MQL5의 테이블 모델에 기반한 테이블 및 헤더 클래스: MVC 개념 적용하기
콘텐츠
소개
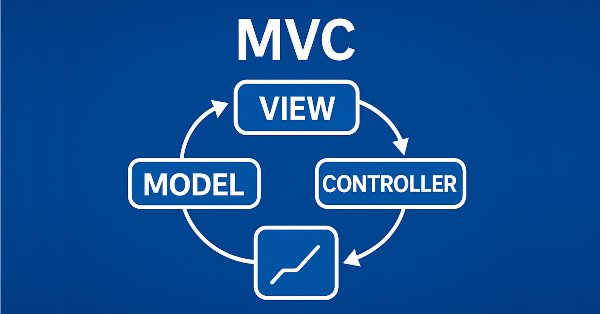
테이블 컨트롤 생성을 다룬 첫 번째 글에서 우리는 MVC 아키텍처 템플릿을 사용하여 MQL5에서 테이블 모델을 만들었습니다. 셀, 행, 테이블 모델 등의 클래스를 개발하여 데이터를 편리하고 구조화된 형태로 정리할 수 있게 되었습니다.
이제 다음 단계인 테이블 클래스 및 테이블 헤더의 개발로 넘어갑니다. 테이블의 열 헤더는 단순한 열 레이블이 아니라 테이블과 그 열을 관리하기 위한 도구입니다. 열을 추가, 삭제 및 이름 변경할 수 있습니다. 물론 테이블은 헤더 클래스 없이도 작동할 수 있지만 이 경우 기능이 제한됩니다. 열 헤더가 없는 단순한 정적 테이블이 생성되므로 열을 제어할 수 있는 기능이 없습니다.
열 제어 기능을 구현하려면 테이블 모델을 세분화해야 합니다. 우리는 열의 구조를 변경하거나 새로운 열을 추가하거나 기존의 열을 삭제하는 등 열로 작업할 수 있는 메서드로 보완할 예정입니다. 이러한 메서드는 테이블 헤더 클래스에서 구조를 편리하게 제어하기 위해 사용됩니다.
이 개발 단계는 다음 글에서 설명할 뷰 및 컨트롤러 구성 요소의 추가 구현을 위한 기초가 됩니다. 이 단계는 운영 데이터를 위한 본격적인 인터페이스를 만드는 과정에서 중요한 이정표입니다.
테이블 모델 개선
현재 테이블 모델은 2차원 배열로 생성되지만 테이블 작업의 유연성과 편의성을 높이기 위해 우리는 초기화 메서드를 추가할 예정입니다. 이렇게 하면 다양한 사용 시나리오에 맞게 모델을 조정할 수 있습니다. 업데이트된 버전의 테이블 모델 클래스에는 다음과 같은 메서드가 표시됩니다:
-
2차원 배열에서 모델 만들기
void CreateTableModel(T &array[][]);이 메서드를 사용하면 기존 2차원 데이터 배열을 기반으로 테이블 모델을 빠르게 만들 수 있습니다.
-
행과 열의 개수가 설정된 빈 모델 만들기
void CreateTableModel(const uint num_rows, const uint num_columns);
이 메서드는 테이블 구조를 미리 알고 있지만 나중에 데이터가 추가되는 경우에 적합합니다.
-
데이터 매트릭스에서 모델 만들기
void CreateTableModel(const matrix &row_data);
이 메서드를 사용하면 데이터 행렬을 사용하여 테이블을 초기화할 수 있으므로 미리 준비된 데이터 집합으로 작업할 때 편리합니다.
-
연결된 목록에서 모델 만들기
void CreateTableModel(CList &list_param);이 경우 데이터 저장에는 배열 배열이 사용되며 하나의 CList 객체(테이블 행의 데이터)에는 테이블 셀에 데이터를 보관하는 다른 CList 객체가 포함됩니다. 이 접근 방식을 사용하면 테이블의 구조와 내용을 동적으로 제어할 수 있습니다.
이러한 변경을 통해 테이블 모델은 다양한 시나리오에서 더욱 다양하고 편리하게 사용될 수 있게 될 것입니다. 예를 들어 미리 준비된 데이터 배열과 동적으로 생성된 목록 모두에서 테이블을 쉽게 만들 수 있습니다.
지난 글에서 테스트 스크립트 파일에서 직접 테이블 모델을 생성하는 모든 클래스에 대해 설명했습니다. 이번에는 이들 클래스들을 include 파일로 보내겠습니다.
이전 문서의 스크립트가 저장된 폴더(기본값: \MQL5\Scripts\TableModel\)에 Tables.mqh라는 이름의 include 파일을 새로 만들고 같은 폴더에 있는 TableModelTest.mq5 파일에서 파일의 시작부터 테스트 스크립트 코드의 시작 부분까지 테이블 모델을 만들기 위한 모든 클래스를 복사합니다. 이제 테이블 모델의 클래스가 포함된 별도의 파일인 Tables.mqh가 생겼습니다. 이 파일을 변경하고 개선합니다.
생성된 파일을 새 폴더인 MQL5\Scripts\Tables\로 이동합니다 - 이 폴더에 이 프로젝트를 생성합니다.
파일/라이브러리 섹션에서 새 클래스의 전방 선언을 추가합니다. 오늘 우리는 이 작업을 할 것이며 이전 글에서 만든 CListObj 객체 목록 클래스가 CreateElement() 메서드에서 이러한 클래스의 객체를 생성할 수 있도록 하기 위해 클래스 선언이 필요합니다:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Include libraries | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #include <Arrays\List.mqh> //--- Forward declaration of classes class CTableCell; // Table cell class class CTableRow; // Table row class class CTableModel; // Table model class class CColumnCaption; // Table column header class class CTableHeader; // Table header class class CTable; // Table class class CTableByParam; // Table class based on parameter array //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Macros | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
매크로 섹션에서 테이블 셀 너비를 19와 같은 문자 단위로 추가합니다. 이 값은 로그에 그려진 테이블의 모든 셀 크기가 동기화되지 않게 만드는 셀의 오른쪽 테두리를 이동하지 않고 날짜-시간 텍스트가 로그의 셀 공간에 완전히 들어맞는 최소 너비 값입니다:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Macros | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #define MARKER_START_DATA -1 // Data start marker in a file #define MAX_STRING_LENGTH 128 // Maximum length of a string in a cell #define CELL_WIDTH_IN_CHARS 19 // Table cell width in characters //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Enumerations | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+
열거형 섹션에서 객체 유형 열거형에 새로운 상수를 추가합니다:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Enumerations | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ enum ENUM_OBJECT_TYPE // Enumeration of object types { OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE_CELL=10000, // Table cell OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE_ROW, // Table row OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE_MODEL, // Table model OBJECT_TYPE_COLUMN_CAPTION, // Table column header OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE_HEADER, // Table header OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE, // Table OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE_BY_PARAM, // Table based on the parameter array data };
CListObj 객체 목록 클래스의 요소 생성 메서드에서 새로운 유형의 객체를 생성하기 위한 새로운 케이스들을 추가합니다:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| List element creation method | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CObject *CListObj::CreateElement(void) { //--- Create a new object depending on the object type in m_element_type switch(this.m_element_type) { case OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE_CELL : return new CTableCell(); case OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE_ROW : return new CTableRow(); case OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE_MODEL : return new CTableModel(); case OBJECT_TYPE_COLUMN_CAPTION : return new CColumnCaption(); case OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE_HEADER : return new CTableHeader(); case OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE : return new CTable(); case OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE_BY_PARAM : return new CTableByParam(); default : return NULL; } }
새 클래스를 생성한 후 CListObj 객체 목록에서 이러한 유형의 객체를 생성할 수 있습니다. 이렇게 하면 이러한 유형의 객체가 포함된 파일에서 목록을 저장하고 로드 할 수 있습니다.
지금처럼 '0' 값이 아닌 빈 행으로 표시되는 셀에 '비어 있는' 값을 설정하려면 어떤 값을 '비어 있는 것'으로 간주할지 결정해야 합니다. 문자열 값의 경우에는 빈 행이 그러한 값이 될 것임은 분명합니다. 숫자 값의 경우 실수형에는 DBL_MAX를, 정수형에는 LONG_MAX를 정의합니다.
이러한 값을 설정하려면 테이블 셀의 객체 클래스에서 보호된 영역에 다음 메서드를 작성합니다:
class CTableCell : public CObject { protected: //--- Combining for storing cell values (double, long, string) union DataType { protected: double double_value; long long_value; ushort ushort_value[MAX_STRING_LENGTH]; public: //--- Set values void SetValueD(const double value) { this.double_value=value; } void SetValueL(const long value) { this.long_value=value; } void SetValueS(const string value) { ::StringToShortArray(value,ushort_value); } //--- Return values double ValueD(void) const { return this.double_value; } long ValueL(void) const { return this.long_value; } string ValueS(void) const { string res=::ShortArrayToString(this.ushort_value); res.TrimLeft(); res.TrimRight(); return res; } }; //--- Variables DataType m_datatype_value; // Value ENUM_DATATYPE m_datatype; // Data type CObject *m_object; // Cell object ENUM_OBJECT_TYPE m_object_type; // Object type in the cell int m_row; // Row index int m_col; // Column index int m_digits; // Data representation accuracy uint m_time_flags; // Date/time display flags bool m_color_flag; // Color name display flag bool m_editable; // Editable cell flag //--- Set "empty value" void SetEmptyValue(void) { switch(this.m_datatype) { case TYPE_LONG : case TYPE_DATETIME: case TYPE_COLOR : this.SetValue(LONG_MAX); break; case TYPE_DOUBLE : this.SetValue(DBL_MAX); break; default : this.SetValue(""); break; } } public: //--- Return cell coordinates and properties
셀에 저장된 값을 형식이 지정된 문자열로 반환하는 메서드는 이제 셀의 값이 '비어 있지 않은지'를 확인하고 값이 '비어 있는 경우' 빈 행을 반환합니다:
public: //--- Return cell coordinates and properties uint Row(void) const { return this.m_row; } uint Col(void) const { return this.m_col; } ENUM_DATATYPE Datatype(void) const { return this.m_datatype; } int Digits(void) const { return this.m_digits; } uint DatetimeFlags(void) const { return this.m_time_flags; } bool ColorNameFlag(void) const { return this.m_color_flag; } bool IsEditable(void) const { return this.m_editable; } //--- Return (1) double, (2) long and (3) string value double ValueD(void) const { return this.m_datatype_value.ValueD(); } long ValueL(void) const { return this.m_datatype_value.ValueL(); } string ValueS(void) const { return this.m_datatype_value.ValueS(); } //--- Return the value as a formatted string string Value(void) const { switch(this.m_datatype) { case TYPE_DOUBLE : return(this.ValueD()!=DBL_MAX ? ::DoubleToString(this.ValueD(),this.Digits()) : ""); case TYPE_LONG : return(this.ValueL()!=LONG_MAX ? ::IntegerToString(this.ValueL()) : ""); case TYPE_DATETIME: return(this.ValueL()!=LONG_MAX ? ::TimeToString(this.ValueL(),this.m_time_flags) : ""); case TYPE_COLOR : return(this.ValueL()!=LONG_MAX ? ::ColorToString((color)this.ValueL(),this.m_color_flag) : ""); default : return this.ValueS(); } } //--- Return a description of the stored value type string DatatypeDescription(void) const { string type=::StringSubstr(::EnumToString(this.m_datatype),5); type.Lower(); return type; } //--- Clear data void ClearData(void) { this.SetEmptyValue(); }
이제 셀의 데이터를 지우는 메서드는 셀에 0을 설정하지 않고 대신 셀에 빈 값을 설정하는 메서드를 호출합니다.
테이블 모델 객체가 생성되는 모든 클래스의 메서드는 이제 객체에 대한 설명을 반환하는 가상 메서드가 됩니다 - 이러한 객체에서 상속되는 경우에 :
//--- (1) Return and (2) display the object description in the journal virtual string Description(void); void Print(void);
테이블 행 클래스에서 새 셀을 생성하여 목록 끝에 추가하는 모든 CreateNewCell() 메서드의 이름이 변경되었습니다:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Table row class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CTableRow : public CObject { protected: CTableCell m_cell_tmp; // Cell object to search in the list CListObj m_list_cells; // List of cells uint m_index; // Row index //--- Add the specified cell to the end of the list bool AddNewCell(CTableCell *cell); public: //--- (1) Set and (2) return the row index void SetIndex(const uint index) { this.m_index=index; } uint Index(void) const { return this.m_index; } //--- Set the row and column positions to all cells void CellsPositionUpdate(void); //--- Create a new cell and add it to the end of the list CTableCell *CellAddNew(const double value); CTableCell *CellAddNew(const long value); CTableCell *CellAddNew(const datetime value); CTableCell *CellAddNew(const color value); CTableCell *CellAddNew(const string value);
이는 셀에 액세스하는 모든 메서드들이 하위 문자열 "셀"로 시작하도록 하기 위해 수행됩니다. 다른 클래스에서는 예를 들어 테이블 행에 액세스하는 메서드가 하위 문자열 "Row"로 시작될 것입니다. 이렇게 하면 클래스 메서드가 질서 있게 됩니다.
테이블 모델을 구축하기 위해 우리는 거의 모든 데이터에서 테이블을 만들 수 있는 보편적인 접근 방식을 개발해야 합니다. 그러한 것들은 예를 들어 구조, 거래 목록, 주문, 포지션 또는 기타 데이터가 될 수 있습니다. 이를 위해 우리는 각 행이 속성 목록이 되는 행 목록을 만들 수 있는 툴킷을 만들어야 합니다. 목록의 각 속성은 테이블의 셀 하나에 해당합니다.
여기서 MqlParam의 입력 파라미터 구조에 주의를 기울여야 합니다. 이 구조는 다음과 같은 기능을 제공합니다:
- 구조에 저장되는 데이터 유형(ENUM_DATATYPE)을 지정합니다.
- 세 개의 필드에 값을 저장합니다:
- integer_value - 정수 데이터의 경우,
- double_value - 실수 데이터의 경우,
- string_value - 문자열 데이터의 경우.
이 구조를 사용하면 다양한 유형의 데이터로 작업할 수 있으므로 거래, 주문 또는 기타 객체의 매개변수 등의 모든 속성을 저장할 수 있습니다.
쉬운 데이터 저장을 위해 표준 라이브러리의 기본 CObject 클래스에서 상속된 CMqlParamObj 클래스를 생성합니다. 이 클래스는 MqlParam 구조가 포함되며 데이터 설정 및 검색을 위한 메서드를 제공합니다. CObject에서 상속해서 이러한 객체를 CList 목록에 저장할 수 있도록 합니다.
전체 클래스를 고려하세요:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Structure parameter object class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CMqlParamObj : public CObject { protected: public: MqlParam m_param; //--- Set the parameters void Set(const MqlParam ¶m) { this.m_param.type=param.type; this.m_param.double_value=param.double_value; this.m_param.integer_value=param.integer_value; this.m_param.string_value=param.string_value; } //--- Return the parameters MqlParam Param(void) const { return this.m_param; } ENUM_DATATYPE Datatype(void) const { return this.m_param.type; } double ValueD(void) const { return this.m_param.double_value; } long ValueL(void) const { return this.m_param.integer_value;} string ValueS(void) const { return this.m_param.string_value; } //--- Object description virtual string Description(void) { string t=::StringSubstr(::EnumToString(this.m_param.type),5); t.Lower(); string v=""; switch(this.m_param.type) { case TYPE_STRING : v=this.ValueS(); break; case TYPE_FLOAT : case TYPE_DOUBLE : v=::DoubleToString(this.ValueD()); break; case TYPE_DATETIME: v=::TimeToString(this.ValueL(),TIME_DATE|TIME_MINUTES|TIME_SECONDS); break; default : v=(string)this.ValueL(); break; } return(::StringFormat("<%s>%s",t,v)); } //--- Constructors/destructor CMqlParamObj(void){} CMqlParamObj(const MqlParam ¶m) { this.Set(param); } ~CMqlParamObj(void){} };
이러한 객체를 CList 목록에 저장하려면 CObject에서 상속된 객체가 필요하기 때문에 이는 MqlParam 구조에 대한 일반적인 래퍼입니다.
생성되는 데이터의 구조는 다음과 같습니다:
- CMqlParamObj 클래스의 객체는 하나의 속성(예: 거래 가격, 거래량 또는 개시 시간)을 나타냅니다,
- 단일 CList 목록은 단일 거래의 모든 속성이 포함된 테이블 행을 나타냅니다,
- 기본 CList 목록에는 각각 하나의 거래, 주문, 포지션 또는 기타 엔티티에 해당하는 행 세트(CList 목록)가 포함됩니다.
따라서 우리는 배열들의 배열과 유사한 구조를 갖게 됩니다:
- 기본 CList 목록은 "행들의 배열"입니다,
- 중첩된 각 CList 목록은 '셀들의 배열'(일부 객체의 속성)입니다.
다음은 과거 거래 목록에 대한 이러한 데이터 구조의 예시입니다:
- 기본 CList 목록은 테이블의 행들을 저장합니다. 각 행은 별도의 CList 목록입니다.
- 중첩된 목록 CList - 각 중첩된 목록은 테이블의 행을 나타내며 속성을 저장하는 CMqlParamObj 클래스의 객체를 포함합니다. 예를 들어:
- 첫 번째 행: 1번 거래의 속성(가격, 거래량, 개장 시간 등),
- 2열: 2번 거래의 속성(가격, 거래량, 개장 시간 등),
- 세번째 행: 3번 거래의 속성(가격, 거래량, 개장 시간 등),
- 기타
- 속성 객체(CMqlParamObj) - 각 객체는 거래 가격 또는 볼륨과 같은 하나의 속성을 저장하며
데이터 구조(CList 리스트)를 구성한 후 테이블 모델의 CreateTableModel(CList &list_param) 메서드로 전달될 수 있습니다. 이 메서드는 데이터를 다음과 같이 해석할 것입니다:
- 기본 CList 목록은 테이블 행들의 목록입니다,
- 중첩된 각 CList 목록은 각 행의 셀들입니다,
- 중첩된 목록 내의 CMqlParamObj 객체는 셀 값들입니다.
이렇게 전달된 목록을 기반으로 소스 데이터와 완전히 일치하는 테이블이 생성됩니다.
이러한 목록을 만드는 편의를 위해 특별한 클래스를 개발합니다. 이 클래스는 다음과 같은 메서드를 제공합니다:
- (CList 목록의) 새로운 행을 만들어 기본 목록에 추가합니다,
- 행에 새로운 속성(CMqlParamObj 객체)을 추가합니다.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class for creating lists of data | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class DataListCreator { public: //--- Add a new row to the CList list_data list static CList *AddNewRowToDataList(CList *list_data) { CList *row=new CList; if(row==NULL || list_data.Add(row)<0) return NULL; return row; } //--- Create a new CMqlParamObj parameter object and add it to CList static bool AddNewCellParamToRow(CList *row,MqlParam ¶m) { CMqlParamObj *cell=new CMqlParamObj(param); if(cell==NULL) return false; if(row.Add(cell)<0) { delete cell; return false; } return true; } };
테이블 모델을 생성하는 메서드에 전달하기 위해 올바른 구조의 목록을 편리하게 생성하는 기능을 제공하는 정적 클래스입니다:
- 필요한 속성(예: 거래 가격)을 지정합니다,
- 이 클래스는 자동으로 CMqlParamObj 객체를 생성하고 여기에 속성 값을 쓴 다음 행에 추가합니다,
- 행이 기본 목록에 추가됩니다.
그런 다음 완성된 목록은 개발을 위해 테이블 모델로 전달될 수 있습니다.
결과적으로 이렇게 개발된 접근 방식을 사용하면 모든 구조 또는 객체의 데이터를 테이블에 작성하기에 적합한 형식으로 변환할 수 있습니다. CList 목록과 CMqlParamObj 객체를 사용하면 유연하고 편리하게 작업할 수 있으며 보조 DataListCreator 클래스는 이러한 목록을 만드는 프로세스를 간소화하게 해줍니다. 이는 모든 데이터와 모든 작업에서 생성되는 범용 테이블 모델을 구축하기 위한 기초가 됩니다.
테이블 모델 클래스에서 테이블 모델을 생성하기 위한 세 가지 메서드와 열 조작을 하기 위한 세 가지 메서드를 새로 추가합니다. 오버로드 된 매개변수 생성자 5개 대신 템플릿 생성자 1개와 테이블 모델을 생성하는 새로운 메서드의 입력 매개변수 유형을 기반으로 하는 새로운 생성자 3개를 추가합니다:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Table model class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CTableModel : public CObject { protected: CTableRow m_row_tmp; // Row object to search in the list CListObj m_list_rows; // List of table rows //--- Create a table model from a two-dimensional array template<typename T> void CreateTableModel(T &array[][]); void CreateTableModel(const uint num_rows,const uint num_columns); void CreateTableModel(const matrix &row_data); void CreateTableModel(CList &list_param); //--- Return the correct data type ENUM_DATATYPE GetCorrectDatatype(string type_name) { return ( //--- Integer value type_name=="bool" || type_name=="char" || type_name=="uchar" || type_name=="short"|| type_name=="ushort" || type_name=="int" || type_name=="uint" || type_name=="long" || type_name=="ulong" ? TYPE_LONG : //--- Real value type_name=="float"|| type_name=="double" ? TYPE_DOUBLE : //--- Date/time value type_name=="datetime" ? TYPE_DATETIME : //--- Color value type_name=="color" ? TYPE_COLOR : /*--- String value */ TYPE_STRING ); } //--- Create and add a new empty string to the end of the list CTableRow *CreateNewEmptyRow(void); //--- Add a string to the end of the list bool AddNewRow(CTableRow *row); //--- Set the row and column positions to all table cells void CellsPositionUpdate(void); public: //--- Return (1) cell, (2) row by index, number (3) of rows, cells (4) in the specified row and (5) in the table CTableCell *GetCell(const uint row, const uint col); CTableRow *GetRow(const uint index) { return this.m_list_rows.GetNodeAtIndex(index); } uint RowsTotal(void) const { return this.m_list_rows.Total(); } uint CellsInRow(const uint index); uint CellsTotal(void); //--- Set (1) value, (2) precision, (3) time display flags and (4) color name display flag to the specified cell template<typename T> void CellSetValue(const uint row, const uint col, const T value); void CellSetDigits(const uint row, const uint col, const int digits); void CellSetTimeFlags(const uint row, const uint col, const uint flags); void CellSetColorNamesFlag(const uint row, const uint col, const bool flag); //--- (1) Assign and (2) cancel the object in the cell void CellAssignObject(const uint row, const uint col,CObject *object); void CellUnassignObject(const uint row, const uint col); //--- (1) Delete and (2) move the cell bool CellDelete(const uint row, const uint col); bool CellMoveTo(const uint row, const uint cell_index, const uint index_to); //--- (1) Return and (2) display the cell description and (3) the object assigned to the cell string CellDescription(const uint row, const uint col); void CellPrint(const uint row, const uint col); CObject *CellGetObject(const uint row, const uint col); public: //--- Create a new string and (1) add it to the end of the list, (2) insert to the specified list position CTableRow *RowAddNew(void); CTableRow *RowInsertNewTo(const uint index_to); //--- (1) Remove or (2) relocate the row, (3) clear the row data bool RowDelete(const uint index); bool RowMoveTo(const uint row_index, const uint index_to); void RowClearData(const uint index); //--- (1) Return and (2) display the row description in the journal string RowDescription(const uint index); void RowPrint(const uint index,const bool detail); //--- (1) Add, (2) remove, (3) relocate a column, (4) clear data, set the column data (5) type and (6) accuracy bool ColumnAddNew(const int index=-1); bool ColumnDelete(const uint index); bool ColumnMoveTo(const uint col_index, const uint index_to); void ColumnClearData(const uint index); void ColumnSetDatatype(const uint index,const ENUM_DATATYPE type); void ColumnSetDigits(const uint index,const int digits); //--- (1) Return and (2) display the table description in the journal virtual string Description(void); void Print(const bool detail); void PrintTable(const int cell_width=CELL_WIDTH_IN_CHARS); //--- (1) Clear the data, (2) destroy the model void ClearData(void); void Destroy(void); //--- Virtual methods of (1) comparing, (2) saving to file, (3) loading from file, (4) object type virtual int Compare(const CObject *node,const int mode=0) const; virtual bool Save(const int file_handle); virtual bool Load(const int file_handle); virtual int Type(void) const { return(OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE_MODEL); } //--- Constructors/destructor template<typename T> CTableModel(T &array[][]) { this.CreateTableModel(array); } CTableModel(const uint num_rows,const uint num_columns) { this.CreateTableModel(num_rows,num_columns); } CTableModel(const matrix &row_data) { this.CreateTableModel(row_data); } CTableModel(CList &row_data) { this.CreateTableModel(row_data); } CTableModel(void){} ~CTableModel(void){} };
새로운 메서드를 살펴보겠습니다.
지정된 수의 행과 열로 테이블 모델을 생성하는 메서드입니다.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Create a table model with specified number of rows and columns | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTableModel::CreateTableModel(const uint num_rows,const uint num_columns) { //--- In the loop based on the number of rows for(uint r=0; r<num_rows; r++) { //--- create a new empty row and add it to the end of the list of rows CTableRow *row=this.CreateNewEmptyRow(); //--- If a row is created and added to the list, if(row!=NULL) { //--- In a loop by the number of columns //--- create all the cells, adding each new one to the end of the list of cells in the row for(uint c=0; c<num_columns; c++) { CTableCell *cell=row.CellAddNew(0.0); if(cell!=NULL) cell.ClearData(); } } } }
이 메서드는 지정된 수의 행과 열이 있는 빈 모델을 만들며 테이블 구조가 미리 알려져 있지만 데이터는 나중에 추가해야 하는 경우에 적합합니다.
지정된 행렬에서 테이블 모델을 생성하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Create a table model from the specified matrix | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTableModel::CreateTableModel(const matrix &row_data) { //--- The number of rows and columns ulong num_rows=row_data.Rows(); ulong num_columns=row_data.Cols(); //--- In the loop based on the number of rows for(uint r=0; r<num_rows; r++) { //--- create a new empty row and add it to the end of the list of rows CTableRow *row=this.CreateNewEmptyRow(); //--- If a row is created and added to the list, if(row!=NULL) { //--- In the loop by the number of columns, //--- create all the cells, adding each new one to the end of the list of cells in the row for(uint c=0; c<num_columns; c++) row.CellAddNew(row_data[r][c]); } } }
이 메서드를 사용하면 데이터 행렬을 사용하여 테이블을 초기화할 수 있으므로 미리 준비된 데이터 집합을 조작할 때 편리합니다.
매개변수 목록에서 테이블 모델을 생성하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Create a table model from the list of parameters | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTableModel::CreateTableModel(CList &list_param) { //--- If an empty list is passed, report this and leave if(list_param.Total()==0) { ::PrintFormat("%s: Error. Empty list passed",__FUNCTION__); return; } //--- Get the pointer to the first row of the table to determine the number of columns //--- If the first row could not be obtained, or there are no cells in it, report this and leave CList *first_row=list_param.GetFirstNode(); if(first_row==NULL || first_row.Total()==0) { if(first_row==NULL) ::PrintFormat("%s: Error. Failed to get first row of list",__FUNCTION__); else ::PrintFormat("%s: Error. First row does not contain data",__FUNCTION__); return; } //--- The number of rows and columns ulong num_rows=list_param.Total(); ulong num_columns=first_row.Total(); //--- In the loop based on the number of rows for(uint r=0; r<num_rows; r++) { //--- get the next table row from list_param CList *col_list=list_param.GetNodeAtIndex(r); if(col_list==NULL) continue; //--- create a new empty row and add it to the end of the list of rows CTableRow *row=this.CreateNewEmptyRow(); //--- If a row is created and added to the list, if(row!=NULL) { //--- In the loop by the number of columns, //--- create all the cells, adding each new one to the end of the list of cells in the row for(uint c=0; c<num_columns; c++) { CMqlParamObj *param=col_list.GetNodeAtIndex(c); if(param==NULL) continue; //--- Declare the pointer to a cell and the type of data to be contained in it CTableCell *cell=NULL; ENUM_DATATYPE datatype=param.Datatype(); //--- Depending on the data type switch(datatype) { //--- real data type case TYPE_FLOAT : case TYPE_DOUBLE : cell=row.CellAddNew((double)param.ValueD()); // Create a new cell with double data and if(cell!=NULL) cell.SetDigits((int)param.ValueL()); // set the precision of the displayed data break; //--- datetime data type case TYPE_DATETIME: cell=row.CellAddNew((datetime)param.ValueL()); // Create a new cell with datetime data and if(cell!=NULL) cell.SetDatetimeFlags((int)param.ValueD()); // set date/time display flags break; //--- color data type case TYPE_COLOR : cell=row.CellAddNew((color)param.ValueL()); // Create a new cell with color data and if(cell!=NULL) cell.SetColorNameFlag((bool)param.ValueD()); // set the flag for displaying the names of known colors break; //--- string data type case TYPE_STRING : cell=row.CellAddNew((string)param.ValueS()); // Create a new cell with string data break; //--- integer data type default : cell=row.CellAddNew((long)param.ValueL()); // Create a new cell with long data break; } } } } }
이 메서드를 사용하면 연결된 목록을 기반으로 테이블 모델을 만들 수 있으므로 동적 데이터 구조를 운영하는 데 유용할 수 있습니다.
데이터 유형(예: double)이 있는 셀을 만들 때 표시 정밀도는 CMqlParamObj 클래스의 매개 변수 객체의 long 값에서 가져온다는 점에 유의할 필요가 있습니다. 즉 위에서 살펴본 대로 DataListCreator 클래스를 사용하여 테이블 구조를 만들 때 매개변수 객체에 필요한 명확한 정보를 추가로 전달할 수 있습니다. 거래의 재무적 결과의 경우 다음과 같이 할 수 있습니다:
//--- Financial result of a trade param.type=TYPE_DOUBLE; param.double_value=HistoryDealGetDouble(ticket,DEAL_PROFIT); param.integer_value=(param.double_value!=0 ? 2 : 1); DataListCreator::AddNewCellParamToRow(row,param);
같은 방식으로 날짜/시간 유형이 있는 테이블 셀에 시간 표시 플래그를 전달하고 색상 유형이 있는 셀에 색상 이름을 표시하는 플래그를 전달할 수 있습니다.
이 테이블에는 테이블 셀의 유형과 CMqlParamObj 객체를 통해 전달되는 매개변수 유형이 표시됩니다:
| CMqlParamObj를 입력합니다. | 셀 더블 유형 | 셀 롱 유형 | 셀 날짜/시간 유형 | 셀 색상 유형 | 셀 문자열 유형 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| double_value | 셀 값 | 사용되지 않음 | 날짜/시간 표시 플래그 | 색상 이름 표시 플래그 | 사용되지 않음 |
| integer_value | 셀 값 정밀도 | 셀 값 | 셀 값 | 셀 값 | 사용되지 않음 |
| string_value | 사용되지 않음 | 사용되지 않음 | 사용되지 않음 | 사용되지 않음 | 셀 값 |
이 표는 일부 데이터로 테이블 구조를 만들 때 이 데이터가 실제 유형(MqlParam double_value 구조 필드에 기록됨)인 경우 테이블 셀에 데이터가 표시될 정밀도 값을 integer_value 필드에 추가로 쓸 수 있다는 것을 보여줍니다. 날짜/시간 및 색상 유형의 데이터도 마찬가지입니다. 그러나 정수 필드는 속성 값 자체가 차지하므로 플래그는 double_value 필드에 기록됩니다.
이는 선택 사항입니다. 동시에 셀의 플래그 및 정밀도 값은 0으로 설정됩니다. 이 값은 특정 셀과 표의 전체 열에 대해 모두 변경될 수 있습니다.
테이블에 새로운 열을 추가하는 방법
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Add a column | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTableModel::ColumnAddNew(const int index=-1) { //--- Declare the variables CTableCell *cell=NULL; bool res=true; //--- In the loop based on the number of rows for(uint i=0;i<this.RowsTotal();i++) { //--- get the next row CTableRow *row=this.GetRow(i); if(row!=NULL) { //--- add a cell of double type to the end of the row cell=row.CellAddNew(0.0); if(cell==NULL) res &=false; //--- clear the cell else cell.ClearData(); } } //--- If the column index passed is not negative, shift the column to the specified position if(res && index>-1) res &=this.ColumnMoveTo(this.CellsInRow(0)-1,index); //--- Return the result return res; }
새로운 열의 인덱스가 메서드에 전달됩니다. 먼저 테이블의 모든 행에서 새로운 셀이 행 끝에 추가되고 전달된 인덱스가 음수가 아닌 경우 모든 새로운 셀이 지정된 인덱스만큼 이동합니다.
열 데이터 유형을 설정하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Set the column data type | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTableModel::ColumnSetDatatype(const uint index,const ENUM_DATATYPE type) { //--- In a loop through all table rows for(uint i=0;i<this.RowsTotal();i++) { //--- get the cell with the column index from each row and set the data type CTableCell *cell=this.GetCell(i, index); if(cell!=NULL) cell.SetDatatype(type); } }
테이블의 모든 행을 반복하여 인덱스별로 각 행의 셀을 가져와서 데이터 유형을 설정합니다. 결과적으로 전체 열의 셀에 하나의 동일한 값이 설정됩니다.
열 데이터 정확도를 설정하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Set the accuracy of the column data | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTableModel::ColumnSetDigits(const uint index,const int digits) { //--- In a loop through all table rows for(uint i=0;i<this.RowsTotal();i++) { //--- get the cell with the column index from each row and set the data accuracy CTableCell *cell=this.GetCell(i, index); if(cell!=NULL) cell.SetDigits(digits); } }
테이블의 모든 행을 반복하여 인덱스별로 각 행의 셀을 가져와서 데이터 유형을 설정합니다. 결과적으로 전체 열의 셀에 동일한 값이 설정됩니다.
테이블 모델 클래스에 메서드를 추가하면 셀 집합을 전체 테이블 열로 작업할 수 있습니다. 표의 열은 표에 헤더가 있는 경우에만 제어될 수 있습니다. 테이블은 헤더 없이 정적으로 표시됩니다.
테이블 헤더 클래스
테이블 헤더는 문자열 값을 가진 열 헤더 객체의 목록입니다. 이들은 CListObj 동적 목록에 있습니다. 그리고 동적 목록은 테이블 헤더 클래스의 기초를 형성합니다.
이를 기반으로 두 개의 클래스가 생성되어야 합니다:
- 테이블 열의 헤더 객체의 클래스.
여기에는 헤더의 텍스트 값, 열 번호, 전체 열의 데이터 유형, 열 셀을 제어하는 메서드가 포함되어 있습니다. - 테이블 헤더 클래스.
여기에는 테이블 열을 제어하기 위한 열 헤더 객체 목록과 액세스 메서드가 포함되어 있습니다.
동일한 파일 \MQL5\Scripts\Tables\Tables.mqh에 코드를 계속 작성하고 테이블 열 헤더 클래스를 작성합니다:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Table column header class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CColumnCaption : public CObject { protected: //--- Variables ushort m_ushort_array[MAX_STRING_LENGTH]; // Array of header symbols uint m_column; // Column index ENUM_DATATYPE m_datatype; // Data type public: //--- (1) Set and (2) return the column index void SetColumn(const uint column) { this.m_column=column; } uint Column(void) const { return this.m_column; } //--- (1) Set and (2) return the column data type ENUM_DATATYPE Datatype(void) const { return this.m_datatype; } void SetDatatype(const ENUM_DATATYPE datatype) { this.m_datatype=datatype;} //--- Clear data void ClearData(void) { this.SetValue(""); } //--- Set the header void SetValue(const string value) { ::StringToShortArray(value,this.m_ushort_array); } //--- Return the header text string Value(void) const { string res=::ShortArrayToString(this.m_ushort_array); res.TrimLeft(); res.TrimRight(); return res; } //--- (1) Return and (2) display the object description in the journal virtual string Description(void); void Print(void); //--- Virtual methods of (1) comparing, (2) saving to file, (3) loading from file, (4) object type virtual int Compare(const CObject *node,const int mode=0) const; virtual bool Save(const int file_handle); virtual bool Load(const int file_handle); virtual int Type(void) const { return(OBJECT_TYPE_COLUMN_CAPTION); } //--- Constructors/destructor CColumnCaption(void) : m_column(0) { this.SetValue(""); } CColumnCaption(const uint column,const string value) : m_column(column) { this.SetValue(value); } ~CColumnCaption(void) {} };
이것은 테이블 셀 클래스의 매우 단순화된 버전입니다. 클래스의 몇 가지 메서드를 고려해 보세요.
두 객체를 비교하는 가상 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Compare two objects | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int CColumnCaption::Compare(const CObject *node,const int mode=0) const { const CColumnCaption *obj=node; return(this.Column()>obj.Column() ? 1 : this.Column()<obj.Column() ? -1 : 0); }
비교는 헤더가 생성된 열의 인덱스를 기준으로 수행됩니다.
파일에 저장하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Save to file | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CColumnCaption::Save(const int file_handle) { //--- Check the handle if(file_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) return(false); //--- Save data start marker - 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF if(::FileWriteLong(file_handle,MARKER_START_DATA)!=sizeof(long)) return(false); //--- Save the object type if(::FileWriteInteger(file_handle,this.Type(),INT_VALUE)!=INT_VALUE) return(false); //--- Save the column index if(::FileWriteInteger(file_handle,this.m_column,INT_VALUE)!=INT_VALUE) return(false); //--- Save the value if(::FileWriteArray(file_handle,this.m_ushort_array)!=sizeof(this.m_ushort_array)) return(false); //--- All is successful return true; }
파일에서 다운로드하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Load from file | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CColumnCaption::Load(const int file_handle) { //--- Check the handle if(file_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) return(false); //--- Load and check the data start marker - 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF if(::FileReadLong(file_handle)!=MARKER_START_DATA) return(false); //--- Load the object type if(::FileReadInteger(file_handle,INT_VALUE)!=this.Type()) return(false); //--- Load the column index this.m_column=::FileReadInteger(file_handle,INT_VALUE); //--- Load the value if(::FileReadArray(file_handle,this.m_ushort_array)!=sizeof(this.m_ushort_array)) return(false); //--- All is successful return true; }
비슷한 방법은 이전 글에서 자세히 설명했습니다. 여기서 로직은 동일합니다. 먼저 데이터 시작 마커와 객체 유형이 기록됩니다. 그 다음 모든 속성을 요소별로 기록됩니다. 읽기는 동일한 순서로 진행됩니다.
객체에 대한 설명을 반환하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Return the object description | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string CColumnCaption::Description(void) { return(::StringFormat("%s: Column %u, Value: \"%s\"", TypeDescription((ENUM_OBJECT_TYPE)this.Type()),this.Column(),this.Value())); }
설명 문자열이 생성되어 다음의 형식으로 반환됩니다 (Object Type: Column XX, Value "Value")
객체 설명을 로그에 출력하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Display the object description in the journal | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CColumnCaption::Print(void) { ::Print(this.Description()); }
로그에서 헤더 설명만 출력합니다.
이제 이러한 객체는 테이블 헤더가 될 목록에 배치되어야 합니다. 테이블 헤더 클래스를 작성:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Table header class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CTableHeader : public CObject { protected: CColumnCaption m_caption_tmp; // Column header object to search in the list CListObj m_list_captions; // List of column headers //--- Add the specified header to the end of the list bool AddNewColumnCaption(CColumnCaption *caption); //--- Create a table header from a string array void CreateHeader(string &array[]); //--- Set the column position of all column headers void ColumnPositionUpdate(void); public: //--- Create a new header and add it to the end of the list CColumnCaption *CreateNewColumnCaption(const string caption); //--- Return (1) the header by index and (2) the number of column headers CColumnCaption *GetColumnCaption(const uint index) { return this.m_list_captions.GetNodeAtIndex(index); } uint ColumnsTotal(void) const { return this.m_list_captions.Total(); } //--- Set the value of the specified column header void ColumnCaptionSetValue(const uint index,const string value); //--- (1) Set and (2) return the data type for the specified column header void ColumnCaptionSetDatatype(const uint index,const ENUM_DATATYPE type); ENUM_DATATYPE ColumnCaptionDatatype(const uint index); //--- (1) Remove and (2) relocate the column header bool ColumnCaptionDelete(const uint index); bool ColumnCaptionMoveTo(const uint caption_index, const uint index_to); //--- Clear column header data void ClearData(void); //--- Clear the list of column headers void Destroy(void) { this.m_list_captions.Clear(); } //--- (1) Return and (2) display the object description in the journal virtual string Description(void); void Print(const bool detail, const bool as_table=false, const int column_width=CELL_WIDTH_IN_CHARS); //--- Virtual methods of (1) comparing, (2) saving to file, (3) loading from file, (4) object type virtual int Compare(const CObject *node,const int mode=0) const; virtual bool Save(const int file_handle); virtual bool Load(const int file_handle); virtual int Type(void) const { return(OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE_HEADER); } //--- Constructors/destructor CTableHeader(void) {} CTableHeader(string &array[]) { this.CreateHeader(array); } ~CTableHeader(void){} };
클래스 메서드를 살펴보겠습니다.
새로운 헤더를 생성하여 열 헤더 목록의 끝에 추가하는 메서드입니다.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Create a new header and add it to the end of the list | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CColumnCaption *CTableHeader::CreateNewColumnCaption(const string caption) { //--- Create a new header object CColumnCaption *caption_obj=new CColumnCaption(this.ColumnsTotal(),caption); if(caption_obj==NULL) { ::PrintFormat("%s: Error. Failed to create new column caption at position %u",__FUNCTION__, this.ColumnsTotal()); return NULL; } //--- Add the created header to the end of the list if(!this.AddNewColumnCaption(caption_obj)) { delete caption_obj; return NULL; } //--- Return the pointer to the object return caption_obj; }
헤더 텍스트가 메서드에 전달됩니다. 지정된 텍스트와 목록의 헤더 수와 동일한 인덱스와 함께 새로운 열 헤더 객체가 생성됩니다. 이것이 마지막 헤더의 인덱스가 될 것입니다. 그런 다음 생성된 객체가 열 헤더 목록의 끝에 배치되고 생성된 헤더에 대한 포인터가 반환됩니다.
지정된 헤더를 목록 끝에 추가하는 메서드입니다.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Add the header to the end of the list | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTableHeader::AddNewColumnCaption(CColumnCaption *caption) { //--- If an empty object is passed, report it and return 'false' if(caption==NULL) { ::PrintFormat("%s: Error. Empty CColumnCaption object passed",__FUNCTION__); return false; } //--- Set the header index in the list and add the created header to the end of the list caption.SetColumn(this.ColumnsTotal()); if(this.m_list_captions.Add(caption)==WRONG_VALUE) { ::PrintFormat("%s: Error. Failed to add caption (%u) to list",__FUNCTION__,this.ColumnsTotal()); return false; } //--- Successful return true; }
열 헤더 객체에 대한 포인터가 메서드로 전달됩니다. 이때 헤더 목록의 끝에 배치되어야 합니다. 이 메서드는 목록에 객체를 추가한 결과를 반환합니다.
문자열 배열에서 테이블 헤더를 생성하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Create a table header from the string array | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTableHeader::CreateHeader(string &array[]) { //--- Get the number of table columns from the array properties uint total=array.Size(); //--- In a loop by array size, //--- create all the headers, adding each new one to the end of the list for(uint i=0; i<total; i++) this.CreateNewColumnCaption(array[i]); }
헤더의 텍스트 배열이 메서드에 전달됩니다. 배열의 크기에 따라 생성할 열 헤더 객체의 수가 결정됩니다. 이는 배열의 헤더 텍스트 값을 루프에서 전달할 때 생성됩니다.
열의 지정된 헤더에 값을 설정하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Set the value to the specified column header | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTableHeader::ColumnCaptionSetValue(const uint index,const string value) { //--- Get the required header from the list and set a new value to it CColumnCaption *caption=this.GetColumnCaption(index); if(caption!=NULL) caption.SetValue(value); }
이 메서드를 사용하면 헤더 인덱스에 지정된 대로 새 텍스트 값을 설정할 수 있습니다.
지정된 열 헤더의 데이터 유형을 설정하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Set the data type for the specified column header | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTableHeader::ColumnCaptionSetDatatype(const uint index,const ENUM_DATATYPE type) { //--- Get the required header from the list and set a new value to it CColumnCaption *caption=this.GetColumnCaption(index); if(caption!=NULL) caption.SetDatatype(type); }
이 메서드를 사용하면 헤더 인덱스로 표시된 열에 저장된 데이터의 새로운 값을 설정할 수 있습니다. 표의 각 열에 대해 열 셀에 저장되는 데이터 유형을 설정할 수 있습니다. 헤더 객체에 데이터 유형을 설정하면 나중에 전체 열에 동일한 값을 설정할 수 있게 됩니다. 그리고 이 열의 헤더에서 이 값을 읽으면 전체 열의 데이터 값을 읽을 수 있습니다.
지정된 열 헤더의 데이터 유형을 반환하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Return the data type of the specified column header | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ENUM_DATATYPE CTableHeader::ColumnCaptionDatatype(const uint index) { //--- Get the required header from the list and return the column data type from it CColumnCaption *caption=this.GetColumnCaption(index); return(caption!=NULL ? caption.Datatype() : (ENUM_DATATYPE)WRONG_VALUE); }
이 메서드를 사용하면 열에 저장된 데이터의 값을 헤더 인덱스로 검색할 수 있습니다. 헤더에서 값을 가져오면 테이블의 이 열의 모든 셀에 저장된 값의 유형을 확인할 수 있습니다.
지정된 열의 헤더를 삭제하는 메서드입니다.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Remove the header of the specified column | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTableHeader::ColumnCaptionDelete(const uint index) { //--- Remove the header from the list by index if(!this.m_list_captions.Delete(index)) return false; //--- Update the indices for the remaining headers in the list this.ColumnPositionUpdate(); return true; }
지정된 인덱스의 객체가 헤더 목록에서 삭제됩니다. 열 헤더 객체를 성공적으로 삭제한 후에는 목록에 있는 나머지 객체의 인덱스를 업데이트해야 합니다.
열 헤더를 지정된 위치로 이동하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Move the column header to the specified position | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTableHeader::ColumnCaptionMoveTo(const uint caption_index,const uint index_to) { //--- Get the desired header by index in the list, turning it into the current one CColumnCaption *caption=this.GetColumnCaption(caption_index); //--- Move the current header to the specified position in the list if(caption==NULL || !this.m_list_captions.MoveToIndex(index_to)) return false; //--- Update the indices of all headers in the list this.ColumnPositionUpdate(); return true; }
지정된 인덱스에서 헤더를 목록의 새로운 위치로 이동시킬 수 있습니다.
모든 헤더에 대해 열의 위치를 설정하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Set the column positions of all headers | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTableHeader::ColumnPositionUpdate(void) { //--- In the loop through all the headings in the list for(int i=0;i<this.m_list_captions.Total();i++) { //--- get the next header and set the column index in it CColumnCaption *caption=this.GetColumnCaption(i); if(caption!=NULL) caption.SetColumn(this.m_list_captions.IndexOf(caption)); } }
목록에서 객체를 삭제하거나 다른 위치로 옮긴 후에는 목록의 다른 모든 객체에 인덱스를 다시 할당하여 해당 인덱스가 목록의 실제 위치와 일치하도록 해야 합니다. 이 메서드는 목록의 모든 객체를 반복해서 실행하고 각 객체의 실제 인덱스를 가져와 객체의 속성으로 설정합니다.
목록에서 열 헤더 데이터를 지우는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Clear column header data in the list | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTableHeader::ClearData(void) { //--- In the loop through all the headings in the list for(uint i=0;i<this.ColumnsTotal();i++) { //--- get the next header and set the empty value to it CColumnCaption *caption=this.GetColumnCaption(i); if(caption!=NULL) caption.ClearData(); } }
목록의 모든 열 헤더 객체를 루프 반복하여 각 일반 객체를 가져와 헤더 텍스트를 빈 값으로 설정합니다. 이렇게 하면 테이블의 각 열 헤더가 완전히 지워집니다.
객체에 대한 설명을 반환하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Return the object description | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string CTableHeader::Description(void) { return(::StringFormat("%s: Captions total: %u", TypeDescription((ENUM_OBJECT_TYPE)this.Type()),this.ColumnsTotal())); }
문자열이 생성되고 다음의 형식으로 반환됩니다(Object Type: Captions total: XX)
객체 설명을 로그에 출력하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Display the object description in the journal | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTableHeader::Print(const bool detail, const bool as_table=false, const int column_width=CELL_WIDTH_IN_CHARS) { //--- Number of headers int total=(int)this.ColumnsTotal(); //--- If the output is in tabular form string res=""; if(as_table) { //--- create a table row from the values of all headers res="|"; for(int i=0;i<total;i++) { CColumnCaption *caption=this.GetColumnCaption(i); if(caption==NULL) continue; res+=::StringFormat("%*s |",column_width,caption.Value()); } //--- Display a row in the journal and leave ::Print(res); return; } //--- Display the header as a row description ::Print(this.Description()+(detail ? ":" : "")); //--- If detailed description if(detail) { //--- In a loop by the list of row headers for(int i=0; i<total; i++) { //--- get the current header and add its description to the final row CColumnCaption *caption=this.GetColumnCaption(i); if(caption!=NULL) res+=" "+caption.Description()+(i<total-1 ? "\n" : ""); } //--- Send the row created in the loop to the journal ::Print(res); } }
이 메서드는 헤더 설명을 표 형식과 열 헤더 목록으로 기록할 수 있습니다.
파일에 저장하고 파일에서 헤더를 다운로드하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Save to file | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTableHeader::Save(const int file_handle) { //--- Check the handle if(file_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) return(false); //--- Save data start marker - 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF if(::FileWriteLong(file_handle,MARKER_START_DATA)!=sizeof(long)) return(false); //--- Save the object type if(::FileWriteInteger(file_handle,this.Type(),INT_VALUE)!=INT_VALUE) return(false); //--- Save the list of headers if(!this.m_list_captions.Save(file_handle)) return(false); //--- Successful return true; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Load from file | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTableHeader::Load(const int file_handle) { //--- Check the handle if(file_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) return(false); //--- Load and check the data start marker - 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF if(::FileReadLong(file_handle)!=MARKER_START_DATA) return(false); //--- Load the object type if(::FileReadInteger(file_handle,INT_VALUE)!=this.Type()) return(false); //--- Load the list of headers if(!this.m_list_captions.Load(file_handle)) return(false); //--- Successful return true; }
메서드의 로직은 코드에 주석 처리되어 있으며 테이블을 생성하기 위해 이미 생성된 다른 클래스의 유사한 메서드와 다르지 않습니다.
이제 테이블 클래스들을 합칠 모든 준비가 완료되었습니다. 테이블 클래스는 모델을 기반으로 테이블을 작성할 수 있어야 하며 테이블 열의 이름을 지정할 헤더가 있어야 합니다. 테이블에서 테이블의 헤더를 지정하지 않으면 테이블은 모델에 따라서만 작성되고 정적이며 테이블의 기능은 보는 것만으로 제한됩니다. 간단한 테이블의 경우 이 정도면 충분합니다. 그러나 컨트롤러 컴포넌트를 사용하여 사용자와 상호 작용하려면 테이블에 테이블의 헤더가 결정되어야 합니다. 이렇게 하면 테이블과 해당 데이터를 제어할 수 있는 다양한 옵션이 생성됩니다. 하지만 이 모든 것은 나중에 하도록 하겠습니다. 이제 테이블 클래스들에 대해 살펴보겠습니다.
테이블 클래스
동일한 파일에 코드를 계속 작성하고 테이블 클래스를 구현합니다:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Table class | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CTable : public CObject { private: //--- Populate the array of column headers in Excel style bool FillArrayExcelNames(const uint num_columns); //--- Return the column name as in Excel string GetExcelColumnName(uint column_number); //--- Return the header availability bool HeaderCheck(void) const { return(this.m_table_header!=NULL && this.m_table_header.ColumnsTotal()>0); } protected: CTableModel *m_table_model; // Pointer to the table model CTableHeader *m_table_header; // Pointer to the table header CList m_list_rows; // List of parameter arrays from structure fields string m_array_names[]; // Array of column headers int m_id; // Table ID //--- Copy the array of header names bool ArrayNamesCopy(const string &column_names[],const uint columns_total); public: //--- (1) Set and (2) return the table model void SetTableModel(CTableModel *table_model) { this.m_table_model=table_model; } CTableModel *GetTableModel(void) { return this.m_table_model; } //--- (1) Set and (2) return the header void SetTableHeader(CTableHeader *table_header) { this.m_table_header=m_table_header; } CTableHeader *GetTableHeader(void) { return this.m_table_header; } //--- (1) Set and (2) return the table ID void SetID(const int id) { this.m_id=id; } int ID(void) const { return this.m_id; } //--- Clear column header data void HeaderClearData(void) { if(this.m_table_header!=NULL) this.m_table_header.ClearData(); } //--- Remove the table header void HeaderDestroy(void) { if(this.m_table_header==NULL) return; this.m_table_header.Destroy(); this.m_table_header=NULL; } //--- (1) Clear all data and (2) destroy the table model and header void ClearData(void) { if(this.m_table_model!=NULL) this.m_table_model.ClearData(); } void Destroy(void) { if(this.m_table_model==NULL) return; this.m_table_model.Destroy(); this.m_table_model=NULL; } //--- Return (1) the header, (2) cell, (3) row by index, number (4) of rows, (5) columns, cells (6) in the specified row, (7) in the table CColumnCaption *GetColumnCaption(const uint index) { return(this.m_table_header!=NULL ? this.m_table_header.GetColumnCaption(index) : NULL); } CTableCell *GetCell(const uint row, const uint col) { return(this.m_table_model!=NULL ? this.m_table_model.GetCell(row,col) : NULL); } CTableRow *GetRow(const uint index) { return(this.m_table_model!=NULL ? this.m_table_model.GetRow(index) : NULL); } uint RowsTotal(void) const { return(this.m_table_model!=NULL ? this.m_table_model.RowsTotal() : 0); } uint ColumnsTotal(void) const { return(this.m_table_model!=NULL ? this.m_table_model.CellsInRow(0) : 0); } uint CellsInRow(const uint index) { return(this.m_table_model!=NULL ? this.m_table_model.CellsInRow(index) : 0); } uint CellsTotal(void) { return(this.m_table_model!=NULL ? this.m_table_model.CellsTotal() : 0); } //--- Set (1) value, (2) precision, (3) time display flags and (4) color name display flag to the specified cell template<typename T> void CellSetValue(const uint row, const uint col, const T value); void CellSetDigits(const uint row, const uint col, const int digits); void CellSetTimeFlags(const uint row, const uint col, const uint flags); void CellSetColorNamesFlag(const uint row, const uint col, const bool flag); //--- (1) Assign and (2) cancel the object in the cell void CellAssignObject(const uint row, const uint col,CObject *object); void CellUnassignObject(const uint row, const uint col); //--- Return the string value of the specified cell virtual string CellValueAt(const uint row, const uint col); protected: //--- (1) Delete and (2) move the cell bool CellDelete(const uint row, const uint col); bool CellMoveTo(const uint row, const uint cell_index, const uint index_to); public: //--- (1) Return and (2) display the cell description and (3) the object assigned to the cell string CellDescription(const uint row, const uint col); void CellPrint(const uint row, const uint col); //--- Return (1) the object assigned to the cell and (2) the type of the object assigned to the cell CObject *CellGetObject(const uint row, const uint col); ENUM_OBJECT_TYPE CellGetObjType(const uint row, const uint col); //--- Create a new string and (1) add it to the end of the list, (2) insert to the specified list position CTableRow *RowAddNew(void); CTableRow *RowInsertNewTo(const uint index_to); //--- (1) Remove or (2) relocate the row, (3) clear the row data bool RowDelete(const uint index); bool RowMoveTo(const uint row_index, const uint index_to); void RowClearData(const uint index); //--- (1) Return and (2) display the row description in the journal string RowDescription(const uint index); void RowPrint(const uint index,const bool detail); //--- (1) Add new, (2) remove, (3) relocate the column and (4) clear the column data bool ColumnAddNew(const string caption,const int index=-1); bool ColumnDelete(const uint index); bool ColumnMoveTo(const uint index, const uint index_to); void ColumnClearData(const uint index); //--- Set (1) the value of the specified header and (2) data accuracy for the specified column void ColumnCaptionSetValue(const uint index,const string value); void ColumnSetDigits(const uint index,const int digits); //--- (1) Set and (2) return the data type for the specified column void ColumnSetDatatype(const uint index,const ENUM_DATATYPE type); ENUM_DATATYPE ColumnDatatype(const uint index); //--- (1) Return and (2) display the object description in the journal virtual string Description(void); void Print(const int column_width=CELL_WIDTH_IN_CHARS); //--- Virtual methods of (1) comparing, (2) saving to file, (3) loading from file, (4) object type virtual int Compare(const CObject *node,const int mode=0) const; virtual bool Save(const int file_handle); virtual bool Load(const int file_handle); virtual int Type(void) const { return(OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE); } //--- Constructors/destructor CTable(void) : m_table_model(NULL), m_table_header(NULL) { this.m_list_rows.Clear();} template<typename T> CTable(T &row_data[][],const string &column_names[]); CTable(const uint num_rows, const uint num_columns); CTable(const matrix &row_data,const string &column_names[]); ~CTable (void); };
헤더와 모델 테이블에 대한 포인터는 클래스에서 선언됩니다. 테이블을 만들려면 먼저 클래스 생성자에게 전달되는 데이터에서 테이블 모델을 만들어야 합니다. 테이블은 각각의 열에 라틴 문자로 구성된 이름이 할당되는 MS Excel 스타일의 열 이름이 포함된 헤더를 자동으로 생성할 수 있습니다.
이름을 계산하는 알고리즘은 다음과 같습니다:
-
한 글자 이름 - 처음 26개 열은 "A"에서 "Z"까지의 문자로 표시됩니다.
-
두 글자 이름 - "Z" 뒤에 오는 열은 두 글자의 조합으로 지정됩니다. 첫 번째 글자는 더 느리게 변경되고 두 번째 글자는 전체 알파벳을 반복합니다. 예를 들어:
- "AA", "AB", "AC", ..., "AZ",
- 다음 "BA", "BB", ..., "BZ",
- 기타
-
세 글자 이름 - "ZZ" 뒤에 오는 열은 세 글자의 조합으로 지정됩니다. 원칙은 동일합니다:
- "AAA", "AAB", ..., "AAZ",
- 그런 다음 "ABA", "ABB", ..., "ABZ"
- 기타
-
일반적인 원칙은 열 이름은 기본이 26인 숫자 체계의 숫자로 간주될 수 있으며 여기서 'A'는 1, 'B'는 2, ..., 'Z'-26에 해당합니다. 예를 들어:
- "A" = 1,
- "Z" = 26,
- "AA" = 27 (1 * 26^1 + 1),
- "AB" = 28 (1 * 26^1 + 2),
- "BA" = 53 (2 * 26^1 + 1).
따라서 알고리즘은 이러한 원칙에 따라 열 이름을 자동으로 생성하여 열 이름을 늘립니다. Excel의 최대 열 수는 프로그램 버전에 따라 다릅니다(예: Excel 2007 이상 버전에서는 16,384개이며 "XFD"로 끝남). 여기서 생성된 알고리즘은 이 그림에만 국한되지 않습니다. INT_MAX의 열 수에 이름을 지정할 수 있습니다:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Return the column name as in Excel | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string CTable::GetExcelColumnName(uint column_number) { string column_name=""; uint index=column_number; //--- Check that the column index is greater than 0 if(index==0) return (__FUNCTION__+": Error. Invalid column number passed"); //--- Convert the index to the column name while(!::IsStopped() && index>0) { index--; // Decrease the index by 1 to make it 0-indexed uint remainder =index % 26; // Remainder after division by 26 uchar char_code ='A'+(uchar)remainder; // Calculate the symbol code (letters) column_name=::CharToString(char_code)+column_name; // Add a letter to the beginning of the string index/=26; // Move on to the next rank } return column_name; } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Populate the array of column headers in Excel style | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTable::FillArrayExcelNames(const uint num_columns) { ::ResetLastError(); if(::ArrayResize(this.m_array_names,num_columns,num_columns)!=num_columns) { ::PrintFormat("%s: ArrayResize() failed. Error %d",__FUNCTION__,::GetLastError()); return false; } for(int i=0;i<(int)num_columns;i++) this.m_array_names[i]=this.GetExcelColumnName(i+1); return true; }
이 메서드를 사용하면 Excel 스타일의 열 이름 배열을 채울 수 있습니다.
클래스의 파라메트릭 생성자를 생각해 보세요.
데이터의 2차원 배열과 헤더의 문자열 배열을 지정하는 템플릿 생성자
//+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Constructor specifying a table array and a header array. | //| Defines the index and names of columns according to column_names | //| The number of rows is determined by the size of the row_data array| //| also used to fill the table | //+-------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> CTable::CTable(T &row_data[][],const string &column_names[]) : m_id(-1) { this.m_table_model=new CTableModel(row_data); if(column_names.Size()>0) this.ArrayNamesCopy(column_names,row_data.Range(1)); else { ::PrintFormat("%s: An empty array names was passed. The header array will be filled in Excel style (A, B, C)",__FUNCTION__); this.FillArrayExcelNames((uint)::ArrayRange(row_data,1)); } this.m_table_header=new CTableHeader(this.m_array_names); }
모든 유형의 데이터 배열은 열거형 ENUM_DATATYPE에서 템플릿 생성자에게 전달됩니다. 그런 다음 테이블에서 사용하는 데이터 유형(double, long, datetime, color, string)으로 변환하여 테이블 모델과 열 헤더의 배열을 만듭니다. 헤더 배열이 비어 있으면 MS Excel 스타일의 헤더가 생성됩니다.
테이블의 행과 열의 수를 나타내는 생성자
//+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Table constructor with definition of the number of columns and rows. | //| The columns will have Excel names "A", "B", "C", etc. | //+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+ CTable::CTable(const uint num_rows,const uint num_columns) : m_table_header(NULL), m_id(-1) { this.m_table_model=new CTableModel(num_rows,num_columns); if(this.FillArrayExcelNames(num_columns)) this.m_table_header=new CTableHeader(this.m_array_names); }
생성자는 MS Excel 스타일의 헤더가 있는 빈 테이블 모델을 생성합니다.
데이터 행렬과 열 헤더 배열을 기반으로 하는 생성자
//+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Table constructor with column initialization according to column_names| //| The number of rows is determined by row_data with matrix type | //+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+ CTable::CTable(const matrix &row_data,const string &column_names[]) : m_id(-1) { this.m_table_model=new CTableModel(row_data); if(column_names.Size()>0) this.ArrayNamesCopy(column_names,(uint)row_data.Cols()); else { ::PrintFormat("%s: An empty array names was passed. The header array will be filled in Excel style (A, B, C)",__FUNCTION__); this.FillArrayExcelNames((uint)row_data.Cols()); } this.m_table_header=new CTableHeader(this.m_array_names); }
double 타입의 데이터 행렬이 생성자에게 전달되어 테이블 모델과 열 헤더 배열을 생성합니다. 헤더 배열이 비어 있으면 MS Excel 스타일의 헤더가 생성됩니다.
클래스 소멸자에서 모델과 테이블 헤더가 소멸됩니다.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Destructor | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CTable::~CTable(void) { if(this.m_table_model!=NULL) { this.m_table_model.Destroy(); delete this.m_table_model; } if(this.m_table_header!=NULL) { this.m_table_header.Destroy(); delete this.m_table_header; } }
두 객체를 비교하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Compare two objects | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int CTable::Compare(const CObject *node,const int mode=0) const { const CTable *obj=node; return(this.ID()>obj.ID() ? 1 : this.ID()<obj.ID() ? -1 : 0); }
프로그램에서 여러 테이블을 생성해야 하는 경우 각 테이블에 식별자를 할당할 수 있습니다. 프로그램의 테이블은 기본적으로 -1 값을 갖는 집합 식별자로 식별할 수 있습니다. 생성된 테이블이 목록(CList, CArrayObj 등)에 배치된 경우 비교 메서드를 사용하면 식별자를 기준으로 테이블을 비교하여 검색 및 정렬할 수 있습니다:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Compare two objects | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int CTable::Compare(const CObject *node,const int mode=0) const { const CTable *obj=node; return(this.ID()>obj.ID() ? 1 : this.ID()<obj.ID() ? -1 : 0); }
헤더 이름 배열을 복사하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Copy the array of header names | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTable::ArrayNamesCopy(const string &column_names[],const uint columns_total) { if(columns_total==0) { ::PrintFormat("%s: Error. The table has no columns",__FUNCTION__); return false; } if(columns_total>column_names.Size()) { ::PrintFormat("%s: The number of header names is less than the number of columns. The header array will be filled in Excel style (A, B, C)",__FUNCTION__); return this.FillArrayExcelNames(columns_total); } uint total=::fmin(columns_total,column_names.Size()); return(::ArrayCopy(this.m_array_names,column_names,0,0,total)==total); }
생성된 테이블 모델의 헤더 배열과 열의 수가 메서드에 전달됩니다. 테이블에 열이 없는 경우 헤더를 만들 필요가 없습니다. 이를 보고하고 거짓을 반환합니다. 전달된 배열의 헤더보다 테이블 모델에 열이 더 많은 경우 모든 헤더가 Excel 스타일로 생성되어 헤더에 캡션이 없는 열이 테이블에 생기지 않도록 합니다.
지정된 셀에 값을 설정하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Set the value to the specified cell | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ template<typename T> void CTable::CellSetValue(const uint row, const uint col, const T value) { if(this.m_table_model!=NULL) this.m_table_model.CellSetValue(row,col,value); }
여기서 우리는 테이블 모델 객체에 대해 동일한 이름을 가진 메서드를 참조합니다.
기본적으로 이 클래스에서는 많은 메서드가 테이블 모델 클래스에서 중복됩니다. 모델이 생성되면 이와 유사한 속성 가져오기 또는 설정 메서드가 호출됩니다.
테이블 셀을 작동하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Set the accuracy to the specified cell | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTable::CellSetDigits(const uint row, const uint col, const int digits) { if(this.m_table_model!=NULL) this.m_table_model.CellSetDigits(row,col,digits); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Set the time display flags to the specified cell | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTable::CellSetTimeFlags(const uint row, const uint col, const uint flags) { if(this.m_table_model!=NULL) this.m_table_model.CellSetTimeFlags(row,col,flags); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Set the flag for displaying color names in the specified cell | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTable::CellSetColorNamesFlag(const uint row, const uint col, const bool flag) { if(this.m_table_model!=NULL) this.m_table_model.CellSetColorNamesFlag(row,col,flag); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Assign an object to a cell | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTable::CellAssignObject(const uint row, const uint col,CObject *object) { if(this.m_table_model!=NULL) this.m_table_model.CellAssignObject(row,col,object); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Cancel the object in the cell | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTable::CellUnassignObject(const uint row, const uint col) { if(this.m_table_model!=NULL) this.m_table_model.CellUnassignObject(row,col); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Return the string value of the specified cell | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string CTable::CellValueAt(const uint row,const uint col) { CTableCell *cell=this.GetCell(row,col); return(cell!=NULL ? cell.Value() : ""); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Delete a cell | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTable::CellDelete(const uint row, const uint col) { return(this.m_table_model!=NULL ? this.m_table_model.CellDelete(row,col) : false); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Move the cell | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTable::CellMoveTo(const uint row, const uint cell_index, const uint index_to) { return(this.m_table_model!=NULL ? this.m_table_model.CellMoveTo(row,cell_index,index_to) : false); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Return the object assigned to the cell | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CObject *CTable::CellGetObject(const uint row, const uint col) { return(this.m_table_model!=NULL ? this.m_table_model.CellGetObject(row,col) : NULL); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Returns the type of the object assigned to the cell | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ENUM_OBJECT_TYPE CTable::CellGetObjType(const uint row,const uint col) { return(this.m_table_model!=NULL ? this.m_table_model.CellGetObjType(row,col) : (ENUM_OBJECT_TYPE)WRONG_VALUE); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Return the cell description | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string CTable::CellDescription(const uint row, const uint col) { return(this.m_table_model!=NULL ? this.m_table_model.CellDescription(row,col) : ""); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Display a cell description in the journal | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTable::CellPrint(const uint row, const uint col) { if(this.m_table_model!=NULL) this.m_table_model.CellPrint(row,col); }
테이블 행으로 작업하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Create a new string and add it to the end of the list | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CTableRow *CTable::RowAddNew(void) { return(this.m_table_model!=NULL ? this.m_table_model.RowAddNew() : NULL); } //+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Create a new string and insert it into the specified position of the list | //+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ CTableRow *CTable::RowInsertNewTo(const uint index_to) { return(this.m_table_model!=NULL ? this.m_table_model.RowInsertNewTo(index_to) : NULL); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Delete a row | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTable::RowDelete(const uint index) { return(this.m_table_model!=NULL ? this.m_table_model.RowDelete(index) : false); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Move the row | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTable::RowMoveTo(const uint row_index, const uint index_to) { return(this.m_table_model!=NULL ? this.m_table_model.RowMoveTo(row_index,index_to) : false); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Clear the row data | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTable::RowClearData(const uint index) { if(this.m_table_model!=NULL) this.m_table_model.RowClearData(index); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Return the row description | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string CTable::RowDescription(const uint index) { return(this.m_table_model!=NULL ? this.m_table_model.RowDescription(index) : ""); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Display the row description in the journal | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTable::RowPrint(const uint index,const bool detail) { if(this.m_table_model!=NULL) this.m_table_model.RowPrint(index,detail); }
새로운 열을 생성하고 지정된 테이블 위치에 추가하는 메서드
//+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Create a new column and adds it to the specified position in the table| //+-----------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTable::ColumnAddNew(const string caption,const int index=-1) { //--- If there is no table model, or there is an error adding a new column to the model, return 'false' if(this.m_table_model==NULL || !this.m_table_model.ColumnAddNew(index)) return false; //--- If there is no header, return 'true' (the column is added without a header) if(this.m_table_header==NULL) return true; //--- Check for the creation of a new column header and, if it has not been created, return 'false' CColumnCaption *caption_obj=this.m_table_header.CreateNewColumnCaption(caption); if(caption_obj==NULL) return false; //--- If a non-negative index has been passed, return the result of moving the header to the specified index //--- Otherwise, everything is ready - just return 'true' return(index>-1 ? this.m_table_header.ColumnCaptionMoveTo(caption_obj.Column(),index) : true); }
테이블 모델이 없는 경우 메서드는 즉시 오류를 반환합니다. 열이 테이블 모델에 성공적으로 추가되었다면 적절한 헤더를 추가해 보세요. 테이블에 헤더가 없는 경우 새로운 열을 생성했는지 성공 여부를 반환합니다. 헤더가 있는 경우 새로운 열 헤더를 추가하고 목록에서 지정된 위치로 이동합니다.
열로 작업하는 다른 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Remove the column | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTable::ColumnDelete(const uint index) { if(!this.HeaderCheck() || !this.m_table_header.ColumnCaptionDelete(index)) return false; return this.m_table_model.ColumnDelete(index); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Move the column | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTable::ColumnMoveTo(const uint index, const uint index_to) { if(!this.HeaderCheck() || !this.m_table_header.ColumnCaptionMoveTo(index,index_to)) return false; return this.m_table_model.ColumnMoveTo(index,index_to); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Clear the column data | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTable::ColumnClearData(const uint index) { if(this.m_table_model!=NULL) this.m_table_model.ColumnClearData(index); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Set the value of the specified header | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTable::ColumnCaptionSetValue(const uint index,const string value) { CColumnCaption *caption=this.m_table_header.GetColumnCaption(index); if(caption!=NULL) caption.SetValue(value); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Set the data type for the specified column | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTable::ColumnSetDatatype(const uint index,const ENUM_DATATYPE type) { //--- If the table model exists, set the data type for the column if(this.m_table_model!=NULL) this.m_table_model.ColumnSetDatatype(index,type); //--- If there is a header, set the data type for it if(this.m_table_header!=NULL) this.m_table_header.ColumnCaptionSetDatatype(index,type); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Set the data accuracy for the specified column | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTable::ColumnSetDigits(const uint index,const int digits) { if(this.m_table_model!=NULL) this.m_table_model.ColumnSetDigits(index,digits); } //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Return the data type for the specified column | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ ENUM_DATATYPE CTable::ColumnDatatype(const uint index) { return(this.m_table_header!=NULL ? this.m_table_header.ColumnCaptionDatatype(index) : (ENUM_DATATYPE)WRONG_VALUE); }
객체 설명을 반환하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Return the object description | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ string CTable::Description(void) { return(::StringFormat("%s: Rows total: %u, Columns total: %u", TypeDescription((ENUM_OBJECT_TYPE)this.Type()),this.RowsTotal(),this.ColumnsTotal())); }
(Object Type) 형식의 문자열을 생성하고 반환: 총 행의 수: XX, 열의 총수: XX)
객체 설명을 로그에 출력하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Display the object description in the journal | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void CTable::Print(const int column_width=CELL_WIDTH_IN_CHARS) { if(this.HeaderCheck()) { //--- Display the header as a row description ::Print(this.Description()+":"); //--- Number of headers int total=(int)this.ColumnsTotal(); string res=""; //--- create a table row from the values of all table column headers res="|"; for(int i=0;i<total;i++) { CColumnCaption *caption=this.GetColumnCaption(i); if(caption==NULL) continue; res+=::StringFormat("%*s |",column_width,caption.Value()); } //--- Add a header to the left row string hd="|"; hd+=::StringFormat("%*s ",column_width,"n/n"); res=hd+res; //--- Display the header row in the journal ::Print(res); } //--- Loop through all the table rows and print them out in tabular form for(uint i=0;i<this.RowsTotal();i++) { CTableRow *row=this.GetRow(i); if(row!=NULL) { //--- create a table row from the values of all cells string head=" "+(string)row.Index(); string res=::StringFormat("|%-*s |",column_width,head); for(int i=0;i<(int)row.CellsTotal();i++) { CTableCell *cell=row.GetCell(i); if(cell==NULL) continue; res+=::StringFormat("%*s |",column_width,cell.Value()); } //--- Display a row in the journal ::Print(res); } } }
이 메서드는 로그에 설명을 출력하며 아래는 헤더와 데이터가 포함된 표입니다.
테이블을 파일에 저장하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Save to file | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTable::Save(const int file_handle) { //--- Check the handle if(file_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) return(false); //--- Save data start marker - 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF if(::FileWriteLong(file_handle,MARKER_START_DATA)!=sizeof(long)) return(false); //--- Save the object type if(::FileWriteInteger(file_handle,this.Type(),INT_VALUE)!=INT_VALUE) return(false); //--- Save the ID if(::FileWriteInteger(file_handle,this.m_id,INT_VALUE)!=INT_VALUE) return(false); //--- Check the table model if(this.m_table_model==NULL) return false; //--- Save the table model if(!this.m_table_model.Save(file_handle)) return(false); //--- Check the table header if(this.m_table_header==NULL) return false; //--- Save the table header if(!this.m_table_header.Save(file_handle)) return(false); //--- Successful return true; }
테이블 모델과 헤더가 모두 생성된 경우에만 저장에 성공합니다. 헤더는 비어 있을 수 있습니다. 즉 열이 없을 수 있지만 객체는 반드시 생성되어야 합니다.
파일에서 테이블을 업로드하는 메서드
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Load from file | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ bool CTable::Load(const int file_handle) { //--- Check the handle if(file_handle==INVALID_HANDLE) return(false); //--- Load and check the data start marker - 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF if(::FileReadLong(file_handle)!=MARKER_START_DATA) return(false); //--- Load the object type if(::FileReadInteger(file_handle,INT_VALUE)!=this.Type()) return(false); //--- Load the ID this.m_id=::FileReadInteger(file_handle,INT_VALUE); //--- Check the table model if(this.m_table_model==NULL && (this.m_table_model=new CTableModel())==NULL) return(false); //--- Load the table model if(!this.m_table_model.Load(file_handle)) return(false); //--- Check the table header if(this.m_table_header==NULL && (this.m_table_header=new CTableHeader())==NULL) return false; //--- Load the table header if(!this.m_table_header.Load(file_handle)) return(false); //--- Successful return true; }
테이블에 모델 데이터와 헤더 데이터가 모두 저장된다고 하면 이 메서드에서는(테이블에 모델이나 헤더가 생성되지 않은 경우) 이들이 모두 미리 생성된 후 파일에서 해당 데이터를 로드합니다.
간단한 테이블 클래스가 준비되었습니다.
이제 간단한 테이블 클래스에서 상속하는 옵션을 고려해 보겠습니다. CList에 기록된 데이터를 기반으로 하는 테이블 클래스를 생성합니다:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Class for creating tables based on the array of parameters | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ class CTableByParam : public CTable { public: virtual int Type(void) const { return(OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE_BY_PARAM); } //--- Constructor/destructor CTableByParam(void) { this.m_list_rows.Clear(); } CTableByParam(CList &row_data,const string &column_names[]); ~CTableByParam(void) {} };
여기서 테이블 유형은 OBJECT_TYPE_TABLE_BY_PARAM으로 반환되며 테이블 모델과 헤더는 클래스 생성자에서 만들어 집니다:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Constructor specifying a table array based on the row_data list | //| containing objects with structure field data. | //| Define the index and names of columns according to | //| column names in column_names | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ CTableByParam::CTableByParam(CList &row_data,const string &column_names[]) { //--- Copy the passed list of data into a variable and //--- create a table model based on this list this.m_list_rows=row_data; this.m_table_model=new CTableModel(this.m_list_rows); //--- Copy the passed list of headers to m_array_names and //--- create a table header based on this list this.ArrayNamesCopy(column_names,column_names.Size()); this.m_table_header=new CTableHeader(this.m_array_names); }
이 예제를 기반으로 다른 종류의 테이블을 만들 수도 있지만 오늘 만든 모든 것으로도 다양한 테이블과 광범위한 데이터를 만들 수 있을 것입니다.
우리가 가진 모든 것을 테스트해 보겠습니다.
결과 테스트
MQL5\Scripts\Tables\ 폴더에서 TestEmptyTable.mq5라는 새로운 스크립트를 만들고 생성한 테이블 클래스 파일을 여기에 연결한 후 빈 4x4 테이블을 생성합니다:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TestEmptyTable.mq5 | //| Copyright 2025, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2025, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Include libraries | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #include "Tables.mqh" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- Create an empty 4x4 table CTable *table=new CTable(4,4); if(table==NULL) return; //--- Display it in the journal and delete the created object table.Print(10); delete table; }
스크립트는 로그에 다음과 같은 출력을 생성합니다:
Table: Rows total: 4, Columns total: 4: | n/n | A | B | C | D | | 0 | | | | | | 1 | | | | | | 2 | | | | | | 3 | | | | |
여기에서는 열 헤더가 MS Excel 스타일로 자동으로 생성됩니다.
다른 스크립트 \MQL5\Scripts\Tables\TestTArrayTable.mq5를 작성합니다:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TestTArrayTable.mq5 | //| Copyright 2025, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2025, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Include libraries | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #include "Tables.mqh" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- Declare and initialize a 4x4 double array double array[4][4]={{ 1, 2, 3, 4}, { 5, 6, 7, 8}, { 9, 10, 11, 12}, {13, 14, 15, 16}}; //--- Declare and initialize the column header array string headers[]={"Column 1","Column 2","Column 3","Column 4"}; //--- Create a table based on the data array and the header array CTable *table=new CTable(array,headers); if(table==NULL) return; //--- Display the table in the journal and delete the created object table.Print(10); delete table; }
스크립트 작업의 결과로 로그에 다음과 같은 테이블이 표시됩니다:
Table: Rows total: 4, Columns total: 4: | n/n | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | | 0 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 | | 1 | 5.00 | 6.00 | 7.00 | 8.00 | | 2 | 9.00 | 10.00 | 11.00 | 12.00 | | 3 | 13.00 | 14.00 | 15.00 | 16.00 |
여기서 열은 클래스 생성자에게 전달되는 헤더 배열에서 이미 제목이 지정되어 있습니다. 테이블을 생성하기 위한 데이터를 나타내는 2차원 배열은 ENUM_DATATYPE 열거형의 모든 유형이 될 수 있습니다.
모든 유형은 테이블 모델 클래스에서 사용되는 5가지 유형인 double, long, date-time, color 및 string으로 자동 변환됩니다.
행렬 데이터 테이블을 테스트하려면 \MQL5\Scripts\Tables\TestMatrixTable.mq5 스크립트를 작성합니다:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TestMatrixTable.mq5 | //| Copyright 2025, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2025, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Include libraries | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #include "Tables.mqh" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- Declare and initialize a 4x4 matrix matrix row_data = {{ 1, 2, 3, 4}, { 5, 6, 7, 8}, { 9, 10, 11, 12}, {13, 14, 15, 16}}; //--- Declare and initialize the column header array string headers[]={"Column 1","Column 2","Column 3","Column 4"}; //--- Create a table based on a matrix and an array of headers CTable *table=new CTable(row_data,headers); if(table==NULL) return; //--- Display the table in the journal and delete the created object table.Print(10); delete table; }
그 결과 2차원 4x4 배열을 기반으로 구축된 테이블과 유사한 테이블이 생성됩니다:
Table: Rows total: 4, Columns total: 4: | n/n | Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | Column 4 | | 0 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 3.00 | 4.00 | | 1 | 5.00 | 6.00 | 7.00 | 8.00 | | 2 | 9.00 | 10.00 | 11.00 | 12.00 | | 3 | 13.00 | 14.00 | 15.00 | 16.00 |
이제 모든 과거 거래를 계산하고 이를 기반으로 거래 테이블을 생성하여 로그에 출력하는 스크립트 \MQL5\Scripts\Tables\TestDealsTable.mq5를 작성합니다:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| TestDealsTable.mq5 | //| Copyright 2025, MetaQuotes Ltd. | //| https://www.mql5.com | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Copyright 2025, MetaQuotes Ltd." #property link "https://www.mql5.com" #property version "1.00" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Include libraries | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #include "Tables.mqh" //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Script program start function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnStart() { //--- Declare a list of deals, the deal parameters object, and the structure of parameters CList rows_data; CMqlParamObj *cell=NULL; MqlParam param={}; //--- Select the entire history if(!HistorySelect(0,TimeCurrent())) return; //--- Create a list of deals in the array of arrays (CList in CList) //--- (one row is one deal, columns are deal property objects) int total=HistoryDealsTotal(); for(int i=0;i<total;i++) { ulong ticket=HistoryDealGetTicket(i); if(ticket==0) continue; //--- Add a new row of properties for the next deal to the list of deals CList *row=DataListCreator::AddNewRowToDataList(&rows_data); if(row==NULL) continue; //--- Create "cells" with the deal parameters and //--- add them to the created deal properties row string symbol=HistoryDealGetString(ticket,DEAL_SYMBOL); int digits=(int)SymbolInfoInteger(symbol,SYMBOL_DIGITS); //--- Deal time (column 0) param.type=TYPE_DATETIME; param.integer_value=HistoryDealGetInteger(ticket,DEAL_TIME); param.double_value=(TIME_DATE|TIME_MINUTES|TIME_SECONDS); DataListCreator::AddNewCellParamToRow(row,param); //--- Symbol name (column 1) param.type=TYPE_STRING; param.string_value=symbol; DataListCreator::AddNewCellParamToRow(row,param); //--- Deal ticket (column 2) param.type=TYPE_LONG; param.integer_value=(long)ticket; DataListCreator::AddNewCellParamToRow(row,param); //--- The order the performed deal is based on (column 3) param.type=TYPE_LONG; param.integer_value=HistoryDealGetInteger(ticket,DEAL_ORDER); DataListCreator::AddNewCellParamToRow(row,param); //--- Position ID (column 4) param.type=TYPE_LONG; param.integer_value=HistoryDealGetInteger(ticket,DEAL_POSITION_ID); DataListCreator::AddNewCellParamToRow(row,param); //--- Deal type (column 5) param.type=TYPE_STRING; ENUM_DEAL_TYPE deal_type=(ENUM_DEAL_TYPE)HistoryDealGetInteger(ticket,DEAL_TYPE); param.integer_value=deal_type; string type=""; switch(deal_type) { case DEAL_TYPE_BUY : type="Buy"; break; case DEAL_TYPE_SELL : type="Sell"; break; case DEAL_TYPE_BALANCE : type="Balance"; break; case DEAL_TYPE_CREDIT : type="Credit"; break; case DEAL_TYPE_CHARGE : type="Charge"; break; case DEAL_TYPE_CORRECTION : type="Correction"; break; case DEAL_TYPE_BONUS : type="Bonus"; break; case DEAL_TYPE_COMMISSION : type="Commission"; break; case DEAL_TYPE_COMMISSION_DAILY : type="Commission daily"; break; case DEAL_TYPE_COMMISSION_MONTHLY : type="Commission monthly"; break; case DEAL_TYPE_COMMISSION_AGENT_DAILY : type="Commission agent daily"; break; case DEAL_TYPE_COMMISSION_AGENT_MONTHLY: type="Commission agent monthly"; break; case DEAL_TYPE_INTEREST : type="Interest"; break; case DEAL_TYPE_BUY_CANCELED : type="Buy canceled"; break; case DEAL_TYPE_SELL_CANCELED : type="Sell canceled"; break; case DEAL_DIVIDEND : type="Dividend"; break; case DEAL_DIVIDEND_FRANKED : type="Dividend franked"; break; case DEAL_TAX : type="Tax"; break; default : break; } param.string_value=type; DataListCreator::AddNewCellParamToRow(row,param); //--- Deal direction (column 6) param.type=TYPE_STRING; ENUM_DEAL_ENTRY deal_entry=(ENUM_DEAL_ENTRY)HistoryDealGetInteger(ticket,DEAL_ENTRY); param.integer_value=deal_entry; string entry=""; switch(deal_entry) { case DEAL_ENTRY_IN : entry="In"; break; case DEAL_ENTRY_OUT : entry="Out"; break; case DEAL_ENTRY_INOUT : entry="InOut"; break; case DEAL_ENTRY_OUT_BY : entry="OutBy"; break; default : break; } param.string_value=entry; DataListCreator::AddNewCellParamToRow(row,param); //--- Deal volume (column 7) param.type=TYPE_DOUBLE; param.double_value=HistoryDealGetDouble(ticket,DEAL_VOLUME); param.integer_value=2; DataListCreator::AddNewCellParamToRow(row,param); //--- Deal price (column 8) param.type=TYPE_DOUBLE; param.double_value=HistoryDealGetDouble(ticket,DEAL_PRICE); param.integer_value=(param.double_value>0 ? digits : 1); DataListCreator::AddNewCellParamToRow(row,param); //--- Stop Loss level (column 9) param.type=TYPE_DOUBLE; param.double_value=HistoryDealGetDouble(ticket,DEAL_SL); param.integer_value=(param.double_value>0 ? digits : 1); DataListCreator::AddNewCellParamToRow(row,param); //--- Take Profit level (column 10) param.type=TYPE_DOUBLE; param.double_value=HistoryDealGetDouble(ticket,DEAL_TP); param.integer_value=(param.double_value>0 ? digits : 1); DataListCreator::AddNewCellParamToRow(row,param); //--- Deal financial result (column 11) param.type=TYPE_DOUBLE; param.double_value=HistoryDealGetDouble(ticket,DEAL_PROFIT); param.integer_value=(param.double_value!=0 ? 2 : 1); DataListCreator::AddNewCellParamToRow(row,param); //--- Deal magic number (column 12) param.type=TYPE_LONG; param.integer_value=HistoryDealGetInteger(ticket,DEAL_MAGIC); DataListCreator::AddNewCellParamToRow(row,param); //--- Deal execution reason or source (column 13) param.type=TYPE_STRING; ENUM_DEAL_REASON deal_reason=(ENUM_DEAL_REASON)HistoryDealGetInteger(ticket,DEAL_REASON); param.integer_value=deal_reason; string reason=""; switch(deal_reason) { case DEAL_REASON_CLIENT : reason="Client"; break; case DEAL_REASON_MOBILE : reason="Mobile"; break; case DEAL_REASON_WEB : reason="Web"; break; case DEAL_REASON_EXPERT : reason="Expert"; break; case DEAL_REASON_SL : reason="SL"; break; case DEAL_REASON_TP : reason="TP"; break; case DEAL_REASON_SO : reason="StopOut"; break; case DEAL_REASON_ROLLOVER : reason="Rollover"; break; case DEAL_REASON_VMARGIN : reason="VMargin"; break; case DEAL_REASON_SPLIT : reason="Split"; break; case DEAL_REASON_CORPORATE_ACTION: reason="Corporate action"; break; default : break; } param.string_value=reason; DataListCreator::AddNewCellParamToRow(row,param); //--- Deal comment (column 14) param.type=TYPE_STRING; param.string_value=HistoryDealGetString(ticket,DEAL_COMMENT); DataListCreator::AddNewCellParamToRow(row,param); } //--- Declare and initialize the table header string headers[]={"Time","Symbol","Ticket","Order","Position","Type","Entry","Volume","Price","SL","TP","Profit","Magic","Reason","Comment"}; //--- Create a table based on the created list of parameters and the header array CTableByParam *table=new CTableByParam(rows_data,headers); if(table==NULL) return; //--- Display the table in the journal and delete the created object table.Print(); delete table; }
결과적으로 셀 너비가 19자인 모든 거래의 테이블이 출력됩니다(기본적으로 테이블 클래스의 인쇄 메서드에서):
Table By Param: Rows total: 797, Columns total: 15: | n/n | Time | Symbol | Ticket | Order | Position | Type | Entry | Volume | Price | SL | TP | Profit | Magic | Reason | Comment | | 0 |2025.01.01 10:20:10 | | 3152565660 | 0 | 0 | Balance | In | 0.00 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 100000.00 | 0 | Client | | | 1 |2025.01.02 00:01:31 | GBPAUD | 3152603334 | 3191672408 | 3191672408 | Sell | In | 0.25 | 2.02111 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 112 | Expert | | | 2 |2025.01.02 02:50:31 | GBPAUD | 3152749152 | 3191820118 | 3191672408 | Buy | Out | 0.25 | 2.02001 | 0.0 | 2.02001 | 17.04 | 112 | TP | [tp 2.02001] | | 3 |2025.01.02 04:43:43 | GBPUSD | 3152949278 | 3191671491 | 3191671491 | Sell | In | 0.10 | 1.25270 | 0.0 | 1.24970 | 0.0 | 12 | Expert | | ... ... | 793 |2025.04.18 03:22:11 | EURCAD | 3602552747 | 3652159095 | 3652048415 | Sell | Out | 0.25 | 1.57503 | 0.0 | 1.57503 | 12.64 | 112 | TP | [tp 1.57503] | | 794 |2025.04.18 04:06:52 | GBPAUD | 3602588574 | 3652200103 | 3645122489 | Sell | Out | 0.25 | 2.07977 | 0.0 | 2.07977 | 3.35 | 112 | TP | [tp 2.07977] | | 795 |2025.04.18 04:06:52 | GBPAUD | 3602588575 | 3652200104 | 3652048983 | Sell | Out | 0.25 | 2.07977 | 0.0 | 2.07977 | 12.93 | 112 | TP | [tp 2.07977] | | 796 |2025.04.18 05:57:48 | AUDJPY | 3602664574 | 3652277665 | 3652048316 | Buy | Out | 0.25 | 90.672 | 0.0 | 90.672 | 19.15 | 112 | TP | [tp 90.672] |
이 예는 첫 번째와 마지막 네 번의 거래를 보여주지만 로그에 출력되는 테이블에 대한 아이디어를 제공합니다.
생성된 모든 파일은 여러분의 학습을 위해 문서에 첨부되어 있습니다. 아카이브 파일의 압축을 터미널 폴더에 풀면 모든 파일이 원하는 폴더에 위치하게 됩니다: MQL5\Scripts\Tables.
결론
이렇게 우리는 MVC 아키텍처의 프레임워크 내에서 테이블 모델(Model)의 기본 구성 요소에 대한 작업을 완료했습니다. 테이블과 헤더 작업을 위한 클래스를 만들고 2차원 배열, 행렬, 거래 내역 등 다양한 유형의 데이터에 대해서도 테스트했습니다.
이제 다음 단계인 View 및 Controller 컴포넌트 개발을 진행합니다. MQL5에는 객체가 사용자 동작에 반응하도록 하는 내장 이벤트 시스템이 있기 때문에 이 두 구성 요소가 밀접하게 연결되어 있습니다.
이는 우리로 하여금 테이블 시각화(뷰 컴포넌트)와 그 제어(컨트롤러 컴포넌트)를 동시에 개발할 수 있게 해 주며 다소 복잡하고 다단계로 구현된 보기 구성 요소의 구현을 단순화해줍니다.
이 글의 모든 예제와 파일은 다운로드할 수 있습니다. 다음 글에서는 Controller와 결합된 View 컴포넌트를 만들어 MQL5에서 본격적인 연산 테이블용 도구를 구현해 보겠습니다.
프로젝트가 완성되면 개발에 사용할 다른 UI 컨트롤을 만들 수 있는 새로운 기회가 열릴 것입니다.
이 글에 사용된 프로그램:
| # | 이름 | 타입 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tables.mqh | Class Library | 테이블 생성을 위한 클래스 라이브러리 |
| 2 | TestEmptyTable.mq5 | Script | 행과 열의 개수 설정하여 빈 테이블 생성을 테스트하는 스크립트 |
| 3 | TestTArrayTable.mq5 | Script | 2차원 데이터 배열을 기반으로 테이블 생성을 테스트하기 위한 스크립트 |
| 4 | TestMatrixTable.mq5 | Script | 데이터 매트릭스를 기반으로 테이블 생성을 테스트하기 위한 스크립트 |
| 5 | TestDealsTable.mq5 | Script | 사용자 데이터(과거 거래 내역)를 기반으로 테이블 생성을 테스트하는 스크립트 |
| 6 | MQL5.zip | 아카이브 | 클라이언트 터미널의 MQL5 디렉터리에 압축을 풀기 위한 위에 제시된 파일의 아카이브 |
MetaQuotes 소프트웨어 사를 통해 러시아어가 번역됨.
원본 기고글: https://www.mql5.com/ru/articles/17803
경고: 이 자료들에 대한 모든 권한은 MetaQuotes(MetaQuotes Ltd.)에 있습니다. 이 자료들의 전부 또는 일부에 대한 복제 및 재출력은 금지됩니다.
이 글은 사이트 사용자가 작성했으며 개인의 견해를 반영합니다. Metaquotes Ltd는 제시된 정보의 정확성 또는 설명 된 솔루션, 전략 또는 권장 사항의 사용으로 인한 결과에 대해 책임을 지지 않습니다.
 새로운 기능: MQL5의 커스텀 인디케이터
새로운 기능: MQL5의 커스텀 인디케이터
 윌리엄 간 메서드(3부): 점성술은 맞는 건가요?
윌리엄 간 메서드(3부): 점성술은 맞는 건가요?
 새 MetaTrader 와 MQL5를 소개해드립니다
새 MetaTrader 와 MQL5를 소개해드립니다
 윌리엄 간 메서드(2부): 간 스퀘어 지표 만들기
윌리엄 간 메서드(2부): 간 스퀘어 지표 만들기