
Integrating External Applications with MQL5 Community OAuth
Contents:
Introduction
For every registered user on the MQL5 community, numerous advantages await. This platform serves as a home for algorithmic traders of both novice and expert levels, accessible to millions of traders worldwide. Recently, I discovered an incredible feature available to all registered users: the Apps section in MQL5 allows you to configure OAuth (Open Authorization) for your external applications. After navigating the complexities of integrating these components, I decided to prepare this article as a simplified guide. Beyond the technical implementation, you'll discover a feature you might have overlooked and gain valuable insights into integration of Android apps with MQL5.
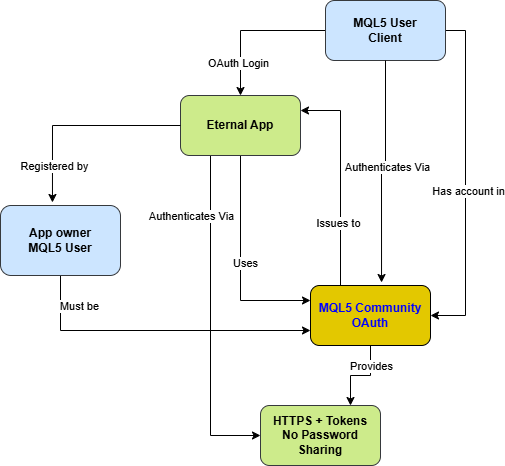
Fig.1. Relational diagram for External App owner and MQL5 users
Why Prefer MQL5 Authorization?
Targeted Access to Your Ideal Audience
As an MQL5 developer, your primary target audience is the MQL5 community itself. By utilizing MQL5 OAuth, you're drawing from a platform specifically designed for traders, developers, and financial analysts. This focused approach eliminates the noise associated with general social platforms.
Specialized Trader Targeting vs. General Social Platforms
Unlike Google or Facebook authentication, which provide generic user data, MQL5 OAuth delivers specialized information about a user's trading expertise. You gain access to their:
- MQL5 Rank (Newbie, Advanced, Professional, Expert Advisor Developer)
- Reputation points earned through community contributions
- Published products in the MQL5 Market
- Trading experience and specialization
- Forum activity and community standing
This specialized data enables you to create highly personalized experiences that generic platforms cannot match.
Immediate Credibility Assessment
When a user authenticates with their MQL5 account, you immediately gain insight into their credibility within the trading community. A user with high reputation points and multiple published products represents a serious, invested community member—valuable information for applications requiring trust and expertise.
Building the Right Client Base
By implementing MQL5 OAuth, you naturally filter your user base to include only those interested in trading and financial technology. This leads to:
- Higher quality user interactions
- More relevant feedback for your application
- Increased potential for monetization
- Lower support costs (users are already familiar with technical concepts)
This specialized data enables you to create highly personalized experiences that generic platforms cannot match.
Immediate Credibility Assessment
When a user authenticates with their MQL5 account, you immediately gain insight into their credibility within the trading community. A user with high reputation points and multiple published products represents a serious, invested community member—valuable information for applications requiring trust and expertise.
Building the Right Client Base
By implementing MQL5 OAuth, you naturally filter your user base to include only those interested in trading and financial technology. This leads to:- Higher quality user interactions
- More relevant feedback for your application
- Increased potential for monetization
- Lower support costs (users are already familiar with technical concepts)
Constraints and Limitations
While powerful, the MQL5 OAuth system does have limitations:
- Niche Audience: Only users with MQL5 accounts can authenticate
- Limited Scope Options: Compared to major platforms, available data scopes are more restricted.
- Community-Centric: Best suited for applications serving the trading/fintech ecosystem.
- Mobile Considerations: Requires careful implementation for Android/iOS applications.
- Documentation Gaps: Some implementation details may require experimentation.
Understanding MQL5 Community OAuth
How It Works: The Technical Flow
MQL5 implements the OAuth 2.0 authorization framework with these key endpoints:- Authorization Endpoint: https://www.mql5.com/en/oauth/login
- Token Endpoint: https://www.mql5.com/api/oauth/access_token
- User Endpoint: https://www.mql5.com/api/oauth/user_info
The flow follows the standard OAuth 2.0 authorization code pattern:
- The user clicks "Login with MQL5" in your application.
- Redirect to the MQL5 authorization page.
- User authenticates and grants permissions.
- Redirect back to your application with the authorization code.
- Exchange code for access token.
- Use a token to fetch user profile data.
Key Components for Developers
- Client ID: Unique identifier for your application
- Client Secret: Confidential key for token exchange (must be protected)
- Redirect URI: Where users return after authorization
- Scopes: Define what user data your application can access
Security Considerations
- Always use HTTPS for all endpoints.
- Store client secrets securely (never in client-side code).
- Implement CSRF protection using state parameters.
- Validate all redirect URIs.
- Implement proper token storage and refresh mechanisms.
Implementation
Step 1: Register Your Application
1. Navigate to your MQL5 account profile → Community → Apps
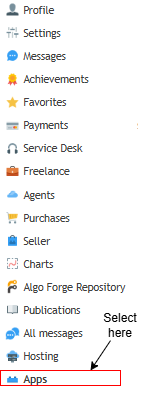
Fig. 2. Accessing Apps in your MQL5.community profile
2. Click "Add New Application."
3. Provide:
- Application Name: Descriptive name for your app
- Main Page URL: Your application's website
- Redirect URI: Your OAuth callback endpoint
4. Save to receive your Client ID and Client Secret.
Before diving into the code, it’s important to understand which parts of the Android project actually matter for integrating MQL5 Community OAuth.
Some readers will open the attached project directly in Android Studio, while others—already comfortable with Kotlin and Android—may prefer to start with a fresh Empty Activity project and adapt the implementation by comparison. Both approaches work.
The goal here is not to teach Android development, but to clearly show how an Android application can participate in the MQL5 Community authentication flow and successfully initiate OAuth login.
For those new to Android development: Don't worry about mastering every aspect. Android Studio has excellent documentation, and there are vast free resources online. The real value here is understanding the authentication pattern—how MQL5 OAuth works and how it differs from generic social logins. The concepts you'll learn apply to any OAuth integration, but with the unique advantage of accessing specialized trader data.
To make the code implementation breakdown below easy to follow, the following files form the core of the project. These are the files you should focus on when launching the project and reading the explanations that follow.
| Source File | Location in Project | Description: |
|---|---|---|
| MainActivity.kt | app/src/main/java/ / | main entry point of the app; launches the app and applies the theme. |
| OAuthConfig.kt | app/src/main/java/ /util/ | holds MQL5 OAuth endpoints, redirect URL, and client ID for MQL5 Community login. |
| LoginActivity.kt | app/src/main/java/ /ui/login/ | handles the login process; opens the MQL5 login page, processes redirects, and captures the authorization code. |
| activity_login.xml | app/src/main/res/layout/ | defines the login screen layout with a “Sign in with MQL5” button to start the OAuth flow. |
| AndroidManifest.xml | app/src/main/ | critical configuration file; declares internet permission and OAuth redirect scheme (mql5profile://oauth). |
| Theme.kt | app/src/main/java/ /ui/theme/ | defines app-wide theme settings for consistent visual styling. |
| styles.xml | app/src/main/res/values/ | contains theme and style definitions to ensure consistent appearance across screens. |
1. Centralized OAuth Configuration (OAuthConfig.kt)
Think of this configuration file as the rulebook for how your app communicates with MQL5's OAuth system. It's where you define all the endpoints and identifiers in one organized place.
This structure matters because professional OAuth providers (Google, GitHub, etc.) use this same pattern. By organizing our configuration this way, we are treating MQL5 Community OAuth as a first-class authentication system—which it truly is for trading applications.
Unlike social logins that give you generic data, notice these endpoints are specifically designed for the MQL5 ecosystem. The USER_URL will return not just basic profile info, but trading reputation, rank, and professional standing—data that's gold for fintech applications.
Kotlin code:
package com.clemencebenjamin.mql5profileviewer.util object OAuthConfig { const val CLIENT_ID = "YOUR_MQL5_CLIENT_ID" const val REDIRECT_URI = "https://your-domain.com/callback.php" const val AUTH_URL = "https://www.mql5.com/en/oauth/login" const val TOKEN_URL = "https://www.mql5.com/api/oauth/access_token" const val USER_URL = "https://www.mql5.com/api/oauth/user_info" }
2. Login Screen Layout (activity_login.xml)
OAuth works best when the entry point is intentional and frictionless. This minimal design tells MQL5 users, "Your professional identity is welcome here."
When a trader sees "Sign in with MQL5" instead of generic social buttons, they recognize this app understands their world. It's like showing a pilot a cockpit instead of a car dashboard—immediate recognition and trust.
No local account creation means zero friction for MQL5 users. They're already invested in their MQL5 identity; why make them create another?
XML code:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center" android:orientation="vertical" android:padding="24dp"> <ImageView android:layout_width="120dp" android:layout_height="120dp" android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher"/> <Button android:id="@+id/btnLogin" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Sign in with MQL5" android:layout_marginTop="24dp"/> </LinearLayout>
3. Android Manifest (MainActivity.kt)
The manifest is Android's configuration blueprint. Here, we're telling Android two crucial things: "This app needs internet access," and "Here's how to handle OAuth callbacks."
xml code:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/Theme.MQL5ProfileViewer"> <activity android:name=".ui.login.LoginActivity" android:exported="true" android:launchMode="singleTop"> <!-- App Launcher --> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN"/> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER"/> </intent-filter> <!-- OAuth Redirect --> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW"/> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/> <category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE"/> <data android:scheme="mql5profile" android:host="oauth"/> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>
That intent-filter with mql5profile://oauth is our app's private handshake with the MQL5 OAuth system. After user authentication on MQL5.com, they're redirected back to this specific address, and Android knows to wake up the app and pass along the authorization code.
This pattern mirrors how professional fintech apps handle authentication—secure, controlled, and user-friendly.
4. OAuth Flow Controller (LoginActivity.kt)
This activity is where the magic happens. It orchestrates the entire OAuth dance between your app and MQL5's servers.
Kotlin code:
package com.clemencebenjamin.mql5profileviewer.ui.login import android.content.Intent import android.os.Bundle import android.widget.Button import android.widget.Toast import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity import androidx.browser.customtabs.CustomTabsIntent import androidx.core.net.toUri import com.clemencebenjamin.mql5profileviewer.R import com.clemencebenjamin.mql5profileviewer.util.OAuthConfig class LoginActivity : AppCompatActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_login) findViewById<Button>(R.id.btnLogin).setOnClickListener { startOAuth() } } private fun startOAuth() { val uri = OAuthConfig.AUTH_URL.toUri().buildUpon() .appendQueryParameter("client_id", OAuthConfig.CLIENT_ID) .appendQueryParameter("redirect_uri", OAuthConfig.REDIRECT_URI) .appendQueryParameter("response_type", "code") .build() CustomTabsIntent.Builder() .build() .launchUrl(this, uri) } override fun onNewIntent(intent: Intent?) { super.onNewIntent(intent) val code = intent?.data?.getQueryParameter("code") if (code != null) { Toast.makeText(this, "MQL5 authentication successful", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show() // Next step: exchange code for access token on backend } } }
Understanding the Flow:
- The user clicks → App constructs the MQL5 authorization URL with your CLIENT_ID.
- CustomTabs opens → User sees the familiar MQL5 login page (trust!).
- The user authenticates → MQL5 asks, "Allow this app to access your profile?"
- Redirect back → MQL5 sends an authorization code to your REDIRECT_URI
- App receives code → The onNewIntent method captures it
Currently, our app has successfully:
- Opened the MQL5 login page
- Accepted real MQL5 credentials
- Handled user consent
- Received a valid OAuth authorization code
This isn't just technical—it's relationship-building. We are leveraging MQL5's established trust to onboard users instantly.
5. Theme Compatibility()
Authentication flows are sensitive to UI glitches. A stable theme ensures the OAuth experience remains seamless, even as Android manages multiple activities and intents.
XML code:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <style name="Theme.MQL5ProfileViewer" parent="Theme.AppCompat.DayNight.NoActionBar"/> </resources>
When users authenticate, they're in a sensitive state—entering credentials, granting permissions. A flicker, crash, or visual glitch can break trust. This theme provides the visual stability that professional authentication demands.
If we were to replace this with Google or Facebook OAuth, you get generic data. With MQL5, we get trading identity—name, reputation, and profile picture. This transforms our app from "another login" to "a professional tool for traders."
Server-Side Component: Completing the MQL5 OAuth Flow
While the Android application successfully initiates authentication and receives user consent, OAuth does not end on the client side. To complete the process securely, a server-side component is required.
This section explains why a server is necessary, how it fits into our system, and how a simple PHP callback script enables the full MQL5 Community OAuth flow.
Why a Server Is Required
OAuth authentication is intentionally split into two stages:
1. Authorization (Client-side)
The Android app redirects the user to MQL5, where they log in and grant permissions.
2. Token Exchange (Server-side)
The authorization code returned by MQL5 must be exchanged for an access token using
- A client secret
- A secure POST request
Why this cannot be done in Android directly:
- Client secrets must never be embedded in mobile apps.
- Android apps are easily decompiled.
- OAuth providers (including MQL5) are designed to trust server-to-server communication.
The server therefore acts as a trusted intermediary between
- The Android application
- The MQL5 OAuth infrastructure
How the Server Fits into Our Architecture
The complete flow now looks like this:
- The Android app redirects the user to MQL5 login.
- The user signs in and grants permission.
- MQL5 redirects to our PHP callback URL.
- The PHP server exchanges the authorization code for an access token.
- The PHP server redirects back to Android using a deep link.
- The Android app resumes with authenticated context.
This design mirrors how professional OAuth integrations are implemented in production systems.
Free PHP Hosting Options for OAuth Prototypes
To demonstrate the concept, we explored free PHP hosting services, which are suitable for learning and prototyping.
Common Free Options:
- InfinityFree
- ByetHost
- AwardSpace
- Atwebpages (used for demonstration)
- Localhost + Ngrok (for testing)
Important Note:
Some free hosting providers restrict outbound POST requests, which may block token exchange. This does not invalidate the implementation—it only highlights hosting limitations.
Despite this, free hosts are still valuable for:
- Proving OAuth feasibility
- Validating redirect and consent flow
- Demonstrating MQL5 Community integration potential
PHP OAuth Callback Script (Server Logic)
The PHP script below represents the server-side OAuth handler.
It is intentionally minimal and focused on one responsibility: completing the OAuth handshake.
Credential Handling Note
In practice, replace the quoted placeholders with values obtained from your MQL5 Community application dashboard. Credentials should never be committed to public repositories.
1. Configuration Section
This section defines the OAuth credentials and endpoints required to communicate with MQL5.
PHP code:
<?php // =============================== // CONFIGURATION // =============================== $CLIENT_ID = "YOUR_MQL5_CLIENT_ID"; $CLIENT_SECRET = "YOUR_MQL5_CLIENT_SECRET"; $REDIRECT_URI = "https://your-domain.com/callback.php"; $TOKEN_URL = "https://www.mql5.com/api/oauth/access_token";
Purpose:
- Identifies your application to MQL5
- Enables secure token exchange
- Keeps OAuth parameters centralized
2. Receiving the Authorization Code
After the user logs in and approves access, MQL5 redirects back to this script with a temporary authorization code.
PHP code:
// =============================== // STEP 1: GET AUTH CODE // =============================== if (!isset($_GET['code'])) { die("Authorization code not found."); } $code = $_GET['code'];
What this confirms:
- The user authenticated successfully
- Permissions were granted
- The OAuth process reached the server safely
3. Exchanging Code for Access Token
This is the most critical step in OAuth.
The server sends a POST request to MQL5 containing
- Client ID.
- Client secret.
- Authorization code.
- Redirect URI.
// =============================== // STEP 2: EXCHANGE CODE FOR TOKEN // =============================== $postData = [ 'grant_type' => 'authorization_code', 'client_id' => $CLIENT_ID, 'client_secret' => $CLIENT_SECRET, 'code' => $code, 'redirect_uri' => $REDIRECT_URI ]; $ch = curl_init($TOKEN_URL); curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true); curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, true); curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, http_build_query($postData)); $response = curl_exec($ch); curl_close($ch); $data = json_decode($response, true); if (!isset($data['access_token'])) { die("Token exchange failed: " . htmlspecialchars($response)); } $accessToken = $data['access_token'];
Why this must run on the server:
- It uses confidential credentials.
- It requires to be a trusted server-to-server communication.
- Furthermore, it complies with OAuth security design.
4. Redirecting Back to Android
Once the token is obtained, the server redirects back to the Android app using a deep link.
PHP code:
// =============================== // STEP 3: REDIRECT BACK TO ANDROID // =============================== $androidRedirect = "mql5profile://oauth?token=" . urlencode($accessToken); header("Location: $androidRedirect"); exit;
Result:
- Android resumes execution.
- The app now holds an authenticated session context.
- Profile data can be fetched in subsequent steps.
Observations & Hosting Limitations
- During implementation, we observed that some free hosting services:
- Successfully handle redirects and authorization,
- Accept inbound requests from MQL5, and
- Block outbound POST requests, preventing token exchange.
Rather than being a failure, this demonstrates the strength of the architecture:
once deployed on a compatible hosting service, the same code completes the OAuth cycle without modification.
Key Takeaway
The server-side component is not optional in OAuth—it is a fundamental security requirement.
Even with free hosting constraints, we successfully validated:
- MQL5 OAuth login
- Permission granting
- Authorization code delivery
- End-to-end system design
This confirms that external applications can reliably authenticate users using MQL5 Community identities, unlocking powerful possibilities for trading-focused platforms.
Testing
Deploying the application involved building the project and launching it on a virtual device. The build completed successfully, the app ran as expected, and the results are presented below in the accompanying screenshots.

Fig. 3. Testing Log in via MQL5 community.
The following three images present still screenshots of the application flow. The first image shows the app’s main page. The second appears after selecting the “Login with MQL5” button, where the MQL5 authentication page is displayed. Finally, upon entering a valid username and password, the app retrieves and displays the real name of the registered user—in this case, my own.
Selecting Continue would normally trigger the backend token-exchange process with the server hosting the PHP callback. However, in this demonstration we did not proceed further because the proposed server environment did not fully meet MQL5’s HTTPS requirements. As a result, the authentication process returned a response, which is explained immediately below these images.
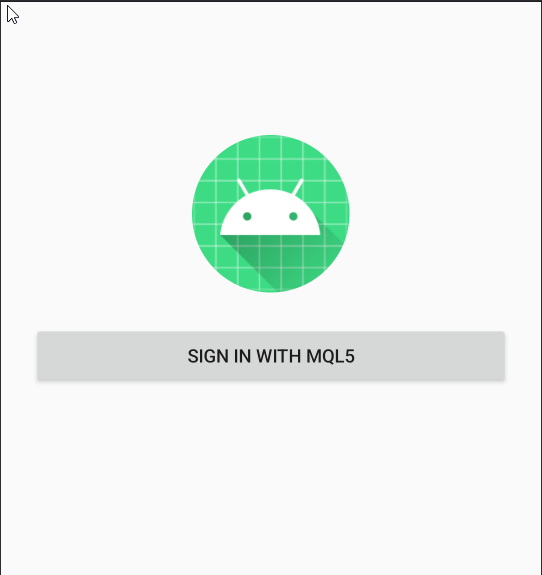
Fig. 4. The starting application page
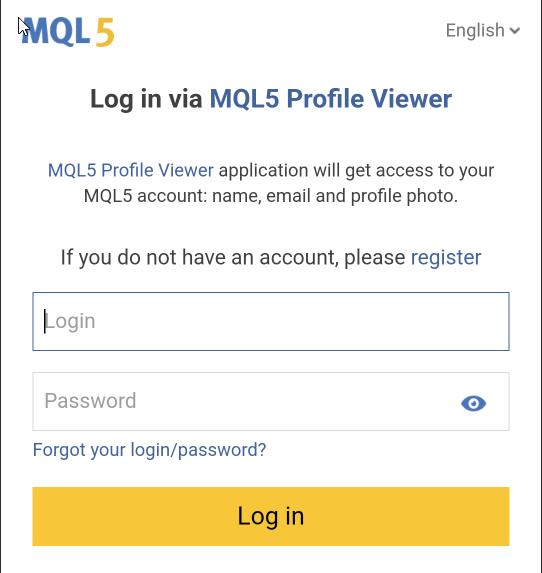
Fig. 5. The login page after selecting Sign in with MQL5

Fig. 6. Select (Continue as per your username) to the authorization page after entering correct MQL5 credentials
Here is what I obtained from selecting the continue button:
Token exchange failed:
405 Method Not Allowed This error occurred after a successful login, during the backend step where the PHP server attempts to exchange the authorization code for an access token using MQL5’s token endpoint.
What the error means:
A 405 error response indicates that the server received the request but rejected it because the HTTP method used is not permitted for that endpoint. In this case, the token endpoint refused the request before a token could be issued.
This typically happens for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Incorrect request method
- The MQL5 token endpoint strictly requires a POST request.
- If the hosting environment blocks or rewrites POST requests, the exchange will fail.
2. Hosting limitations
- Some free hosting providers restrict outbound HTTPS POST requests or cURL usage.
- Others proxy or block requests to external APIs for security reasons.
3. HTTPS compliance issues
- MQL5 OAuth requires a valid HTTPS callback.
- If the certificate is missing, weak, or not trusted, the request may be rejected upstream.
Conclusion
In this project, we successfully demonstrated how MQL5 Community OAuth can be integrated with external applications. These applications may be web-based or mobile-based—in our case, we used Android purely for demonstration purposes. A clean and functional source project is attached, which you are free to explore, extend, and deploy.
To run the project, you will need Android Studio installed on your computer and an active MQL5 Community account. From your MQL5 profile dashboard, navigate to Apps (located on the left panel) and create a new application. You will be required to provide:
- The application name.
- The main page URL, which must point to the location where your PHP callback script is hosted
You may notice that this article does not go deep into Android-specific development. This is intentional. The primary objective here is to build confidence in the concept and demonstrate that external applications can reliably leverage MQL5 Community OAuth. For more in-depth Android knowledge, there is abundant documentation and learning material available online.
The attached project is error-free and ready to run, but you will need to personalize it. This includes:
- Replacing the client ID with the one generated for your own MQL5 application
- Configuring the server URL that hosts your OAuth callback PHP script
- Ensuring that only the client ID (never the secret) is used in the Android app for security reasons
Once configured, build and run the application to test the complete OAuth flow.
Regarding backend servers, you will need to choose a hosting solution that is not function-limited and fully supports HTTPS, outbound POST requests, and OAuth workflows. For production-level applications, investing in a secure and reliable backend is strongly recommended.
I hope this brief foundation serves as a solid starting point for building trader-centric applications that integrate seamlessly with the MQL5 Community. Such integrations open the door to expanding the ecosystem and strengthening the developer network around algorithmic trading tools.
A table of attachments is provided below—review the files carefully and explore them at your own pace.
If you have questions or suggestions, feel free to open a discussion in the comments section below the article, where the developer community is always ready to help.
Until the next publication, stay safe and keep building.
Attachments
The attached files include a PHP callback source and the MQL5 Profile Viewer ZIP archive. Extract the ZIP file to access the full Android project, explore the included files, and review the table below for a brief description of each component.| File name | Description |
|---|---|
| callback.php | Server-side OAuth callback script responsible for receiving the authorization code from the MQL5 Community, securely exchanging it for an access token, and redirecting the authenticated result back to the Android application. This file must be hosted on an HTTPS-enabled server. |
| MQL5ProfileViewer.zip | Complete Android Studio project source code demonstrating MQL5 Community OAuth integration. The project includes the login flow, deep-link handling, and user authentication logic. You must personalize the client ID and backend callback URL before building and running the application. |
Warning: All rights to these materials are reserved by MetaQuotes Ltd. Copying or reprinting of these materials in whole or in part is prohibited.
This article was written by a user of the site and reflects their personal views. MetaQuotes Ltd is not responsible for the accuracy of the information presented, nor for any consequences resulting from the use of the solutions, strategies or recommendations described.
 Features of Custom Indicators Creation
Features of Custom Indicators Creation
 Custom Indicator Workshop (Part 1): Building the Supertrend Indicator in MQL5
Custom Indicator Workshop (Part 1): Building the Supertrend Indicator in MQL5
 Features of Experts Advisors
Features of Experts Advisors
 Employing Game Theory Approaches in Trading Algorithms
Employing Game Theory Approaches in Trading Algorithms
- Free trading apps
- Over 8,000 signals for copying
- Economic news for exploring financial markets
You agree to website policy and terms of use