0
202
1. Trend-Following Models:
- Definition: These models aim to enter in the direction of the existing trend.
- Use of Indicators: Moving Averages, Trendlines, and trend confirmation indicators such as the Average Directional Index (ADX).
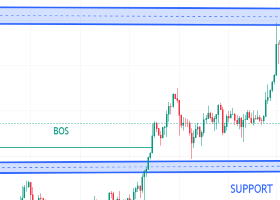
2. Breakout Models:
- Definition: Entry occurs when the price breaks through significant support or resistance levels.
- Use of Indicators: Bollinger Bands, Donchian Channels, Support and Resistance zones.
3. Retracement Models:
- Definition: Entry occurs during a trend correction or retracement to capitalize on the continuation of the trend.
- Use of Indicators: Fibonacci Retracement levels, Moving Averages.
4. Momentum Models:
- Definition: Entry is based on the strength of price movement to profit from short-term momentum.
- Use of Indicators: Relative Strength Index (RSI), Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), Stochastic Oscillator.
5. Price Action Models:
- Definition: Entry is based on the direct interpretation of price movements and patterns.
- Use of Indicators: Candlestick patterns, chart formations like Head and Shoulders or triangles.
6. Fundamental Models:
- Definition: Entry is based on economic data and events.
- Use of Indicators: Interest rates, economic data, political events.
Key Considerations:
- Backtesting: Each model should be tested on historical data to verify its effectiveness.
- Risk Management: Implementation of clear stop-loss levels and position sizes in conjunction with the chosen model.
- Market Conditions: Consideration of current market conditions and adjustment of the model accordingly.