. Finally, the test statistic can be compared against anyone of these values to determine whether a series is stationary or not.
Based on this overview, there are three important components we have to implement. First is the ordinary least squares regression model. Probably the most important component, as any errors here will propagate to other stages of the test. This will be used to determine the most appropriate autoregressive model of the series being analyzed. Besides the model parameters we also need to calculate various properties of a model, such as its Akaike information criteria and Bayesian information criteria.
The second component relates to the calculation of the p-value. The p-value is determined by the a test statistic derived from the t-statistic of the optimal autoregressive model. A t-statistic is a measure used to determine if there is a significant difference between the means of two groups. It is calculated by taking the difference between the sample means and dividing it by the standard error of the difference. In this context the t-statistic is computed by dividing the model's parameters by the model's standard error. The method employed to calculate the p-value was proposed by J.G. MacKinnon and is therefore called MacKinnon's approximate p-value method. It provides an approximation for the p-value associated with critical values from statistical tests.
The last component needed to complete the ADF test is the computation of the critical values. These values are derived from approximations given in an academic paper written by MacKinnon.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Ordinary least squares class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class OLS { private: matrix m_exog, //design matrix m_pinv, //pseudo-inverse of matrix m_cov_params, //covariance of matrix m_m_error, //error matrix m_norm_cov_params; //normalized covariance matrix vector m_endog, //dependent variables m_weights, //weights m_singularvalues, //singular values of solution m_params, //coefficients of regression model(solution) m_tvalues, //test statistics of model m_bse, //standard errors of model m_resid; //residuals of model ulong m_obs, //number of observations m_model_dof, //degrees of freedom of model m_resid_dof, //degrees of freedom of residuals m_kconstant, //number of constants m_rank; //rank of design matrix double m_aic, //Akiake information criteria m_bic, //Bayesian information criteria m_scale, //scale of model m_llf, //loglikelihood of model m_sse, //sum of squared errors m_rsqe, //r-squared of model m_centeredtss, //centered sum of squares m_uncenteredtss; //uncentered sum of squares uint m_error; //error flag // private methods ulong countconstants(void); void scale(void); void sse(void); void rsqe(void); void centeredtss(void); void uncenteredtss(void); void aic(void); void bic(void); void bse(void); void llf(void); void tvalues(void); void covariance_matrix(void); public: //constructor OLS(void); //destructor ~OLS(void); //public methods bool Fit(vector &y_vars,matrix &x_vars); double Predict(vector &inputs); double Predict(double _input); //get properties of OLS model ulong ModelDOF(void) { if(m_error) return 0; else return m_model_dof;} ulong ResidDOF(void) { if(m_error) return 0; else return m_resid_dof;} double Scale(void) { if(m_error) return EMPTY_VALUE; else return m_scale; } double Aic(void) { if(m_error) return EMPTY_VALUE; else return m_aic; } double Bic(void) { if(m_error) return EMPTY_VALUE; else return m_bic; } double Sse(void) { if(m_error) return EMPTY_VALUE; else return m_sse; } double Rsqe(void) { if(m_error) return EMPTY_VALUE; else return m_rsqe; } double C_tss(void) { if(m_error) return EMPTY_VALUE; else return m_centeredtss;} double Loglikelihood(void) { if(m_error) return EMPTY_VALUE; return m_llf; } vector Tvalues(void) { if(m_error) return m_m_error.Col(0); return m_tvalues; } vector Residuals(void) { if(m_error) return m_m_error.Col(0); return m_resid; } vector ModelParameters(void) { if(m_error) return m_m_error.Col(0); return m_params; } vector Bse(void) { if(m_error) return m_m_error.Col(0); return m_bse; } matrix CovarianceMatrix(void) { if(m_error) return m_m_error; return m_cov_params; } };
OLS.mqh contains the definition of the OLS class, representing an ordinary least squares regression model. The class has several public methods. The first of which is "Fit()", the first method that users should call after creating an instance of this class. It requires as input a vector and a matrix. The vector "y_vars" should be filled with the dependent values and "x_vars" is the design matrix ."Fit()" will return true on successful execution at which point any other public method can be called. All these methods return a specific property of a computed model. These properties are summarized in the table below.
| Return data type | Value returned on error | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ulong | 0 | ModelDOF() | the degress of freedom for a model |
| ulong | 0 | ResidDOF() | the degrees of freedom for a model's residuals |
| double | EMPTY_VALUE | Scale() | this is the variance of the error term, indicating the variability in the dependent variable not explained by the independent variables |
| double | EMPTY_VALUE | Aic() | Akaike's information criteria |
| double | EMPTY_VALUE | Bic() | Bayesian's information criteria |
| double | EMPTY_VALUE | Sse() | the sum of squared errors of the model |
| double | EMPTY_VALUE | Rsqe() | this is the R-squared metric of the model, ie the coefficient of determination |
| double | EMPTY_VALUE | C_tss() | this is the total sum of squared errors centred about the mean |
| double | EMPTY_VALUE | Loglikelihood() | The likelihood function for the OLS model |
| vector | vector of empty values | Tvalues() | provides the t-statistic for a each parameter estimate of a model |
| vector | vector of empty values | Residuals() | the residuals of the model, ie the difference between the predicted and actual values |
| vector | vector of empty values | Bse() | the standard errors of the parameter estimates |
| matrix | matrix of empty values | CovarianceMatrix() | matrix displaying the variances of variables and the covariances between the variables |
"Predict()" has two overloads that differ by their input data types. Which are either a vector or a scalar value of type double. Both return a single predition given new independent variable(s).
The next part of our implementation moves to the ADF.mqh file. This file will contain a collection of function definitions relating to the ADF test. One of these functions will be "adfuller()". We include OLS.mqh for the OLS class, Math.mqh from the standard library and also specialfunctions.mqh of the Alglib library.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ADF.mqh | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #include<Math\Stat\Math.mqh> #include<Math\Alglib\specialfunctions.mqh> #include<OLS.mqh>
The next part of our implementation moves to the ADF.mqh file. This file will contain a collection of function definitions as well as that of the CAdf class. We include OLS.mqh for the OLS class, Math.mqh from the standard library and also specialfunctions.mqh of the Alglib library. ADF.mqh begins with the definition of some enumerations. ENUM_INFO_CRIT represents the options available when it comes to determining the optimal regression model for a particular series. It defines the metrics used to select the right model. ENUM_TRIM, ENUM_ORIGINAL, ENUM_HAS_CONST and ENUM_TREND are used in the construction of a design matrix.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Information criterion | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum ENUM_INFO_CRIT { INFO_NONE=0, INFO_AIC, INFO_BIC }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Options for trimming invalid observations | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum ENUM_TRIM { TRIM_NONE=0, TRIM_FORWARD, TRIM_BACKWARD, TRIM_BOTH }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| options for how to handle original data set | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum ENUM_ORIGINAL { ORIGINAL_EX=0, ORIGINAL_IN, ORIGINAL_SEP }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Constant and trend used in regression model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum ENUM_TREND { TREND_NONE=0, TREND_CONST_ONLY, TREND_LINEAR_ONLY, TREND_LINEAR_CONST, TREND_QUAD_LINEAR_CONST }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Options for how to handle existing constants | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum ENUM_HAS_CONST { HAS_CONST_RAISE=0, HAS_CONST_SKIP, HAS_CONST_ADD };
The "Adfuller()" method of CAdf returns a boolean value that signifies successfull execution of the test, NOT THE STATIONARITY OF A SERIES. If false is returned then an error must have occurred. Any errors will be accompanied by verbose messages output to the terminal's journal. It takes as input an array of a series to be analyzed. Other arguments to the function are optional. In most cases users will not have to concern themselves with these parameters. Calling the function with the aforementioned parameters should suffice.
//+---------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|Class CAdf | //| encapsulates the the Augmented Dickey Fuller Test for Stationarity| //+---------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CAdf { private: double m_adf_stat, //adf statistic m_bestic, //optimal bic or aic m_pvalue; //p-value ulong m_usedlag; //lag used for optimal reg model vector m_critvals; //estimated critical values OLS *m_ols; //internal ordinary least squares reg model // private methods bool gridsearch(vector &LHS, matrix &RHS, ulong f_lag, ulong l_lag,ENUM_INFO_CRIT crit, double &b_ic, ulong &best_lag); bool lagmat(matrix &in,matrix &out[],ulong mlag,ENUM_TRIM trim=TRIM_BOTH,ENUM_ORIGINAL original=ORIGINAL_IN); bool prepare_lhs_rhs(vector &lhs, matrix &rhs, double &in[], double &in_diff[],ulong lag); public: CAdf(void); ~CAdf(void); bool Adfuller(double &array[],ulong max_lag = 0,ENUM_TREND trend = TREND_CONST_ONLY, ENUM_INFO_CRIT autolag=INFO_AIC); vector CriticalValues(void) { return m_critvals; } double AdfStatistic(void) { return m_adf_stat; } double Pvalue(void) { return m_pvalue; } };
"max_lag" defines the maximum number of lags of the regression model. "trend" is an enumeration that allows specification of the trend and constant configuration of the regression model."autolag" determines what metric is used to select the optimal model that best describes the input series. Within "Adfuller()", the function parameters are checked first before being used to construct the dependent and independent variables of a regression model.
Several variations of this initial design matrix are sampled in order to determine which one best fits the input series. The criteria used to come up with the best model is dependent on the value of the "autolag" parameter. The search is done by the "gridsearch()" function.
Once the best model is found, the lag property of this model, refering to the number of columns included from the initial design matrix, is used to define the optimal model. Whose parameters will be used to estimate the stationarity of the series. The first t-statistic of the optimal OLS model defines the ADF statistic of the ADF test. The p-value is computed by the "mackinnop()" function. Calling CAdf's "Pvalue()" method returns the corresponding p-value.
//+----------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| calculates MacKinnon's approximate p-value for a given test statistic| //+----------------------------------------------------------------------+ double mackinnonp(double teststat, ENUM_TREND trend = TREND_CONST_ONLY,ulong nseries = 1, uint lags =0) { vector small_scaling = {1, 1, 1e-2}; vector large_scaling = {1, 1e-1, 1e-1, 1e-2}; double tau_star_nc []= {-1.04, -1.53, -2.68, -3.09, -3.07, -3.77}; double tau_min_nc []= {-19.04, -19.62, -21.21, -23.25, -21.63, -25.74}; double tau_max_nc []= {double("inf"), 1.51, 0.86, 0.88, 1.05, 1.24}; double tau_star_c []= {-1.61, -2.62, -3.13, -3.47, -3.78, -3.93}; double tau_min_c []= {-18.83, -18.86, -23.48, -28.07, -25.96, -23.27}; double tau_max_c []= {2.74, 0.92, 0.55, 0.61, 0.79, 1}; double tau_star_ct []= {-2.89, -3.19, -3.50, -3.65, -3.80, -4.36}; double tau_min_ct []= {-16.18, -21.15, -25.37, -26.63, -26.53, -26.18}; double tau_max_ct []= {0.7, 0.63, 0.71, 0.93, 1.19, 1.42}; double tau_star_ctt []= {-3.21, -3.51, -3.81, -3.83, -4.12, -4.63}; double tau_min_ctt []= {-17.17, -21.1, -24.33, -24.03, -24.33, -28.22}; double tau_max_ctt []= {0.54, 0.79, 1.08, 1.43, 3.49, 1.92}; double tau_nc_smallp [][3]= { {0.6344, 1.2378, 3.2496}, {1.9129, 1.3857, 3.5322}, {2.7648, 1.4502, 3.4186}, {3.4336, 1.4835, 3.19}, {4.0999, 1.5533, 3.59}, {4.5388, 1.5344, 2.9807} }; double tau_c_smallp [][3]= { {2.1659, 1.4412, 3.8269}, {2.92, 1.5012, 3.9796}, {3.4699, 1.4856, 3.164}, {3.9673, 1.4777, 2.6315}, {4.5509, 1.5338, 2.9545}, {5.1399, 1.6036, 3.4445} }; double tau_ct_smallp [][3]= { {3.2512, 1.6047, 4.9588}, {3.6646, 1.5419, 3.6448}, {4.0983, 1.5173, 2.9898}, {4.5844, 1.5338, 2.8796}, {5.0722, 1.5634, 2.9472}, {5.53, 1.5914, 3.0392} }; double tau_ctt_smallp [][3]= { {4.0003, 1.658, 4.8288}, {4.3534, 1.6016, 3.7947}, {4.7343, 1.5768, 3.2396}, {5.214, 1.6077, 3.3449}, {5.6481, 1.6274, 3.3455}, {5.9296, 1.5929, 2.8223} }; double tau_nc_largep [][4]= { {0.4797, 9.3557, -0.6999, 3.3066}, {1.5578, 8.558, -2.083, -3.3549}, {2.2268, 6.8093, -3.2362, -5.4448}, {2.7654, 6.4502, -3.0811, -4.4946}, {3.2684, 6.8051, -2.6778, -3.4972}, {3.7268, 7.167, -2.3648, -2.8288} }; double tau_c_largep [][4]= { {1.7339, 9.3202, -1.2745, -1.0368}, {2.1945, 6.4695, -2.9198, -4.2377}, {2.5893, 4.5168, -3.6529, -5.0074}, {3.0387, 4.5452, -3.3666, -4.1921}, {3.5049, 5.2098, -2.9158, -3.3468}, {3.9489, 5.8933, -2.5359, -2.721} }; double tau_ct_largep [][4]= { {2.5261, 6.1654, -3.7956, -6.0285}, {2.85, 5.272, -3.6622, -5.1695}, {3.221, 5.255, -3.2685, -4.1501}, {3.652, 5.9758, -2.7483, -3.2081}, {4.0712, 6.6428, -2.3464, -2.546}, {4.4735, 7.1757, -2.0681, -2.1196} }; double tau_ctt_largep [][4]= { {3.0778, 4.9529, -4.1477, -5.9359}, {3.4713, 5.967, -3.2507, -4.2286}, {3.8637, 6.7852, -2.6286, -3.1381}, {4.2736, 7.6199, -2.1534, -2.4026}, {4.6679, 8.2618, -1.822, -1.9147}, {5.0009, 8.3735, -1.6994, -1.6928} }; vector maxstat,minstat,starstat; matrix tau_smallps, tau_largeps; switch(trend) { case TREND_NONE: if(!maxstat.Assign(tau_max_nc) || !minstat.Assign(tau_min_nc) || !starstat.Assign(tau_star_nc)|| !tau_smallps.Assign(tau_nc_smallp)|| !tau_largeps.Assign(tau_nc_largep)) { Print("assignment error :", GetLastError()); return double("inf"); } else break; case TREND_CONST_ONLY: if(!maxstat.Assign(tau_max_c) || !minstat.Assign(tau_min_c) || !starstat.Assign(tau_star_c)|| !tau_smallps.Assign(tau_c_smallp)|| !tau_largeps.Assign(tau_c_largep)) { Print("assignment error :", GetLastError()); return double("inf"); } else break; case TREND_LINEAR_CONST: if(!maxstat.Assign(tau_max_ct) || !minstat.Assign(tau_min_ct) || !starstat.Assign(tau_star_ct)|| !tau_smallps.Assign(tau_ct_smallp)|| !tau_largeps.Assign(tau_ct_largep)) { Print("assignment error :", GetLastError()); return double("inf"); } else break; case TREND_QUAD_LINEAR_CONST: if(!maxstat.Assign(tau_max_ctt) || !minstat.Assign(tau_min_ctt) || !starstat.Assign(tau_star_ctt)|| !tau_smallps.Assign(tau_ctt_smallp)|| !tau_largeps.Assign(tau_ctt_largep)) { Print("assignment error :", GetLastError()); return double("inf"); } else break; default: Print(__FUNCTION__," Error invalid input for trend argument"); return double("nan"); } if(teststat>maxstat[nseries-1]) return 1.0; else if(teststat<minstat[nseries-1]) return 0.0; vector tau_coef; if(teststat<=starstat[nseries-1]) tau_coef = small_scaling*(tau_smallps.Row(nseries-1)); else tau_coef = large_scaling*(tau_largeps.Row(nseries-1)); double rv,tau[]; ArrayResize(tau,int(tau_coef.Size())); for(ulong i=0; i<tau_coef.Size(); i++) tau[i]=tau_coef[tau_coef.Size()-1-i]; rv=polyval(tau,teststat); return CNormalDistr::NormalCDF(rv); }Whilst the critical values are calculated by "mackinnoncrit()". Whose results can be accessed through the CAdf method "CriticalValues()".
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|Computes critical values | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ vector mackinnoncrit(ulong nseries = 1,ENUM_TREND trend = TREND_CONST_ONLY, ulong num_obs=ULONG_MAX) { matrix tau_nc_2010 [] = {{ {-2.56574, -2.2358, -3.627, 0}, // N [] = 1 {-1.94100, -0.2686, -3.365, 31.223}, {-1.61682, 0.2656, -2.714, 25.364} } }; matrix tau_c_2010 [] = { { {-3.43035, -6.5393, -16.786, -79.433}, // N [] = 1, 1% {-2.86154, -2.8903, -4.234, -40.040}, // 5 % {-2.56677, -1.5384, -2.809, 0} }, // 10 % { {-3.89644, -10.9519, -33.527, 0}, // N [] = 2 {-3.33613, -6.1101, -6.823, 0}, {-3.04445, -4.2412, -2.720, 0} }, { {-4.29374, -14.4354, -33.195, 47.433}, // N [] = 3 {-3.74066, -8.5632, -10.852, 27.982}, {-3.45218, -6.2143, -3.718, 0} }, { {-4.64332, -18.1031, -37.972, 0}, // N [] = 4 {-4.09600, -11.2349, -11.175, 0}, {-3.81020, -8.3931, -4.137, 0} }, { {-4.95756, -21.8883, -45.142, 0}, // N [] = 5 {-4.41519, -14.0405, -12.575, 0}, {-4.13157, -10.7417, -3.784, 0} }, { {-5.24568, -25.6688, -57.737, 88.639}, // N [] = 6 {-4.70693, -16.9178, -17.492, 60.007}, {-4.42501, -13.1875, -5.104, 27.877} }, { {-5.51233, -29.5760, -69.398, 164.295}, // N [] = 7 {-4.97684, -19.9021, -22.045, 110.761}, {-4.69648, -15.7315, -5.104, 27.877} }, { {-5.76202, -33.5258, -82.189, 256.289}, // N [] = 8 {-5.22924, -23.0023, -24.646, 144.479}, {-4.95007, -18.3959, -7.344, 94.872} }, { {-5.99742, -37.6572, -87.365, 248.316}, // N [] = 9 {-5.46697, -26.2057, -26.627, 176.382}, {-5.18897, -21.1377, -9.484, 172.704} }, { {-6.22103, -41.7154, -102.680, 389.33}, // N [] = 10 {-5.69244, -29.4521, -30.994, 251.016}, {-5.41533, -24.0006, -7.514, 163.049} }, { {-6.43377, -46.0084, -106.809, 352.752}, // N [] = 11 {-5.90714, -32.8336, -30.275, 249.994}, {-5.63086, -26.9693, -4.083, 151.427} }, { {-6.63790, -50.2095, -124.156, 579.622}, // N [] = 12 {-6.11279, -36.2681, -32.505, 314.802}, {-5.83724, -29.9864, -2.686, 184.116} } }; matrix tau_ct_2010 [] = { { {-3.95877, -9.0531, -28.428, -134.155}, // N [] = 1 {-3.41049, -4.3904, -9.036, -45.374}, {-3.12705, -2.5856, -3.925, -22.380} }, { {-4.32762, -15.4387, -35.679, 0}, // N [] = 2 {-3.78057, -9.5106, -12.074, 0}, {-3.49631, -7.0815, -7.538, 21.892} }, { {-4.66305, -18.7688, -49.793, 104.244}, // N [] = 3 {-4.11890, -11.8922, -19.031, 77.332}, {-3.83511, -9.0723, -8.504, 35.403} }, { {-4.96940, -22.4694, -52.599, 51.314}, // N [] = 4 {-4.42871, -14.5876, -18.228, 39.647}, {-4.14633, -11.2500, -9.873, 54.109} }, { {-5.25276, -26.2183, -59.631, 50.646}, // N [] = 5 {-4.71537, -17.3569, -22.660, 91.359}, {-4.43422, -13.6078, -10.238, 76.781} }, { {-5.51727, -29.9760, -75.222, 202.253}, // N [] = 6 {-4.98228, -20.3050, -25.224, 132.03}, {-4.70233, -16.1253, -9.836, 94.272} }, { {-5.76537, -33.9165, -84.312, 245.394}, // N [] = 7 {-5.23299, -23.3328, -28.955, 182.342}, {-4.95405, -18.7352, -10.168, 120.575} }, { {-6.00003, -37.8892, -96.428, 335.92}, // N [] = 8 {-5.46971, -26.4771, -31.034, 220.165}, {-5.19183, -21.4328, -10.726, 157.955} }, { {-6.22288, -41.9496, -109.881, 466.068}, // N [] = 9 {-5.69447, -29.7152, -33.784, 273.002}, {-5.41738, -24.2882, -8.584, 169.891} }, { {-6.43551, -46.1151, -120.814, 566.823}, // N [] = 10 {-5.90887, -33.0251, -37.208, 346.189}, {-5.63255, -27.2042, -6.792, 177.666} }, { {-6.63894, -50.4287, -128.997, 642.781}, // N [] = 11 {-6.11404, -36.4610, -36.246, 348.554}, {-5.83850, -30.1995, -5.163, 210.338} }, { {-6.83488, -54.7119, -139.800, 736.376}, // N [] = 12 {-6.31127, -39.9676, -37.021, 406.051}, {-6.03650, -33.2381, -6.606, 317.776} } }; matrix tau_ctt_2010 [] = { { {-4.37113, -11.5882, -35.819, -334.047}, // N [] = 1 {-3.83239, -5.9057, -12.490, -118.284}, {-3.55326, -3.6596, -5.293, -63.559} }, { {-4.69276, -20.2284, -64.919, 88.884}, // N [] =2 {-4.15387, -13.3114, -28.402, 72.741}, {-3.87346, -10.4637, -17.408, 66.313} }, { {-4.99071, -23.5873, -76.924, 184.782}, // N [] = 3 {-4.45311, -15.7732, -32.316, 122.705}, {-4.17280, -12.4909, -17.912, 83.285} }, { {-5.26780, -27.2836, -78.971, 137.871}, // N [] = 4 {-4.73244, -18.4833, -31.875, 111.817}, {-4.45268, -14.7199, -17.969, 101.92} }, { {-5.52826, -30.9051, -92.490, 248.096}, // N [] = 5 {-4.99491, -21.2360, -37.685, 194.208}, {-4.71587, -17.0820, -18.631, 136.672} }, { {-5.77379, -34.7010, -105.937, 393.991}, // N [] = 6 {-5.24217, -24.2177, -39.153, 232.528}, {-4.96397, -19.6064, -18.858, 174.919} }, { {-6.00609, -38.7383, -108.605, 365.208}, // N [] = 7 {-5.47664, -27.3005, -39.498, 246.918}, {-5.19921, -22.2617, -17.910, 208.494} }, { {-6.22758, -42.7154, -119.622, 421.395}, // N [] = 8 {-5.69983, -30.4365, -44.300, 345.48}, {-5.42320, -24.9686, -19.688, 274.462} }, { {-6.43933, -46.7581, -136.691, 651.38}, // N [] = 9 {-5.91298, -33.7584, -42.686, 346.629}, {-5.63704, -27.8965, -13.880, 236.975} }, { {-6.64235, -50.9783, -145.462, 752.228}, // N [] = 10 {-6.11753, -37.056, -48.719, 473.905}, {-5.84215, -30.8119, -14.938, 316.006} }, { {-6.83743, -55.2861, -152.651, 792.577}, // N [] = 11 {-6.31396, -40.5507, -46.771, 487.185}, {-6.03921, -33.8950, -9.122, 285.164} }, { {-7.02582, -59.6037, -166.368, 989.879}, // N [] = 12 {-6.50353, -44.0797, -47.242, 543.889}, {-6.22941, -36.9673, -10.868, 418.414} } }; vector ret_vector = {0,0,0}; switch(trend) { case TREND_CONST_ONLY: process(tau_c_2010,ret_vector,num_obs,nseries); break; case TREND_NONE: process(tau_nc_2010,ret_vector,num_obs,nseries); break; case TREND_LINEAR_CONST: process(tau_ct_2010,ret_vector,num_obs,nseries); break; case TREND_QUAD_LINEAR_CONST: process(tau_ctt_2010,ret_vector,num_obs,nseries); break; default: Print("Invalid input for trend argument"); return ret_vector; } return ret_vector; }
Testing and validation
To validate that our implementation is running correctly we will first conduct an ADF test in Python, on a random series. Then we will run the ADF test on the same series in Metatrader 5 and compare the output.
The code for the ADF test in Python is listed below.
import numpy as np from statsmodels.tsa.stattools import adfuller #initialize array with 100 elements x = np.array([0.97841555,0.31931195,0.68205832,0.56256707,0.05741117,0.30310286, 0.13354023,0.61382247,0.20699517,0.61969826,0.55718307,0.90422809, 0.24220947,0.08719106,0.26714434,0.39439596,0.93919107,0.07756139, 0.53188798,0.5074042,0.40468052,0.41235659,0.79233157,0.58948591, 0.22049794,0.68278894,0.09500558,0.40421058,0.9971231,0.29665678, 0.08254796,0.8089725,0.61434576,0.97610604,0.84084868,0.8034953, 0.765576,0.25014613,0.16268394,0.34259495,0.40085009,0.8416158, 0.6321962,0.45165205,0.12209775,0.40556958,0.96253644,0.30619429, 0.70573114,0.51574979,0.90168104,0.80757639,0.94321618,0.58849563, 0.38905617,0.04574506,0.63134219,0.89198262,0.24102367,0.45749333, 0.76804682,0.50868223,0.91132151,0.7372344,0.32551467,0.27799709, 0.04059095,0.86024797,0.74600612,0.01264258,0.89364963,0.99373472, 0.36177673,0.47173929,0.15124127,0.77354455,0.45131917,0.27258213, 0.69618127,0.35105122,0.1261404,0.21705172,0.88979093,0.97598448, 0.03787156,0.54034132,0.58336702,0.61701685,0.11673483,0.99940389, 0.99371688,0.04428256,0.00239077,0.34609507,0.57588045,0.20222325, 0.20684364,0.29630613,0.65178447,0.86559185]) #perform ADF test on array result = adfuller(x) #print ADF statistic and p-value print(f"ADF statistic: {result[0]}, p-value:{result[1]}") #print critical values print(f"Critical values:{result[4]}")
Next, we run the MQL5 version of ADF test on the same array, the script program code is shown below.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ADF_test.mq5 | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #include<ADF.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //---series double rand_array[] = { 0.97841555,0.31931195,0.68205832,0.56256707,0.05741117,0.30310286, 0.13354023,0.61382247,0.20699517,0.61969826,0.55718307,0.90422809, 0.24220947,0.08719106,0.26714434,0.39439596,0.93919107,0.07756139, 0.53188798,0.5074042,0.40468052,0.41235659,0.79233157,0.58948591, 0.22049794,0.68278894,0.09500558,0.40421058,0.9971231,0.29665678, 0.08254796,0.8089725,0.61434576,0.97610604,0.84084868,0.8034953, 0.765576,0.25014613,0.16268394,0.34259495,0.40085009,0.8416158, 0.6321962,0.45165205,0.12209775,0.40556958,0.96253644,0.30619429, 0.70573114,0.51574979,0.90168104,0.80757639,0.94321618,0.58849563, 0.38905617,0.04574506,0.63134219,0.89198262,0.24102367,0.45749333, 0.76804682,0.50868223,0.91132151,0.7372344,0.32551467,0.27799709, 0.04059095,0.86024797,0.74600612,0.01264258,0.89364963,0.99373472, 0.36177673,0.47173929,0.15124127,0.77354455,0.45131917,0.27258213, 0.69618127,0.35105122,0.1261404,0.21705172,0.88979093,0.97598448, 0.03787156,0.54034132,0.58336702,0.61701685,0.11673483,0.99940389, 0.99371688,0.04428256,0.00239077,0.34609507,0.57588045,0.20222325, 0.20684364,0.29630613,0.65178447,0.86559185 }; //---variables that will be used to store test results CAdf adf; //--- Do ADF test if(adf.Adfuller(rand_array)) Print("ADF test statistic: ", adf.AdfStatistic(), " P-value:", adf.Pvalue(),"\nCritical values \n",adf.CriticalValues()); else Print("ADF test failed"); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Running the python script first:
LD 0 18:30:22.912 Test_adfuller (NFLX_us,Daily) ADF statistic: -8.495443215534635, p-value:1.2796318143567197e-13
GJ 0 18:30:22.913 Test_adfuller (NFLX_us,Daily) Critical values:{'1%': -3.4989097606014496, '5%': -2.891516256916761, '10%': -2.5827604414827157} And then the MetaTrader 5 script next , we can see the results are the same.
DO 0 18:30:48.460 ADF_test (NFLX_us,D1) ADF test statistic: -8.495443215534634 P-value:1.2796318143567197e-13 ND 0 18:30:48.460 ADF_test (NFLX_us,D1) Critical values OL 0 18:30:48.460 ADF_test (NFLX_us,D1) [-3.49890976060145,-2.891516256916761,-2.582760441482716]
Cointegration
Correlation and cointegration are statistical concepts used to measure relationships between variables, especially in the context of time series data. While both measure relationships, they serve different purposes and are applied in distinct scenarios. Correlation refers to the statistical measure of the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two variables.
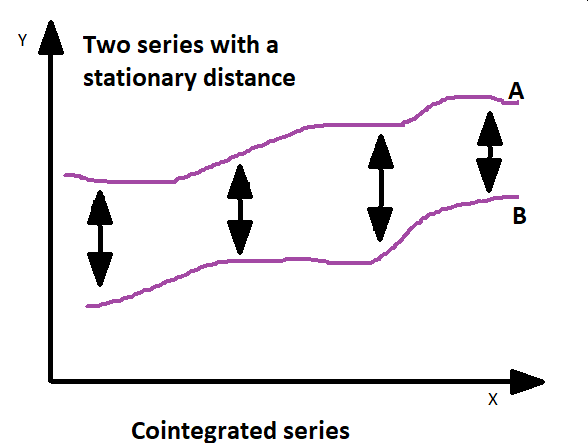
Cointegration, on the other hand, deals with the relationship between non-stationary time series variables that possess a long-term equilibrium or steady relationship. In simpler terms, it identifies whether there exists a combination of two or more non-stationary variables that have a stable, long-run relationship when considered together. Cointegration is useful in identifying pairs of variables that move together over time, despite short-term fluctuations. It implies that the variables are linked in the long run, making it possible to exploit this relationship for trading strategies or modeling.
Cointegration is typically assessed using statistical tests like the Engle-Granger test or Johansen test. These tests check if a linear combination of non-stationary variables creates a stationary series, indicating a long-term relationship. The Engle-Granger test is a two-step procedure to test for cointegration between two variables in a time series setting. It involves estimating a regression model and then conducting tests on the residuals to determine whether cointegration exists. If the residuals of the regression model are found to be stationary, it suggests cointegration between the two variables. In this case, it indicates that despite the variables not being individually stationary, a linear combination of them is stationary.
The Engle-Granger test is limited in that it cannot handle multiple sequences simultaneously. This limitation is adressed by the Johansen test. Which is essentially an extension of the Engle-Granger approach to test for cointegration among multiple series in a vector autoregressive model. We will not be looking at the Johansen test in this article, we limit ourselves to dealing with only two series at a time.
CointegrationTest.mqh contains the function CCoint class. It implements the augmented Engle-Granger test with the help of the CAdf class. The test is conducted by calling CCoint's "Aeg()" method. Two input arrays containing series to be tested are required. The optional input parameters "trend", "max_lag", and "autolag", are similar to the parameters of the "Adfuller()" method in CAdf. Again for most tests the default values should be sufficient. As it will be demonstrated in the next section. The results of the cointegration test are obtained by calling three methods of CCoint. The first "CointStatistic", returns the ADF statistic from the internal ADF test. "CriticalValues()" returns a vector of the critical values of the test. The p-value can be obtained by calling "Pvalue()".
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| CointegrationTest.mqh | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #include<ADF.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //|Class CCoint | //| implements cointegration test of two series | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CCoint { private: double m_coint_stat; //ADF test statistic double m_coint_pvalue; //cointegration p-value vector m_coint_critvalues; //Cointegration critical values CAdf *m_adf; //CAdf object pointer public: CCoint(void); ~CCoint(void); bool Aeg(double &in_one[],double &in_two[],ENUM_TREND trend = TREND_CONST_ONLY,ulong max_lag=0,ENUM_INFO_CRIT autolag=INFO_AIC); double CointStatistic(void){ return m_coint_stat; } double Pvalue(void) { return m_coint_pvalue;} vector CriticalValues(void){ return m_coint_critvalues;} }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Constructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CCoint::CCoint(void) { m_adf = new CAdf(); m_coint_critvalues = vector::Zeros(3); m_coint_stat=m_coint_pvalue=EMPTY_VALUE; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Destructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CCoint::~CCoint(void) { if(CheckPointer(m_adf)==POINTER_DYNAMIC) delete m_adf; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Test for cointegration | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CCoint::Aeg(double &in_one[],double &in_two[],ENUM_TREND trend = TREND_CONST_ONLY,ulong max_lag=0,ENUM_INFO_CRIT autolag=INFO_AIC) { //--- if(CheckPointer(m_adf)==POINTER_INVALID) { Print("Critical Internal error: Invalid CAdf pointer"); return false; } //--- if(in_one.Size()<1 || in_two.Size()<1 || in_one.Size()!=in_two.Size()) { Print(__FUNCTION__," Invalid input for one or both arrays"); return false; } vector y1,temp; matrix y2; if(!y1.Assign(in_one) || !temp.Assign(in_two) || !y2.Resize(temp.Size(),1) || !y2.Col(temp,0)) { Print(__FUNCTION__," Assignment error: ", GetLastError()); return false; } ulong obs,kvars=1; obs = y2.Rows(); kvars++; matrix xx; if(trend==TREND_NONE) { if(!xx.Copy(y2)) { Print(__FUNCTION__," Assignment error: ", GetLastError()); return false; } } else if(!addtrend(y2,xx,trend,false)) { Print(__FUNCTION__," Assignment error: ", GetLastError()); return false; } OLS ols; if(!ols.Fit(y1,xx)) return false; if(ols.Rsqe()< 1 - 100*SQRTEPS) { double resid[]; vector resd = ols.Residuals(); ArrayResize(resid,int(resd.Size())); for(uint i = 0; i<resid.Size(); i++) resid[i]=resd[i]; if(!m_adf.Adfuller(resid,max_lag,TREND_NONE,autolag)) return false; m_coint_stat = m_adf.AdfStatistic(); } else { Print("They are (almost) perfectly collinear.\nCointegration test is not reliable in this case"); m_coint_stat=double("nan"); } if(trend==TREND_NONE) m_coint_critvalues.Fill(double("nan")); else m_coint_critvalues = mackinnoncrit(kvars,trend,obs-1); m_coint_pvalue = mackinnonp(m_coint_stat,trend,kvars); return true; }
Testing symbols for cointegration
For the final demonstration we will create a MQL5 script that uses CCoint to test a list of symbols for cointegration. Users input a list of symbols, delimited by commas. Set the start date and history length of the close prices to be studied. "ConfidenceLevel" enables users to select the desired level of significance. This determines the critical value that will be compared to the ADF statistic for the final result.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| SymbolCointegrationTester.mq5 | //| Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2023, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #property script_show_inputs #include <CointegrationTest.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| enumeration maps to confidence levels of 99%,95%, and 90% | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum ENUM_CONFIDENCE_LEVEL { CONF_99=0,//99% CONF_95,//95% CONF_90 //90% }; //--- input parameters input string Symbols = "FB_us,GOOG_us,MSFT_us,NFLX_us,NVDA_us,AAPL_us,TSLA_us";//Comma separated list of symbols to test input ENUM_TIMEFRAMES TimeFrame = PERIOD_D1; input datetime StartDate=D'2022.01.01 00:00:01'; input int Size = 250;//History length input ENUM_CONFIDENCE_LEVEL ConfidenceLevel=CONF_90; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //---Check Size input value if(Size<100) { Print("Invalid input for Size"); return; } //---array for symbols string symbols[]; //---process list of symbols from user input int num_symbols = StringSplit(Symbols,StringGetCharacter(",",0),symbols); //---incase list contains ending comma if(symbols[num_symbols-1]=="") num_symbols--; //---in case there are less than two symbols specified if(num_symbols<2) { Print("Invalid input. Please list at least two symbols"); return; } //---output matrix of indices matrix sym_combos; //---fill sym_combos with index values of symbols array PairedCombinations(symbols,sym_combos,num_symbols); //---price arrays for pair of symbols double symA_prices [], symB_prices[]; //---output vectors holding results of cointegration test vector stats, critvals; //---symbol pairs and result output string symA,symB,result; //---CCoint object CCoint coint; //---loop through all paired combinations from list for(ulong i=0; i<sym_combos.Rows(); i++) { //--- get symbol pair for current combination symA = symbols[int(sym_combos[i][0])]; symB = symbols[int(sym_combos[i][1])]; //--- get prices for the pair of symbols if(CopyClose(symA,TimeFrame,StartDate,Size,symA_prices)<Size|| CopyClose(symB,TimeFrame,StartDate,Size,symB_prices)<Size) { Print("Failed to copy close prices ", ::GetLastError()); return; } //--- test the pair for cointegreation if(!coint.Aeg(symA_prices,symB_prices)) { Print("Cointegration test failed ", ::GetLastError()); return; } //--- vector critvals = coint.CriticalValues(); //--- prepare results output for a test if(coint.CointStatistic()<critvals[ConfidenceLevel]) result="likely cointegrated."; else result="likely not cointegrated."; //--- output the result from cointegration test Print(symA," and ",symB, " are ", result); } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Combinations: generates paired combinations | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool PairedCombinations(string &in[], matrix &out,int count = 0) { //---check input array if(in.Size()<1) { Print(__FUNCTION__," input array is empty"); return false; } //---set value for upto equal to the number of elements that should be //---considered in the input array int upto = (count>1 && count<ArraySize(in))?count:ArraySize(in); //--- calculate the number of rows equivalent to number of combinations ulong rows = ulong(MathFactorial(upto)/(MathFactorial(2)*MathFactorial(upto-2))); //---resize output matrix accordingly out.Resize(rows,2); //---fill output matrix with indexes of input array for(uint i=0,z=0; i<in.Size(); i++) { for(uint k = i+1; k<in.Size(); k++,z++) { out[z][0]=i; out[z][1]=k; } } //---return return true; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
In our example we will test the symbols Google,Facebook,Microsoft,NetFlix,Nvidia,Apple and Tesla. The results from running script are shown below.
HN 0 18:37:31.239 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) FB_us and GOOG_us are likely not cointegrated. PQ 0 18:37:31.280 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) FB_us and MSFT_us are likely not cointegrated. IE 0 18:37:31.322 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) FB_us and NFLX_us are likely not cointegrated. MG 0 18:37:31.365 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) FB_us and NVDA_us are likely not cointegrated. PH 0 18:37:31.411 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) FB_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated. NL 0 18:37:31.453 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) FB_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated. EO 0 18:37:31.496 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) GOOG_us and MSFT_us are likely not cointegrated. ES 0 18:37:31.540 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) GOOG_us and NFLX_us are likely not cointegrated. FE 0 18:37:31.582 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) GOOG_us and NVDA_us are likely not cointegrated. CF 0 18:37:31.623 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) GOOG_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated. EJ 0 18:37:31.665 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) GOOG_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated. HM 0 18:37:31.705 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) MSFT_us and NFLX_us are likely not cointegrated. RN 0 18:37:31.744 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) MSFT_us and NVDA_us are likely not cointegrated. LP 0 18:37:31.785 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) MSFT_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated. OD 0 18:37:31.825 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) MSFT_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated. IG 0 18:37:31.866 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) NFLX_us and NVDA_us are likely not cointegrated. QI 0 18:37:31.906 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) NFLX_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated. FP 0 18:37:31.946 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) NFLX_us and TSLA_us are likely cointegrated. EO 0 18:37:31.987 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) NVDA_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated. RS 0 18:37:32.026 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) NVDA_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated. DE 0 18:37:32.072 SymbolCointegrationTester (NFLX_us,D1) AAPL_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated.
They show that NetFlix and Tesla are likely cointegrated at a confidence level of 90%.
The code for conducting the same test in Python follows, along with the results.
""" Script demonstrates use of coint() from statsmodels to test symbols for cointegration """ # imports from statsmodels.tsa.stattools import coint from itertools import combinations from datetime import datetime import MetaTrader5 as mt5 import pandas as pd import numpy as np import pytz #initialize connection to mt5 if not mt5.initialize(): print("initialize() failed ") mt5.shutdown() #set up timezone infomation tz=pytz.timezone("Etc/UTC") #use time zone to set correct date for history data extraction startdate = datetime(2022,1,1,hour=0,minute=0,second=1,tzinfo=tz) #list the symbols Symbols = ["FB_us","GOOG_us","MSFT_us","NFLX_us","NVDA_us","AAPL_us","TSLA_us"] #set length of data history num_bars = 250 #set up the shape of the data structure to store prices data = np.zeros((num_bars,len(Symbols))) prices = pd.DataFrame(data,columns=Symbols) #fill prices dataframe with close prices for symbol in Symbols: prices[symbol]=[rate[4] for rate in mt5.copy_rates_from(symbol,mt5.TIMEFRAME_D1,startdate,num_bars)] #we donot need mt5 from here mt5.shutdown() #generate pairs from Symbols list pairs = list(combinations(prices.columns,2)) #set our desired significance level, 0.01->99%, 0.05->95%, 0.1->90% confidence_level = 0.1 #do the test for cointegration on each pair and print results for pair in pairs: df=prices[list(pair)] adf_stat,pvalue,critvalues=coint(df.values[:,0],df.values[:,1]) if pvalue < confidence_level: print(pair[0]," and ",pair[1], " are likely cointegrated") else: print(pair[0]," and ",pair[1], " are likely not cointegrated")
Python results
MR 0 18:35:17.835 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) FB_us and GOOG_us are likely not cointegrated GE 0 18:35:17.851 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) FB_us and MSFT_us are likely not cointegrated DI 0 18:35:17.867 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) FB_us and NFLX_us are likely not cointegrated CJ 0 18:35:17.867 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) FB_us and NVDA_us are likely not cointegrated MO 0 18:35:17.882 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) FB_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated JQ 0 18:35:17.898 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) FB_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated CD 0 18:35:17.914 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) GOOG_us and MSFT_us are likely not cointegrated MF 0 18:35:17.930 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) GOOG_us and NFLX_us are likely not cointegrated QK 0 18:35:17.946 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) GOOG_us and NVDA_us are likely not cointegrated HM 0 18:35:17.962 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) GOOG_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated OO 0 18:35:17.978 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) GOOG_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated MS 0 18:35:17.978 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) MSFT_us and NFLX_us are likely not cointegrated PD 0 18:35:17.994 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) MSFT_us and NVDA_us are likely not cointegrated MF 0 18:35:18.010 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) MSFT_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated RJ 0 18:35:18.042 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) MSFT_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated RM 0 18:35:18.058 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) NFLX_us and NVDA_us are likely not cointegrated GP 0 18:35:18.074 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) NFLX_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated LN 0 18:35:18.089 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) NFLX_us and TSLA_us are likely cointegrated EF 0 18:35:18.105 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) NVDA_us and AAPL_us are likely not cointegrated QI 0 18:35:18.121 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) NVDA_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated OJ 0 18:35:18.137 SymbolCointegration (NFLX_us,Daily) AAPL_us and TSLA_us are likely not cointegrated
Conclusion
So far we have looked at the implementation of the Augmented Dickey-Fuller in MQL5 and used it to implement Engle-Granger's test for cointegration. The ADF test is an important tool for those interested in exploring pairs trading strategies or statistical arbitrage. All the code described in the article is enclosed in the zip file. The table below lists all the contents of this file.
| File | Description |
|---|---|
| Mql5\include\OLS.mqh | Contains the definition of the OLS class, which implements ordinary least squares regression |
| Mql5\include\ADF.mqh | Contains the definition of variousfunctions and the CAdf class implementing the ADF test |
| Mql5\include\CointegrationTest.mqh | Defines the CCoint class which implements a cointegration test using the Augmented Engle-Granger technique |
| Mql5\scripts\ADF_test.mq5 | This is the MQL5 script used to test the MQL5 implementation of the ADF test |
| Mql5\scripts\SymbolCointegrationTester.mq5 | script for testing symbols in MetaTrader 5 for cointegration |
| Mql5\scripts\Test_adfuller.py | Is a python script using the statsmodels implementation of the ADF test used to validate our MQL5 implementation |
| Mql5\scripts\SymbolCointegration.py | Python version of SymbolCointegrationTester |
Warning: All rights to these materials are reserved by MetaQuotes Ltd. Copying or reprinting of these materials in whole or in part is prohibited.
This article was written by a user of the site and reflects their personal views. MetaQuotes Ltd is not responsible for the accuracy of the information presented, nor for any consequences resulting from the use of the solutions, strategies or recommendations described.
 Data label for time series mining (Part 5):Apply and Test in EA Using Socket
Data label for time series mining (Part 5):Apply and Test in EA Using Socket
 Building Your First Glass-box Model Using Python And MQL5
Building Your First Glass-box Model Using Python And MQL5
 Developing an MQTT client for Metatrader 5: a TDD approach — Part 5
Developing an MQTT client for Metatrader 5: a TDD approach — Part 5
- Free trading apps
- Over 8,000 signals for copying
- Economic news for exploring financial markets
You agree to website policy and terms of use
Check out the new article: Implementation of the Augmented Dickey Fuller test in MQL5.
Author: Francis Dube
Hello Francis,
I have read the article and tested the code which worked fine to me. In your article you defined:
Cointegration
Correlation and cointegration are statistical concepts used to measure relationships between variables, especially in the context of time series data. While both measure relationships, they serve different purposes and are applied in distinct scenarios. Correlation refers to the statistical measure of the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two variables.
and we know that correlation can be positive and negative.
My question here is can we also have cointegration which is also negative? In general your article covers the positive part.
How the code could be changed to cover the second case to have two symbols which are likely cointegrated but negatively i.e. when one of these symbols is growing up, its pair is falling down and vice versa with a level of confidence > 90%?
Thank you in advance.
Hello, Francis,
I have read the article and tested the code which works fine. In your article you have defined:
And we know that correlation can be positive and negative.
My question is, can we also have cointegration which is also negative? Overall your article covers the positive part.
How can we modify the code to cover the second case to have two symbols that are probably cointegrated but negatively, i.e. when one of these symbols goes up, its pair goes down and vice versa with a confidence level > 90%?
Thanks in advance.