
风险管理(第一部分):建立风险管理类的基础知识
概述
在本文中,我们将探讨交易中的风险管理意味着什么,以及为什么它对自动化操作至关重要。我们将从基本概念开始,为理解适当的风险管理如何影响金融市场的成败奠定基础。
稍后,我们将逐步构建一个 MQL5 类,该类实现了一个完整的风险管理系统,允许控制手数大小、最大损失和预期利润等关键方面。
什么是风险管理?
风险管理是任何交易策略的基本支柱。其主要目的是监控和控制未平仓头寸,确保损失不超过交易者设定的限额,如每日、每周或整体损失。
此外,风险管理根据用户的规则和偏好确定每笔交易的适当手数。这不仅保护了资本,还优化了策略绩效,确保交易符合既定的风险状况。
简而言之,良好的风险管理不仅可以降低灾难性损失的可能性,还可以为做出明智的财务决策提供一个有纪律的框架。
在自动交易中的重要性
风险管理在自动化交易中起着至关重要的作用,因为它作为一个控制系统,可以防止代价高昂的错误,如过度交易或过度暴露于不必要的风险。在交易机器人的背景下,决策是完全自动做出的,适当的风险管理可以确保策略以有纪律和高效的方式执行。
这在资金挑战等情况下尤其有价值,在这些情况下,遵守严格的每日、每周或总损失限额可能是通过或失败的区别。风险管理能够精确地建立这些边界,保护用户的资本,并在竞争环境中优化性能。
此外,它通过设定明确的限制来避免过度交易或承担不成比例的风险,从而帮助机器人以更具战略性的方式运作。通过自动计算手数并限制每笔交易的损失,风险管理不仅可以保护资金,还可以让交易者放心,因为他们知道他们的机器人在受控和安全的参数范围内运行。
风险管理的关键概念
在开始编码之前,了解风险管理中涉及的主要变量和概念至关重要。这些概念构成了保护用户资本并确保受控运营的有效系统的基础。下面,我们将逐一进行分析:
1.每日最大亏损
这是机器人在一天(24小时)内可以累积的最大损失。如果达到这个限制,机器人通常会关闭所有未平仓交易,并暂停任何交易活动,直到第二天。这一概念有助于防止连续亏损的交易严重影响资本。
2.每周最大亏损
类似于每日损失限额,但适用于一周的时间范围。如果机器人超过这个阈值,它将停止交易,直到下周开始。此参数非常适合防止长时间内的重大损失。
3.最大总亏损
这代表了绝对损失限额,当达到该限额时,会触发特殊的恢复策略。这种策略可能包括减少交易量和更谨慎地交易,以逐步收回损失的资本。这一概念有助于控制整体账户风险。
4.每笔交易的最大亏损
定义单笔交易可能产生的最大损失。该值至关重要,因为它允许根据用户愿意接受的风险水平自动计算每笔交易的最佳手数。
5.每日、每周和总利润
这些是记录不同时期累计利润的变量。这些指标可用于评估自动化机器人的性能,并根据获得的结果调整策略。
创建包含文件并解释计划
在本节中,我们将开始编写包含文件。
1.在 MetaTrader 平台顶部,单击“IDE”按钮:
![]()
2.在 MetaEditor 的左上角,单击“文件”选项卡,然后选择“新”。将出现以下窗口:
3.选择“包括”,然后单击“下一步”:
4.通过指定名称和作者来设置包含:
我们已完成文件创建。这仅仅是个开始。现在,让我们来看看我们的风险管理系统将如何运作的计划。
下图显示了风险管理将如何运作:
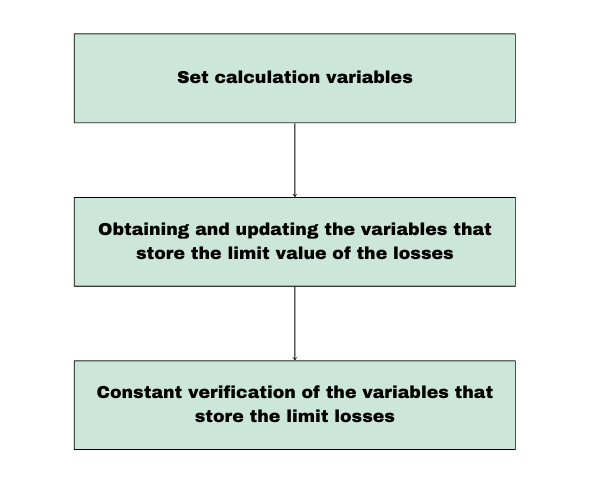
| 部分 | 描述 | 执行频率 |
|---|---|---|
| 1.设置计算变量 | 在这个初始阶段(只执行一次),建立了计算损益所需的所有变量。 主要任务包括:
| 执行一次,或每当配置 EA 时执行。 |
| 2. 损失和利润的计算 | 在此阶段,计算账户损益的当前状态。这包括:
| 根据配置,每天执行,开仓交易时执行或每周执行。 |
| 3. 实时验证 | 在实时运行期间,EA 会不断检查(每次报价时)以确保当前损失未超过定义的限制。 如果任何损失变量超过其阈值,EA 将立即关闭所有未平仓头寸,以防止进一步损失。 | 每次报价(实时过程)。 |
考虑到上述所有因素,我们继续创建第一个函数。
创建手数计算函数
在开发类本身之前,我们必须首先创建允许我们计算适当手数大小的函数。
计算理想手数
为了确定理想的手数,我们首先需要计算总手数,这代表了我们的账户可以买卖的最大交易量。此计算基于开仓一手所需的保证金(以账户货币计算)。一旦知道这个值,我们就将账户的可用预付款除以所需的预付款,对结果进行四舍五入,从而获得账户允许的最大手数。
先决条件
在进行计算之前,我们需要确定任何给定交易品种每手所需的预付款。在这个例子中,我们的交易品种是黄金(XAUUSD),尽管同样的过程也适用于任何其他金融工具。
主要目标是建立有效计算手数的坚实基础 —— 动态适应账户余额和可用预付款。
如图所示,购买一手黄金所需的初始预付款约为1326美元。因此,要计算允许的最大手数,我们只需将账户的可用预付款除以每手所需的预付款即可。这种关系可以表达如下:
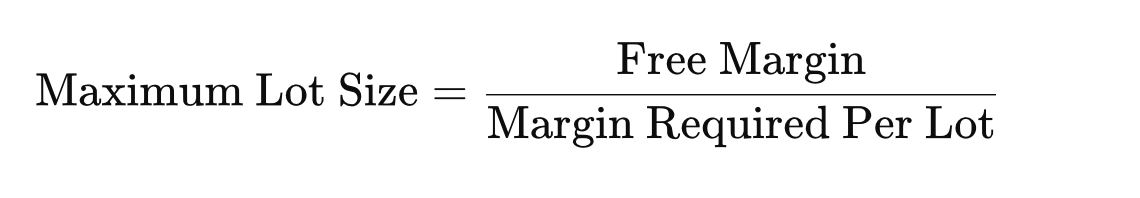
可用预付款:
- 可用预付款代表您账户中可用于开立新交易的可用资金。在 MetaTrader 中,其计算方式如下:
![]()
计算任何订单类型的价格
现在我们知道如何计算最大手数,下一步就是在代码中实现这个逻辑。然而,在我们这样做之前,我们必须确定订单执行的价格。为了实现这一点,我们将创建一个名为 PriceByOrderType 的函数,它将根据订单类型计算并返回相应的价格。
double PriceByOrderType(const string symbol, const ENUM_ORDER_TYPE order_type, double DEVIATION = 100, double STOP_LIMIT = 50)
输入:
- symbol:将执行订单的交易品种(例如 EURUSD)。
- order_type:订单类型,基于 ENUM_ORDER_TYPE 枚举。
- DEVIATION:允许的价格偏差(以点数为单位)。
- STOP_LIMIT:STOP_LIMIT 类型订单的距离(以点数为单位)。
第一步,创建所需的变量
首先,我们声明将存储交易品种的小数位数、点值和当前买入/卖出价格的变量,所有这些都在 MqlTick 结构中。
int digits=0; double point=0; MqlTick tick={};
第二步,为变量赋值
我们使用内置函数来检索交易品种信息,例如小数位数、点值和当前价格。
获取 SYMBOL_POINT 值:ResetLastError(); if(!SymbolInfoDouble(symbol, SYMBOL_POINT, point)) { Print("SymbolInfoDouble() failed. Error ", GetLastError()); return 0; }
获取 SYMBOL_DIGITS 值:
long value=0; if(!SymbolInfoInteger(symbol, SYMBOL_DIGITS, value)) { Print("SymbolInfoInteger() failed. Error ", GetLastError()); return 0; } digits=(int)value;
获取当前交易品种价格:
if(!SymbolInfoTick(symbol, tick)) { Print("SymbolInfoTick() failed. Error ", GetLastError()); return 0; }
第三步, 根据订单类型计算价格
根据订单类型,我们使用 switch 结构返回对应的价格:
switch(order_type) { case ORDER_TYPE_BUY : return(tick.ask); case ORDER_TYPE_SELL : return(tick.bid); case ORDER_TYPE_BUY_LIMIT : return(NormalizeDouble(tick.ask - DEVIATION * point, digits)); case ORDER_TYPE_SELL_LIMIT : return(NormalizeDouble(tick.bid + DEVIATION * point, digits)); case ORDER_TYPE_BUY_STOP : return(NormalizeDouble(tick.ask + DEVIATION * point, digits)); case ORDER_TYPE_SELL_STOP : return(NormalizeDouble(tick.bid - DEVIATION * point, digits)); case ORDER_TYPE_BUY_STOP_LIMIT : return(NormalizeDouble(tick.ask + DEVIATION * point - STOP_LIMIT * point, digits)); case ORDER_TYPE_SELL_STOP_LIMIT : return(NormalizeDouble(tick.bid - DEVIATION * point + STOP_LIMIT * point, digits)); default : return(0); }
这是该函数的最终实现:
double PriceByOrderType(const string symbol, const ENUM_ORDER_TYPE order_type, double DEVIATION = 100, double STOP_LIMIT = 50) { int digits=0; double point=0; MqlTick tick={}; //--- we get the Point value of the symbol ResetLastError(); if(!SymbolInfoDouble(symbol, SYMBOL_POINT, point)) { Print("SymbolInfoDouble() failed. Error ", GetLastError()); return 0; } //--- we get the Digits value of the symbol long value=0; if(!SymbolInfoInteger(symbol, SYMBOL_DIGITS, value)) { Print("SymbolInfoInteger() failed. Error ", GetLastError()); return 0; } digits=(int)value; //--- we get the latest prices of the symbol if(!SymbolInfoTick(symbol, tick)) { Print("SymbolInfoTick() failed. Error ", GetLastError()); return 0; } //--- Depending on the type of order, we return the price switch(order_type) { case ORDER_TYPE_BUY : return(tick.ask); case ORDER_TYPE_SELL : return(tick.bid); case ORDER_TYPE_BUY_LIMIT : return(NormalizeDouble(tick.ask - DEVIATION * point, digits)); case ORDER_TYPE_SELL_LIMIT : return(NormalizeDouble(tick.bid + DEVIATION * point, digits)); case ORDER_TYPE_BUY_STOP : return(NormalizeDouble(tick.ask + DEVIATION * point, digits)); case ORDER_TYPE_SELL_STOP : return(NormalizeDouble(tick.bid - DEVIATION * point, digits)); case ORDER_TYPE_BUY_STOP_LIMIT : return(NormalizeDouble(tick.ask + DEVIATION * point - STOP_LIMIT * point, digits)); case ORDER_TYPE_SELL_STOP_LIMIT : return(NormalizeDouble(tick.bid - DEVIATION * point + STOP_LIMIT * point, digits)); default : return(0); } }
另外,我们需要一个函数来根据订单类型获取市价单类型:
ENUM_ORDER_TYPE MarketOrderByOrderType(ENUM_ORDER_TYPE type) { switch(type) { case ORDER_TYPE_BUY : case ORDER_TYPE_BUY_LIMIT : case ORDER_TYPE_BUY_STOP : case ORDER_TYPE_BUY_STOP_LIMIT : return(ORDER_TYPE_BUY); case ORDER_TYPE_SELL : case ORDER_TYPE_SELL_LIMIT : case ORDER_TYPE_SELL_STOP : case ORDER_TYPE_SELL_STOP_LIMIT : return(ORDER_TYPE_SELL); } return(WRONG_VALUE); }
计算最大手数
GetMaxLot 根据可用的可用预付款和指定的订单类型计算可以开仓的最大手数。它是一种关键的风险管理工具,可确保交易符合经纪商设定的预付款要求。
1.创建函数参数
该函数采用以下参数:
double GetMaxLote(ENUM_ORDER_TYPE type, double DEVIATION = 100, double STOP_LIMIT = 50)
- Type:定义订单类型,例如 ORDER_TYPE_BUY 或 ORDER_TYPE_SELL。此参数对于正确计算价格和预付款很重要。
- DEVIATION:指定挂单允许的点数偏差。其默认值为 100。
- STOP_LIMIT:表示 STOP_LIMIT 订单的点数距离。其默认值为 50。
2.初始化所需的变量
声明了四个 double 类型的变量和一个 ORDER_TYPE 枚举变量用于计算:
//--- Set variables double VOLUME = 1.0; //Initial volume size ENUM_ORDER_TYPE new_type = MarketOrderByOrderType(type); double price = PriceByOrderType(_Symbol, type, DEVIATION, STOP_LIMIT); // Price for the given order type double volume_step = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_VOLUME_STEP); // Volume step for the symbol double margin = EMPTY_VALUE; // Required margin, initialized as empty
3. 计算一手所需的预付款
OrderCalcMargin 函数用于确定当前市场条件下开仓一手所需的预付款。如果函数失败,则会打印错误消息并且函数返回 0:
ResetLastError(); if (!OrderCalcMargin(new_type, _Symbol, VOLUME, price, margin)) { Print("OrderCalcMargin() failed. Error ", GetLastError()); return 0; // Exit the function if margin calculation fails }
4.计算最大手数
使用前面提到的公式来计算最大手数。这涉及将可用预付款除以所需预付款,根据允许的交易量步长对结果进行标准化,并将其向下舍入以避免错误:
double result = MathFloor((AccountInfoDouble(ACCOUNT_MARGIN_FREE) / margin) / volume_step) * volume_step;
5. 返回结果
最后,返回计算出的最大手数:
return result; // Return the maximum lot size
完整函数:
double GetMaxLote(ENUM_ORDER_TYPE type, double DEVIATION = 100, double STOP_LIMIT = 50) { //--- Set variables double VOLUME = 1.0; // Initial volume size ENUM_ORDER_TYPE new_type = MarketOrderByOrderType(type); double price = PriceByOrderType(_Symbol, type, DEVIATION, STOP_LIMIT); // Price for the given order type double volume_step = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_VOLUME_STEP); // Volume step for the symbol double margin = EMPTY_VALUE; // Required margin, initialized as empty //--- Get margin for one lot ResetLastError(); if (!OrderCalcMargin(new_type, _Symbol, VOLUME, price, margin)) { Print("OrderCalcMargin() failed. Error ", GetLastError()); return 0; // Exit the function if margin calculation fails } //--- Calculate the maximum lot size double result = MathFloor((AccountInfoDouble(ACCOUNT_MARGIN_FREE) / margin) / volume_step) * volume_step; return result; // Return the maximum lot size }
创建利润计算函数
一旦确定最大手数的函数完成,下一步就是开发计算从特定日期到当前时间的利润的函数。这至关重要,因为在评估每个分时报价时,需要确定是否已超过最大损失变量。为此,我们使用存储利润数据的变量。例如,要验证是否已经超过每日最大亏损,除了当前净值之外,还必须知道累计每日利润。
当前利润的计算将使用旨在访问订单和交易历史记录的函数来执行。这使我们能够获得特定时期内有关利润和损失的准确和最新的信息。
详细函数说明
1.变量初始化和错误重置
double total_net_profit = 0.0; // Initialize the total net profit ResetLastError(); // Reset any previous errors
- total_net_profit:初始化为 0.0,表示尚未计算净利润。
- ResetLastError:确保在执行开始之前清除代码中的所有先前错误。
开始日期验证(start_date):
if((start_date > 0 || start_date != D'1971.01.01 00:00'))此行检查提供的 start_date 是否有效(即,不是无效的默认日期,例如 1971.01.01,也不是为零的日期)。如果日期有效,代码将继续选择交易历史记录。
3.交易历史选择
if(!HistorySelect(start_date, TimeCurrent())) { Print("Error when selecting orders: ", _LastError); return 0.0; // Exit if unable to select the history }
- HistorySelect:选择从指定的 start_date 到当前时间 (TimeCurrent) 的交易历史记录。
- 如果历史选择失败,则打印错误消息,并且函数返回 0。
4.获取交易总数
int total_deals = HistoryDealsTotal(); // Get the total number of deals in history
- HistoryDealsTotal:返回交易历史记录中的交易总数,允许遍历每笔交易。
5.遍历所有交易
for(int i = 0; i < total_deals; i++) { ulong deal_ticket = HistoryDealGetTicket(i); // Retrieve the deal ticket
- 此时,for 循环开始迭代历史记录中的所有交易。
- HistoryDealGetTicket:检索位置 i 处的唯一交易单,这是访问交易详情所必需的。
6.过滤掉“余额”操作
if(HistoryDealGetInteger(deal_ticket, DEAL_TYPE) == DEAL_TYPE_BALANCE) continue;
如果交易类型是余额操作(例如存款、取款或调整而不是真实交易),则跳过该操作,循环继续到下一个记录。
7.获取交易详情
ENUM_DEAL_ENTRY deal_entry = (ENUM_DEAL_ENTRY)HistoryDealGetInteger(deal_ticket, DEAL_ENTRY); // Get deal entry type long deal_close_time_long = HistoryDealGetInteger(deal_ticket, DEAL_TIME); // Get deal close time (as long) datetime deal_close_time = (datetime)deal_close_time_long; // Explicit conversion to datetime ulong position_id = HistoryDealGetInteger(deal_ticket, DEAL_POSITION_ID); // Get the position ID
- deal_entry:定义交易是进场还是退出(用于确定操作是开仓交易还是平仓交易)。
- deal_close_time:表示交易结束时间,为方便起见,转换为日期时间。
- position_id:与交易相关的仓位的 ID,用于验证幻数。
8.按日期和类型过滤交易
if(deal_close_time >= start_date && (deal_entry == DEAL_ENTRY_OUT || deal_entry == DEAL_ENTRY_IN))该条件确保仅考虑结束时间大于或等于 start_date 的交易,并且它们是有效的进场或退出交易。
9.按幻数和包含类型筛选优惠
if((HistoryDealGetInteger(deal_ticket, DEAL_MAGIC) == specific_magic || specific_magic == GetMagic(position_id)) || include_all_magic == true)
- HistoryDealGetInteger:获得交易的幻数。
- 如果交易幻数与提供的 specific_magic 匹配,或者允许包含所有交易(include_all_magic == true),则计算交易的净利润。
10.计算交易的净利润:
double deal_profit = HistoryDealGetDouble(deal_ticket, DEAL_PROFIT); // Retrieve profit from the deal double deal_commission = HistoryDealGetDouble(deal_ticket, DEAL_COMMISSION); // Retrieve commission double deal_swap = HistoryDealGetDouble(deal_ticket, DEAL_SWAP); // Retrieve swap fees double deal_net_profit = deal_profit + deal_commission + deal_swap; // Calculate net profit for the deal total_net_profit += deal_net_profit; // Add to the total net profit
- deal_profit:获取交易的利润。
- deal_commission:获取交易收取的佣金。
- deal_swap:获取库存费(利息或隔夜费用)。
然后将这三个值的总和计算为交易的净利润,并将其添加到 total_net_profit 中。
11.返回总净利润:
return NormalizeDouble(total_net_profit, 2); // Return the total net profit rounded to 2 decimals最后,返回总净利润,使用 NormalizeDouble 四舍五入到小数点后两位,以确保该值的格式正确,可供进一步使用。
完整函数:
double GetNetProfitSince(bool include_all_magic, ulong specific_magic, datetime start_date) { double total_net_profit = 0.0; // Initialize the total net profit ResetLastError(); // Reset any previous errors // Check if the start date is valid if((start_date > 0 || start_date != D'1971.01.01 00:00')) { // Select the order history from the given start date to the current time if(!HistorySelect(start_date, TimeCurrent())) { Print("Error when selecting orders: ", _LastError); return 0.0; // Exit if unable to select the history } int total_deals = HistoryDealsTotal(); // Get the total number of deals in history // Iterate through all deals for(int i = 0; i < total_deals; i++) { ulong deal_ticket = HistoryDealGetTicket(i); // Retrieve the deal ticket // Skip balance-type deals if(HistoryDealGetInteger(deal_ticket, DEAL_TYPE) == DEAL_TYPE_BALANCE) continue; ENUM_DEAL_ENTRY deal_entry = (ENUM_DEAL_ENTRY)HistoryDealGetInteger(deal_ticket, DEAL_ENTRY); // Get deal entry type long deal_close_time_long = HistoryDealGetInteger(deal_ticket, DEAL_TIME); // Get deal close time (as long) datetime deal_close_time = (datetime)deal_close_time_long; // Explicit conversion to datetime ulong position_id = HistoryDealGetInteger(deal_ticket, DEAL_POSITION_ID); // Get the position ID // Check if the deal is within the specified date range and is a valid entry/exit deal if(deal_close_time >= start_date && (deal_entry == DEAL_ENTRY_OUT || deal_entry == DEAL_ENTRY_IN)) { // Check if the deal matches the specified magic number or if all deals are to be included if((HistoryDealGetInteger(deal_ticket, DEAL_MAGIC) == specific_magic || specific_magic == GetMagic(position_id)) || include_all_magic == true) { double deal_profit = HistoryDealGetDouble(deal_ticket, DEAL_PROFIT); // Retrieve profit from the deal double deal_commission = HistoryDealGetDouble(deal_ticket, DEAL_COMMISSION); // Retrieve commission double deal_swap = HistoryDealGetDouble(deal_ticket, DEAL_SWAP); // Retrieve swap fees double deal_net_profit = deal_profit + deal_commission + deal_swap; // Calculate net profit for the deal total_net_profit += deal_net_profit; // Add to the total net profit } } } } return NormalizeDouble(total_net_profit, 2); // Return the total net profit rounded to 2 decimals }
获取订单幻数的附加函数:
ulong GetMagic(const ulong ticket) { HistoryOrderSelect(ticket); return HistoryOrderGetInteger(ticket,ORDER_MAGIC); }
使用简单脚本和包含文件进行实际测试
我们现在将创建一个函数,将绝对距离转换为当前交易品种的点数单位。这种转换是交易的基础,因为点数是计算价格水平、止损和目标的标准度量。
数学公式
计算点数距离的公式很简单:
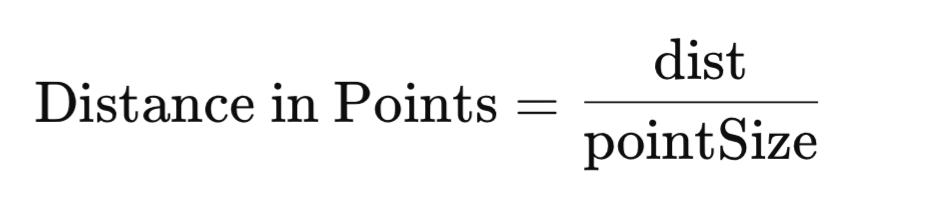
其中:
- dist 是我们要转换的绝对距离。
- pointSize 是金融工具的一个点的大小(例如,EUR/USD 为 0.0001)。
用代码表示公式
为了在 MQL5 中实现此公式,我们遵循以下步骤:
-
获取点大小(pointSize)。
我们使用 SymbolInfoDouble 函数来获取当前交易品种的点大小。参数 _Symbol 代表当前运行的交易品种,SYMBOL_POINT 提供其点大小。
- 将距离除以点大小并将其转换为整数
我们将距离(dist)除以点大小(pointSize)来计算点的数量。然后,我们使用 int 将结果转换为整数,因为点数值始终是整数。
double pointSize = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_POINT);
return (int)(dist / pointSize);
完成函数
以下是该函数的最终形式:
int DistanceToPoint(double dist) { double pointSize = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_POINT); // Get the point size for the current symbol return (int)(dist / pointSize); // Calculate and return the distance in points }
为了将本文中涵盖的概念付诸实践,我们将创建两个脚本。
接下来,我们将开发两个重要函数:一个是根据每笔交易的风险计算理想的手数,另一个是基于手数和每笔交易风险计算交易品种的理想止损点。
函数:根据每笔交易的风险计算理想手数
GetIdealLot 函数通过考虑每笔交易允许的最大损失和止损距离(StopLoss)来计算理想手数(nlot)。这确保所有交易都符合用户定义的风险限额。
void GetIdealLot( double& nlot, // Calculated ideal lot double glot, // Gross Lot (max lot accorsing to the balance) double max_risk_per_operation, // Maximum allowed risk per trade (in account currency) double& new_risk_per_operation, // Calculated risk for the adjusted lot (in account currency) long StopLoss // Stop Loss distance (in points) )
参数说明
- nlot:通过该函数调整理想手数。
- glot:使用所有可用账户资金可以开立的总(最大)手数。
- max_risk_per_operation:每笔交易允许的最大风险,以账户货币表示。
- new_risk_per_operation:考虑到计算出的手数(nlot),调整交易的实际风险。这表示如果价格达到止损点将会损失多少。
- StopLoss:止损距离(以点为单位)。
1.初步验证
该函数首先检查 StopLoss 值是否大于零,因为无效的止损会使风险计算变得不可能。
if(StopLoss <= 0) { Print("[ERROR SL] Stop Loss distance is less than or equal to zero, now correct the stoploss distance: ", StopLoss); nlot = 0.0; return; }
2.初始化变量
初始化以下变量以供后续计算:
- spread:交易品种的当前点差。
- tick_value:每个分时报价的值,表示最小价格变动在账户货币中所占的金额。
- step:允许的最小手数增量。
new_risk_per_operation = 0; // Initialize the new risk long spread = (long)SymbolInfoInteger(_Symbol, SYMBOL_SPREAD); double tick_value = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_TRADE_TICK_VALUE); double step = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_VOLUME_STEP);
3.当前风险计算(rpo)
当前每次操作的风险 (rpo) 使用以下公式计算:
![]()
在代码中:
double rpo = (glot * (spread + 1 + (StopLoss * tick_value)));
4.检查最大风险
该函数评估当前风险(rpo)是否超过每笔交易的最大可接受风险(max_risk_per_operation):
情况1.风险超过最高水平
- 手数大小根据最大可接受风险按比例调整。
- 调整后的手数向下舍入到最接近的允许增量(步长)。
- 计算与该调整手数相对应的新风险。
if(rpo > max_risk_per_operation) { double new_lot = (max_risk_per_operation / rpo) * glot; new_lot = MathFloor(new_lot / step) * step; new_risk_per_operation = new_lot * (spread + 1 + (StopLoss * tick_value)); nlot = new_lot; }
情况2.风险在可接受的范围内
- 如果当前风险未超过设定的限值,则保留原始值:
else { new_risk_per_operation = rpo; // Current risk nlot = glot; // Gross lot }
最后,我们将创建最后一个函数,根据每笔交易允许的最大损失和用户指定的手数大小来计算止损:
long GetSL(const ENUM_ORDER_TYPE type , double risk_per_operation , double lot) { long spread = (long)SymbolInfoInteger(_Symbol, SYMBOL_SPREAD); double tick_value = SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_TRADE_TICK_VALUE); double result = ((risk_per_operation/lot)-spread-1)/tick_value; return long(MathRound(result)); }
参数说明
- type:订单类型(买入或卖出),尽管它在本函数中不直接使用。
- risk_per_operation:账户货币每笔交易允许的最大损失。
- lot:用户定义的手数。
循序渐进的逻辑
1.基本公式
计算每次操作风险(rpo)的基本公式如下:
![]()
在此函数中,我们将隔离止损,以根据 rpo、手数大小和其他相关因素计算其值。
2.隔离止损
- 将等式两边除以手数:
![]()
- 从两边减去 spread 和 1:
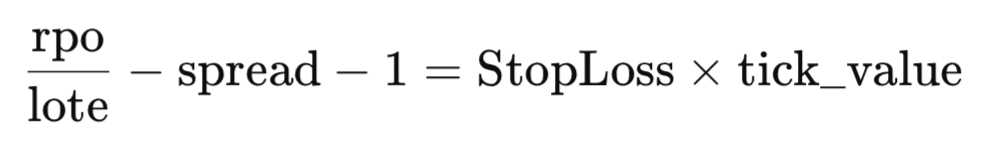
- 除以 tick_value 来隔离止损:
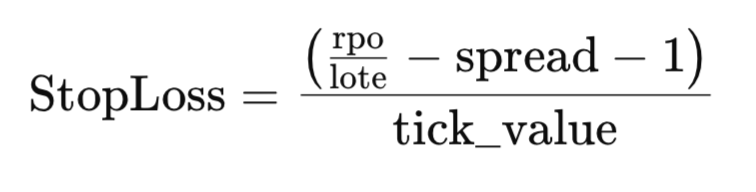
代码实现
上面的公式直接转化为函数体中的计算:
double result = ((risk_per_operation / lot) - spread - 1) / tick_value;
- risk_per_operation / lot:计算每手单位的风险。
- - spread - 1:减去点差和任何额外的预付款。
- / tick_value:通过除以分时报价值将结果转换为点数。
然后对结果进行四舍五入并转换为长整型以匹配所需的格式。
return long(MathRound(result));
最后,我们将创建两个脚本,根据每笔交易定义的风险计算理想手数和理想止损(SL)。这两个脚本都使用简单但高效的逻辑,根据账户余额和用户定义的参数自动进行这些计算。
第一个脚本:计算理想手数
此脚本根据每笔交易的风险百分比、以点数定义的止损和订单类型计算理想手数。
-
脚本属性
- #property strict:确保代码遵守严格的编译规则。
- #property script_show_inputs:允许用户通过图形界面输入参数。
- 输入参数
input double percentage_risk_per_operation = 1.0; //Risk per operation in % input long sl = 600; //Stops Loss in points input ENUM_ORDER_TYPE Order_Type = ORDER_TYPE_BUY; //Order Type
计算每笔交易的风险
该公式根据定义的百分比计算用户愿意在每笔交易中承担风险的账户货币金额:
double risk_per_operation = ((percentage_risk_per_operation/100.0) * AccountInfoDouble(ACCOUNT_BALANCE));
调用理想手数计算函数
GetIdealLot(new_lot, GetMaxLote(Order_Type), risk_per_operation, new_risk_per_operation, sl);
用户信息:有关计算值的详细信息(例如理想手数和调整风险)将打印到控制台和图表上,以便于参考。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Get Lot By Risk Per Trade and SL.mq5 | //| Your name | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Your name" #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #property strict #property script_show_inputs input double percentage_risk_per_operation = 1.0; // Risk per operation in % input long sl = 600; // Stop Loss in points input ENUM_ORDER_TYPE Order_Type = ORDER_TYPE_BUY; // Order Type #include <Risk Management.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Main script function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { // Calculate the maximum allowable risk per operation in account currency double risk_per_operation = ((percentage_risk_per_operation / 100.0) * AccountInfoDouble(ACCOUNT_BALANCE)); // Print input and calculated risk details Print("Risk Per operation: ", risk_per_operation); Print("SL in points: ", sl); Print("Order type: ", EnumToString(Order_Type)); double new_lot; double new_risk_per_operation; // Calculate the ideal lot size GetIdealLot(new_lot, GetMaxLote(Order_Type), risk_per_operation, new_risk_per_operation, sl); // Check if the lot size is valid if (new_lot <= 0) { Print("The stop loss is too large or the risk per operation is low. Increase the risk or decrease the stop loss."); } else { // Display calculated values Print("Ideal Lot: ", new_lot); Print("Maximum loss with SL: ", sl, " | Lot: ", new_lot, " is: ", new_risk_per_operation); Comment("Ideal Lot: ", new_lot); } Sleep(1000); Comment(" "); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
第二个脚本:计算理想 SL
此脚本根据用户指定的手数和每笔交易的最大风险计算止损点。
input double percentage_risk_per_operation = 1.0; //Risk per operation in % input double Lot = 0.01; //lot input ENUM_ORDER_TYPE Order_Type = ORDER_TYPE_BUY; //Order Type
计算理想的止损:GetSL 函数用于确定止损点数:
long new_sl = GetSL(Order_Type, risk_per_operation, Lot);
检查结果:如果计算出的止损值无效(new_sl 小于或等于 0),则会通知用户。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Get Sl by risk per operation and lot.mq5 | //| Your name | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Your name" #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #property strict #property script_show_inputs input double percentage_risk_per_operation = 1.0; // Risk per operation in % input double Lot = 0.01; // Lot size input ENUM_ORDER_TYPE Order_Type = ORDER_TYPE_BUY; // Order Type #include <Risk Management.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Main script function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { // Calculate the maximum allowable risk per operation in account currency double risk_per_operation = ((percentage_risk_per_operation / 100.0) * AccountInfoDouble(ACCOUNT_BALANCE)); // Print input and calculated risk details Print("Risk Per operation: ", risk_per_operation); Print("Lot size: ", Lot); Print("Order type: ", EnumToString(Order_Type)); // Calculate the ideal stop loss long new_sl = GetSL(Order_Type, risk_per_operation, Lot); // Check if the SL is valid if (new_sl <= 0) { Print("The lot size is too high or the risk per operation is too low. Increase the risk or decrease the lot size."); } else { // Display calculated values Print("For lot: ", Lot, ", and risk: ", risk_per_operation, ", the ideal SL is: ", new_sl); Comment("Ideal SL: ", new_sl); } Sleep(1000); Comment(" "); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+现在,为了将脚本付诸实践,我们使用它来根据每笔交易的给定风险获得理想的手数。我们将在与黄金对应的 XAUUSD 交易品种上对其进行测试。
参数为止损 200 点、每笔交易风险为账户余额的 1.0%,并将订单类型指定为 ORDER_TYPE_BUY,则结果如下:
专家选项卡中显示的结果对应于 0.01 手数、200 点止损和每笔交易风险 3.81,即账户余额的 1%。
结论
我们已经完成了本系列的第一部分,重点开发风险管理类中将使用的核心函数。这些函数对于获取利润数据和执行额外计算至关重要。在下一部分中,我们将探索如何使用 MQL5 控制库将我们所学到的一切集成到图形界面中。
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自西班牙语
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/es/articles/16820
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 MQL5交易管理面板开发(第九部分):代码组织(4):交易管理面板类
MQL5交易管理面板开发(第九部分):代码组织(4):交易管理面板类
 MQL5中的高级内存管理与优化技术
MQL5中的高级内存管理与优化技术
 您应当知道的 MQL5 向导技术(第 53 部分):市场促进指数
您应当知道的 MQL5 向导技术(第 53 部分):市场促进指数
 在 MQL5 中自动化交易策略(第 13 部分):构建头肩形态交易算法
在 MQL5 中自动化交易策略(第 13 部分):构建头肩形态交易算法