
Nachrichtenhandel leicht gemacht (Teil 1): Erstellen einer Datenbank
Einführung
In diesem Artikel werden wir lernen, eine Datenbank zu erstellen, in der wir Daten aus dem MQL5-Wirtschaftskalender speichern werden. Diese Daten können später, in den nächsten Artikeln, zum Handel mit den Nachrichten verwendet werden. Wir werden auch untersuchen, wie man grundlegende SQL-Abfragen ausführt, um bestimmte organisierte Informationen aus dieser Datenbank abzurufen. Der gesamte Prozess wird in der MQL5-IDE durchgeführt.
Händler verfolgen aufmerksam die Nachrichtenquellen auf Informationen, die sich auf die Märkte auswirken könnten. Dazu gehören geopolitische Ereignisse, die Bekanntgabe von Unternehmensgewinnen, politische Ereignisse und Wirtschaftsberichte wie das BIP-Wachstum oder Beschäftigungszahlen. Händler reagieren schnell auf wichtige Nachrichten, um von den daraus resultierenden Marktveränderungen zu profitieren. Je nachdem, wie die Nachrichten interpretiert werden, kann es notwendig sein, Vermögenswerte zu kaufen oder zu verkaufen. In diesem Artikel werden wir uns auf wirtschaftliche Ereignisse konzentrieren, da sie uns über den MQL5-Wirtschaftskalender leicht zugänglich sind.
Warum eine Datenbank erstellen?
Eine Datenbank ist eine strukturierte Sammlung von Daten, die elektronisch gespeichert und abgerufen werden. Datenbanken können große Datenmengen effizient verwalten und speichern und ermöglichen so verschiedene Aktivitäten wie Datenanalyse, -speicherung und -verwaltung. In MQL5 arbeiten wir mit SQLite-Datenbanken, die von der SQLite-Datenbank-Engine erstellt und verwaltet werden. SQLite-Datenbanken können jede beliebige Dateierweiterung haben, aber in der Regel handelt es sich um Einzeldateien mit den Erweiterungen .sqlite, .sqlite3 oder .db. Diese Dateien enthalten alle Daten und Strukturen von Datenbanken, einschließlich Tabellen, Triggern, Indizes und anderen Metadaten.
Datenbanken eignen sich hervorragend für die Bearbeitung großer Datenmengen und vereinfachen das Abrufen von Daten ab einem bestimmten Datum oder Ereignis, ohne dass komplexe Schleifen erforderlich sind. Außerdem ist der MQL5-Wirtschaftskalender im Strategietester unzugänglich. Wenn Sie also Ihre Strategie anhand von Nachrichten testen wollen, wie würden Sie das tun?
Die Antwort ist die Verwendung einer Datenbank, für weitere Informationen über Datenbanken sehen Sie sich diese Vorlesungsfolien und vorzugsweise diesen MQL5 Artikel. Außerdem werde ich ein hervorragendes SQLite-Anleitung hinzufügen.
Währungen im MQL5-Wirtschaftskalender
| No | Symbol | Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | NZD | Neuseeländischer Dollar |
| 2. | EUR | Euro |
| 3. | JPY | Japanischer Yen |
| 4. | CAD | Kanadischer Dollar |
| 5. | AUD | Australischer Dollar |
| 6. | CNY | Chinesischer Yuan |
| 7. | SGD | Singapur-Dollar |
| 8. | BRL | Brasilianischer Real |
| 9. | MXN | Mexikanischer Peso |
| 10. | ZAR | Südafrikanischer Rand |
| 11. | HKD | Hongkong-Dollar |
| 12. | INR | Indische Rupie |
| 13. | NOK | Norwegische Krone |
| 14. | USD | Vereinigte Staaten Dollar |
| 15. | GBP | Pfund Sterling |
| 16. | CHF | Schweizer Franken |
| 17. | KRW | Südkoreanischer Won |
| 18. | SEK | Schwedische Krone |
Die obige Tabelle ist in keiner bestimmten Reihenfolge.
Im MQL5-Kalender sind mehrere Währungen verfügbar, aber einige von ihnen werden von Brokern nicht häufig verwendet oder sind für Händler nicht leicht zugänglich. So sind beispielsweise der brasilianische Real und der südkoreanische Won nicht überall erhältlich. Selbst wenn es Ihnen gelingt, einen Broker zu finden, der mit diesen exotischen Währungen handelt, sind die Spreads in der Regel ungünstig für den Handel. Ich spreche aus persönlicher Erfahrung.
Erstellen der Datenbank
Bevor wir die Datenbank erstellen, müssen wir uns zunächst mit der Sommerzeit befassen und mit der Frage, warum sich dies auf unser Backtesting auswirken würde. Die Sommerzeit (DST) ist die Praxis, die Uhr in den wärmeren Monaten des Jahres, typischerweise von Frühling bis Herbst, um eine Stunde vorzustellen, um das Tageslicht besser zu nutzen und Energie zu sparen.
In Gebieten, in denen die Sommerzeit gilt, kann sich die Ortszeit während der Übergangszeit im Frühjahr und Herbst um eine Stunde ändern. Dies kann sich auf die Öffnungs- und Schließungszeiten der Finanzmärkte auswirken. Wenn zum Beispiel die Sommerzeit beginnt und die Uhren um eine Stunde vorgestellt werden, kann der Markt in der Ortszeit früher öffnen. Wenn dagegen die Sommerzeit endet und die Uhren eine Stunde zurückgestellt werden (Normalzeit), kann die Marktöffnungszeit in der Ortszeit später erscheinen. Wir müssen auch anerkennen, dass verschiedene Regionen der Welt ihre eigene Sommerzeit haben können, um ihren eigenen Jahreszeiten Rechnung zu tragen.
Die https://www.timeanddate.com/time US hat eine eigene DST, die in der Regel am zweiten Sonntag im März eines jeden Jahres beginnt und am ersten Sonntag im November desselben Jahres endet. Auch die europäischen Länder haben ihre eigene DST, die in der Regel am letzten Sonntag im März eines jeden Jahres beginnt und am letzten Sonntag im Oktober desselben Jahres endet. Australien ist ein weiteres Land, das ebenfalls die Sommerzeit praktiziert. Deren Zeitumstellung passiert in der Regel am ersten Sonntag im Oktober und endet am ersten Sonntag im April des folgenden Jahres.
Um die Sommerzeitanpassung zu berücksichtigen, können einige Börsen und Finanzmärkte ihre Handelszeiten oder Zeitzonen ändern. Die Börsen können geänderte Handelszeiten veröffentlichen, um der lokalen Zeitumstellung Rechnung zu tragen, oder ihre Zeitzone an den von ihnen praktizierten Sommerzeitplan anpassen, um den Marktteilnehmern Einheitlichkeit und Klarheit zu garantieren.
Wenn ein Makler beispielsweise die US-Sommerzeit praktiziert, wäre die Zeitzone vor der Sommerzeit zur Veranschaulichung GMT+2. Wenn dann die US-Sommerzeit beginnt, ändert sich die Zeitzone auf GMT+3. Sie würden den Zeitunterschied zwischen den US-Nachrichten auf dem Server des Brokers vor oder während der US-Sommerzeit nicht bemerken, da sie miteinander synchronisiert wären. Nehmen wir als Beispiel das Ereignis US NFP (Non Farm Payrolls). Angenommen, das NFP wird um 14 Uhr auf dem Broker-Server vor der US-Sommerzeit veröffentlicht, dann würde die Zeit um 14 Uhr während der US-Sommerzeit gleich bleiben, obwohl sich die Zeitzone auf GMT+3 geändert hat.

Wenn andererseits die britische Pressemitteilung zur Beschäftigung um 8 Uhr vor der britischen und US-amerikanischen Sommerzeit veröffentlicht wird und der Broker die Zeitzone ändert, wenn die US-amerikanische Sommerzeit beginnt, und die britische Pressemitteilung zur Beschäftigung vor Beginn der britischen (EU-)Sommerzeit veröffentlicht wird, würde die britische Pressemitteilung zur Beschäftigung um 7 Uhr morgens nach der Zeit des Brokers veröffentlicht werden. Wenn die Sommerzeit im Vereinigten Königreich beginnt und sich mit der Sommerzeit in den USA überschneidet, werden die britischen Arbeitsmarktnachrichten wieder um 8 Uhr veröffentlicht.
Ich weiß, dass das alles sehr verwirrend ist. Zum Glück für uns werden wir dies in unsere Datenbank aufnehmen, sodass wir genaue Daten haben, wann die Ereignisse eintreten, um sie später zu überprüfen. Wir müssen feststellen, ob der Makler die US-amerikanische Sommerzeit, die britische (EU) Sommerzeit, die australische Sommerzeit oder gar keine Sommerzeit anwendet. Wir werden auch Wirtschaftskalendertabellen für jeden Sommerzeittyp erstellen, sodass wir den Zeitplan ändern können, um einen Backtest für Bildungszwecke durchzuführen.
Umsetzung
Wir werden drei DaylightSavings-Kurse anbieten:
- DaylightSavings_AU
- DaylightSavings_UK
- DaylightSavings_US
class CDaylightSavings_AU:CObject { private: CTimeManagement Time; CDaylightSavings_AU(datetime startdate,datetime enddate); CObject *List() { return savings;}//Gets the list of Daylight savings time datetime StartDate; datetime EndDate; CArrayObj *savings; CArrayObj *getSavings; CDaylightSavings_AU *dayLight; public: CDaylightSavings_AU(void); ~CDaylightSavings_AU(void); bool isDaylightSavings(datetime Date);//This function checks if a given date falls within Daylight Savings Time. bool DaylightSavings(int Year,datetime &startDate,datetime &endDate);//Check if Daylight Savings Dates are available for a certain Year void adjustDaylightSavings(datetime EventDate,string &AdjustedDate);//Will adjust the date's time zone depending on Daylight Savings };
Wir erstellen eine Klasse mit dem Namen:
CDaylightSavings_AU
die abgeleitet wird von
CObject
Diese Klasse besteht darin, eine Liste zu erstellen, die alle Sommerzeitdaten ab 2007 speichert, da dies das früheste im Wirtschaftskalender von MQL5 gespeicherte Datum ist
CDaylightSavings_AU::CDaylightSavings_AU(void) { savings = new CArrayObj(); //Daylight savings dates to readjust dates in the database for accurate testing in the strategy tester savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2006.10.29 03:00:00',D'2007.03.25 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2007.10.28 03:00:00',D'2008.04.06 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2008.10.05 03:00:00',D'2009.04.05 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2009.10.04 03:00:00',D'2010.04.04 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2010.10.03 03:00:00',D'2011.04.03 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2011.10.02 03:00:00',D'2012.04.01 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2012.10.07 03:00:00',D'2013.04.07 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2013.10.06 03:00:00',D'2014.04.06 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2014.10.05 03:00:00',D'2015.04.05 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2015.10.04 03:00:00',D'2016.04.03 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2016.10.02 03:00:00',D'2017.04.02 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2017.10.01 03:00:00',D'2018.04.01 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2018.10.07 03:00:00',D'2019.04.07 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2019.10.06 03:00:00',D'2020.04.05 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2020.10.04 03:00:00',D'2021.04.04 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2021.10.03 03:00:00',D'2022.04.03 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2022.10.02 03:00:00',D'2023.04.02 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2023.10.01 03:00:00',D'2024.04.07 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2024.10.06 03:00:00',D'2025.04.06 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2025.10.05 03:00:00',D'2026.04.05 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2026.10.04 03:00:00',D'2027.04.04 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2027.10.03 03:00:00',D'2028.04.02 02:00:00')); savings.Add(new CDaylightSavings_AU(D'2028.10.01 03:00:00',D'2029.04.01 02:00:00')); }
verwenden wir dann die boolesche Funktion
bool isDaylightSavings(datetime Date);//This function checks if a given date falls within Daylight Savings Time.
So stellen Sie fest, ob ein Datumsparameter innerhalb der Sommerzeitdaten liegt
bool CDaylightSavings_AU::isDaylightSavings(datetime Date) { // Initialize a list to store daylight savings periods. getSavings = List(); // Iterate through all the periods in the list. for(int i=0; i<getSavings.Total(); i++) { // Access the current daylight savings period. dayLight = getSavings.At(i); // Check if the given date is within the current daylight savings period. if(Time.DateIsInRange(dayLight.StartDate,dayLight.EndDate,Date)) { // If yes, return true indicating it is daylight savings time. return true; } } // If no period matches, return false indicating it is not daylight savings time. return false; }
werden wir auch eine andere boolesche Funktion verwenden
bool DaylightSavings(int Year,datetime &startDate,datetime &endDate);//Adjusts time when it is daylight savings an hour behind if outside
Um festzustellen, ob das Jahr in der Liste der Sommerzeitdaten enthalten ist, die wir oben initialisiert haben, fügen wir das Startdatum und das Enddatum zu den Variablen startDate und endDate hinzu
bool CDaylightSavings_US::DaylightSavings(int Year,datetime &startDate,datetime &endDate) { // Initialize a list to store daylight savings periods. getSavings = List(); bool startDateDetected=false,endDateDetected=false; // Iterate through all the periods in the list. for(int i=0; i<getSavings.Total(); i++) { dayLight = getSavings.At(i); if(Year==Time.ReturnYear(dayLight.StartDate))//Check if a certain year's date is available within the Daylight Savings start dates in the List { startDate = dayLight.StartDate; startDateDetected = true; } if(Year==Time.ReturnYear(dayLight.EndDate))//Check if a certain year's date is available within the Daylight Savings end dates in the List { endDate = dayLight.EndDate; endDateDetected = true; } if(startDateDetected&&endDateDetected)//Check if both Daylight Savings start and end dates are found for a certain Year { return true; } } startDate = D'1970.01.01 00:00:00';//Set a default start date if no Daylight Saving date is found endDate = D'1970.01.01 00:00:00';//Set a default end date if no Daylight Saving date is found return false; }
Unsere letzte öffentliche Funktion in dieser Klasse
void adjustDaylightSavings(datetime EventDate,string &AdjustedDate);//Will adjust the date's time -zone depending on Daylight Savings
ändert eine String-Variable AdjustedDate per Referenz mit dem EventDate
void CDaylightSavings_AU::adjustDaylightSavings(datetime EventDate,string &AdjustedDate) { if(isDaylightSavings(TimeTradeServer()))//Check if the current trade server time is already within the Daylight Savings Period { if(isDaylightSavings(EventDate))//Checks if the event time is during daylight savings { AdjustedDate = TimeToString(EventDate);//storing normal event time } else { AdjustedDate = TimeToString((datetime)(EventDate-Time.HoursS()));//storing event time and removing an hour for DST } } else { if(isDaylightSavings(EventDate))//Checks if the event time is during daylight savings { AdjustedDate = TimeToString((datetime)(Time.HoursS()+EventDate));//storing event time and adding an hour for DST } else { AdjustedDate = TimeToString(EventDate);//storing normal event time } } }
Wir werden nun zu unserer nächsten Header-Datei in diesem Projekt übergehen, die für Zeitmanipulationen bestimmt ist:
CTimeManagement
die eine Klasse in demselben Projekt ist:
class CTimeManagement { private: MqlDateTime today;//private variable MqlDateTime timeFormat;//private variable public: bool DateIsInRange(datetime FirstTime,datetime SecondTime,datetime compareTime);//Checks if a date is within two other dates bool DateIsInRange(datetime Start,datetime End,datetime CompareStart,datetime CompareEnd);//Check if two dates(Start&End) are within CompareStart & CompareEnd bool DateisToday(datetime TimeRepresented);//Checks if a date is within the current day int SecondsS(int multiple=1);//Returns seconds int MinutesS(int multiple=1);//Returns Minutes in seconds int HoursS(int multiple=1);//Returns Hours in seconds int DaysS(int multiple=1);//Returns Days in seconds int WeeksS(int multiple=1);//Returns Weeks in seconds int MonthsS(int multiple=1);//Returns Months in seconds int YearsS(int multiple=1);//Returns Years in seconds int ReturnYear(datetime time);//Returns the Year for a specific date datetime TimeMinusOffset(datetime standardtime,int timeoffset);//Will return a datetime type of a date with an subtraction offset in seconds datetime TimePlusOffset(datetime standardtime,int timeoffset);//Will return a datetime type of a date with an addition offset in seconds };
die zuvor aufgerufene Funktion:
Time.DateIsInRange(dayLight.StartDate,dayLight.EndDate,Date)
ist eine einfache Funktion, die prüft, ob ein einzelnes Datum zwischen zwei anderen Daten liegt:
bool CTimeManagement::DateIsInRange(datetime FirstTime,datetime SecondTime,datetime compareTime) { if(FirstTime<=compareTime&&SecondTime>compareTime) { return true; } return false; }
Derselbe Funktionsname mit unterschiedlichen Parametern:
bool DateIsInRange(datetime Start,datetime End,datetime CompareStart,datetime CompareEnd);
ist ebenso einfach, diese Funktion prüft, ob zwei Daten zwischen zwei anderen Daten liegen:
bool CTimeManagement::DateIsInRange(datetime Start,datetime End,datetime CompareStart,datetime CompareEnd) { if(Start<=CompareStart&&CompareEnd<End) { return true; } return false; }
Wir werden eine Funktion brauchen, um zu wissen, ob ein bestimmtes Datum heute ist, deshalb habe ich diese Funktion deklariert:
bool DateisToday(datetime TimeRepresented);//Checks if a date is within the current day
die das Jahr, den Monat und den Tag der aktuellen Uhrzeit und des Datums „TimeRepresented“ vergleicht
bool CTimeManagement::DateisToday(datetime TimeRepresented) { MqlDateTime TiM; TimeToStruct(TimeRepresented,TiM); TimeCurrent(today); if(TiM.year==today.year&&TiM.mon==today.mon&&TiM.day==today.day) { return true; } return false; }
Um eine Datumszeit mit einem Offset zu erhalten, gibt es zwei Funktionen:
datetime TimeMinusOffset(datetime standardtime,int timeoffset);//Will return a datetime type of a date with an subtraction offset in seconds
und:
datetime TimePlusOffset(datetime standardtime,int timeoffset);//Will return a datetime type of a date with an addition offset in seconds
Wenn wir ein Datum mit einem negativen Versatz von einer Stunde (oder einer beliebigen Zeiteinheit) erhalten wollen, verwenden wir:
datetime CTimeManagement::TimeMinusOffset(datetime standardtime,int timeoffset) { standardtime-=timeoffset; return standardtime; }
Wenn wir hingegen ein Datum mit einem positiven Offset wollen, verwenden wir:
datetime CTimeManagement::TimePlusOffset(datetime standardtime,int timeoffset) { standardtime+=timeoffset; return standardtime; }
Ich habe mich entschlossen, eine Include-Datei zu erstellen, in der globale Variablen und Strukturen sowie Enum-Typen gespeichert werden, die in Zukunft in verschiedenen Klassen und dem Experten verwendet werden sollen.
Diese Include-Datei heißt CommonVariables und speichert die allgemeine Variablen:
string broker=AccountInfoString(ACCOUNT_COMPANY);//Getting brokers name via AccountInfoString int Str = StringReplace(broker," ","");//Removing or replacing any spaces in the broker's name with an empty string int Str1 = StringReplace(broker,".","");//Removing or replacing any dots in the broker's name with an empty string int Str2 = StringReplace(broker,",","");//Removing or replacing any commas in the broker's name with an empty string #define BROKER_NAME broker//Broker's Name #define NEWS_TRADING_FOLDER "NewsTrading"//Name of main folder in common/files #define NEWS_CALENDAR_FOLDER StringFormat("%s\\NewsCalendar",NEWS_TRADING_FOLDER)//name of subfolder in NewsTrading #define NEWS_CALENDAR_BROKER_FOLDER StringFormat("%s\\%s",NEWS_CALENDAR_FOLDER,BROKER_NAME)//Name of subfolder in NewsCalendar #define NEWS_DATABASE_FILE StringFormat("%s\\Calendar.sqlite",NEWS_CALENDAR_BROKER_FOLDER)//Name of sqlite file in subfolder in "Broker's Name" #define NEWS_TEXT_FILE StringFormat("%s\\CalendarOpen.txt",NEWS_CALENDAR_BROKER_FOLDER)//Name of text file to indicate Calendar is open. struct Calendar { ulong EventId;//Event Id string CountryName;//Event Country string EventName;//Event Name string EventType;//Event Type string EventImportance;//Event Importance string EventDate;//Event Date string EventCurrency;//Event Currency string EventCode;//Event Code string EventSector;//Event Sector string EventForecast;//Event Forecast Value string EventPreval;//Event Previous Value string EventImpact;//Event Impact string EventFrequency;//Event Frequency }; enum DST_type { US_DST,//US Daylight Savings UK_DST,//UK(EU) Daylight Savings AU_DST,//AU Daylight Savings DST_NONE//No Daylight Savings Available };
Wenn wir Dateien im Ordner „Common“ erstellen, möchte ich die Dateien nach Ordnern organisieren, damit es einfach ist, die Dateien im Ordner „Common“ zu koordinieren.
Ich habe also die Klasse erstellt:
class CFolders wodurch die Ordner im Ordner „Common“ in der Reihenfolge NewsTrading/NewsCalendar/Broker erstellt werden. Wir werden diese Aufgabe dem Konstruktor der Klasse überlassen.
class CFolders { private: bool CreateFolder(string FolderPath);//Will create a folder with the FolderPath string parameter public: CFolders(void);//Class's constructor };
innerhalb des Konstruktors:
CFolders::CFolders(void) { if(CreateFolder(NEWS_TRADING_FOLDER))//Will create the NewsTrading Folder { if(CreateFolder(NEWS_CALENDAR_FOLDER))//Will create the NewsCalendar Folder { if(!CreateFolder(NEWS_CALENDAR_BROKER_FOLDER))//Will create the Broker Folder { Print("Something went wrong with creating folder: ",NEWS_CALENDAR_BROKER_FOLDER); } } } }
Funktion, die im Konstruktor aufgerufen wird, um die einzelnen Ordner zu erstellen:
bool CFolders::CreateFolder(string FolderPath) { //--- attempt to create a folder relative to the MQL5\Files path if(FolderCreate(FolderPath,FILE_COMMON)) { //--- successful execution return true; } else { PrintFormat("Failed to create the folder %s. Error code %d",FolderPath,GetLastError()); } //--- execution failed return false; }
Kerzen sind sehr wichtig, wir müssen Informationen über die Höchst-, Tiefst-, Eröffnungs- und Schlusskurse einer bestimmten Kerze sammeln. Zu diesem Zweck werden wir eine weitere Klasse erstellen, die diese Informationen für uns sammelt, wenn sie in anderen Programmen im Projekt benötigt werden. Der Name der Klasse lautet:
class CCandleProperties Wir werden nun die Funktionen in dieser Klasse deklarieren:
class CCandleProperties { private: CTimeManagement Time; public: double Open(int CandleIndex,ENUM_TIMEFRAMES Period=PERIOD_CURRENT,string SYMBOL=NULL);//Retrieve Candle OpenPrice double Close(int CandleIndex,ENUM_TIMEFRAMES Period=PERIOD_CURRENT,string SYMBOL=NULL);//Retrieve Candle ClosePrice double High(int CandleIndex,ENUM_TIMEFRAMES Period=PERIOD_CURRENT,string SYMBOL=NULL);//Retrieve Candle HighPrice double Low(int CandleIndex,ENUM_TIMEFRAMES Period=PERIOD_CURRENT,string SYMBOL=NULL);//Retrieve Candle LowPrice bool IsLargerThanPreviousAndNext(datetime CandleTime,int Offset,string SYMBOL);//Determine if one candle is larger than two others };
Wir werfen einen kurzen Blick auf:
double Open(int CandleIndex,ENUM_TIMEFRAMES Period=PERIOD_CURRENT,string SYMBOL=NULL);//Retrieve Candle Open Price
In dieser Funktion geben wir den Eröffnungskurs einer Kerze zurück, basierend auf dem ganzzahligen Parameter CandleIndex (Kerzenindex) und dem Zeitrahmen der Kerze sowie dem Symbol der Kerze:
double CCandleProperties::Open(int CandleIndex,ENUM_TIMEFRAMES Period=PERIOD_CURRENT,string SYMBOL=NULL) { return iOpen(((SYMBOL==NULL)?Symbol():SYMBOL),Period,CandleIndex);//return candle open price }
Um zu überprüfen, ob ein wirtschaftliches Ereignis an einem bestimmten Datum stattgefunden hat, da die Makler ihre Zeitzonen verschieben können. Wir werden ein Datum für ein wirtschaftliches Ereignis ermitteln und mit diesem Datum die M15-Kerze für diesen Zeitpunkt betrachten, dann die Höhe der Kerze (iHigh-iLow) berechnen und diese Höhe mit der M15-Kerze eine Stunde vor dem Ereignis und eine Stunde danach vergleichen. Da wirtschaftliche Ereignisse normalerweise zu sehr volatilen Marktpreisen führen, sollten wir eine sehr lange Kerze bemerken, wenn das Ereignis eintritt. Wir werden die M15-Kerze verwenden, um dem Markt genügend Zeit zu geben, diese lange Kerze zu bilden. Wenn der Broker seine Zeitzone verschoben hat, kann es sein, dass das im MQL5-Wirtschaftskalender gespeicherte Ereignisdatum nicht mit der Volatilität der Kerze zu der bestimmten Zeit auf der Kerze des Brokers übereinstimmt, aber diese Volatilität kann eine Stunde später oder eine Stunde vor dem angegebenen Datum vorhanden sein. Die Funktion, die wir für diese Validierungsprüfung verwenden werden, lautet:
bool IsLargerThanPreviousAndNext(datetime CandleTime,int Offset,string SYMBOL);//Determine if one candle is larger than two others
Diese Funktion prüft, ob die Höhe der Kerze an einem bestimmten Datum größer ist als die Kerze mit einem Zeitversatz vor und nach diesem angegebenen Datum.
bool CCandleProperties::IsLargerThanPreviousAndNext(datetime CandleTime,int Offset,string SYMBOL) { int CandleIndex = iBarShift(SYMBOL,PERIOD_M15,CandleTime);//Assign candle index of candletime int CandleIndexMinusOffset = iBarShift(SYMBOL,PERIOD_M15,Time.TimeMinusOffset(CandleTime,Offset));//Assign candle index of candletime minus time offset int CandleIndexPlusOffset = iBarShift(SYMBOL,PERIOD_M15,Time.TimePlusOffset(CandleTime,Offset));//Assign candle index of candletime plus time offset double CandleHeight = High(CandleIndex,PERIOD_M15,SYMBOL)-Low(CandleIndex,PERIOD_M15,SYMBOL);//Assign height of M15 candletime in pips double CandleHeightMinusOffset = High(CandleIndexMinusOffset,PERIOD_M15,SYMBOL)-Low(CandleIndexMinusOffset,PERIOD_M15,SYMBOL);//Assign height of M15 candletime minus offset in Pips double CandleHeightPlusOffset = High(CandleIndexPlusOffset,PERIOD_M15,SYMBOL)-Low(CandleIndexPlusOffset,PERIOD_M15,SYMBOL);//Assign height of M15 candletime plus offset in Pips //--Determine if candletime height is greater than candletime height minus offset and candletime height plus offset if(CandleHeight>CandleHeightMinusOffset&&CandleHeight>CandleHeightPlusOffset) { return true;//Candletime is likely when the news event occurred } return false;//Candletime is unlikely when the real news data was released }
Wir gehen zur Klasse News über, die direkt mit dem Abrufen von Werten aus dem Wirtschaftskalender von MQL5 arbeitet und dem Speichern von Daten
der Werte in eine Datenbank, dem Testen und schließlich dem Handel dient:
class CNews { //Private Declarations Only accessible by this class/header file private: CTimeManagement Time;//TimeManagement Object declaration CDaylightSavings_UK Savings_UK;//DaylightSavings Object for the UK and EU CDaylightSavings_US Savings_US;//DaylightSavings Object for the US CDaylightSavings_AU Savings_AU;//DaylightSavings Object for the AU CCandleProperties Candle;//CandleProperties Object string CurrencyBase,CurrencyProfit,EURUSD;//String variables declarations for working with EURUSD bool EurusdIsSelected,EurusdIsFound,is_Custom;//Boolean variables declarations for working with EURUSD bool timeIsShifted;//Boolean variable declaration will be used to determine if the broker changes it's time zone datetime DaylightStart,DaylightEnd;//Datetime variables declarations for start and end dates for Daylight Savings //Structure Declaration for DST struct DST { bool result; datetime date; }; bool AutoDetectDST(DST_type &dstType);//Function will determine Broker DST DST_type DSTType;//variable of DST_type enumeration declared in the CommonVariables class/header file bool InsertIntoTable(int db,DST_type Type,Calendar &Evalues[]);//Function for inserting Economic Data in to a database's table void CreateAutoDST(int db);//Function for creating and inserting Recommend DST for the Broker into a table bool CreateTable(int db,string tableName,bool &tableExists);//Function for creating a table in a database void CreateRecords(int db);//Creates a table to store records of when last the Calendar database was updated/created bool UpdateRecords();//Checks if the main Calendar database needs an update or not void EconomicDetails(Calendar &NewsTime[]);//Gets values from the MQL5 economic Calendar //Public declarations accessable via a class's Object public: ~CNews(void);//Deletes a text file created when the Calendar database is being worked on void CreateEconomicDatabase();//Creates the Calendar database for a specific Broker datetime GetLastestNewsDate();//Gets the latest/newest date in the Calendar database };
Hier gibt es eine Menge auszupacken, wir werden zunächst einen Blick auf folgende Punkte werfen
bool AutoDetectDST(DST_type &dstType);//Function will determine Broker DST
Nach dem Namen dieser Funktion ist ihr Hauptzweck, den DST-Zeitplan zu erhalten, den der Makler verwendet, wir werden diese Informationen durch die Enumeration:
enum DST_type { US_DST,//US Daylight Savings UK_DST,//UK(EU) Daylight Savings AU_DST,//AU Daylight Savings DST_NONE//No Daylight Savings Available };
die als Referenz der Funktion AutoDectectDST übergeben wird, gibt diese Funktion false zurück, wenn die Sommerzeit des Brokers bekannt ist oder nicht erkannt wurde.
bool CNews::AutoDetectDST(DST_type &dstType) { MqlCalendarValue values[];//Single array of MqlCalendarValue type string eventtime[];//Single string array variable to store NFP(Nonfarm Payrolls) dates for the 'United States' from the previous year int lastyear = Time.ReturnYear(Time.TimeMinusOffset(iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,0),Time.YearsS()));//Will store the previous year into an integer datetime lastyearstart = StringToTime(StringFormat("%s.01.01 00:00:00",(string)lastyear));//Will store the start date for the previous year datetime lastyearend = StringToTime(StringFormat("%s.12.31 23:59:59",(string)lastyear));//Will store the end date for the previous year if(CalendarValueHistory(values,lastyearstart,lastyearend,"US"))//Getting last year's calendar values for CountryCode = 'US' { for(int x=0; x<(int)ArraySize(values); x++) { if(values[x].event_id==840030016)//Get only NFP Event Dates { ArrayResize(eventtime,eventtime.Size()+1,eventtime.Size()+2);//Increasing the size of eventtime array by 1 eventtime[eventtime.Size()-1] = TimeToString(values[x].time);//Storing the dates in an array of type string } } } datetime ShiftStart=D'1970.01.01 00:00:00',ShiftEnd=D'1970.01.01 00:00:00';//datetime variables to store the broker's time zone shift(change) DST previousresult,currentresult;//Variables of structure type DST declared at the beginning of the class EURUSD="";//String variable assigned empty string EurusdIsSelected = false;//Boolean variable assigned value false EurusdIsFound = false;//Boolean variable assigned value false for(int i=0;i<SymbolsTotal(true);i++)//Will loop through all the Symbols inside the Market Watch { string SymName = SymbolName(i,true);//Assign the Symbol Name of index 'i' from the list of Symbols inside the Market Watch CurrencyBase = SymbolInfoString(SymName,SYMBOL_CURRENCY_BASE);//Assign the Symbol's Currency Base CurrencyProfit = SymbolInfoString(SymName,SYMBOL_CURRENCY_PROFIT);//Assign the Symbol's Currency Profit SymbolExist(SymName,is_Custom);//Get the boolean value into 'is_Custom' for whether the Symbol Name is a Custom Symbol(Is not from the broker) //-- Check if the Symbol outside the Market Watch has a SYMBOL_CURRENCY_BASE of EUR //-- and a SYMBOL_CURRENCY_PROFIT of USD, and this Symbol is not a Custom Symbol(Is not from the broker) if(CurrencyBase=="EUR"&&CurrencyProfit=="USD"&&!is_Custom) { EURUSD = SymName;//Assigning the name of the EURUSD Symbol found inside the Market Watch EurusdIsFound = true;//EURUSD Symbol was found in the Trading Terminal for your Broker break;//Will end the for loop } } if(!EurusdIsFound)//Check if EURUSD Symbol was already Found in the Market Watch { for(int i=0; i<SymbolsTotal(false); i++)//Will loop through all the available Symbols outside the Market Watch { string SymName = SymbolName(i,false);//Assign the Symbol Name of index 'i' from the list of Symbols outside the Market Watch CurrencyBase = SymbolInfoString(SymName,SYMBOL_CURRENCY_BASE); CurrencyProfit = SymbolInfoString(SymName,SYMBOL_CURRENCY_PROFIT); SymbolExist(SymName,is_Custom);//Get the boolean value into 'is_Custom' for whether the Symbol Name is a Custom Symbol(Is not from the broker) //-- Check if the Symbol outside the Market Watch has a SYMBOL_CURRENCY_BASE of EUR //-- and a SYMBOL_CURRENCY_PROFIT of USD, and this Symbol is not a Custom Symbol(Is not from the broker) if(CurrencyBase=="EUR"&&CurrencyProfit=="USD"&&!is_Custom) { EurusdIsSelected = SymbolSelect(SymName,true);//Adding the EURUSD Symbol to the Market Watch if(EurusdIsSelected)//Check if this program added EURUSD Symbol to Market Watch { EURUSD = SymName;//Assigning the name of the EURUSD Symbol found outside the Market Watch EurusdIsFound = true;//EURUSD Symbol was found in the Trading Terminal for your Broker break;//Will end the for loop } } } } if(!EurusdIsFound)//Check if EURUSD Symbol was Found in the Trading Terminal for your Broker { Print("Cannot Find EURUSD!"); Print("Cannot Create Database!"); Print("Server DST Cannot be Detected!"); dstType = DST_NONE;//Assigning enumeration value DST_NONE, Broker has no DST(Daylight Savings Time) return false;//Returning False, Broker's DST schedule was not found } for(uint i=0;i<eventtime.Size();i++) { currentresult.result = Candle.IsLargerThanPreviousAndNext((datetime)eventtime[i],Time.HoursS(),EURUSD);//Store the result of if the event date is the larger candlestick currentresult.date = (datetime)eventtime[i];//Store the eventdate from eventtime[i] timeIsShifted = ((currentresult.result!=previousresult.result&&i>0)?true:false);//Check if there is a difference between the previous result and the current result //--- Print Event Dates and if the event date's candle is larger than the previous candle an hour ago and the next candle an hour ahead Print("Date: ",eventtime[i]," is Larger: ",Candle.IsLargerThanPreviousAndNext((datetime)eventtime[i],Time.HoursS(),EURUSD)," Shifted: ",timeIsShifted); if(timeIsShifted)//Check if the Larger candle has shifted from the previous event date to the current event date in eventtime[i] array { if(ShiftStart==D'1970.01.01 00:00:00')//Check if the ShiftStart variable has not been assigned a relevant value yet { ShiftStart=currentresult.date;//Store the event date for when the time shift began } ShiftEnd=previousresult.date;//Store the event date timeshift } previousresult.result = currentresult.result;//Store the previous result of if the event date is the larger candlestick previousresult.date = currentresult.date;//Store the event date from eventtime[i] } if(ShiftStart==D'1970.01.01 00:00:00'&&eventtime.Size()>0)//Check if the ShiftStart variable has not been assigned a relevant value and the event dates are more than zero { Print("Broker ServerTime unchanged!"); dstType = DST_NONE;//Assigning enumeration value DST_NONE, Broker has no DST(Daylight Savings Time) return true;//Returning True, Broker's DST schedule was found successfully } if(Savings_AU.DaylightSavings(lastyear,DaylightStart,DaylightEnd)) { if(Time.DateIsInRange(DaylightStart,DaylightEnd,ShiftStart,ShiftEnd)) { Print("Broker ServerTime Adjusted For AU DST"); if(EurusdIsSelected)//Check if this program added EURUSD Symbol to Market Watch { SymbolSelect(EURUSD,false);//Remove EURUSD Symbol from Market Watch } dstType = AU_DST;//Assigning enumeration value AU_DST, Broker has AU DST(Daylight Savings Time) return true;//Returning True, Broker's DST schedule was found successfully } } else { Print("Something went wrong!"); Print("Cannot Find Daylight-Savings Date For AU"); Print("Year: %d Cannot Be Found!",lastyear); if(EurusdIsSelected)//Check if this program added EURUSD Symbol to Market Watch { SymbolSelect(EURUSD,false);//Remove EURUSD Symbol from Market Watch } dstType = DST_NONE;//Assigning enumeration value DST_NONE, Broker has no DST(Daylight Savings Time) return false;//Returning False, Broker's DST schedule was not found } if(Savings_UK.DaylightSavings(lastyear,DaylightStart,DaylightEnd)) { if(Time.DateIsInRange(DaylightStart,DaylightEnd,ShiftStart,ShiftEnd)) { Print("Broker ServerTime Adjusted For UK DST"); if(EurusdIsSelected)//Check if this program added EURUSD Symbol to Market Watch { SymbolSelect(EURUSD,false);//Remove EURUSD Symbol from Market Watch } dstType = UK_DST;//Assigning enumeration value UK_DST, Broker has UK/EU DST(Daylight Savings Time) return true;//Returning True, Broker's DST schedule was found successfully } } else { Print("Something went wrong!"); Print("Cannot Find Daylight-Savings Date For UK"); Print("Year: %d Cannot Be Found!",lastyear); if(EurusdIsSelected)//Check if this program added EURUSD Symbol to Market Watch { SymbolSelect(EURUSD,false);//Remove EURUSD Symbol from Market Watch } dstType = DST_NONE;//Assigning enumeration value DST_NONE, Broker has no DST(Daylight Savings Time) return false;//Returning False, Broker's DST schedule was not found } if(Savings_US.DaylightSavings(lastyear,DaylightStart,DaylightEnd)) { if(Time.DateIsInRange(DaylightStart,DaylightEnd,ShiftStart,ShiftEnd)) { Print("Broker ServerTime Adjusted For US DST"); if(EurusdIsSelected)//Check if this program added EURUSD Symbol to Market Watch { SymbolSelect(EURUSD,false);//Remove EURUSD Symbol from Market Watch } dstType = US_DST;//Assigning enumeration value US_DST, Broker has US DST(Daylight Savings Time) return true;//Returning True, Broker's DST schedule was found successfully } } else { Print("Something went wrong!"); Print("Cannot Find Daylight-Savings Date For US"); Print("Year: %d Cannot Be Found!",lastyear); if(EurusdIsSelected)//Check if this program added EURUSD Symbol to Market Watch { SymbolSelect(EURUSD,false);//Remove EURUSD Symbol from Market Watch } dstType = DST_NONE;//Assigning enumeration value DST_NONE, Broker has no DST(Daylight Savings Time) return false;//Returning False, Broker's DST schedule was not found } if(EurusdIsSelected)//Check if this program added EURUSD Symbol to Market Watch { SymbolSelect(EURUSD,false);//Remove EURUSD Symbol from Market Watch } Print("Cannot Detect Broker ServerTime Configuration!"); dstType = DST_NONE;//Assigning enumeration value DST_NONE, Broker has no DST(Daylight Savings Time) return false;//Returning False, Broker's DST schedule was not found }
Ok, die obige Funktion ist langatmig, lassen Sie sie uns aufschlüsseln. Im ersten Teil werden wir die Wirtschaftsdaten für NFP aus dem Vorjahr sammeln, d.h. wenn das aktuelle Jahr 2024 ist, werden wir alle Daten für 2023 sammeln, da wir das ganze Jahr analysieren müssen, um den wahrscheinlichen Sommerzeitplan des Maklers zu erhalten. Diese Daten werden in unserem einzelnen String-Array eventtime gespeichert.
MqlCalendarValue values[];//Single array of MqlCalendarValue type string eventtime[];//Single string array variable to store NFP(Nonfarm Payrolls) dates for the 'United States' from the previous year int lastyear = Time.ReturnYear(Time.TimeMinusOffset(iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,0),Time.YearsS()));//Will store the previous year into an integer datetime lastyearstart = StringToTime(StringFormat("%s.01.01 00:00:00",(string)lastyear));//Will store the start date for the previous year datetime lastyearend = StringToTime(StringFormat("%s.12.31 23:59:59",(string)lastyear));//Will store the end date for the previous year if(CalendarValueHistory(values,lastyearstart,lastyearend,"US"))//Getting last year's calendar values for CountryCode = 'US' { for(int x=0; x<(int)ArraySize(values); x++) { if(values[x].event_id==840030016)//Get only NFP Event Dates { ArrayResize(eventtime,eventtime.Size()+1,eventtime.Size()+2);//Increasing the size of event time array by 1 eventtime[eventtime.Size()-1] = TimeToString(values[x].time);//Storing the dates in an array of type string } } }
Wir müssen diese Daten dann für das EURUSD-Symbol verwenden, da der XAUUSD (GOLD) und andere Indizes wie der US30 (Dow Jones) auch ohne Nachrichtenereignisse sehr volatil sind, während der EURUSD meist stabil ist und erst bei wirtschaftlichen Ereignissen wirklich volatil wird. Dies macht es einfacher zu erkennen, wann ein wirtschaftliches Ereignis eingetreten ist, da der Markt aufgrund des Ereignisses wahrscheinlich einen Ausschlag zeigen würde. Dies ist auch der Grund, warum wir uns auf die NFP-Ereignisse konzentrieren werden, da sie regelmäßig diese Marktspitzen in den Kursen verursachen. Mit diesen Informationen benötigen wir also das EURUSD-Symbol. Zuerst werden wir alle verfügbaren Symbole im Broker überprüfen, um EURUSD zu finden und auszuwählen. Wenn wir EURUSD nicht finden, wird false zurückgegeben.
EURUSD="";//String variable assigned empty string EurusdIsSelected = false;//Boolean variable assigned value false EurusdIsFound = false;//Boolean variable assigned value false for(int i=0;i<SymbolsTotal(true);i++)//Will loop through all the Symbols inside the Market Watch { string SymName = SymbolName(i,true);//Assign the Symbol Name of index 'i' from the list of Symbols inside the Market Watch CurrencyBase = SymbolInfoString(SymName,SYMBOL_CURRENCY_BASE);//Assign the Symbol's Currency Base CurrencyProfit = SymbolInfoString(SymName,SYMBOL_CURRENCY_PROFIT);//Assign the Symbol's Currency Profit SymbolExist(SymName,is_Custom);//Get the boolean value into 'is_Custom' for whether the Symbol Name is a Custom Symbol(Is not from the broker) //-- Check if the Symbol outside the Market Watch has a SYMBOL_CURRENCY_BASE of EUR //-- and a SYMBOL_CURRENCY_PROFIT of USD, and this Symbol is not a Custom Symbol(Is not from the broker) if(CurrencyBase=="EUR"&&CurrencyProfit=="USD"&&!is_Custom) { EURUSD = SymName;//Assigning the name of the EURUSD Symbol found inside the Market Watch EurusdIsFound = true;//EURUSD Symbol was found in the Trading Terminal for your Broker break;//Will end the for loop } } if(!EurusdIsFound)//Check if EURUSD Symbol was already Found in the Market Watch { for(int i=0; i<SymbolsTotal(false); i++)//Will loop through all the available Symbols outside the Market Watch { string SymName = SymbolName(i,false);//Assign the Symbol Name of index 'i' from the list of Symbols outside the Market Watch CurrencyBase = SymbolInfoString(SymName,SYMBOL_CURRENCY_BASE); CurrencyProfit = SymbolInfoString(SymName,SYMBOL_CURRENCY_PROFIT); SymbolExist(SymName,is_Custom);//Get the boolean value into 'is_Custom' for whether the Symbol Name is a Custom Symbol(Is not from the broker) //-- Check if the Symbol outside the Market Watch has a SYMBOL_CURRENCY_BASE of EUR //-- and a SYMBOL_CURRENCY_PROFIT of USD, and this Symbol is not a Custom Symbol(Is not from the broker) if(CurrencyBase=="EUR"&&CurrencyProfit=="USD"&&!is_Custom) { EurusdIsSelected = SymbolSelect(SymName,true);//Adding the EURUSD Symbol to the Market Watch if(EurusdIsSelected)//Check if this program added EURUSD Symbol to Market Watch { EURUSD = SymName;//Assigning the name of the EURUSD Symbol found outside the Market Watch EurusdIsFound = true;//EURUSD Symbol was found in the Trading Terminal for your Broker break;//Will end the for loop } } } } if(!EurusdIsFound)//Check if EURUSD Symbol was Found in the Trading Terminal for your Broker { Print("Cannot Find EURUSD!"); Print("Cannot Create Database!"); Print("Server DST Cannot be Detected!"); dstType = DST_NONE;//Assigning enumeration value DST_NONE, Broker has no DST(Daylight Savings Time) return false;//Returning False, Broker's DST schedule was not found }
Nachdem wir EURUSD gefunden haben, werden wir alle NFP-Daten durchgehen und die M15-Kerzen für jedes einzelne Datum finden und die Höhe der Kerze mit den Offset-Daten von einer Stunde vor und nach dem Ereignis vergleichen, um zu erkennen, dass das Ereignis wahrscheinlich eingetreten ist. Wenn die Ereignisdaten nicht mit der Volatilität in den Kerzen übereinstimmen, speichern wir das erste Ereignisdatum, an dem diese Diskrepanz auftritt, und das Datum, an dem sie endet, in den Variablen ShiftStart und ShiftEnd.
for(uint i=0;i<eventtime.Size();i++) { currentresult.result = Candle.IsLargerThanPreviousAndNext((datetime)eventtime[i],Time.HoursS(),EURUSD);//Store the result of if the event date is the larger candlestick currentresult.date = (datetime)eventtime[i];//Store the event date from eventtime[i] timeIsShifted = ((currentresult.result!=previousresult.result&&i>0)?true:false);//Check if there is a difference between the previous result and the current result //--- Print Event Dates and if the event date's candle is larger than the previous candle an hour ago and the next candle an hour ahead Print("Date: ",eventtime[i]," is Larger: ",Candle.IsLargerThanPreviousAndNext((datetime)eventtime[i],Time.HoursS(),EURUSD)," Shifted: ",timeIsShifted); if(timeIsShifted)//Check if the Larger candle has shifted from the previous event date to the current event date in eventtime[i] array { if(ShiftStart==D'1970.01.01 00:00:00')//Check if the ShiftStart variable has not been assigned a relevant value yet { ShiftStart=currentresult.date;//Store the event date for when the time shift began } ShiftEnd=previousresult.date;//Store the event date timeshift } previousresult.result = currentresult.result;//Store the previous result of if the event date is the larger candlestick previousresult.date = currentresult.date;//Store the event date from eventtime[i] }
Sobald wir die Daten für ShiftStart und ShiftEnd haben, prüfen wir, ob die Daten mit den Daten für den Beginn und das Ende der Sommerzeit übereinstimmen. Wenn es eine Übereinstimmung gibt, weisen wir den Sommerzeitplan in der Variablen dstType zu und geben true zurück. Wenn wir kein ShiftStart-Datum haben (ShiftStart=D'1970.01.01 00:00:00') und die Größe des Arrays eventtime größer als Null ist, wissen wir, dass der Broker keinem Sommerzeitplan folgt.
if(ShiftStart==D'1970.01.01 00:00:00'&&eventtime.Size()>0)//Check if the ShiftStart variable has not been assigned a relevant value and the event dates are more than zero { Print("Broker ServerTime unchanged!"); dstType = DST_NONE;//Assigning enumeration value DST_NONE, Broker has no DST(Daylight Savings Time) return true;//Returning True, Broker's DST schedule was found successfully } if(Savings_AU.DaylightSavings(lastyear,DaylightStart,DaylightEnd)) { if(Time.DateIsInRange(DaylightStart,DaylightEnd,ShiftStart,ShiftEnd)) { Print("Broker ServerTime Adjusted For AU DST"); if(EurusdIsSelected)//Check if this program added EURUSD Symbol to Market Watch { SymbolSelect(EURUSD,false);//Remove EURUSD Symbol from Market Watch } dstType = AU_DST;//Assigning enumeration value AU_DST, Broker has AU DST(Daylight Savings Time) return true;//Returning True, Broker's DST schedule was found successfully } } else { Print("Something went wrong!"); Print("Cannot Find Daylight-Savings Date For AU"); Print("Year: %d Cannot Be Found!",lastyear); if(EurusdIsSelected)//Check if this program added EURUSD Symbol to Market Watch { SymbolSelect(EURUSD,false);//Remove EURUSD Symbol from Market Watch } dstType = DST_NONE;//Assigning enumeration value DST_NONE, Broker has no DST(Daylight Savings Time) return false;//Returning False, Broker's DST schedule was not found } if(Savings_UK.DaylightSavings(lastyear,DaylightStart,DaylightEnd)) { if(Time.DateIsInRange(DaylightStart,DaylightEnd,ShiftStart,ShiftEnd)) { Print("Broker ServerTime Adjusted For UK DST"); if(EurusdIsSelected)//Check if this program added EURUSD Symbol to Market Watch { SymbolSelect(EURUSD,false);//Remove EURUSD Symbol from Market Watch } dstType = UK_DST;//Assigning enumeration value UK_DST, Broker has UK/EU DST(Daylight Savings Time) return true;//Returning True, Broker's DST schedule was found successfully } } else { Print("Something went wrong!"); Print("Cannot Find Daylight-Savings Date For UK"); Print("Year: %d Cannot Be Found!",lastyear); if(EurusdIsSelected)//Check if this program added EURUSD Symbol to Market Watch { SymbolSelect(EURUSD,false);//Remove EURUSD Symbol from Market Watch } dstType = DST_NONE;//Assigning enumeration value DST_NONE, Broker has no DST(Daylight Savings Time) return false;//Returning False, Broker's DST schedule was not found } if(Savings_US.DaylightSavings(lastyear,DaylightStart,DaylightEnd)) { if(Time.DateIsInRange(DaylightStart,DaylightEnd,ShiftStart,ShiftEnd)) { Print("Broker ServerTime Adjusted For US DST"); if(EurusdIsSelected)//Check if this program added EURUSD Symbol to Market Watch { SymbolSelect(EURUSD,false);//Remove EURUSD Symbol from Market Watch } dstType = US_DST;//Assigning enumeration value US_DST, Broker has US DST(Daylight Savings Time) return true;//Returning True, Broker's DST schedule was found successfully } } else { Print("Something went wrong!"); Print("Cannot Find Daylight-Savings Date For US"); Print("Year: %d Cannot Be Found!",lastyear); if(EurusdIsSelected)//Check if this program added EURUSD Symbol to Market Watch { SymbolSelect(EURUSD,false);//Remove EURUSD Symbol from Market Watch } dstType = DST_NONE;//Assigning enumeration value DST_NONE, Broker has no DST(Daylight Savings Time) return false;//Returning False, Broker's DST schedule was not found } if(EurusdIsSelected)//Check if this program added EURUSD Symbol to Market Watch { SymbolSelect(EURUSD,false);//Remove EURUSD Symbol from Market Watch } Print("Cannot Detect Broker ServerTime Configuration!"); dstType = DST_NONE;//Assigning enumeration value DST_NONE, Broker has no DST(Daylight Savings Time) return false;//Returning False, Broker's DST schedule was not found }
Sobald wir den Zeitplan für die Sommerzeit erkannt haben, müssen wir diese Informationen für die spätere Implementierung speichern, damit wir beim Testen der wirtschaftlichen Ereignisse wissen, welchen Kalender wir verwenden müssen.
void CreateAutoDST(int db);//Function for creating and inserting Recommend DST for the Broker into a table
Ein einzelner Datensatz wird in der Tabelle AutoDST gespeichert.
void CNews::CreateAutoDST(int db) { bool failed=false;//boolean variable if(!DatabaseTableExists(db,"AutoDST"))//Checks if the table 'AutoDST' exists in the databse 'Calendar' { //--- create the table AutoDST if(!DatabaseExecute(db,"CREATE TABLE AutoDST(DST STRING NOT NULL);"))//Will attempt to create the table 'AutoDST' { Print("DB: create the AutoDST table failed with code ", GetLastError()); DatabaseClose(db);//Close the database return;//Exits the function if creating the table failed } } else { return;//Exits the function if the table AutoDST table already exists } //Sql query/request to insert the recommend DST for the Broker using the DSTType variable to determine which string data to insert string request_text=StringFormat("INSERT INTO 'AutoDST'(DST) VALUES ('%s')",((DSTType==US_DST)?"Data_US": (DSTType==UK_DST)?"Data_UK":(DSTType==AU_DST)?"Data_AU":"Data_None")); if(!DatabaseExecute(db, request_text))//Will attempt to run this sql request/query { Print(GetLastError()); PrintFormat("INSERT INTO 'AutoDST'(DST) VALUES ('%s')",((DSTType==US_DST)?"Data_US": (DSTType==UK_DST)?"Data_UK":(DSTType==AU_DST)?"Data_AU":"Data_None"));//Will print the sql query if failed failed=true;//assign true if the request failed } if(failed) { //--- roll back all transactions and unlock the database DatabaseTransactionRollback(db); PrintFormat("%s: DatabaseExecute() failed with code %d", __FUNCTION__, GetLastError()); } }
Wir brauchen eine Funktion, die unsere Kalendertabellen erstellt, damit wir diese Funktion wiederverwenden können, um unsere individuellen Kalender an die verschiedenen Sommerzeitpläne anzupassen.
bool CreateTable(int db,string tableName,bool &tableExists);//Function for creating a table in a database
In dieser Funktion CreateTable werden wir nur die Tabellen „Data_UK“ für UK DST,“Data_US“ für US DST,“Data_AU“ für AU DST und „Data_None“ für None DST erstellen. Die Zeichenfolge tableName ist der Parameter für den Suffixnamen der Tabelle, z. B. „US“.
bool CNews::CreateTable(int db,string tableName,bool &tableExists) { if(DatabaseTableExists(db,StringFormat("Data_%s",tableName)))//Checks if a table 'Data_%s' exists in the database 'Calendar' { tableExists=true;//Assigns true to tableExists variable if(!DatabaseExecute(db,StringFormat("DROP TABLE Data_%s",tableName)))//We will drop the table if the table already exists { //If the table failed to be dropped/deleted PrintFormat("Failed to drop table Data_%s with code %d",tableName,GetLastError()); DatabaseClose(db);//Close the database return false;//will terminate execution of the rest of the code below and return false, when the table cannot be dropped } } if(!DatabaseTableExists(db,StringFormat("Data_%s",tableName)))//If the database table 'Data_%s' doesn't exist { //--- create the table 'Data' with the following columns if(!DatabaseExecute(db,StringFormat("CREATE TABLE Data_%s(" "ID INT NOT NULL," "EVENTID INT NOT NULL," "COUNTRY STRING NOT NULL," "EVENTNAME STRING NOT NULL," "EVENTTYPE STRING NOT NULL," "EVENTIMPORTANCE STRING NOT NULL," "EVENTDATE STRING NOT NULL," "EVENTCURRENCY STRING NOT NULL," "EVENTCODE STRING NOT NULL," "EVENTSECTOR STRING NOT NULL," "EVENTFORECAST STRING NOT NULL," "EVENTPREVALUE STRING NOT NULL," "EVENTIMPACT STRING NOT NULL," "EVENTFREQUENCY STRING NOT NULL," "PRIMARY KEY(ID));",tableName)))//Checks if the table was successfully created { Print("DB: create the Calendar table failed with code ", GetLastError()); DatabaseClose(db);//Close the database return false;//Function returns false if creating the table failed } } return true;//Function returns true if creating the table was successful }
Jetzt müssen wir Daten in die von uns erstellten Tabellen einfügen, aber zuerst müssen wir diese Daten erhalten. Unsere nächste Funktion
void EconomicDetails(Calendar &NewsTime[]);//Gets values from the MQL5 economic Calendar
Ruft alle verfügbaren wirtschaftlichen Ereignisse per Referenz im NewsTime Calendar Array ab
void CNews::EconomicDetails(Calendar &NewsTime[]) { int Size=0;//to keep track of the size of the events in the NewsTime array MqlCalendarCountry countries[]; int count=CalendarCountries(countries);//Get the array of country names available in the Calendar string Country_code=""; for(int i=0; i<count; i++) { MqlCalendarValue values[]; datetime date_from=0;//Get date from the beginning datetime date_to=(datetime)(Time.MonthsS()+iTime(Symbol(),PERIOD_D1,0));//Date of the next month from the current day if(CalendarValueHistory(values,date_from,date_to,countries[i].code)) { for(int x=0; x<(int)ArraySize(values); x++) { MqlCalendarEvent event; ulong event_id=values[x].event_id;//Get the event id if(CalendarEventById(event_id,event)) { ArrayResize(NewsTime,Size+1,Size+2);//Readjust the size of the array to +1 of the array size StringReplace(event.name,"'","");//Removing or replacing single quotes(') from event name with an empty string NewsTime[Size].CountryName = countries[i].name;//storing the country's name from the specific event NewsTime[Size].EventName = event.name;//storing the event's name NewsTime[Size].EventType = EnumToString(event.type);//storing the event type from (ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_TYPE) to a string NewsTime[Size].EventImportance = EnumToString(event.importance);//storing the event importance from (ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_IMPORTANCE) to a string NewsTime[Size].EventId = event.id;//storing the event id NewsTime[Size].EventDate = TimeToString(values[x].time);//storing normal event time NewsTime[Size].EventCurrency = countries[i].currency;//storing event currency NewsTime[Size].EventCode = countries[i].code;//storing event code NewsTime[Size].EventSector = EnumToString(event.sector);//storing event sector from (ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_SECTOR) to a string if(values[x].HasForecastValue())//Checks if the event has a forecast value { NewsTime[Size].EventForecast = (string)values[x].forecast_value;//storing the forecast value into a string } else { NewsTime[Size].EventForecast = "None";//storing 'None' as the forecast value } if(values[x].HasPreviousValue())//Checks if the event has a previous value { NewsTime[Size].EventPreval = (string)values[x].prev_value;//storing the previous value into a string } else { NewsTime[Size].EventPreval = "None";//storing 'None' as the previous value } NewsTime[Size].EventImpact = EnumToString(values[x].impact_type);//storing the event impact from (ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_IMPACT) to a string NewsTime[Size].EventFrequency = EnumToString(event.frequency);//storing the event frequency from (ENUM_CALENDAR_EVENT_FREQUENCY) to a string Size++;//incrementing the Calendar array NewsTime } } } } }
Wenn wir unsere Daten haben, müssen wir sie nun in die Kalendertabellen einfügen.
bool InsertIntoTable(int db,DST_type Type,Calendar &Evalues[]);//Function for inserting Economic Data in to a database's table
Die Funktion InsertIntoTable hilft bei der Durchführung dieser Aufgabe. Sie hat drei Parameter.
1. Dieser Eingabeparameter ist der Integer-Wert der Datenbank.
int db 2. Dieser Eingabeparameter ist der Zeitplan für die Sommerzeit.
DST_type Type
3. Diese Array-Referenz ist eine Eingabe der Kalenderereignisse, die wir von unserer vorherigen Funktion EconomicDetails abgerufen hätten.
Calendar &Evalues[]
In dieser Funktion ändern wir die einzelnen Veranstaltungsdaten, wenn sie innerhalb der Sommerzeit liegen, fügen wir eine Stunde zum Veranstaltungsdatum hinzu, wenn die aktuelle Serverzeit in der Sommerzeit liegt, entfernen wir eine Stunde vom Veranstaltungsdatum. Speichern Sie dann alle wirtschaftlichen Ereignisdaten in der Kalendertabelle Data_%s.
bool CNews::InsertIntoTable(int db,DST_type Type,Calendar &Evalues[]) { string tableName;//will store the table name suffix for(uint i=0; i<Evalues.Size(); i++)//Looping through all the Economic Events { string Date;//Will store the date for the economic event switch(Type)//Switch statement to check all possible 'case' scenarios for the variable Type { case DST_NONE://if(Type==DST_NONE) then run code below Date = Evalues[i].EventDate;//Assign the normal Economic EventDate tableName = "None";//Full table name will be 'Data_None' break;//End switch statement case US_DST://if(Type==US_DST) then run code below Savings_US.adjustDaylightSavings(StringToTime(Evalues[i].EventDate),Date);//Assign by Reference the Economic EventDate adjusted for US DST(Daylight Savings Time) tableName = "US";//Full table name will be 'Data_US' break;//End switch statement case UK_DST://if(Type==UK_DST) then run code below Savings_UK.adjustDaylightSavings(StringToTime(Evalues[i].EventDate),Date);//Assign by Reference the Economic EventDate adjusted for UK DST(Daylight Savings Time) tableName = "UK";//Full table name will be 'Data_UK' break;//End switch statement case AU_DST://if(Type==AU_DST) then run code below Savings_AU.adjustDaylightSavings(StringToTime(Evalues[i].EventDate),Date);//Assign by Reference the Economic EventDate adjusted for AU DST(Daylight Savings Time) tableName = "AU";//Full table name will be 'Data_AU' break;//End switch statement default://if(Type==(Unknown value)) then run code below Date = Evalues[i].EventDate;//Assign the normal Economic EventDate tableName = "None";//Full table name will be 'Data_None' break;//End switch statement } string request_text = StringFormat("INSERT INTO 'Data_%s'(ID,EVENTID,COUNTRY,EVENTNAME,EVENTTYPE,EVENTIMPORTANCE,EVENTDATE,EVENTCURRENCY,EVENTCODE," "EVENTSECTOR,EVENTFORECAST,EVENTPREVALUE,EVENTIMPACT,EVENTFREQUENCY)" "VALUES (%d,%d,'%s','%s', '%s', '%s', '%s','%s','%s','%s','%s','%s','%s','%s')", tableName, i, Evalues[i].EventId, Evalues[i].CountryName, Evalues[i].EventName, Evalues[i].EventType, Evalues[i].EventImportance, Date, Evalues[i].EventCurrency, Evalues[i].EventCode, Evalues[i].EventSector, Evalues[i].EventForecast, Evalues[i].EventPreval, Evalues[i].EventImpact, Evalues[i].EventFrequency);//Inserting all the columns for each event record if(!DatabaseExecute(db, request_text))//Checks whether the event was inserted into the table 'Data_%s' { Print(GetLastError()); PrintFormat("INSERT INTO 'Data_%s'(ID,EVENTID,COUNTRY,EVENTNAME,EVENTTYPE,EVENTIMPORTANCE,EVENTDATE,EVENTCURRENCY,EVENTCODE," "EVENTSECTOR,EVENTFORECAST,EVENTPREVALUE,EVENTIMPACT,EVENTFREQUENCY)" "VALUES (%d,%d,'%s','%s', '%s', '%s', '%s','%s','%s','%s','%s','%s','%s','%s')", tableName, i, Evalues[i].EventId, Evalues[i].CountryName, Evalues[i].EventName, Evalues[i].EventType, Evalues[i].EventImportance, Date, Evalues[i].EventCurrency, Evalues[i].EventCode, Evalues[i].EventSector, Evalues[i].EventForecast, Evalues[i].EventPreval, Evalues[i].EventImpact, Evalues[i].EventFrequency);//Will print the sql query to check for any errors or possible defaults in the query/request return false;//Will end the loop and return false, as values failed to be inserted into the table } } return true;//Will return true, all values were inserted into the table successfully }
Sobald wir unsere Tabellen erstellt und Wirtschaftsdaten in sie eingefügt haben, benötigen wir einen Zeitstempel, wann diese Aktion durchgeführt wurde. Dies dient dazu, zu wissen, wann die Tabelle aktualisiert werden soll.
void CreateRecords(int db);//Creates a table to store records of when last the Calendar database was updated/created
Wir erstellen eine Tabelle namens Records und speichern die aktuelle Serverzeit in dieser Tabelle jedes Mal, wenn wir die Kalendertabellen erstellen oder aktualisieren.
void CNews::CreateRecords(int db) { bool failed=false; if(!DatabaseTableExists(db,"Records"))//Checks if the table 'Records' exists in the databse 'Calendar' { //--- create the table if(!DatabaseExecute(db,"CREATE TABLE Records(RECORDEDTIME INT NOT NULL);"))//Will attempt to create the table 'Records' { Print("DB: create the Records table failed with code ", GetLastError()); DatabaseClose(db);//Close the database return;//Exits the function if creating the table failed } } //Sql query/request to insert the current time into the 'RECORDEDTIME' column in the table 'Records' string request_text=StringFormat("INSERT INTO 'Records'(RECORDEDTIME) VALUES (%d)",(int)TimeCurrent()); if(!DatabaseExecute(db, request_text))//Will attempt to run this sql request/query { Print(GetLastError()); PrintFormat("INSERT INTO 'Records'(RECORDEDTIME) VALUES (%d)",(int)TimeCurrent()); failed=true;//assign true if the request failed } if(failed) { //--- roll back all transactions and unlock the database DatabaseTransactionRollback(db); PrintFormat("%s: DatabaseExecute() failed with code %d", __FUNCTION__, GetLastError()); } }
Jetzt haben wir im Grunde alle unsere Funktionen fertig, es gibt noch drei, auf die ich mich konzentrieren möchte. Hier die Erste:
bool UpdateRecords();//Checks if the main Calendar database needs an update or not
Diese Funktion gibt false zurück, wenn der maximale Datensatz in der Tabelle „Records“ innerhalb des aktuellen Datums liegt (d. h. die Kalendertabellen wurden bereits am aktuellen Tag erstellt oder aktualisiert und es müssen heute keine weiteren Aktualisierungen vorgenommen werden). Die Funktion gibt dann true zurück, wenn die Kalendertabellen nicht existieren oder die Kalenderdatenbank nicht existiert oder der maximale Datensatz in der Tabelle „Records“ nicht innerhalb des aktuellen Datums (Tages) liegt.
bool CNews::UpdateRecords() { //--- open/create int db=DatabaseOpen(NEWS_DATABASE_FILE, DATABASE_OPEN_READONLY|DATABASE_OPEN_COMMON);//try to open database Calendar if(db==INVALID_HANDLE)//Checks if the database was able to be opened { //if opening the database failed if(!FileIsExist(NEWS_DATABASE_FILE,FILE_COMMON))//Checks if the database Calendar exists in the common folder { return true;//Returns true when the database was failed to be opened and the file doesn't exist in the common folder } } if(!DatabaseTableExists(db,"Records"))//If the database table 'Records' doesn't exist { DatabaseClose(db); return true; } int recordtime=0;//will store the maximum date recorded in the database table 'Records' string request_text="SELECT MAX(RECORDEDTIME) FROM Records";//Sql query to determine the lastest or maximum date recorded int request=DatabasePrepare(db,request_text);//Creates a handle of a request, which can then be executed using DatabaseRead() if(request==INVALID_HANDLE)//Checks if the request failed to be completed { Print("DB: ",NEWS_DATABASE_FILE, " request failed with code ", GetLastError()); DatabaseClose(db); return true; } for(int i=0; DatabaseRead(request); i++)//Will read all the results from the sql query/request { if(!DatabaseColumnInteger(request, 0, recordtime))//Will assign the first column value to the variable 'recordtime' { Print(i, ": DatabaseRead() failed with code ", GetLastError()); DatabaseFinalize(request);//Removes a request created in DatabasePrepare() DatabaseClose(db);//Closes the database return true; } } DatabaseFinalize(request);//Removes a request created in DatabasePrepare() DatabaseClose(db);//Closes the database if(!Time.DateisToday((datetime)recordtime))//Checks if the recorded time/date is today(current day) { return true; } return false; }
Die zweite Funktion, auf die ich mich konzentrieren möchte, ist:
datetime GetLastestNewsDate();//Gets the lastest/newest date in the Calendar database
Diese Funktion ähnelt der letzten Funktion namens UpdateRecords, aber der Unterschied besteht darin, dass GetLastestNewsDate nur die maximale aufgezeichnete Zeit in der Tabelle Records zurückgibt, die später verwendet wird, um den Nutzer zu benachrichtigen, wenn er versucht, ein Datum im Strategietester zu testen, das größer als dieses Datum ist. Wir würden dem Nutzer/Händler mitteilen, dass es nach diesem Datum keine wirtschaftlichen Ereignisse mehr zu testen gibt.
datetime CNews::GetLastestNewsDate() { //--- open the database 'Calendar' in the common folder int db=DatabaseOpen(NEWS_DATABASE_FILE, DATABASE_OPEN_READONLY|DATABASE_OPEN_COMMON); if(db==INVALID_HANDLE)//Checks if 'Calendar' failed to be opened { if(!FileIsExist(NEWS_DATABASE_FILE,FILE_COMMON))//Checks if 'Calendar' database exists { return 0;//Will return the earliest date which is 1970.01.01 00:00:00 } } string eventtime="1970.01.01 00:00:00";//string variable with the first/earliest possible date in MQL5 //Sql query to determine the lastest or maximum recorded time from which the database was updated. string request_text="SELECT MAX(RECORDEDTIME) FROM Records"; int request=DatabasePrepare(db,request_text); if(request==INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("DB: ",NEWS_DATABASE_FILE, " request failed with code ", GetLastError()); DatabaseClose(db); return true; } for(int i=0; DatabaseRead(request); i++)//Will read all the results from the sql query/request { if(!DatabaseColumnText(request, 0,eventtime))//Will assign the first column(column 0) value to the variable 'eventtime' { Print(i, ": DatabaseRead() failed with code ", GetLastError()); DatabaseFinalize(request);//Finalize request DatabaseClose(db);//Closes the database 'Calendar' return 0;//Will end the for loop and will return the earliest date which is 1970.01.01 00:00:00 } } DatabaseFinalize(request); DatabaseClose(db);//Closes the database 'Calendar' return StringToTime(eventtime);//Returns the string eventtime converted to datetime }
Wir gehen nun zu der Funktion über, die die Kalenderdatenbank erstellt und alle anderen Funktionen aufruft, die wir zuvor erstellt haben, um die Tabellen in dieser Datenbank zu erstellen und Werte in diese Tabellen einzufügen.
void CreateEconomicDatabase();//Creates the Calendar database for a specific Broker
Dies ist die Funktion, die wir aufrufen, wenn der Expert Advisor an den Chart angehängt wird, um unsere Datenbank zu erstellen.
void CNews::CreateEconomicDatabase() { Print("Please wait..."); if(FileIsExist(NEWS_DATABASE_FILE,FILE_COMMON))//Check if the database exists { if(!UpdateRecords())//Check if the database is up to date { return;//will terminate execution of the rest of the code below } } else { if(!AutoDetectDST(DSTType))//Check if AutoDetectDST went through all the right procedures { return;//will terminate execution of the rest of the code below } } if(FileIsExist(NEWS_TEXT_FILE,FILE_COMMON))//Check if the database is open { return;//will terminate execution of the rest of the code below } Calendar Evalues[];//Creating a Calendar array variable bool failed=false,tableExists=false; int file=INVALID_HANDLE; datetime lastestdate=D'1970.01.01 00:00:00'; //--- open/create the database 'Calendar' int db=DatabaseOpen(NEWS_DATABASE_FILE, DATABASE_OPEN_READWRITE | DATABASE_OPEN_CREATE| DATABASE_OPEN_COMMON);//will try to open/create in the common folder if(db==INVALID_HANDLE)//Checks if the database 'Calendar' failed to open/create { Print("DB: ",NEWS_DATABASE_FILE, " open failed with code ", GetLastError()); return;//will terminate execution of the rest of the code below } else { file=FileOpen(NEWS_TEXT_FILE,FILE_WRITE|FILE_ANSI|FILE_TXT|FILE_COMMON);//try to create a text file 'NewsDatabaseOpen' in common folder if(file==INVALID_HANDLE) { DatabaseClose(db);//Closes the database 'Calendar' if the News text file failed to be created return;//will terminate execution of the rest of the code below } } DatabaseTransactionBegin(db);//Starts transaction execution Print("Please wait..."); //-- attempt to create the calendar tables if(!CreateTable(db,"None",tableExists)||!CreateTable(db,"US",tableExists) ||!CreateTable(db,"UK",tableExists)||!CreateTable(db,"AU",tableExists)) { FileClose(file);//Closing the file 'NewsDatabaseOpen.txt' FileDelete(NEWS_TEXT_FILE,FILE_COMMON);//Deleting the file 'NewsDatabaseOpen.txt' return;// } EconomicDetails(Evalues);//Retrieving the data from the Economic Calendar if(tableExists)//Checks if there is an existing table within the Calendar Database { //if there is an existing table we will notify the user that we are updating the table. PrintFormat("Updating %s",NEWS_DATABASE_FILE); } else { //if there isn't an existing table we will notify the user that we about to create one PrintFormat("Creating %s",NEWS_DATABASE_FILE); } //-- attempt to insert economic event data into the calendar tables if(!InsertIntoTable(db,DST_NONE,Evalues)||!InsertIntoTable(db,US_DST,Evalues) ||!InsertIntoTable(db,UK_DST,Evalues)||!InsertIntoTable(db,AU_DST,Evalues)) { failed=true;//Will assign true if inserting economic vaules failed in any of the Data tables } if(failed)//Checks if the event/s failed to be recorded/inserted into the database table 'Data_%s' { //--- roll back all transactions and unlock the database DatabaseTransactionRollback(db); PrintFormat("%s: DatabaseExecute() failed with code %d", __FUNCTION__, GetLastError()); FileClose(file);//Close the text file 'NEWS_TEXT_FILE' FileDelete(NEWS_TEXT_FILE,FILE_COMMON);//Delete the text file, as we are reverted/rolled-back the database ArrayRemove(Evalues,0,WHOLE_ARRAY);//Removes the values in the array } else//if all the events were recorded or inserted into the tables 'Data_%s' { if(tableExists) { //Let the user/trader know that the database was updated PrintFormat("%s Updated",NEWS_DATABASE_FILE); } else { //Let the user/trader know that the database was created PrintFormat("%s Created",NEWS_DATABASE_FILE); } CreateRecords(db);//Will create the 'Records' table and insert the current time CreateAutoDST(db);//Will create the 'AutoDST' table and insert the broker's DST schedule FileClose(file);//Close the text file 'NEWS_TEXT_FILE' FileDelete(NEWS_TEXT_FILE,FILE_COMMON);//Delete the text file, as we are about to close the database ArrayRemove(Evalues,0,WHOLE_ARRAY);//Removes the values in the array } //--- all transactions have been performed successfully - record changes and unlock the database DatabaseTransactionCommit(db); DatabaseClose(db);//Close the database }
Wir gehen nun zum Expert Advisor über, der den gesamten Code ausführt, den wir in den verschiedenen Klassen und Dateien erstellt haben, die wir in diesem NewsTrading-Projekt erstellt haben:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| NewsTrading.mq5 | //| Copyright 2024, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #include "News.mqh" CNews NewsObject; #include "TimeManagement.mqh" CTimeManagement CTM; #include "WorkingWithFolders.mqh" CFolders Folder();//Calling the class's constructor //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- if(!MQLInfoInteger(MQL_TESTER))//Checks whether the program is in the strategy tester { //Checks whether the database file exists and whether it has been modified in the current date if((!CTM.DateisToday((datetime)FileGetInteger(NEWS_DATABASE_FILE,FILE_MODIFY_DATE,true)))||(!FileIsExist(NEWS_DATABASE_FILE,FILE_COMMON))) { /* In the Do while loop below, the code will check if the terminal is connected to the internet. If the the program is stopped the loop will break, if the program is not stopped and the terminal is connected to the internet the function CreateEconomicDatabase will be called from the News.mqh header file's object called NewsObject and the loop will break once called. */ bool done=false; do { if(IsStopped()) { done=true; } if(!TerminalInfoInteger(TERMINAL_CONNECTED)) { Print("Waiting for connection..."); Sleep(500); continue; } else { Print("Connection Successful!"); NewsObject.CreateEconomicDatabase();//calling the database create function done=true; } } while(!done); } } else { //Checks whether the database file exists if(!FileIsExist(NEWS_DATABASE_FILE,FILE_COMMON)) { Print("Necessary Files Do not Exist!"); Print("Run Program outside of the Strategy Tester"); Print("Necessary Files Should be Created First"); return(INIT_FAILED); } //Checks whether the lastest database date includes the time and date being tested datetime lastestdate = CTM.TimePlusOffset(NewsObject.GetLastestNewsDate(),CTM.DaysS());//Day after the lastest recorded time in the database if(lastestdate<TimeCurrent()) { Print("Necessary Files OutDated!"); Print("Database Dates End at: ",lastestdate); Print("Dates after %s will not be available for backtest",lastestdate); Print("To Update Files:"); Print("Run Program outside of the Strategy Tester"); } } //--- return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { //--- } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { //--- } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
Jetzt müssen wir nur noch die Dateien und den Expert Advisor kompilieren, den Expert Advisor in ein Chart einfügen und mit der Analyse dessen beginnen, was wir kodiert haben.
Und vor allem: Sehen Sie, was der Wirtschaftskalender zu bieten hat.
Dies sind unsere Projektdateien
MQL5 Wirtschaftskalender Aufschlüsselung
Sobald alles kompiliert ist, öffnen wir das Handelsterminal, suchen das Navigator-Fenster und öffnen unseren NewsTrading-Ordner.
Wir werden nun den Expert Advisor an einen Chart Ihrer Wahl anhängen. In diesem Artikel werden wir die Option „Algo-Handel zulassen“ nicht aktivieren, da kein Handel stattfinden wird. Drücken Sie einfach auf OK und hängen Sie den Experten an.
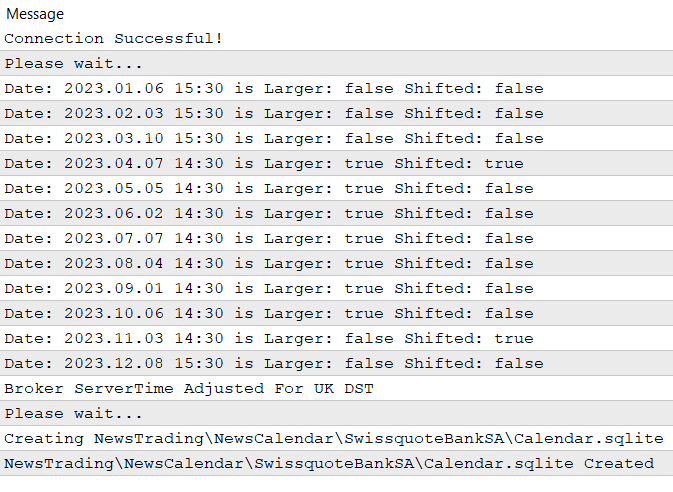
Sobald der Experte an das Chart angehängt ist, sollten Sie auf der Registerkarte Experten unten im Terminal einen gedruckten Text sehen, der den Nutzer darüber informiert, dass die Datenbank erfolgreich erstellt wurde.
Jetzt müssen Sie die IDE-Schaltfläche im oberen Bereich des Handelsterminals suchen. Sobald Sie die Schaltfläche gefunden haben, drücken Sie sie und es öffnet sich ein weiteres Fenster
neben dem Handelsterminal. Suchen Sie die Schaltfläche Datei im oberen linken Bereich der IDE und wählen Sie den Ordner Open MetaQuotes Common Data.
![]()
Ihr Dateiverzeichnis sollte ähnlich aussehen wie das obige Bild, das Ihnen die Dateien in diesem Ordner namens Dateien anzeigt.
Sie werden sehen, dass neben dem NewsTrading-Ordner viele andere erstellt wurden.
![]()
Sobald Sie alle Ordner geöffnet haben, finden Sie die SQLite-Datenbank Ihres Brokers mit den einzelnen Kalendern.
Wir kehren nun zur MQL5-IDE zurück.
Wählen Sie das Ordnersymbol oben links in der IDE, es sollten sich im MetaTrader Common Folder befinden.
Dann suchen wir die Kalender-SQLite-Datenbank des Brokers und öffnen sie.
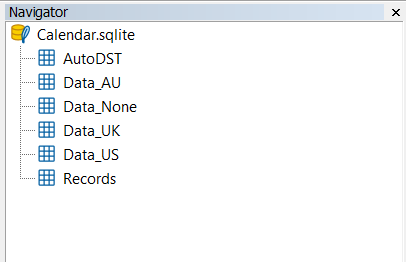
Sie sollten den Inhalt der Datenbank im Navigator-Fenster sehen. Wir klicken mit der rechten Maustaste auf die erste Tabelle und wählen „Open Table“.
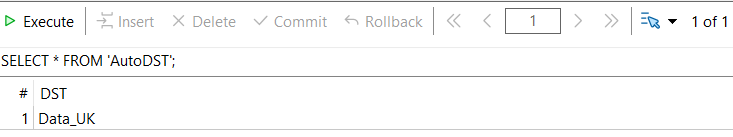
Die Tabelle wird geöffnet und alle Datensätze (*) aus „AutoDST“ werden angezeigt. Es gibt immer nur einen Datensatz in dieser Tabelle, da dies die von unserem Makler empfohlene Sommerzeit-Kalendertabelle ist.
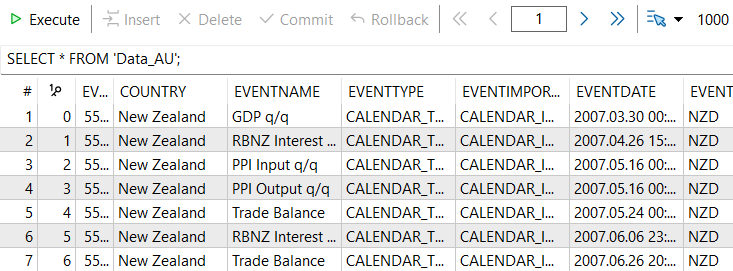
Sobald wir die Tabelle „Data_AU“ öffnen, werden alle Datensätze in dieser Tabelle sowie alle Spalten angezeigt.
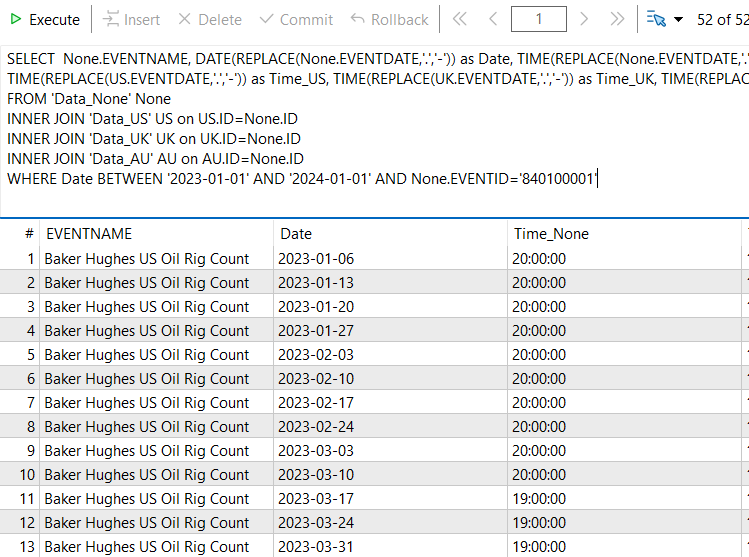
SQL-Abfrage:
SELECT None.EVENTNAME, DATE(REPLACE(None.EVENTDATE,'.','-')) as Date, TIME(REPLACE(None.EVENTDATE,'.','-')) as Time_None, TIME(REPLACE(US.EVENTDATE,'.','-')) as Time_US, TIME(REPLACE(UK.EVENTDATE,'.','-')) as Time_UK, TIME(REPLACE(AU.EVENTDATE,'.','-')) as Time_AU FROM 'Data_None' None INNER JOIN 'Data_US' US on US.ID=None.ID INNER JOIN 'Data_UK' UK on UK.ID=None.ID INNER JOIN 'Data_AU' AU on AU.ID=None.ID WHERE Date BETWEEN '2023-01-01' AND '2024-01-01' AND None.EVENTID='840100001';
Ziel: Diese Abfrage soll den Ereignisnamen der Ereignis-ID = „840100001“ und das Ereignisdatum als „Date“ und die Uhrzeit als „Zeit_None“ für die Daten zwischen „2023-01-01“ und „2024-01-01“ aus der Tabelle „Time_None“, sowie die Auswahl derselben Ereignis-ID aus den Tabellen „Data_UK“, „Data_US“, „Data_AU“, aber nur die Anzeige der Uhrzeit der Ereignisse aus diesen Tabellen als „Time_UK“, „Time_US“, „Time_AU“. In dieser Abfrage wollen wir die Zeitdifferenz zwischen den verschiedenen Kalendertabellen für dasselbe Ereignis für das gesamte Jahr 2023 anzeigen.
In der obigen SQL-Abfrage geben wir der Tabelle „Data_None“ einen Alias namens None, der Tabelle „Data_US“ geben wir einen Alias namens US, der Tabelle „Data_UK“ geben wir einen Alias namens UK und der Tabelle „Data_AU“ geben wir einen Alias namens AU.
Wir WÄHLEN:
None.EVENTNAME
aus der Tabelle „Data_None“.
Mit der SQL Function:
REPLACE(None.EVENTDATE,'.','-')
Die Punktzeichen („.“) im Wert von None.EVENTDATE werden durch Bindestrichzeichen („-“) ersetzt. Das liegt daran, dass die SQL-Funktion:
DATE()
nur Datumsangaben in datetime mit einem Bindestrich als Trennzeichen akzeptiert und keine Datumsangaben in datetime mit einem Punkt als Trennzeichen. Diese Funktion wandelt datetime in date um.
TIME()
Die obige SQL-Funktion konvertiert datetime in time.
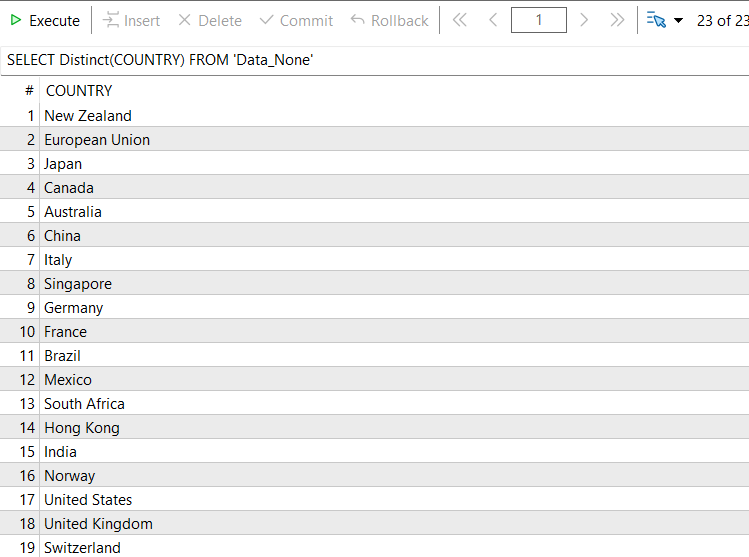
SQL-Abfrage:
SELECT Distinct(COUNTRY) FROM 'Data_None';
Ziel: Diese Abfrage liefert uns alle eindeutigen Länder, die Datensätze in der Kalendertabelle „Data_None“ haben.
Wenn Sie die Ergebnisse Ihrer SQL-Abfragen für eine spätere Analyse aufbewahren möchten, können Sie einfach mit der rechten Maustaste auf eines der Ergebnisse klicken und die CSV-Datei exportieren, die dann in eine Excel-Datei umgewandelt werden kann
für weitere Wirkungsanalysen.
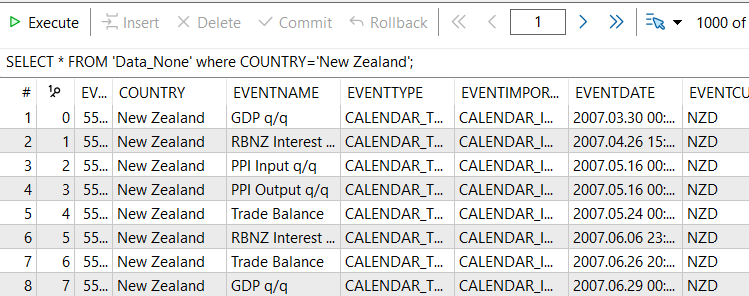
SQL-Abfrage:
SELECT * FROM 'Data_None' where COUNTRY='New Zealand';
Ziel: Diese Abfrage liefert uns alle Datensätze für ein bestimmtes Land. In diesem Fall ist das Neuseeland.
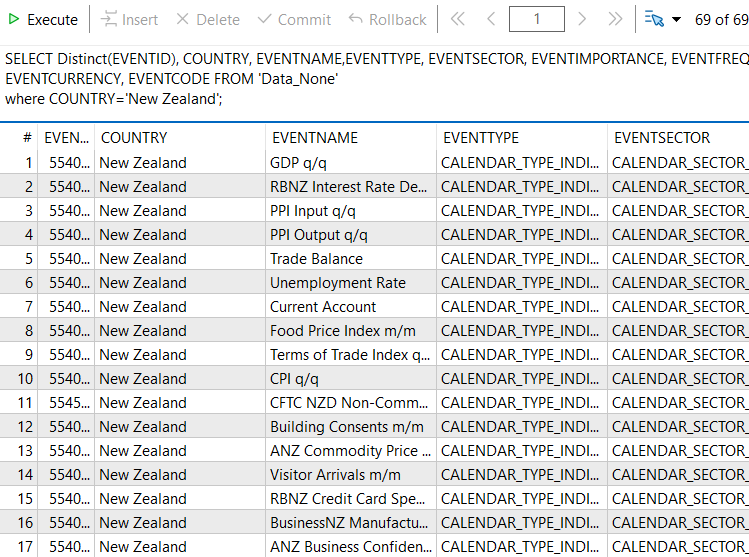
SQL-Abfrage:
SELECT Distinct(EVENTID), COUNTRY, EVENTNAME,EVENTTYPE, EVENTSECTOR, EVENTIMPORTANCE, EVENTFREQUENCY, EVENTCURRENCY, EVENTCODE FROM 'Data_None' where COUNTRY='New Zealand';
Ziel: Diese Abfrage ruft alle eindeutigen Ereignis-IDs für ein bestimmtes Land ab und wählt bestimmte Spalten wie „EVENTNAME“ und „EVENTSECTOR“ usw. aus.
Aber eben nicht „EVENTDATE“, da jedes „EVENTID“ ein anderes „EVENTDATE“ hat. Der Versuch, das „EVENTDATE“ in diese Abfrage aufzunehmen, führt zu Fehlern.
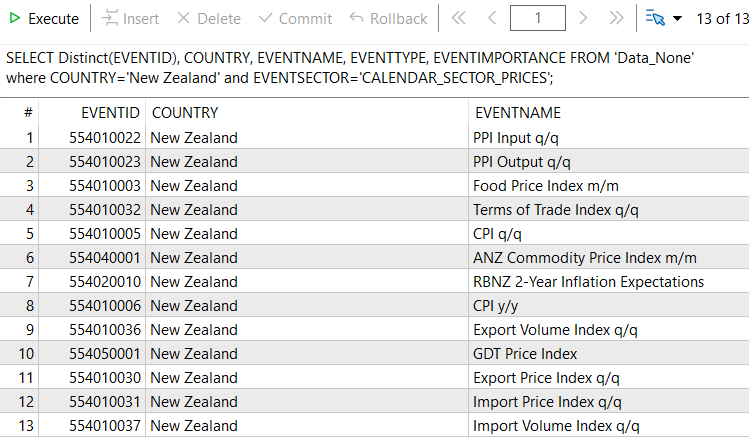
SQL-Abfrage:
SELECT Distinct(EVENTID), COUNTRY, EVENTNAME, EVENTTYPE, EVENTIMPORTANCE FROM 'Data_None' where COUNTRY='New Zealand' and EVENTSECTOR='CALENDAR_SECTOR_PRICES';
Ziel: Diese Abfrage ruft alle eindeutigen Ereignis-IDs für ein bestimmtes „COUNTRY“ und „EVENTSECTOR“ ab
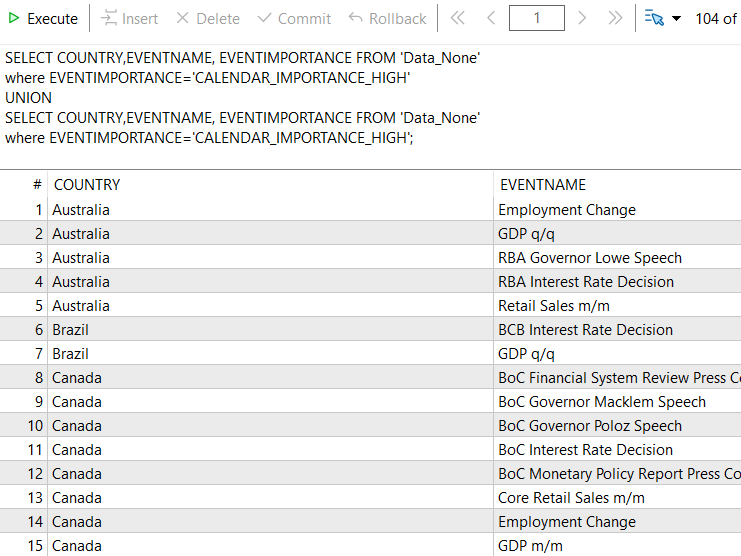
SQL-Abfrage:
SELECT COUNTRY,EVENTNAME, EVENTIMPORTANCE FROM 'Data_None' where EVENTIMPORTANCE='CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_HIGH' UNION SELECT COUNTRY,EVENTNAME, EVENTIMPORTANCE FROM 'Data_None' where EVENTIMPORTANCE='CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_HIGH';
Ziel: Diese Abfrage ruft alle eindeutigen Datensätze für die Ereigniswichtigkeit „CALENDAR_IMPORTANCE_HIGH“ ab.
Schlussfolgerung
Aus diesem Artikel können Sie viel mitnehmen. Ich hoffe, Sie haben nach der Lektüre dieses Artikels etwas Neues gelernt und einige neue Ideen bekommen. In diesem Artikel haben wir erläutert, warum die Verwendung von einer Datenbank die richtige Wahl war und welche Vorteile eine Datenbank zu zu verwenden ist. Wir sind auch alle Währungen durchgegangen, die der Wirtschaftskalender von MQL5 anbietet, und das Konzept von DST (Daylight savings). Außerdem haben wir verschiedene wichtige Dateien für die Erstellung der Kalenderdatenbank und die Überprüfung, ob die Datenbank aktualisiert oder erstellt werden soll, programmiert.
Schließlich haben wir uns mit dem Auffinden der Datenbankdateien befasst, nachdem sie erstellt wurden, und mit dem Extrahieren bestimmter Daten unter Verwendung grundlegender SQL-Abfragen, um die Tabelle zu manipulieren. Im nächsten Artikel werden wir das Risikomanagement durchgehen. Auf Wiedersehen für jetzt.
Übersetzt aus dem Englischen von MetaQuotes Ltd.
Originalartikel: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/14324
Warnung: Alle Rechte sind von MetaQuotes Ltd. vorbehalten. Kopieren oder Vervielfältigen untersagt.
Dieser Artikel wurde von einem Nutzer der Website verfasst und gibt dessen persönliche Meinung wieder. MetaQuotes Ltd übernimmt keine Verantwortung für die Richtigkeit der dargestellten Informationen oder für Folgen, die sich aus der Anwendung der beschriebenen Lösungen, Strategien oder Empfehlungen ergeben.
 Eine generische Optimierungsformulierung (GOF) zur Implementierung von Custom Max mit Nebenbedingungen
Eine generische Optimierungsformulierung (GOF) zur Implementierung von Custom Max mit Nebenbedingungen
 MQL5-Assistenten-Techniken, die Sie kennen sollten (Teil 13): DBSCAN für eine Klasse für Expertensignale
MQL5-Assistenten-Techniken, die Sie kennen sollten (Teil 13): DBSCAN für eine Klasse für Expertensignale
 Datenwissenschaft und maschinelles Lernen (Teil 21): Neuronale Netze entschlüsseln, Optimierungsalgorithmen entmystifiziert
Datenwissenschaft und maschinelles Lernen (Teil 21): Neuronale Netze entschlüsseln, Optimierungsalgorithmen entmystifiziert
 Entwicklung eines MQTT-Clients für Metatrader 5: ein TDD-Ansatz — Teil 6
Entwicklung eines MQTT-Clients für Metatrader 5: ein TDD-Ansatz — Teil 6
- Freie Handelsapplikationen
- Über 8.000 Signale zum Kopieren
- Wirtschaftsnachrichten für die Lage an den Finanzmärkte
Sie stimmen der Website-Richtlinie und den Nutzungsbedingungen zu.
Schöner Artikel und gut gestaltete Code.
Ich mochte den Ansatz, den Sie gefolgt, um den Broker DST-Typ durch die Preisreaktionen auf NFP der Vereinigten Staaten auf EURUSD-Charts zu erhalten, es funktioniert einwandfrei.
Ich habe auch die DST-Anpassungen der Non-Farm-Payrolls (NFP)-Ereignisse der USA bei mehreren Brokern (DST_NONE, DST_UK und DST_US) getestet und es hat sich gezeigt, dass sie in der Methode CDaylightSavings_AU::adjustDaylightSavings() und ihren Geschwistern in den anderen beiden Klassen korrekt berechnet werden. Die Leistung des Prozesses zur Ermittlung der Tageslichtzeiten kann jedoch erheblich gesteigert werden, wenn die DST-Umschaltzeiten direkt mit Hilfe mathematischer Gleichungen berechnet werden, anstatt die hart kodierten Werte linear in CArrayObj() zu suchen. Siehe hier.
Beachten Sie auch, dass SymbolInfoString(SymName,SYMBOL_CURRENCY_BASE) bei einigen Brokern, die diese Eigenschaft auf ihren Servern nicht korrekt konfigurieren, fehlschlagen kann (sie setzen die Basiswährung von EURUSD"fälschlicherweise" auf USD statt auf EUR), daher ist es sicherer, StringSubstr(SymName,0,3) zu verwenden.
Danke!