带有预测性的三角套利
概述
本文是有关三角套利策略的。文章中包含两个基于深度学习模型的三角套利示例。这些模型和使用的EA可以在文章的附件中找到。三角套利利用汇率差来获得无风险利润。
什么是三角套利?
套利非常有趣,它在体育博彩中是被禁止的。想象一下,你预测皇家马德里赢得2024年冠军的赔率为1.25,而多特蒙德的赔率为3.60,这意味着皇家马德里有100/1.25=80%的胜率,而多特蒙德有27.7%的胜率。如果你把这两个胜率加起来,会得到107.7%,这是因为博彩公司想要赚钱,那超过100%的部分就是他们的佣金。但是,假设你找到了第二家博彩公司,他们给多特蒙德的胜率设定为19%,对应的赔率为5.26。那么你可以在第一家博彩公司下注皇家马德里,在第二家博彩公司下注多特蒙德,如果你对每支球队下注的金额恰当,你就能在这场比赛中赢得金钱,因为两家博彩公司的胜率加起来小于100%。以上举一个简单的例子,用来解释说明为什么套利在体育博彩中被禁止,以及什么是套利。
想象一下,你是一个“合法”的人,你不想因为套利而导致你的体育账户被封。你知道,即使你下注了皇家马德里,如果你等到比赛的第70分钟,根据比赛是平局还是皇家马德里进球,你仍然可以进行“合法”的套利,从而获得多特蒙德的赔率并确保双赢……这听起来有点风险,但这就是我们可以利用深度学习的地方。我们知道皇家马德里会进球,所以你有98%的概率能获得那些赔率(这是通过预测值与实际值之间的协同整合得到的)。这就是深度学习与套利结合的新颖之处。
现在,我们已经知道了什么是套利,以及如何在深度学习的帮助下赢得更多,那么什么是三角套利呢?其实它与套利相似,但涉及三对交易。为什么呢?因为它主要用于外汇和加密货币市场,这些市场使用A/B这样的符号表示货币对,如果你要解决这个问题,就需要三个方程:(A/B) * (B/C) * (C/A)。当这个乘积大于1时,你按照一种方式乘法操作;当小于1时,则按照另一种方式。
为什么你不能在所有账户上都进行三角套利?
如果你有一个零点差账户,三角套利可以在一秒或更短的时间内完成。如果你有价差(点差),那么在这样短的时间内是不可能战胜价差的。但是,就像我之前说的,不用担心,EA在两种情况下都能盈利。我的账户不是零点差账户,所以这篇文章将使用带有点差的示例。
我们究竟需要EA做什么?
EA使用Python中设定的预测,并将其转换为ONNX模型,以便在MT5的EA中使用。这就是为什么我会详细讲解整个过程,以确保每个人都能使用这个EA。如果你已经了解如何制作ONNX模型,那么你可以直接跳到EA的部分。
您将开启首次安装:
- Python 3.10
您可以在Microsoft商城中找到,只需单击安装即可。
-Visual Studio代码
您可以在Microsoft商城里找到,只需点击安装,即可一切就绪。
之后,您需要从这里安装Visual Studio 2019或C++(需安装一个python库):
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-US/cpp/windows/latest-supported-vc-redist?view=msvc-170#visual-studio-2015-2017-2019-and-2022 完成此操作后,您必须将python脚本文件夹添加到指定路径中。 还须将“.py”添加到PATHEXT中。
完成所有这些后,我们现在可以像这样安装库。
打开VSC -> 终端 ->新终端。
VSC可能会要求您安装python扩展库(只需单击“确定”)。同样只需复制(然后按Enter键):
pip install MetaTrader5==5.0.4200 pip install pandas==2.2.1 pip install scipy==1.12.0 pip install statsmodels==0.14.1 pip install numpy==1.26.4 pip install tensorflow==2.15.0 pip install tf2onnx==1.16.1 pip install scikit-learn==1.4.1.post1 pip install keras==2.15.0 pip install matplotlib==3.8.3
以上应该没有问题,如果有问题,您可以提出。
一旦完成了所有必要的安装并且没有出错,我们就可以继续进行.py测试模型。我将复制粘贴这个实例:
# python libraries import MetaTrader5 as mt5 import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import pandas as pd import tf2onnx from datetime import timedelta, datetime # input parameters symbol1 = "EURGBP" symbol2 = "GBPUSD" symbol3 = "EURUSD" sample_size1 = 200000 optional = "_M1_test" timeframe = mt5.TIMEFRAME_M1 #end_date = datetime.now() end_date = datetime(2024, 3, 4, 0) inp_history_size = 120 sample_size = sample_size1 symbol = symbol1 optional = optional inp_model_name = str(symbol)+"_"+str(optional)+".onnx" if not mt5.initialize(): print("initialize() failed, error code =",mt5.last_error()) quit() # we will save generated onnx-file near our script to use as resource from sys import argv data_path=argv[0] last_index=data_path.rfind("\\")+1 data_path=data_path[0:last_index] print("data path to save onnx model",data_path) # and save to MQL5\Files folder to use as file terminal_info=mt5.terminal_info() file_path=terminal_info.data_path+"\\MQL5\\Files\\" print("file path to save onnx model",file_path) # set start and end dates for history data #end_date = datetime.now() #end_date = datetime(2024, 5, 1, 0) start_date = end_date - timedelta(days=inp_history_size*20) # print start and end dates print("data start date =",start_date) print("data end date =",end_date) # get rates eurusd_rates = mt5.copy_rates_from(symbol, timeframe , end_date, sample_size ) # create dataframe df=pd.DataFrame() df = pd.DataFrame(eurusd_rates) print(df) # Extraer los precios de cierre directamente datas = df['close'].values """# Calcular la inversa de cada valor inverted_data = 1 / datas # Convertir los datos invertidos a un array de numpy si es necesario data = inverted_data.values""" data = datas.reshape(-1,1) # Imprimir los resultados """data = datas""" # scale data from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler scaler=MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0,1)) scaled_data = scaler.fit_transform(data) # training size is 80% of the data training_size = int(len(scaled_data)*0.80) print("Training_size:",training_size) train_data_initial = scaled_data[0:training_size,:] test_data_initial = scaled_data[training_size:,:1] # split a univariate sequence into samples def split_sequence(sequence, n_steps): X, y = list(), list() for i in range(len(sequence)): # find the end of this pattern end_ix = i + n_steps # check if we are beyond the sequence if end_ix > len(sequence)-1: break # gather input and output parts of the pattern seq_x, seq_y = sequence[i:end_ix], sequence[end_ix] X.append(seq_x) y.append(seq_y) return np.array(X), np.array(y) # split into samples time_step = inp_history_size x_train, y_train = split_sequence(train_data_initial, time_step) x_test, y_test = split_sequence(test_data_initial, time_step) # reshape input to be [samples, time steps, features] which is required for LSTM x_train =x_train.reshape(x_train.shape[0],x_train.shape[1],1) x_test = x_test.reshape(x_test.shape[0],x_test.shape[1],1) # define model from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Activation, Conv1D, MaxPooling1D, Dropout, Flatten, LSTM from keras.metrics import RootMeanSquaredError as rmse from tensorflow.keras import callbacks model = Sequential() model.add(Conv1D(filters=256, kernel_size=2, activation='relu',padding = 'same',input_shape=(inp_history_size,1))) model.add(MaxPooling1D(pool_size=2)) model.add(LSTM(100, return_sequences = True)) model.add(Dropout(0.3)) model.add(LSTM(100, return_sequences = False)) model.add(Dropout(0.3)) model.add(Dense(units=1, activation = 'sigmoid')) model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss= 'mse' , metrics = [rmse()]) # Set up early stopping early_stopping = callbacks.EarlyStopping( monitor='val_loss', patience=5, restore_best_weights=True, ) # model training for 300 epochs history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs = 300 , validation_data = (x_test,y_test), batch_size=32, callbacks=[early_stopping], verbose=2) # evaluate training data train_loss, train_rmse = model.evaluate(x_train,y_train, batch_size = 32) print(f"train_loss={train_loss:.3f}") print(f"train_rmse={train_rmse:.3f}") # evaluate testing data test_loss, test_rmse = model.evaluate(x_test,y_test, batch_size = 32) print(f"test_loss={test_loss:.3f}") print(f"test_rmse={test_rmse:.3f}") # save model to ONNX output_path = data_path+inp_model_name onnx_model = tf2onnx.convert.from_keras(model, output_path=output_path) print(f"saved model to {output_path}") output_path = file_path+inp_model_name onnx_model = tf2onnx.convert.from_keras(model, output_path=output_path) print(f"saved model to {output_path}") # finish mt5.shutdown() #prediction using testing data #prediction using testing data test_predict = model.predict(x_test) print(test_predict) print("longitud total de la prediccion: ", len(test_predict)) print("longitud total del sample: ", sample_size) plot_y_test = np.array(y_test).reshape(-1, 1) # Selecciona solo el último elemento de cada muestra de prueba plot_y_train = y_train.reshape(-1,1) train_predict = model.predict(x_train) #print(plot_y_test) #calculate metrics from sklearn import metrics from sklearn.metrics import r2_score #transform data to real values value1=scaler.inverse_transform(plot_y_test) #print(value1) # Escala las predicciones inversas al transformarlas a la escala original value2 = scaler.inverse_transform(test_predict.reshape(-1, 1)) #print(value2) #calc score score = np.sqrt(metrics.mean_squared_error(value1,value2)) print("RMSE : {}".format(score)) print("MSE :", metrics.mean_squared_error(value1,value2)) print("R2 score :",metrics.r2_score(value1,value2)) #sumarize model model.summary() #Print error value11=pd.DataFrame(value1) value22=pd.DataFrame(value2) #print(value11) #print(value22) value111=value11.iloc[:,:] value222=value22.iloc[:,:] print("longitud salida (tandas de 1 minuto): ",len(value111) ) #print("en horas son " + str((len(value111))*60*24)+ " minutos") print("en horas son " + str(((len(value111)))/60)+ " horas") print("en horas son " + str(((len(value111)))/60/24)+ " dias") # Calculate error error = value111 - value222 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Plot error plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) plt.scatter(range(len(error)), error, color='blue', label='Error') plt.axhline(y=0, color='red', linestyle='--', linewidth=1) # Línea horizontal en y=0 plt.title('Error de Predicción ' + str(symbol)) plt.xlabel('Índice de la muestra') plt.ylabel('Error') plt.legend() plt.grid(True) plt.savefig(str(symbol)+str(optional)+'.png') rmse_ = format(score) mse_ = metrics.mean_squared_error(value1,value2) r2_ = metrics.r2_score(value1,value2) resultados= [rmse_,mse_,r2_] # Abre un archivo en modo escritura with open(str(symbol)+str(optional)+"results.txt", "w") as archivo: # Escribe cada resultado en una línea separada for resultado in resultados: archivo.write(str(resultado) + "\n") # finish mt5.shutdown() #show iteration-rmse graph for training and validation plt.figure(figsize = (18,10)) plt.plot(history.history['root_mean_squared_error'],label='Training RMSE',color='b') plt.plot(history.history['val_root_mean_squared_error'],label='Validation-RMSE',color='g') plt.xlabel("Iteration") plt.ylabel("RMSE") plt.title("RMSE" + str(symbol)) plt.legend() plt.savefig(str(symbol)+str(optional)+'1.png') #show iteration-loss graph for training and validation plt.figure(figsize = (18,10)) plt.plot(history.history['loss'],label='Training Loss',color='b') plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'],label='Validation-loss',color='g') plt.xlabel("Iteration") plt.ylabel("Loss") plt.title("LOSS" + str(symbol)) plt.legend() plt.savefig(str(symbol)+str(optional)+'2.png') #show actual vs predicted (training) graph plt.figure(figsize=(18,10)) plt.plot(scaler.inverse_transform(plot_y_train),color = 'b', label = 'Original') plt.plot(scaler.inverse_transform(train_predict),color='red', label = 'Predicted') plt.title("Prediction Graph Using Training Data" + str(symbol)) plt.xlabel("Hours") plt.ylabel("Price") plt.legend() plt.savefig(str(symbol)+str(optional)+'3.png') #show actual vs predicted (testing) graph plt.figure(figsize=(18,10)) plt.plot(scaler.inverse_transform(plot_y_test),color = 'b', label = 'Original') plt.plot(scaler.inverse_transform(test_predict),color='g', label = 'Predicted') plt.title("Prediction Graph Using Testing Data" + str(symbol)) plt.xlabel("Hours") plt.ylabel("Price") plt.legend() plt.savefig(str(symbol)+str(optional)+'4.png') ################################################################################################ EURJPY 1 # python libraries import MetaTrader5 as mt5 import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import pandas as pd import tf2onnx # input parameters inp_history_size = 120 sample_size = sample_size1 symbol = symbol2 optional = optional inp_model_name = str(symbol)+"_"+str(optional)+".onnx" if not mt5.initialize(): print("initialize() failed, error code =",mt5.last_error()) quit() # we will save generated onnx-file near our script to use as resource from sys import argv data_path=argv[0] last_index=data_path.rfind("\\")+1 data_path=data_path[0:last_index] print("data path to save onnx model",data_path) # and save to MQL5\Files folder to use as file terminal_info=mt5.terminal_info() file_path=terminal_info.data_path+"\\MQL5\\Files\\" print("file path to save onnx model",file_path) # set start and end dates for history data from datetime import timedelta, datetime #end_date = datetime.now() #end_date = datetime(2024, 5, 1, 0) start_date = end_date - timedelta(days=inp_history_size*20) # print start and end dates print("data start date =",start_date) print("data end date =",end_date) # get rates eurusd_rates2 = mt5.copy_rates_from(symbol, timeframe , end_date, sample_size) # create dataframe df=pd.DataFrame() df2 = pd.DataFrame(eurusd_rates2) print(df2) # Extraer los precios de cierre directamente datas2 = df2['close'].values """inverted_data = 1 / datas # Convertir los datos invertidos a un array de numpy si es necesario data = inverted_data.values""" data2 = datas2.reshape(-1,1) # Convertir los datos invertidos a un array de numpy si es necesario #data = datas.values # Imprimir los resultados # scale data from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler scaler2=MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0,1)) scaled_data2 = scaler2.fit_transform(data2) # training size is 80% of the data training_size2 = int(len(scaled_data2)*0.80) print("Training_size:",training_size2) train_data_initial2 = scaled_data2[0:training_size2,:] test_data_initial2 = scaled_data2[training_size2:,:1] # split a univariate sequence into samples def split_sequence(sequence, n_steps): X, y = list(), list() for i in range(len(sequence)): # find the end of this pattern end_ix = i + n_steps # check if we are beyond the sequence if end_ix > len(sequence)-1: break # gather input and output parts of the pattern seq_x, seq_y = sequence[i:end_ix], sequence[end_ix] X.append(seq_x) y.append(seq_y) return np.array(X), np.array(y) # split into samples time_step = inp_history_size x_train2, y_train2 = split_sequence(train_data_initial2, time_step) x_test2, y_test2 = split_sequence(test_data_initial2, time_step) # reshape input to be [samples, time steps, features] which is required for LSTM x_train2 =x_train2.reshape(x_train2.shape[0],x_train2.shape[1],1) x_test2 = x_test2.reshape(x_test2.shape[0],x_test2.shape[1],1) # define model from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Activation, Conv1D, MaxPooling1D, Dropout, Flatten, LSTM from keras.metrics import RootMeanSquaredError as rmse from tensorflow.keras import callbacks model = Sequential() model.add(Conv1D(filters=256, kernel_size=2, activation='relu',padding = 'same',input_shape=(inp_history_size,1))) model.add(MaxPooling1D(pool_size=2)) model.add(LSTM(100, return_sequences = True)) model.add(Dropout(0.3)) model.add(LSTM(100, return_sequences = False)) model.add(Dropout(0.3)) model.add(Dense(units=1, activation = 'sigmoid')) model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss= 'mse' , metrics = [rmse()]) # Set up early stopping early_stopping = callbacks.EarlyStopping( monitor='val_loss', patience=5, restore_best_weights=True, ) # model training for 300 epochs history2 = model.fit(x_train2, y_train2, epochs = 300 , validation_data = (x_test2,y_test2), batch_size=32, callbacks=[early_stopping], verbose=2) # evaluate training data train_loss2, train_rmse2 = model.evaluate(x_train2,y_train2, batch_size = 32) print(f"train_loss={train_loss2:.3f}") print(f"train_rmse={train_rmse2:.3f}") # evaluate testing data test_loss2, test_rmse2 = model.evaluate(x_test2,y_test2, batch_size = 32) print(f"test_loss={test_loss2:.3f}") print(f"test_rmse={test_rmse2:.3f}") # save model to ONNX output_path = data_path+inp_model_name onnx_model = tf2onnx.convert.from_keras(model, output_path=output_path) print(f"saved model to {output_path}") output_path = file_path+inp_model_name onnx_model = tf2onnx.convert.from_keras(model, output_path=output_path) print(f"saved model to {output_path}") # finish mt5.shutdown() #prediction using testing data #prediction using testing data test_predict2 = model.predict(x_test2) print(test_predict2) print("longitud total de la prediccion: ", len(test_predict2)) print("longitud total del sample: ", sample_size) plot_y_test2 = np.array(y_test2).reshape(-1, 1) # Selecciona solo el último elemento de cada muestra de prueba plot_y_train2 = y_train2.reshape(-1,1) train_predict2 = model.predict(x_train2) #print(plot_y_test) #calculate metrics from sklearn import metrics from sklearn.metrics import r2_score #transform data to real values value12=scaler2.inverse_transform(plot_y_test2) #print(value1) # Escala las predicciones inversas al transformarlas a la escala original value22 = scaler2.inverse_transform(test_predict2.reshape(-1, 1)) #print(value2) #calc score score2 = np.sqrt(metrics.mean_squared_error(value12,value22)) print("RMSE : {}".format(score2)) print("MSE :", metrics.mean_squared_error(value12,value22)) print("R2 score :",metrics.r2_score(value12,value22)) #sumarize model model.summary() #Print error value112=pd.DataFrame(value12) value222=pd.DataFrame(value22) #print(value11) #print(value22) value1112=value112.iloc[:,:] value2222=value222.iloc[:,:] print("longitud salida (tandas de 1 min): ",len(value1112) ) #print("en horas son " + str((len(value1112))*60*24)+ " minutos") print("en horas son " + str(((len(value1112)))/60)+ " horas") print("en horas son " + str(((len(value1112)))/60/24)+ " dias") # Calculate error error2 = value1112 - value2222 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Plot error plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) plt.scatter(range(len(error2)), error2, color='blue', label='Error') plt.axhline(y=0, color='red', linestyle='--', linewidth=1) # Línea horizontal en y=0 plt.title('Error de Predicción ' + str(symbol)) plt.xlabel('Índice de la muestra') plt.ylabel('Error') plt.legend() plt.grid(True) plt.savefig(str(symbol)+str(optional)+'.png') rmse_2 = format(score2) mse_2 = metrics.mean_squared_error(value12,value22) r2_2 = metrics.r2_score(value12,value22) resultados2= [rmse_2,mse_2,r2_2] # Abre un archivo en modo escritura with open(str(symbol)+str(optional)+"results.txt", "w") as archivo: # Escribe cada resultado en una línea separada for resultado in resultados2: archivo.write(str(resultado) + "\n") # finish mt5.shutdown() #show iteration-rmse graph for training and validation plt.figure(figsize = (18,10)) plt.plot(history2.history['root_mean_squared_error'],label='Training RMSE',color='b') plt.plot(history2.history['val_root_mean_squared_error'],label='Validation-RMSE',color='g') plt.xlabel("Iteration") plt.ylabel("RMSE") plt.title("RMSE" + str(symbol)) plt.legend() plt.savefig(str(symbol)+str(optional)+'1.png') #show iteration-loss graph for training and validation plt.figure(figsize = (18,10)) plt.plot(history2.history['loss'],label='Training Loss',color='b') plt.plot(history2.history['val_loss'],label='Validation-loss',color='g') plt.xlabel("Iteration") plt.ylabel("Loss") plt.title("LOSS" + str(symbol)) plt.legend() plt.savefig(str(symbol)+str(optional)+'2.png') #show actual vs predicted (training) graph plt.figure(figsize=(18,10)) plt.plot(scaler2.inverse_transform(plot_y_train2),color = 'b', label = 'Original') plt.plot(scaler2.inverse_transform(train_predict2),color='red', label = 'Predicted') plt.title("Prediction Graph Using Training Data" + str(symbol)) plt.xlabel("Hours") plt.ylabel("Price") plt.legend() plt.savefig(str(symbol)+str(optional)+'3.png') #show actual vs predicted (testing) graph plt.figure(figsize=(18,10)) plt.plot(scaler2.inverse_transform(plot_y_test2),color = 'b', label = 'Original') plt.plot(scaler2.inverse_transform(test_predict2),color='g', label = 'Predicted') plt.title("Prediction Graph Using Testing Data" + str(symbol)) plt.xlabel("Hours") plt.ylabel("Price") plt.legend() plt.savefig(str(symbol)+str(optional)+'4.png') ############################################################################################## JPYUSD # python libraries import MetaTrader5 as mt5 import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import pandas as pd import tf2onnx # input parameters inp_history_size = 120 sample_size = sample_size1 symbol = symbol3 optional = optional inp_model_name = str(symbol)+"_"+str(optional)+".onnx" if not mt5.initialize(): print("initialize() failed, error code =",mt5.last_error()) quit() # we will save generated onnx-file near our script to use as resource from sys import argv data_path=argv[0] last_index=data_path.rfind("\\")+1 data_path=data_path[0:last_index] print("data path to save onnx model",data_path) # and save to MQL5\Files folder to use as file terminal_info=mt5.terminal_info() file_path=terminal_info.data_path+"\\MQL5\\Files\\" print("file path to save onnx model",file_path) # set start and end dates for history data from datetime import timedelta, datetime #end_date = datetime.now() #end_date = datetime(2024, 5, 1, 0) start_date = end_date - timedelta(days=inp_history_size*20) # print start and end dates print("data start date =",start_date) print("data end date =",end_date) # get rates eurusd_rates3 = mt5.copy_rates_from(symbol, timeframe , end_date, sample_size) # create dataframe df3=pd.DataFrame() df3 = pd.DataFrame(eurusd_rates3) print(df3) # Extraer los precios de cierre directamente datas3 = df3['close'].values """# Calcular la inversa de cada valor inverted_data = 1 / datas # Convertir los datos invertidos a un array de numpy si es necesario data = inverted_data.values""" data3 = datas3.reshape(-1,1) # Imprimir los resultados """data = datas""" # scale data from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler scaler3=MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0,1)) scaled_data3 = scaler3.fit_transform(data3) # training size is 80% of the data training_size3 = int(len(scaled_data3)*0.80) print("Training_size:",training_size3) train_data_initial3 = scaled_data3[0:training_size3,:] test_data_initial3 = scaled_data3[training_size3:,:1] # split a univariate sequence into samples def split_sequence(sequence, n_steps): X, y = list(), list() for i in range(len(sequence)): # find the end of this pattern end_ix = i + n_steps # check if we are beyond the sequence if end_ix > len(sequence)-1: break # gather input and output parts of the pattern seq_x, seq_y = sequence[i:end_ix], sequence[end_ix] X.append(seq_x) y.append(seq_y) return np.array(X), np.array(y) # split into samples time_step = inp_history_size x_train3, y_train3 = split_sequence(train_data_initial3, time_step) x_test3, y_test3 = split_sequence(test_data_initial3, time_step) # reshape input to be [samples, time steps, features] which is required for LSTM x_train3 =x_train3.reshape(x_train3.shape[0],x_train3.shape[1],1) x_test3 = x_test3.reshape(x_test3.shape[0],x_test3.shape[1],1) # define model from keras.models import Sequential from keras.layers import Dense, Activation, Conv1D, MaxPooling1D, Dropout, Flatten, LSTM from keras.metrics import RootMeanSquaredError as rmse from tensorflow.keras import callbacks model = Sequential() model.add(Conv1D(filters=256, kernel_size=2, activation='relu',padding = 'same',input_shape=(inp_history_size,1))) model.add(MaxPooling1D(pool_size=2)) model.add(LSTM(100, return_sequences = True)) model.add(Dropout(0.3)) model.add(LSTM(100, return_sequences = False)) model.add(Dropout(0.3)) model.add(Dense(units=1, activation = 'sigmoid')) model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss= 'mse' , metrics = [rmse()]) # Set up early stopping early_stopping = callbacks.EarlyStopping( monitor='val_loss', patience=5, restore_best_weights=True, ) # model training for 300 epochs history3 = model.fit(x_train3, y_train3, epochs = 300 , validation_data = (x_test3,y_test3), batch_size=32, callbacks=[early_stopping], verbose=2) # evaluate training data train_loss3, train_rmse3 = model.evaluate(x_train3,y_train3, batch_size = 32) print(f"train_loss={train_loss3:.3f}") print(f"train_rmse={train_rmse3:.3f}") # evaluate testing data test_loss3, test_rmse3 = model.evaluate(x_test3,y_test3, batch_size = 32) print(f"test_loss={test_loss3:.3f}") print(f"test_rmse={test_rmse3:.3f}") # save model to ONNX output_path = data_path+inp_model_name onnx_model = tf2onnx.convert.from_keras(model, output_path=output_path) print(f"saved model to {output_path}") output_path = file_path+inp_model_name onnx_model = tf2onnx.convert.from_keras(model, output_path=output_path) print(f"saved model to {output_path}") # finish mt5.shutdown() #prediction using testing data #prediction using testing data test_predict3 = model.predict(x_test3) print(test_predict3) print("longitud total de la prediccion: ", len(test_predict3)) print("longitud total del sample: ", sample_size) plot_y_test3 = np.array(y_test3).reshape(-1, 1) # Selecciona solo el último elemento de cada muestra de prueba plot_y_train3 = y_train3.reshape(-1,1) train_predict3 = model.predict(x_train3) #print(plot_y_test) #calculate metrics from sklearn import metrics from sklearn.metrics import r2_score #transform data to real values value13=scaler3.inverse_transform(plot_y_test3) #print(value1) # Escala las predicciones inversas al transformarlas a la escala original value23 = scaler3.inverse_transform(test_predict3.reshape(-1, 1)) #print(value2) #calc score score3 = np.sqrt(metrics.mean_squared_error(value13,value23)) print("RMSE : {}".format(score3)) print("MSE :", metrics.mean_squared_error(value13,value23)) print("R2 score :",metrics.r2_score(value13,value23)) #sumarize model model.summary() #Print error value113=pd.DataFrame(value13) value223=pd.DataFrame(value23) #print(value11) #print(value22) value1113=value113.iloc[:,:] value2223=value223.iloc[:,:] print("longitud salida (tandas de 1 hora): ",len(value1113) ) #print("en horas son " + str((len(value1113))*60*24)+ " minutos") print("en horas son " + str(((len(value1113)))/60)+ " horas") print("en horas son " + str(((len(value1113)))/60/24)+ " dias") # Calculate error error3 = value1113 - value2223 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Plot error plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) plt.scatter(range(len(error3)), error3, color='blue', label='Error') plt.axhline(y=0, color='red', linestyle='--', linewidth=1) # Línea horizontal en y=0 plt.title('Error de Predicción ' + str(symbol)) plt.xlabel('Índice de la muestra') plt.ylabel('Error') plt.legend() plt.grid(True) plt.savefig(str(symbol)+str(optional)+'.png') rmse_3 = format(score3) mse_3 = metrics.mean_squared_error(value13,value23) r2_3 = metrics.r2_score(value13,value23) resultados3= [rmse_3,mse_3,r2_3] # Abre un archivo en modo escritura with open(str(symbol)+str(optional)+"results.txt", "w") as archivo: # Escribe cada resultado en una línea separada for resultado in resultados3: archivo.write(str(resultado) + "\n") # finish mt5.shutdown() #show iteration-rmse graph for training and validation plt.figure(figsize = (18,10)) plt.plot(history3.history['root_mean_squared_error'],label='Training RMSE',color='b') plt.plot(history3.history['val_root_mean_squared_error'],label='Validation-RMSE',color='g') plt.xlabel("Iteration") plt.ylabel("RMSE") plt.title("RMSE" + str(symbol)) plt.legend() plt.savefig(str(symbol)+str(optional)+'1.png') #show iteration-loss graph for training and validation plt.figure(figsize = (18,10)) plt.plot(history3.history['loss'],label='Training Loss',color='b') plt.plot(history3.history['val_loss'],label='Validation-loss',color='g') plt.xlabel("Iteration") plt.ylabel("Loss") plt.title("LOSS" + str(symbol)) plt.legend() plt.savefig(str(symbol)+str(optional)+'2.png') #show actual vs predicted (training) graph plt.figure(figsize=(18,10)) plt.plot(scaler3.inverse_transform(plot_y_train3),color = 'b', label = 'Original') plt.plot(scaler3.inverse_transform(train_predict3),color='red', label = 'Predicted') plt.title("Prediction Graph Using Training Data" + str(symbol)) plt.xlabel("Hours") plt.ylabel("Price") plt.legend() plt.savefig(str(symbol)+str(optional)+'3.png') #show actual vs predicted (testing) graph plt.figure(figsize=(18,10)) plt.plot(scaler3.inverse_transform(plot_y_test3),color = 'b', label = 'Original') plt.plot(scaler3.inverse_transform(test_predict3),color='g', label = 'Predicted') plt.title("Prediction Graph Using Testing Data" + str(symbol)) plt.xlabel("Hours") plt.ylabel("Price") plt.legend() plt.savefig(str(symbol)+str(optional)+'4.png') ################################################################################################ ############################################################################################## """ import onnxruntime as ort import numpy as np # Cargar el modelo ONNX sesion = ort.InferenceSession("EURUSD_M1_inverse_test.onnx") # Obtener el nombre de la entrada y la salida del modelo input_name = sesion.get_inputs()[0].name output_name = sesion.get_outputs()[0].name # Crear datos de entrada de prueba como un array de numpy # Asegúrate de que los datos de entrada coincidan con la forma y el tipo esperado por el modelo input_data = [1,120] #np.random.rand(1, 10).astype(np.float32) # Ejemplo: entrada de tamaño [1, 10] # Realizar la inferencia result = sesion.run([output_name], {input_name: input_data}) # Imprimir el resultado print(result) """
这个.py脚本将会生成三个ONNX模型,以及一些图表和数据,便于您检查一切是否正常。
数据来源于一个txt文件,每个数字分别代表RMSE(均方根误差)、MSE(均方误差)和R2(决定系数)。
在运行此脚本之前,您必须设置品种、样本量、时间范围和结束日期(从结束日期往前计算周期数)。
可选变量是一个字符串,您可以在其中添加一些内容,如M1 Ticks或结束日期(end_date)...任何您想要用于保存ONNX文件、图表和数据的内容。
symbol1 = "EURGBP" symbol2 = "GBPUSD" symbol3 = "EURUSD" sample_size1 = 200000 optional = "_M1_test" timeframe = mt5.TIMEFRAME_M1 #end_date = datetime.now() end_date = datetime(2024, 3, 4, 0)
如果要在策略测试器中进行测试,请根据需要修改日期。如果想要进行交易,您只需要使用end_date。
end_date = datetime.now() ***如果您在使用零点差账户进行交易,您可以尝试使用最小价格变动(Ticks)而不是周期(Periods),您只需要更改以下设置:***
eurusd_rates = mt5.copy_rates_from(symbol, timeframe , end_date, sample_size)
以及这一项:
eurusd_rates = mt5.copy_ticks_from(symbol, end_date, sample_size, mt5.COPY_TICKS_ALL)
这里您会获得Bid(买入价)和Ask(卖出价)的最小价格变动(Ticks)数据。我认为Ticks的数量是有限制的。如果您需要更多Ticks数据,您可以使用这个方法从品种下载所有的Ticks: 从品种下载所有数据 是免费的。
要运行这个.py文件,您只需用VSC打开它,并点击‘运行’->‘无调试运行’(同时确保MetaTrader 5已经打开)。然后等待它运行完成。
您最终会获得一些图表、文本文件和ONNX文件。您需要将ONNX文件保存在MQL5/Files文件夹中,并在EA代码中指定相同的路径。
依靠代码中的这一行完成了这项工作。
# and save to MQL5\Files folder to use as file terminal_info=mt5.terminal_info() file_path=terminal_info.data_path+"\\MQL5\\Files\\" print("file path to save onnx model",file_path)
请注意,如果您希望在其他文件夹中存储更多ONNX文件,则必须指定路径。
.py导出的图像如下:
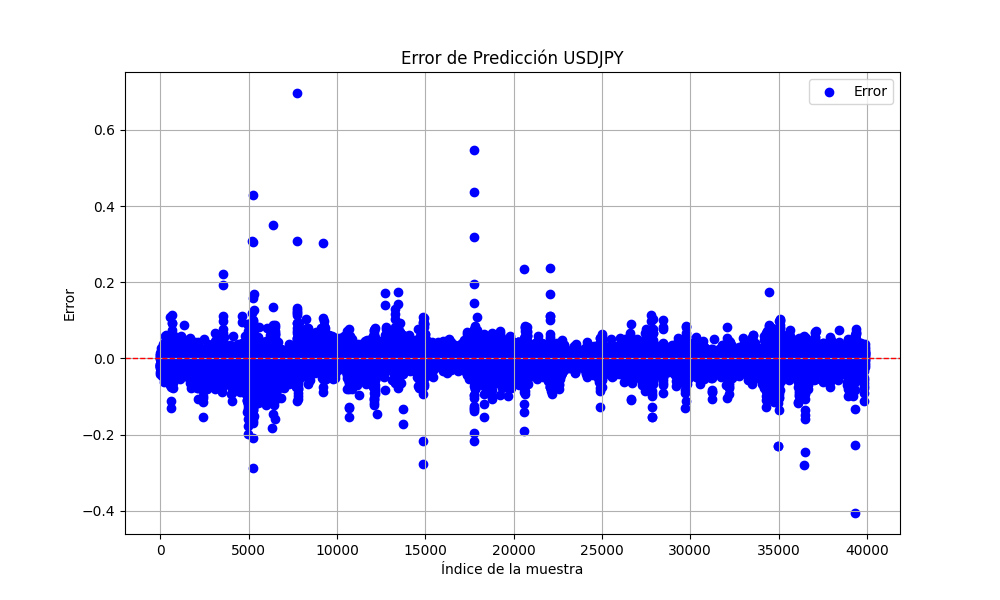
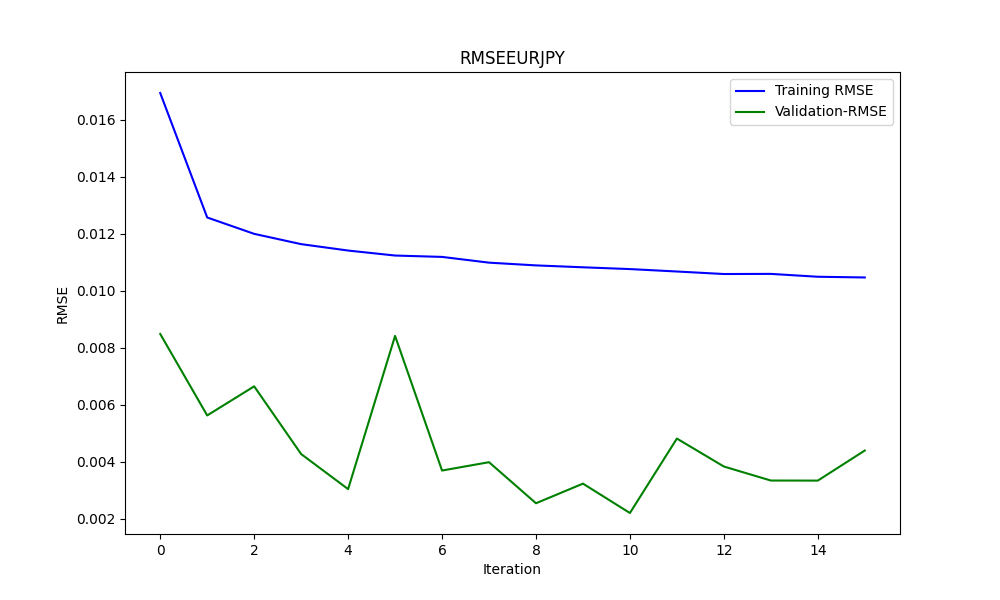
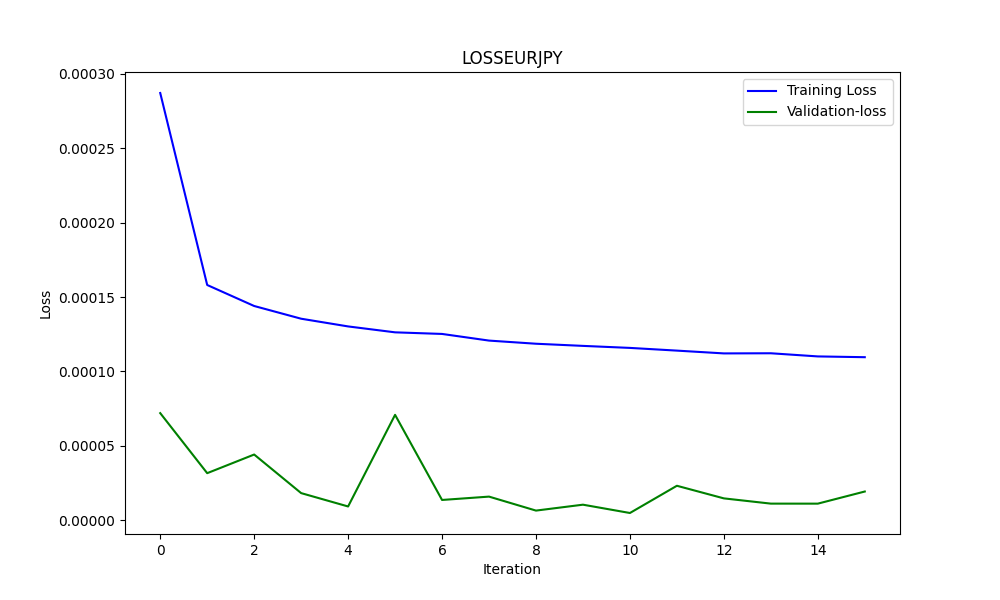
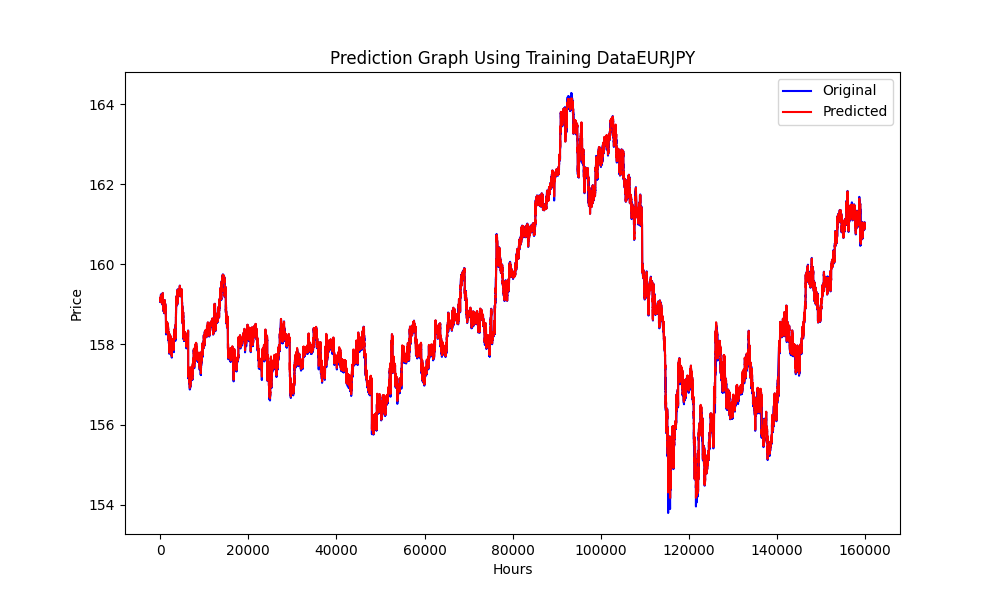
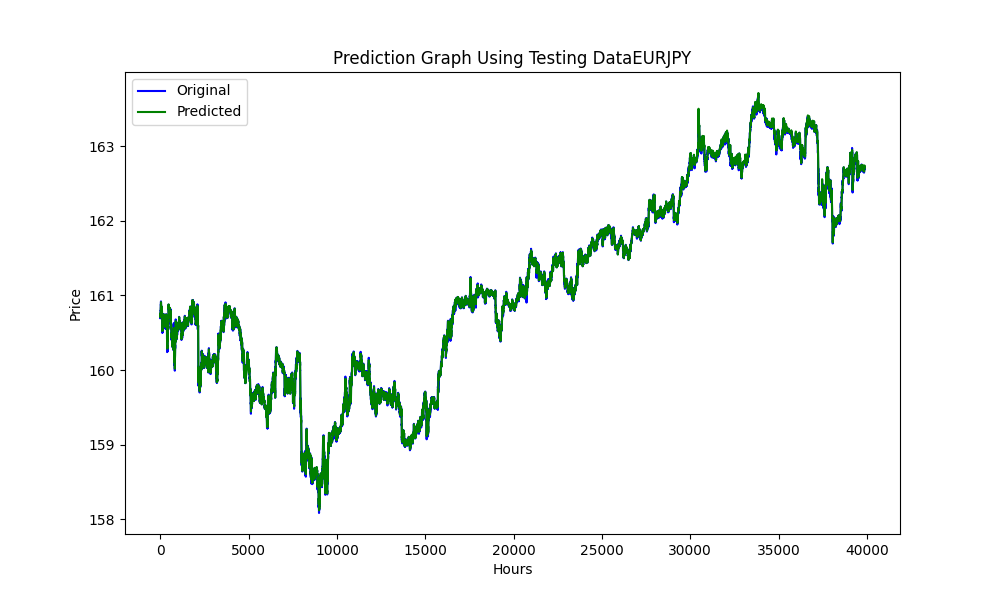
此图展示了RMSE、MSE和R2值
0.023019903957086384 0.0005299159781934813 0.999707563612641
基于以上信息,我们可以判断模型是否存在过拟合或欠拟合的情况。
在这种情况下:
均方根误差(RMSE)是用于衡量残差(即预测误差)的标准差。残差表示数据点与回归线之间的距离;而RMSE则反映了这些残差分布的离散程度。换句话说,RMSE值反映数据点围绕最佳拟合线的密集程度。
RMSE值越小,表示拟合度越高。如果得出的RMSE值非常小,这表明模型与数据集的拟合度非常高。
均方误差(MSE)与均方根误差(RMSE)类似,但在求平均值之前先对误差进行平方,这样做会给予较大误差更高的权重。它是衡量估测值质量的另一种指标——它始终为非负数,且越接近零的值表示越好。
非常小的MSE值进一步证实了模型预测值与实际数据点非常接近。
R2是一种统计量,代表在回归模型中,与一个或多个自变量相关的因变量的方差比例。当𝑅2值为1时,表示回归预测完美地拟合了数据。
我们的R2值非常接近1,这表明您的模型覆盖了均值周围几乎所有的变化,这是非常好的。
综上所述,这些指标表明您的模型在预测或拟合数据集方面表现得异常出色。
为了判断模型是否过拟合,我们使用图表,比如在这个案例中的第二张图表。
以下是基于图表的分析:
-
训练损失(蓝色线):
- 这条线最初显示急剧下降,表明模型正在快速从训练数据集中进行学习。随着迭代的进行,训练损失继续下降,但速度变慢,这是很正常的,因为模型开始收敛到最小值。
-
验证损失(绿色线):
- 在整个训练过程中,验证损失一直保持极低且相对稳定。这表明模型具有很好的泛化能力,而不仅仅是记忆训练数据。小幅波动表明验证集性能在迭代之间存在变化,但始终保持在一个非常狭窄的范围内。
总体而言,该图表展示了一个非常成功的训练过程,具有出色的收敛性和泛化能力。较低的验证损失表明模型在未见数据上表现良好,假设验证集能够覆盖一般问题的领域。
完成所有这些后,我们将其传递给EA。
具有预测功能的三角套利EA
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| ONNX_Triangular EURUSD-USDJPY-EURJPY.mq5| //| Copyright 2024, Javier S. Gastón de Iriarte Cabrera. | //| https://www.mql5.com/en/users/jsgaston/news | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2024, Javier S. Gastón de Iriarte Cabrera." #property link "https://www.mql5.com/en/users/jsgaston/news" #property version "1.04" #property strict #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> #define MAGIC (965334) #resource "/Files/art/arbitrage triangular/eurusdjpy/EURUSD__M1_test.onnx" as uchar ExtModel[] #resource "/Files/art/arbitrage triangular/eurusdjpy/USDJPY__M1_test.onnx" as uchar ExtModel2[] #resource "/Files/art/arbitrage triangular/eurusdjpy/EURJPY__M1_test.onnx" as uchar ExtModel3[] CTrade ExtTrade; #define SAMPLE_SIZE 120 input double lotSize = 3.0; //input double slippage = 3; // Add these inputs to allow dynamic control over SL and TP distances input double StopLossPips = 50.0; // Stop Loss in pips input double TakeProfitPips = 100.0; // Take Profit in pips //input double maxSpreadPoints = 10.0; input ENUM_TIMEFRAMES Periodo = PERIOD_CURRENT; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string symbol1 = Symbol(); input string symbol2 = "USDJPY"; input string symbol3 = "EURJPY"; int ticket1 = 0; int ticket2 = 0; int ticket3 = 0; int ticket11 = 0; int ticket22 = 0; int ticket33 = 0; input bool isArbitrageActive = true; double spreads[1000]; // Array para almacenar hasta 1000 spreads int spreadIndex = 0; // Índice para el próximo spread a almacenar long ExtHandle=INVALID_HANDLE; //int ExtPredictedClass=-1; datetime ExtNextBar=0; datetime ExtNextDay=0; float ExtMin=0.0; float ExtMax=0.0; long ExtHandle2=INVALID_HANDLE; //int ExtPredictedClass=-1; datetime ExtNextBar2=0; datetime ExtNextDay2=0; float ExtMin2=0.0; float ExtMax2=0.0; long ExtHandle3=INVALID_HANDLE; //int ExtPredictedClass=-1; datetime ExtNextBar3=0; datetime ExtNextDay3=0; float ExtMin3=0.0; float ExtMax3=0.0; float predicted=0.0; float predicted2=0.0; float predicted3=0.0; float predicted2i=0.0; float predicted3i=0.0; float lastPredicted1=0.0; float lastPredicted2=0.0; float lastPredicted3=0.0; float lastPredicted2i=0.0; float lastPredicted3i=0.0; int Order=0; input double targetProfit = 100.0; // Eur benefit goal input double maxLoss = -50.0; // Eur max loss input double perVar = 0.005; // Percentage of variation to make orders ulong tickets[6]; // Array para almacenar los tickets de las órdenes double sl=0.0; double tp=0.0; int Abrir = 0; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { ExtTrade.SetExpertMagicNumber(MAGIC); Print("EA de arbitraje ONNX iniciado"); //--- create a model from static buffer ExtHandle=OnnxCreateFromBuffer(ExtModel,ONNX_DEFAULT); if(ExtHandle==INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("OnnxCreateFromBuffer error ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- since not all sizes defined in the input tensor we must set them explicitly //--- first index - batch size, second index - series size, third index - number of series (only Close) const long input_shape[] = {1,SAMPLE_SIZE,1}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(ExtHandle,ONNX_DEFAULT,input_shape)) { Print("OnnxSetInputShape error ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- since not all sizes defined in the output tensor we must set them explicitly //--- first index - batch size, must match the batch size of the input tensor //--- second index - number of predicted prices (we only predict Close) const long output_shape[] = {1,1}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(ExtHandle,0,output_shape)) { Print("OnnxSetOutputShape error ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //--- create a model from static buffer ExtHandle2=OnnxCreateFromBuffer(ExtModel2,ONNX_DEFAULT); if(ExtHandle2==INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("OnnxCreateFromBuffer error ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- since not all sizes defined in the input tensor we must set them explicitly //--- first index - batch size, second index - series size, third index - number of series (only Close) const long input_shape2[] = {1,SAMPLE_SIZE,1}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(ExtHandle2,ONNX_DEFAULT,input_shape2)) { Print("OnnxSetInputShape error ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- since not all sizes defined in the output tensor we must set them explicitly //--- first index - batch size, must match the batch size of the input tensor //--- second index - number of predicted prices (we only predict Close) const long output_shape2[] = {1,1}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(ExtHandle2,0,output_shape2)) { Print("OnnxSetOutputShape error ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //--- create a model from static buffer ExtHandle3=OnnxCreateFromBuffer(ExtModel3,ONNX_DEFAULT); if(ExtHandle3==INVALID_HANDLE) { Print("OnnxCreateFromBuffer error ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- since not all sizes defined in the input tensor we must set them explicitly //--- first index - batch size, second index - series size, third index - number of series (only Close) const long input_shape3[] = {1,SAMPLE_SIZE,1}; if(!OnnxSetInputShape(ExtHandle3,ONNX_DEFAULT,input_shape3)) { Print("OnnxSetInputShape error ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } //--- since not all sizes defined in the output tensor we must set them explicitly //--- first index - batch size, must match the batch size of the input tensor //--- second index - number of predicted prices (we only predict Close) const long output_shape3[] = {1,1}; if(!OnnxSetOutputShape(ExtHandle3,0,output_shape3)) { Print("OnnxSetOutputShape error ",GetLastError()); return(INIT_FAILED); } return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { if(ExtHandle!=INVALID_HANDLE) { OnnxRelease(ExtHandle); ExtHandle=INVALID_HANDLE; } if(ExtHandle2!=INVALID_HANDLE) { OnnxRelease(ExtHandle2); ExtHandle2=INVALID_HANDLE; } if(ExtHandle3!=INVALID_HANDLE) { OnnxRelease(ExtHandle3); ExtHandle3=INVALID_HANDLE; } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { SymbolProcessor processor; // Crear instancia de SymbolProcessor string A = processor.GetFirstThree(symbol1); string B = processor.GetLastThree(symbol1); string C = processor.GetFirstThree(symbol2); string D = processor.GetLastThree(symbol2); string E = processor.GetFirstThree(symbol3); string F = processor.GetLastThree(symbol3); if((A != E) || (B != C) || (D != F)) { Print("Wrongly selected symbols"); return; } //--- check new day if(TimeCurrent()>=ExtNextDay) { GetMinMax(); GetMinMax2(); GetMinMax3(); //--- set next day time ExtNextDay=TimeCurrent(); ExtNextDay-=ExtNextDay%PeriodSeconds(Periodo); ExtNextDay+=PeriodSeconds(Periodo); } //--- check new bar if(TimeCurrent()<ExtNextBar) { return; } //--- set next bar time ExtNextBar=TimeCurrent(); ExtNextBar-=ExtNextBar%PeriodSeconds(); ExtNextBar+=PeriodSeconds(); //--- check min and max float close=(float)iClose(symbol1,Periodo,0); if(ExtMin>close) ExtMin=close; if(ExtMax<close) ExtMax=close; float close2=(float)iClose(symbol2,Periodo,0); if(ExtMin2>close2) ExtMin2=close2; if(ExtMax2<close2) ExtMax2=close2; float close3=(float)iClose(symbol3,Periodo,0); if(ExtMin3>close3) ExtMin3=close3; if(ExtMax3<close3) ExtMax3=close3; lastPredicted1=predicted; lastPredicted2=predicted2; lastPredicted3=predicted3; lastPredicted2i=predicted2i; lastPredicted3i=predicted3i; //--- predict next price PredictPrice(); PredictPrice2(); PredictPrice3(); /* */ double price1 = SymbolInfoDouble(symbol1, SYMBOL_BID);///////////////// double price2 = SymbolInfoDouble(symbol2, SYMBOL_BID); double price2i = 1/price2; double price3 = SymbolInfoDouble(symbol3, SYMBOL_ASK); double price3i = 1/price3; double price11 = SymbolInfoDouble(symbol1, SYMBOL_ASK);///////////////// double price22 = SymbolInfoDouble(symbol2, SYMBOL_ASK); double price22i = 1/price22; double price33 = SymbolInfoDouble(symbol3, SYMBOL_BID); double price33i = 1/price33; predicted2i = 1/predicted2; predicted3i = 1/predicted3; //double lotSize = 1.0; // Lote base double lotSize2 = lotSize * predicted / predicted2; /// tengo dudas con usar el invertido o no invertido double lotSize3 = lotSize * predicted / predicted3; double lotSize22 = lotSize * predicted / predicted2; /// tengo dudas con usar el invertido o no invertido double lotSize33 = lotSize * predicted / predicted3; // Redondear lotes a un múltiplo aceptable por tu bróker lotSize2 = NormalizeDouble(lotSize2, 2); // Asume 2 decimales para lotes lotSize3 = NormalizeDouble(lotSize3, 2); lotSize22 = NormalizeDouble(lotSize22, 2); // Asume 2 decimales para lotes lotSize33 = NormalizeDouble(lotSize33, 2); int totalPositions = PositionsTotal(); if(Order==1 || Order==2) { // Verificar y cerrar órdenes si se cumplen las condiciones Print("Verificar y cerrar órdenes si se cumplen las condiciones"); CheckAndCloseOrders(); } if(!isArbitrageActive || ArePositionsOpen()) { Print("Arbitraje inactivo o ya hay posiciones abiertas."); return; } double varia11 = 100.0 - (close*100/predicted); double varia21 = 100.0 - (close2*100/predicted2); double varia31 = 100.0 - (predicted3*100/close3); double varia12 = 100.0 - (predicted*100/close); double varia22 = 100.0 - (predicted2*100/close2); double varia32 = 100.0 - (close3*100/predicted3); if((varia11 > perVar) && (varia21 > perVar) && (varia31 > perVar)) { Print("se debería proceder a apertura de ordenes de derechas"); Abrir = 1; } if((varia12 > perVar) && (varia22 > perVar) && (varia32 > perVar)) { Print("se debería proceder a apertura de ordenes de izquierdas"); Abrir = 2; } if(Abrir == 1 && (predicted*predicted2*predicted3i>1)) { Print("orden derecha"); // Inicia el arbitraje si aún no está activo if(isArbitrageActive) { if((ticket1 == 0 && ticket2 == 0 && ticket3 ==0) && (Order==0) && totalPositions ==0) { Print("Preparando para abrir órdenes"); Order = 1; MqlTradeRequest request; MqlTradeResult result; { MqlRates rates[]; ArraySetAsSeries(rates,true); int copied=CopyRates(symbol1,0,0,1,rates); CalculateSL(true,rates[0].close,symbol1); CalculateTP(true,rates[0].close,symbol1); if(ExtTrade.Buy(lotSize, symbol1, rates[0].close, sl, tp, "Arbitraje")) { tickets[0] = ExtTrade.ResultDeal(); // Getting the ticket of the last trade Print("Order placed with ticket: ", tickets[0]); } else { Print("Failed to place order: ", GetLastError()); } } { MqlRates rates[]; ArraySetAsSeries(rates,true); int copied=CopyRates(symbol2,0,0,1,rates); CalculateSL(true,rates[0].close,symbol2); CalculateTP(true,rates[0].close,symbol2); if(ExtTrade.Buy(lotSize2, symbol2, rates[0].close, sl, tp, "Arbitraje")) { tickets[1] = ExtTrade.ResultDeal(); // Getting the ticket of the last trade Print("Order placed with ticket: ", tickets[1]); } else { Print("Failed to place order: ", GetLastError()); } } { MqlRates rates[]; ArraySetAsSeries(rates,true); int copied=CopyRates(symbol3,0,0,1,rates); CalculateSL(false,rates[0].close,symbol3); CalculateTP(false,rates[0].close,symbol3); if(ExtTrade.Sell(lotSize3, symbol3, rates[0].close, sl, tp, "Arbitraje")) { tickets[2] = ExtTrade.ResultDeal(); // Getting the ticket of the last trade Print("Order placed with ticket: ", tickets[2]); } else { Print("Failed to place order: ", GetLastError()); } } ticket1=1; ticket2=1; ticket3=1; Abrir=0; return; } else { Print(" no se puede abrir ordenes"); } } } if(Abrir == 2 && (predicted*predicted2*predicted3i<1)) { Print("Orden Inversa"); // Inicia el arbitraje si aún no está activo if(isArbitrageActive) { if((ticket11 == 0 && ticket22 == 0 && ticket33 ==0) && (Order==0) && totalPositions==0) { Print("Preparando para abrir órdenes"); Order = 2; MqlTradeRequest request; MqlTradeResult result; { MqlRates rates[]; ArraySetAsSeries(rates,true); int copied=CopyRates(symbol1,0,0,1,rates); CalculateSL(false,rates[0].close,symbol1); CalculateTP(false,rates[0].close,symbol1); if(ExtTrade.Sell(lotSize, symbol1, rates[0].close, sl, tp, "Arbitraje")) { tickets[3] = ExtTrade.ResultDeal(); // Getting the ticket of the last trade Print("Order placed with ticket: ", tickets[3]); } else { Print("Failed to place order: ", GetLastError()); } } { MqlRates rates[]; ArraySetAsSeries(rates,true); int copied=CopyRates(symbol2,0,0,1,rates); CalculateSL(false,rates[0].close,symbol2); CalculateTP(false,rates[0].close,symbol2); if(ExtTrade.Sell(lotSize2, symbol2, rates[0].close, sl, tp, "Arbitraje")) { tickets[4] = ExtTrade.ResultDeal(); // Getting the ticket of the last trade Print("Order placed with ticket: ", tickets[4]); } else { Print("Failed to place order: ", GetLastError()); } } { MqlRates rates[]; ArraySetAsSeries(rates,true); int copied=CopyRates(symbol3,0,0,1,rates); CalculateSL(true,rates[0].close,symbol3); CalculateTP(true,rates[0].close,symbol3); if(ExtTrade.Buy(lotSize3, symbol3, rates[0].close, sl, tp, "Arbitraje")) { tickets[5] = ExtTrade.ResultDeal(); // Getting the ticket of the last trade Print("Order placed with ticket: ", tickets[5]); } else { Print("Failed to place order: ", GetLastError()); } } ticket11=1; ticket22=1; ticket33=1; Abrir=0; return; } else { Print(" no se puede abrir ordenes"); } } } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Postions are open function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool ArePositionsOpen() { // Check for positions on symbol1 if(PositionSelect(symbol1) && PositionGetDouble(POSITION_VOLUME) > 0) return true; // Check for positions on symbol2 if(PositionSelect(symbol2) && PositionGetDouble(POSITION_VOLUME) > 0) return true; // Check for positions on symbol3 if(PositionSelect(symbol3) && PositionGetDouble(POSITION_VOLUME) > 0) return true; return false; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Price prediction function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void PredictPrice(void) { static vectorf output_data(1); // vector to get result static vectorf x_norm(SAMPLE_SIZE); // vector for prices normalize //--- check for normalization possibility if(ExtMin>=ExtMax) { Print("ExtMin>=ExtMax"); //ExtPredictedClass=-1; return; } //--- request last bars if(!x_norm.CopyRates(_Symbol,Periodo,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,1,SAMPLE_SIZE)) { Print("CopyRates ",x_norm.Size()); //ExtPredictedClass=-1; return; } float last_close=x_norm[SAMPLE_SIZE-1]; //--- normalize prices x_norm-=ExtMin; x_norm/=(ExtMax-ExtMin); //--- run the inference if(!OnnxRun(ExtHandle,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,x_norm,output_data)) { Print("OnnxRun"); //ExtPredictedClass=-1; return; } //--- denormalize the price from the output value predicted=output_data[0]*(ExtMax-ExtMin)+ExtMin; //return predicted; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Price prediction function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void PredictPrice2(void) { static vectorf output_data2(1); // vector to get result static vectorf x_norm2(SAMPLE_SIZE); // vector for prices normalize //--- check for normalization possibility if(ExtMin2>=ExtMax2) { Print("ExtMin2>=ExtMax2"); //ExtPredictedClass=-1; return; } //--- request last bars if(!x_norm2.CopyRates(symbol2,Periodo,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,1,SAMPLE_SIZE)) { Print("CopyRates ",x_norm2.Size()); //ExtPredictedClass=-1; return; } float last_close2=x_norm2[SAMPLE_SIZE-1]; //--- normalize prices x_norm2-=ExtMin2; x_norm2/=(ExtMax2-ExtMin2); //--- run the inference if(!OnnxRun(ExtHandle2,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,x_norm2,output_data2)) { Print("OnnxRun"); //ExtPredictedClass=-1; return; } //--- denormalize the price from the output value predicted2=output_data2[0]*(ExtMax2-ExtMin2)+ExtMin2; //--- classify predicted price movement //return predicted2; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Price prediction function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void PredictPrice3(void) { static vectorf output_data3(1); // vector to get result static vectorf x_norm3(SAMPLE_SIZE); // vector for prices normalize //--- check for normalization possibility if(ExtMin3>=ExtMax3) { Print("ExtMin3>=ExtMax3"); //ExtPredictedClass=-1; return; } //--- request last bars if(!x_norm3.CopyRates(symbol3,Periodo,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,1,SAMPLE_SIZE)) { Print("CopyRates ",x_norm3.Size()); //ExtPredictedClass=-1; return; } float last_close3=x_norm3[SAMPLE_SIZE-1]; //--- normalize prices x_norm3-=ExtMin3; x_norm3/=(ExtMax3-ExtMin3); //--- run the inference if(!OnnxRun(ExtHandle3,ONNX_NO_CONVERSION,x_norm3,output_data3)) { Print("OnnxRun"); //ExtPredictedClass=-1; return; } //--- denormalize the price from the output value predicted3=output_data3[0]*(ExtMax3-ExtMin3)+ExtMin3; //--- classify predicted price movement //return predicted2; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Get minimal and maximal Close for last 120 values | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void GetMinMax(void) { vectorf closeMN; closeMN.CopyRates(symbol1,Periodo,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,0,SAMPLE_SIZE); ExtMin=closeMN.Min(); ExtMax=closeMN.Max(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Get minimal and maximal Close for last 120 values | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void GetMinMax2(void) { vectorf closeMN2; closeMN2.CopyRates(symbol2,Periodo,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,0,SAMPLE_SIZE); ExtMin2=closeMN2.Min(); ExtMax2=closeMN2.Max(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Get minimal and maximal Close for last 120 values | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void GetMinMax3(void) { vectorf closeMN3; closeMN3.CopyRates(symbol3,Periodo,COPY_RATES_CLOSE,0,SAMPLE_SIZE); ExtMin3=closeMN3.Min(); ExtMax3=closeMN3.Max(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Symbols class returns both pairs of a symbol | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class SymbolProcessor { public: // Método para obtener los primeros tres caracteres de un símbolo dado string GetFirstThree(string symbol) { return StringSubstr(symbol, 0, 3); } // Método para obtener los últimos tres caracteres de un símbolo dado string GetLastThree(string symbol) { if(StringLen(symbol) >= 3) return StringSubstr(symbol, StringLen(symbol) - 3, 3); else return ""; // Retorna un string vacío si el símbolo es demasiado corto } }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Calculate total profit from all open positions for the current symbol //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CalculateCurrentArbitrageProfit() { double totalProfit = 0.0; int totalPositions = PositionsTotal(); // Get the total number of open positions // Loop through all open positions for(int i = 0; i < totalPositions; i++) { // Get the ticket of the position at index i ulong ticket = PositionGetTicket(i); if(PositionSelectByTicket(ticket)) // Select the position by its ticket { // Add the profit of the current position to the total profit totalProfit += PositionGetDouble(POSITION_PROFIT); //Print("totalProfit ", totalProfit); } } return totalProfit; // Return the total profit of all open positions } // Función para cerrar todas las órdenes void CloseAllOrders() { string symbols[] = {symbol1, symbol2, symbol3}; for(int i = 0; i < ArraySize(symbols); i++) { if(ExtTrade.PositionClose(symbols[i], 3)) Print("Posición cerrada correctamente para ", symbols[i]); else Print("Error al cerrar posición para ", symbols[i], ": Error", GetLastError()); } // Resetea tickets y ordenes ticket1 = 0; ticket2 = 0; ticket3 = 0; ticket11 = 0; ticket22 = 0; ticket33 = 0; Order = 0; Print("Todas las órdenes están cerradas"); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Check and close orders funcion | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // Función para verificar y cerrar órdenes void CheckAndCloseOrders() { double currentProfit = CalculateCurrentArbitrageProfit(); // Condiciones para cerrar las órdenes if((currentProfit >= targetProfit || currentProfit <= maxLoss)) { CloseAllOrders(); // Cierra todas las órdenes Print("Todas las órdenes cerradas. Beneficio/Pérdida actual: ", currentProfit); } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Get order volume function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double GetOrderVolume(int ticket) { if(PositionSelectByTicket(ticket)) { double volume = PositionGetDouble(POSITION_VOLUME); return volume; } else { Print("No se pudo seleccionar la posición con el ticket: ", ticket); return 0; // Retorna 0 si no se encuentra la posición } } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // Function to get the price and calculate SL dynamically double CalculateSL(bool isBuyOrder,double entryPrice,string simbolo) { double pointSize = SymbolInfoDouble(simbolo, SYMBOL_POINT); int digits = (int)SymbolInfoInteger(simbolo, SYMBOL_DIGITS); double pipSize = pointSize * 10; if(isBuyOrder) { sl = NormalizeDouble(entryPrice - StopLossPips * pipSize, digits); tp = NormalizeDouble(entryPrice + TakeProfitPips * pipSize, digits); } else { sl = NormalizeDouble(entryPrice + StopLossPips * pipSize, digits); tp = NormalizeDouble(entryPrice - TakeProfitPips * pipSize, digits); } return sl; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // Function to get the price and calculate TP dynamically double CalculateTP(bool isBuyOrder,double entryPrice, string simbolo) { double pointSize = SymbolInfoDouble(simbolo, SYMBOL_POINT); int digits = (int)SymbolInfoInteger(simbolo, SYMBOL_DIGITS); double pipSize = pointSize * 10; if(isBuyOrder) { sl = NormalizeDouble(entryPrice - StopLossPips * pipSize, digits); tp = NormalizeDouble(entryPrice + TakeProfitPips * pipSize, digits); } else { sl = NormalizeDouble(entryPrice + StopLossPips * pipSize, digits); tp = NormalizeDouble(entryPrice - TakeProfitPips * pipSize, digits); } return tp; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ // Function to handle errors and retry bool TryOrderSend(MqlTradeRequest &request, MqlTradeResult &result) { for(int attempts = 0; attempts < 5; attempts++) { if(OrderSend(request, result)) { return true; } else { Print("Failed to send order on attempt ", attempts + 1, ": Error ", GetLastError()); Sleep(1000); // Pause before retrying to avoid 'context busy' errors } } return false; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
有关EA的说明
策略
我们现在已经知道什么是三角套利,但是,我在代码中增加了一个预测值和实际收盘价之间的最小金额差异,这个差异是这两个值之间的百分比变化率,您可以自行输入来修改这个金额:
input double perVar = 0.005; // Percentage of variation to make orders
*** 请注意,在代码中包含这样的逻辑:***
EUR USD | EUR |^(-1)
---- x --- x | ---- |
USD JPY | JPY | 以上所有都符合这样的逻辑,所以如果您使用其他货币对,也都需要进行相应的修改。
我将附上另一个例子(EURUSD - GBPUSD - EURGBP),以便你能看到其中的变化。它使用以下逻辑:
EUR | GBP |^(-1) | EUR |^(-1)
---- x | --- | x | ---- |
USD | USD | | GBP | 整个策略基于这样一个逻辑:当您按照该逻辑进行乘法运算时,如果结果大于1,您可以朝右向(即增加价值的方向)进行乘法运算;如果结果小于1,则朝相反的左向(即减少价值的方向)进行运算。
然而,EA的策略是,我们不使用实际价格,而是使用预测价格。
这个逻辑意味着,如果您朝右向操作(即买入),就相当于在价格上进行了乘法运算(增加了价值)。如果您朝左向操作(即卖出),那就相当于进行了除法运算(减少了价值)。您可以在代码中观察到这些变化。
手数(lot sizes)必须根据最高价格来选择,这就是为什么在EUR-USD-JPY这样的货币对中,最小手数大约是2或3手。
关于手数的逻辑如下:
double lotSize2 = lotSize * predicted / predicted2; double lotSize3 = lotSize * predicted / predicted3;
这里predicted 代表 EURUSD 的预测价格,predicted2 代表 USDJPY 的预测价格,而 predicted3 代表 EURJPY 的预测价格。
在最后一部分,将手数(lot size)标准化以符合经纪商的要求。
lotSize2 = NormalizeDouble(lotSize2, 2); lotSize3 = NormalizeDouble(lotSize3, 2);
实例
在这个例子中,我们使用EUR-USD-JPY货币对。
使用以下逻辑
EUR USD | EUR |^(-1)
---- x --- x | ---- |
USD JPY | JPY | 我们将使用200,000分钟的时间跨度(样本量)进行训练和测试,直到4月3日。这将为我们提供大约17天的预测数据。
因此,在策略测试器中的测试将从4月3日开始,一直持续到当月的21日,并且我们将选择1分钟的时间周期。
对于首次测试,我们将使用以下输入参数和设置(请仔细检查货币对,因为它们将被添加到EA(OONX)中):
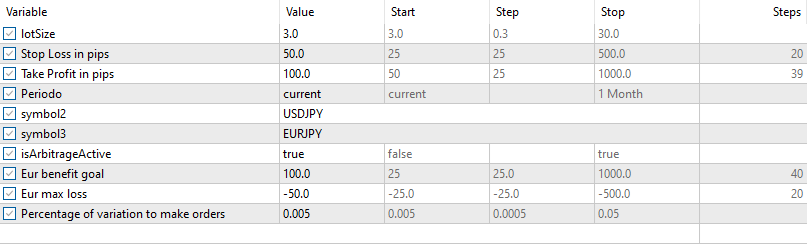
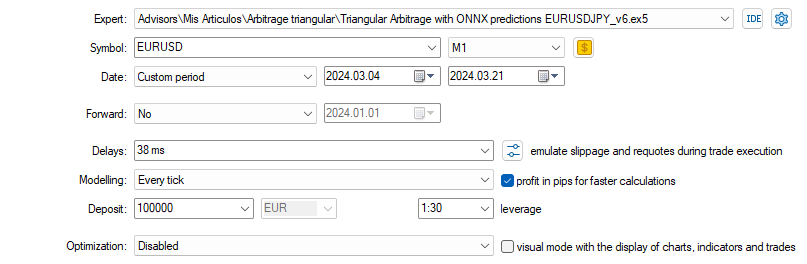
结果如下:
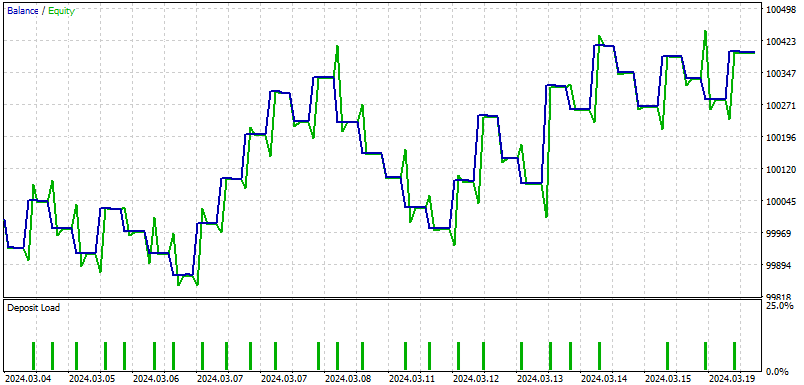
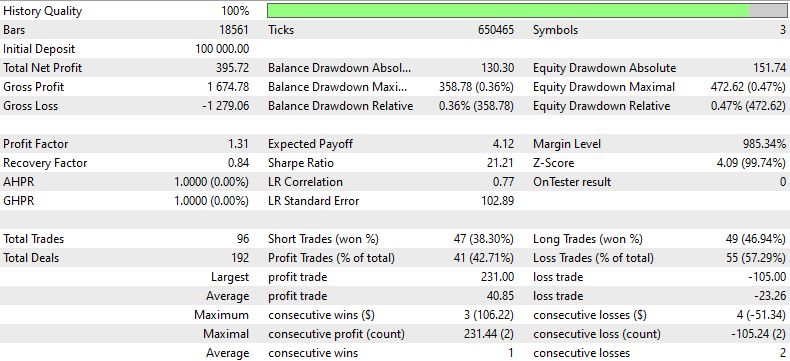
以下是针对本EA回测结果的总结:
本回溯测试报告利用历史数据,对某交易策略在特定时间段内的表现进行了详细分析。策略以100,000美元的初始存款开启,总毛利为1,674.78美元,总毛损高达1,279.06美元,但最终实现了395.72美元的总净利润。1.31的利润因子表明,毛利超出了毛损31%,这体现了在盈利与亏损之间,该策略具备盈利的能力。
使用策略共进行了96笔交易,其中盈利交易与亏损交易的比例大致相当,短仓盈利交易占比38.30%,长仓盈利交易占比46.94%。然而,策略总体上亏损交易的数量更多(55笔,占比57.29%),这凸显了在交易选择或退出策略方面有待改进。
0.84的恢复因子表明风险处于中等水平,策略能够恢复最大回撤的84%。此外,最大回撤相对较高,达到了358.78美元(占账户总额的0.36%),这表明虽然策略能够盈利,但也经历了必须从重大下跌中恢复过来的情况。
回溯测试结果还显示,在净值方面出现了大幅回撤,账户的最大净值回撤率为0.47%。结合21.21的夏普比率来看,这表明收益远高于所承担的风险,这确实还不错。然而,较低的平均连续获胜次数(3次交易)与较高的平均连续亏损次数(2次交易)相比,表明该策略可能还需要通过改进其方法来保持获胜交易的一致性,从而获益。
结论
在本文中,基于便于使用的MT5平台和Python编程,来分解利用预测进行三角套利这一理念。想象一下,您拥有一个秘密公式,能让你玩转货币兑换游戏,将美元兑换成欧元,再将欧元兑换成日元,最后又兑换回美元,目标是结束时拥有的资金总额比开始时更多。当然,这不是魔术,而是关于使用一种叫作ONNX的特殊预测模型以及三角套利策略,这些模型和策略会从过去的货币价格中学习来预测未来的价格,从而指导你的交易操作。
本文对于设置全部所需内容非常有帮助,它会向您展示如何安装所有必需的工具,如Python和Visual Studio Code,以及如何让电脑准备好开始测试。文章用简洁的语言进行解释说明,确保无论您的交易账户是基础型还是高级型,都能知道如何调整策略。
总体来说,本文是任何想要涉足外汇交易游戏并应用一些最先进的技术的交易者们的绝佳资源。它会引导您了解如何设置和运行你的交易系统的细节,让你能够借助最新的人工智能和机器学习技术,在交易中占据优势。无论您是编程新手或是交易新手,这篇指南都会一步步地引导您,教你如何实现向自动化交易的数字化飞跃。
我希望您会像我一样享受阅读本文的过程。
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/14873
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 开发多币种 EA 交易(第 7 部分):根据前向时间段选择组
开发多币种 EA 交易(第 7 部分):根据前向时间段选择组
 构建K线图趋势约束模型(第三部分):在使用该系统时检测趋势变化
构建K线图趋势约束模型(第三部分):在使用该系统时检测趋势变化
 神经网络变得简单(第 79 部分):在状态上下文中的特征聚合查询(FAQ)
神经网络变得简单(第 79 部分):在状态上下文中的特征聚合查询(FAQ)

Minmax 的作用是将 0 和 1 之间的值正常化(即:不使用价格值,而是使用从 a 到 b 的值)。
我不明白其他 q 的意思,请详细解释一下(我写这篇文章已经有一段时间了)。
您好、
如果您能粘贴 q 的详细信息,我就能更快地解决问题(文章是很久以前写的)。
根据我的记忆,你不能使用相同的手数。原因是使用的货币对价格不同。
Minmax 的工作原理是在 0 和 1 之间进行归一化(即:使用从 a 到 b 的值,而不是价格值)。
我不明白其他的问题,请再解释一下(我写这篇文章已经很久了)。
安装Visual Studio Code 有什么必要?
安装Visual Studio Code 有什么必要?
对于初学者来说......这是个不错的想法