A Deep Trend-Following Trading Strategy For Equity Markets
15 January 2025, 09:44
1
401
What is a trend-following trading strategy and what is its application?
A trend-following trading strategy in the world of technical analysis involves making investment decisions based on the prevailing price trends of an asset. The fundamental principle behind this trading strategy is that assets in motion tend to continue moving in the same direction; meaning that upward or downward trends are likely to persist for some time. Traders who employ this strategy make profits by riding these trends; they do this by entering positions after identifying a trend and exiting them upon observing signs of trend reversal. This approach often uses indicators such as Moving Averages (MA), the Average Directional Index (ADX), and Momentum Oscillators to confirm the presence and also the strength of a trend.
The importance of trend following lies in its simplicity and adaptability. This strategy can be applied to the analysis of various financial markets. If traders focus on trends rather than relying on price predictions, they can benefit from stable movements and somewhat avoid the risks associated with sudden market movements. This approach can be particularly effective in volatile markets. One of the most significant advantages of trend following is stress reduction; it eliminates the need to predict market ups and downs. This strategy can yield considerable returns during strong trends. Additionally, by defining predetermined entry and exit points, it minimizes losses and protects the trader's profit, thus aiding in effective risk management.

Identifying Types of Trends in Price Charts
Trends in financial markets can be classified into three main categories, which we will discuss below:
Bullish or Uptrend
A bullish trend can be identified when new highs and lows are higher than the previous highs and lows, indicating an overall increase in the asset's price.
Bearish or Downtrend
In a bearish trend, new highs and lows are at lower levels compared to previous highs and lows, which signifies an overall price decrease.
Sideways or Range Bound
A sideways trend occurs when the price moves within a horizontal range. This market condition is somewhat indecisive and provides little information about the overall price direction.
Trend Identification Tools and the Impact of Time Frames
To identify these trends, traders use various tools such as trend lines and channels. Trend lines are straight lines drawn on a chart to connect successive highs or lows, helping to visualize the trend direction. An uptrend line is drawn by connecting higher lows, while a downtrend line connects lower highs. The next option is channels, which are formed by drawing parallel lines above and below the trend line, creating a corridor that shows the probable range of price fluctuation.
Time frames play a crucial role in recognizing trends. Shorter time frames, such as minute or hourly charts, can reveal immediate and smaller trends, which are useful for day traders. On the other hand, longer time frames, like daily, weekly, or monthly charts, help in identifying more significant and long-term trends. By analyzing multiple time frames, traders can gain a comprehensive understanding of market direction and align short-term strategies with overarching trends.
Tools Used for Identifying Market Trends
To discern trends, traders employ various tools including moving averages, technical indicators, and price patterns. Here's an introduction and explanation of each:
1. Moving Averages (MAs):
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): This calculates the average of a selected price range over a specific period. When the price is above the SMA, it might indicate an uptrend; below it could suggest a downtrend.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): This gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to new information. Traders often use EMAs for identifying shorter-term trends.
2. Technical Indicators:
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): This indicator shows the relationship between two moving averages of a security's price. The MACD line crossing above the signal line can indicate a bullish trend, while crossing below might signal a bearish trend.
- ADX (Average Directional Index): This helps gauge trend strength without indicating direction. An ADX above 25 typically suggests a strong trend, either up or down.
- RSI (Relative Strength Index): While primarily an oscillator for indicating overbought or oversold conditions, RSI can also show trend direction when it consistently stays above 50 (bullish) or below 50 (bearish).
3. Price Patterns:
- Head and Shoulders: This pattern can signal a reversal from a bullish to bearish trend (or vice versa in its inverse form).
- Triangles: Symmetrical, ascending, and descending triangles can indicate continuation or reversal patterns depending on the breakout direction.
- Flags and Pennants: Short-term continuation patterns that signal a brief consolidation before the trend continues.
Double Tops and Bottoms: These patterns suggest potential trend reversals after a significant move up or down.
By combining these tools, traders can confirm trends, filter out market noise, and make more informed decisions about entry and exit points in the market. However, no tool is infallible, and it's crucial to use them in conjunction with other forms of analysis for the best results.
Identifying Entry Points in Uptrends and Downtrends
To enter a trade during an uptrend or downtrend, traders need to identify clear entry points using various tools and signals. In an uptrend, the entry point is often identified when the price breaks above a resistance level or when an indicator gives a buy signal. Conversely, in a downtrend, the entry point is identified when the price breaks below a support level or when an indicator gives a sell signal. Below, we explain how to identify entry signals using different tools.
Moving Averages
In an uptrend, when the price breaks above the 50 or 200-day simple moving average (SMA), or when a short-term exponential moving average (EMA) (e.g., 12-day) crosses above a longer-term EMA (e.g., 26-day), these can be considered buy signals.
In a downtrend, when the price falls below the moving averages, or when a short-term EMA crosses below a longer-term EMA, sell signals are issued.
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
A buy signal in an uptrend occurs when the MACD line crosses above the signal line, especially if both are above the zero line.
A sell signal in a downtrend occurs when the MACD line crosses below the signal line, particularly if both are below the zero line.
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
In an uptrend, the RSI reaching above 30 from an oversold condition can be a buy signal.
In a downtrend, the RSI falling below 70 from an overbought condition can be a sell signal.
Average Directional Index (ADX)
A strong ADX value (above 25) can confirm the strength of the trend and support buy or sell signals from other indicators.
Identifying Exit Points in Uptrends and Downtrends
To exit a trade during uptrends or downtrends, traders look for signs of the trend weakening or reversing.
Exit points can be identified using support and resistance lines. In an uptrend, when the price approaches a significant resistance level, an exit point might be identified indicating a potential reversal or consolidation. Conversely, in a downtrend, an exit point could be when the price approaches a support level, suggesting a possible reversal or halt in the trend.
Using Stop Loss and Take Profit Orders
Stop Loss Order
Setting a stop loss order automatically closes a trade at a predetermined price to limit potential losses. In an uptrend trade, you can set the stop loss just below the support level. For a downtrend trade, it can be placed just above the resistance level. This ensures that if the market moves against the trade, the loss is minimized and controlled.
Take Profit Order
A take profit order closes the trade at a predetermined price to secure profit. In an uptrend trade, this type of order can be placed at a target resistance level where the trader anticipates the price might reverse. In a downtrend trade, it can be set at a target support level. Setting this order allows traders to secure their earned profits without needing to constantly monitor the market.
Risk Management in Trend Trading Strategy
No trading strategy is immune to risk, and unexpected market fluctuations can put your assets at risk at any moment. Therefore, here are some tips to help you reduce trading risks.
Trailing Stop - Floating Stop Loss
A trailing stop loss allows traders to adjust their stop loss with the market price movement. In an uptrend, the stop loss gradually moves upward, protecting the gains made. Similarly, in a downtrend, the stop loss moves downward with the price, thereby reducing risk. This tool helps traders minimize their trading risks while securing profits and capitalizing on market trends.
Monitoring and Adjustment
Traders should regularly monitor their trades and adjust their stop loss and take profit levels in response to changes in market conditions or the emergence of new support and resistance levels. This regular monitoring and adjustment enable traders to react more effectively to unexpected market changes and optimize their trades according to new conditions.
The Importance of Risk Management
Risk management is a vital element in trend-following strategies. It aims to protect capital and minimize potential losses, ensuring the long-term success of traders.
Markets are typically unpredictable, and trends can reverse suddenly. Effective risk management allows traders to avoid significant losses, remain in the market for longer periods, and capitalize on profitable opportunities.
Position Sizing
Determining the appropriate amount of capital for each trade helps traders optimize their risk and prevent the negative impacts of overexposing their capital to risk. For example, traders typically allocate a percentage of their total capital to a single trade in such a way that even if there's a loss, the overall portfolio isn't significantly affected. This approach ensures that no single trade can substantially impact the total capital negatively.
Risk to Reward Ratio
This ratio, which compares the potential profit of a trade to the potential loss, is a key component in evaluating the value of a trade. By setting a favorable ratio, like 1:3, traders ensure that the potential profit of a trade is several times the risk involved. This approach helps ensure that even if some trades result in losses, there are enough profitable trades to lead to long-term profitability.
Review and Evaluation of Previous Trend Trades
One of the activities that both familiarizes you more with trend trading strategies and enhances your capabilities is the review and evaluation of trades previously executed based on this strategy.
To do this:
- Record all trading records including entry and exit points, trade sizes, and market conditions.
- Evaluate key metrics such as risk-to-reward ratio and profitability to assess the strategy's performance.
- Review your trades to find out the reasons behind their success or failure and identify existing patterns.
- Identify common mistakes like poor timing or emotional decision-making, analyze their root causes, and adjust your strategy based on these analyses.
- Test the revised strategy with historical data and keep it up-to-date.
- Improving the strategy is an ongoing process and should be updated with new insights and market changes.
Keeping accurate trading data is essential for performance evaluation, error analysis, strategy adjustment, and tax compliance, laying the groundwork for sustainable success in trading.

Advantages of Trend Trading Strategy
- Simplicity:It's easy to understand and implement, making it accessible to both novice and experienced traders.
- Suitable for Volatile Markets:Performs well in volatile markets; it captures significant price movements, allowing traders to profit from notable market trends.
- Quantitative Approach:Often relies on clear, objective indicators like moving averages, thereby reducing emotional decision-making.
Versatile Application: It's a versatile strategy that can be applied to various markets, including stocks, cryptocurrencies, commodities, and forex.
Disadvantages of Trend Trading Strategy
- Poor Performance in Range-Bound Markets: In neutral or choppy markets where there's no clear trend, it struggles, often giving false signals that can lead to potential losses.
- Lag of Indicators: Many trend trading strategies use lagging indicators which can result in late entries and exits, causing the trader to miss part of the trend.
Market Dependency: It heavily depends on market volatility; long periods without trends can significantly affect the trader's performance.
Overcoming Challenges in Trend Following Strategy
Traders can enhance the effectiveness of this strategy by acknowledging its limitations and combining it with complementary strategies and robust risk management, thereby managing different market conditions more successfully.
- Adaptive Indicators: Use adaptive indicators that adjust to different market conditions to reduce lag and increase responsiveness.
- Combining with Other Strategies: To improve performance in range-bound markets, integrate this strategy with others like Mean Reversion.
Risk Management: To avoid significant losses, employ stringent risk management techniques such as stop-loss orders and position sizing.
Market Analysis: Conduct a comprehensive and thorough analysis to identify trending markets and avoid those that are likely to range.
Regular Review and Adjustment: Continuously review and adjust the strategy based on market feedback and performance metrics to stay aligned with current market conditions.
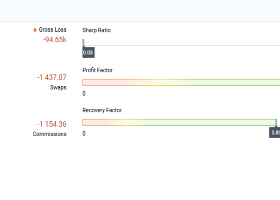
Examining Several Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Trend Trading Strategies
Below, we will review 2 examples of trades executed based on trend strategies to understand the level of success and risk involved.
Successful Outcome: Apple (AAPL) Bull Market
From mid-2016 to early 2020, Apple's stock experienced a strong upward trend driven by high revenues and robust product offerings. During this period, trend-following traders who utilized moving averages entered trades on pullbacks and exited at breakout points, thus securing significant profits from this bullish phase.
Unsuccessful Outcome: Crude Oil Volatility
From 2014 to 2016, crude oil prices experienced a notable downward trend followed by a neutral and ranging market. As prices fluctuated without a clear direction, trend-following traders encountered numerous false signals and small losses, highlighting the limitations of this strategy in a non-trending market.
How to Adapt Trend Trading Strategies to Different Market Conditions
Indicator Adaptation
Utilizing adaptive indicators such as Adaptive Moving Average (AMA) or Exponential Moving Average (EMA) can help capture trends earlier and exit on reversals sooner, reducing lag and improving performance.
Combining Strategies
Combine mean reversion techniques with trend-following strategies to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations in ranging markets while waiting for the next trend to emerge.
Improving Risk Management
Establish strict stop-loss levels and manage position sizes to limit potential losses and avoid incurring irreversible damage during prolonged periods of market uncertainty.
Market Analysis and Selection
By conducting comprehensive fundamental analysis and identifying markets influenced by economic cycles, geopolitical events, or technological advancements, focus on markets with a higher potential for trending.
Key Tips for Success in Trend Trading Strategies
To succeed in trend-following trading, adhering to several important principles is crucial. First, diligently follow the trends and avoid predicting market reversals. Utilizing reliable indicators to identify and confirm trends is essential. Risk management through setting stop-loss orders and controlling position sizes is vital. Additionally, discipline in trading and continuous monitoring of market conditions for strategy updates is necessary.
To improve skills, it is advisable to study relevant books, participate in online courses, join trading communities, and utilize market analysis tools. Beginner traders should start with small steps and maintain a trading journal. Moreover, diversifying strategies and using advanced analyses can enhance performance.
Final Thought
Trend trading strategies can be highly effective when applied with discipline, proper risk management, and continuous improvement. Using reliable resources, staying informed, and adapting to market changes enable both amateur and experienced traders to enhance their skills and increase their chances of success in trades.