
使用MQL5和Python构建自优化EA(第二部分):调整深度神经网络
概述
我们社区的成员热衷于将人工智能(AI)融入他们的交易策略,这需要针对特定市场调整AI模型。每个AI模型都有可调节的参数,这些参数对其性能有着显著影响;一种市场下的最优设置可能并不适用于另一种市场。本文将展示如何通过优化算法(特别是Nelder-Mead算法)来定制AI模型,使其性能优于默认设置。我们将应用这种算法,利用MetaTrader 5终端的数据微调深度神经网络,然后将优化后的模型以ONNX格式导出,以便在EA中使用。对于那些对这些概念不太熟悉的读者,我们将在文章中提供详细的解释。Nelder-Mead优化算法
Nelder-Mead算法是解决噪声、不可微分以及非线性多模态优化问题的常用选择。该算法由其发明者约翰·内尔德(John Nelder)和罗杰·米德(Roger Mead)命名,他们在1965年的论文《函数最小化的单纯形法》中首次介绍了这一算法。可以用于单变量和多变量优化问题。
Nelder-Mead算法不依赖导数信息;相反,它是一种基于模式搜索的优化算法。它需要用户提供一个起始点。根据选定的起始点,算法可能会陷入误导性的局部最优解。因此,使用不同的起始点多次执行优化过程,可以增加找到全局最优解的机会。
该算法通过使用一种称为单纯形的几何形状来工作。单纯形的顶点数量等于输入变量的数量加一。单纯形的点(顶点)会被评估,并且会根据这些评估结果,使用简单的规则来移动这些点。算法具有某些停止条件,例如达到最大迭代次数或实现评估值的最小变化。如果没有进一步的改进,或者超过了允许的迭代次数,优化过程就会停止。

图1:Roger Mead

图2:John Nelder
那么,让我们开始吧。
我们先从MetaTrader 5终端获取我们需要的数据。首先,我们打开MetaTrader 5终端,并在上下文菜单中点击“符号”图标。从那里,我们选择“柱形图”并搜索您想要使用的交易品种。一旦您请求了数据,只需点击“导出”,数据将以CSV格式供您使用。
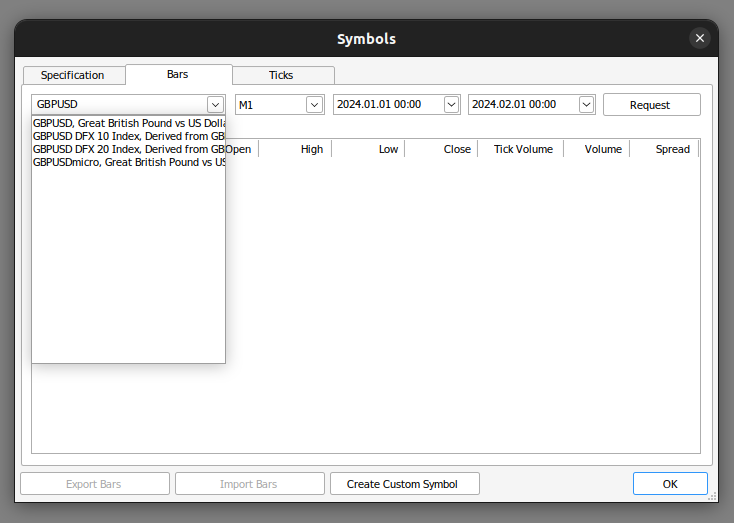
图3:搜索您需要的数据
既然我们的数据已经准备好,我们可以从导入所需的库开始。
#import libraries we need import pandas as pd import numpy as np from numpy.random import randn,rand import seaborn as sns
然后我们读取准备好的数据。
#Read in our market data brent = pd.read_csv("/home/volatily/market_data/Market Data UK Brent Oil.csv", sep="\t")
我们需要标记数据。
#Preparing to label the data look_ahead = 20 #Defining the target brent["Target"] = brent["Close"].shift(-look_ahead) #Drop missing values brent.dropna(inplace=True)
让我们导入优化所需的库。
#In this article we will cover some techniques for hyper-parameter tuning from scipy.optimize import minimize from sklearn.neural_network import MLPRegressor from sklearn.model_selection import TimeSeriesSplit from sklearn.metrics import root_mean_squared_error import time
现在,我们将创建时间序列交叉验证对象。
#Define the time series split parameters splits = 5 gap = look_ahead #Create the time series split object tscv = TimeSeriesSplit(n_splits=splits,gap=gap) #Create a dataframe to store our accuracy current_error_rate = pd.DataFrame(index = np.arange(0,splits),columns=["Current Error"])
让我们为模型定义预测变量和目标变量。
#Define the predictors and the target predictors = ["Open","High","Low","Close"] target = "Target"
我们现在定义希望最小化的函数:模型的交叉验证误差。请注意,这仅用于演示目的。理想情况下,我们会将数据集一分为二,在一半数据上进行优化,而在另一半数据上测量模型的准确性。然而,在这个演示中,我们使用相同的数据集来优化模型并测量其准确性。
#Define the objective function def objective(x): #The parameter x represents a new value for our neural network's settings #In order to find optimal settings, we will perform 10 fold cross validation using the new setting #And return the average RMSE from all 10 tests #We will first turn the model's Alpha parameter, which controls the amount of L2 regularization model = MLPRegressor(hidden_layer_sizes=(5,2),alpha=x[0],early_stopping=True,shuffle=False,learning_rate_init=x[1],tol=x[2]) #Now we will cross validate the model for i,(train,test) in enumerate(tscv.split(brent)): #The data X_train = brent.loc[train[0]:train[-1],predictors] y_train = brent.loc[train[0]:train[-1],target] X_test = brent.loc[test[0]:test[-1],predictors] y_test = brent.loc[test[0]:test[-1],target] #Train the model model.fit(X_train,y_train) #Measure the RMSE current_error_rate.iloc[i,0] = root_mean_squared_error(y_test,model.predict(X_test)) #Return the Mean CV RMSE return(current_error_rate.iloc[:,0].mean())
回想一下,Nelder-Mead算法需要一个初始起点。为了找到一个好的起点,我们将在相关参数上进行线性搜索。我们将使用一个for循环来测量参数分别设置为0.1、0.01等时的准确性。这将帮助我们识别出算法的一个潜在的良好起点。
#Let us measure how much time this takes. start = time.time() #Create a dataframe to measure the error rates starting_point_error = pd.DataFrame(index=np.arange(0,21),columns=["Average CV RMSE"]) starting_point_error["Iteration"] = np.arange(0,21) #Let us first find a good starting point for our optimization algorithm for i in np.arange(0,21): #Set a new starting point new_starting_point = (10.0 ** -i) #Store error rates starting_point_error.iloc[i,0] = objective([new_starting_point,new_starting_point,new_starting_point]) #Record the time stamp at the end stop = time.time() #Report the amount of time taken print(f"Completed in {stop - start} seconds")
现在让我们来观察误差水平。
| 平均交叉验证均方根误差(CV RMSE) | 迭代: |
|---|---|
| 0.91546 | 0 |
| 0.267167 | 1 |
| 14.846035 | 2 |
| 15.763264 | 3 |
| 56.820397 | 4 |
| 75.202923 | 5 |
| 72.562681 | 6 |
| 64.33746 | 7 |
| 88.980977 | 8 |
| 83.791834 | 9 |
| 82.871215 | 10 |
| 88.031151 | 11 |
| 65.532539 | 12 |
| 78.177191 | 13 |
| 85.063947 | 14 |
| 88.631589 | 15 |
| 74.369735 | 16 |
| 86.133656 | 17 |
| 90.482654 | 18 |
| 102.803612 | 19 |
| 74.636781 | 20 |
正如我们看到的那样,在迭代0到2之间,我们似乎错过了一片最优区域。从那以后,我们的误差一直在增加。我们还可以通过可视化来观察这些信息。
sns.lineplot(data=starting_point_error,x="Iteration",y="Average CV RMSE")
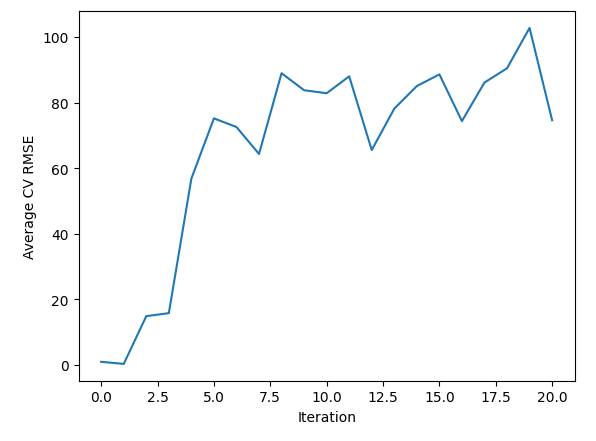
图4:可视化线性搜索结果
既然我们已经对一个良好的起点可能是什么有了初步的想法,那么让我们定义一个函数,提供一个随机点,这个点位于我们认为最优值可能存在的范围内。
pt = abs(((10 ** -1) + rand(3) * ((10 ** 0) - (10 ** -1)))) pt
请注意,我们正在获取一个包含3个随机值的数组,因为我们正在对神经网络上的3个不同参数进行优化。让我们从现在开始进行超参数调整。
start = time.time() result = minimize(objective,pt,method="nelder-mead") stop = time.time() print(f"Task completed in {stop - start} seconds")
让我们来解读优化的结果。
result
success: False
status: 1
fun: 0.12022686955703668
x: [ 7.575e-01 3.577e-01 2.621e-01]
nit: 225
nfev: 600
final_simplex: (array([[ 7.575e-01, 3.577e-01, 2.621e-01],
[ 7.575e-01, 3.577e-01, 2.621e-01],
[ 7.575e-01, 3.577e-01, 2.621e-01],
[ 7.575e-01, 3.577e-01, 2.621e-01]]), array([ 1.202e-01, 2.393e-01, 2.625e-01, 8.978e-01])
首先,观察顶部显示的用户友好信息。该信息表明算法已超出函数评估的最大次数。回想我们之前指定的关于导致优化停止的场景条件。尽管我们可以尝试增加允许的迭代次数,但这并不能保证更好的性能。
我们可以看到键“fun”,它表示算法从函数中达到的最优输出。接下来是按键“x”,它显示了获取最优输出的x值。
我们还可以观察到“nit”键,它告诉我们函数执行的迭代次数。最后,“nfev”键表明算法调用目标函数以评估其输出的次数。回想一下,我们的目标函数执行了5折交叉验证并返回了平均错误率。这意味着每调用函数一次,我们就会拟合我们的神经网络5次。因此,600次函数评估意味着我们拟合了我们的神经网络3000次!
现在,让我们比较我们构建的默认模型和定制模型。
#Let us compare our customised model and the defualt model custom_model = MLPRegressor(hidden_layer_sizes=(5,2),alpha=result.x[0],early_stopping=True,shuffle=False,learning_rate_init=result.x[1],tol=result.x[2]) #Default model default_model = MLPRegressor(hidden_layer_sizes=(5,2))
我们将准备时间序列分割对象。
#Define the time series split parameters splits = 10 gap = look_ahead #Create the time series split object tscv = TimeSeriesSplit(n_splits=splits,gap=gap) #Create a dataframe to store our accuracy model_error_rate = pd.DataFrame(index = np.arange(0,splits),columns=["Default Model","Custom Model"])
我们现在将交叉验证每个模型。
#Now we will cross validate the model for i,(train,test) in enumerate(tscv.split(brent)): #The data X_train = brent.loc[train[0]:train[-1],predictors] y_train = brent.loc[train[0]:train[-1],target] X_test = brent.loc[test[0]:test[-1],predictors] y_test = brent.loc[test[0]:test[-1],target] #Our model model = MLPRegressor(hidden_layer_sizes=(5,2),alpha=result.x[0],early_stopping=True,shuffle=False,learning_rate_init=result.x[1],tol=result.x[2]) #Train the model model.fit(X_train,y_train) #Measure the RMSE model_error_rate.iloc[i,1] = root_mean_squared_error(y_test,model.predict(X_test))
让我们观察一下我们的误差指标。
model_error_rate
| 默认模型 | 定制模型 |
|---|---|
| 0.153904 | 0.550214 |
| 0.113818 | 0.501043 |
| 82.188345 | 0.52897 |
| 0.114108 | 0.117466 |
| 0.114718 | 0.112892 |
| 77.508403 | 0.258558 |
| 0.109191 | 0.304262 |
| 0.142143 | 0.363774 |
| 0.163161 | 0.153202 |
| 0.120068 | 2.20102 |
让我们也通过可视化观察结果。
model_error_rate["Default Model"].plot(legend=True) model_error_rate["Custom Model"].plot(legend=True)
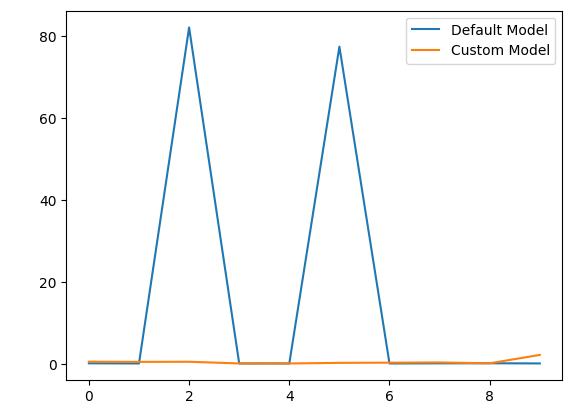
图 5:可视化我们的定制模型性能
正如我们所观察到的那样,定制模型的表现优于默认模型。然而,如果我们为训练模型和评估其准确性使用了不同的数据集,我们的测试将更具说服力。在两种情况下使用相同的数据集并不是理想的流程。
接下来,我们准备将深度神经网络转换为其ONNX的表示形式。ONNX,即开放神经网络交换格式,是一种标准化格式,允许在任何兼容框架下训练的AI模型被用于不同的程序。例如,ONNX允许我们在Python中训练一个AI模型,然后将其用于MQL5,甚至是Java程序(前提是Java API支持ONNX)。
首先,我们导入所需的库。
#Now we will prepare to export our neural network into ONNX format from skl2onnx.common.data_types import FloatTensorType from skl2onnx import convert_sklearn import onnxruntime as ort import netron
让我们定义模型的输入形状,请记住我们的模型有4个输入。
#Define the input types initial_type = [("float_input",FloatTensorType([1,4]))]
拟合我们的定制模型。
#Fit our custom model custom_model.fit(brent.loc[:,["Open","High","Low","Close"]],brent.loc[:,"Target"])
归功于skl2onnx库,使得创建我们深度神经网络的ONNX表示形式变得非常简单。
#Create the onnx represantation onnx = convert_sklearn(custom_model,initial_types=initial_type,target_opset=12)
定义我们ONNX的文件名称。
#The name of our ONNX file onnx_filename = "Brent_M1.onnx"
现在我们将写入ONNX文件。
#Write out the ONNX file with open(onnx_filename,"wb") as f: f.write(onnx.SerializeToString())
让我们检查ONNX模型的参数。
#Now let us inspect our ONNX model onnx_session = ort.InferenceSession(onnx_filename) input_name = onnx_session.get_inputs()[0].name output_name = onnx_session.get_outputs()[0].name
让我们看一下输入形状。
for i, input_tensor in enumerate(onnx_session.get_inputs()): print(f"{i + 1}. Name: {input_tensor.name}, Data Type: {input_tensor.type}, Shape: {input_tensor.shape}")
观察我们模型的输出形状。
for i, output_tensor in enumerate(onnx_session.get_outputs()): print(f"{i + 1}. Name: {output_tensor.name}, Data Type: {output_tensor.type}, Shape: {output_tensor.shape}")
现在我们可以通过Netron可视化观察我们的模型。这些步骤帮助我们确保ONNX的输入和输出形状符合我们的预期。
#We can also inspect our model visually using netron.
netron.start(onnx_filename)
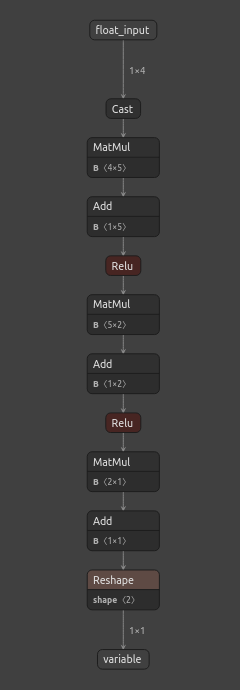
图 6:我们神经网络的ONNX表示
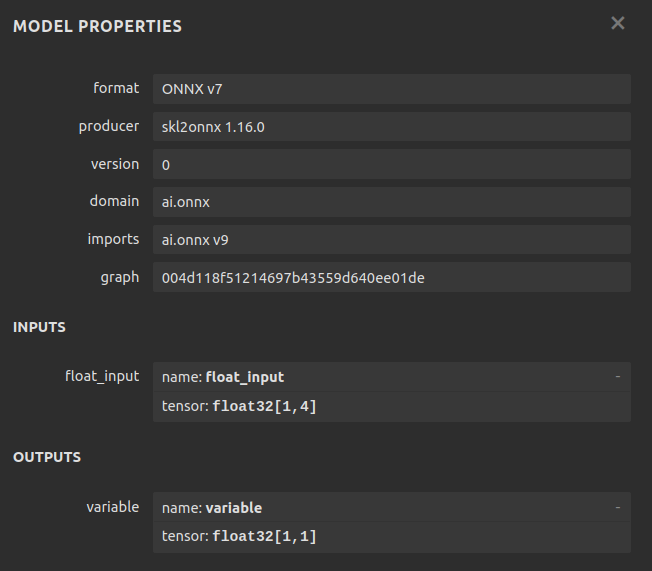
图 7:我们ONNX模型的元数据
Netron是一个开源的Python库,它使我们能够可视化地检查ONNX模型,查看其参数并审查元数据。对于那些对在MetaTrader 5中使用ONNX模型感兴趣的读者,有许多很好的文章可供参考。在这一主题上,我最喜欢的一位作者是Omega。
在MQL5中实现
随着我们的ONNX模型配置最终确定,我们可以开始在MQL5中构建EA。
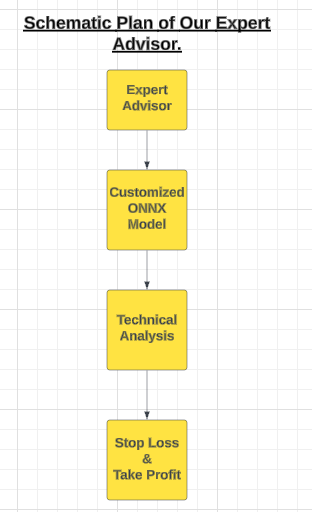
图 8:我们的EA示意图
我们的EA将使用定制的ONNX模型来生成入场信号。然而,所有优秀的交易者都会谨慎行事,不会全部执行他们收到的每一个入场信号。为了在我们的EA中注入这种规则,我们将编程让它在开仓之前等待技术指标的确认。
这些技术指标将帮助我们有效地把握入场时机。一旦仓位开启,用户定义的止损水平将负责关闭它们。第一步是将ONNX模型指定为我们应用程序的资源。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Custom Deep Neural Network.mq5 | //| Gamuchirai Zororo Ndawana | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Gamuchirai Zororo Ndawana" #property link "https://www.mql5.com/en/gamuchiraindawa" #property version "1.00" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Load the ONNX model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #resource "\\Files\\Brent_M1.onnx" as const uchar ModelBuffer[];
接下来,我们将加载交易库,这对于管理我们的仓位是必不可少的。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Libraries we need | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #include <Trade/Trade.mqh> CTrade Trade;
现在我们可以继续为程序创建全局变量。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Gloabal variables | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ long model; //The handler for our ONNX model vector forecast = vector::Zeros(1); //Our model's forecast const int states = 3; //The total number of states the system can be in vector state = vector::Zeros(states); //The state of our system int mfi_handler,wpr_handler; //Handlers for our technical indicators vector mfi_reading,wpr_reading; //The values of our indicators will be kept in vectors double minimum_volume, trading_volume; //Smallest lot size allowed & our calculated lotsize double ask_price, bid_price; //Market rates
让我们定义用户输入,以便我们可以修改EA的行为。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Inputs | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ input int mfi_period = 20; //Money Flow Index Period input int wpr_period = 30; //Williams Percent Range Period input int lot_multiple = 20; //How big should our lot sizes be? input double sl_width = 2; //How tight should the stop loss be? input double max_profit = 10; //Close the position when this profit level is reached. input double max_loss = 10; //Close the position when this loss level is reached.
我们的应用程序需要辅助函数来执行特定的例程。我们首先定义一个管理应用程序状态的函数。这个应用程序将有三种状态:状态0表示我们没有任何仓位,而状态1和2分别表示多头(买入)或空头(卖出)仓位。
根据当前状态,应用程序将能够访问不同的功能。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| This function is responsible for updating the system state | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void update_state(int index) { //--- Reset the system state state = vector::Zeros(states); //--- Now update the current state state[index] = 1; }
接下来,我们需要一个在启动应用程序时验证用户输入的函数。例如,这个函数将确保所有技术指标的周期都大于0。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| This function will ensure that user inputs are valid | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool valid_inputs(void) { //--- Let us validate the inputs the user passed return((mfi_period > 0)&&(wpr_period > 0) && (max_profit >= 0) && (max_loss >= 0) && (lot_multiple >= 0) && (sl_width >= 0)); }
我们的EA会持续检查利润水平是否达到用户指定的输入值。例如,如果用户设置的最大获利目标为1美元,那么一旦仓位达到1美元的利润,就会自动平仓,即使还未达到止盈水平。同样的逻辑也适用于止损:仓位会根据最先达到的阈值关闭,无论是止损水平还是最大亏损水平。这一功能旨在为定义可接受的风险水平提供灵活性。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| This function will check our profit levels | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void check_profit_level(void) { //--- Let us check if the user set a max profit/loss limit if(max_loss > 0 || max_profit > 0) { //--- If true, let us inspect whether we have passed the limit. if((PositionGetDouble(POSITION_PROFIT) > max_profit) || (PositionGetDouble(POSITION_PROFIT) < (max_loss * -1))) { //--- Close the position Trade.PositionClose(Symbol()); } } }
既然我们有一个基于人工智能的系统,让我们构建一个函数来检查我们的模型是否预测了可能对我们当前仓位不利的市场走势。这样的信号可以作为市场情绪变化的早期迹象。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| If we predict a reversal, let's close our positions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void find_reversal(void) { //--- We have a position if(((state[1] == 1) && (forecast[0] < iClose(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,0))) || ((state[2] == 1) && (forecast[0] > iClose(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,0)))) { Trade.PositionClose(Symbol()); } }
接下来,我们将定义一个函数来检查有效的入场信号。如果入场信号满足两个条件,则被认为是有效的:首先,它必须获得基于更高时间框架上价格水平变化的支持;其次,我们的AI模型必须预测出与这一更高趋势一致的价格走势。如果这两个条件都得到满足,我们随后将检查我们的技术指标以获得最终的确认。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| This function will determine if we have a valid entry | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void find_entry(void) { //--- First we want to know if the higher timeframes are moving in the same direction we want to go double higher_time_frame_trend = iClose(Symbol(),PERIOD_W1,16) - iClose(Symbol(),PERIOD_W1,0); //--- If price levels appreciated, the difference will be negative if(higher_time_frame_trend < 0) { //--- We may be better off only taking buy opportunities //--- Buy opportunities are triggered when the model's prediction is greater than the current price if(forecast[0] > iClose(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,0)) { //--- We will use technical indicators to time our entries bullish_sentiment(); } } //--- If price levels depreciated, the difference will be positive if(higher_time_frame_trend > 0) { //--- We may be better off only taking sell opportunities //--- Sell opportunities are triggered when the model's prediction is less than the current price if(forecast[0] < iClose(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,0)) { //--- We will use technical indicators to time our entries bearish_sentiment(); } } }
现在,轮到负责解读我们技术指标的函数。解读这些指标有多种方法,但我更倾向于以50为中心。通过这种方式,大于50的值被认为是看涨情绪,而低于50的值则表明是看跌情绪。我们将使用资金流量指数(MFI)作为我们的成交量指标,以及威廉百分比范围(WPR)作为我们的趋势强度指标。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| This function will interpret our indicators for buy signals | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void bullish_sentiment(void) { //--- For bullish entries we want strong volume readings from our MFI //--- And confirmation from our WPR indicator wpr_reading.CopyIndicatorBuffer(wpr_handler,0,0,1); mfi_reading.CopyIndicatorBuffer(mfi_handler,0,0,1); if((wpr_reading[0] > -50) && (mfi_reading[0] > 50)) { //--- Get the ask price ask_price = SymbolInfoDouble(Symbol(),SYMBOL_ASK); //--- Make sure we have no open positions if(PositionsTotal() == 0) Trade.Buy(trading_volume,Symbol(),ask_price,(ask_price - sl_width),(ask_price + sl_width),"Custom Deep Neural Network"); update_state(1); } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| This function will interpret our indicators for sell signals | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void bearish_sentiment(void) { //--- For bearish entries we want strong volume readings from our MFI //--- And confirmation from our WPR indicator wpr_reading.CopyIndicatorBuffer(wpr_handler,0,0,1); mfi_reading.CopyIndicatorBuffer(mfi_handler,0,0,1); if((wpr_reading[0] < -50) && (mfi_reading[0] < 50)) { //--- Get the bid price bid_price = SymbolInfoDouble(Symbol(),SYMBOL_BID); if(PositionsTotal() == 0) Trade.Sell(trading_volume,Symbol(),bid_price,(bid_price + sl_width),(bid_price - sl_width),"Custom Deep Neural Network"); //--- Update the state update_state(2); } }
接下来,我们将专注于从我们的ONNX模型中获取预测。请记住,我们的模型期望输入的形状为 [1, 4],并返回形状为 [1, 1] 的输出。我们定义向量来相应地存储输入和输出,然后使用OnnxRun函数来获取模型的预测结果。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| This function will fetch forecasts from our model | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void model_predict(void) { //--- First we get the input data ready vector input_data = {iOpen(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,0),iHigh(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,0),iLow(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,0),iClose(_Symbol,PERIOD_CURRENT,0)}; //--- Now we need to perform inferencing if(!OnnxRun(model,ONNX_DATA_TYPE_FLOAT,input_data,forecast)) { Comment("Failed to obtain a forecast from the model: ",GetLastError()); forecast[0] = 0; return; } //--- We succeded! Comment("Model forecast: ",forecast[0]); }
现在我们可以开始构建应用程序的事件处理程序,该程序将在EA初始化时被调用。我们的程序将首先验证用户输入,然后定义我们ONNX模型的输入和输出形状。接下来,我们将设置技术指标,获取市场数据,最后将我们的系统状态设置为0。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- Make sure user inputs are valid if(!valid_inputs()) { Comment("Invalid inputs were passed to the application."); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- Create the ONNX model from the buffer model = OnnxCreateFromBuffer(ModelBuffer,ONNX_DEFAULT); //--- Check if we were succesfull if(model == INVALID_HANDLE) { Comment("[ERROR] Failed to create the ONNX model from the buffer: ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- Set the input shape of the model ulong input_shape[] = {1,4}; //--- Check if we were succesfull if(!OnnxSetInputShape(model,0,input_shape)) { Comment("[ERROR] Failed to set the ONNX model input shape: ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- Set the output shape of the model ulong output_shape[] = {1,1}; //--- Check if we were succesfull if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(model,0,output_shape)) { Comment("[ERROR] Failed to set the ONNX model output shape: ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- Setup the technical indicators wpr_handler = iWPR(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,wpr_period); mfi_handler = iMFI(Symbol(),PERIOD_CURRENT,mfi_period,VOLUME_TICK); //--- Fetch market data minimum_volume = SymbolInfoDouble(Symbol(),SYMBOL_VOLUME_MIN); trading_volume = minimum_volume * lot_multiple; //--- Set the system to state 0, indicating we have no open positions update_state(0); //--- Everything went fine return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
我们应用程序的一个关键部分是去初始化程序。在这个事件处理程序中,我们将释放EA未使用时不再需要的任何资源。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { //--- Free the onnx resources OnnxRelease(model); //--- Free the indicator resources IndicatorRelease(wpr_handler); IndicatorRelease(mfi_handler); //--- Detach the expert advisor ExpertRemove(); }
最后,我们需要定义我们的OnTick事件处理程序。我们的行为将取决于系统的状态。如果我们没有开放仓位(状态0),那么首要任务是从模型中获取预测,并识别潜在的入场机会。如果我们有开放仓位(状态1为多头或状态2为空头),我们的关注点将转移到管理仓位上。包括监控潜在的反转,以及检查风险水平、获利目标和最大获利水平。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { //--- Which state is the system in? if(state[0] == 1) { //--- Being in this state means we have no open positions, let's analyse the market to try find one model_predict(); find_entry(); } if((state[1] == 1) || (state[2] == 1)) { //--- Being in this state means we have an position open, if our model forecasts a reversal move we will close model_predict(); find_reversal(); check_profit_level(); } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
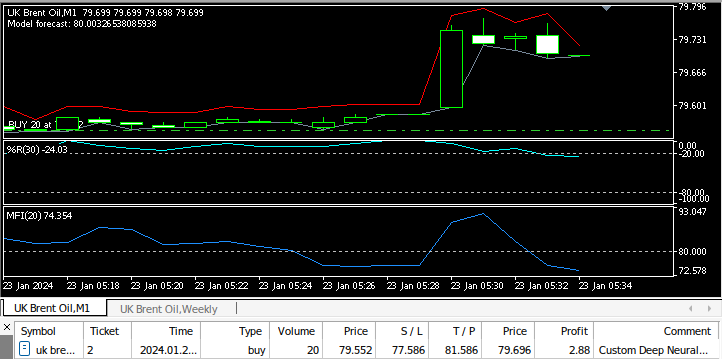
图 9:测试我们的EA
结论
本文为我们提供了一个关于使用优化算法进行模型超参数选择的简单入门。在未来的文章中,我们将采用一种更稳健的方法,使用两个专门的数据集:一个用于优化模型,另一个用于交叉验证并将其性能与使用默认设置的模型进行比较。
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/15413
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 神经网络变得简单(第 94 部分):优化输入序列
神经网络变得简单(第 94 部分):优化输入序列
 开发回放系统(第 57 部分):了解测试服务
开发回放系统(第 57 部分):了解测试服务
 开发回放系统(第 58 部分):重返服务工作
开发回放系统(第 58 部分):重返服务工作
 您应当知道的 MQL5 向导技术(第 22 部分):条件化生成式对抗网络(cGAN)
您应当知道的 MQL5 向导技术(第 22 部分):条件化生成式对抗网络(cGAN)