
Manuale MQL5: Sviluppo di un Expert Advisor multi-valuta con un numero illimitato di parametri
Introduzione
L'Expert Advisor multi-valuta considerato nel precedente articolo "MQL5 Cookbook: Manuale MQL5: Multi-Currency Expert Advisor - Approccio semplice, ordinato e veloce", può essere molto utile se il numero di simboli e parametri della strategia di trading utilizzati è piccolo. Tuttavia, esiste una restrizione sul numero di parametri di input di un Expert Advisor in MQL5: non dovrebbero essere superiori a 1024.
E anche se questo numero sarà molto spesso sufficiente, è molto scomodo usare un elenco così enorme di parametri. Ogni volta che è richiesta una modifica o un'ottimizzazione dei parametri per un determinato simbolo, è necessario cercare i parametri per quel simbolo specifico nell'elenco dei parametri lunghi.
In questo articolo, creeremo un modello che utilizza un singolo set di parametri per l'ottimizzazione di un sistema di trading, consentendo al contempo un numero illimitato di parametri. L'elenco dei simboli verrà creato in un file di testo standard (*.txt). Anche i parametri di input per ciascun simbolo verranno memorizzati nei file.
Va detto qui che l'Expert Advisor lavorerà su un simbolo nella normale modalità operativa, ma sarai in grado di testarlo nello Strategy Tester su una varietà di simboli selezionati (su ciascun simbolo separatamente).
Sarebbe, infatti, ancora più conveniente creare l'elenco dei simboli direttamente nella finestra Market Watch, considerando che consente anche di salvare set di simboli già pronti. Potremmo anche fare in modo che l'Expert Advisor ottenga l'elenco dei simboli nella finestra Market Watch direttamente dallo Strategy Tester. Ma sfortunatamente, al momento non è possibile accedere alla finestra Market Watch dallo Strategy Tester, quindi dovremo creare manualmente l'elenco dei simboli in anticipo o utilizzando uno script.
Sviluppo dell’ Expert Advisor
L'Expert Advisor multi-valuta descritto nel precedente articolo Manuale MQL5: Multi-Currency Expert Advisor - Approccio semplice, ordinato e veloce" sarà preso come modello. Decidiamo prima i parametri di input. Come accennato in precedenza, lasceremo solo una serie di parametri. Di seguito è riportato l'elenco dei parametri di input dell'Expert Advisor:
//--- Input parameters of the Expert Advisor sinput long MagicNumber =777; // Magic number sinput int Deviation =10; // Slippage sinput string delimeter_00=""; // -------------------------------- sinput int SymbolNumber =1; // Number of the tested symbol sinput bool RewriteParameters =false; // Rewriting parameters sinput ENUM_INPUTS_READING_MODE ParametersReadingMode=FILE; // Parameter reading mode sinput string delimeter_01=""; // -------------------------------- input int IndicatorPeriod =5; // Indicator period input double TakeProfit =100; // Take Profit input double StopLoss =50; // Stop Loss input double TrailingStop =10; // Trailing Stop input bool Reverse =true; // Position reversal input double Lot =0.1; // Lot input double VolumeIncrease =0.1; // Position volume increase input double VolumeIncreaseStep =10; // Volume increase step
Solo i parametri con il modificatore di input verranno scritti in un file. Inoltre, dovremmo espandere i tre nuovi parametri che non abbiamo mai incontrato prima.
- SymbolNumber - questo parametro indica il numero del simbolo dal file che contiene l'elenco dei simboli. Se è impostato su 0, tutti i simboli dell'elenco verranno testati. Se si va oltre l'elenco, il test non verrà eseguito.
- RewriteParameters - se questo valore del parametro è impostato su true, il file con i parametri del simbolo specificato (numero nel parametro SymbolNumber) verrà riscritto utilizzando i valori dei parametri di input correnti. In alternativa, se è impostato su false, i parametri verranno letti da un file.
- ParametersReadingMode - questo parametro indica la modalità di lettura rispetto ai parametri di input. Il tipo di parametro è il ENUM_INPUTS_READING_MODE enumerazione personalizzata che offre due opzioni: leggere da un file e utilizzare i parametri correnti.
Codice dell'enumerazione ENUM_INPUTS_READING_MODE:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Input parameter reading modes | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum ENUM_INPUTS_READING_MODE { FILE = 0, // File INPUT_PARAMETERS = 1 // Input parameters };
Il numero di simboli è stato precedentemente determinato utilizzando la costante NUMBER_OF_SYMBOLS. Questo valore ora dipende da diverse modalità, quindi lo cambieremo nella variabile globale SYMBOLS_COUNT:
//--- Number of traded symbols. It is calculated and depends on the testing mode and the number of symbols in the file int SYMBOLS_COUNT=0;
All'inizio del codice di Expert Advisor, dichiariamo un'altra costante, TESTED_PARAMETERS_COUNT, che determina le dimensioni delle matrici e il numero di iterazioni di loop durante l'iterazione sui parametri di input:
//--- Number of tested/optimized parameters #define TESTED_PARAMETERS_COUNT 8
Il file con l'elenco dei simboli, così come la cartella dei file contenente i parametri per ciascun simbolo devono essere collocati nella cartella comune del terminale in quanto è possibile accedervi a livello di programma sia durante il normale funzionamento di Expert Advisor che durante il test.
Ora dobbiamo preparare gli array con cui lavorare in seguito. Tutti gli array nell'Expert Advisor multi-valuta dell'articolo precedente che modificheremo sono statici, cioè con una dimensione preimpostata degli elementi. Dovremmo renderli tutti dinamici poiché la dimensione dipenderà ora dal numero di simboli utilizzati nel file e dalla modalità di lettura dei parametri di input. Aggiungeremo anche nuovi array (evidenziati in giallo) necessari per lavorare con i file:
//--- Arrays of input parameters string InputSymbols[]; // Symbol names //--- int InputIndicatorPeriod[]; // Indicator periods double InputTakeProfit[]; // Take Profit values double InputStopLoss[]; // Stop Loss values double InputTrailingStop[]; // Trailing Stop values bool InputReverse[]; // Values of position reversal flags double InputLot[]; // Lot values double InputVolumeIncrease[]; // Position volume increases double InputVolumeIncreaseStep[]; // Volume increase steps //--- Array of handles for indicator agents int spy_indicator_handles[]; //--- Array of signal indicator handles int signal_indicator_handles[]; //--- Data arrays for checking trading conditions struct PriceData { double value[]; }; PriceData open[]; // Opening price of the bar PriceData high[]; // High price of the bar PriceData low[]; // Low price of the bar PriceData close[]; // Closing price of the bar PriceData indicator[]; // Array of indicator values //--- Arrays for getting the opening time of the current bar struct Datetime { datetime time[]; }; Datetime lastbar_time[]; //--- Array for checking the new bar for each symbol datetime new_bar[]; //--- Array of input parameter names for writing to the file string input_parameters[TESTED_PARAMETERS_COUNT]= { "IndicatorPeriod", // Indicator period "TakeProfit", // Take Profit "StopLoss", // Stop Loss "TrailingStop", // Trailing Stop "Reverse", // Position reversal "Lot", // Lot "VolumeIncrease", // Position volume increase "VolumeIncreaseStep" // Volume increase step }; //--- Array for untested symbols string temporary_symbols[]; //--- Array for storing input parameters from the file of the symbol selected for testing or trading double tested_parameters_from_file[]; //--- Array of input parameter values for writing to the file double tested_parameters_values[TESTED_PARAMETERS_COUNT];
Quindi dobbiamo determinare le dimensioni delle matrici e inizializzarle ai valori.
La matrice di valori dei parametri di input creata in precedenza verrà inizializzata nella funzione InitializeTestedParametersValues() che verrà creata nel file InitializeArrays.mqh. Tale matrice verrà utilizzata per scrivere i valori dei parametri di input nel file.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Initializing the array of tested input parameters | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void InitializeTestedParametersValues() { tested_parameters_values[0]=IndicatorPeriod; tested_parameters_values[1]=TakeProfit; tested_parameters_values[2]=StopLoss; tested_parameters_values[3]=TrailingStop; tested_parameters_values[4]=Reverse; tested_parameters_values[5]=Lot; tested_parameters_values[6]=VolumeIncrease; tested_parameters_values[7]=VolumeIncreaseStep; }
Ora consideriamo le operazioni sui file. Innanzitutto, crea un'altra libreria di funzioni, FileFunctions.mqh, nella cartella UnlimitedParametersEA\Include del tuo Expert Advisor. Questa libreria verrà utilizzata per creare funzioni relative alla lettura e alla scrittura di dati in un file. Includerlo nel file principale dell'Expert Advisor e in altri file del progetto.
//---Include custom libraries #include "Include\Enums.mqh" #include "Include\InitializeArrays.mqh" #include "Include\Errors.mqh" #include "Include\FileFunctions.mqh" #include "Include\TradeSignals.mqh" #include "Include\TradeFunctions.mqh" #include "Include\ToString.mqh" #include "Include\Auxiliary.mqh"
Iniziamo con la creazione di una funzione per la lettura dell'elenco dei simboli da un file di testo - ReadSymbolsFromFile(). Questo file (nomizziamolo TestedSymbols.txt) deve essere inserito nella sottocartella \Files della cartella comune del terminale client MetaTrader 5. Nel mio caso sarà C:\ProgramData\MetaQuotes\Terminal\Common ma è necessario controllare attentamente il percorso utilizzando lo TERMINAL_COMMONDATA_PATH costante:
TerminalInfoString(TERMINAL_COMMONDATA_PATH)
Per verificare la funzionalità, aggiungere alcuni simboli al file di testo creato, separando ciascuno dei simboli con un'interruzione di riga ("\r\n"):
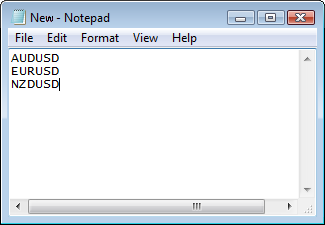
Fig. 1. Elenco dei simboli nel file dalla cartella comune del terminale.
Inoltre, diamo un'occhiata al codice della funzione ReadSymbolsFromFile():
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returning the number of strings (symbols) in the file and | //| filling the temporary array of symbols temporary_symbols[] | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //--- When preparing the file, symbols in the list should be separated with a line break int ReadSymbolsFromFile(string file_name) { int strings_count=0; // String counter //--- Open the file for reading from the common folder of the terminal int file_handle=FileOpen(file_name,FILE_READ|FILE_ANSI|FILE_COMMON); //--- If the file handle has been obtained if(file_handle!=INVALID_HANDLE) { ulong offset =0; // Offset for determining the position of the file pointer string text =""; // The read string will be written to this variable //--- Read until the current position of the file pointer reaches the end of the file or until the program is deleted while(!FileIsEnding(file_handle) || !IsStopped()) { //--- Read until the end of the string or until the program is deleted while(!FileIsLineEnding(file_handle) || !IsStopped()) { //--- Read the whole string text=FileReadString(file_handle); //--- Get the position of the pointer offset=FileTell(file_handle); //--- Go to the next string if this is not the end of the file // For this purpose, increase the offset of the file pointer if(!FileIsEnding(file_handle)) offset++; //--- Move it to the next string FileSeek(file_handle,offset,SEEK_SET); //--- If the string is not empty if(text!="") { //--- Increase the string counter strings_count++; //--- Increase the size of the array of strings, ArrayResize(temporary_symbols,strings_count); //--- Write the read string to the current index temporary_symbols[strings_count-1]=text; } //--- Exit the nested loop break; } //--- If this is the end of the file, terminate the main loop if(FileIsEnding(file_handle)) break; } //--- Close the file FileClose(file_handle); } //--- Return the number of strings in the file return(strings_count); }
Qui, il file di testo viene letto riga per riga. Il nome di ogni strumento finanziario che è stato letto è scritto nell'array temporaneo temporary_symbols[] creato in precedenza (l'effettiva accessibilità del simbolo sul server commerciale verrà verificata in seguito). Inoltre, alla fine la funzione restituisce il numero di stringhe lette, ovvero il numero di simboli su cui verrà testato il nostro Expert Advisor.
Torniamo al file InitializeArrays.mqh in cui creeremo la funzione InitializeInputSymbols() per riempire la matrice InputSymbols[] di nomi di simboli dichiarati in precedenza. I principianti probabilmente lo troveranno piuttosto complesso, quindi ho fornito commenti dettagliati al codice:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Filling the InputSymbol[] array of symbols | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void InitializeInputSymbols() { int strings_count=0; // Number of strings in the symbol file string checked_symbol=""; // To check the accessibility of the symbol on the trade server //--- Get the number of symbols from the "TestedSymbols.txt" file strings_count=ReadSymbolsFromFile("TestedSymbols.txt"); //--- In optimization mode or in one of the two modes (testing or visualization), provided that the symbol NUMBER IS SPECIFIED if(IsOptimization() || ((IsTester() || IsVisualMode()) && SymbolNumber>0)) { //--- Determine the symbol to be involved in parameter optimization for(int s=0; s<strings_count; s++) { //--- If the number specified in the parameters and the current loop index match if(s==SymbolNumber-1) { //--- Check whether the symbol is on the trade server if((checked_symbol=GetSymbolByName(temporary_symbols[s]))!="") { //--- Set the number of symbols SYMBOLS_COUNT=1; //--- Set the size of the array of symbols ArrayResize(InputSymbols,SYMBOLS_COUNT); //--- Write the symbol name InputSymbols[0]=checked_symbol; } //--- Exit return; } } } //--- In testing or visualization mode, if you need to test ALL symbols from the list in the file if((IsTester() || IsVisualMode()) && SymbolNumber==0) { //--- Parameter reading mode: from the file if(ParametersReadingMode==FILE) { //--- Iterate over all symbols in the file for(int s=0; s<strings_count; s++) { //--- Check if the symbol is on the trade server if((checked_symbol=GetSymbolByName(temporary_symbols[s]))!="") { //--- Increase the symbol counter SYMBOLS_COUNT++; //--- Set the size of the array of symbols ArrayResize(InputSymbols,SYMBOLS_COUNT); //--- Write the symbol name InputSymbols[SYMBOLS_COUNT-1]=checked_symbol; } } //--- Exit return; } //--- Parameter reading mode: from input parameters of the Expert Advisor if(ParametersReadingMode==INPUT_PARAMETERS) { //--- Set the number of symbols SYMBOLS_COUNT=1; //--- Set the size of the array of symbols ArrayResize(InputSymbols,SYMBOLS_COUNT); //--- Write the current symbol name InputSymbols[0]=Symbol(); //--- Exit return; } } //--- In normal operation mode of the Expert Advisor, use the current chart symbol if(IsRealtime()) { //--- Set the number of symbols SYMBOLS_COUNT=1; //--- Set the size of the array of symbols ArrayResize(InputSymbols,SYMBOLS_COUNT); //--- Write the symbol name InputSymbols[0]=Symbol(); } //--- }
Una volta che la dimensione della matrice di parametri di input è stata determinata dal numero di simboli utilizzati, è necessario impostare la dimensione di tutte le altre matrici di parametri di input. Implementiamolo come funzione separata - ResizeInputParametersArrays():
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Setting the new size for arrays of input parameters | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void ResizeInputParametersArrays() { ArrayResize(InputIndicatorPeriod,SYMBOLS_COUNT); ArrayResize(InputTakeProfit,SYMBOLS_COUNT); ArrayResize(InputStopLoss,SYMBOLS_COUNT); ArrayResize(InputTrailingStop,SYMBOLS_COUNT); ArrayResize(InputReverse,SYMBOLS_COUNT); ArrayResize(InputLot,SYMBOLS_COUNT); ArrayResize(InputVolumeIncrease,SYMBOLS_COUNT); ArrayResize(InputVolumeIncreaseStep,SYMBOLS_COUNT); }
Ora, dobbiamo creare la funzionalità che ci consentirà di leggere i valori dei parametri di input per ciascun simbolo, nonché di scrivere quei valori di parametro in un file separato (per ciascun simbolo) a seconda della modalità di input selezionata e delle impostazioni di Expert Advisor. Questo sarà fatto in modo simile a come leggiamo l'elenco dei simboli dal file. È un compito complesso, quindi spezzeremolo in diverse procedure.
Innanzitutto, dovremmo imparare a leggere i valori dei parametri di input da un file a un array. La matrice conterrà valori di tipo doppio. In seguito convertiremo alcuni di essi (periodo indicatore e flag di inversione di posizione) rispettivamente in tipi int e bool. L'handle del file aperto e la matrice in cui sono archiviati i valori dei parametri del file vengono passati alla funzione ReadInputParametersValuesFromFile():
//+----------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Reading parameters from the file and storing them in the passed array| //| Text file format: key=value //+----------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool ReadInputParametersValuesFromFile(int handle,double &array[]) { int delimiter_position =0; // Number of the symbol position "=" in the string int strings_count =0; // String counter string read_string =""; // The read string ulong offset =0; // Position of the pointer (offset in bytes) //--- Move the file pointer to the beginning of the file FileSeek(handle,0,SEEK_SET); //--- Read until the current position of the file pointer reaches the end of the file while(!FileIsEnding(handle)) { //--- If the user deleted the program if(IsStopped()) return(false); //--- Read until the end of the string while(!FileIsLineEnding(handle)) { //--- If the user deleted the program if(IsStopped()) return(false); //--- Read the string read_string=FileReadString(handle); //--- Get the index of the separator ("=") in the read string delimiter_position=StringFind(read_string,"=",0); //--- Get everything that follows the separator ("=") until the end of the string read_string=StringSubstr(read_string,delimiter_position+1); //--- Place the obtained value converted to the double type in the output array array[strings_count]=StringToDouble(read_string); //--- Get the current position of the file pointer offset=FileTell(handle); //--- If it's the end of the string if(FileIsLineEnding(handle)) { //--- Go to the next string if it's not the end of the file if(!FileIsEnding(handle)) //--- Increase the offset of the file pointer by 1 to go to the next string offset++; //--- Move the file pointer relative to the beginning of the file FileSeek(handle,offset,SEEK_SET); //--- Increase the string counter strings_count++; //--- Exit the nested loop for reading the string break; } } //--- If it's the end of the file, exit the main loop if(FileIsEnding(handle)) break; } //--- Return the fact of successful completion return(true); }
Quali handle di file e array passeremo a questa funzione? Dipenderà da quali simboli lavoreremo dopo averli letti dal file "TestedSymbols.txt". Ogni simbolo corrisponderà a un determinato file di testo contenente i valori dei parametri di input. Esistono due scenari di casi da considerare:
- Il file esiste e leggiamo i valori dei parametri di input da tale file utilizzando la funzione ReadInputParametersValuesFromFile() descritta in precedenza.
- Il file non esiste o è necessario riscrivere i valori dei parametri di input esistenti.
Il formato del file di testo (un file .ini, sebbene sia possibile scegliere qualsiasi altra estensione ritenuta necessaria) contenente i valori dei parametri di input sarà semplice:
input_parameter_name1=value input_parameter_name2=value .... input_parameter_nameN=value
Combiniamo questa logica in un'unica funzione, ReadWriteInputParameters(), il cui codice è fornito di seguito:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Reading/writing input parameters from/to a file for a symbol | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void ReadWriteInputParameters(int symbol_number,string path) { string file_name=path+InputSymbols[symbol_number]+".ini"; // File name //--- Print("Find the file '"+file_name+"' ..."); //--- Open the file with input parameters of the symbol int file_handle_read=FileOpen(file_name,FILE_READ|FILE_ANSI|FILE_COMMON); //--- Scenario #1: the file exists and parameter values do not need to be rewritten if(file_handle_read!=INVALID_HANDLE && !RewriteParameters) { Print("The file '"+InputSymbols[symbol_number]+".ini' exists, reading..."); //--- Set the array size ArrayResize(tested_parameters_from_file,TESTED_PARAMETERS_COUNT); //--- Fill the array with file values ReadInputParametersValuesFromFile(file_handle_read,tested_parameters_from_file); //--- If the array size is correct if(ArraySize(tested_parameters_from_file)==TESTED_PARAMETERS_COUNT) { //--- Write parameter values to arrays InputIndicatorPeriod[symbol_number] =(int)tested_parameters_from_file[0]; Print("InputIndicatorPeriod[symbol_number] = "+(string)InputIndicatorPeriod[symbol_number]); InputTakeProfit[symbol_number] =tested_parameters_from_file[1]; InputStopLoss[symbol_number] =tested_parameters_from_file[2]; InputTrailingStop[symbol_number] =tested_parameters_from_file[3]; InputReverse[symbol_number] =(bool)tested_parameters_from_file[4]; InputLot[symbol_number] =tested_parameters_from_file[5]; InputVolumeIncrease[symbol_number] =tested_parameters_from_file[6]; InputVolumeIncreaseStep[symbol_number] =tested_parameters_from_file[7]; } //--- Close the file and exit FileClose(file_handle_read); return; } //--- Scenario #2: If the file does not exist or the parameters need to be rewritten if(file_handle_read==INVALID_HANDLE || RewriteParameters) { //--- Close the handle of the file for reading FileClose(file_handle_read); //--- Get the handle of the file for writing int file_handle_write=FileOpen(file_name,FILE_WRITE|FILE_CSV|FILE_ANSI|FILE_COMMON,""); //--- If the handle has been obtained if(file_handle_write!=INVALID_HANDLE) { string delimiter="="; // Separator //--- Write the parameters for(int i=0; i<TESTED_PARAMETERS_COUNT; i++) { FileWrite(file_handle_write,input_parameters_names[i],delimiter,tested_parameters_values[i]); Print(input_parameters_names[i],delimiter,tested_parameters_values[i]); } //--- Write parameter values to arrays InputIndicatorPeriod[symbol_number] =(int)tested_parameters_values[0]; InputTakeProfit[symbol_number] =tested_parameters_values[1]; InputStopLoss[symbol_number] =tested_parameters_values[2]; InputTrailingStop[symbol_number] =tested_parameters_values[3]; InputReverse[symbol_number] =(bool)tested_parameters_values[4]; InputLot[symbol_number] =tested_parameters_values[5]; InputVolumeIncrease[symbol_number] =tested_parameters_values[6]; InputVolumeIncreaseStep[symbol_number] =tested_parameters_values[7]; //--- Depending on the indication, print the relevant message if(RewriteParameters) Print("The file '"+InputSymbols[symbol_number]+".ini' with parameters of the '"+EXPERT_NAME+".ex5 Expert Advisor has been rewritten'"); else Print("The file '"+InputSymbols[symbol_number]+".ini' with parameters of the '"+EXPERT_NAME+".ex5 Expert Advisor has been created'"); } //--- Close the handle of the file for writing FileClose(file_handle_write); } }
L'ultima funzione di file CreateInputParametersFolder() creerà una cartella con il nome di Expert Advisor nella cartella comune del terminale client. Questa è la cartella da cui verranno letti/scritti i file di testo (nel nostro caso, i file .ini) con i valori dei parametri di input. Proprio come nella funzione precedente, controlleremo se la cartella esiste. Se la cartella è stata creata correttamente o esiste già, la funzione restituirà il percorso o una stringa vuota in caso di errore:
//+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Creating a folder for files of input parameters in case the folder does not exist| //| and returns the path in case of success | //+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ string CreateInputParametersFolder() { long search_handle =INVALID_HANDLE; // Folder/file search handle string EA_root_folder =EXPERT_NAME+"\\"; // Root folder of the Expert Advisor string returned_filename =""; // Name of the found object (file/folder) string search_path =""; // Search path string folder_filter ="*"; // Search filter (* - check all files/folders) bool is_root_folder =false; // Flag of existence/absence of the root folder of the Expert Advisor //--- Find the root folder of the Expert Advisor search_path=folder_filter; //--- Set the search handle in the common folder of the terminal search_handle=FileFindFirst(search_path,returned_filename,FILE_COMMON); //--- If the first folder is the root folder, flag it if(returned_filename==EA_root_folder) is_root_folder=true; //--- If the search handle has been obtained if(search_handle!=INVALID_HANDLE) { //--- If the first folder is not the root folder if(!is_root_folder) { //--- Iterate over all files to find the root folder while(FileFindNext(search_handle,returned_filename)) { //--- Process terminated by the user if(IsStopped()) return(""); //--- If it is found, flag it if(returned_filename==EA_root_folder) { is_root_folder=true; break; } } } //--- Close the root folder search handle FileFindClose(search_handle); //search_handle=INVALID_HANDLE; } //--- Otherwise print an error message else Print("Error when getting the search handle or " "the folder '"+TerminalInfoString(TERMINAL_COMMONDATA_PATH)+"' is empty: ",ErrorDescription(GetLastError())); //--- Based on the check results, create the necessary folder search_path=EXPERT_NAME+"\\"; //--- If the root folder of the Expert Advisor does not exist if(!is_root_folder) { //--- Create it. if(FolderCreate(EXPERT_NAME,FILE_COMMON)) { //--- If the folder has been created, flag it is_root_folder=true; Print("The root folder of the '..\\"+EXPERT_NAME+"\\ Expert Advisor has been created'"); } else { Print("Error when creating " "the root folder of the Expert Advisor: ",ErrorDescription(GetLastError())); return(""); } } //--- If the required folder exists if(is_root_folder) //--- Return the path to create a file for writing parameters of the Expert Advisor return(search_path+"\\"); //--- In case of errors, return an empty string return(""); }
Mettiamo ora insieme le chiamate di funzione sopra in una singola funzione - InitializeInputParametersArrays(). Questa funzione copre 4 opzioni di inizializzazione dei parametri di input quando si lavora con Expert Advisor:
- Modalità operativa standard (o ottimizzazione dei parametri per un simbolo selezionato) utilizzando i valori dei parametri di input correnti
- Riscrittura dei parametri nei file durante il test o l'ottimizzazione
- Test di un simbolo selezionato
- Test di tutti i simboli nell'elenco dal file
Tutte le operazioni sono spiegate in commenti dettagliati al codice:
//+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Initializing arrays of input parameters depending on the mode | //+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ void InitializeInputParametersArrays() { string path=""; // To determine the folder that contains files with input parameters //--- Mode #1 : // - standard operation mode of the Expert Advisor OR // - optimization mode OR // - reading from input parameters of the Expert Advisor without rewriting the file if(IsRealtime() || IsOptimization() || (ParametersReadingMode==INPUT_PARAMETERS && !RewriteParameters)) { //--- Initialize parameter arrays to current values InitializeWithCurrentValues(); return; } //--- Mode #2 : // - rewriting parameters in the file for the specified symbol if(RewriteParameters) { //--- Initialize parameter arrays to current values InitializeWithCurrentValues(); //--- If the folder of the Expert Advisor exists or in case no errors occurred when it was being created if((path=CreateInputParametersFolder())!="") //--- Write/read the file of symbol parameters ReadWriteInputParameters(0,path); //--- return; } //--- Mode #3 : // - testing (it may be in visualization mode, without optimization) the Expert Advisor on a SELECTED symbol if((IsTester() || IsVisualMode()) && !IsOptimization() && SymbolNumber>0) { //--- If the folder of the Expert Advisor exists or in case no errors occurred when it was being created if((path=CreateInputParametersFolder())!="") { //--- Iterate over all symbols (in this case, the number of symbols = 1) for(int s=0; s<SYMBOLS_COUNT; s++) //--- Write or read the file of symbol parameters ReadWriteInputParameters(s,path); } return; } //--- Mode #4 : // - testing (it may be in visualization mode, without optimization) the Expert Advisor on ALL symbols if((IsTester() || IsVisualMode()) && !IsOptimization() && SymbolNumber==0) { //--- If the folder of the Expert Advisor exists and // no errors occurred when it was being created if((path=CreateInputParametersFolder())!="") { //--- Iterate over all symbols for(int s=0; s<SYMBOLS_COUNT; s++) //--- Write or read the file of symbol parameters ReadWriteInputParameters(s,path); } return; } }
Nelle modalità #1 e #2 usiamo la funzione InitializeWithCurrentValues(). Inizializza l'indice zero (unico) ai valori dei parametri di input correnti. In altre parole, questa funzione viene utilizzata quando è richiesto un solo simbolo:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Initializing arrays of input parameters to current values | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void InitializeWithCurrentValues() { InputIndicatorPeriod[0]=IndicatorPeriod; InputTakeProfit[0]=TakeProfit; InputStopLoss[0]=StopLoss; InputTrailingStop[0]=TrailingStop; InputReverse[0]=Reverse; InputLot[0]=Lot; InputVolumeIncrease[0]=VolumeIncrease; InputVolumeIncreaseStep[0]=VolumeIncreaseStep; }
Ora dobbiamo fare la cosa più semplice, ma la più importante: implementare chiamate consecutive delle funzioni di cui sopra dal punto di ingresso, le OnInit() funzione:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnInit() { //--- Initialize the array of tested input parameters for writing to the file InitializeTestedParametersValues(); //--- Fill the array of symbol names InitializeInputSymbols(); //--- Set the size of arrays of input parameters ResizeInputParametersArrays(); //--- Initialize arrays of indicator handles InitializeIndicatorHandlesArrays(); //--- Initialize arrays of input parameters depending on the operation mode of the Expert Advisor InitializeInputParametersArrays(); //--- Get agent handles from the "EventsSpy.ex5" indicator GetSpyHandles(); //--- Get indicator handles GetIndicatorHandles(); //--- Initialize the new bar InitializeNewBarArray(); //--- Initialize price arrays and indicator buffers ResizeDataArrays(); }
Quindi, abbiamo finito con il codice. Puoi familiarizzare con le funzioni descritte usando i file allegati all'articolo, non c'è nulla di complicato in essi. Ora, andiamo oltre per vedere cosa abbiamo ottenuto come risultato e come può essere utilizzato.
Ottimizzazione dei parametri e test expert advisor
Come già accennato, dovresti avere il file TestedSymbols.txt con l'elenco dei simboli nella cartella comune del terminale client. Come esempio/a scopo di test, creeremo un elenco di tre simboli: AUDUSD, EURUSD e NZDUSD. Ora ottimizzeremo uno dopo l’altro i parametri di input per ciascun simbolo. Il tester strategico deve essere impostato come mostrato di seguito:
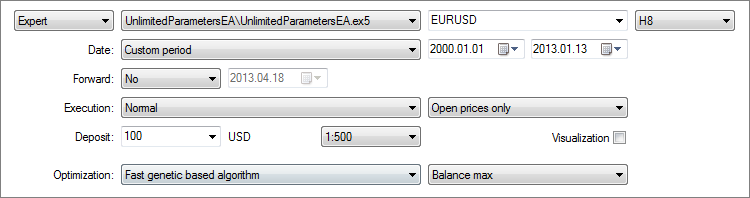
Fig. 2. Impostazioni di Strategy Tester.
È possibile impostare qualsiasi simbolo (nel nostro caso, EURUSD) nella scheda "Impostazioni" poiché non influisce sull'Expert Advisor. Quindi selezioniamo i parametri per l'ottimizzazione dell'Expert Advisor:
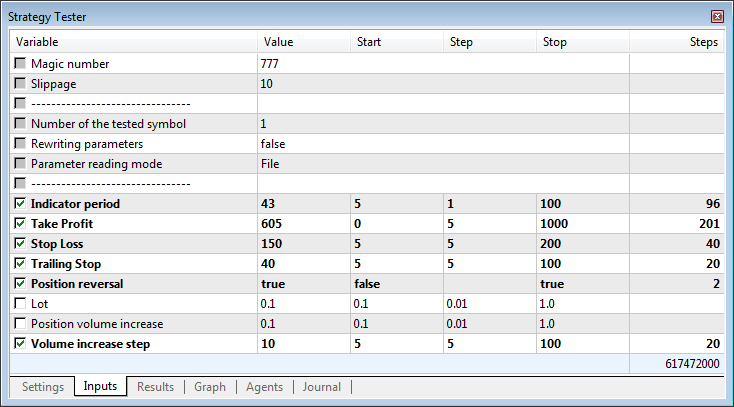
Fig. 3. Parametri di input dell'Expert Advisor.
La figura precedente mostra che il parametro SymbolNumber (Numero del simbolo testato) è impostato su 1. Ciò significa che durante l'esecuzione dell'ottimizzazione Expert Advisor utilizzerà il primo simbolo dell'elenco dal file TestedSymbols.txt. Nel nostro caso, è AUDUSD.
Nota:a causa delle peculiarità di questo Expert Advisor (l'elenco dei simboli è impostato leggendo dal file di testo), l'ottimizzazione con agenti remoti non sarà possibile.
Cercheremo di aggirare questa restrizione in uno dei seguenti articoli di questa serie.
Dopo aver completato l'ottimizzazione, è possibile eseguire test, studiando i risultati di diversi passaggi di ottimizzazione. Se si desidera che Expert Advisor legga i parametri dal file, è necessario selezionare File nell'elenco a discesa del parametro ParametersReadingMode (modalità di lettura dei parametri). Per poter utilizzare i parametri correnti di Expert Advisor (impostati nella scheda "Impostazioni", è necessario selezionare l'opzione Parametri di input.
L'opzione Parametri di input è certamente necessaria per visualizzare i risultati dell'ottimizzazione. Quando si esegue il test per la prima volta, Expert Advisor creerà una cartella con il nome corrispondente nella cartella comune del terminale. La cartella creata conterrà un file con i parametri correnti del simbolo testato. Nel nostro caso, questo è AUDUSD.ini. Puoi vedere il contenuto di questo file nella figura seguente:
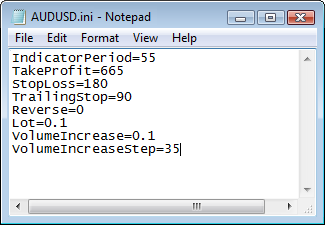
Fig. 4. Elenco dei parametri di input nel file del simbolo.
Una volta trovata la combinazione di parametri richiesta, è necessario impostaretrue nel parametro RewriteParameters (Riscrittura dei parametri) ed eseguire nuovamente il test. Il file dei parametri verrà aggiornato. In seguito è possibile impostare nuovamente false e controllare altri risultati dei passaggi di ottimizzazione. È inoltre conveniente confrontare i risultati dei valori scritti nel file con quelli impostati nei parametri di input semplicemente passando da un'opzione all'altro del parametro Modalità di lettura dei parametri.
Quindi, eseguiamo l'ottimizzazione per EURUSD, che è il secondo simbolo nell'elenco dal file dell'elenco dei simboli. Per fare ciò, dobbiamo impostare il valore del parametro del Numero del simbolo testato uguale a 2. Dopo l'ottimizzazione, e dopo aver determinato i parametri e averli scritti nel file, lo stesso dovrà essere fatto anche per il terzo simbolo della lista.
Una volta che i parametri per tutti i simboli sono stati scritti nel file, è possibile visualizzare i risultati per ciascun simbolo separatamente, specificando il numero del simbolo, oppure visualizzare il risultato cumulativo per tutti i simboli, impostando il numero del simbolo testato su 0. Ho ottenuto il seguente risultato cumulativo per tutti i simboli:
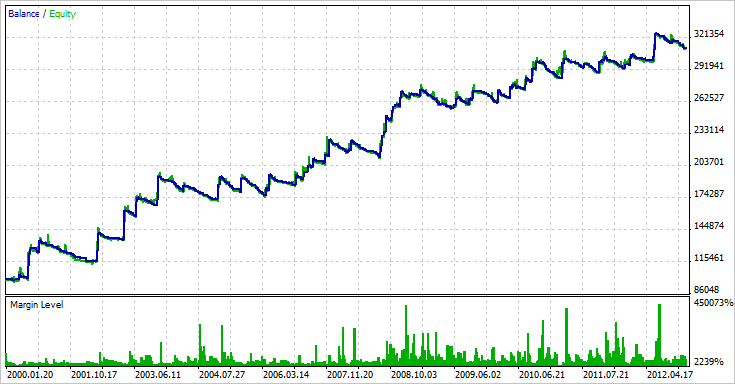
Fig. 5. Risultato cumulativo dell'Expert Advisor multivaluta.
Conclusione
Di conseguenza, abbiamo un modello abbastanza conveniente per gli Expert Advisor multi-valuta. Può essere sviluppato ulteriormente, se lo si desidera. Allegato all'articolo è l'archivio scaricabile con i file dell'Expert Advisor per la vostra considerazione. Dopo aver decompresso, posizionare la cartella UnlimitedParametersEA nella cartella terminale <MetaTrader 5>\MQL5\Experts. L'indicatore EventsSpy.mq5 deve essere posizionato nella cartella terminale <MetaTrader 5>\MQL5\Indicators. Oltre a ciò, non dimenticare di creare il file di testo TestedSymbols.txt nella cartella comune del terminale client.
Tradotto dal russo da MetaQuotes Ltd.
Articolo originale: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/650
Avvertimento: Tutti i diritti su questi materiali sono riservati a MetaQuotes Ltd. La copia o la ristampa di questi materiali in tutto o in parte sono proibite.
Questo articolo è stato scritto da un utente del sito e riflette le sue opinioni personali. MetaQuotes Ltd non è responsabile dell'accuratezza delle informazioni presentate, né di eventuali conseguenze derivanti dall'utilizzo delle soluzioni, strategie o raccomandazioni descritte.
- App di trading gratuite
- Oltre 8.000 segnali per il copy trading
- Notizie economiche per esplorare i mercati finanziari
Accetti la politica del sito e le condizioni d’uso
Ciao Anatoli,
Grazie per aver condiviso questo grande EA.
Sto testando l'EA e non c'è nessun file 'AUDUSD.ini' che viene creato nella cartella 'common', né altrove. Tu dici che"Per poter utilizzare i parametri correnti dell'Expert Advisor (impostati nella scheda "Impostazioni"), è necessario selezionare l' opzioneParametri di ingresso ", ma non vedo dove effettuare questa selezione, né nella scheda "Impostazioni" né altrove. Suppongo che questo possa essere il motivo per cui il file '.ini' non viene creato. Potete per favore chiarire?
Ho letto nel file 'FileFunctions.mqh' alla riga 87 i due scenari. Con 'print' probabilmente dovrei ricevere un messaggio nella schermata a comparsa o nel diario riguardo al file '.ini', ma non è così.
Il diario ne riporta alcuni simili a questa riga: "testato con l'errore "errore critico di runtime 502 nella funzione OnInit (array fuori range, modulo Experts\UnlimitedParametersEA.ex5, file InitializeArrays.mqh, riga 168, col 24)" in 16 ms". Questo si riferisce a 'InputIndicatorPeriod'. Con H8 specificato, perché è così ed è una causa di fallimento del file '.ini'?
Grazie mille.
Grazie per questa presentazione ottimamente documentata e di facile comprensione.
daveM
Ciao Anatoli,
Grazie per aver condiviso questo grande EA.