
利用 EX5 库来推动您的项目开发
简介
对于经验丰富的读者来说,在库中隐藏函数与类实施的目的已无需解释。你们当中那些主动寻找新想法的人可能想知道,隐藏 .ex5 文件中类/函数的实施细节,会让您能够同其他开发人员共享自己的专有算法,设立共同项目并在网络中宣传它们。
而且,在 MetaQuotes 团队不遗余力地引入直接继承 ex5 库类可能性的同时,我们现在就要付诸实施了。
目录
1. 函数的导出与导入
2. 类隐藏实施的导出
3. .ex5 文件中变量的初始化
4. 导出类的继承
5. ex5 库的发布
1. 函数的导出与导入
这是构建类导出的一种基本方法。要将您的函数用于其它程序,要考虑到三件重要的事情:
- 要创建的文件的扩展名必须是 .mq5 (而非 .mqh),才能在 .ex5 文件中进行编译;
- 该文件应包含 #property 库预处理器指令;
- 关键词 "export" 应置于所需导出函数的标题后
Example 1. Let us create a function to be used in other programs //--- library.mq5 #property library int libfunc (int a, int b) export { int c=a+b; Print("a+b="+string(с)); return(с); }
完成该文件的编译后,您会得到 library.ex5 文件,之后,libfunc 即可通过这里用于另一程序。
导入函数的过程亦非常简单。它是利用 #import 预处理器指令执行的。
Example 2. We will use the export function libfunc() in our script //--- uses.mq5 #import "library.ex5" int libfunc(int a, int b); #import void OnStart() { libfunc(1, 2); }
要记住,编译器会在 MQL5\Libraries 文件夹中搜索 .ex5 文件。所以,如果 library.ex5 未于该文件夹下,您就必须得指定相对路径名。
例如:
#import "..\Include\MyLib\library.ex5" // the file is located in the MQL5\Include\MyLib folder #import "..\Experts\library.ex5" // the file is located in the MQL5\Experts\ folder
为了您未来的使用,函数不但可以导入到目标 .mq5 文件中,亦可导入到 .mqh 文件中。
为举例说明实际应用,我们采用一些图形。
我们要创建一个待导出的函数库。这些函数会在图表上显示按钮、编辑、标签及矩形标签之类的图形对象,从图表中删除对象,以及重置图表的颜色参数。
图示如下:
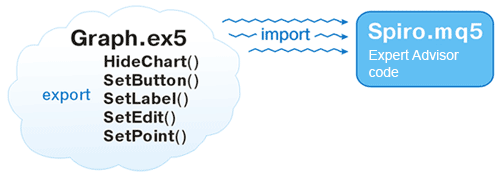
本文末尾有完整的 Graph.mq5 文件。这里,我们只提供绘图函数 Edit (编辑)的一个模板示例。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| SetEdit | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void SetEdit(long achart,string name,int wnd,string text,color txtclr,color bgclr,color brdclr, int x,int y,int dx,int dy,int corn=0,int fontsize=8,string font="Tahoma",bool ro=false) export { ObjectCreate(achart,name,OBJ_EDIT,wnd,0,0); ObjectSetInteger(achart,name,OBJPROP_CORNER,corn); ObjectSetString(achart,name,OBJPROP_TEXT,text); ObjectSetInteger(achart,name,OBJPROP_COLOR,txtclr); ObjectSetInteger(achart,name,OBJPROP_BGCOLOR,bgclr); ObjectSetInteger(achart,name,OBJPROP_BORDER_COLOR,brdclr); ObjectSetInteger(achart,name,OBJPROP_FONTSIZE,fontsize); ObjectSetString(achart,name,OBJPROP_FONT,font); ObjectSetInteger(achart,name,OBJPROP_XDISTANCE,x); ObjectSetInteger(achart,name,OBJPROP_YDISTANCE,y); ObjectSetInteger(achart,name,OBJPROP_XSIZE,dx); ObjectSetInteger(achart,name,OBJPROP_YSIZE,dy); ObjectSetInteger(achart,name,OBJPROP_SELECTABLE,false); ObjectSetInteger(achart,name,OBJPROP_READONLY,ro); ObjectSetInteger(achart,name,OBJPROP_BORDER_TYPE,0); ObjectSetString(achart,name,OBJPROP_TOOLTIP,""); }
所需函数的导入及其使用,都将在目标文件 Spiro.mq5 中实施:
Example 3. Using imported functions //--- Spiro.mq5 – the target file of the Expert Advisor //--- importing some graphics functions #import "Graph.ex5" void SetLabel(long achart, string name, int wnd, string text, color clr, int x, int y, int corn=0, int fontsize=8, string font="Tahoma"); void SetEdit(long achart, string name, int wnd, string text, color txtclr, color bgclr, color brdclr, int x, int y, int dx, int dy, int corn=0, int fontsize=8, string font="Tahoma", bool ro=false); void SetButton(long achart, string name, int wnd, string text, color txtclr, color bgclr, int x, int y, int dx, int dy, int corn=0, int fontsize=8, string font="Tahoma", bool state=false); void HideChart(long achart, color BackClr); #import //--- prefix for chart objects string sID; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnInit() { HideChart(0, clrWhite); sID="spiro."; DrawParam(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| DrawParam | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void DrawParam() { color bgclr=clrWhite, clr=clrBlack; //--- bigger radius SetLabel(0, sID+"stR.", 0, "R", clr, 10, 10+3); SetEdit(0, sID+"R.", 0, "100", clr, bgclr, clr, 40, 10, 50, 20); //--- smaller radius SetLabel(0, sID+"str.", 0, "r", clr, 10, 35+3); SetEdit(0, sID+"r.", 0, "30", clr, bgclr, clr, 40, 35, 50, 20); //--- distance to the center SetLabel(0, sID+"stD.", 0, "D", clr, 10, 60+3); SetEdit(0, sID+"D.", 0, "40", clr, bgclr, clr, 40, 60, 50, 20); //--- drawing accuracy SetLabel(0, sID+"stA.", 0, "Alfa", clr, 10, 85+3); SetEdit(0, sID+"A.", 0, "0.04", clr, bgclr, clr, 40, 85, 50, 20); //--- drawing accuracy SetLabel(0, sID+"stN.", 0, "Rotor", clr, 10, 110+3); SetEdit(0, sID+"N.", 0, "10", clr, bgclr, clr, 40, 110, 50, 20); //--- draw button SetButton(0, sID+"draw.", 0, "DRAW", bgclr, clr, 39, 135, 51, 20); }
EA 运行后,这些对象就会显示于图表上方:
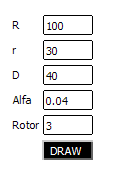
可以看出,导出与导入函数的过程一点都不难,但是一定要阅读“帮助”中的具体限制内容:导出、导入。
2. 类隐藏实施的导出
由于 MQL5 中的类至今仍不能直接导出,所以我们不得不求助于一种多少有些花哨的方法。该法基于多态性与虚函数。事实上,从 ex5 模块返回的并非该类本身,而是一个所创建的类对象。我们姑且称之为隐藏实施对象。
此法的本质在于将所需类划分为两个,以使函数和变量的声明开放公共访问,且其实施细节隐藏于一个不公开的 .ex5 文件中。
下面即其简单例证。有一个 CSpiro 类,我们想与其他开发人员共享,但不披露其实施细节。假设它包含变量、构造函数、析构函数及工作函数。
要导出此类,我们应如下操作:
- 创建 CSpiro 类后代的一份拷贝。我们称之为 ISpiro (首字母 C 换成了 I,因为是从 "interface" 一词衍生而来)
- 将所有变量及虚函数留在初始 CSpiro 类中。
- 函数实施细节则应构成一个新的 ISpiro 类。
- 向其添加将创建一个不公开 ISpiro 实例的导出函数。
- 注意!所有所需函数均应冠以 virtual 前缀
结果我们得到两个文件:
Example 4. Hiding of the class implementation in the ex5 module //--- Spiro.mqh – public file, the so called header file //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class CSpiro | //| Spirograph draw class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CSpiro { public: //--- prefix of the chart objects string m_sID; //--- offset of the chart center int m_x0,m_y0; //--- color of the line color m_clr; //--- chart parameters double m_R,m_r,m_D,m_dAlfa,m_nRotate; public: //--- constructor CSpiro() { }; //--- destructor ~CSpiro() { }; virtual void Init(int ax0,int ay0,color aclr,string asID) { }; virtual void SetData(double aR,double ar,double aD,double adAlpha,double anRotate) { }; public: virtual void DrawSpiro() { }; virtual void SetPoint(int x,int y) { }; };
请注意:所有函数类均利用关键词 virtual 声明。
//--- ISpiro.mq5 – hidden implementation file #include "Spiro.mqh" //--- importing some functions #import "..\Experts\Spiro\Graph.ex5" void SetPoint(long achart,string name,int awnd,int ax,int ay,color aclr); void ObjectsDeleteAll2(long achart=0,int wnd=-1,int type=-1,string pref="",string excl=""); #import CSpiro *iSpiro() export { return(new ISpiro); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Сlass ISpiro | //| Spirograph draw class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class ISpiro : public CSpiro { public: ISpiro() { m_x0=0; m_y0=0; }; ~ISpiro() { ObjectsDeleteAll(0,0,-1); }; virtual void Init(int ax0,int ay0,color aclr,string asID); virtual void SetData(double aR,double ar,double aD,double adAlpha,double anRotate); public: virtual void DrawSpiro(); virtual void SetPoint(int x,int y); }; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Init | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void ISpiro::Init(int ax0,int ay0,color aclr,string asID) { m_x0=ax0; m_y0=ay0; m_clr=aclr; m_sID=asID; m_R=0; m_r=0; m_D=0; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| SetData | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void ISpiro::SetData(double aR,double ar,double aD,double adAlpha,double anRotate) { m_R=aR; m_r=ar; m_D=aD; m_dAlfa=adAlpha; m_nRotate=anRotate; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| DrawSpiro | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void ISpiro::DrawSpiro() { if(m_r<=0) { Print("Error! r==0"); return; } if(m_D<=0) { Print("Error! D==0"); return; } if(m_dAlfa==0) { Print("Error! Alpha==0"); return; } ObjectsDeleteAll2(0,0,-1,m_sID+"pnt."); int n=0; double a=0; while(a<m_nRotate*2*3.1415926) { double x=(m_R-m_r)*MathCos(a)+m_D*MathCos((m_R-m_r)/m_r*a); double y=(m_R-m_r)*MathSin(a)-m_D*MathSin((m_R-m_r)/m_r*a); SetPoint(int(m_x0+x),int(m_y0+y)); a+=m_dAlfa; } ChartRedraw(0); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| SetPoint | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void ISpiro::SetPoint(int x,int y) { Graph::SetPoint(0,m_sID+"pnt."+string(x)+"."+string(y),0,x,y,m_clr); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
可以看出,隐藏类已于 .mq5 文件中实施,且包含预处理器命令 #property library。因此,前文中列出的所有规则也都得到了遵守。
还要注意 SetPoint 函数的范围解析操作符。它在 Graph 库和 CSpiro 类两个位置进行声明。为让编译器调用所需函数,我们明确指定其使用 ::操作并赋予文件名称。
Graph::SetPoint(0, m_sID+"pnt."+string(x)+"."+string(y), 0, x, y, m_clr);
现在,我们可以纳入头文件,并将其实施导入到作为结果的 EA 当中了。
图示如下:
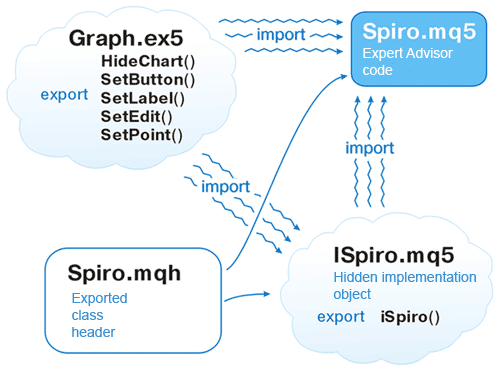
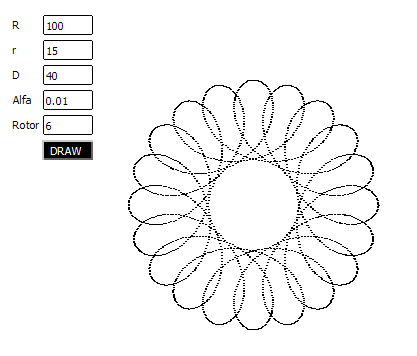
Example 5. Using export objects //--- Spiro.mq5 - the target file of the Expert Advisor //--- importing some functions #import "Graph.ex5" void SetLabel(long achart, string name, int wnd, string text, color clr, int x, int y, int corn=0, int fontsize=8, string font="Tahoma"); void SetEdit(long achart, string name, int wnd, string text, color txtclr, color bgclr, color brdclr, int x, int y, int dx, int dy, int corn=0, int fontsize=8, string font="Tahoma", bool ro=false); void SetButton(long achart, string name, int wnd, string text, color txtclr, color bgclr, int x, int y, int dx, int dy, int corn=0, int fontsize=8, string font="Tahoma", bool state=false); void HideChart(long achart, color BackClr); #import //--- including the chart class #include <Spiro.mqh> //--- importing the object #import "ISpiro.ex5" CSpiro *iSpiro(); #import //--- object instance CSpiro *spiro; //--- prefix for chart objects string sID; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnInit() { HideChart(0, clrWhite); sID="spiro."; DrawParam(); //--- object instance created spiro=iSpiro(); //--- initializing the drawing spiro.Init(250, 200, clrBlack, sID); //--- setting the calculation parameters spiro.SetData(100, 30, 40, 0.04, 10); //--- drawing spiro.DrawSpiro(); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert deinitialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnDeinit(const int reason) { delete spiro; // deleting the object }
结果您将能够更改图表中的对象参数,并绘制对象的图表
3. .ex5 文件中变量的初始化
通常情况下,您的 ISuperClass 都会使用 globals.mqh 包含文件中的变量。而这些变量可以类似的方式纳入,以供您在其它文件中使用。
例如:
Example 6. Public include file //--- globals.mqh #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> //--- instance of the trade function object extern CTrade *_trade;
_trade 对象唯一的实例,是在您的程序中进行初始化,但却是在隐藏的 ISuperClass 类中使用。
为此,应将您创建的一个指向该对象的指针从 ISuperClass 类传递到 .ex5 文件。
如果是从 .ex5 文件接收对象,则最容易实现,所示如下:
Example 7. Initialization of variables upon creation of the object //--- ISuperClass.mq5 –hidden implementation file #property library CSuperClass *iSuperClass(CTrade *atrade) export { //--- saving the pointer _trade=atrade; //--- returning the object of the hidden implementation of ISuperClass of the open CSuperClass class return(new ISuperClass); } //... the remaining code
由此,收到其模块中的对象后,所需的所有变量均完成初始化。
事实上,公共全局变量可能有很多,类型也多种多样。那些并不急于随时更改 iSuperClass 函数头的人,最好是创建一个聚集所有使用它的全局变量与函数的专用类。
Example 8. Public include file //--- globals.mqh #include <Trade\Trade.mqh> //--- trade "object" extern CTrade *_trade; //--- name of the Expert Advisor of the system extern string _eaname; //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| class __extern | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class __extern // all extern parameters for passing between the ex5 modules are accumulated here { public: //--- the list of all public global variables to be passed //--- trade "object" CTrade *trade; //--- name of the Expert Advisor of the system string eaname; public: __extern() { }; ~__extern() { }; //--- it is called when passing the parameters into the .ex5 file void Get() { trade=_trade; eaname=_eaname; }; // getting the variables //--- it is called in the .ex5 file void Set() { _trade=trade; _eaname=eaname; }; // setting the variables }; //--- getting the variables and pointer for passing the object into the .ex5 file __extern *_GetExt() { _ext.Get(); return(GetPointer(_ext)); } //--- the only instance for operation extern __extern _ext;ISuperClass.mq5 文件会如下实施:
Example 9. //--- ISuperClass.mq5 –hidden implementation file #property library CSuperClass *iSuperClass(__extern *aext) export { //--- taking in all the parameters aext.Set(); //--- returning the object return(new ISuperClass); } //--- ... the remaining code
函数调用现在亦会转换成为一种简化、且可扩展(最重要)的形式。
Example 10. Using export objects in the presence of public global variables //--- including global variables (usually located in SuperClass.mqh) #include "globals.mqh" //--- including the public header class #include "SuperClass.mqh" //--- getting the hidden implementation object #import "ISuperClass.ex5" CSuperClass *iSuperClass(); #import //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- creating the hidden implementation object providing for the passing of all parameters CSuperClass *sc=iSuperClass(_GetExt()); //--- ... the remaining code }
4. 导出类的继承
您必须清楚:这种导出对象的方式,暗示着直接的简单继承根本就不可能。隐藏实施对象的导出,意味着对象本身就是继承链条的最后一环,而且是最终可被使用的一环。
一般情况下,您可以通过编写一个附加中间类来创建继承的一个“模拟”。而这里,我们当然还需要多态性和虚拟性。
Example 11. Emulation of inheritance of hidden classes //--- including the public header class #include "SuperClass.mqh" //--- getting the hidden implementation object #import "ISuperClass.ex5" CSuperClass *iSuperClass(); #import class _CSuperClass { public: //--- instance of the hidden implementation object CSuperClass *_base; public: //--- constructor _CSuperClass() { _base=iSuperClass(_GetExt()); }; //--- destructor ~_CSuperClass() { delete _base; }; //--- further followed by all functions of the base CSuperClass class //--- working function called from the hidden implementation object virtual int func(int a, int b) { _base.func(a,b); }; };
这里唯一的问题就是访问 CSuperClass 的变量。可以看出,它们并不存在于后代的声明中,而是位于 _base 变量中。通常来讲,它不会影响到可用性,前提是有一个标头类 SuperClass.mqh。
自然,如果您主要关注的是专有函数,那么,您无需提前创建与其相关的 ISuperClass 包装程序。它足够导出这些专有函数,并允许外部开发人员创建其自有的包装程序类,之后就方便继承了。
- 类独立函数的导出
- .mqh 标头文件及其 .ex5 实施
- 变量在 .ex5 文件中的实施
5. ex5 库的发布
2011 年 11 月,MetaQuotes 开始提供对于文件资源库访问的权限。更多详情,请参阅声明。
该资源库允许您存储您的开发内容,而且,更重要的是,为其他开发人员提供了访问这里的权限。此工具将允许您轻松发布自己文件的新版本,从而确保使用这些文件的开发人员快速访问它们。
而且,公司网站也赋予您一次机会,以收费或免费的形式在市场中提供您自己的函数库。
总结
现在,您已经知道如何利用函数或类对象的导出来创建 ex5 库,而且可以将您的知识应用于实践了。上述所有资源,都能让您与其他开发人员建立起更为密切的合作:致力于共同的项目、在“市场”中宣传它们,或是提供访问 ex5 库函数的权限。
本文由MetaQuotes Ltd译自俄文
原文地址: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/362
注意: MetaQuotes Ltd.将保留所有关于这些材料的权利。全部或部分复制或者转载这些材料将被禁止。
本文由网站的一位用户撰写,反映了他们的个人观点。MetaQuotes Ltd 不对所提供信息的准确性负责,也不对因使用所述解决方案、策略或建议而产生的任何后果负责。
 AutoElliottWaveMaker - 用于艾略特波浪半自动分析的 MetaTrader 5 工具
AutoElliottWaveMaker - 用于艾略特波浪半自动分析的 MetaTrader 5 工具
 保证 MQL5 代码的安全:密码保护,钥匙生成器,时间限制,远程许可证及先进的 EA 许可证密钥加密技术
保证 MQL5 代码的安全:密码保护,钥匙生成器,时间限制,远程许可证及先进的 EA 许可证密钥加密技术
 如何在"应用商店"中发布产品
如何在"应用商店"中发布产品
 Trademinator 3:交易机器的崛起
Trademinator 3:交易机器的崛起
...
是否计划实现类的导出或类似功能?
是的,但不是现在。
至少可以导出类。
它能在 MT4 中使用吗?
好吧,至少有可能导出类。
它能在 MT4 中使用吗?
7 年了,现在还是 "不行"。
我忘了 MT4,它已经成为过去了。