
メタトレーダー5クライアントターミナルにおける適応型トレーディングシステムとその使用
導入
世界中の何百、何千ものトレーダーが、MetaQuotes Software Corpによって開発されたトレーディングプラットフォームを利用しています。成功の鍵となったのは、長年の経験にもとづく卓越したテクノロジと、最高のソフトウェアソリューションです。
多くの人がすでに、新しいMQL5言語で利用できるようになった新たな機会を予想していました。その主な特徴は、高いパフォーマンスと、オブジェクト指向プログラミングの可能性です。加えて、メタトレーダー5クライアントターミナルにおけるマルチカレンシーストラテジーテスターの出現により、多くのトレーダーが、複雑なトレーディングシステムの開発、習得、使用を行うための独自ツールを手に入れました。
この秋、Automated Trading Championship 2010が始まります;MQL5で書かれた何千ものトレーディングロボットが参加する予定です。コンペでは、最大ストラテジーを獲得したエキスパートアドバイザが勝利を収めます。しかし、最も効果的なストラテジーとは何でしょう?
メタトレーダー5ターミナルのストラテジーテスターを用いると、特定期間内に最大利益を獲得するシステムパラメータの最良なセットを探すことができます。しかし、これをリアルタイムで実行できるでしょうか?エキスパートアドバイザによる、いくつかのストラテジーを用いたバーチャルトレーディングの案が「エキスパートアドバイザ内部におけるエキスパートアドバイザの競争」という記事で検討されましたが、これはMQL4での実装を含むものです。
本稿では、オブジェクト指向プログラミング、データを扱うクラスそして標準ライブラリのトレードクラスを用いることにより、MQL5による適応型分析の作成と分析がたいへん容易になってきたことを示していきます。
1.適応型トレーディングストラテジー
マーケットは、常に変化しています。トレーディングストラテジーは、現在のマーケット条件に適応していなければなりません。
ストラテジーの最大利益をもたらすパラメータ値は、パラメータの継続的変更や検証結果分析による最適化を用いることなしに、見つけることができます。
図1では、10のエキスパートアドバイザ (MA_3,...MA_93)の資産増減曲線を示しています;それぞれ移動平均ストラテジーによっていますが、異なる期間(3,13,..93)のトレードです。EURUSD、H1において検証が行われ、検証期間は4.01.2010-20.08.2010です。
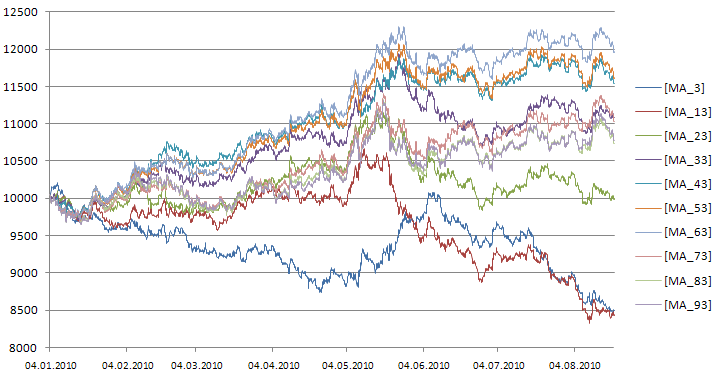
図110のエキスパートアドバイザについての取引資産増減曲線ダイアグラム
図1に示すように、エキスパートアドバイザは最初の2週間はほぼ同じ結果を示しましたが、 その後、利益がはっきりと分かれ始めました。検証期間が終わると、ピリオド63、53、そして43のエキスパートアドバイザが最良のトレーディング結果を示しました。
マーケットは最良の結果を選択します。その選択にしたがってみませんか?単一のエキスパートアドバイザで10のストラテジーを組み合わせて各ストラテジーの「バーチャル」トレーディングができるようにし、リアルトレーディングの最良のストラテジーを定期的に(例えば、新規バーの始め、など) 決定し、シグナルにしたがってトレードを行うと、一体どうなるでしょうか?
図2に、得られた適応型ストラテジーの結果を示します。適応型トレーディングによる取引資産増減曲線が、赤色で示されています。半分以上の期間、適応型ストラテジーの資産増減曲線の形が、最終的な勝者であるMA_63 strategyのそれと同じであることに注目してください。
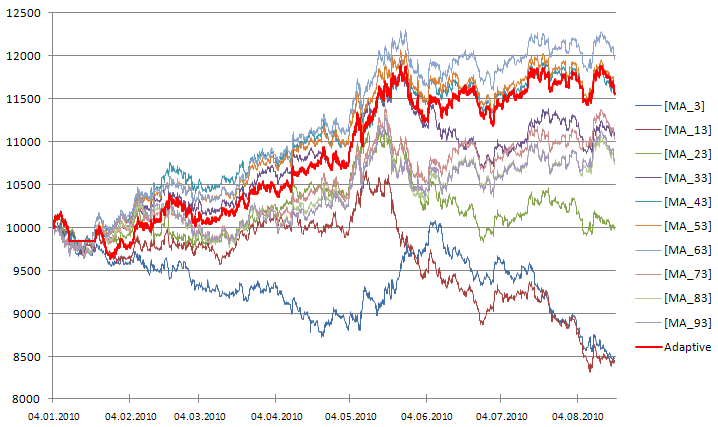
図210のトレードシステムからのシグナルを用いた、適応型トレーディングによる取引資産増減曲線
残高曲線が、同様のダイナミクスを示しています(図3):
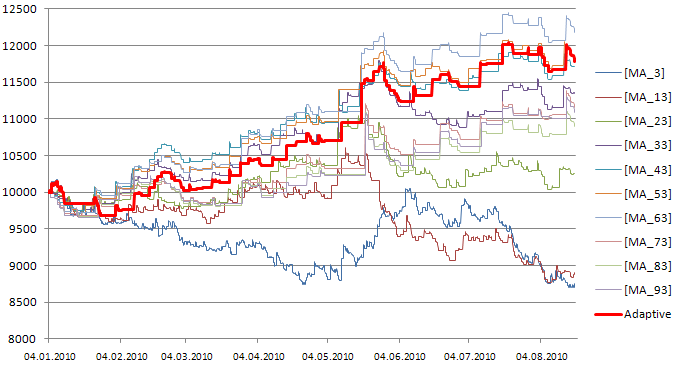
図310のトレーディングシステムからのシグナルを用いた、適応型ストラテジーの残高曲線
現時点においてどのストラテジーも利益をもたらさない場合には、適応型システムはトレード操作を行うべきではありません。このようなケースの例を図4に示します(期間:2010年1月4日から22日まで)。
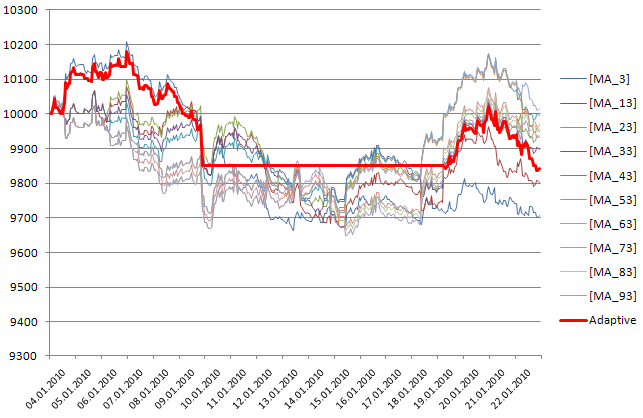
図4利益をもたらすストラテジーがなく、適応型ストラテジが新しいポジションをストップした期間
2010年1月の開始以降、最大効率はMA_3 strategyにより示されます。MA_3(青色)がこの時点でマネー最大量を示した後、適応型ストラテジー(赤色)のシグナルが追従しました。1月8日から20日までの期間、考慮されたすべてのストラテジーがネガティブな結果となったため、適応型ストラテジーは新しいトレードポジションをオープンしませんでした。
すべてのストラテジーがネガティブな結果となる場合には、トレードを避けることがより好ましくなります。これは、利益を生まないトレードをストップし、マネーを節約しておくことができるという点で、重要なことです。
2.適応型トレーディングストラテジーの実行
本セクションでは、いくつかのトレーディングストラテジーを同時に用いて「バーチャル」トレーディングを実行し、シグナルにしたがって、最大利益をもたらすリアルトレーディングを選択するストラクチャを検討していきます。オブジェクト指向アプローチを使うことで、このプログラムのソリューションがたいへん簡単になることに注目してください。
まず、適応型エキスパートアドバイザのコードを調査し、次に、適応型システムの機能が実装されるCAdaptiveStrategyを精査して、その後、CSampleStrategyクラス-バーチャルトレーディング機能が実行されるトレーディングストラテジーの基本クラス、を示します。
さらに、2つの下位クラス-移動平均とストキャスティクスによるトレーディングストラテジーを表すCStrategyMAクラスとCStrategyStochクラス、を検討していきます。これらのストラクチャを分析した後には、独自ストラテジーのクラスを容易に書いたり追加したりすることができるようになるでしょう。
2.1. エキスパートアドバイザのコード
エキスパートアドバイザのコードは非常にシンプルです:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Adaptive_Expert_Sample.mq5 | //| Copyright 2010, MetaQuotes Software Corp. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2010, MetaQuotes Software Corp." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" #include <CAdaptiveStrategy.mqh> CAdaptiveStrategy Adaptive_Expert; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { return(Adaptive_Expert.Expert_OnInit()); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { Adaptive_Expert.Expert_OnDeInit(reason); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert tick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { Adaptive_Expert.Expert_OnTick(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
最初の3行でプログラムのプロパティを定義し、その後、プリプロセッサにCAdaptiveStrategy.mqhファイルをインクルードするよう指示する#include 指令へと続きます。かぎ括弧は、ファイルが標準ディレクトリ(通常は、terminal_folder\MQL5\Include)から読み込まれなければならないことを意味します。
次の行には、Adaptive_Expertオブジェクト(CAdaptiveStrategyクラスのインスタンス)の宣言が含まれます;エキスパートアドバイザでのOnInit、OnDeinit、およびOnTick関数のコードは、それぞれ対応するExpert_OnInit、Expert_OnDeInit、およびExpert_OnTickの各関数と、the Adaptive_Expertオブジェクトの呼び出しで構成されています。
2.2 CAdaptiveStrategyクラス
適応型エキスパートアドバイザのクラス(CAdaptiveStrategyクラス)はCAdaptiveStrategy.mqhファイルに配置されています。インクルードファイルから始めていきましょう:
#include <Arrays\ArrayObj.mqh> #include <Trade\PositionInfo.mqh> #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> #include <CStrategyMA.mqh> #include <CStrategyStoch.mqh>
ArrayObj.mqhファイルをインクルードする理由は、基本クラスCObjectとその下位コードで生成されるクラスインスタンスへのポインタの動的な配列を表すCArrayObjクラスのオブジェクトを用いた、異なるストラテジーのクラスを容易に扱うためです。このオブジェクトはm_all_strategies配列であり、トレーディングストラテジーの「コンテナ」として使われます。
各ストラテジーはクラスとして表されます。ここでは、移動平均とストキャスティクスによるトレーディングストラテジーを表す、CStrategyMAクラスおよびCStrategyStochクラスを含むファイルをインクルードしました。
現在のポジションのプロパティをリクエストし、トレード操作を実行するためには、標準ライブラリのCPositionInfoクラスとCTradeクラスを使用します。これが、PositionInfo.mqhファイルとTrade.mqhファイルをインクルードする理由です。
CAdaptiveStrategyクラスのストラクチャを見てみましょう。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class CAdaptiveStrategy | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CAdaptiveStrategy { protected: CArrayObj *m_all_strategies; // objects of trade strategies void ProceedSignalReal(int state,double trade_volume); int RealPositionDirection(); public: // initialization of the adaptive strategy int Expert_OnInit(); // deinitialization of the adaptive strategy int Expert_OnDeInit(const int reason); // check of trade conditions and opening of virtual positions void Expert_OnTick(); };
統一されたオブジェクトへのアプローチを実行するために、トレーディングストラテジー(あるいはむしろ、それらのクラスのインスタンス)は、ストラテジークラスの「コンテナ」として用いられる、(CArrayObj型の)動的配列m_all_strategiesに格納されます。これが、SampleStrategyというトレーディングストラテジーのクラスが、 CObjectクラスから生成される理由です。
ProceedSignalReal関数は、リアルポジションの方向と大きさを指定の方向と大きさに「同期」します:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| This method is intended for "synchronization" of current | //| real trade position with the value of the 'state' state | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CAdaptiveStrategy::ProceedSignalReal(int state,double trade_volume) { CPositionInfo posinfo; CTrade trade; bool buy_opened=false; bool sell_opened=false; if(posinfo.Select(_Symbol)) // if there are open positions { if(posinfo.Type()==POSITION_TYPE_BUY) buy_opened=true; // a buy position is opened if(posinfo.Type()==POSITION_TYPE_SELL) sell_opened=true; // a sell position is opened // if state = 0, then we need to close open positions if((state==POSITION_NEUTRAL) && (buy_opened || sell_opened)) { if(!trade.PositionClose(_Symbol,200)) Print(trade.ResultRetcodeDescription()); } //reverse: closing buy position and opening sell position if((state==POSITION_SHORT) && (buy_opened)) { if(!trade.PositionClose(_Symbol,200)) Print(trade.ResultRetcodeDescription()); if(!trade.PositionOpen(_Symbol,ORDER_TYPE_SELL,trade_volume,SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol,SYMBOL_BID),0,0)) Print(trade.ResultRetcodeDescription()); } //reverse: close sell position and open buy position if(((state==POSITION_LONG) && (sell_opened))) { if(!trade.PositionClose(_Symbol,200)) Print(trade.ResultRetcodeDescription()); if(!trade.PositionOpen(_Symbol,ORDER_TYPE_BUY,trade_volume,SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol,SYMBOL_ASK),0,0)) Print(trade.ResultRetcodeDescription()); } } else // if there are no open positions { // open a buy position if(state==POSITION_LONG) { if(!trade.PositionOpen(_Symbol,ORDER_TYPE_BUY,0.1,SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol,SYMBOL_ASK),0,0)) Print(trade.ResultRetcodeDescription()); } // open a sell position if(state==POSITION_SHORT) { if(!trade.PositionOpen(_Symbol,ORDER_TYPE_SELL,0.1,SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol,SYMBOL_BID),0,0)) Print(trade.ResultRetcodeDescription()); } } }
トレードクラスを用いると、トレードポジションをより簡単に扱えることに注目してください。ここでは、マーケットポジションのプロパティをリクエストし、トレード操作を実行するために、それぞれCPositionInfoクラスと CTradeクラスのオブジェクトを用います。
RealPositionDirection関数で、リアルオープンポジションのパラメータをリクエストし、その指令を返します:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns direction (0,+1,-1) of the current real position | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int CAdaptiveStrategy::RealPositionDirection() { int direction=POSITION_NEUTRAL; CPositionInfo posinfo; if(posinfo.Select(_Symbol)) // if there are open positions { if(posinfo.Type()==POSITION_TYPE_BUY) direction=POSITION_LONG; // a buy position is opened if(posinfo.Type()==POSITION_TYPE_SELL) direction=POSITION_SHORT; // a short position is opened } return(direction); }
ここで、СAdaptiveStrategyクラスの主な機能を見ていきましょう。
Expert_OnInit:関数
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Function of initialization of the Adaptive Expert Advisor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int CAdaptiveStrategy::Expert_OnInit() { //--- Create array of objects m_all_strategies //--- we will put our object with strategies in it m_all_strategies=new CArrayObj; if(m_all_strategies==NULL) { Print("Error of creation of the object m_all_strategies"); return(-1); } // create 10 trading strategies CStrategyMA (trading by moving averages) // initialize them, set parameters // and add to the m_all_strategies container for(int i=0; i<10; i++) { CStrategyMA *t_StrategyMA; t_StrategyMA=new CStrategyMA; if(t_StrategyMA==NULL) { delete m_all_strategies; Print("Error of creation of object of the CStrategyMA type"); return(-1); } //set period for each strategy int period=3+i*10; // initialize strategy t_StrategyMA.Initialization(period,true); // set details of the strategy t_StrategyMA.SetStrategyInfo(_Symbol,"[MA_"+IntegerToString(period)+"]",period,"Moving Averages "+IntegerToString(period)); //t_StrategyMA.Set_Stops(3500,1000); //add the object of the strategy to the array of objects m_all_strategies m_all_strategies.Add(t_StrategyMA); } for(int i=0; i<m_all_strategies.Total(); i++) { CSampleStrategy *t_SampleStrategy; t_SampleStrategy=m_all_strategies.At(i); Print(i," Strategy name:",t_SampleStrategy.StrategyName(), " Strategy ID:",t_SampleStrategy.StrategyID(), " Virtual trading:",t_SampleStrategy.IsVirtualTradeAllowed()); } //--- return(0); }
トレーディングストラテジーのセットが、Expert_OnInit関数に用意されています。まず、m_all_strategiesという動的配列のオブジェクトが作成されます。
このケースでは、CStrategyMAクラスで10のインスタンスを作成しました。それぞれ、Initialization関数を用いて初期化されました(このケースでは、異なる期間を設定し「バーチャル」トレーディングを有効にしました)。
次に、SetStrategyInfo関数を用いて、金融手段、ストラテジー名とコメントを設定します。
必要に応じてSet_Stops(TP,SL)関数を用いて、 「バーチャル」トレーディングで実行されるテイクプロフィットとストップロスの(ポイントによる)値を指定することができます。この行は、今回はコメントアウトしています。
ストラテジークラスの作成と調整が終わったら、m_all_strategiesコンテナに追加します。
トレーディングストラテジーのすべてのクラスは、トレーディング条件のチェックを実行するCheckTradeConditions()関数を備えています。適応型ストラテジーのクラスでは、この関数は各新規バーの先頭で呼び出され、これにより、ストラテジーがインディケータの値をチェックして「バーチャル」トレード運用を行うことができます。
10の特定された移動平均(3、13、23...93)の代わりに、何百もの移動平均(CStrategyMAクラスの場合はインスタンス)を追加することができます:
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) { CStrategyMA *t_StrategyMA; t_StrategyMA=new CStrategyMA; if(t_StrategyMA==NULL) { delete m_all_strategies; Print("Error of creation of object of the CStrategyMA type"); return(-1); } //set period for each strategy int period=3+i*10; // initialization of strategy t_StrategyMA.Initialization(period,true); // set details of the strategy t_StrategyMA.SetStrategyInfo(_Symbol,"[MA_"+IntegerToString(period)+"]",period,"Moving Averages "+IntegerToString(period)); //add the object of the strategy to the array of objects m_all_strategies m_all_strategies.Add(t_StrategyMA); }
あるいは、ストキャスティクス(CStrategyStochクラスのインスタンス)のシグナルにより動作するストラテジークラスを追加することができます:
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) { CStrategyStoch *t_StrategyStoch; t_StrategyStoch=new CStrategyStoch; if(t_StrategyStoch==NULL) { delete m_all_strategies; printf("Error of creation of object of the CStrategyStoch type"); return(-1); } //set period for each strategy int Kperiod=2+i*5; int Dperiod=2+i*5; int Slowing=3+i; // initialization of strategy t_StrategyStoch.Initialization(Kperiod,Dperiod,Slowing,true); // set details of the strategy string s=IntegerToString(Kperiod)+"/"+IntegerToString(Dperiod)+"/"+IntegerToString(Slowing); t_StrategyStoch.SetStrategyInfo(_Symbol,"[Stoch_"+s+"]",100+i," Stochastic "+s); //add the object of the strategy to the array of objects m_all_strategies m_all_strategies.Add(t_StrategyStoch); }
この場合、コンテナには移動平均の10ストラテジーと、ストキャスティクスの5ストラテジーとが含まれます。
トレーディングストラテジーのインスタンスは、CObjectクラスの下位クラスである必要が、またCheckTradeConditions()関数を含む必要があります。それらをCSampleStrategyクラスから引き継ぐと、より好ましいです。トレーディングストラテジーを実行するクラスは異なっていてもよく、クラス数の制限もありません。
Expert_OnInit関数は、m_all_strategiesコンテナに存在するストラテジーのリストをもって終了します。コンテナ内のすべてのストラテジーが、CSampleStrategyクラスの下位に認識されていることに注目してください。トレーディングストラテジーのクラス、CStrategyMAとCStrategyStochもまた、その下位クラスです。
同様のトリックが、Expert_OnDeInit関数でも用いられます。コンテナ内で、各ストラテジーのSaveVirtualDeals関数を呼び出します;この関数は、実行されたバーチャル取引履歴を格納します。
ストラテジー名を、パラメータとして渡されるファイルの名称に用います。次に、Deinitialization()関数を呼び出してm_all_strategiesコンテナを削除することで、ストラテジーの初期化を解消します:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Function of deinitialization the adaptive Expert Advisor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int CAdaptiveStrategy::Expert_OnDeInit(const int reason) { // deinitialize all strategies for(int i=0; i<m_all_strategies.Total(); i++) { CSampleStrategy *t_Strategy; t_Strategy=m_all_strategies.At(i); t_Strategy.SaveVirtualDeals(t_Strategy.StrategyName()+"_deals.txt"); t_Strategy.Deinitialization(); } //delete the array of object with strategies delete m_all_strategies; return(0); }
ストラテジーによって実行されるバーチャル取引について知る必要がなければ、tStrategy.SaveVirtualDealsによって呼び出される行を削除してください。ストラテジーテスターを用いる際、ファイルは/tester_directory/Files/ディレクトリに保存されることに注意してください。
新たなティック操作ごとに呼び出される、CAdaptiveStrategyクラスのExpert_OnTick関数を考えてみましょう。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Function of processing ticks of the adaptive strategy | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CAdaptiveStrategy::Expert_OnTick() { CSampleStrategy *t_Strategy; // recalculate the information about positions for all strategies for(int i=0; i<m_all_strategies.Total(); i++) { t_Strategy=m_all_strategies.At(i); t_Strategy.UpdatePositionData(); } // the expert advisor should check the conditions of making trade operations only when a new bar comes if(IsNewBar()==false) { return; } // check trading conditions for all strategies for(int i=0; i<m_all_strategies.Total(); i++) { t_Strategy=m_all_strategies.At(i); t_Strategy.CheckTradeConditions(); } //search for the best position //prepare the array performance[] double performance[]; ArrayResize(performance,m_all_strategies.Total()); //request the current effectiveness for each strategy, //each strategy returns it in the Strategyperformance() function for(int i=0; i<m_all_strategies.Total(); i++) { t_Strategy=m_all_strategies.At(i); performance[i]=t_Strategy.StrategyPerformance(); } //find the strategy (or rather its index in the m_all_strategies container) //with maximum value of Strategyperformance() int best_strategy_index=ArrayMaximum(performance,0,WHOLE_ARRAY); //this strategy is - t_Strategy t_Strategy=m_all_strategies.At(best_strategy_index); //request the direction of its current position int best_direction=t_Strategy.PositionDirection(); string s=s+" "+t_Strategy.StrategyName()+" "+DoubleToString(t_Strategy.GetVirtualEquity())+" "+IntegerToString(best_direction); Print(TimeCurrent()," TOTAL=",m_all_strategies.Total(), " BEST IND=",best_strategy_index, " BEST STRATEGY="," ",t_Strategy.StrategyName(), " BEST=",performance[best_strategy_index]," =", " BEST DIRECTION=",best_direction, " Performance=",t_Strategy.StrategyPerformance()); //if the best strategy has a negative result and doesn't have open positions, it's better to stay away from trading if((performance[best_strategy_index]<0) && (RealPositionDirection()==POSITION_NEUTRAL)) {return;} if(best_direction!=RealPositionDirection()) { ProceedSignalReal(best_direction,t_Strategy.GetCurrentLotSize()); } }
このコードはたいへんシンプルです。コンテナ内に配置される各ストラテジーは、現在の価格を用いて、バーチャルポジションの現在の財政的結果を再計算することができなければなりません。これは、UpdatePositionData()関数の呼び出しによって行われます。ここでもう一度、CSampleStrategyクラスの継承者としてストラテジーを呼び出します。
すべてのトレード運用は、新規バーの最初に実行されます(IsNewBar()関数が、新規バーをチェックする他のメソッドと同様に、このタイミングを決定します)。このケースでは、1つのバーの形成終了が、以前のバーのすべてのデータ(価格とインディケータの値)がこれ以上変わらないことを意味するため、トレーディング条件に対応した分析が可能となります。すべてのストラテジーに対してCheckTradeConditions関数を呼び出してチェックを実行し、バーチャルトレード運用を実行することができます。
さて、m_all_strategies配列内のすべてのストラテジーの中から、最も成功しているストラテジーを探す必要があります。これを行うために、Performance[]配列を用いて、各ストラテジーのStrategyPerformance()関数が返す値を格納しました。基本クラスCSampleStrategyには、「バーチャル」な資産と残高の現在価値の間の差分として、この関数が含まれます。
最も成功しているストラテジーのインデックス検索は、ArrayMaximum関数により実行されます。最良のストラテジーが、現時点ではマイナスの利益となりリアルのオープンポジションを持たない場合には、トレードを行わないほうが好ましく、これがこの関数から抜ける理由となります(セクション1を参照してください)。
さらに、このストラテジのバーチャルポジションの方向(best_direction)をリクエストします。これが現在のリアルポジションの方向と異なる場合は、リアルポジションの現在の方向が( ProceedSignalReal関数を用いて)best_directionの方向に修正されます。
2.3 CSampleStrategyクラス
m_all_strategiesコンテナに配置されるストラテジーは、CSampleStrategyクラスの継承者として見なされました。
このクラスはトレーディングストラテジーの基礎となるものです;バーチャルトレーディングの実行が含まれます。本稿では、スワップを考慮しない、バーチャルトレーディング実行の単純化されたケースを検討します。トレーディングストラテジークラスは、CSampleStrategyクラスから継承される必要があります。
このクラスのストラクチャを見てみましょう。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| CSampleStrategy.mqh | //| Copyright 2010, MetaQuotes Software Corp. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2010, MetaQuotes Software Corp." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #include <Object.mqh> #define POSITION_NEUTRAL 0 // no position #define POSITION_LONG 1 // long position #define POSITION_SHORT -1 // short position #define SIGNAL_OPEN_LONG 10 // signal to open a long position #define SIGNAL_OPEN_SHORT -10 // signal to open a short position #define SIGNAL_CLOSE_LONG -1 // signal to close a long position #define SIGNAL_CLOSE_SHORT 1 // signal to close a short position //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Structure for storing the parameters of virtual position | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ struct virtual_position { string symbol; // symbol int direction; // direction of the virtual position (0-no open position,+1 long,-1 short) double volume; // volume of the position in lots double profit; // current profit of the virtual position on points double stop_loss; // Stop Loss of the virtual position double take_profit; // Take Profit of the virtual position datetime time_open; // date and time of opening the virtual position datetime time_close; // date and time of closing the virtual position double price_open; // open price of the virtual position double price_close; // close price of the virtual position double price_highest; // maximum price during the life of the position double price_lowest; // minimal price during the lift of the position double entry_eff; // effectiveness of entering double exit_eff; // effectiveness of exiting double trade_eff; // effectiveness of deal }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class CSampleStrategy | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CSampleStrategy: public CObject { protected: int m_strategy_id; // Strategy ID string m_strategy_symbol; // Symbol string m_strategy_name; // Strategy name string m_strategy_comment; // Comment MqlTick m_price_last; // Last price MqlRates m_rates[]; // Array for current quotes bool m_virtual_trade_allowed; // Flag of allowing virtual trading int m_current_signal_state; // Current state of strategy double m_current_trade_volume; // Number of lots for trading double m_initial_balance; // Initial balance (set in the constructor, default value is 10000) int m_sl_points; // Stop Loss int m_tp_points; // Take Profit virtual_position m_position; // Virtual position virtual_position m_deals_history[]; // Array of deals int m_virtual_deals_total; // Total number of deals double m_virtual_balance; // "Virtual" balance double m_virtual_equity; // "Virtual" equity double m_virtual_cumulative_profit; // cumulative "virtual" profit double m_virtual_profit; // profit of the current open "virtual" position //checks and closes the virtual position by stop levels if it is necessary bool CheckVirtual_Stops(virtual_position &position); // recalculation of position and balance void RecalcPositionProperties(virtual_position &position); // recalculation of open virtual position in accordance with the current prices void Position_RefreshInfo(virtual_position &position); // open virtual short position void Position_OpenShort(virtual_position &position); // closes virtual short position void Position_CloseShort(virtual_position &position); // opens virtual long position void Position_OpenLong(virtual_position &position); // closes the virtual long position void Position_CloseLong(virtual_position &position); // closes open virtual position void Position_CloseOpenedPosition(virtual_position &position); // adds closed position to the m_deals_history[] array (history of deals) void AddDealToHistory(virtual_position &position); //calculates and returns the recommended volume that will be used in trading virtual double MoneyManagement_CalculateLots(double trade_volume); public: // constructor void CSampleStrategy(); // destructor void ~CSampleStrategy(); //returns the current size of virtual balance double GetVirtualBalance() { return(m_virtual_balance); } //returns the current size of virtual equity double GetVirtualEquity() { return(m_virtual_equity); } //returns the current size of virtual profit of open position double GetVirtualProfit() { return(m_virtual_profit); } //sets Stop Loss and Take Profit in points void Set_Stops(int tp,int sl) {m_tp_points=tp; m_sl_points=sl;}; //sets the current volume in lots void SetLots(double trade_volume) {m_current_trade_volume=trade_volume;}; //returns the current volume in lots double GetCurrentLots() { return(m_current_trade_volume); } // returns strategy name string StrategyName() { return(m_strategy_name); } // returns strategy ID int StrategyID() { return(m_strategy_id); } // returns the comment of strategy string StrategyComment() { return(m_strategy_comment); } // sets the details of strategy (symbol, name and ID of strategy) void SetStrategyInfo(string symbol,string name,int id,string comment); // set the flag of virtual trading (allowed or not) void SetVirtualTradeFlag(bool pFlag) { m_virtual_trade_allowed=pFlag; }; // returns flag of allowing virtual trading bool IsVirtualTradeAllowed() { return(m_virtual_trade_allowed); }; // returns the current state of strategy int GetSignalState(); // sets the current state of strategy (changes virtual position if necessary) void SetSignalState(int state); // changes virtual position in accordance with the current state void ProceedSignalState(virtual_position &position); // sets the value of cumulative "virtual" profit void SetVirtualCumulativeProfit(double cumulative_profit) { m_virtual_cumulative_profit=cumulative_profit; }; //returns the effectiveness of strategy () double StrategyPerformance(); //updates position data void UpdatePositionData(); //closes open virtual position void CloseVirtualPosition(); //returns the direction of the current virtual position int PositionDirection(); //virtual function of initialization virtual int Initialization() {return(0);}; //virtual function of checking trade conditions virtual bool CheckTradeConditions() {return(false);}; //virtual function of deinitialization virtual int Deinitialization() {return(0);}; //saves virtual deals to a file void SaveVirtualDeals(string file_name); };
ここではコード記述の詳細な分析は行いません。その他の情報はCSampleStrategy.mqh内にありますので、参照してください。新規バーをチェックする関数-IsNewBarについても、そこで述べられています。
3.トレーディングストラテジーのクラス
本セクションでは、適応型エキスパートアドバイザで用いられるトレーディングストラテジーのクラスストラクチャーに焦点を当てます。
3.1CStrategyMAクラス-移動平均によるトレーディングストラテジー
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| CStrategyMA.mqh | //| Copyright 2010, MetaQuotes Software Corp. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2010, MetaQuotes Software Corp." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #include <CSampleStrategy.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class CStrategyMA for implementation of virtual trading | //| by the strategy based on moving average | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CStrategyMA : public CSampleStrategy { protected: int m_handle; // handle of the Moving Average (iMA) indicator int m_period; // period of the Moving Average indicator double m_values[]; // array for storing values of the indicator public: // initialization of the strategy int Initialization(int period,bool virtual_trade_flag); // deinitialization of the strategy int Deinitialization(); // checking trading conditions and opening virtual positions bool CheckTradeConditions(); };
CStrategyMAクラスは、バーチャルトレーディングの機能全体が実行されるCSampleStrategyの下位クラスです。
この保護されたセクションには、ストラテジーのクラスで用いられる内部変数が含まれます。変数には以下のようなものがあります:m_handle-iMAインディケータのハンドル、m_period-移動平均期間、m_values[]-CheckTradeConditions関数がインディケータの現在の値を取得するために用いる配列。
パブリックセクションには、トレーディングストラテジーの実行を可能にする3つの関数が含まれます。
- Initialization関数.ストラテジーはここで初期化されます。インディケータを作成する必要があれば、ここで作成します。
- Deinitialization関数.ストラテジーの初期化がここで解消されます。インディケータのハンドルがここで解放されます。
- СheckTradeConditions関数.ここで、ストラテジーはトレーディング条件をチェックし、バーチャルトレーディング用のトレーディングシグナルを生成します。バーチャルトレーディング操作を実行するには、CStrategyの上位クラスであるSetSignalState関数が呼び出されます;以下の4トレーディングシグナルの1つが渡されます。
- ロングポジションをオープンするシグナル(SIGNAL_OPEN_LONG)
- ショートポジションをオープンするシグナル(SIGNAL_OPEN_SHORT)
- ロングポジションをクローズするシグナル(SIGNAL_CLOSE_LONG)
- ショートポジションをクローズするシグナル(SIGNAL_CLOSE_SHORT)
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Strategy Initialization Method | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int CStrategyMA::Initialization(int period,bool virtual_trade_flag) { // set period of the moving average m_period=period; // set specified flag of virtual trading SetVirtualTradeFlag(virtual_trade_flag); //set indexation of arrays like the one of timeseries ArraySetAsSeries(m_rates,true); ArraySetAsSeries(m_values,true); //create handle of the indicator m_handle=iMA(_Symbol,_Period,m_period,0,MODE_EMA,PRICE_CLOSE); if(m_handle<0) { Alert("Error of creation of the MA indicator - error number: ",GetLastError(),"!!"); return(-1); } return(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Strategy Deinitialization Method | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int CStrategyMA::Deinitialization() { Position_CloseOpenedPosition(m_position); IndicatorRelease(m_handle); return(0); }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Checking trading conditions and opening virtual positions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CStrategyMA::CheckTradeConditions() { RecalcPositionProperties(m_position); double p_close; // get history data of the last three bars if(CopyRates(_Symbol,_Period,0,3,m_rates)<0) { Alert("Error of copying history data - error:",GetLastError(),"!!"); return(false); } // Copy the current price of closing of the previous bar (it is bar 1) p_close=m_rates[1].close; // close price of the previous bar if(CopyBuffer(m_handle,0,0,3,m_values)<0) { Alert("Error of copying buffers of the Moving Average indicator - error number:",GetLastError()); return(false); } // buy condition 1: MA rises bool buy_condition_1=(m_values[0]>m_values[1]) && (m_values[1]>m_values[2]); // buy condition 2: previous price is greater than the MA bool buy_condition_2=(p_close>m_values[1]); // sell condition 1: // MA falls bool sell_condition_1=(m_values[0]<m_values[1]) && (m_values[1]<m_values[2]); // sell condition 2: // previous price is lower than the MA bool sell_condition_2=(p_close<m_values[1]); int new_state=0; if(buy_condition_1 && buy_condition_2) new_state=SIGNAL_OPEN_LONG; if(sell_condition_1 && sell_condition_2) new_state=SIGNAL_OPEN_SHORT; if((GetSignalState()==SIGNAL_OPEN_SHORT) && (buy_condition_1 || buy_condition_2)) new_state=SIGNAL_CLOSE_SHORT; if((GetSignalState()==SIGNAL_OPEN_LONG) && (sell_condition_1 || sell_condition_2)) new_state=SIGNAL_CLOSE_LONG; if(GetSignalState()!=new_state) { SetSignalState(new_state); } return(true); };
このコンセプトはシンプルです-インディケータの状態と価格にもとづいてシグナルタイプ(new_state)が決定され、次にバーチャルトレーディングの現在の状況が(GetSignalState関数を用いて)リクエストされます;そして、それらが同一でない場合は、SetSignalState関数が呼び出されてバーチャルポジションが「修正」されます。
3.2CStrategyStochクラス-ストキャスティクスによるトレーディングストラテジー
iStochasticオシレータの主要シグナル行の交差にもとづいてトレードを行うクラスのコードを、以下に示します:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| CStrategyStoch.mqh | //| Copyright 2010, MetaQuotes Software Corp. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2010, MetaQuotes Software Corp." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #include <CSampleStrategy.mqh> //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class CStrategyStoch for implementation of virtual trading by | //| the strategy of intersection of lines of stochastic oscillator | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CStrategyStoch : public CSampleStrategy { protected: int m_handle; // handle of the Stochastic Oscillator (iStochastic) int m_period_k; // K-period (number of bars for calculations) int m_period_d; // D-period (period of primary smoothing) int m_period_slowing; // final smoothing double m_main_line[]; // array for storing indicator values double m_signal_line[]; // array for storing indicator values public: // initialization of strategy int Initialization(int period_k,int period_d,int period_slowing,bool virtual_trade_flag); // deinitialization of strategy int Deinitialization(); // checking trading conditions and opening virtual positions bool CheckTradeConditions(); }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Strategy Initialization Method | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int CStrategyStoch::Initialization(int period_k,int period_d,int period_slowing,bool virtual_trade_flag) { // Set period of the oscillator m_period_k=period_k; m_period_d=period_d; m_period_slowing=period_slowing; // set specified flag of the virtual trading SetVirtualTradeFlag(virtual_trade_flag); // set indexation of arrays like the one of timeseries ArraySetAsSeries(m_rates,true); ArraySetAsSeries(m_main_line,true); ArraySetAsSeries(m_signal_line,true); // create handle of the indicator m_handle=iStochastic(_Symbol,_Period,m_period_k,m_period_d,m_period_slowing,MODE_SMA,STO_LOWHIGH); if(m_handle<0) { Alert("Error of creating the Stochastic indicator - error number: ",GetLastError(),"!!"); return(-1); } return(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Strategy Deinitialization Method | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int CStrategyStoch::Deinitialization() { // close all open positions Position_CloseOpenedPosition(m_position); // release handle of the indicator IndicatorRelease(m_handle); return(0); }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Checking Trading Conditions and Opening Virtual Positions | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CStrategyStoch::CheckTradeConditions() { // call the functions of recalculation of position parameters RecalcPositionProperties(m_position); double p_close; // get history data of the last 3 bars if(CopyRates(_Symbol,_Period,0,3,m_rates)<0) { Alert("Error of copying history data - error:",GetLastError(),"!!"); return(false); } // copy the current close price of the previous bar (it is bar 1) p_close=m_rates[1].close; // close price of the previous bar if((CopyBuffer(m_handle,0,0,3,m_main_line)<3) || (CopyBuffer(m_handle,1,0,3,m_signal_line)<3)) { Alert("Error of copying buffers of the Stochastic indicator - error number:",GetLastError()); return(false); } // buy condition: crossing the signal line by the main one from bottom up bool buy_condition=((m_signal_line[2]<m_main_line[2]) && (m_signal_line[1]>m_main_line[1])); // sell condition: crossing the signal line by the main one from top downwards bool sell_condition=((m_signal_line[2]>m_main_line[2]) && (m_signal_line[1]<m_main_line[1])); int new_state=0; if(buy_condition) new_state=SIGNAL_OPEN_LONG; if(sell_condition) new_state=SIGNAL_OPEN_SHORT; if((GetSignalState()==SIGNAL_OPEN_SHORT) && (buy_condition)) new_state=SIGNAL_CLOSE_SHORT; if((GetSignalState()==SIGNAL_OPEN_LONG) && (sell_condition)) new_state=SIGNAL_CLOSE_LONG; if(GetSignalState()!=new_state) { SetSignalState(new_state); } return(true); };
見てわかるように、 CStrategyStochクラスとCStrategyMAクラスのストラクチャの違いは単に、初期化関数(パラメータが異なる)、用いられるインディケータのタイプ 、そしてトレーディングシグナルのみです。
したがって、適応型エキスパートアドバイザに独自のストラテジーを用いるためには、そうしたタイプのクラスのフォーマットとしてリライトして、m_all_strategiesコンテナにロードする必要があります。
4. 適応型トレーディングストラテジーの分析結果
本セクションでは、適応型ストラテジーとその改良方法の実際に関するいくつかの側面について議論していきます。
4.1 逆シグナルを用いたストラテジーをともなうシステムの改良
移動平均は、トレンドが存在しない場合には役立ちません。このような状況には、これまでにすでに直面しています-図3において、1月8日から20日までの期間はトレンドが存在しなかったことが分かります;そのためトレーディングにおいて、移動平均を用いるすべての10ストラテジーがバーチャルロスをもたらしました。適応型システムは、マネーを獲得できるストラテジーが存在しない場合、トレーディングを中止しました。そのような、ネガティブな影響を避ける方法があるでしょうか?
ここまでの10ストラテジー(MA_3、MA_13、... MA_93)に、トレーディングシグナルが反転する10のクラスCStrategyMAinvを追加してみましょう(諸条件は同じですが、SIGNAL_OPEN_LONG/SIGNAL_OPEN_SHORTと SIGNAL_CLOSE_LONG/SIGNAL_CLOSE_SHORTの位置が互いに変わりました)。したがって、10のトレンドストラテジー(CStrategyMAクラスのインスタンス)に加えて、さらに10の反トレンドストラテジー( CStrategyMAinvクラスのインスタンス)を備えることになります。
20のストラテジーからなる適応型システムを用いた結果を、図5に示します。
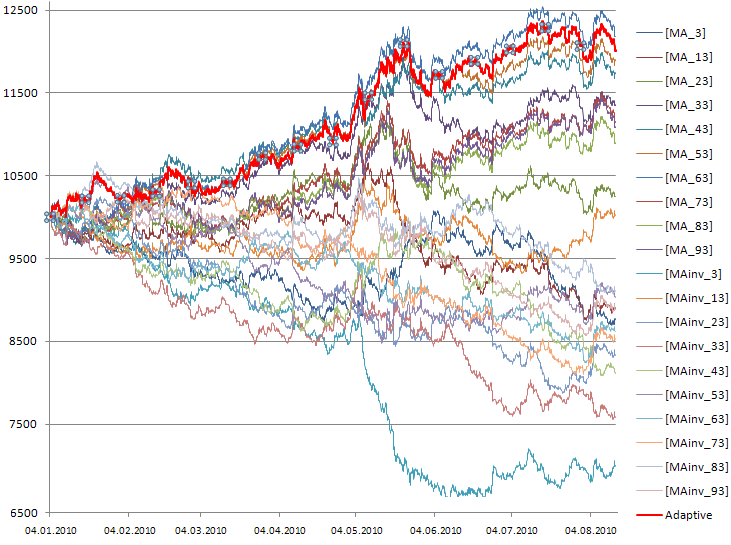
図520のトレーディングシグナルを用いる適応型ストラテジーの取引資産ダイアグラム:10の移動平均CAdaptiveMAと、それらが「ミラーリングされた」10のCAdaptiveMAinv
図5に見られるように、すべてのCAdaptiveMAストラテジーがネガティブな結果である場合には、CAdaptiveMAinvストラテジーにしたがうことで、エキスパートアドバイザが、トレード初期において不都合なドローダウンを避けることができました。
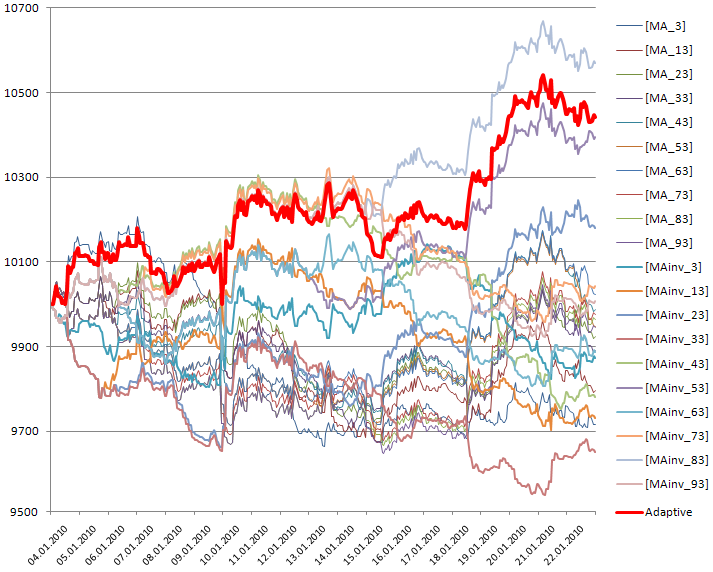
図6適応型ストラテジーが「反トレンド」であるCAdaptiveMAinvCAdaptiveMAinvストラテジーを用いた期間
預金を失うのは反トレンドストラテジーを用いる時間の問題であるため、このようなアプローチは、一見認められないかもしれません。しかしこのケースは、単一のストラテジーに縛られているわけではありません。マーケットは、その時々でどのストラテジーが効果的であるかをよりよく知っています。
適応型システムの強みは、どのストラテジーをいつ用いるべきであるかを、マーケット自身が提示することにあります。
ストラテジーのロジックから抽象化することができるのです-ストラテジーが効果的であるなら、効果的である方法に意味はありません。適応型アプローチには、ストラテジーのただ1つの成功基準-効果的であること、が用いられます。
4.2最悪のストラテジーのシグナルに投資する価値があるか?
上記のような反転のトリックから、最悪のストラテジーのシグナルを用いる潜在的可能性が想起されます。あるストラテジーが利益を生まない(そして最悪である)ならば、逆に活用することで利益を得ることができるでしょうか?
単純にシグナルを変更することで、勝算のないストラテジーを利益を生み出すものに変えることができるでしょうか?この問いに答えるためには、CAdaptiveStrategyクラスのExpert_OnTick()関数において、ArrayMaximumを ArrayMinimumに変更し、BestDirection変数に-1を掛けて方向変換を行う必要があります。
加えて、効果を生み出さない場合のバーチャルトレーディングの制約をコメントアウトする必要があります(なぜなら、最悪のストラテジーを分析しようとしているからです):
//if((Performance[BestStrategyIndex]<0) && (RealPositionDirection()==0)) {return;}
最悪のストラテジーのシグナルを反転して用いる適応型エキスパートアドバイザの資産ダイアグラムを、図7に示します:
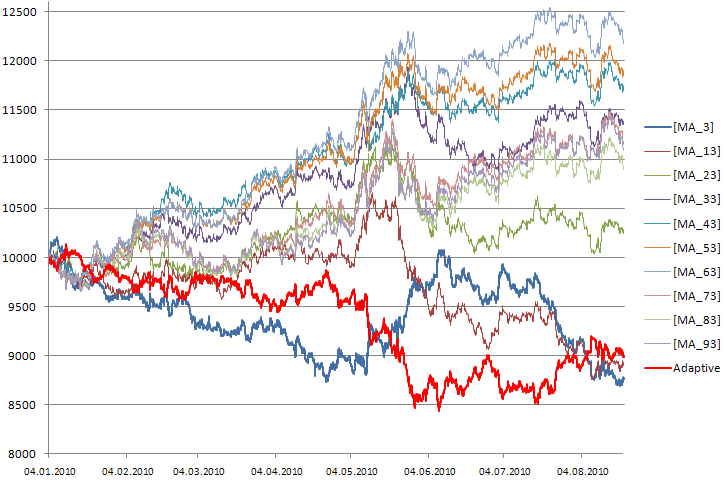
図710のストラテジーの取引資産ダイアグラムと、最悪のシステムのシグナルを反転して用いた適応型システム
このケースでは、成功から最もかけ離れたストラテジーは、ほとんどが、期間3(MA_3)の移動平均の交差位置にもとづいていました。図7に見られるように、MA_3(青色)と適応型ストラテジー(赤色)との間には逆の相関が存在していますが、適応型システムの財政的な結果に影響はありません。
最悪のストラテジーのシグナルをコピーし(反転させ)ても、トレードの効果を改良することはできません。
4.2 なぜ移動平均の束は見た目ほど効果的ではないのか?
10の移動平均の代わりに、期間の異なるその他何百ものCStrategyMAストラテジーをm_all_strategiesコンテナに加えて、たくさんの移動平均を用いることができます。
このためには、CAdaptiveStrategyクラスのコードを若干変更します:
for(int i=0; i<100; i++) { CStrategyMA *t_StrategyMA; t_StrategyMA=new CStrategyMA; if(t_StrategyMA==NULL) { delete m_all_strategies; Print("Error of creation of object of the CStrategyMA type"); return(-1); } //set period for each strategy int period=3+i*10; // initialization of strategy t_StrategyMA.Initialization(period,true); // set details of the strategy t_StrategyMA.SetStrategyInfo(_Symbol,"[MA_"+IntegerToString(period)+"]",period,"Moving Averages "+IntegerToString(period)); //add the object of the strategy to the array of objects m_all_strategies m_all_strategies.Add(t_StrategyMA); }
しかし、近接する移動平均は交差を免れず、また先頭が常に変わるため、適応型システムは必要以上に頻繁に、ポジションのオープン/クローズのステータスをを切り替えることになることを理解しなくてはなりません。結果的に、適応型システムの特徴が損なわれることになります。これは、システムの統計的特徴(ストラテジーテスターの「Results」タブで)を比較することで確認できます。
近接するパラメータを持つ多くのストラテジーにもとづいた適応型システムを、作るべきではありません。
5考慮すべき事項
m_all_strategiesコンテナには何千ものインクルード対象のインスタンスを格納することができ、異なるパラメータのすべてのストラテジーを追加することもできます;しかしAutomated Trading Championship 2010で勝利を収めるためには、高度なマネー管理システムを開発する必要があります。履歴データ(およびクラスコード)の検証用に、0.1ロット相当の取引量を用いていることに注意してください。
5.1 適応型エキスパートアドバイザの収益性を増やすには?
CSampleStrategyクラスには、バーチャル関数MoneyManagement_CalculateLotsがあります:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| The function returns the recommended volume for a strategy | //| Current volume is passed to it as a parameter | //| Volume can be set depending on: | //| current m_virtual_balance and m_virtual_equity | //| current statistics of deals (located in m_deals_history) | //| or any other thing you want | //| If a strategy doesn't require change of volume | //| you can return the passed value of volume: return(trade_volume);| //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CSampleStrategy::MoneyManagement_CalculateLots(double trade_volume) { //return what we've got return(trade_volume); }
トレードの量を管理するには、m_deals_history[]配列に記録されるバーチャル取引の結果と特徴に関する統計的情報を用いることができます。
取引量を増やす必要があれば(例えばm_deals_history[]の最後のバーチャル取引が収益的である場合、2倍にする;もしくは減らす)、対応する方法により返された値を変更しなければなりません。
5.2 取引統計を用いてストラテジーのパフォーマンスを計算する
CSampleStrategyクラスで実行されるStrategyPerformance()関数CSampleStrategyは、ストラテジーのパフォーマンス計算を目的とし、以下のように用いられます。
//+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Function StrategyPerformance - the function of strategy effectiveness | //+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+ double CSampleStrategy::StrategyPerformance() { //returns effectiveness of a strategy //in this case it's the difference between the amount //of equity at the moment and the initial balance, //i.e. the amount of assets earned by the strategy double performance=(m_virtual_equity-m_initial_balance); return(performance); }
ストラテジー効率の法則は複雑で、例えば、エントリや退場の効率性、また、取引、収益、ドローダウンの効率性などが含まれる場合があります。
エントリや退場の効率性、および取引の効率性の計算(m_deals_history[]配列を構成するentry_eff、exit_eff、およびtrade_effフィールドによる)は、バーチャルトレーディングの間、自動的に実行されます(CSampeStrategyクラスを参照してください)。この統計情報を、ストラテジー効率の独自かつより複雑なレートを作成するために用いることができます。
例えば、過去3回の取引における利益を効率性の特徴として用いることができます(m_deals_history[]の取引アーカイブから、pos_Profitフィールドを用います):
double CSampleStrategy::StrategyPerformance() { //if there are deals, multiply this value by the result of three last deals if(m_virtual_deals_total>0) { int avdeals=MathRound(MathMin(3,m_virtual_deals_total)); double sumprofit=0; for(int j=0; j<avdeals; j++) { sumprofit+=m_deals_history[m_virtual_deals_total-1-j].profit; } double performance=sumprofit/avdeals; } return(performance); }
この関数を変更したい場合にはCSampleStrategy内のみで変更を行い、適応型システムにおいて、すべてのトレーディングストラテジーで同一でなければなりません。しかし、収益と残高の差分もまた、効率性に関する良いファクターであることを覚えておいてください。
5.3 テイクプロフィットとストップロスの利用
固定ストップレベルを設定すると、トレーディングシステムの有効性を変更することができます(Set_Stops関数の呼び出しにより可能となります;バーチャルトレーディングのポイントにおけるストップレベルを設定することができます)。レベルを指定すれば、バーチャルポジションのクローズを自動で実行することができます;この機能はCSampleStrategyクラスに実装されています。
(2.2 移動平均クラスの機能、を参照してください。この例では、ストップレベルを設定する機能はコメントアウトされています。
5.4 バーチャルな累積収益を定期的にゼロ化する
適応型アプローチには、一般的なストラテジーと同じ欠点があります。主なストラテジーが敗れ始めると、適応型システムも同様に負け始めます。そのため、時にすべてのストラテジーの作業結果を「ゼロ化」し、すべてのバーチャルポジションをクローズする必要があります。
このためには、次の関数をCSampleStrategyクラス内で実行します。
// sets a value for cumulative "virtual profit" void SetVirtualCumulativeProfit(double cumulative_profit) { m_virtual_cumulative_profit=cumulative_perofit; }; //closes an open virtual position void CloseVirtualPosition();
このようなCheckPointを、時によっては、例えばN個のバーそれぞれの後などで、用いることが可能です。
5.5 奇跡はない
適応型システムは聖杯ではないことを、覚えておく必要があります(USDJPY H1、4.01.2010-20.08.2010):
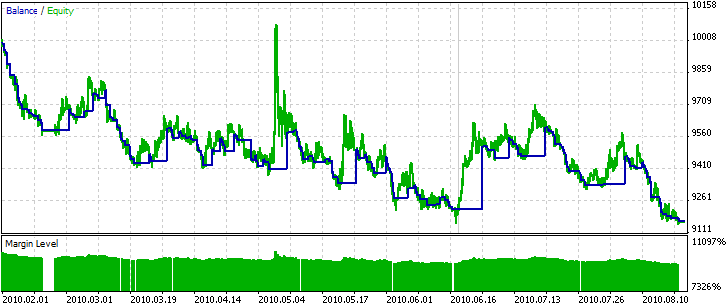
図810の最良プログラムのシグナルを用いた、適応型システムの残高および資産曲線(USDJPY H1)
すべてのストラテジーの資産曲線を図9に示します。
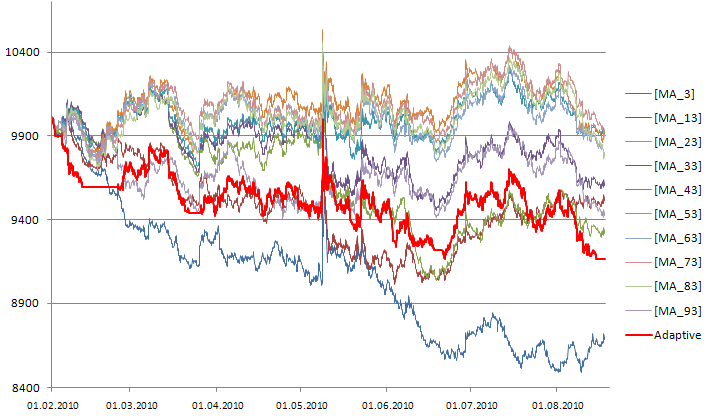
図910のストラテジーにもとづく適応型システムの取引資産曲線(USDJPY H1)
適応型システムに収益性のあるストラテジーが存在しない場合は、それを用いることは効果的ではありません。収益性のあるストラテジーを用いてください。
もう1つ、重要かつ興味深い点を検討しなければなりません。トレードの最も初期の段階では、適応型システムの行動に注意を払ってください:
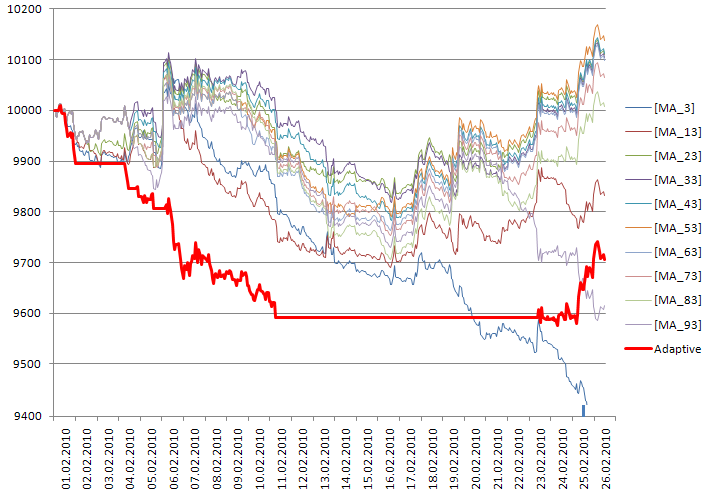
図10適応型ストラテジーである10のストラテジーによる取引資産曲線
当初、すべてのストラテジーがネガティブな結果となり適応型ストラテジーは取引を停止しました;次に、ポジティブな結果をもたらすストラテジーとの間で切り替えを開始し;その後、すべてのストラテジーが再度収益を生み出さなくなりました。
すべてのストラテジーの残高は、最初は同じです。しばらく経ってから初めて、ある、もしくは別のストラテジーが先導役となります;したがって適応型ストラテジーにおいて制限を設定し、最初のバーでは取引を避けることを推奨します。このためには、CAdaptiveStrategyクラスにExpert_OnTick関数を、新規バーが現れるごとに値が増加する変数とともに補います。
初めは、マーケットが最良のストラテジーを選択するまでは、リアルのトレーディングを避けるべきです。
結論
本稿では、各ストラテジーが独自の「バーチャル」トレード操作を行う多くのストラテジーで構成される、適応型システムの例を検討してきました。リアルトレーディングは、その時点で最大利益となるストラテジーにしたがって行われます。
オブジェクト指向アプローチ、データを扱うクラス、さらに標準ライブラリのトレードクラスのおかげで、システムのアーキテクチャはシンプルかつスケーラブルになりました;今や、数百のトレードストラテジーを含む適応型システムを、簡単に作成し、分析することができるのです。
追記適応型システムの挙動を簡単に分析できるよう、CSampleStrategyクラスのデバッグバージョン(the adaptive-systems-mql5-sources-debug-en.zipアーカイブ)を添付しています。このバージョンの違いは、処理の際にテキストファイルが作成されることです;このファイルに、システムに含まれるストラテジーのバーチャル残高/資産の変動ダイナミクスについてのサマリーレポートが含まれています。
MetaQuotes Ltdによってロシア語から翻訳されました。
元の記事: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/143
警告: これらの資料についてのすべての権利はMetaQuotes Ltd.が保有しています。これらの資料の全部または一部の複製や再プリントは禁じられています。
 MQL5のExpert Advisorsのテストと最適化を行うためのガイド
MQL5のExpert Advisorsのテストと最適化を行うためのガイド
 「新しいトレーディングの特質」に基づいたエキスパートアドバイザー : Bill Williams著
「新しいトレーディングの特質」に基づいたエキスパートアドバイザー : Bill Williams著
 メタトレーダー5における検証の原則
メタトレーダー5における検証の原則
- 無料取引アプリ
- 8千を超えるシグナルをコピー
- 金融ニュースで金融マーケットを探索

EMAはインクリメンタルに計算でき、CPUとRAMをほとんど使わないので、通常はEMAに基づいています。
EMAはインクリメンタルに計算でき、CPUとRAMをほとんど使わないからです。