
字符串:ASCII 符号表和用途
简介
本文将分析 ASCII 符号表及其使用方法。我们还将处理某些新函数,基于 ASCII 表特性的操作原理,然后我们将创建一个包括这些 MQL4 语言函数的新库。这些函数在其他编程语言中相当受欢迎,但并没有纳入到内置函数列表中。此外,我们还将深入研究函数处理字符串的基础。我相信你们在这款有用的数据类型中必然能够学习到新知识。
什么是 ASCII?
ASCII 是美国资讯交换标准码(American Standard Code for Information Interchange)的英文缩写。这套标准基于英文字母表。ASCII 代码显示计算机、通讯设备及其他处理文本的设备内的文本。ASCII 创于 1963 年并于 1967 年首次作为标准发布。1986 年进行了最后一次修订。想知道更多详细资料,请访问:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ASCII.稍后我们将了解,如何使用 MQL4 选项显示 ASCII,现在,我们首先来看看处理字符串的基础。
编写库的原理
要编写这种类型的库,我们需要了解一些关键节点。我们首先要看一看应如何遍历所有符号,例如数据数组的过程。相同的代码部分总会在任何函数中重复,旨在符号化处理。作为示例,让我们编写简单的脚本,首先显示公共字符串,然后是经过处理的字符串,其中每个符号以一个空格隔开。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| StringExpereriment1.mq4 | //| Copyright © 2007, Antonio Banderass. All rights reserved | //| banderassa@ukr.net | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright © 2007, Antonio Banderass. All rights reserved" #property link "banderassa@ukr.net" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| start | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int start() { string s1 = "Just_a_string", s2, symbol = "s"; int lenght = StringLen(s1); MessageBox(s1); for(int x = 0; x < lenght; x++) { symbol = StringSetChar(symbol, 0, StringGetChar(s1, x)); s2 = s2 + symbol + " "; } MessageBox(s2); return(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
让我们来分析一下每个字符串的值。
string s1 = "Just_a_string", s2, symbol = "s";
确定字符串类型的三个变量:
- s1 - 要处理的初始字符串;
- s2 - 包含结果的字符串;
- 符号 - 每个符号用于临时储存的字符串。
请注意,将以一个符号进行初始化。如果不这么做,我们所得到的字符串将缺少首个符号。问题在于,标准 MQL4 函数 StringGetChar() 变动已创建符号,这就是为什么我们进行常规操作时需要至少一个符号。
int lenght = StringLen(s1);
确定整数类型变量以储存字符串长度。为此,调用决定字符串长度 StringLen() 的标准函数,此函数带有单一参数——我们需要知道其长度字符串。
MessageBox(s1);
for(int x = 0; x < lenght; x++)
确定进行符号化处理的周期。请注意,计数器将通过归零初始化,因为字符串中的符号类似数组从零开始索引。开始执行周期后,使用比较运算符“less”,因为最后符号的长度位置为 1。
symbol = StringSetChar(symbol, 0, StringGetChar(s1, x));
此字符串中用到了两个标准函数:StringSetChar() 和 StringGetChar()。第一个函数允许替换字符串中的一个符号,第二个函数——将符号代码置于指定位置。函数 StringSetChar() 有三个参数:
- 要替换符号的字符串;
- 要替换的符号位置(请记住,字符串中的符号类似数组从零开始索引。)
- 要替换的符号代码。
函数以更改后的字符串形式返回结果。另一个重要的函数 - StringGetChar。它有两个参数:
- 带有应识别其代码的符号字符串;
- 带有应识别其代码的符号位置。
函数返回符号代码。当函数 StringGetChar 返回符号代码时,我将其调用至函数 StringSetChar 参数所在位置。因此,使用此函数,我们可以记住用于进一步处理的当前符号。执行周期期间,字符串 s1 的每个符号将分配给变量。
s2 = s2 + symbol + " ";
我们可以使用加法运算(+)轻松绑定字符串(连接)。在每个周期循环中,我们在结果字符串中添加一个符号和一个空格。
MessageBox(s2);
显示结果。请注意,我们从第一个符号开始阅读,虽然反过来也是可以的。在这种情况下,我们有一个较短的代码和较少的变量。如果无所谓从哪一边开始字符串处理,则使用以下变量://+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| StringExperiment2.mq4 | //| Copyright © 2007, Antonio Banderass. All rights reserved | //| banderassa@ukr.net | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright © 2007, Antonio Banderass. All rights reserved" #property link "banderassa@ukr.net" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| start | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int start() { string s1 = "Just_a_string", s2, symbol = "s"; int lenght = StringLen(s1) - 1; MessageBox(s1); while(lenght >= 0) { symbol = StringSetChar(symbol, 0, StringGetChar(s1, lenght)); s2 = s2 + symbol + " "; lenght--; } MessageBox(s2); return(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
现在你可以看到,我们用 ‘while’ 取代周期 ‘for’,前者可允许忽略计数器 x。为此,我们使用可变长度。我们将进一步使用两个模板之一进行函数编写,取决于处理序列是否重要。在示例中,我们按逆序获取带符号的字符串,即处理序列在此非常重要。
显示所有 ASCII 符号。
现在我们尝试显示所有 ASCII 符号。记住,函数 StringSetChar() 和函数 StringGetChar() 根据代码将 ASCII 上的相应符号插入指定位置并根据符号返回代码。StringSetChar() 有第三个参数整数值。这是出自 ASCII 符号表上的代码。让我们来编写特殊脚本以决定每个符号的代码://+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| StringExperiment3.mq4 | //| Copyright © 2007, Antonio Banderass. All rights reserved | //| banderassa@ukr.net | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright © 2007, Antonio Banderass. All rights reserved" #property link "banderassa@ukr.net" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| start | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int start() { string s, symbol = "s"; for(int x = 0; x < 256; x++) { symbol = StringSetChar(symbol, 0, x); s = s + x + " = " + symbol + " \t"; if(x % 10 == 0) s = s + " \n"; } MessageBox(s); return(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
脚本使用内置 MQL4 函数,新字符串的字符串常数以及让表格可视化的制表符。现在编译并启动脚本。你将看到 ASCII 符号表:
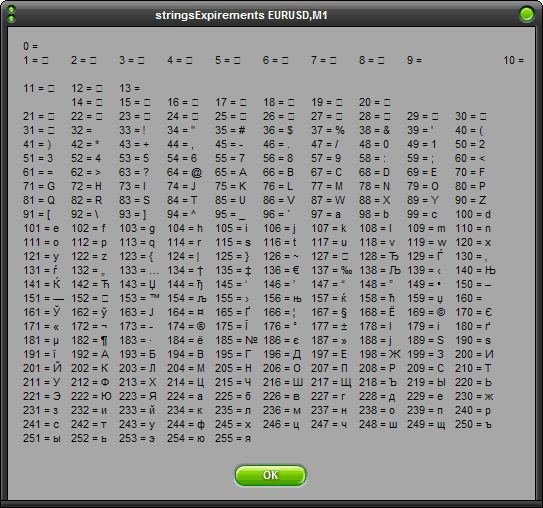
请仔细观察。你将清晰看到所有符号,从数字、字母到特殊符号都应有尽有,部分对你而言可能比较陌生。首先是一个代码,然后在标志“=”后将出现符号本身。我标记出了部分重要的符号组合:
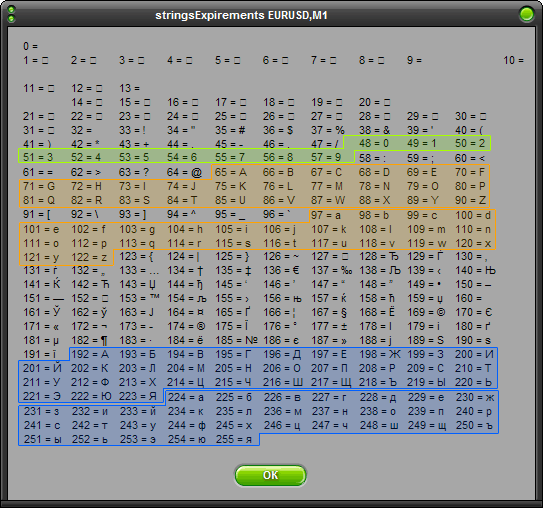
请注意字母的排列。字母是以字母表顺序排列的。这一特点随后将用于编写某些函数,如将字母从大写转换为小写,反之亦然。
现在,我们处理新函数,最后在这些函数基础上创建库。
StringUpperCase 和 StringLowerCase
有两个非常流行的函数可用于转换字符串的大小写。实现这种转换的基础是,所有大写字母的代码均由 32 个小写字母移位而来。可从表格中看到。实际操作中,如果我们尝试使用以下代码找到符号 ‘A’, ‘Z’, ‘a’, ‘z’, 的代码:
string s = "AZaz"; MessageBox("A = " + StringGetChar(s, 0)); MessageBox("Z = " + StringGetChar(s, 1)); MessageBox("a = " + StringGetChar(s, 2)); MessageBox("z = " + StringGetChar(s, 3));
则结果如下所述:相应的,A= 65, Z= 90, a= 97, z= 122。所以我们应将此特性考虑进去。我们来查看函数的源代码:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| StringUpperCase | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string StringUpperCase(string str) { string s = str; int lenght = StringLen(str) - 1, symbol; while(lenght >= 0) { symbol = StringGetChar(s, lenght); if((symbol > 96 && symbol < 123) || (symbol > 223 && symbol < 256)) s = StringSetChar(s, lenght, symbol - 32); else if(symbol > -33 && symbol < 0) s = StringSetChar(s, lenght, symbol + 224); lenght--; } return(s); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| StringLowerCase | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string StringLowerCase(string str) { string s = str; int lenght = StringLen(str) - 1, symbol; while(lenght >= 0) { symbol = StringGetChar(s, lenght); if((symbol > 64 && symbol < 91) || (symbol > 191 && symbol < 224)) s = StringSetChar(s, lenght, symbol + 32); else if(symbol > -65 && symbol < -32) s = StringSetChar(s, lenght, symbol + 288); lenght--; } return(s); }如果处理序列无关紧要,则使用周期。函数便于使用,唯一的参数是应转换为正确大小写的字符串:
string s1 = "UPPER_REGISTER_STRING"; string s2 = "lower_register_string"; MessageBox(StringLowerCase(s1)); // upper_register_string MessageBox(StringUpperCase(s2)); // LOWER_REGISTER_STRING
StringCompare
在 MQL4 中,应使用“==”在运算符级别进行字符串的比较。有趣的是,字符串的比较取决于大小写,即字符串”STRING” 和 ”string” 不同。
if("STRING" == "string") // FALSE MessageBox("TRUE"); else MessageBox("FALSE");
如果要在不忽略字体的情况下比较两个字符串,则使用 StringCompare()。这个函数将像比较运算符一样,返回bool 类型的值。实现很简单。函数对预先转换为小写字体的字符窜进行比较:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| StringCompare | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool StringCompare(string s1, string s2) { return(StringLowerCase(s1) == StringLowerCase(s2)); }
应用示例:
if(StringCompare("STRING", "string")) // TRUE MessageBox("TRUE"); else MessageBox("FALSE");
StringIsDigit
此函数检查字符串内容。如果字符串仅保存数字,则其返回 true,否则 - false。。实现非常简单,基于以下事实,数字符号在同一排中,并拥有 48 - 58 的代码。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| StringIsDigit | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool StringIsDigit(string str) { bool result = true; string s = str; int lenght = StringLen(str) - 1, symbol; while(lenght > 0) { symbol = StringGetChar(s, lenght); if(!(symbol > 47 && symbol < 58)) { result = false; break; } lenght--; } return(result); }
应用示例:
if(StringIsDigit("1234567890")) // TRUE MessageBox("TRUE"); else MessageBox("FALSE"); if(StringIsDigit("1234notdigit")) // FALSE MessageBox("TRUE"); else MessageBox("FALSE");
StringIsAlpha
此函数和前面那个函数一样,允许确定字符串是否只含有字母。其实现方式非常类似:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| StringIsAlpha | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool StringIsAlpha(string str) { bool result = false; string s = str; int lenght = StringLen(str) - 1, symbol; while(lenght > 0) { symbol = StringGetChar(s, lenght); if((symbol > 96 && symbol < 123) || (symbol > 64 && symbol < 91) || (symbol > 191 && symbol < 256) || (symbol > -65 && symbol < 0)) { result = true; break; } lenght--; } return(result); }
应用示例:
if(StringIsAlpha("thereAreSomeLetters")) // TRUE MessageBox("TRUE"); else MessageBox("FALSE"); if(StringIsAlpha("thereAreSomeDigits12345")) // FALSE MessageBox("TRUE"); else MessageBox("FALSE");
创建库
现在我们将所有这些函数收集进一个库内。为此,在 MetaEditor 4 内点击 ’File -> New -> Library -> Next’。在域名处写下 stringProcess,然后点击 OK。然后插入上述函数代码并保存。之后,创建带有函数原型的文件,点击 ‘File -> New -> Include(*.MQH) -> OK'.在域名处写下stringProcess,, -> 好现在插入所有新函数的原型,并指定导出指令:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| stringProcess.mqh | //| Antonio Banderass Copyright © 2007 | //| banderassa@ukr.net | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Antonio Banderass Copyright © 2007" #property link "banderassa@ukr.net" //+--- #import "stringProcess.ex4" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| prototypes | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string StringUpperCase(string str); string StringLowerCase(string str); bool StringCompare(string s1, string s2); bool StringIsDigit(string str); bool StringIsAlpha(string str);
使用库 stringProcess
要使用库,则包含带有函数原型的头文件,然后你便可以调用所需函数。以下是在脚本中的使用示例:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| stringProcessLibraryTest.mq4 | //| Antonio Banderass Copyright © 2007 | //| banderassa@ukr.net | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Antonio Banderass Copyright © 2007" #property link "banderassa@ukr.net" #include <stringProcess.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int start() { if(StringIsDigit("1234567890")) // TRUE MessageBox("TRUE"); else MessageBox("FALSE"); if(StringIsDigit("1234notdigit")) // FALSE MessageBox("TRUE"); else MessageBox("FALSE"); return(0); }
总结
现在,你已经对 ASCII 符号表有所了解,也学会了如何使用其构建特性来设计新的函数。你所编写的新函数在其他编程语言中很流行,却没有包含在 MQL4 中。你已经基于这些函数创建了用于字符串处理的小型库。我认为这个库应在接受结果时而非交易时使用。例如,如果你为你的 Expert Advisor 自行开发报告系统,则部分函数将对你有用。此外,你还会发现许多我可能都不知道的有用之处。愿你财运亨通!
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自英文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/en/articles/1474
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 MQL4 语言入门。简介
MQL4 语言入门。简介
 如何更容易地检测和修复 Expert Advisor 代码内的错误
如何更容易地检测和修复 Expert Advisor 代码内的错误
 自动选择经纪公司,以便 Expert Advisor 高效运行
自动选择经纪公司,以便 Expert Advisor 高效运行
 意见调查:交易者对移动终端的评估
意见调查:交易者对移动终端的评估